
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol. , 28 October 2024
Sec. Experimental Pharmacology and Drug Discovery
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1447077
 MingJu Chen1†
MingJu Chen1† Yuxiao Wu2†
Yuxiao Wu2† Hongxuan Yang1
Hongxuan Yang1 Tianfeng Liu1
Tianfeng Liu1 Tongkun Han3
Tongkun Han3 Wangqiang Dai1
Wangqiang Dai1 Junyue Cen1
Junyue Cen1 Fan Ouyang1
Fan Ouyang1 Jingjing Chen1
Jingjing Chen1 Jianxin Liu4*
Jianxin Liu4* Lin Zhou2*
Lin Zhou2* Xuguang Hu1*
Xuguang Hu1*Introduction: This study aimed to establish a fermentation system based on Lactobacillus casei (LC) and Arctium lappa L. root (AR) to investigate its effects. The objectives included comparing metabolite profiles pre- and post-fermentation using untargeted metabolomics and evaluating the impact of LC-AR in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice.
Methods: Untargeted metabolomics was used to analyze differences in metabolites before and after fermentation. In vitro antioxidant activity, liver injury, lipid levels, pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, and cholesterol-related mRNA expression were assessed. 16S rRNA sequencing was conducted to evaluate changes in gut microbiota composition.
Results: LC-AR exhibited stronger antioxidant activity and higher metabolite levels than AR. It also improved liver injury as well as better regulation of lipid levels, pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, and cholesterol-related mRNA. 16S rRNA analysis revealed that LC-AR decreased the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, which correlated negatively with triglycerides, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
Discussion: These findings suggest that LC-AR may serve as a promising functional food and drug raw material for improving hyperlipidemia, particularly through its beneficial effects on gut microbiota and lipid regulation.
Hyperlipidemia is a metabolic illness characterized by excessive lipid levels and is a key risk factor for stroke and cardiovascular diseases (Crea, 2023; Alloubani et al., 2021; Stewart et al., 2020) Multiple clinical studies have proved that statins and fibrates exhibit good performance in reducing blood lipids and even the incidence of stroke and cardiovascular diseases. However, their side-effects, such as muscle soreness, liver damage, and renal toxicity, make them unsuitable for long-term use (Alloubani et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). Therefore, it is necessary to find a mild alternative therapy with low side effects.
Arctium lappa L. (AL) is a herb of the genus Arctium in the Asteraceae family, which is a special plant of medicinal edible homology and an important member of a variety of traditional Chinese medicine formula (Nam et al., 2021; Song et al., 2018). AL exhibits anti-inflammatory (Zhang H. L. et al., 2020), anti-viral (Dias et al., 2017), and anti-constipation (Takeda et al., 1992) properties. Each part of AL has different pharmacological effects. Particullarly, the root of AL, A. lappa Lactobacillus root (AR), is rich in polysaccharides (Gao et al., 2023), polyphenols (Moro et al., 2020), flavonoids, and other bioactive components, and has underlying research significance. Past studies have shown that the ethanolic extract of AR can ameliorate obesity and liver steatosis in rats (Ma et al., 2022). In addition, the distilled water extract of AR can regulate lipid profile levels and ameliorate atherosclerotic symptoms in high fat diet-induced quail atherosclerosis (Wang et al., 2016). These results indicate that AR performs well in ameliorating lipid profile levels. However, no studies have yet revealed the effects of AR on improving hyperlipidemia and its specific mechanisms.
Lactobacillus, as a probiotic, is present in essential organs, such as the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts of humans and other mammals, playing a role in regulating microbial community homeostasis (Un-Nisa et al., 2022). It plays an important role in the microbiota of mammals and even ecosystems. It's well known, improving the dysbiosis of gut microbiota can serve as a crucial mechanism for preventing and treating hyperlipidemia caused by lipid metabolism disorders (Liu et al., 2023). Furthermore, Lactobacillus has been proven to ameliorate symptoms such as elevated cholesterol and hyperlipidemia in mice (Liu et al., 2020; Chai et al., 2022). Thus, there is a good prospect to expand the application of lactobacillus.
Fermentation is one of the methods used in processing traditional Chinese medicine, which has the characteristics of reducing toxicity and enhancing curative effects. In contrast to traditional fermentation technology, modern fermentation technology is mostly probiotic fermentation with Chinese herbs, offering advantages such as well-defined fermentation substrate, controllable processes, and optimization possibilities (Yang et al., 2023). Fermentation technology has great potential in the field of biomedicine, especially in the development of traditional Chinese medicine and modern pharmaceuticals (Diez-Ozaeta and Astiazaran, 2022). China’s traditional fermented medicine, Massa Medicata Fermentata, has a long history and is widely used in clinical practice as a digestive agent, with the functions of strengthening the spleen and gut and promoting digestion (Fu et al., 2020).
Of particular interest is the potential of traditional Chinese herbal fermentation and its apparent efficacy in improving hyperlipidemia. For instance, another traditional fermented Chinese medicine, Monascus purpureus Went, has been clinically proven to significantly reduce LDL-C, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, and was well tolerated in patients with hyperlipidemia (Lin et al., 2005). Huang et al. (2019) found that the theabrownin in fermented Pu-erh tea alleviates hypercholesterolemia by modulating the gut microbiota, suggesting that the reduction of gut bile-salt hydrolase (BSH) microbes and/or decreased FXR-FGF15 signaling could be potential therapeutic mechanisms for treating hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia. Meanwhile, Zheng Y. et al. (2024) demonstrated that compared to Bergamot, only fermented Bergamot (Laoxianghuang) could decrease the content of isobutyric acid and isovaleric acid, which are detrimental to gut health, making it more advantageous in improving the gut microbiota of patients with hyperlipidemia. In our recent research, the fermentation of Lactobacillus acidophilus and dandelion was found to improve symptoms in mice with hyperuricemia (Ma et al., 2023). Based on this, traditional Chinese fermented medicines seem to be an effective potential supplementary treatment for hyperlipidemia.
Overall, the present study harnesses the advantages of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, probiotics, and fermentation systems using AR as a fermentation substrate, with Lactobacillus as the added strain for liquid fermentation. From various perspectives, including lipid levels, inflammatory factor levels, and gut microbiota composition, we explore the impact and mechanisms of Lactobacillus fermentation of AR on hyperlipidemic mice. Investigate its potential in improving hyperlipidemia, providing a theoretical foundation for the expansion of related fields.
Lactobacillus acidophilus GDMCC1.412 (LA), Lactobacillus casei GDMCC1.159 (LC), and Lactobacillus plantarum GDMCC1.191 (LP) were obtained from Guangdong Microbial Center (Guangzhou, China). Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC7469 (LR) and De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) medium were purchased from Huankai Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Zhaoqing, China). AR was purchased from Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Zhenpin Yaozhuang. Cholesterol esterase (CEase), sodium taurocholate, p-NPB, Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, 2, 2′-azinobis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS), 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), simvastatin, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose were purchased from Macklin Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Pancreatic lipase (PL) was purchased from Meilun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Dalian, China), and the gallic acid standard was purchased from Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2-Chloro-L-phenylalanine was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), aspartate transaminase (AST), and alanine amioTransferase (ALT) kits were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Reagent Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Tumor necrosis factor receptor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) Elisa kits were purchased from Jiangsu Enzymatic Immunization Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China).
AR was crushed and sifted through a 50-mesh sieve, and then mixed with the MRS medium at a liquid-to-material ratio of 1:10 (v/v). The resulting mixture (AR-MRS) was sterilized at 121°C for 20 min and subsequently cooled to ambient temperature. LA, LC, LP, and LR were grown in MRS broth at 37°C for 48 h, and the above passage procedure was repeated once. Four types of activated Lactobacillus (LA, LC, LP, and LR) were used as the fermentation seed liquids. Lactobacillus was inoculated into the AR-MRS solution at a seeding volume of 5% (v/v) and fermented at 37°C for 96 h. The resulting fermentation liquid was centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was collected as the final product (LA-AR, LC-AR, LP-AR, and LR-AR) (Ma et al., 2023).
For determining the activity of cholesterol esterase (CEase), Zhang X. et al. (2020) method was used with minor modification. CEase solution configuration: An appropriate amount of CEase was dissolved in sodium phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.0 to obtain a CEase solution with a final concentration of 1.05 U/mL.
p-NPB solution configuration: An appropriate amount of sodium taurine cholate was dissolved in sodium phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.0 to obtain a sodium taurine cholate solution with a final concentration of 5.16 mM. An appropriate amount of p-NPB was dissolved in 5.16 mM sodium taurine cholate solution to obtain a p-NPB solution with a final concentration of 1 mM.
Sample measurement: 50 μL CEase solution (1.05 U/mL), 50 μL phosphate buffer, and 50 μL sample solution with different concentrations (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 mg/mL) were mixed evenly and added to a 96-well plate and incubated at 37°C in a thermostatic incubator for 10 min. Then, 50 μL of p-NPB solution was added to the mixture, mixed evenly, and incubated for 5 min, and the absorbance value of the above mixture was measured at 405 nm. The final result was expressed as IC50. The inhibition rate of CEase activity was calculated as follows:
A1: absorbance value of the sample, A2: absorbance value of the enzyme replaced with an equal volume buffer solution, A3: absorbance value of the sample replaced with an equal volume buffer solution, A4: Absorbance value of the sample and enzyme replaced with an equal volume buffer solution.
For determining the activity of pancreatic lipase (PL), Zhang Q. et al. (2020) method was used with minor modifications. PL solution configuration: An appropriate amount of PL was dissolved in sodium phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.0 to obtain a PL solution with a final concentration of 6 mg/mL.
p-NPB solution configuration: An appropriate amount of p-NPB was dissolved in sodium phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.0 to obtain a p-NPB solution with a final concentration of 1 mM.
Sample measurement: 50 μL PL solution (6 mg/mL), 50 μL phosphate buffer, and 50 μL sample solution with different concentrations (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 mg/mL) were mixed evenly, added to the 96-well plate, and incubated at 37°C in the thermostatic incubator for 10 min. Then, 50 μL of the p-NPB solution was added to the mixture, mixed evenly, and incubated for 5 min, and the absorbance value of the above mixture was measured at 405 nm. The final result was expressed as IC50. The inhibition rate of PL enzyme activity was calculated as follows:
Aa: absorbance value of the sample, Ab: absorbance value of the enzyme replaced with an equal volume buffer solution, Ac: absorbance value of the sample replaced with an equal volume buffer solution, Ad: Absorbance value of the sample and enzyme replaced with an equal volume buffer solution.
The phenolic content was determined in accordance with the method described in Lyu et al.’s paper (Lyu et al., 2020) with minor modifications. First, 0.1 mL of the sample solution was mixed with 0.2 mL Folin-Ciocalteu reagent and shaken well. Then, 0.4 mL of 12% Na2CO3 was added to the mixture, to which 4.3 mL of distilled water was added and the volume was adjusted to 5 mL. The mixture was incubated at ambient temperature in the dark for 1 h. The absorbance of the resulting mixture was measured at 765 nm. The total phenolic content was expressed as the Gallic acid equivalent (mg GAE/g).
The scavenging capacity of DPPH• free radicals was determined in accordance with Li Z. et al. (2018) method with simple modifications. A 2 mL DPPH solution (0.1 mg/mL) was mixed with 1 mL of the sample and incubated in the dark for 30 min. The absorption value of the mixture was measured at 517 nm. Equation 3 was used to calculate the DPPH• free radicals’ scavenging capacity for each sample:
A0: absorbance value of equal volume anhydrous ethanol instead of the sample, AS: absorption value of the sample mixed with DPPH solution.
