- 1Department of Nephrology, The Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, China
- 2Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, China
- 3Department of Hemodialysis, The No. 2 Hospital of Hohhot, Hohhot, China
- 4The First Department of Specialty Medicine, Inner Mongolia Corps Hospital of The Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Hohhot, China
Introduction: Eculizumab is a C5 complement inhibitor approved by the FDA for the targeted treatment of four rare diseases, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG), and aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G-positive optic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (AQP4-IgG+NMOSD). The current study was conducted to assess real-world adverse events (AEs) associated with eculizumab through data mining of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS).
Methods: Disproportionality analyses, including Reporting Ratio Ratio (ROR), Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR), Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network (BCPNN), and Multi-Item Gamma Poisson Shrinker (MGPS) algorithms were used to quantify the signals of eculizumab-associated AEs.
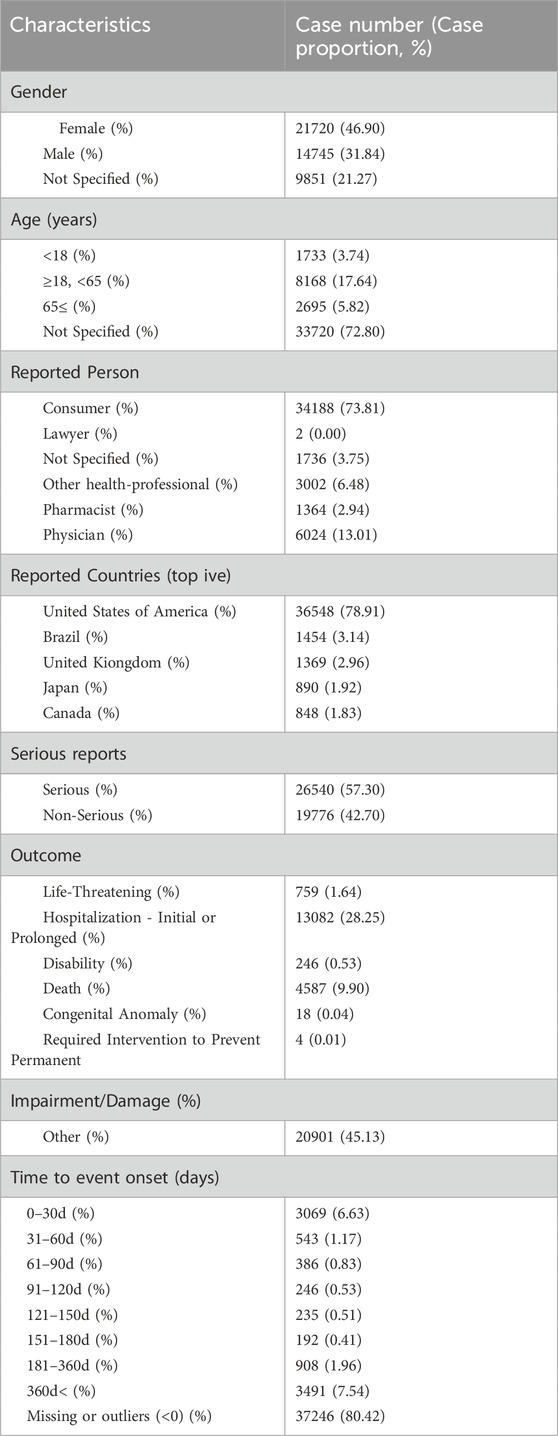
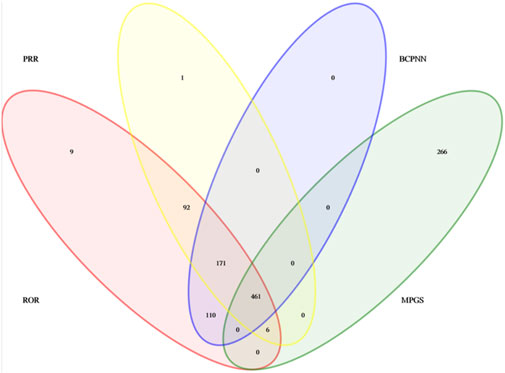
Results: A total of 46,316 eculizumab-related ADEs reports were identified by analyzing 19,418,776 reports in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. A total of 461 PTs were identified as satisfying by all four algorithms. These PTs reported adverse reactions consistent with the specifications, such as fatigue, nasopharyngitis, meningococcal infection, fever, and anemia. Some PTs, such as aplastic anemia, gene mutation, mastication disorder, kidney fibrosis, BK virus infection, abnormal neutrophil count, C3 glomerulopathy, neuroblastoma, and glomerulonephritis membranoproliferative, were also detected outside the instructions. The median time to onset of eculizumab adverse events was 159 days (interquartile range [IQR] 11∼738 days). In addition, at the PT level, 51 PTs were determined to have an imbalance in the occurrence of ADEs between the sexes.
Conclusion: These findings provide valuable insights into the occurrence of ADEs following the use of eculizumab and could support clinical monitoring and risk identification efforts.
1 Introduction
In the complement pathway, activated C5 releases the allergenic toxins C5a and C5b, which interact with C6-C9 and membrane-inserted compartments to form membrane attack complexes (MACs) that lead to lysis, damage or activation of target cells (Ricklin et al., 2016). Eculizumab (Soliris) is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the C5-terminal complement and inhibits the cleavage of C5 to C5a and C5b via complement activation (Miyamoto, 2014). It is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG), and aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G-positive optic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (AQP4-IgG+NMOSD), which play important roles in the allopathic treatment of complement-associated immune disorders. Eculizumab was introduced introduced to China for treating PNH and aHUS in adults and children on 5 September 2018 (Li-li et al., 2022a). Relevant data suggest that eculizumab treatment leads to a decrease in transfusion dependency, a decrease in the incidence of hemolysis and thrombosis, and an improvement in quality of life (Kelly et al., 2011). Concerning eculizumab biosimilars, two variants are currently available: Bkemv (eculizumab-aeeb) and Epysqli (eculizumab-aagh). On 29 May 2024, the U.S. FDA granted approval to Amgen’s Bkemv as the first biosimilar interchangeable with AstraZeneca’s Soliris (eculizumab), for the reduction of hemolysis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and for the inhibition of complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathy in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). Produced by Samsung Bioepis Co. Ltd., Epysqli was initially approved in the European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway on 26 May 2023, and received FDA approval on 19 July 2024. Given that biosimilars may have different therapeutic efficacy and safety profiles, it is important to investigate information about their availability and potential impact.
Despite the promising therapeutic effects of eculizumab, its use since its introduction has been found to increase the risk of certain pathogenic infections, particularly meningococcal infections, for which the FDA black box warns (Crew et al., 2019). Other common adverse reactions include headache, nasopharyngitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hypertension and upper respiratory tract infection (Nishimura et al., 2023). It is therefore crucial to determine the real-world risk of ADE associated with eculizumab to ensure its safe and rational use.
