- 1Department of Orthopedics, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 2Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), which are usually considered not to encode proteins, are widely involved in important activities including signal transduction and cell proliferation. However, recent studies have shown that small peptides encoded by ncRNAs (SPENs) have important roles in the development of malignant tumors. Some SPENs participate in the regulation of skeleton reorganization, intercellular adhesion, signaling and other processes of tumor cells, with effects on the invasive and migratory abilities of the cells. Therefore, SPENs have potential applications as therapeutic targets and biomarkers of malignant tumors. Invasion and migration of malignant tumor cells are the main reasons for poor prognosis of cancer patients and represent the most challenging aspects of treatment of malignant tumors. Currently, the main treatments for tumors include surgery, radiotherapy, targeted drug therapy. Surgery, however, is reserved for early stages of cancer and carries risks and costs. Radiotherapy and targeted therapy have serious side effects. This review describes the mechanisms of SPENs and their roles in tumor invasion and migration, with the aim of providing new targets for tumor diagnosis and treatment.
1 Introduction
Malignant tumors, which are associated with high morbidity and mortality, represent a global public health challenge (Liu et al., 2024). Owing to the difficulty of early diagnosis, some tumors are found in the middle to late stages of the disease, with serious effects on patient survival and prognosis. Therefore, in-depth research is needed to identify biomarkers involved in the regulation of malignant transformation to better predict the progression of malignant tumors. These could have applications in both clinical diagnosis and targeted adjuvant therapy to improve the overall survival of patients (Li et al., 2022).
Only about 2% of the genes in the human genome are coding genes; the vast majority of transcripts lack coding open reading frames and are regarded as non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs); these include microRNAs, circular RNAs, and long ncRNAs (Miano et al., 2021; Panni et al., 2020; Wang J. et al., 2019; Wang Y. et al., 2019). However, owing to technological advances, circular RNAs and lncRNAs have been found to have short open reading frames that can be translated into small peptides of about 100 amino acids (aa) in length (Gao et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). These small peptides, in turn, have been shown to have various biological functions, which are listed in the corresponding databases (Andrews and Rothnagel, 2014; Dragomir et al., 2020). Many ncRNAs are similar to coding RNAs (messenger RNAs, mRNAs) and are also transcribed by RNA polymerase II via the processes of polyadenylation, 5′-end capping and RNA splicing (Chen, 2016). In addition, deep sequencing of ribosomal profiles has shown that many transcripts of ncRNAs bind to the ribosome (Gelsinger et al., 2020), suggesting that ncRNAs may be able to encode proteins in the same way as mRNAs.
Small peptides encoded by ncRNAs (SPENs) have important roles in organisms. In recent years, studies published in Science, Nature, Cell, Molecular Cancer and other journals have reported that some SPENs (less than 100 aa in length, e.g., sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+, Toddler, myoregulin, small regulatory polypeptide of amino acid response) are involved in the processes of myogenesis, embryogenesis, and tumorigenesis (Nelson et al., 2016; Matsumoto et al., 2017; Anderson et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2020) Cancer-associated small integral membrane open reading frame 1 was the first functional small peptide found to be carcinogenic; it interacts with squalene epoxidase, a key enzyme in cholesterol synthesis, to regulate the metabolic homeostasis of cancer cells. Knockdown of cancer-associated small integral membrane open reading frame 1 led to a reduction in the proliferation of breast cancer cells (Polycarpou-Schwarz et al., 2018). In another study, HOXB-AS3, a 53-aa conserved small peptide encoded by the lncRNA HOXB-AS3, was shown to inhibit the growth of colon cancer, and its deletion was identified as a key oncogenic factor in colon cancer metabolism (Huang et al., 2017). In addition, the 59-aa small peptide SMIM30, encoded by lncRNA LINC00998, has been reported to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development by regulating cell proliferation and migration (Pang et al., 2020) These studies indicate that SPENs participate in tumorigenesis and development of tumors through complex mechanisms. This enriches our knowledge of tumor regulatory molecules, providing new directions for tumor research with potential clinical applications (Zhu et al., 2020).
Invasion and migration are central processes in tumor biology. They are critical to tumor development owing to their role in metastasis and are major causes of poor patient prognosis and cancer-related mortality (Ahmad et al., 2023). This review focuses on the mechanisms of SPENs and their roles in tumor invasion and migration, aiming to provide new strategies for clinical diagnosis and treatment of various cancers.