The ABTS + free radicals’ scavenging capacity was determined according to Li Z. et al. (2018) method with simple modifications. A 2 mL ABTS solution was mixed with 1 mL of the sample and incubated in the dark for 6 min. The absorption value of the mixture was measured at 734 nm. Equation 4 was used to calculate the ABTS + free radicals’ scavenging capacity for each sample:
A0: absorbance value of equal volume distilled water instead of the sample, AZ: absorption value of the sample mixed with ABTS solution.
Metabolite Sample Preparation: transfer an appropriate amount of fermentation broth into a centrifuge tube, concentrate it to dryness, and then dissolve it with 500 µL of methanol solution. Centrifuge the mixture at 12,000 rpm and 4°C for 10 min. Collect the entire supernatant and dry it. Subsequently, dissolve the sample in 150 µL of 2-Chloro-L-phenylalanine solution (prepared in 80% methanol-water). Filter the solution through a 0.22 µm microporous membrane to obtain the sample for analysis (Dunn et al., 2011).
An untargeted metabolomics analysis was conducted using the Thermo Vanquish ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States).
Thermo Vanquish ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States). The chromatographic column employed was ACQUITY UPLC® HSST3 (2.1 mm × 150 mm, 1.8 μm) from Waters (Milford, MA, United States).
In the positive ion mode, the mobile phase comprised 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (C) and 0.1% formic acid in water (D). The gradient elution program was as follows: 0–1 min, 2% C; 1–9 min, 2%–50% C; 9–12 min, 50%–98% C; 12–13.5 min, 98% C; 13.5–14 min, 98%–2% C; and 14–20 min, 2% C. In the negative ion mode, the mobile phase included acetonitrile (A) and 5 mM ammonium formate in water (B). The gradient elution program was as follows: 0–1 min, 2% A; 1–9 min, 2%–50% A; 9–12 min, 50%–98% A; 12–13.5 min, 98% A; 13.5–14 min, 98%–2% A; and 14–17 min, 2% A. The column temperature was set at 40°C, and the flow rate and injection volume were 0.25 mL/min and 2 μL, respectively (Zelena et al., 2009).
The Q Exactive mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States) was used for MS data acquisition. The sheath gas flow rate and auxiliary gas flow rate were set at 30 and 10 arb, respectively. The capillary temperature was maintained at 325°C, with positive and negative ion spray voltages set at 3.50 and −2.50 kV, respectively.
The R package XCMS was used for peak detection, filtering, and alignment, resulting in a comprehensive table of substance quantification. Substance identification was conducted using public databases, such as HMDB (http://www.hmdb.ca) (Wishart, 2020), MassBank (http://www.massbank.jp/) (Horai et al., 2010), LipidMaps (http://www.lipidmaps.org) (Sud et al., 2007), mzCloud (https://www.mzcloud.org) (Abdelrazig et al., 2020), and KEGG (WIXON and KELL, 2000). Ropls software was utilized for all multivariate data analyses, and models were established based on principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA).
Fifty-six C57BL/6 male mice, aged 6 weeks, were acquired from Guangdong Zhi-yuan Experimental Animal Co., Ltd., bearing certificate number No.44826500000863. After a week of adaptive feeding, the mice were randomly divided into seven groups (n = 8): the control group (CON); the model group (MOD), which was fed a high-fat diet; the positive group (SIM), which was treated with simvastatin at a dose of 5 mg/kg/d; the low-dose group (AL) treated with AR at a dose of 1 g/kg/d; the high-dose group (AH) treated with AR at a dose of 4 g/kg/d; the low-dose group (LL) treated with AR fermented by LC at a dose of 1 g/kg/d; and the high-dose group (LH) treated with AR fermented by LC at a dose of 4 g/kg/d. The remaining groups were given a diet high in fat, containing 40% high fat, 2% cholesterol, and 0.5% sodium cholate, while the control group followed a regular diet. Each mice group received the drug or saline once per day by tube feeding at a dose of 0.1 mL of fluid per 10 g of body weight. Weekly weight records were maintained. After undergoing different treatments for a duration of 8 weeks, blood samples were collected after a 12-h period of fasting, and subsequently, the serum was frozen at −80°C. After collecting the blood samples, the mice were euthanized using cervical dislocation. The small intestine and liver were meticulously taken and weighed. Prior to the analysis, all these samples were stored at −80°C. The experimental protocol was conducted in accordance with the Regulations for the Management of Laboratory Animals (issued by the National Science and Technology Commission of the People’s Republic of China) and received approval from the Animal Ethics Committee of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University (Approval Number gdpulacspf-2017688).
The serum levels of LDL-C, HDL-C, TG, T-CHO, ALT, and AST were measured using commercial kits (Nanjing, China), and those of IL-6 and TNF-α in the blood were evaluated using a commercial enzyme immunoassay kit (ELISA).
Following a 24 h fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde, thin slices of the liver were obtained and subsequently embedded in paraffin. Hematoxylin and eosin stained sections were then used to observe the histopathological changes under a Nikon Eclipse Ci-L optical microscope.
RNA was extracted from both the entire liver and the small intestine using Trizol lysate. Before conducting further tests, the RNA concentration was assessed using a nucleic acid analyzer, ensuring purity values ranging from 1.8 to 2.0. Next, the RNA was converted into cDNA using a reverse transcription kit. Finally, the cDNA that was transcribed in the opposite direction, along with a dye that emitted light, was used as reference and inserted into a real-time polymerase chain reaction machine for the response. The average was calculated by repeating each sample three times and correcting it with the internal reference GAPDH. The 2−ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the relative expression of the target gene mRNA. Supplementary Table S1 displays the primer sequences.
DNA was extracted from the cecal contents using a DNA extraction kit, and the purity of the DNA was checked via 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The target fragment within the bacterial 16S V3 and V4 regions was selected, and the universal bacterial primers 338F 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′ and 806R 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′ were used as amplification primers for PCR. The PCR products were purified, quantified, and homogenized to create a sequencing library. Then, library QC was performed for constructing libraries. Qualified libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform. The high-throughput sequencing was carried out by Beijing Biomarker Technologies Co., LTD. (Beijing, China).
Sequencing result processing:
Raw reads filtration: Raw reads were first filtered by Trimmomatic v0.33. Then, the primer sequences were identified and removed using cutadapt 1.9.1, resulting in high-quality reads without primer sequences.
DADA2 de-noise: De-noising was carried out using the DADA2 method in the R library to remove chimeric sequences, producing non-chimeric reads.
Bioinformatic analysis: This included feature identification (OTUs clustering), diversity analysis, differential analysis, and correlation analysis.
The data results are expressed as mean ± SD. GraphPad Prism 8.0 was employed for statistical analysis. Significant differences between the groups were determined using a one-way analysis of variance. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
CEase and PL are jointly involved in the metabolism, digestion, and absorption of dietary cholesterol esters, fat-soluble vitamins, TGs, and other substrates (Mudgil et al., 2021). The targeted inhibition of CEase and PL activities can indirectly improve the symptoms of metabolic disorders, such as obesity and hyperlipidemia. This study established five subgroups to investigate the effects of fermentation, as well as different strains, on fermented AR. The subgroups included a control group (AR) and four experimental groups (LC-AR, LA-AR, LR-AR, and LP-AR). Compared to the control group, the CEase activity in all four experimental groups showed a significant reduction (p < 0.001) (Table 1). Especially, the LC-AR group exhibited the most pronounced decrease in CEase activity (p < 0.001), with a reduction of 56.70% compared to the AR group. This suggests that the inhibitory effect of AR on CEase is significantly enhanced after fermentation with different bacterial strains, with the LC-AR group demonstrating the strongest inhibitory effect. In addition, compared to the control group (AR), the PL activities in the LC-AR, LA-AR, and LR-AR groups all showed a significant reduction (p < 0.001). However, no significant difference in PL activity (p > 0.05) was observed in the LP-AR group. Among these, the LR-AR group decreased most markedly in PL activity (p < 0.001), with a reduction of 26.60% compared to the AR group.
These findings suggests that the fermentation of AR by different types of lactobacillus have varying in vitro lipid-lowering effects. This is attributable to the distinct metabolic characteristics and production of different metabolites during the metabolic processes of LA, LC, LP, and LR (Fiorino et al., 2023). Overall, the CEase activities in the LC-AR group were significantly lower than those in the other groups, while the PL activities in both the LC-AR and LR-AR groups were significantly lower than in the other groups, with no significant difference between the two. More importantly, research indicates that LC has a notable regulatory effect on lipid metabolism disorders in hyperlipidemia mice, suggesting its promising potential in improving hyperlipidemia (Qian et al., 2019; Yang D. et al., 2019). Based on the CEase and PL activities of each experimental group, and considering overall better in vitro hypolipidemic activity, LC was selected as the experimental strain for the subsequent fermentation of AR.
There appears to be a certain correlation between the oxidative stress generated by the accumulation of adipose tissue and the development of metabolic complications (Le et al., 2014). Meanwhile, phenolic compounds exhibit a certain level of antioxidant activity both in vitro and in vivo (Liu et al., 2022).
Based on the variation in phenolic compound content (Table 2), the LC-AR group (13.17 ± 0.10 mg/g) exhibited a significant increase of 1.08 ± 0.03 times compared to the AR group (6.34 ± 0.15 mg/g) (p < 0.001). Simultaneously, the in vitro antioxidant capacity of the samples was investigated through DPPH• and ABTS + free radical scavenging experiments. Typically, IC50 can be used to assess the in vitro antioxidant capacity of samples. A lower IC50 value indicates that the samples can more efficiently eliminate free radicals at the same equivalent. Interestingly, after fermentation, the clearance rates of the DPPH• free radical (3.11 ± 0.12) and ABTS + free radical (0.61 ± 0.02) of the LC-AR group showed a significant reduction in IC50 values compared to the AR group (p < 0.001), by 22.10% and 40.20% times, respectively. This suggests that LC fermentation of AR can increase its total phenolic content and enhance its in vitro antioxidant activity.
Based on the UPLC–MS/MS untargeted metabolomic analysis, the differences in the metabolite composition between AR and LC-AR were assessed. Through comparison of database information, including mass-to-charge ratio, retention time, and peak area, a preliminary identification of 276 compounds was achieved (Supplementary Table S2). These involved 25 phenolic compounds, 37 amino acids and their derivatives, and 21 lipid metabolites.
Using multivariate statistical techniques, we conducted a macroscopic analysis of the differences in metabolites between AR and LC-AR. Unsupervised PCA was employed for data dimensionality reduction (Figure 1A). The two-dimensional PCA scatter plot formed by the first principal component (PC1) and the second principal component (PC2) revealed a significant separation between the AR and LC-AR groups, indicating substantial differences in the compositions of metabolites between the two groups. Simultaneously, the relatively small separation within each group suggested the stability of the experimental system.