The Adverse Drug Event (ADE) Spontaneous Reporting System database is a major source for mining signals of adverse drug reactions (REN et al., 2011). The FAERS database, with data from national health workers or patients, reflects to some extent the occurrence of drug ADEs in the real world and can therefore help to uncover adverse reactions that are difficult to detect in premarket clinical studies of drugs (Xu, 2015). Given that the adverse reactions in the eculizumab specification are primarily from clinical trials,we utilized the FAERS database for disproportionality analyses to monitor and evaluate the long-term safety of eculizumab, providing a comprehensive and valuable reference for its safety in the real world.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data sources
We implemented a retrospective pharmacovigilance study using data from the FAERS database from January 2007 to the third quarter of 2023. FAERS can be accessed at https://fis.fda.gov/extensions/FPD-QDE-FAERS/FPD-QDE-FAERS.html. Documents in FAERS describe demographic and management information (DEMO), drug information (DRUG), reporting source (RPSR), preferred terms (PT) for adverse event coding (REAC), patient outcomes (OUTC), therapeutic period of the reported medication (THER), indications for use of medication (INDI), and deleted cases (DELE) (Chen et al., 2022). In this study, all the ASCII packet data for 67 quarters from the first quarter of 2007 to the third quarter of 2023 were extracted and imported into SAS 9.4 software for data cleaning and analysis.
2.2 Data processing
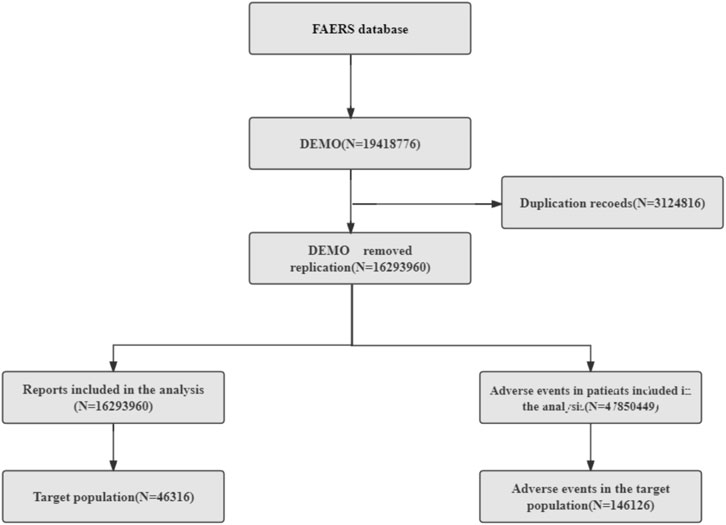
We screened 19,418,776 patients from the FAERS database. First, we removed duplicate records (3,124,816); selected the PRIMARYID, CASEID, and FDA_DT fields of the DEMO table according to the FDA-recommended method for removing duplicate reports; sorted them by CASEID, FDA_DT, and PRIMARYID; and retained the largest FDA_DT value for reports with the same CASEID, followed by retaining the largest PRIMARYID value for reports with both the same CASEID and FDA_DT. We ultimately included 46,316 reports with eculizumab as the primary treatment and 146,126 cases of adverse events for further analysis (Figure 1). The 3D structure of eculizumab was derived from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) (Kim et al., 2023).
2.3 Data mapping
The most current MedDRA dictionary (MedDRA 26.1) was applied to describe ADEs in the FAERS database in terms of system organ class (SOC) and preferred terms (PT).
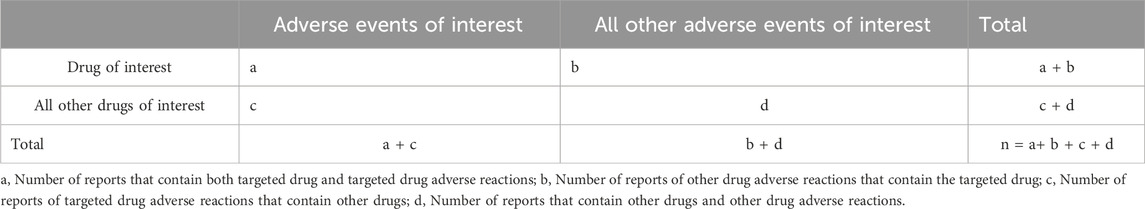
Table 1 shows the screening conditions for the target drug population. The field (DRUGNAME) in the FAERS database indicates the name of the drug, and the field (PROD_AI) indicates the product composition. At the same time, the degree of suspicion was limited to the report of the “Primary Suspect Drug (PS)”.
2.4 Data mining
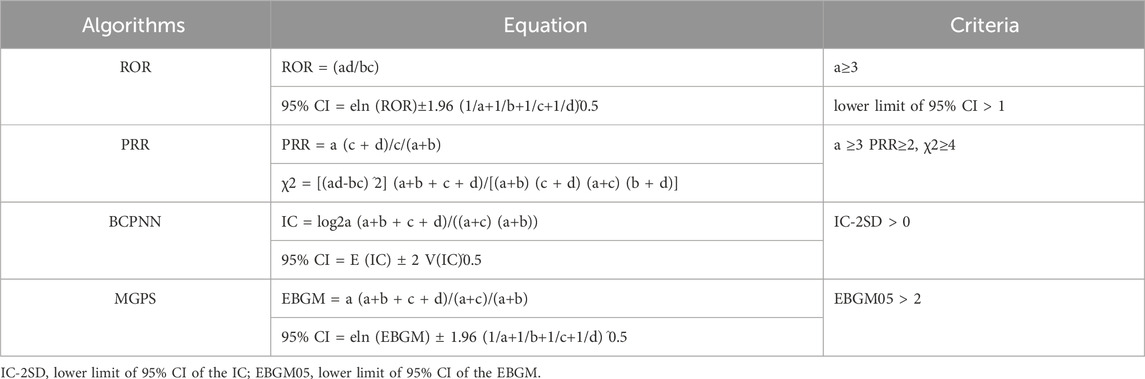
Many organizations have used disproportionality analyses to identify adverse drug reactions (ADEs) from spontaneous reporting data (Seabroke et al., 2016). Disproportionality analysis mainly serves as a mechanism to formulate hypotheses regarding potential causal connections between pharmaceuticals and their adverse outcomes. This should precede a detailed clinical evaluation of the specific individual case reports involved. The method relies on comparing the observed to the expected frequencies of reports for each specific drug-adverse event pairing (Caster et al., 2020). Therefore, this study used the reporting odds ratio (ROR), the proportional reporting ratio (PRR) (CHEN et al., 2021), the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) (Yanxin et al., 2022), (which also belongs to the PRR, and the difference from the previous PRR is that the thresholds are set differently), the Bayesian confidence propagation neural network (BCPNN) (Zhou et al., 2023) and the multi-item Gamma Poisson Shrinker (MGPS) to tap into the ADE risk signals associated with eculizumab, and the higher the values of the four parameters are, the stronger the signal value (Cui et al., 2023) (Tables 2, 3). In this study signal strength was judged according to 0 < IC-2SD ≤ 1.5 weak signal (+); 1.5 < IC-2SD ≤ 3.0 medium intensity signal (++); 3.0 < IC-2SD high intensity signal (++++) in BCPNN (Guan et al., 2022). The drug label for eculizumab was obtained from Daily Med (https://daily.med.nlm.nih.gov/Daily Med/index.cfm) (Cui et al., 2023).