2 Invasion and migration
2.1 Overview of tumor cell invasion and migration
Invasion is the process by which tumor cells break out of their original location of growth and invade surrounding normal tissues. The cancer cells use a variety of mechanisms to destroy the structure of the surrounding tissue so that they can spread and metastasize to other sites. Migration, on the other hand, refers to the ability of tumor cells to spread to other parts of the body through the blood or lymphatic system. This process can be roughly divided into the following three steps. First, the migration ability of cancer cells is enhanced after they are detached from the tumor, enabling them to further destroy the extracellular matrix (ECM) and basement membrane and form an invasive growth in normal tissue (Joshi et al., 2023). Second, the surviving cancer cells escape from the wall of the blood vessels, grow and proliferate in suitable tissues and organs, and form a metastatic cancerous focus. Last, a network of neovascularization is formed inside the metastatic focus, which promotes proliferation of the cancerous cells and enables a new round of metastasis (Spano et al., 2012). Invasion and migration processes have crucial roles in the development and progression of tumors. Abnormally active cell migration and invasion mechanisms lead to the formation of abnormal structures around the tumor, resulting in the development of invasive cancers. Therefore, elucidating the mechanisms of these processes can provide a better understanding the mechanisms of cancer development and enable the development more effective therapeutic strategies to improve patient survival and quality of life.
2.2 Roles of invasion and migration in tumorigenesis and development of tumors
Invasion and migration are important aspects of tumor dissemination, and together they constitute the process of tumor metastasis (van Zijl et al., 2011). This process can cause extensive harm and also represents a challenge in cancer treatment, as widespread metastasis often means that advanced cancer cannot be surgically eradicated (Izdebska et al., 2023).
Invasion and migration are central processes in tumor biology (Wu et al., 2021). Invasion involves the degradation and penetration of tumor cells into surrounding tissues, whereas migration involves the movement of tumor cells and colonization of new sites. The two processes are usually driven by complex interactions between tumor cells and the surrounding environment. The molecular mechanisms of invasion and migration are complex and varied. Cancer cells gain motility by remodeling of their tight cell–cell and cell–matrix adhesions, which allows them to leave the primary tumor and invade surrounding tissues (Valastyan and Weinberg, 2011; Christofori, 2006; Lim et al., 2017). Then, the cancer cells secrete a variety of enzymes to degrade the matrix of surrounding tissues. These enzymes break down the ECM and basement membrane stroma, thereby providing a pathway for cancer cells to spread and metastasize (Mondal et al., 2020). In addition, cancer cells release signaling factors, which promote invasion and metastasis by activating signals associated with these processes (Hashemi Goradel et al., 2019; Todd and Johnson, 2020) These changes allow tumor cells to escape the primary site and form new tumor foci at distant sites.
3 SPENs
For a long time, RNAs have been divided into two main categories: mRNAs and ncRNAs (Yasuda and Hayashizaki, 2008). mRNAs act as carriers of genetic information and direct protein synthesis, whereas ncRNAs were once called the “dark matter of the genome” because they were thought to not directly code for proteins. However, recent studies have revealed that some ncRNAs can encode small peptides. This discovery has greatly expanded our understanding of RNA function and opened a new chapter in biological research.
Small peptides encoded by ncRNAs are synthesized through different mechanisms from those associated with classical mRNA-encoded proteins. These comprise ribosome-independent mechanisms, involving the regulation of tRNA half-life, editing, and modification; and ribosome-dependent mechanisms, in which the open reading frames of the ncRNAs are recognized by the ribosome and translated into small peptides.
SPENs have a small molecular weight, usually between 10 and 100 aa. Despite their small molecular weight, these peptides have important regulatory functions in organisms, including signal transduction, protein interactions, and regulation of gene expression (Dong et al., 2023). In addition, SPENs usually have high specificity and sensitivity and function under specific physiological or pathological conditions. SPENs perform a wide variety of functions in organisms, participating in cell signal transduction, cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. SPENs can also interact with specific proteins to change their activity or localization, as well as acting as molecular chaperones and participating in the assembly and regulation of other biomolecules. SPENs also have important roles in the onset and development of cancers.
4 Mechanisms of SPENs in tumor invasion and migration
Although relatively little research has focused on the roles of SPENs in tumor biology, some studies have provided insight into their functions. SPENs play important parts in cancer cell invasion and migration through a variety of mechanisms (Figure 1). For example, they can regulate protein functions and activities by binding to specific proteins and forming complexes. These proteins may be involved in processes such as cell adhesion and cell signaling, which have crucial roles in tumor cell invasion and migration; thus the regulation of these processes by SPENs may directly affect the migratory and invasive behavior of tumor cells. In addition, SPENs can influence the reorganization and dynamics of the cytoskeleton, an important structure within the cell that maintains cell morphology and motility. Through effects on the assembly and stability of the cytoskeleton, small peptides proximally alter cell morphology and motility, thereby playing a key part in tumor invasion and migration (Hu et al., 2022; Zhang Y. et al., 2024; Ye et al., 2023) (Figure 2).