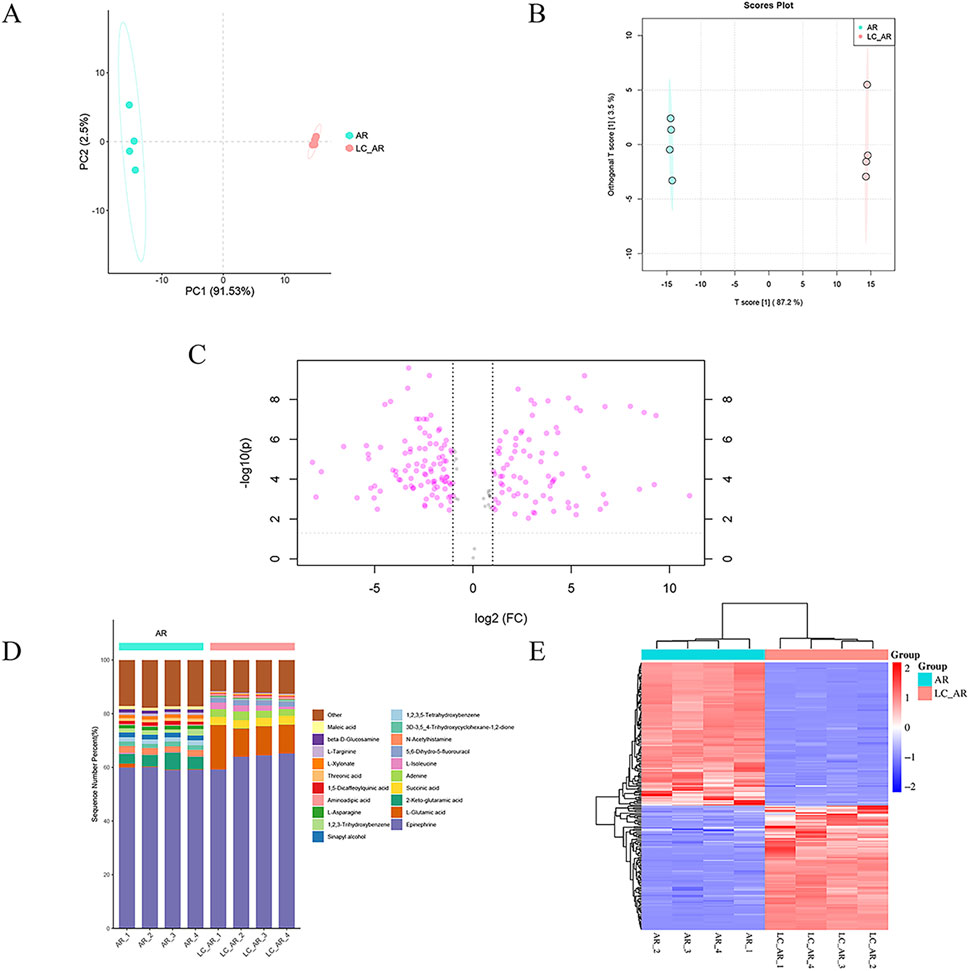
Figure 1. The plot of (A) PCA and (B) OPLS-DA scores, (C) Volcano plot, (D) percentage stacked Columns, (E) clustered heatmap for AR and LC-AR, n = 4.
Furthermore, we employed supervised OPLS-DA to enhance the effectiveness of the data analysis. OPLS-DA decomposes the X matrix into two types: information correlated with Y and uncorrelated with Y. By eliminating the uncorrelated data variations, the classification information is concentrated mainly on one principal component, effectively filtering out noise unrelated to the classification information. As shown in Figure 1B, there was a high degree of separation between the AR and LC-AR groups. Simultaneously, in the OPLS-DA model developed in this study, the values of R2X, R2Y, and Q2 were 0.906, 1, and 0.999, respectively, all approaching 1, indicating the model’s effectiveness and rationality. In contrast, the model utilized the value importance in projection (VIP) values and p-values as critical indicators of the extent of metabolite changes. Generally, VIP > 1 and p < 0.05 are considered significant differential metabolites, with higher VIP values and lower p-values indicating a greater contribution to the grouping. Based on this, the OPLS-DA model screened 198 significant differential metabolites (Supplementary Table S3).
To visually analyze the differences in metabolite changes between the AR and LC-AR groups, we created three typical metabolomic analysis visualizations—volcano plot, percentage stacked columns, and clustering heatmap (Figures 1C–E)—and compared the data between these two groups. In the volcano plot, the abscissa represents the fold change of metabolites, indicated by log2 (Fold Change, FC), while the ordinate represents the T-test p-value, denoted as -log10 (p). As shown in Figure 1C, each point represents a specific metabolite. Generally, metabolites with -log10 (p) > 1.301 and |log2 (FC)| > 1 exhibit significant differences. Compared to the AR group, the LC-AR group showed 79 significantly upregulated metabolites and 97 significantly downregulated metabolites. Percentage stacked columns are formed of the top 20 metabolites based on relative abundance (Figure 1D). Epinephrine is the most abundant metabolite in both the AR and LC-AR groups, constituting the highest percentage content. The second-highest percentage content in the AR and LC-AR groups is found in 2-Keto-glutaramic acid and L-Glutamic acid, respectively. Simultaneously, L-Glutamic acid shows the most significant variation in content among the LC-AR group metabolites. A clustered heatmap (Figure 1E), where red denotes an increase in metabolite content and blue denotes a decrease, also allows us to see the variations in metabolites between the two groups. The heatmap shows a clear separation between the AR and LC-AR groups, which suggests that the two groups’ metabolite contents differ significantly.
The hyperlipidemia caused by a long-term high-fat diet is characterized by symptoms such as weight gain and abnormal liver status (Li et al., 2020). The weekly weight fluctuations and final weights of each group of animals are documented in Figures 2A, B. Following 8 weeks of feeding, the body weight of the mice in the high-fat model group significantly rose compared to the control group (p < 0.01). The body weight of mice in each treatment group showed a significant decrease compared to the model group (p < 0.01).
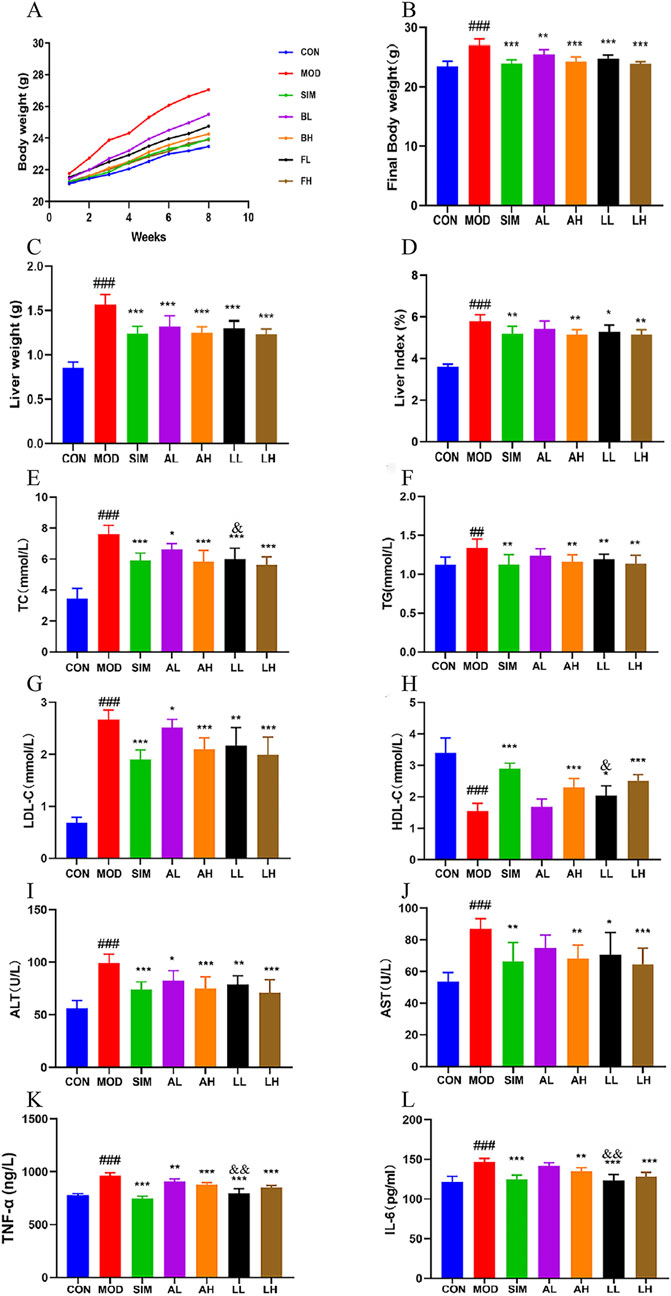
Figure 2. Effects of AR and LC-AR in mice with hyperlipidemia. (A) The body weight curve; (B) the final weight; (C) the weight of the liver; (D) The liver index; (E) TC level; (F) TG level; (G) LDL-C level; (H) HDL-C level; (I) ALT level; (J) AST level; (K) TNF-α; (L) IL-6 level. Data were expressed as mean ± SD, n = 8. Compared with the CON group, # significant at p < 0.05; ## significant at p < 0.01; and ### significant at p < 0.001; compared with MOD group, * significant at p < 0.05; ** significant at p < 0.01; and *** significant at p < 0.001; compared with AL group, & significant at p < 0.05.
Compared to the control group, the model group of rats showed a significant increase in liver weight and liver index (p < 0.01) (Figures 1C, D). Compared to the model group, the liver weights of the mice in each treatment group showed a significant decrease (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). The SIM, AH, LL, and LH groups exhibited a highly significant reduction in liver index (p < 0.01). However, the AL group showed no significant difference in liver index compared to the model group (p > 0.05).
These findings suggest that both AR and LC-AR can effectively alleviate symptoms such as weight gain and liver weight gain induced by hyperlipidemia to a certain extent.
Dysregulation of lipid levels is a prominent feature of hyperlipidemia (Rauf et al., 2022), and Ha et al. (2018) confirmed that consuming AL can improve serum lipid levels and vascular elasticity in the human body, playing a secondary role in promoting vascular health. The levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C in the model group were significantly elevated compared to the normal group (Figures 2E–H), while HDL-C levels were significantly reduced (p < 0.01), indicating the successful establishment of the hyperlipidemic model. Following 8 weeks of treatment, the levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C experienced a significant reduction in the SIM, AH, LL, and LH groups, while the HDL-C level showed a significant increase (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences in TG and HDL-C between the AL and model groups (p > 0.05). In addition, the LL group showed a significant decrease in TC levels and a significant increase in HDL-C levels compared to the AL group (p < 0.05). Briefly, both AR and LC-AR can improve lipid-level disorders, with LC-AR being slightly more effective than AR.
Lipid-level disorders can further lead to hepatocellular steatosis, ultimately evolving into fatty liver and other complications. Meanwhile, when liver cells are damaged, AST and ALT in the cytoplasm are released into the bloodstream (Chen et al., 2020). According to Figures 2I, J, the levels of AST and ALT in the serum of the model group were considerably elevated compared to the control group (p < 0.05). In contrast to the model group, the levels of AST and ALT in the serum of the mice in the SIM, AH, LL, and LH groups showed a significant decrease (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Simultaneously, the ALT levels in the AL group showed a significant decrease compared to the model group (p < 0.05), while the AST levels did not exhibit a significant difference (p > 0.05). Both AR and LC-AR have the potential to improve liver damage caused by hyperlipidemia.
The establishment of hyperlipidemia models is accompanied by high expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines, which have become potential risk factors for various complications (Soujanya and Jayadeep, 2022). For these pro-inflammatory substances, the model group exhibited significantly higher levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in their serum compared to the normal group (p < 0.01) (Figures 2K, L). Compared to the model group, serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels in the SIM, AH, LL, and LH groups were significantly decreased (p < 0.01). Compared to the MOD group, the AL group showed a significant decrease in TNF-α levels (p < 0.05), while IL-6 levels did not exhibit a significant difference (p > 0.05). Meanwhile, the TNF-α and IL-6 levels in the LL group showed a significant decrease compared to the AL group (p < 0.01). These findings indicate that both AR and LC-AR demonstrated a certain degree of anti-inflammatory effects, and at low doses, the efficacy of LC-AR appeared to be superior to that of AR.