3 Results
3.1 Annual distribution of eculizumab-related ADE reports
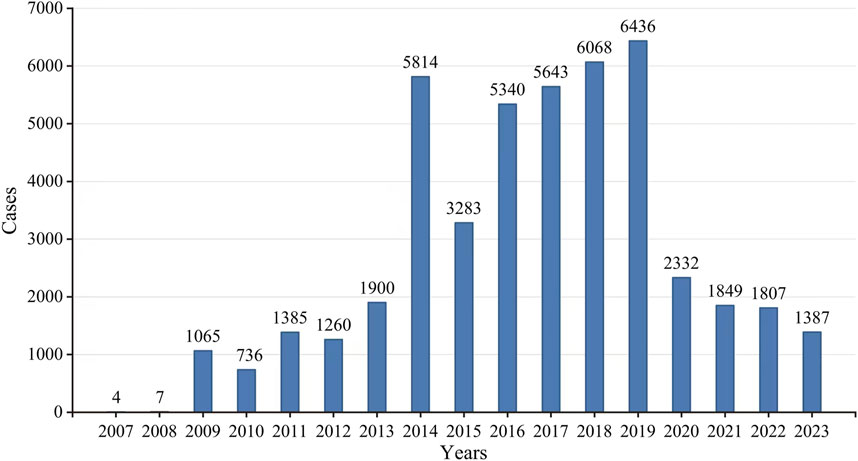
According to the FAERS database, there were a total of 19,418,776 ADE reports from the first quarter of 2007 to the third quarter of 2023, from which a total of 46,316 ADE reports were screened for eculizumab monotherapy as the first suspected drug. Overall, the number of ADE reports increased substantially in 2014, declined steeply in 2015, showed a small increase from 2016 to 2019, and then declined substantially again in 2020; the number of reports stabilized in the latter years, as the data for 2023 were only counted for three-quarters, and the number of predicted reports did not differ much from that of the previous year; therefore, the number of reports stabilized in the latter years (Figure 2).
3.2 General characteristics of the real-world population
Table 4 shows the population characteristics of reports of ADEs associated with eculizumab; of the 46,316 ADE reports, there were more female patients (46.90%) than male patients (31.84%), the age concentration was 18–65 years (17.64%), the source of the reports was predominantly consumers (73.81%), followed by physicians (13.01%). The country of reporting country was the United States (78.91%), and 26,540 (57.30%) serious ADEs were reported, with hospitalization being the main reason (28.25%).
3.3 Time-to-onset analysis of eculizumab-related ADEs
Onset times for eculizumab-associated ADEs were extracted from the FAERS database and analyzed. After removing all missing or incorrect onset reports, a total of 9070 ADEs with available onset times were included in the analysis. The median onset time was 159 days, with an interquartile range (IQR) of 11–738 days (Figure 3). The time to onset (TTO) of ADEs induced by eculizumab is defined as the interval between EVENT_DT (the date of onset of ADEs in the DEM O file) and S TART_DT (the date of eculizumab initiation in the THER file).
3.4 Signal detection at the system organ class level
A total of 461 eculizumab-induced ADEs were detected, covering 23 SOCs, in compliance with the four algorithms (Figure 4). The SOCs with the highest percentage of signals were investigated. The SOCs with the greatest number of PTs were general disorders and administration site conditions (Figure 5), with 24,916 patients and 17.05%, respectively. Supplementary Table S1 shows the specific distribution.
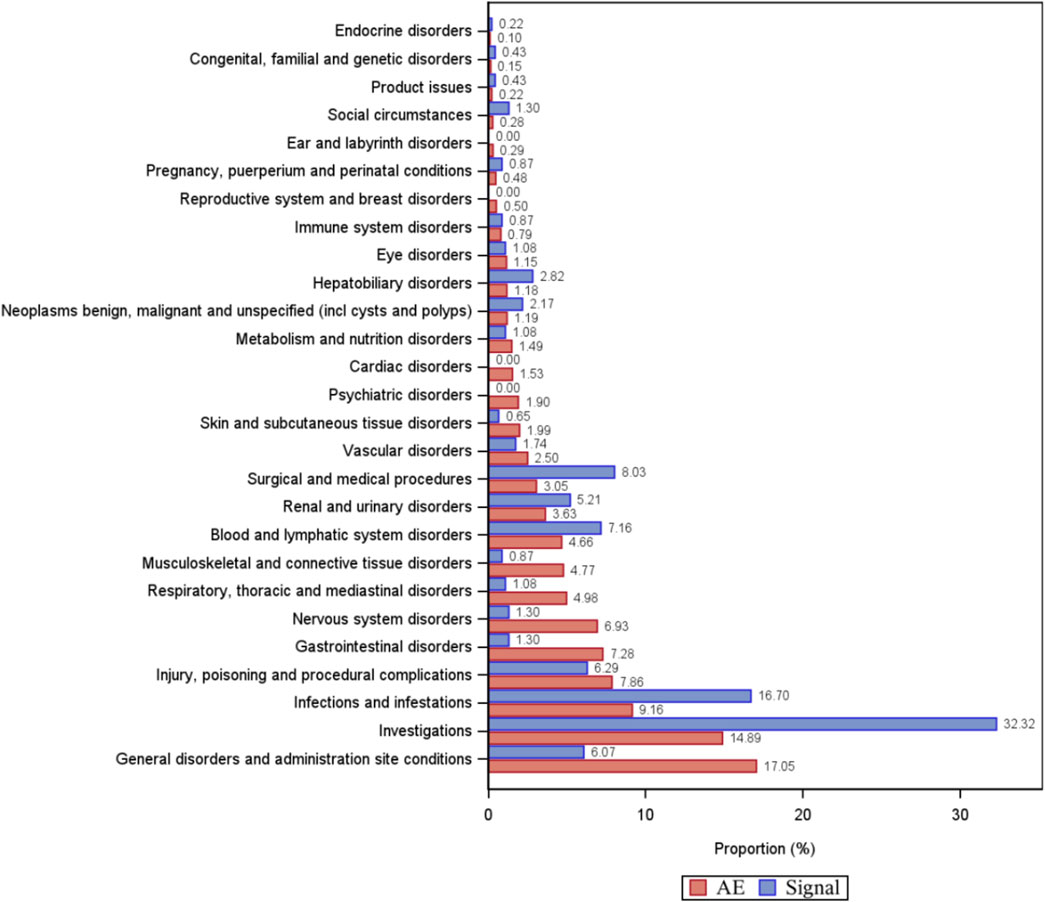
Figure 5. Percentage of the number of PT types and percentage of adverse event cases under organ system classification (SOC). AE, percentage of adverse event cases; Signal, percentage of PT types.