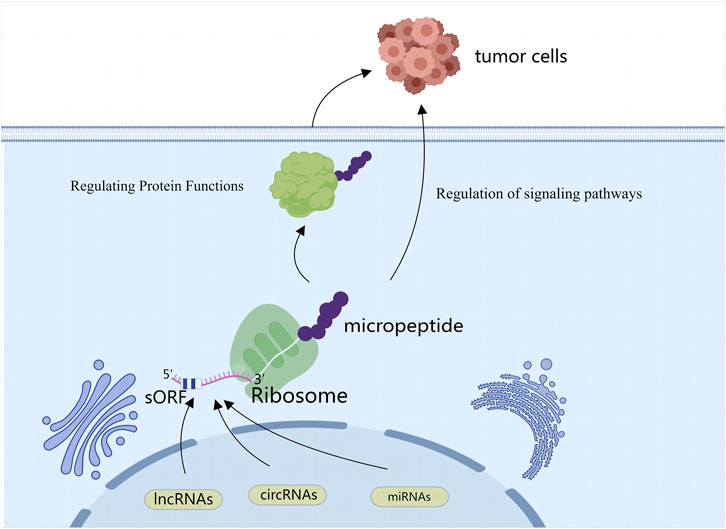
Figure 1. SPENs refer to small peptides encoded by ncRNAs (lncRNAs, circRNAs, miRNAs). Some ncRNAs can generate small peptides through unconventional translation mechanisms, and these peptides influence behaviors of cancer cells by regulating protein functions and participating in signaling pathways.
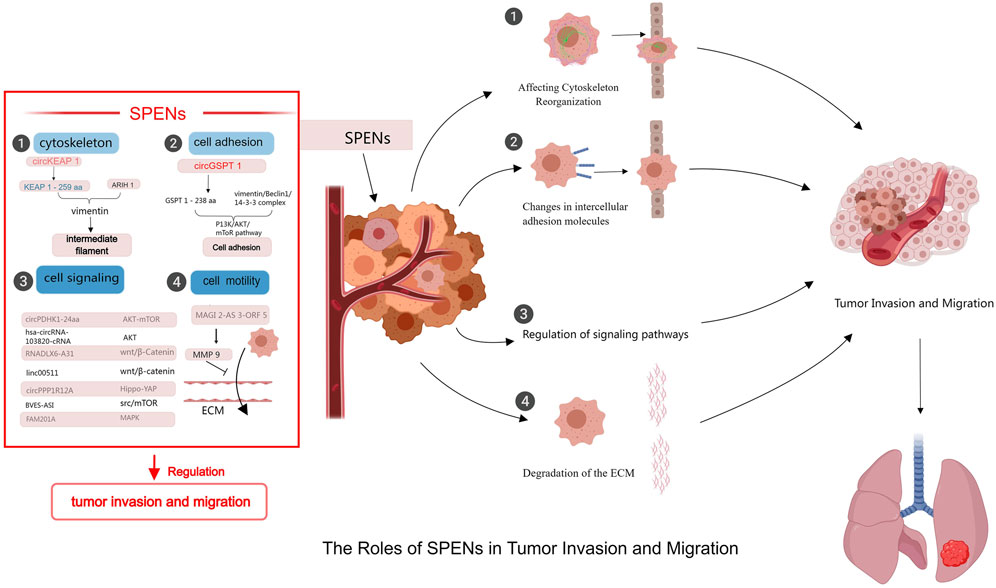
Figure 2. Mechanisms of SPENs on tumor invasion and migration. SPENs play significant roles in tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating protein functions, participating in signal transduction, affecting cytoskeleton reorganization, and influencing the extracellular matrix.
In recent years, studies of SPENs have confirmed that several ncRNAs can encode small peptides and regulate various malignant tumor phenotypes (Polycarpou-Schwarz et al., 2018). Mechanisms of tumor-associated functional peptides encoded by ncRNAs in invasion and migration have been reported in the following tumor types: gastric cancer, intestinal cancer, clear cell renal cell carcinoma, osteosarcoma, neuroblastoma, lung cancer, and breast cancer (Table 1).