The damage caused by hyperlipidemia includes liver injury and degeneration (Wang et al., 2023). According to Figure 3, the normal group exhibited no signs of fatty degeneration or inflammatory infiltration in liver cells. The liver cells are abundant, arranged orderly, with normal nuclei. However, the mice in the model group exhibited severe swelling of liver cells due to a high-fat diet. Numerous lipid droplets are observed within most liver cells, with some droplets being large and showing evident fatty degeneration and inflammatory infiltration. Furthermore, the mice in the SIM, AH, LL, and LH groups exhibited mild-to-moderate hepatocyte swelling in the liver cells. Simultaneously, there was a reduction in lipid droplet count, and both fatty degeneration and liver cell inflammation infiltration showed significant improvement. In the AL group, there was a certain improvement in inflammatory infiltration of liver cells, but significant lipid droplets were still present, showing no significant deviation from the model group. This suggests that AR and LC-AR can improve liver damage caused by hyperlipidemia.
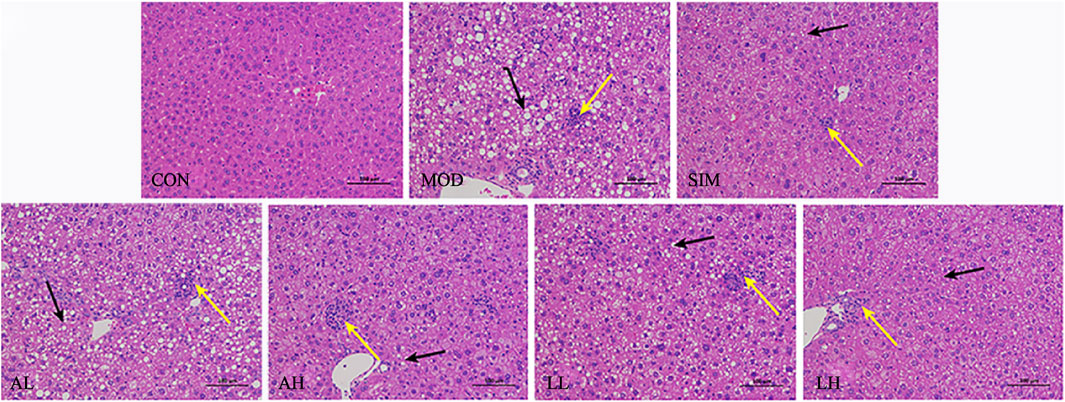
Figure 3. Effect of AR and LC-AR on the pathology of liver tissue. Steatosis is indicated by black arrows, inflammation is indicated by yellow arrows, and the morphology of liver tissue was analyzed using H and E staining at a magnification of 200.
We evaluated the expression levels of cholesterol-related mRNA, including HMGCR, SREBP-2, CYP7A1 (liver), and NPC1L1 (small intestine) (Figure 4), to explore the molecular basis of the anti-hyperlipidemic effects of AR and LC-AR. Compared to the control group, the model group showed a significant increase in HMGCR, SREBP-2, and NPC1L1 mRNA levels (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). When compared to the model group, the AH, LL, and LH groups exhibited a significant decrease in HMGCR, SREBP-2, and NPC1L1 mRNA levels (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). Meanwhile, the model group had a significant decrease in CYP7A1 mRNA levels (p < 0.05), with only the LL and LH groups showing significant increases in CYP7A1 mRNA levels (p < 0.01, p < 0.05).
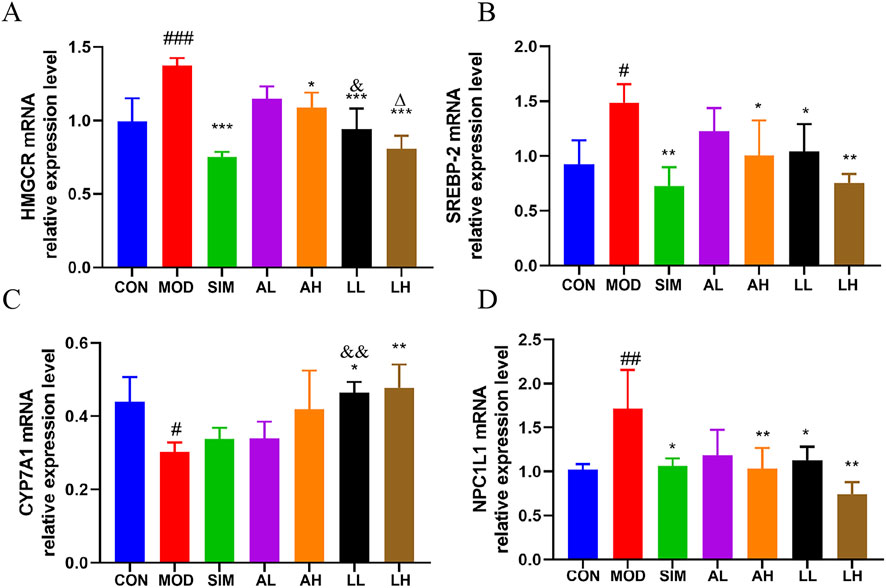
Figure 4. Alterations in gene expression related to cholesterol in the liver and small intestine caused by AR and LC-AR; (A) HMGCR in liver; (B) SREBP-2 in Liver; (C) CYP7A1 in Liver; (D) NPC1L1 in small intestine; the results were reported as the mean ± SD, n = 8. Compared the CON group, # significant at p < 0.05, ## significant at p < 0.01, and ### significant at p < 0.001. In relation to the MOD group, * significant at p < 0.05, ** significant at p < 0.01, and *** significant at p < 0.001. Compared the AL group, & significant at p < 0.05, and && significant at p < 0.01. When compared to the AH group, ∆ significant at p < 0.05.
Additionally, the HMGCR mRNA levels in the LL group were significantly lower than those in the AL group, while the CYP7A1 mRNA levels were significantly higher than those in the AL group (p < 0.05). The results indicate that LC-AR is superior to AR in downregulating hepatic HMGCR and SREBP-2 to inhibit cholesterol synthesis, upregulating hepatic CYP7A1 to promote cholesterol breakdown, and downregulating small intestine NPC1L1 to inhibit cholesterol absorption.
Gut microbiota represents a vast bacterial community present in the gastrointestinal tract. Jia et al. (2021) argued that a normal gut microbiota is crucial for maintaining lipid metabolism homeostasis. To investigate the impact of a high-fat diet on gut microbiota and whether AR and LC-AR can improve gut microbiota imbalance caused by hyperlipidemia, the bacterial community composition in the gut was analyzed using 16S rRNA sequencing. Based on operational taxonomic units (OTUs), the Venn diagram (Figure 5A) shows an intersection of 158 OTUs among all groups, with the model group having a lower OTU count (1401) compared to the control group (1560). Meanwhile, we applied multivariate statistical techniques to analyze the differences in gut microbiota composition between the groups from a macroscopic perspective. The PCA in Figure 5B demonstrates a clear separation between the control and model groups, with each treatment group tending toward the control group.
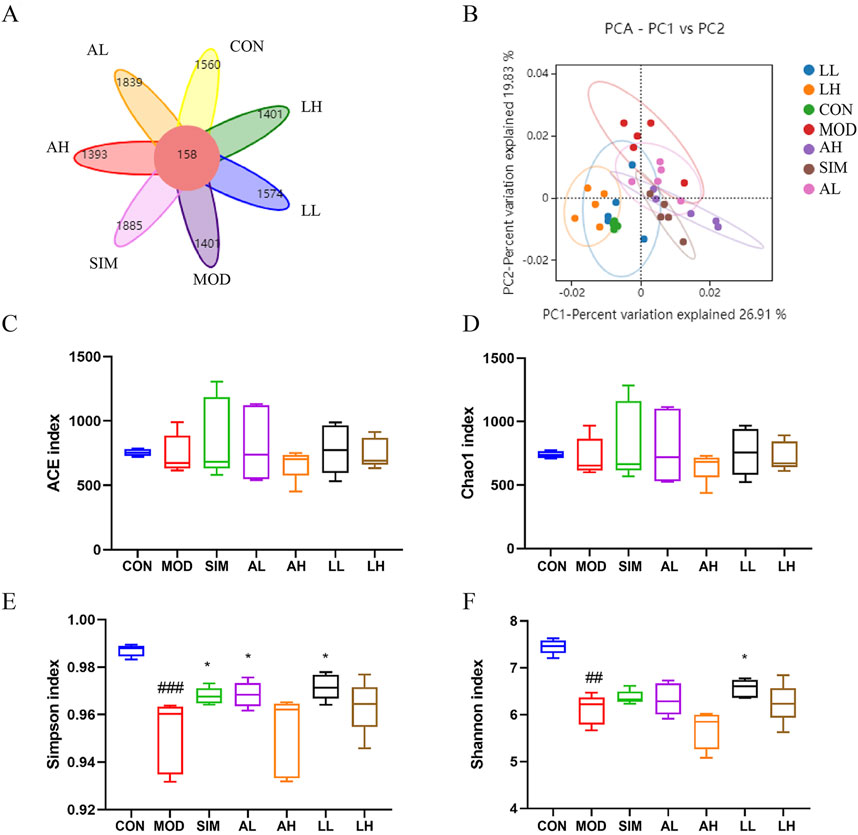
Figure 5. Effects of AR and LC-AR on the mice’s gut microbiota makeup. (A) Wayne diagram, (B) the PCA plot of the OUT level, (C) ACE index, (D) Chao 1 index, (E) Shannon index, and the (F) Simpson index, the data were represented as the mean ± SD, n = 5. Compared with the CON group, # significant at p < 0.05; ## significant at p < 0.01; and ### significant at p < 0.001; compared with MOD group, * significant at p < 0.05; ** significant at p < 0.01; and *** significant at p < 0.001.
Alpha diversity analysis was conducted using ACE, Chao1, Simpson, and Shannon indices as the evaluation criteria (Figures 5C–F). ACE and Chao1 indices represent the abundance of the microbiota, while Simpson and Shannon indices represent the diversity of the microbiota. The ACE and Chao1 indices showed no significant differences among the groups (p > 0.05), indicating that the abundance of gut microbiota was affected by neither the high-fat diet nor the treatment with AR and LC-AR. Furthermore, compared to the control group, the Simpson and Shannon indices of the model group significantly decreased (p < 0.01). Meanwhile, the Simpson index in the SIM, BL, and FL groups, as well as the Shannon index in the FL group, all showed significant increases compared to the model group (p < 0.05). The above results indicate that AR and LC-AR can improve the diversity of gut microbiota to some extent.
In microbiology, microbial species are classified into eight hierarchical levels: domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Based on the OTU analysis, a species analysis was performed at the phylum level to assess the microbial composition within different groups (Figure 6A). In general, bacterial phylum with a relative abundance greater than 0.5% is defined as major phylum, also referred to as the dominant phylum. Firmicutes was evidently the predominant bacterial phylum in all groups. The relative abundance of Firmicutes in the model group significantly increased compared to the control group (p < 0.05), while that in the SIM, AH, and LL groups significantly decreased (p < 0.05) (Figure 6B).