3.5 Signal detection at the preferred terms level
From 46,316 eculizumab-related ADE reports, 5,436 risk signals (PTs) were mined, and 461 PTs satisfied all four algorithms simultaneously. The complete results are presented in Supplementary Table S2. We ranked the signal strength of all PTs with more than 30 ADE cases (a> 30) based on the value of the EBGM 05 (the most conservative algorithm) (Sakaeda et al., 2013). The distribution of the top 100 signal strengths is shown in Table 5. These PTs reported adverse reactions consistent with the specifications, such as fatigue, nasopharyngitis, back pain, meningococcal infection, fever, and anemia. Some PTs, such as those associated with hemoglobinuria, hemolysis, decreased platelet count, increased blood lactate dehydrogenase, Budd-Chiari syndrome, thrombotic microangiopathy (Sahin et al., 2016; Raina et al., 2019), myasthenia gravis, meuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, and eyelid ptosis, are closely related to the primary disease. However, attention needs to be paid to whether it is an exacerbation of a preexisting condition, especially in the case of hemolysis and thrombotic microangiopathy, which occur with high frequency and signal strength. According to the instructions, these PTs can still occur after stopping the medication, so attention must still be given to them. Several out-of-specification and clinically significant PTs were also identified, such as aplastic anemia, gene mutation, mastication disorder, kidney fibrosis, BK virus infection, abnormal neutrophil count, C3 glomerulopathy, neuroblastoma, and glomerulonephritis membranoproliferative. In addition, there were some cases of PT with moderate intensity of IC signals, although there were fewer cases, such as EB viraemia [n = 16, IC025 2.81 (1.66)], varicella [n = 27, IC025 2.24 (1.52)], Neisseria infections [n = 15, IC025 5.92 (2.89)], gonococcal infections [n = 15, IC025 6.84 (2.98)], Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis [n = 25, IC025 2.68 (1.83)], and positive tests for norovirus [n = 9, IC025 3.51 (1.55)], which suggests a need for clinical attention. In summary, real data analysis based on the FAERS database can provide a clinical dosing reference for eculizumab.
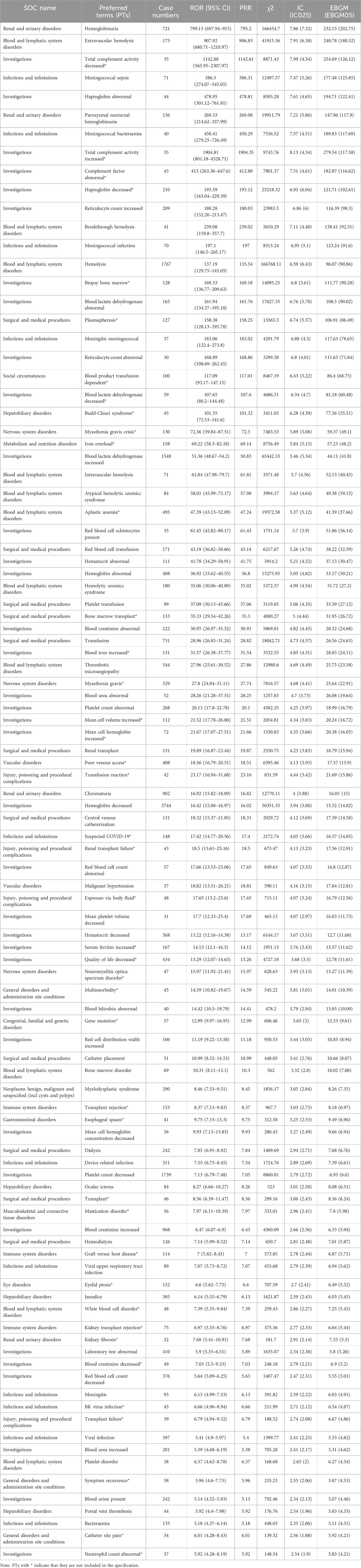
Table 5. The top 100 adverse events with respect to signal strength in target drug signal detection.
3.6 PT distribution of key SOCs
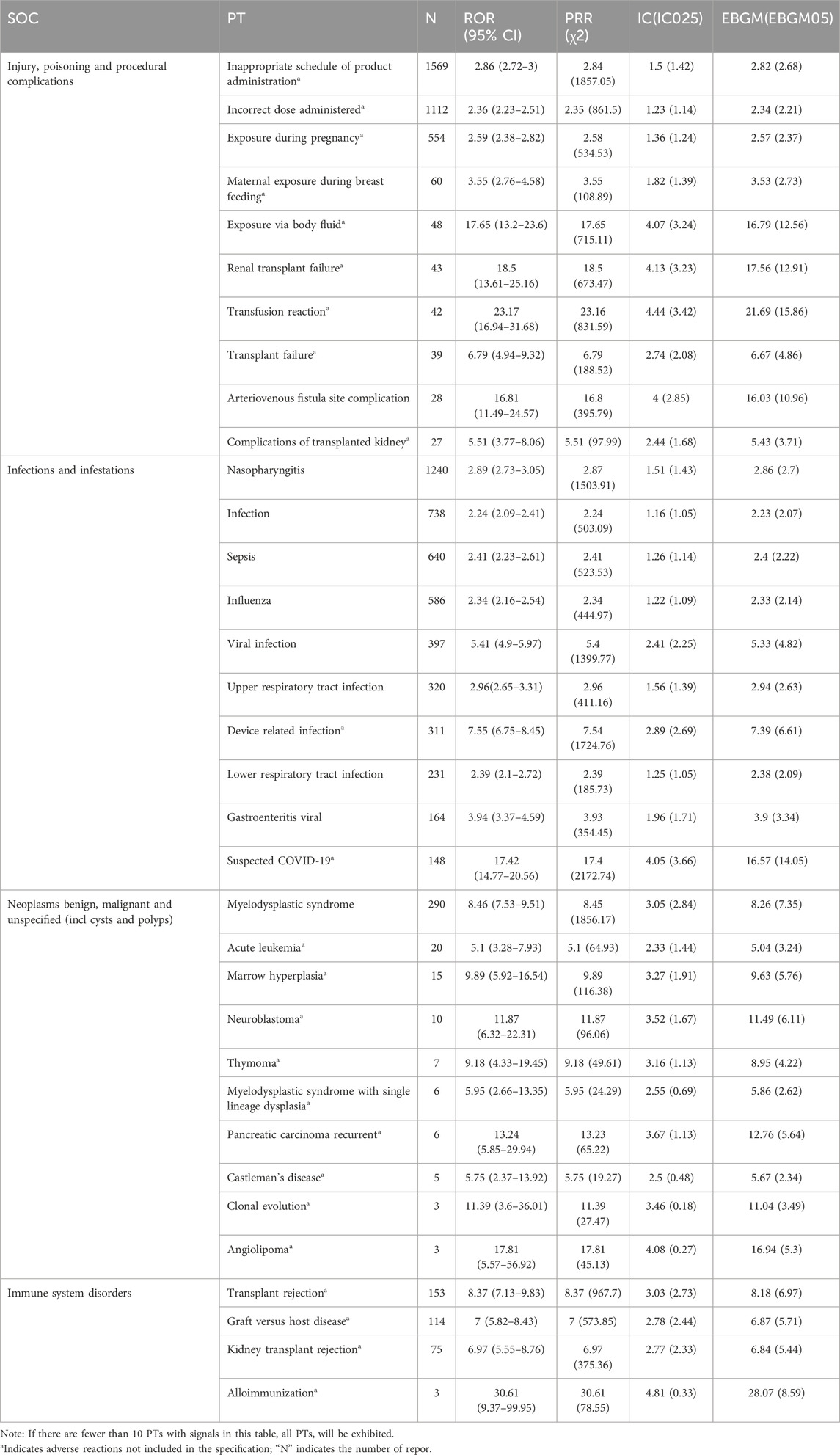
Since most of the risk signals of the SOCs in the first and second orders of reporting were related to the primary disease treated with eculizumab, the SOCs in the third and fourth orders of reporting (injury, poisoning and procedural complications, infections and infestations), as well as immune disorders of clinical concern and benign, malignant and tumors of undetermined nature (including cystic and polypoid), were selected as the key SOCs to be analyzed in the present study. Table 6 shows the distribution of the top 10 PTs in terms of frequency of occurrence under each of the above SOCs, and PTs in immune system diseases and benign, malignant, and tumors of unknown nature were not included in the manual.