4.1 Changes in intercellular adhesion molecules
In normal tissues, cells adhere to each other, forming an interdependent system that promotes their survival. By contrast, cancer cells weaken intercellular adhesion and enhance cell migration by altering the expression of intercellular adhesion molecules, such as those involved in epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Lee et al., 2017). EMT is the phenotypic transformation of epithelial cells to acquire mesenchymal features, a crucial process in tumor cell migration (Pantia et al., 2023). Waveform protein, an important marker of EMT, can cause tumor cells to lose adhesion and disrupt their tight junction structure, change the structure of the cytoskeleton, and increase the invasiveness and distant metastasis of tumor cells (Strouhalova et al., 2020; Ohara et al., 2020). Hu et al., (2022) demonstrated that a novel tumor suppressor protein, GSPT1-238aa, encoded by circGSPT1, interacts with the waveform protein/Beclin 1/14-3-3 complex and regulates autophagy in gastric cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Zhang Y. et al., (2024) showed that KEAP1-259aa, a small peptide encoded by circKEAP1, binds to waveform proteins in the cytoplasm, where it promotes the proteasomal degradation of waveform proteins through interaction with ARIH1, an E3 ligase. In addition to mediating cell adhesion, cell adhesion molecules act as tumor suppressors, limiting tumor growth and migration through contact inhibition. Weakening of cell adhesion allows tumor cells to gain motility and invasiveness, escape the original tumor site, and metastasize to distant organs. Important adhesion molecules include integrin, cadherin, selectin, the immunoglobulin superfamily (e.g., intercellular adhesion molecule-1, neural cell adhesion molecule, vascular cell adhesion molecule, carcinoembryonic antigen, and deleted in colon cancer), CD44, and the 67 kD laminin receptor (Staff, 2001; Moh and Shen, 2009). Calcineurin family members form relatively strong calcium-dependent homotypic adhesions with neighboring cells through their cytoplasmic structural domains, thereby maintaining the stability of cell–cell adhesion. Integrin receptors are calcium-dependent heterodimers composed of noncovalently linked alpha and beta subunits. Members of the integrin family of molecules connect the ECM to the cytoskeleton and transduce signals controlling adhesion and migration in both directions. Members of the selectin family enable transient cell–cell adhesion by interacting with ligands on glycoproteins and glycolipids in the carbohydrate portion of the sialic acid-Lewis X tetrasaccharide. Members of the immunoglobulin superfamily mediate calcium-independent cell–cell adhesion through structural domains, regulate adhesion, and recognize both homophilic and heterophilic ligands (von Lersner et al., 2019).
4.2 Degradation of the ECM
The ECM is a fundamental core component of body tissues and organs and is essential for the existence of multicellular organisms (Cox, 2021). The ECM, which consists of collagen, polysaccharides, proteoglycans, etc., not only provides physical support for cells but also participates in essential processes such as cell growth, differentiation, migration, and signaling. ECM degradation is the pathological basis for the development of many diseases; moreover, degradation of the ECM, including the basement membrane, is a key step in tumor invasion and metastasis, because tumor cells must cross the basement membrane several times to invade surrounding tissues. The various components of the ECM are degraded by specific protein hydrolases; thus, the degradation of the entire ECM requires the synergistic action of multiple matrix hydrolases. Tumor cells facilitate their own invasion and migration by secreting enzymes that rupture the structure of the ECM, enabling them to penetrate the ECM barrier and invade surrounding tissues and blood vessels; they then travel via the circulatory system to other sites, eventually forming metastatic tumors. The proteolytic enzymes associated with ECM degradation by tumor cells can be divided into four major groups: serine proteases (e.g., plasma fibrinolytic plasminogen activator), metalloproteinases, elastases, and cysteine proteases; the first two groups have been investigated in depth. Tumor biomarkers have key roles in cancer screening, diagnosis and prognosis, detection of progression, prediction of recurrence, and evaluation of treatment efficacy (Huang, 2018). MMP9 regulates ECM degradation during tumor metastasis. Degradation and is considered a marker of cell migration and invasion. Zhang Z. et al., (2024) showed that the fluorescence intensity of MMP9 was significantly reduced by overexpression of MAGI2-AS3-ORF5, a small peptide encoded by a non-coding RNA. A transwell assay further revealed that accumulation of MAGI2-AS3-ORF5 reduced numbers of migrating breast cancer cells. In addition, it was found to regulate the migration of breast cancer cells through ECM-associated proteins.