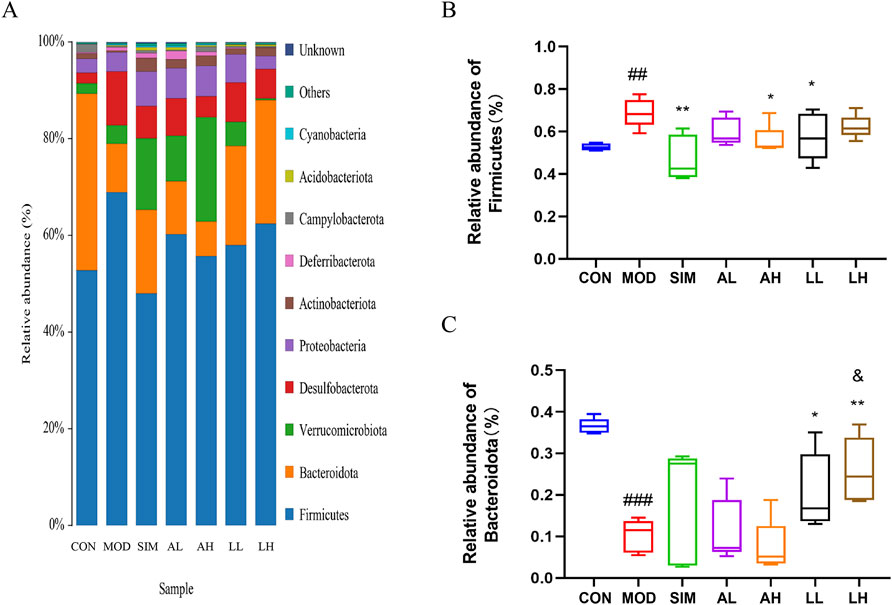
Figure 6. Effects of AR and LC-AR on the relative abundance of gut microbiota at the phylum level. (A) Gut microbiota relative abundance at the phylum level, (B) Firmicutes relative abundance, and (C) Bacteroidota relative abundance. The data were represented as the mean ± SD, n = 5. In comparison to the CON group, the significance levels were as follows: # significant at p < 0.05; ## significant at p < 0.01; and ### significant at p < 0.001; compared with MOD group, * significant at p < 0.05; ** significant at p < 0.01; and *** significant at p < 0.001. Compared to the AL group, & significant at p < 0.05.
In addition, Bacteroidota had the second-highest relative abundance in all groups. According to Figure 6C, the relative abundance of Bacteroidota in the model group significantly decreased compared to the control group (p < 0.05), while that in the LL and LH groups significantly increased (p < 0.05).
AR and LC-AR can modulate gut microbiota homeostasis by downregulating the relative abundance of Firmicutes phylum and upregulating that of Bacteroidota phylum to potentially ameliorate hyperlipidemia induced by a high-fat diet.
We conducted further analysis of the composition of gut microbiota at the family level (Figure 7). In general, a bacterial family with a relative abundance greater than 0.5% is defined as a major family, also referred to as a dominant family. Lachnospiraceae, Muribaculaceae, Oscillospiraceae, and [Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group are dominant bacterial families in the microbial composition of each group (Figure 7A). According to Figures 7B, C, the relative abundances of Lachnospiraceae and Muribaculaceae in the model group significantly decreased compared to the control group (p < 0.05), while those in the LL and LH groups exhibited varying degrees of increase. Additionally, the relative abundances of Oscillospiraceae and [Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group in the model group significantly increased compared to the control group (p < 0.05), whereas those in the SIM, AL, AH, LL, and LH groups exhibited varying degrees of reduction (Figures 7D, E).
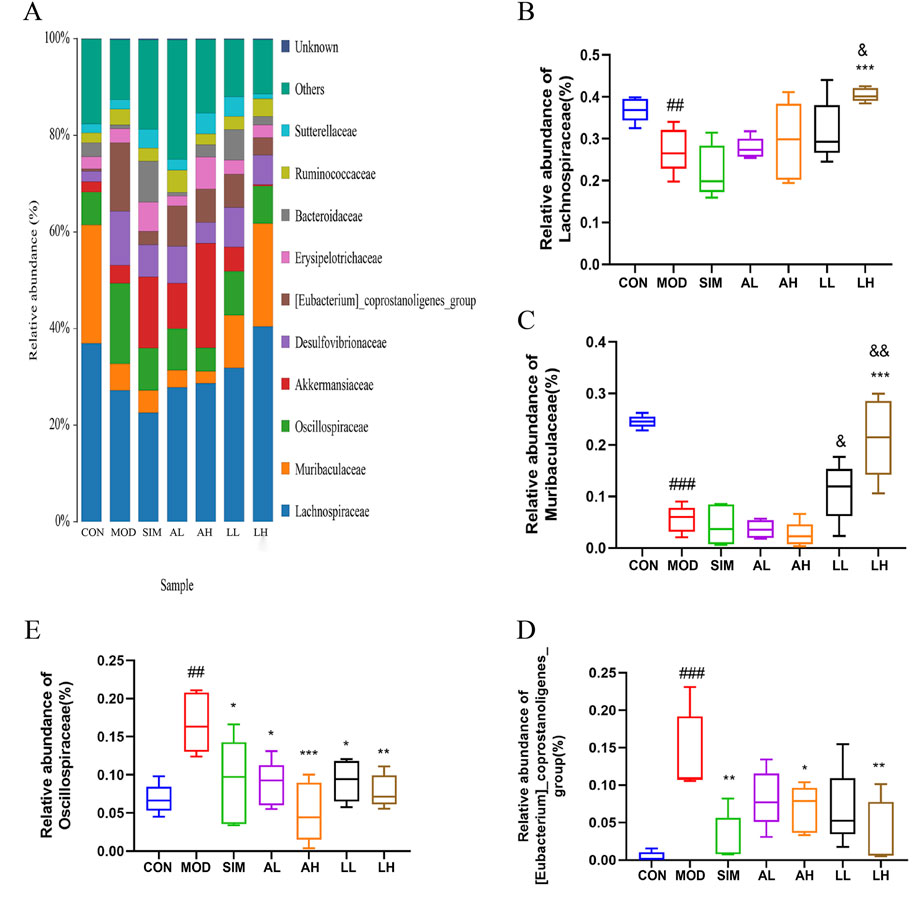
Figure 7. Effects of AR and LC-AR on the relative abundance of gut microbiota at the family level. (A)The gut microbiota’s abundance at the family level, (B) Lachnospiraceae relative abundance, (C) Muribaculaceae relative abundance, (D) [Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group relative abundance, and (E) Oscillospiraceae relative abundance were expressed as mean ± SD, n = 5. In comparison to the CON group, # significant at p < 0.05; ## significant at p < 0.01; ### significant at p < 0.001. When compared to the MOD group, * significant at p < 0.05; ** significant at p < 0.01; *** significant at p < 0.001. Compared to the AL group, & significant at p < 0.05, && significant at p < 0.01.
AR and LC-AR can modulate gut microbiota homeostasis by downregulating the relative abundance of Oscillospiraceae and [Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group and upregulating that of Lachnospiraceae and Muribaculaceae at the family level.
The linear discriminant analysis algorithm-based LDA effect size technique was used to analyze microbiota species exhibiting significant differences among different groups (Figure 8A). Bacteroidota, Bacteroidia, Bacteroidales, and Muribaculaceae were the major significantly different microbial species distinguishing the control group from the other groups. In contrast, f_Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group, Oscillospiraceae, Clostridia, and Firmicutes were the significantly different microbial species in the model group, which indicates the pathogenic mechanisms of hyperlipidemia. Additionally, Lachnospiraceae and g_unclassified_desulfovibrionaceae were identified as significantly different microbial species in the LH and LL groups, respectively. These results indicate significant species variations among the groups.
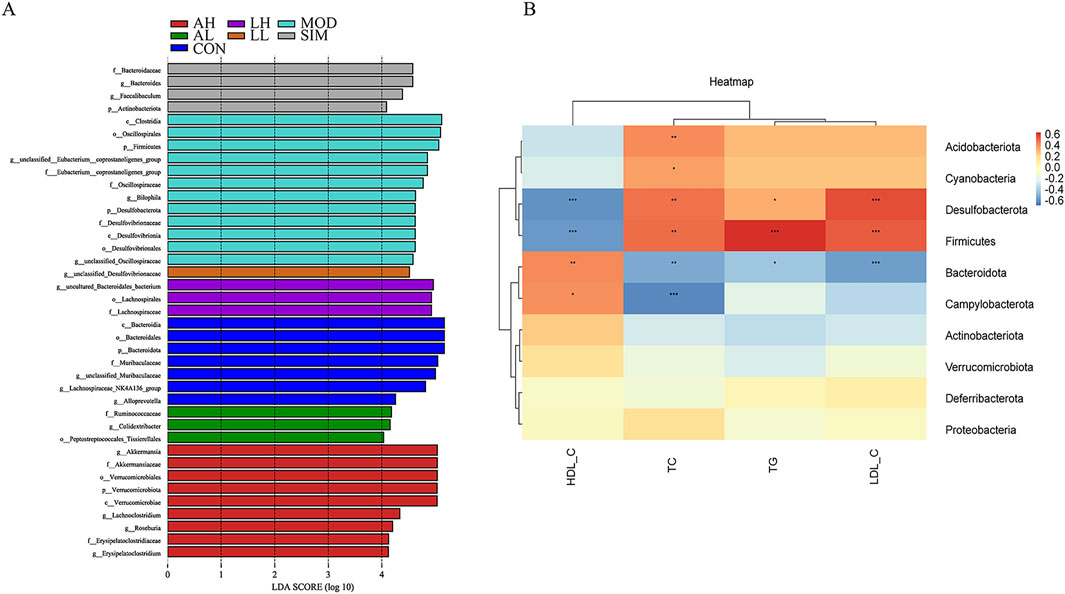
Figure 8. Effects of AR and LC-AR on significant differences in gut microbiota and correlation analysis between lipid levels and gut microbiota. (A) Significant difference analysis based on LEfSe (Log LDA > 4.0); (B) Correlation Analysis Heatmap Based on Spearman’s Correlation. The intensity of colors represents the degree of association between the gut microbiota and lipid levels, with blue indicating a negative connection and red indicating a positive correlation. * significant at p < 0.05, ** significant at p < 0.01, and *** significant at p < 0.001.
To explore in depth the potential link between hyperlipidemia and gut microbiota, we conducted a correlation analysis of selected species at the phylum level of the gut microbiome and lipid levels (Figure 8B). Based on the color variations in the correlation heatmap, Acidobacteriota and Cyanobacteria were significantly positively correlated with TC (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Both Desulfobacterota and Firmicutes exhibited a significant negative correlation with HDL-C and a significant positive correlation with TC, TG, and LDL-C (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Campylobacterota and Bacteroidota were both significantly positively correlated with HDL-C, and Bacteroidota was significantly negatively correlated with TC, TG, and LDL-C. However, Campylobacterota was only significantly negatively correlated with TC (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Overall, Acidobacteriota, Cyanobacteria, Desulfobacterota, Firmicutes, Campylobacterota, and Bacteroidota are pivotal microbial species through which AR and LC-AR improve the lipid levels by modulating gut microbiota.
Hyperlipidemia is generally linked to metabolic disturbances, and consuming a diet rich in fats and cholesterol may contribute to the condition (Zhang Q. et al., 2020). Imbalances in gut microbiota and disruptions in lipid levels are common complications of hyperlipidemia (Tong et al., 2018). Modulating the gut microbiota equilibrium and improving the lipid levels can be the primary strategies for alleviating hyperlipidemia.