3.7 Subgroup analysis
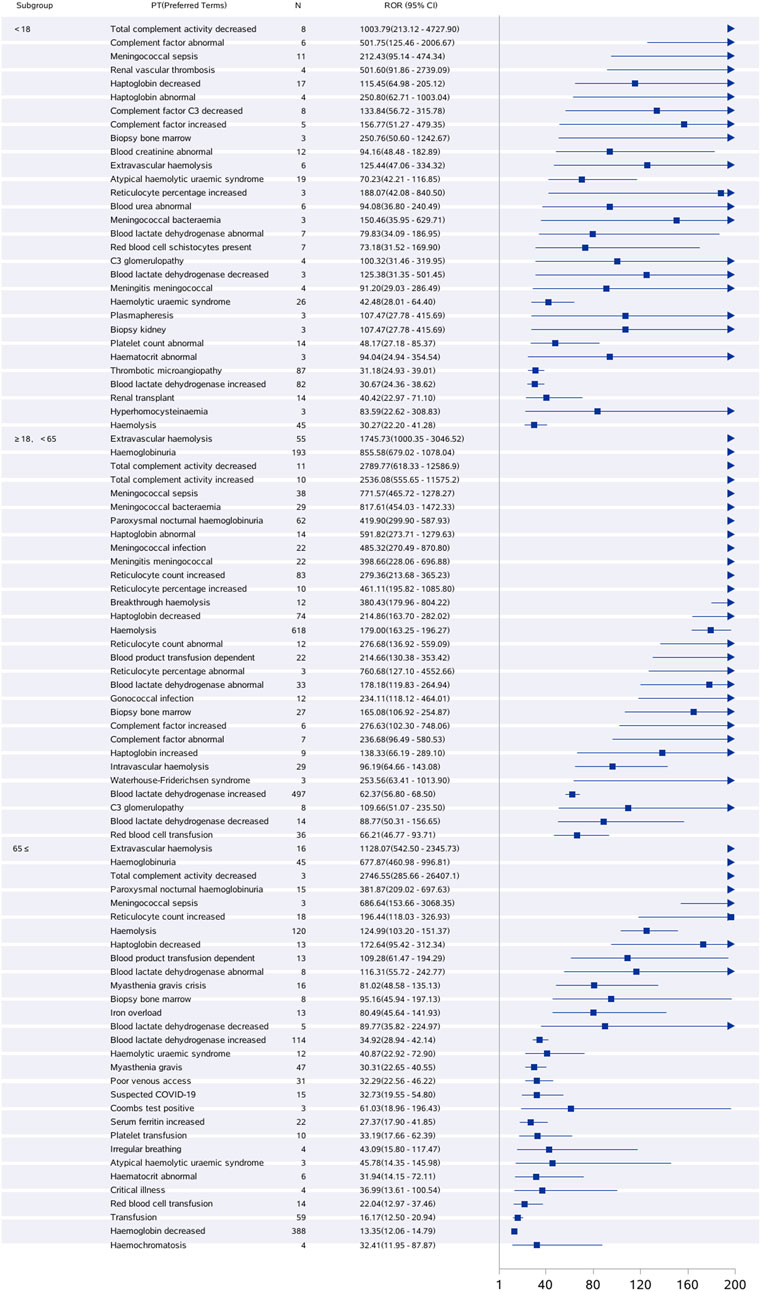
3.7.1 Age subgroup
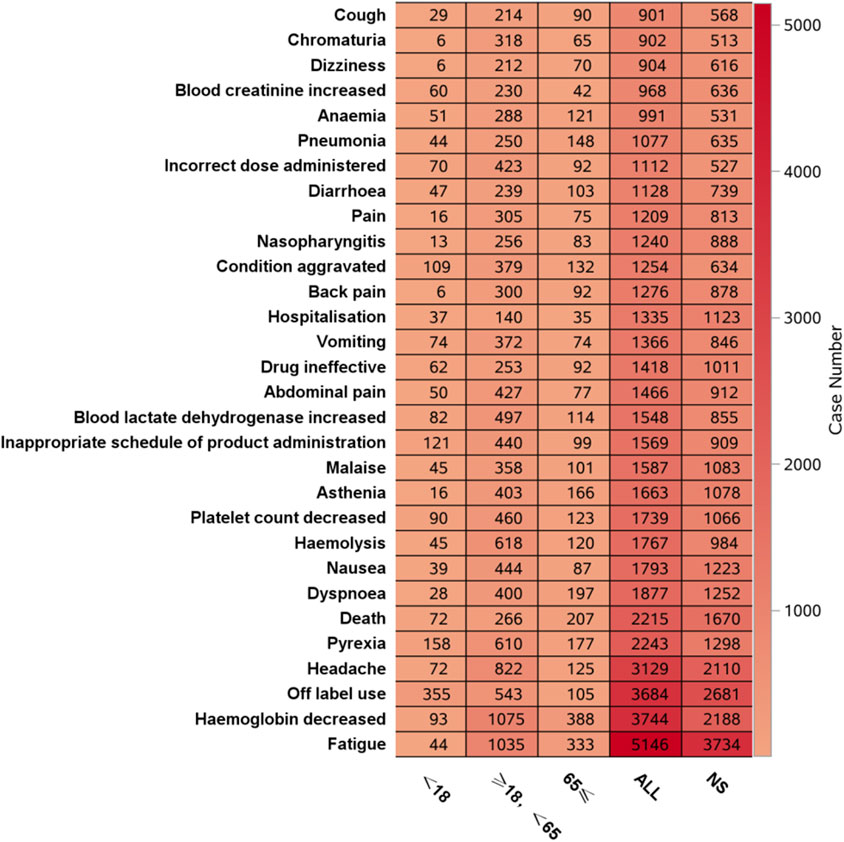
Figure 6 shows that the most frequent PT in the <18 years age group was “off-label use”, and in the ≥18 years, <65 years age group and ≥65 years age group, the most frequent PT was “Hemoglobin decreased”. Figure 7 shows the top 30 orders of signal strength by age, calculated as the ROR (95% CI). In the <18-year-old group, the strong signals were decreased total complement activity, abnormal complement factors, meningococcal sepsis, renal vascular thrombosis, and reduced binding bead protein. In the ≥18-year-old group, the signals were strong for extravascular hemolysis, hemoglobinuria, decreased total complement activity, increased total complement activity, meningococcal sepsis, and meningococcal bacteremia. In the ≥65-year-old group, the signals were strong for extravascular hemolysis, decreased hemoglobinuria, decreased total complement activity, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, meningococcal sepsis, and elevated reticulocyte count. Meningococcal sepsis, which had the highest signal intensity in all three groups, had the highest signal intensity, with a ROR (95% CI) of 771.57 (465.72-1278.27) in the ≥18-year-old group, <65-year-old group, and three cases of the Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, which were not reported in the other two groups. In the <18 years group, hyperhomocysteinemia was found to be overspecified.