4.3 Cytoskeletal alterations
The cytoskeleton, which comprises cytoplasmic cytoskeleton and nuclear cytoskeleton parts, consists of intermediate fibers, microfilaments, and microtubules, which exist in the cytoplasm and are assembled by a network of proteins. As well as its involvement in activities such as cell division, motility, material movement, and signal transduction, it plays a crucial part in maintaining the basic shape and structure of the cell. Dysfunction or abnormal expression of constituents of the cytoskeleton may thus lead to changes in cell morphology and structure, which in turn may trigger a series of physiopathological processes. Recent studies have also identified an important role of the cytoskeleton in tumor migration and invasion. Cancer cells have a high degree of plasticity, and the deformability of cells is increased by altering the structure and function of the cytoskeleton, thereby promoting cell migration and invasion. Microfilaments, the most important component of the cytoskeleton, consist of fibrinogen, actin, and microkeratin; they enable cell migration and invasion through dynamic reorganization and depolymerization. Intermediate fibers are the most stable part of the cytoskeleton and have an important role in supporting cells. Waveform protein, which is among the most important intermediate fiber proteins, provides physical scaffolding for various organelles in the cell, thereby maintaining cytoskeletal conformation and cellular morphology as well as the integrity and mobility of bridge particles (Guo et al., 2013). Zhang Y. et al. (2024) found that circKEAP1 encodes the protein KEAP1-259aa, which binds to waveform proteins and facilitates their degradation by interacting with the E3 ligase ARIH1, which in turn inhibits tumor migration.
4.4 Regulation of signaling pathways
Signaling pathways are intracellular information transfer systems that involve various biochemical reactions and signal transduction processes. Abnormalities of these signaling pathways may lead to cellular dysfunction. Cancer cells participate in the regulation of cell invasion and migration through activation of various signaling pathways, including the Rho GTPase family, PI3k/Akt, and MAPK pathways. A newly discovered circular RNA, circPPP1R12A, encodes a small peptide named circPPP1R12A-73aa. Zheng et al. (2019) demonstrated experimentally that circPPP1R12A-73aa promotes the migration ability and invasiveness of colon cancer through activation of the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Zheng et al. (2023) found that lncRNA BVES-AS1 encodes peptide BVES-AS1-201-50aa, which promotes cell migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by enhancing activation of the Src/mTOR pathway. Ye et al. (2023) showed that neuroblastoma-associated small protein, a small peptide encoded by FAM201A, interacts with fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) through the ubiquitin proteasome pathway to reduce the expression of FABP5, thereby suppressing cellular migration and invasion through the MAPK signaling pathway and inhibiting neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. Huang et al. (2024) demonstrated that circPDHK1 encodes a novel peptide, PDHK1-241aa, which promotes invasion and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting AKT dephosphorylation and activating the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway through its interaction with PPP 1CA. Zhou et al., (2024) demonstrated that a 188-aa peptide encoded by hsa_circRNA_103820 inhibits cell migration and invasion by inactivating the AKT pathway in lung cancer. Xu et al., (2022) showed that the lncRNA DLX6-AS1, encoding peptide SMIM30, promotes migration and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer cells through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Tan et al. (2023) showed that the small peptide LINC00511-133 aa is encoded by LINC00511 and promotes invasiveness of breast cancer cells by regulating expression levels of Wnt/β-catenin-pathway-associated proteins Bax, cMyc, and cyclin D1, as well as facilitating the entry of β-catenin proteins into the nucleus.
5 Conclusion and outlook
This article focuses on an emerging area of research: the role of SPENs in tumor invasion and migration. We review the mechanisms by which SPENs act in tumor invasion and migration, highlighting the previously unrecognized complexity of ncRNAs. It is an exciting issue to address why discove the role of SPENs in tumor invasion and migration. Invasion and migration are key processes in tumor metastasis, which is of clinical significance as the vast majority of cancer patients die from metastatic rather than primary tumors. In-depth studies of the mechanisms underlying these processes are thus conducive to the development of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for cancer. SPENs, which represent a newly discovered function of RNAs, both enrich existing protein libraries and provide new directions for protein-related research; they also opens up new avenues for cancer treatment. Research into the coding properties of ncRNAs is ongoing; however, the detection and identification of small peptides remains challenging owing to the immaturity of experimental techniques. In addition, many studies have failed to distinguish between the functions of SPENs and those of ncRNAs themselves; this should be considered in the future. Moreover, although some SPENs have been shown to have functional features, their mechanisms of action are not yet clear; challenges remain regarding how to verify their activities and functions. Therefore, further studies are needed. However, despite our current limited understanding in this field, we expect more breakthroughs and advances as research continues and the technology develops. SPENs have the potential to play important parts in drug development and in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, which will be beneficial to human health and quality of life.