Inhibiting the activity of PL and cholesterol esterase CEase can delay the digestion and absorption of a high-fat diet (Chatatikun and Kwanhian, 2020). Toma et al. (2014) found that the potential of Moringa stenopetala leaves to lower lipid levels is attributable to their significant inhibition of PL and CEase activities. Therefore, PL and CEase are frequently used to assess the in vitro lipid-lowering effects of drugs. To identify strains that may be more suitable for improving hyperlipidemia, we assessed the in vitro hypolipidemic activity of various Lactobacillus fermenting AR and found that the AR fermentation by LC exhibited superior inhibitory effects on PL and CEase compared to other strains. Kapila and Sinha, 2006 found that LC, exhibiting relatively strong in vitro antioxidant activity, also demonstrated effective cholesterol-lowering effects in mice. Qian et al. (2019) indicated that LC can improve the lipid metabolism levels in mice with hyperlipidemia. There was a significant increase in the total phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity of LC-AR, accompanied with a notable correlation. This result was foreseeable, as the cellulase produced by LC can hydrolyze the cellulose of AR, releasing more phenolic compounds, which exhibit significant in vitro antioxidant activity (El-Saadony et al., 2021). Additionally, LC itself possesses strong antioxidant capabilities (Kapila and Sinha, 2006). Natural antioxidants seem to have a certain potential for improving liver damage caused by oxidative stress (Li W. et al., 2018), further validating the effectiveness of selecting LC as the fermentation strain. In fact, flavonoids and polysaccharides also exhibit potent in vitro antioxidant activity (Li Z. et al., 2018; Gandhi et al., 2020), providing new insights for the related research.
The metabolites of fermentation are the final products of the fermentation process, and the composition of metabolite species determines their potential to play a specific crucial role within the organism. In this study, untargeted metabolomics was employed to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the changes in the species and levels of metabolites prior to and following fermentation. Among the 198 significantly different metabolites, there was a significant upregulation in the levels of 8 phenolic compounds (such as epinephrine, genistein, apigenin, gallic acid, and eriodictyol), 20 amino acids and their derivatives (such as L-Glutamic acid, L-Serine, and L-Isoleucine), and 9 fatty acids [such as 3-(methylthio)propionic acid, and palmitoleic acid]. Figure 1D shows that the metabolite with the highest relative abundance in both the AR and LC-AR groups is epinephrine. Hormone-sensitive triglyceride lipase is a neutral lipase and a rate-limiting enzyme in fat breakdown, which is capable of hydrolyzing TGs and other lipid and water-soluble substrates. There was a report that exogenous epinephrine can increase the activity of neutral lipase in rat soleus muscle in vitro (Langfort et al., 1999). Similarly, Prats et al. (2006) demonstrated that exogenous epinephrine can reduce intramuscular TGs and intramuscular lipid droplets in rat soleus muscle. Additionally, multiple studies have demonstrated that dietary phenolic compounds, such as genistein (Tang et al., 2015), apigenin (Xu et al., 2021), gallic acid (Huang et al., 2018), and eriodictyol (Kwon and Choi, 2019), can improve symptoms associated with hyperlipidemia in rats or mice, including lipid level abnormalities, liver lipid accumulation, and liver damage. In particular, eriodictyol exhibits a significant protective effect against liver injury (Zheng et al., 2023).
Among the 20 amino acids and their derivatives, one of the precursors of glutathione, the L-isomer of glutamic acid (L-Glutamic acid, as shown in Figure 1D), shows a significant increase in content after fermentation. Salyha and Salyha (2018) pointed out that L-Glutamic acid can alleviate or inhibit chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress in rats. The abundance of L-Glutamic acid in LC-AR seems to support its superior performance over AR in vitro antioxidant experiments. Interestingly, the experiments conducted by Sim et al. (2015) demonstrated that supplementing L-Serine can reduce neutral lipid accumulation and TG concentration in the livers of alcohol-induced fatty liver mice and rats. Additionally, Niu et al. (2023) found that empagliflozin can accelerate the clearance of toxic lipids in non-alcoholic fatty liver mice by upregulating L-Isoleucine levels, thereby alleviating liver damage caused by lipotoxicity. Among the 9 fatty acids, 3-(methylthio) propanoic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of methionine and a type of fatty acid. Sugiyama et al. (1986) found that supplementing 3-(methylthio) propanoic acid can improve liver lipid levels and plasma cholesterol levels in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Palmitoleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid. The experiments conducted by Yang Z. H. et al. (2019) demonstrated that the dietary supplementation of palmitoleic acid can improve the plasma levels of LDL-C receptor-deficient mice (TC, TGs, free cholesterol, and phospholipids) and the lipid/lipoprotein profile in the liver. Similarly, the expression levels of mRNA associated with fatty acid synthesis, such as SREBP1c, FASN, and SCD1 mRNA, showed a significant downregulation after being supplemented with palmitoleic acid. Additionally, there was an upregulation in the expression levels of mRNA related to bile acid synthesis and Cyp7a1 mRNA, promoting cholesterol metabolism.
Body weight and liver weight increase are apparent manifestations of hyperlipidemia (Mudgil et al., 2021). Simultaneously, the abnormalities in TC, TG, and LDL-C elevation, along with an abnormal decrease in HDL-C, are common characteristics of hyperlipidemia (Yang et al., 2022). Dyslipidemia can elevate the levels of inflammatory cytokines, leading to the occurrence of inflammatory reactions (Alzahrani et al., 2022). Additionally, proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) can stimulate TG synthesis and secretion and activate cholesterol synthesis, further affecting the body’s lipid levels (Jung and Choi, 2014). Moreover, an imbalance in the lipid levels will gradually affect the normal functioning of liver cells (Chen et al., 2020). We found that supplementation with LC-AR reduced body weight and liver weight in hyperlipidemic mice. Regarding lipid levels, it decreased the levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C while increasing the level of HDL-C. Meanwhile, the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 were effectively suppressed. Additionally, LC-AR improved the levels of liver damage markers AST and ALT in the blood, as well as hepatic tissue degeneration at the histological level. Thus, it can be seen that LC-AR performs well in improving the underlying abnormal indicators of hyperlipidemia. Diez-Ozaeta and Astiazaran (2022) emphasized the health benefits of fermented foods and the promising prospects for development in the context of hyperlipidemia. According to Yan et al. (2022), probiotic-fermented rice buckwheat alleviated lipid abnormalities in hyperlipidemic mice.
Cholesterol level is closely related to hyperlipidemia, and the factors influencing cholesterol level include the absorption, synthesis, transport, and excretion of cholesterol. We found that LC-AR can inhibit the expression levels of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase (HMGCR), sterol-regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBP-2) in the liver, and Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) mRNA in the small intestine while promoting the expression of Cholesterol 7-alpha hydroxylase (CYP7A1) mRNA (in the liver). HMGCR is a rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis, and its activation leads to increased cholesterol synthesis, which may result in hepatic cholesterol accumulation and hypercholesterolemia (Li et al., 2019). CYP7A1 is a rate-limiting enzyme in the bile acid synthesis pathway that promotes the conversion of cholesterol to bile acid and reduces cholesterol accumulation (Li et al., 2021). SREBP-2 primarily regulates the expression of cholesterol synthesis of mRNA (Song et al., 2015). NPC1L1 is a highly expressed transmembrane protein in mammalian small intestine epithelial cells and plays a crucial role in cholesterol absorption (Zhang et al., 2022). NPC1L1 inhibitors have been shown to lower the plasma levels of TGs and cholesterol, thereby regulating lipid metabolism (Tavares et al., 2020). Yang W. S. et al. (2019) found that Chitooligosaccharide tablets can regulate serum cholesterol synthesis levels by upregulating CYP7A1 and downregulating HMGCR and SREBP-2 mRNA expression. Therefore, SREBP-2, HMGCR, CYP7A1, and NPC1L1 mRNA can be effective targets for reducing cholesterol accumulation in the body.
The composition and function of gut microbiota are associated with the host’s energy metabolism and health (Cheng et al., 2022). Most research considers the dysbiosis of gut microbiota to be another important factor leading to hyperlipidemia. Hyperlipidemia typically causes an increase in the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidota (Jiang et al., 2021; De et al., 2011). Similar to our work, there was an increase in the relative abundance of Firmicutes and a decrease in that of Bacteroidota at the phylum level. After supplementation with LC-AR, there was a certain degree of reversal of the trend of an increased Firmicutes/Bacteroidota ratio. Zhang W. et al. (2022) demonstrated that bacterial cellulose reduced the Firmicutes/Bacteroidota relative abundance ratio and improved the activity of gut microbiota in hyperlipidemic mice. Also, a decrease in the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes in the gut microbiota is found significantly correlated with various inflammatory markers (Zhang et al., 2023). Therefore, interventions that restrict the elevation of Firmicutes or promote the reduction of Bacteroidota contribute to the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
Additionally, at the family level, supplementation with LC-AR increased the relative abundance of Lachnospiraceae and Muribaculaceae while decreasing the relative abundance of [Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group and Oscillospiraceae. Reportedly, both Lachnospiraceae and Muribaculaceae can produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (Soares et al., 2021; Ye et al., 2021). Previous research has indicated that butyrate salts, a type of SCFAs produced by Lachnospiraceae, can maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier and suppress inflammation in mice (Ma et al., 2020). Niu et al. (2022) suggested that Lachnospiraceae can regulate the absorption of nutrients in the gut and inhibit the growth and proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. However, Oscillospiraceae is significantly associated with lipid abnormalities and systemic inflammatory responses (Farzam, 2022). Related studies have suggested that the Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group is positively correlated with lipid levels, such as TC, TG, and LDL-C (Lei et al., 2023). Overall, at the phylum and family taxonomic levels, LC-AR demonstrated the potential to ameliorate hyperlipidemia resulting from the dysbiosis of gut microbiota.
According to our research findings, the fermentation of LC enhances the effectiveness of AR in improving hyperlipidemia. The main mechanism through which LC-AR exerts its anti-hyperlipidemic effects is the regulation of lipid levels and cholesterol-related mRNA, as well as the gut microbiota. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report related to the LC fermented AR. However, this research is still in the exploratory phase, with the experimental model limited to animal experiments, and it lacks comparisons with existing drugs such as statins and fibrates, or with the efficacy of traditional fermented Chinese medicines. Further clinical trials are needed to evaluate its potential as an alternative to current treatment options. Additionally, the specific active components in LC-AR and the exact mechanisms underlying its antihyperlipidemic effects require further investigation.
This study highlights the potential of LC-AR as a promising supplement for improving hyperlipidemia. The selection of LC was based on in vitro lipid-lowering experiments, and the combination with AR demonstrated higher polyphenol content and superior antioxidant activity compared to AR alone. Simultaneously, the variations in metabolite levels revealed by untargeted metabolomics provided support for the feasibility of the experiment. LC-AR showed favorable effects in regulating the lipid levels (TC, TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C) and liver injury markers (AST and ALT), proinflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α and IL-6) and regulating the expression of cholesterol-related mRNA (HMGCR, SREBP-2, CYP7A1, and NPC1L1 mRNA). Additionally, LC-AR exhibited positive changes in liver tissue pathology and alterations in gut microbiota species. These findings are significant as they offer a new perspective on the study of traditional Chinese medicine’s effects on hyperlipidemia. They contribute to the theoretical understanding of the transformation and utilization of LC and AR, and provide a scientific basis for considering LC-AR as a potential therapeutic supplement and drug raw materials for hyperlipidemia.