3.7.2 Gender differences in eculizumab-associated ADEs
At the PT level, using the ROR and a ≥3; ROR >1, the lower limit of the 95% CI > 1, suggests that female patients are more likely than male patients to report a particular ADE, and the larger the value is, the stronger the association, and ROR <1, the upper limit of the 95% CI < 1; thus, male patients are more likely to report that the smaller the value of the ADE is, the stronger the association (Bate and Evans, 2009). A total of 51 PTs were identified among the 461 PTs, revealing an imbalance in ADE occurrence between males and females. Headache, pain, hypertension, urinary tract infection, poor venous access, bronchitis, cytomegalovirus infection, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura were more likely to occur in females, and hemolysis, elevated blood lactate dehydrogenase, dysphagia, myelodysplastic syndromes, graft-versus-host disease, abnormal white blood cell counts, pulmonary hemorrhage, BK virus infection, staphylococcal bacteremia, chickenpox, elevated hemoglobin, and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis were more likely to occur in males (Figure 8).
4 Discussion
We conducted a postmarketing pharmacovigilance analysis of eculizumab by collecting and evaluating real-world data from the largest sample to identify potential new adverse reactions to eculizumab and analyze the timing of adverse reactions and sex differences. The results of this study will help guide the safe clinical use of this drug.
4.1 Infection-related adverse reactions
The most common symptom under this SOC was nasopharyngitis, and the strongest signals were meningococcal bacteremia and meningococcal line septicemia. One study included 131 patients for analysis, including 107 patients with Neisseria meningitidis infection (81.7%), ten patients with Neisseria gonorrhea infection (7.7%), and patients with infections caused by other pathogens, including other genera of Neisseria, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus niger, Staphylococcus, P. aeruginosa, Clostridium difficile, and varicella-zoster virus (Li-li et al., 2022b). Fatal meningococcal infections occurred in patients treated with Soliris. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) encourages patients treated with eculizumab to receive vaccines against serotypes A, C, W, Y, and B, which should be given to patients at least 2 weeks before the first dose of Soliris is given. However, between 2008 and 2016, 16 cases of meningococcal disease were identified in patients treated with eculizumab in the United States; 11 of these cases were caused by ungroupable Neisseria meningitidis. Fourteen patients were documented to have received at least one dose of meningococcal vaccine before the onset of disease (McNamara et al., 2017). Because meningococcal vaccination may not prevent all cases of meningococcal infection in eculizumab-treated patients, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis be considered; all patients should be monitored for early signs of meningococcal infection (Socié et al., 2019).
4.2 Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
The most frequent occurrences were products given at the wrong time and incorrect doses. According to the Soliris instruction manual, the recommended dose and duration of administration for the treatment of PNH are 600 mg weekly for the first 4 weeks, followed by a fifth dose of 900 mg and thereafter 900 mg every 2 weeks. In 2013, eculizumab was approved in Japan for the treatment of complement-mediated aHUS at a dosage of 900 mg weekly for 4 weeks in adult patients, followed by 1,200 mg maintenance in week five and then 1,200 mg maintenance every 2 weeks (TianQi and XiaoWen, 2020). The recommended mode of administration in the instructions is intravenous infusion. The optimal duration of eculizumab therapy in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is still unclear, but several prospective studies have shown that in patients with aHUS, it is safe to discontinue eculizumab once a complete remission has been achieved in the majority of patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) (Fakhouri et al., 2021; Brodsky, 2021). This requires that we, as healthcare professionals, manage the duration of treatment to minimize the incidence of adverse events and the cost of treatment. Second, 548 cases of exposure during pregnancy have been reported, with studies showing that eculizumab was not present in breast milk and that the levels observed in cord blood samples were insufficient to affect neonatal complement concentrations. Eculizumab may be considered safe in pregnancy, but due to the paucity of safety data, it is still not possible to completely exclude mothers and fetuses from treatment for PNH, aHUS, and HELLP syndrome (Sarno et al., 2019).
4.3 Adverse reactions associated with various neurological disorders
Among the various neurological disorders, the most frequent were headache (3119 cases), myasthenia gravis, myasthenia gravis crisis, optic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders, cerebral thrombosis and cerebral venous thrombosis, although not included in the eculizumab specification, which were associated with the primary disease. It is also worth noting that patients with refractory generalized myasthenia gravis treated with eculizumab may experience worsening symptoms (Howard et al., 2017). Patients should be informed of the possibility of these risk signals when using the drug clinically.
4.4 Tumor-related adverse reactions
The Eculizumab instructions mention malignant melanoma and myelodysplastic syndromes as rare. The top 10 PTs in terms of ADE reports are shown in Table 6, with the majority of PTs not included in the instructions. It has been shown that patients with PNH on eculizumab report more hematological tumors than patients with aHUS, with a reporting rate of approximately 5.0 cases per 12 years, and with regard to solid tumors, skin tumors were more common in patients with PNH (74% solid tumors) than in patients with aHUS (100% solid tumors), with the rate of reporting of solid tumors remaining stable over time; at approximately 5.0 cases per 15 years, hematological tumors were leukemia and lymphoma, and solid tumors were gastrointestinal, skin, genital, breast, and others (respiratory, hepatobiliary, central nervous system, renal; <5% each) (Socié et al., 2019). For safety reasons, patients using eculizumab should be monitored for tumorigenesis, and eculizumab should be used with caution in patients with a history of malignancy or in patients who develop malignancy.