Author contributions
JL: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XC: Writing–original draft, Investigation. LM: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. ZX: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. WX: Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by General Scientific Research Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education (No. JYTMS20230100).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1442196/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
ncRNA, Non-coding RNAs; SPENs, small peptides encoded by non-coding RNAs; aa, amino acids; mRNA, messenger RNAs; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FABP5, fatty acid binding protein 5.
References
Ahmad, M., Weiswald, L. B., Poulain, L., Denoyelle, C., and Meryet-Figuiere, M. (2023). Involvement of lncRNAs in cancer cells migration, invasion and metastasis: cytoskeleton and ECM crosstalk. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 42, 173. doi:10.1186/s13046-023-02741-x
Anderson, D. M., Anderson, K. M., Chang, C. L., Makarewich, C. A., Nelson, B. R., McAnally, J. R., et al. (2015). A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance. Cell. 160, 595–606. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.009
Andrews, S. J., and Rothnagel, J. A. (2014). Emerging evidence for functional peptides encoded by short open reading frames. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 193–204. doi:10.1038/nrg3520
Chen, L. L. (2016). Linking long noncoding RNA localization and function. Trends biochem. Sci. 41, 761–772. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2016.07.003
Christofori, G. (2006). New signals from the invasive front. Nature 441, 444–450. doi:10.1038/nature04872
Cox, T. R. (2021). The matrix in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 21, 217–238. doi:10.1038/s41568-020-00329-7
Dong, X., Zhang, K., Xun, C., Chu, T., Liang, S., Zeng, Y., et al. (2023). Small open reading frame-encoded micro-peptides: an emerging protein world. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 10562. doi:10.3390/ijms241310562
Dragomir, M. P., Manyam, G. C., Ott, L. F., Berland, L., Knutsen, E., Ivan, C., et al. (2020). FuncPEP: a database of functional peptides encoded by non-coding RNAs. Noncoding RNA 6, 41. doi:10.3390/ncrna6040041
Gao, J., Pan, H., Li, J., Jiang, J., and Wang, W. (2024). A peptide encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. PeerJ 12, e16806. doi:10.7717/peerj.16806
Gelsinger, D. R., Dallon, E., Reddy, R., Mohammad, F., Buskirk, A. R., and DiRuggiero, J. (2020). Ribosome profiling in archaea reveals leaderless translation, novel translational initiation sites, and ribosome pausing at single codon resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 5201–5216. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa304
Guo, M., Ehrlicher, A. J., Mahammad, S., Fabich, H., Jensen, M. H., Moore, J. R., et al. (2013). The role of vimentin intermediate filaments in cortical and cytoplasmic mechanics. Biophys. J. 105, 1562–1568. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2013.08.037
Han, X., Chen, L., Sun, P., Wang, X., Zhao, Q., Liao, L., et al. (2024). A novel lncRNA-hidden polypeptide regulates malignant phenotypes and pemetrexed sensitivity in A549 pulmonary adenocarcinoma cells. Amino Acids 56, 15. doi:10.1007/s00726-023-03361-7
Hashemi Goradel, N., Najafi, M., Salehi, E., Farhood, B., and Mortezaee, K. (2019). Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: a review. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 5683–5699. doi:10.1002/jcp.27411
Hu, F., Peng, Y., Chang, S., Luo, X., Yuan, Y., Zhu, X., et al. (2022). Vimentin binds to a novel tumor suppressor protein, GSPT1-238aa, encoded by circGSPT1 with a selective encoding priority to halt autophagy in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 545, 215826. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215826
Huang, B., Ren, J., Ma, Q., Yang, F., Pan, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). A novel peptide PDHK1-241aa encoded by circPDHK1 promotes ccRCC progression via interacting with PPP1CA to inhibit AKT dephosphorylation and activate the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 23, 34. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-01940-0
Huang, H. (2018). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: recent advances. Sensors (Basel) 18, 3249. doi:10.3390/s18103249
Huang, J. Z., Chen, M., Chen, D., Gao, X. C., Zhu, S., Huang, H., et al. (2017). A peptide encoded by a putative lncRNA HOXB-AS3 suppresses colon cancer growth. Mol. Cell. 68, 171–184. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2017.09.015
Izdebska, M., Zielińska, W., Krajewski, A., and Grzanka, A. (2023). Fascin in migration and metastasis of breast cancer cells – a review. Adv. Med. Sci. 68, 290–297. doi:10.1016/j.advms.2023.08.003