The 16s rRNA data presented in the study has been deposited in the NCBI (SRA) repository, accession number PRJNA1174375. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The animal study was approved by The Animal Ethics Committee of Guangdong Pharmaceutical Univercity. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
MC: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. YW: Writing–original draft, Methodology, Visualization. HY: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. TL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. TH: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. WD: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. JuC: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. FO: Software, Writing–review and editing. JiC: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. JL: Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. XH: Project administration, Resources, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82274357) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 82274178).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1447077/full#supplementary-material
Abdelrazig, S., Safo, L., Rance, G. A., Fay, M. W., Theodosiou, E., Topham, P. D., et al. (2020). Metabolic characterisation of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1 using LC-MS-based metabolite profiling. RSC Adv. 2 (54), 32548–32560. doi:10.1039/d0ra05326k
Alloubani, A., Nimer, R., and Samara, R. (2021). Relationship between hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease and stroke: a systematic review. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 17 (6), e051121189015. doi:10.2174/1573403X16999201210200342
Alzahrani, N. S., Alshammari, G. M., El-Ansary, A., Yagoub, A. E. A., Amina, M., Saleh, A., et al. (2022). Anti-hyperlipidemia, hypoglycemic, and hepatoprotective impacts of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) grains and their ethanol extract on rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients 14 (9), 1791. doi:10.3390/nu14091791
Chai, Z., Yan, Y., Zan, S., Meng, X., and Zhang, F. (2022). Probiotic-fermented blueberry pomace alleviates obesity and hyperlipidemia in high-fat diet C57BL/6J mice. Food Res. Int. 157, 111396. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111396
Chatatikun, M., and Kwanhian, W. (2020). Phenolic profile of nipa palm vinegar and evaluation of its antilipidemic activities. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 6769726. doi:10.1155/2020/6769726
Chen, Y., Li, R., Hu, N., Yu, C., Song, H., Li, Y., et al. (2020). Baihe Wuyao decoction ameliorates CCl4-induced chronic liver injury and liver fibrosis in mice through blocking TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling, anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 263, 113227. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113227
Cheng, L., Wei, Y., Xu, L., Peng, L., Wang, Y., and Wei, X. (2022). Gut microbiota differentially mediated by qingmao tea and qingzhuan tea alleviated high-fat-induced obesity and associated metabolic disorders: the impact of microbial fermentation. Foods 11 (20), 3210. doi:10.3390/foods11203210
Crea, F. (2023). Targeting hypercholesterolaemia: challenges and opportunities. Eur. Heart J. 44 (25), 2263–2266. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehad415
De, B. J. P., Waligora-Dupriet, A. J., and Butel, M. J. (2011). Intestinal microbiota in inflammation and insulin resistance: relevance to humans. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 14 (4), 334–340. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e328347924a
Dias, M. M., Zuza, O., Riani, L. R., de, F. P. P., Pinto, P. L. S., Silva, M. P., et al. (2017). In vitro schistosomicidal and antiviral activities of Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) against Schistosoma mansoni and Herpes simplex virus-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 94, 489–498. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.116
Diez-Ozaeta, I., and Astiazaran, O. J. (2022). Fermented foods: an update on evidence-based health benefits and future perspectives. Food Res. Int. 156, 111133. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111133
Dunn, W. B., Broadhurst, D., Begley, P., Zelena, E., Francis-McIntyre, S., Anderson, N., et al. (2011). Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 30 (7), 1060–1083. doi:10.1038/nprot.2011.335
El-Saadony, M. T., Alagawany, M., Patra, A. K., Kar, I., Tiwari, R., Dawood, M. A. O., et al. (2021). The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: an overview. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 117, 36–52. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2021.07.007
Farzam, K. (2022). Lipid disorders in children: diagnosis and treatment. Future Cardiol. 18 (12), 915–920. doi:10.2217/fca-2022-0062
Fiorino, G. M., Tlais, A. Z. A., Losito, I., Filannino, P., Gobbetti, M., and Di, C. R. (2023). Triacylglycerols hydrolysis and hydroxy- and epoxy-fatty acids release during lactic fermentation of plant matrices: an extensive study showing inter- and intra-species capabilities of lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. 412, 135552. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135552
Fu, F. Q., Xu, M., Wei, Z., and Li, W. (2020). Biostudy on traditional Chinese medicine Massa Medicata Fermentata. ACS Omega 6 (19), 10987–10994. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c00816
Gandhi, G. R., Vasconcelos, A. B. S., Wu, D. T., Li, H. B., Antony, P. J., Li, H., et al. (2020). Citrus flavonoids as promising phytochemicals targeting diabetes and related complications: a systematic review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Nutrients 12 (10), 2907. doi:10.3390/nu12102907
Gao, D., Chen, H., Li, H., Yang, X., Guo, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Extraction, structural characterization, and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides derived from Arctium lappa L. Front. Nutr. 10, 1149137. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1149137
Ha, M. S., Kim, J. H., Kim, Y. S., and Kim, D. Y. (2018). Effects of aquarobic exercise and burdock intake on serum blood lipids and vascular elasticity in Korean elderly women. Exp. Gerontol. 101, 63–68. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2017.11.005
Horai, H., Arita, M., Kanaya, S., Nihei, Y., Ikeda, T., Suwa, K., et al. (2010). MassBank: a public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 45 (7), 703–714. doi:10.1002/jms.1777
Huang, D. W., Chang, W. C., Yang, H. J., Wu, J. S., and Shen, S. C. (2018). Gallic acid alleviates hypertriglyceridemia and fat accumulation via modulating glycolysis and lipolysis pathways in perirenal adipose tissues of rats fed a high-fructose diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (1), 254. doi:10.3390/ijms19010254
Huang, F., Zheng, X., Ma, X., Jiang, R., Zhou, W., Zhou, S., et al. (2019). Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 31 (1), 4971. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12896-x
Jia, X., Xu, W., Zhang, L., Li, X., Wang, R., and Wu, S. (2021). Impact of gut microbiota and microbiota-related metabolites on hyperlipidemia. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11, 634780. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.634780
Jiang, T., Xu, C., Liu, H., Liu, M., Wang, M., Jiang, J., et al. (2021). Linderae radix ethanol extract alleviates diet-induced hyperlipidemia by regulating bile acid metabolism through gut microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 627920. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.627920
Jung, U. J., and Choi, M. S. (2014). Obesity and its metabolic complications: the role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15 (4), 6184–6223. doi:10.3390/ijms15046184
Kapila, S., and Sinha, P. R. (2006). Antioxidative and hypocholesterolemic effect of Lactobacillus casei ssp casei (biodefensive properties of lactobacilli). Indian J. Med. Sci. 60 (9), 361–370. doi:10.4103/0019-5359.27220
Kwon, E. Y., and Choi, M. S. (2019). Dietary eriodictyol alleviates adiposity, hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and inflammation in diet-induced obese mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (5), 1227. doi:10.3390/ijms20051227
Langfort, J., Ploug, T., Ihlemann, J., Saldo, M., Holm, C., and Galbo, H. (1999). Expression of hormone-sensitive lipase and its regulation by adrenaline in skeletal muscle. Biochem. J. 340 (Pt 2), 459–465. doi:10.1042/bj3400459
Le, L. S., Simard, G., Martinez, M. C., and Andriantsitohaina, R. (2014). Oxidative stress and metabolic pathologies: from an adipocentric point of view. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 908539. doi:10.1155/2014/908539
Lei, S., He, S., Li, X., Zheng, B., Zhang, Y., and Zeng, H. (2023). Effect of lotus seed resistant starch on small intestinal flora and bile acids in hyperlipidemic rats. Food Chem. 404 (Pt A), 134599. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134599
Li, H., Yu, X. H., Ou, X., Ouyang, X. P., and Tang, C. K. (2021). Hepatic cholesterol transport and its role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerosis. Prog. Lipid Res. 83, 101109. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2021.101109
Li, J., Wu, H., Liu, Y., and Yang, L. (2020). High fat diet induced obesity model using four strainsof mice: kunming, C57BL/6, BALB/c and ICR. Exp. Anim. 69 (3), 326–335. doi:10.1538/expanim.19-0148
Li, Q., Zhang, H., Zou, J., Feng, X., and Feng, D. (2019). Bisphenol A induces cholesterol biosynthesis in HepG2 cells via SREBP-2/HMGCR signaling pathway. J. Toxicol. Sci. 44 (7), 481–491. doi:10.2131/jts.44.481
Li, W., Jiang, N., Li, B., Wan, M., Chang, X., Liu, H., et al. (2018). Antioxidant activity of purified ulvan in hyperlipidemic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 113, 971–975. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.104
Li, Z., Teng, J., Lyu, Y., Hu, X., Zhao, Y., and Wang, M. (2018). Enhanced antioxidant activity for apple juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC14917. Molecules 24 (1), 51. doi:10.3390/molecules24010051
Lin, C. C., Li, T. C., and Lai, M. M. (2005). Efficacy and safety of Monascus purpureus Went rice in subjects with hyperlipidemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 153 (5), 679–686. doi:10.1530/eje.1.02012
Liu, G., Zhu, W., Zhang, J., Song, D., Zhuang, L., Ma, Q., et al. (2022). Antioxidant capacity of phenolic compounds separated from tea seed oil in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. 371, 131122. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131122
Liu, M., Shi, W., Huang, Y., Wu, Y., and Wu, K. (2023). Intestinal flora: a new target for traditional Chinese medicine to improve lipid metabolism disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1134430. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1134430
Liu, P., Yu, S., Liu, J., Zhou, Y., Cao, R., Zhou, Y., et al. (2020). Effects of Lactobacillus on hyperlipidemia in high-fat diet-induced mouse model. Arch. Med. Sci. 19 (3), 792–799. doi:10.5114/aoms.2020.98927
Lyu, J. I., Ryu, J., Jin, C. H., Kim, D. G., Kim, J. M., Seo, K. S., et al. (2020). Phenolic compounds in extracts of Hibiscus acetosella (cranberry Hibiscus) and their antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Molecules 25 (18), 4190. doi:10.3390/molecules25184190
Ma, K., Sheng, W., Gao, R., Feng, J., Huang, W., Cui, L., et al. (2022). Ethanolic extract of root from Arctium lappa L ameliorates obesity and hepatic steatosis in rats by regulating the AMPK/ACC/CPT-1 pathway. J. Food Biochem. 46 (12), e14455. doi:10.1111/jfbc.14455
Ma, L., Ni, Y., Wang, Z., Tu, W., Ni, L., Zhuge, F., et al. (2020). Spermidine improves gut barrier integrity and gut microbiota function in diet-induced obese mice. Gut Microbes 12 (1), 1–19. doi:10.1080/19490976.2020.1832857
Ma, Q. W., Chen, M. J., Liu, Y., Tong, Y., Liu, T. F., Wu, L. L., et al. (2023). Lactobacillus acidophilus fermented dandelion improves hyperuricemia and regulates gut microbiota. Fermentation 9 (4), 352. doi:10.3390/fermentation9040352
Moro, T. M. A., T, P. S., and Clerici, M. (2020). Burdock (Arctium lappa L) roots as a source of inulin-type fructans and other bioactive compounds: current knowledge and future perspectives for food and non-food applications. Food Res. Int. 141, 109889. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109889
Mudgil, P., Baba, W. N., Kamal, H., FitzGerald, R. J., Hassan, H. M., Ayoub, M. A., et al. (2021). A comparative investigation into novel cholesterol esterase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptides from cow and camel casein hydrolysates generated upon enzymatic hydrolysis and in-vitro digestion. Food Chem. 367, 130661. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130661