4.5 Adverse reactions associated with immune system disorders
As with all proteins, eculizumab is potentially immunogenic, and antibodies to eculizumab were detected in 2% of patients with PHN using ELISA and in 3% of patients with aHUS and 2% of patients with NMOSD using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL)-bridged immunogenicity analysis. In this real-world study, only four PTs were screened from 5,436 PTs for relevant immune system disorders that met the four algorithms: transplant rejection, graft-versus-host disease, renal transplant rejection, and allogeneic rejection. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a major complication of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) (Toubai et al., 2008). Patients with AA/PNH (plastic anemia/paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria) syndrome may need to be “transitioned” to treatment with eculizumab before bone marrow transplantation to reduce the risk of intravascular hemolysis and thrombosis (DeZern et al., 2018). A previous report examining the outcomes of 21 patients treated with HSCT (hematopoietic stem cell transplantation) between 2007 and 2017 who had received prior treatment with eculizumab revealed that HSCT still had a mortality rate of nearly 30%, mainly due to infection and acute graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) (Vallet et al., 2018).
4.6 Timing of the onset of adverse effects and sex differences
The median time to onset of eculizumab adverse events analyzed in our study was 159 days, with an interquartile range (IQR) of 11∼738 days. Early and timely recognition and management of eculizumab treatment-induced adverse events are critical. A study showed that women are more likely to suffer adverse drug reactions than men (Zopf et al., 2009). This was also confirmed in the present study, where women were more likely than men to have the same positive signal value.
4.7 Eculizumab biosimilars
The clinical safety of eculizumab biosimilars is paramount. Two such biosimilars have been identified: Bkemv (eculizumab-aeeb) and Epysqli (eculizumab-aagh). On 29 May 2024, the U.S. FDA granted approval to Amgen’s Bkemv as the first biosimilar interchangeable with AstraZeneca’s Soliris (eculizumab), used for reducing hemolysis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and tinhibiting complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathy in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). Epysqli, manufactured by Samsung Bioepis Co. Ltd., obtained initial approval in the European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway on 26 May 2023, and later received FDA approval on 19 July 2024. Adverse reaction data on eculizumab were gathered from the FAERS database from the first quarter of 2007 to the third quarter of 2023, prior to FDA approval of these biosimilars. The analysis timeframe was extended to include post-approval adverse reactions related to the biosimilars; however, due to the recent approvals, no data is currently available. Additionally, the Vigibase database, which was searched without time constraints, revealed 51,275 adverse reaction reports involving eculizumab’s active ingredient. However, the database does not specify whether the reactions were linked to the original drug or a biosimilar, thus no specific reports for biosimilars were identified. Although no safety data for the biosimilars were found, ongoing surveillance will continue. Literature on adverse reactions to generic drugs was also reviewed. In a Phase III, randomised, double-blind, multi-national clinical trial comparing SB12 (the proposed eculizumab biosimilar) with the reference eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH), treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 72% of patients in the SB12 treatment group and 68% in the ECU treatment group, respectively. The results demonstrate equivalence between SB12 and ECU and support the use of SB12 in PNH patients (Jang et al., 2023). With the FDA approval of eculizumab biosimilars, they will be widely used and in-depth studies of their safety and equivalence would be needed.
Despite the advantages of data mining, FAERS, as a passive surveillance system, has many limitations. First, it is not possible to determine whether the reported events are related to drugs; at the same time, the reported information is usually insufficient and difficult to evaluate accurately. In addition, the FAERS cannot be used to calculate the incidence of ADEs in the population because of duplicated reports, underreporting, etc. (DONG et al., 2017). Therefore, the Eculizumab ADE risk signals revealed in this study need to be confirmed by high-quality, multicenter clinical studies. Among other things, prospective studies can then test any hypotheses derived using pharmacovigilance databases.
5 Conclusion
In this study, a total of 46,316 reports of adverse drug events (ADE) caused by eculizumab monotherapy as the first suspected drug were screened through signal mining in the FAERS database, and 461 PTs satisfying the four algorithms were identified at the same time, covering 23 SOCs, which were scientifically and systematically analyzed at the level of organ classification and PT, as well as disease onset time and differences in sex and age. This study provides a reference for clinical drug safety.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
X-FW: Writing–original draft. L-RB: Writing–review and editing. T-LH: Writing–review and editing. R-FX: Writing–review and editing. W-NG: Writing–review and editing. J-YW: Writing–review and editing. J-RZ: Writing–review and editing. Z-LF: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. YM: Writing–review and editing. S-FW: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the General Project of Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation (No. 2022MS08063), the Key Research and Development and Achievement Transformation Project in the Social Welfare Field of the 14th Five-Year Plan in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (No. 2022YFSH0087), Inner Mongolia Medical University Affiliated Hospital Talent Training Project - Sailing Series, the Inner Mongolia Health Science and Technology Project in 2022 (No. 202201293), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81960143), the Inner Mongolia Grassland Talents Program Young Innovative Talent Project (No. Q2022082), the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Kidney and Blood Purification (No. 14DZ226022, 20DZ2271600), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai, Science and Technology Program of the Joint Fund of Scientific Research for the Public Hospitals of Inner Mongolia Academy of Medical Sciences (2024GLLH0337), and the Trinity College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Cultivation Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University (No. SWYT2020008).
Acknowledgments
We thank Gang Chen MD, PhD for his assistance in subject design, who works in Department of Nephrology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1440907/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
ADE, Adverse drug events; FAERS, Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System; ROR, Reporting Odds Ratio; PRR, Proportional Reporting Ratio; MHRA, Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency; ASCII, American Standard Code for Information Interchange; BCPNN, Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network; MGPS, Muti-item Gamma Poisson Shrinker; PT, Preferred Terms; SOC, System Organ Class; IQR, Interquartile range; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; aHUS, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome; gMG, generalized myasthenia gravis; AQP4-IgG+NMOSD, aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G-positive optic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders; DEMO, demographic and management information; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; PS, Primary Suspect; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; FDA, The Food and Drug Administration.