Joshi, V. B., Gutierrez Ruiz, O. L., and Razidlo, G. L. (2023). The cell biology of metastatic invasion in pancreatic cancer: updates and mechanistic insights. Cancers (Basel) 15, 2169. doi:10.3390/cancers15072169
Lee, H. M., Hwang, K. A., and Choi, K. C. (2017). Diverse pathways of epithelial mesenchymal transition related with cancer progression and metastasis and potential effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on epithelial mesenchymal transition process. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 457, 103–113. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.026
Li, H., Gao, J., Liu, L., and Zhang, S. (2022). LINC00958: a promising long non-coding RNA related to cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 151, 113087. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113087
Lim, W. C., Kim, H., Kim, Y. J., Choi, K. C., Lee, I. H., Lee, K. H., et al. (2017). Dioscin suppresses TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses A549 lung cancer migration and invasion. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 27, 3342–3348. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.06.014
Liu, W., Wang, Y., Xia, L., and Li, J. (2024). Research progress of plant-derived natural products against drug-resistant cancer. Nutrients 16, 797. doi:10.3390/nu16060797
Matsumoto, A., Pasut, A., Matsumoto, M., Yamashita, R., Fung, J., Monteleone, E., et al. (2017). mTORC1 and muscle regeneration are regulated by the LINC00961-encoded SPAR polypeptide. Nature 541, 228–232. doi:10.1038/nature21034
Miano, V., Codino, A., Pandolfini, L., and Barbieri, I. (2021). The non-coding epitranscriptome in cancer. Brief. Funct. Genomics 20, 94–105. doi:10.1093/bfgp/elab003
Moh, M. C., and Shen, S. (2009). The roles of cell adhesion molecules in tumor suppression and cell migration: a new paradox. Cell. adh. Migr. 3, 334–336. doi:10.4161/cam.3.4.9246
Mondal, S., Adhikari, N., Banerjee, S., Amin, S. A., and Jha, T. (2020). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in cancer: a minireview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 194, 112260. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112260
Nelson, B. R., Makarewich, C. A., Anderson, D. M., Winders, B. R., Troupes, C. D., Wu, F., et al. (2016). A peptide encoded by a transcript annotated as long noncoding RNA enhances SERCA activity in muscle. Science 351, 271–275. doi:10.1126/science.aad4076
Ohara, M., Ohara, K., Kumai, T., Ohkuri, T., Nagato, T., Hirata-Nozaki, Y., et al. (2020). Phosphorylated vimentin as an immunotherapeutic target against metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 69, 989–999. doi:10.1007/s00262-020-02524-9
Pang, Y. N., Liu, Z. Y., Han, H., Wang, B., Li, W., Mao, C., et al. (2020). Peptide SMIM30 promotes HCC development by inducing SRC/YES1 membrane anchoring and MAPK pathway activation. J. Hepatol. 73, 1155–1169. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.028
Panni, S., Lovering, R. C., Porras, P., and Orchard, S. (2020). Non-coding RNA regulatory networks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 1863, 194417. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.194417
Pantia, S., Kangsamaksin, T., Janvilisri, T., and Komyod, W. (2023). Asiatic acid inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell viability and migration via suppressing STAT3 and Claudin-1. Pharm. (Basel) 16, 902. doi:10.3390/ph16060902
Polycarpou-Schwarz, M., Groß, M., Mestdagh, P., Schott, J., Grund, S. E., Hildenbrand, C., et al. (2018). The cancer-associated microprotein CASIMO1 controls cell proliferation and interacts with squalene epoxidase modulating lipid droplet formation. Oncogene 37, 4750–4768. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0281-5
Spano, D., Heck, C., De Antonellis, P., Christofori, G., and Zollo, M. (2012). Molecular networks that regulate cancer metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 22, 234–249. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.03.006
Staff, A. C. (2001). An introduction to cell migration and invasion. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 61, 257–268. doi:10.1080/00365510152378978
Strouhalova, K., Přechová, M., Gandalovičová, A., Brábek, J., Gregor, M., and Rosel, D. (2020). Vimentin intermediate filaments as potential target for cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel) 12, 184. doi:10.3390/cancers12010184
Tan, Z., Zhao, L., Huang, S., Jiang, Q., Wei, Y., Wu, J. L., et al. (2023). Small peptide LINC00511-133aa encoded by LINC00511 regulates breast cancer cell invasion and stemness through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol. Cell. Probes 69, 101913. doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2023.101913
Todd, V. M., and Johnson, R. W. (2020). Hypoxia in bone metastasis and osteolysis. Cancer Lett. 489, 144–154. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.06.004