Nam, Y. K., Kim, M. H., Ha, I. J., and Yang, W. M. (2021). Derma-hc, a new developed herbal formula, ameliorates cutaneous lichenification in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26 (5), 2359. doi:10.3390/ijms22052359
Niu, K., Bai, P., Yang, B., Feng, X., and Qiu, F. (2022). Asiatic acid alleviates metabolism disorders in ob/ob mice: mechanistic insights. Food Funct. 13 (13), 6934–6946. doi:10.1039/d2fo01069k
Niu, S., Ren, Q., Chen, S., Pan, X., Yue, L., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Metabolic and hepatic effects of empagliflozin on nonalcoholic fatty liver mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 16, 2549–2560. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S422327
Prats, C., Donsmark, M., Qvortrup, K., Londos, C., Sztalryd, C., Holm, C., et al. (2006). Decrease in intramuscular lipid droplets and translocation of HSL in response to muscle contraction and epinephrine. J. Lipid Res. 47 (11), 2392–2399. doi:10.1194/jlr.M600247-JLR200
Qian, Y., Li, M., Wang, W., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Hu, Q., et al. (2019). Effects of lactobacillus casei YBJ02 on lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic mice. J. Food Sci. 84 (12), 3793–3803. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.14787
Rauf, A., Akram, M., Anwar, H., Daniyal, M., Munir, N., Bawazeer, S., et al. (2022). Therapeutic potential of herbal medicine for the management of hyperlipidemia: latest updates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 29 (27), 40281–40301. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-19733-7
Salyha, N., and Salyha, Y. (2018). Protective role of l-glutamic acid and l-cysteine in mitigation the chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 64, 155–163. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2018.10.010
Sim, W. C., Yin, H. Q., Choi, H. S., Choi, Y. J., Kwak, H. C., Kim, S. K., et al. (2015). L-serine supplementation attenuates alcoholic fatty liver by enhancing homocysteine metabolism in mice and rats. J. Nutr. 145 (2), 260–267. doi:10.3945/jn.114.199711
Soares, E., Soares, A. C., Trindade, P. L., Monteiro, E. B., Martins, F. F., Forgie, A. J., et al. (2021). Jaboticaba (Myrciaria jaboticaba) powder consumption improves the metabolic profile and regulates gut microbiome composition in high-fat diet-fed mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 144, 112314. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112314
Song, H. S., Koo, H. J., Park, B. K., Kwon, J. E., Jang, S. A., Baek, H. J., et al. (2018). The suppressive effect of the three-herb extract mixture on vascular and liver inflammation in atherogenic diet with high fructose-fed mice. Pharm. Biol. 56 (1), 32–42. doi:10.1080/13880209.2017.1412468
Song, Y., Xu, C., Shao, S., Liu, J., Xing, W., Xu, J., et al. (2015). Thyroid-stimulating hormone regulates hepatic bile acid homeostasis via SREBP-2/HNF-4α/CYP7A1 axis. J. Hepatol. 62 (5), 1171–1179. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.006
Soujanya, K. V., and Jayadeep, A. P. (2022). Obesity-associated biochemical markers of inflammation and the role of grain phytochemicals. J. Food Biochem. 46 (9), e14257. doi:10.1111/jfbc.14257
Stewart, J., McCallin, T., Martinez, J., Chacko, S., and Yusuf, S. (2020). Hyperlipidemia. Pediatr. Rev. 41 (8), 393–402. doi:10.1542/pir.2019-0053
Sud, M., Fahy, E., Cotter, D., Brown, A., Dennis, E. A., Glass, C. K., et al. (2007). LMSD: LIPID MAPS structure database. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (Database issue), D527–D532. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl838
Sugiyama, K., Akai, H., and Muramatsu, K. (1986). Effects of methionine and related compounds on plasma cholesterol level in rats fed a high cholesterol diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 32 (5), 537–549. doi:10.3177/jnsv.32.537
Takeda, H., Nakajima, A., and Kiriyama, S. (1992). Beneficial effect of dietary fiber on the upper gastrointestinal transit time in rats suffering from a toxic dose of amaranth. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 56 (4), 551–555. doi:10.1271/bbb.56.551
Tang, C., Zhang, K., Zhao, Q., and Zhang, J. (2015). Effects of dietary genistein on plasma and liver lipids, hepatic gene expression, and plasma metabolic profiles of hamsters with diet-induced hyperlipidemia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 (36), 7929–7936. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01590
Tavares, T. B., Santos, I. B., de, B. G. F., Ognibene, D. T., da, R. A. P. M., de, M. R. S., et al. (2020). Therapeutic effects of açaí seed extract on hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced obesity in male mice: a comparative effect with rosuvastatin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 72 (12), 1921–1932. doi:10.1111/jphp.13356
Toma, A., Makonnen, E., Mekonnen, Y., Debella, A., and Addisakwattana, S. (2014). Intestinal α-glucosidase and some pancreatic enzymes inhibitory effect of hydroalcholic extract of Moringa stenopetala leaves. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 14, 180. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-14-180
Tong, X., Xu, J., Lian, F., Yu, X., Zhao, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2018). Structural alteration of gut microbiota during the amelioration of human type 2 diabetes with hyperlipidemia by metformin and a traditional Chinese herbal formula: a multicenter, randomized, open label clinical trial. mBio 9 (3), e02392–e02317. doi:10.1128/mBio.02392-17
Un-Nisa, A., Khan, A., Zakria, M., Siraj, S., Ullah, S., Tipu, M. K., et al. (2022). Updates on the role of probiotics against different health issues: focus on lactobacillus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (1), 142. doi:10.3390/ijms24010142
Wang, F., Yao, W., Yu, D., Hao, Y., Wu, Y., and Zhang, X. (2023). Protective role of thymoquinone in hyperlipidemia-induced liver injury in LDL-R-/-mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 23 (1), 276. doi:10.1186/s12876-023-02895-0
Wang, M., Xu, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, N., Ge, W., and Song, R. (2021). Integrated multiplatform-based metabonomics and network analysis to explore the mechanism of Polygonum cuspidatum on hyperlipidemia. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 30, 122769. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122769
Wang, Z., Li, P., Wang, C., Jiang, Q., Zhang, L., Cao, Y., et al. (2016). Protective effects of Arctium lappa L. root extracts (AREs) on high fat diet induced quail atherosclerosis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 16, 6. doi:10.1186/s12906-016-0987-2
Wishart, D. S. (2020). Metabolomic data exploration and analysis with the human metabolome database. Methods Mol. Biol. 2104, 165–184. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0239-3_10
Wixon, J., and Kell, D. (2000). Website review: the kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes—KEGG. Available at: http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/.17;48, 55. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(200004)
Xu, Q., Li, Y. C., Du, C., Wang, L. N., and Xiao, Y. H. (2021). Effects of apigenin on the expression of LOX-1, bcl-2, and bax in hyperlipidemia rats. Chem. Biodivers. 18 (8), e2100049. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202100049
Yan, J., Xue, Q., Chen, W., Wang, K., Peng, D., Jiang, J., et al. (2022). Probiotic-fermented rice buckwheat alleviates high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in mice by suppressing lipid accumulation and modulating gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 155, 111125. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111125
Yang, D., Hu, C., Deng, X., Bai, Y., Cao, H., Guo, J., et al. (2019). Therapeutic effect of Chitooligosaccharide tablets on lipids in high-fat diets induced hyperlipidemic rats. Molecules 24 (3), 514. doi:10.3390/molecules24030514
Yang, H. Y., Han, L., Lin, Y. Q., Li, T., Wei, Y., Zhao, L. H., et al. (2023). Probiotic fermentation of herbal medicine: progress, challenges, and opportunities. Am. J. Chin. Med. 51 (5), 1105–1126. doi:10.1142/S0192415X23500519
Yang, W. S., Kim, J. C., Lee, J. Y., Kim, C. H., and Hwang, C. W. (2019). Antihyperlipidemic and antioxidative potentials of onion (Allium cepa L.) extract fermented with a novel lactobacillus casei HD-010. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 3, 3269047. doi:10.1155/2019/3269047
Yang, Z., Zhu, X., Wen, A., Ran, J., Qin, L., and Zhu, Y. (2022). Coix seed-based milk fermented with Limosilactobacillus reuteri improves lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice fed with a high-fat diet. Front. Nutr. 9, 921255. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.921255
Yang, Z. H., Pryor, M., Noguchi, A., Sampson, M., Johnson, B., Pryor, M., et al. (2019). Dietary palmitoleic acid attenuates atherosclerosis progression and hyperlipidemia in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 63 (12), e1900120. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201900120
Ye, J., Zhao, Y., Chen, X., Zhou, H., Yang, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). Pu-erh tea ameliorates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high fat diet fed mice. Food Res. Int. 144, 110360. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110360
Zelena, E., Dunn, W. B., Broadhurst, D., Francis-McIntyre, S., Carroll, K. M., Begley, P., et al. (2009). Development of a robust and repeatable UPLC-MS method for the long-term metabolomic study of human serum. Anal. Chem. 81 (4), 1357–1364. doi:10.1021/ac8019366
Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, L., Zhao, X., Xu, Y., et al. (2023). Maternal folic acid supplementation during pregnancy prevents hepatic steatosis in male offspring of rat dams fed high-fat diet, which is associated with the regulation of gut microbiota. Nutrients 15 (22), 4726. doi:10.3390/nu15224726
Zhang, H. L., Wu, Q. X., Wei, X., and Qin, X. M. (2020). Pancreatic lipase and cholesterol esterase inhibitory effect of Camellia nitidissima Chi flower extracts in vitro and in vivo. Food Biosci. 37, 100682. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100682
Zhang, Q., Fan, X., Ye, R., Hu, Y., Zheng, T., Shi, R., et al. (2020). The effect of simvastatin on gut microbiota and lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic rats induced by a high-fat diet. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 522. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00522
Zhang, R., Liu, W., Zeng, J., Meng, J., Jiang, H., Wang, J., et al. (2022). Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 inhibitors for reducing cholesterol absorption. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 230, 114111. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114111
Zhang, W., Zhang, Q. Y., Wang, J. J., Zhang, L. L., and Dong, Z. Z. (2022). Efficiency assessment of bacterial cellulose on lowering lipid levels in vitro and improving lipid metabolism in vivo. Molecules 27 (11), 3495. doi:10.3390/molecules27113495
Zhang, X., Zhang, N., Kan, J., Sun, R., Tang, S., Wang, Z., et al. (2020). Anti-inflammatory activity of alkali-soluble polysaccharides from Arctium lappa L. and its effect on gut microbiota of mice with inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 154, 773–787. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.111
Zheng, X., Wu, X., Wen, Q., Tang, H., Zhao, L., Shi, F., et al. (2023). Eriodictyol alleviated LPS/D-GalN-Induced acute liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Nutrients 15 (20), 4349. doi:10.3390/nu15204349
Zheng, Y., Wang, Y., Luo, D., Lin, L., Lu, X., Gao, J., et al. (2024). Effect of Bergamot and laoxianghuang polysaccharides on gut microbiota derived from patients with hyperlipidemia: an integrative analysis of microbiome and metabolome during in vitro fermentation. Foods 10 (14), 2039. doi:10.3390/foods11142039
Keywords: Arctium lappa L. root, lactobacillus, fermented, hyperlipidemia, lipid level, gut microbiota
Citation: Chen M, Wu Y, Yang H, Liu T, Han T, Dai W, Cen J, Ouyang F, Chen J, Liu J, Zhou L and Hu X (2024) Effects of fermented Arctium lappa L. root by Lactobacillus casei on hyperlipidemic mice. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1447077. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1447077
Received: 11 June 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 28 October 2024.
Edited by:
Hua Li, Air Force Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Chen, Wu, Yang, Liu, Han, Dai, Cen, Ouyang, Chen, Liu, Zhou and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianxin Liu, bGl1amlhbnhpbjMzODVAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Lin Zhou, emhvdWxpbkBnZHB1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xuguang Hu, aHhndWFuZzIxQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.