Valastyan, S., and Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell. 147, 275–292. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
van Zijl, F., Krupitza, G., and Mikulits, W. (2011). Initial steps of metastasis: cell invasion and endothelial transmigration. Mutat. Res. 728, 23–34. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.05.002
von Lersner, A., Droesen, L., and Zijlstra, A. (2019). Modulation of cell adhesion and migration through regulation of the immunoglobulin superfamily member ALCAM/CD166. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 36, 87–95. doi:10.1007/s10585-019-09957-2
Wang, J., Zhu, S., Meng, N., He, Y., Lu, R., and Yan, G. R. (2019a). ncRNA-encoded peptides or proteins and cancer. Mol. Ther. 27, 1718–1725. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.09.001
Wang, Y., Huang, T., Sun, X., and Wang, Y. (2019b). Identification of a potential prognostic lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA signature in endometrial cancer based on the competing endogenous RNA network. J. Cell. Biochem. 120, 18845–18853. doi:10.1002/jcb.29200
Wu, J. S., Jiang, J., Chen, B. J., Wang, K., Tang, Y. L., and Liang, X. H. (2021). Plasticity of cancer cell invasion: patterns and mechanisms. Transl. Oncol. 14, 100899. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100899
Wu, P., Mo, Y., Peng, M., Tang, T., Zhong, Y., Deng, X., et al. (2020). Emerging role of tumor-related functional peptides encoded by LncRNA and circRNA. Mol. Cancer 19, 22. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-1147-3
Xu, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, X., Jiang, W., Wu, S., et al. (2022). A peptide encoded by a long non-coding RNA DLX6-AS1 facilitates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer cell. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 32, 43–53. doi:10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2022043172
Yasuda, J., and Hayashizaki, Y. (2008). The RNA continent. Adv. Cancer Res. 99, 77–112. doi:10.1016/S0065-230X(07)99003-X
Ye, M., Gao, R., Chen, S., Bai, J., Chen, J., Lu, F., et al. (2023). FAM201A encodes small protein NBASP to inhibit neuroblastoma progression via inactivating MAPK pathway mediated by FABP5. Commun. Biol. 6, 714. doi:10.1038/s42003-023-05092-7
Zhang, Y., Liu, Z., Zhong, Z., Ji, Y., Guo, H., Wang, W., et al. (2024a). A tumor suppressor protein encoded by circKEAP1 inhibits osteosarcoma cell stemness and metastasis by promoting vimentin proteasome degradation and activating anti-tumor immunity. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43, 52. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-02971-7
Zhang, Z., Yi, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Zhao, Y., He, R., et al. (2024b). LncRNA MAGI2-AS3-encoded polypeptide restrains the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells. Mol. Biotechnol. 66, 1409–1423. doi:10.1007/s12033-023-00801-3
Zhao, W., Zhang, Y., and Zhu, Y. (2021). Circular RNA circβ-catenin aggravates the malignant phenotype of non-small-cell lung cancer via encoding a peptide. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 35, e23900. doi:10.1002/jcla.23900
Zheng, W., Guo, Y., Zhang, G., Bai, J., Song, Y., Song, X., et al. (2023). Peptide encoded by lncRNA BVES-AS1 promotes cell viability, migration, and invasion in colorectal cancer cells via the SRC/mTOR signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 18, e0287133. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0287133
Zheng, X., Chen, L., Zhou, Y., Wang, Q., Zheng, Z., Xu, B., et al. (2019). A novel protein encoded by a circular RNA circPPP1R12A promotes tumor pathogenesis and metastasis of colon cancer via Hippo-YAP signaling. Mol. Cancer 18, 47. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1010-6
Zhou, J., Yao, L., Su, Y., and Tian, L. (2024). IGF2BP3 loss inhibits cell progression by upregulating has_circRNA_103820, and hsa_circRNA_103820-encoded peptide inhibits cell progression by inactivating the AKT pathway in lung cancer. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 103, e14473. doi:10.1111/cbdd.14473
Keywords: non-coding RNA, tumor, small peptide, invasion, migration
Citation: Liu J, Chang X, Manji L, Xu Z and Xiao W (2024) Roles of small peptides encoded by non-coding RNAs in tumor invasion and migration. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1442196. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1442196
Received: 01 June 2024; Accepted: 30 August 2024;
Published: 16 September 2024.
Edited by:
Jing-Quan Wang, St. John’s University, United StatesReviewed by:
Magesh Muthu, Wayne State University, United StatesHiba Muwafaq Saleem, University of Anbar, Iraq
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Chang, Manji, Xu and Xiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wan’an Xiao, d2F4aWFvQGNtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Jie Liu1,2
Jie Liu1,2 Laeeqa Manji
Laeeqa Manji Zhijie Xu
Zhijie Xu Wan’an Xiao
Wan’an Xiao