References
Bate, A., and Evans, S. J. (2009). Quantitative signal detection using spontaneous ADR reporting. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 18 (6), 427–436. doi:10.1002/pds.1742
Brodsky, R. A. (2021). Eculizumab and aHUS: to stop or not. Blood 137, 2419–2420. doi:10.1182/blood.2020010234
Caster, O., Aoki, Y., Gattepaille, L. M., and Grundmark, B. (2020). Disproportionality analysis for pharmacovigilance signal detection in small databases or subsets: recommendations for limiting false-positive associations. Drug Saf. 43, 479–487. doi:10.1007/s40264-020-00911-w
Chen, G., Li, X., Cui, Q., Zhou, Y., Zhao, B., Mei, D., et al. (2022). Acute kidney injury following SGLT2 inhibitors among diabetic patients: a pharmacovigilance study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 54 (11), 2949–2957. doi:10.1007/s11255-022-03211-7
Chen, C., Ziyan, J. I. N., Xinyi, X. U., Zhang, C., Bin, W. U., and Ting, X. U. (2021). Safety comparison of axitinib and everolimus in the treatment of renal cancer:analysis of adverse events based on pharmacovigilance database. Anti-tumor Pharm. 11 (04), 385–393. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1264.2021.04.01
Crew, P. E., Abara, W. E., McCulley, L., Waldron, P. E., Kirkcaldy, R. D., Weston, E. J., et al. (2019). Disseminated gonococcal infections in patients receiving eculizumab: a case series. Clin. Infect. Dis. 69 (4), 596–600. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy958
Cui, Z., Cheng, F., Wang, L., Zou, F., Pan, R., Tian, Y., et al. (2023). A pharmacovigilance study of etoposide in the FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) database, what does the real world say. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1259908. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1259908
DeZern, A. E., Jones, R. J., and Brodsky, R. A. (2018). Eculizumab bridging before bone marrow transplant for marrow failure disorders is safe and does not limit engraftment. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 24 (12), e26–e30. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.07.032
Dong, D., Wu, G.-zhi, Wang, T., Jia, L. I. U., Wei-yi, XIONG, and Dan, WANG (2017). The enlightens on Ca rrying out reporting responsibility of manufactures in China from reviewing the post ma rketing surveillance system in US. Chin. J. Pharmacovigil. 14 (10), 607–610.
Fakhouri, F., Fila, M., Hummel, A., Ribes, D., Sellier-Leclerc, A. L., Ville, S., et al. (2021). Eculizumab discontinuation in children and adults with atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome: a prospective multicenter study. Blood 137, 2438–2449. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009280
Guan, Y., Ji, L., Zheng, L., Yang, J., Qin, Y., Ding, N., et al. (2022). Development of a drug risk analysis and assessment system and its application in signal excavation and analysis of 263 cases of fluoroquinolone-induced adverse reactions. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 892503. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.892503
Howard, J. F. Jr, Utsugisawa, K., Benatar, M., Murai, H., Barohn, R. J., Illa, I., et al. (2017). Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody-positive refractory generalised myasthenia gravis (REGAIN): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 16 (12), 976–986. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30369-1
Jang, J. H., Gomez, R. D., Bumbea, H., Nogaieva, L., Wong, L. L. L., Lim, S. M., et al. (2023). A phase III, randomised, double-blind, multi-national clinical trial comparing SB12 (proposed eculizumab biosimilar) and reference eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. EJHaem 4, 26–36. doi:10.1002/jha2.632
Kelly, R. J., Hill, A., Arnold, L. M., Brooksbank, G. L., Richards, S. J., Cullen, M., et al. (2011). Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood 117 (25), 6786–6792. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-02-333997
Kim, S., Chen, J., Cheng, T., Gindulyte, A., Jia, H., Siqian, H., et al. (2023). PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 51 (D1), D1373–D1380. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac956
Li-li, H. A. I., Meng, L. V., Tao, L. I., Xing-ru, T. A. O., Yan-yan, DUAN, and Zhang, M. (2022a). Literature analysis of non-infectious adverse reactions induced by eculizumab. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 42 (03), 293–298. doi:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.03.12
Li-li, H. A. I., Tao, L. I., Ya-bing, XING, and Meng, L. V. (2022b). Literature analysis of infectious adverse reactions induced by eculizumab. ChinJ HospPharm 42 (17), 1825–1829. doi:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.17.16
McNamara, L. A., Topaz, N., Wang, X., Hariri, S., Fox, L., and MacNeil, J. R. (2017). High risk for invasive meningococcal disease among patients receiving eculizumab (Soliris) despite receipt of meningococcal vaccine. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 66, 734–737. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6627e1
Nishimura, J. I., Kawaguchi, T., Ito, S., Murai, H., Shimono, A., Matsuda, T., et al. (2023). Real-world safety profile of eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, or generalized myasthenia gravis: an integrated analysis of post-marketing surveillance in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 118 (4), 419–431. doi:10.1007/s12185-023-03630-x
Raina, R., Krishnappa, V., Blaha, T., Kann, T., Hein, W., Burke, L., et al. (2019). Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome: an update on pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Ther. Apher. Dial. 23 (1), 4–21. doi:10.1111/1744-9987.12763
Ren, J.-tian, Wang, S.-feng, Hou, Y.-fang, Xiao-xi, D. U., and Li-ming, L. I. (2011). Compa rative study on the common signal detection methods of adve rse drug reaction. Chin. J. Pharmacovigil. 8 (05), 294–298.
Ricklin, D., Reis, E. S., and Lambris, J. D. (2016). Complement in disease: a defence system turning offensive. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 12 (7), 383–401. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2016.70
Sahin, F., Akay, O. M., Ayer, M., Dal, M. S., Ertop, S., Ilhan, O., et al. (2016). Pesg PNH diagnosis, follow-up and treatment guidelines. Am. J. Blood Res. 6 (2), 19–27.
Sakaeda, T., Tamon, A., Kadoyama, K., and Okuno, Y. (2013). Data mining of the public version of the FDA adverse event reporting system. Int. J. Med. Sci. 10 (7), 796–803. doi:10.7150/ijms.6048
Sarno, L., Tufano, A., Maruotti, G. M., Martinelli, P., Balletta, M. M., and Russo, D. (2019). Eculizumab in pregnancy: a narrative overview. J. Nephrol. 32 (1), 17–25. doi:10.1007/s40620-018-0517-z
Seabroke, S., Candore, G., Juhlin, K., Quarcoo, N., Wisniewski, A., Arani, R., et al. (2016). Performance of stratified and subgrouped disproportionality analyses in spontaneous databases. Drug Saf. 39 (4), 355–364. doi:10.1007/s40264-015-0388-3
Socié, G., Caby-Tosi, M. P., Marantz, J. L., Cole, A., Bedrosian, C. L., Gasteyger, C., et al. (2019). Eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome: 10-year pharmacovigilance analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 185, 297–310. doi:10.1111/bjh.15790
TianQi, T. U., and XiaoWen, T. U. (2020). Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of atypical haemolytic uremic syndrome. BEIJING Med. 42 (02), 139–141. doi:10.15932/j.0253-9713.2020.02.013
Toubai, T., Sun, Y., and Reddy, P. (2008). GVHD pathophysiology: is acute different from chronic. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 21 (2), 101–117. doi:10.1016/j.beha.2008.02.005
Vallet, N., de Fontbrune, F. S., Loschi, M., Desmier, D., Villate, A., Barraco, F., et al. (2018). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria previously treated with eculizumab: a retrospective study of 21 patients from SFGM-TC centers. Haematologica 103 (3), e103–e105. doi:10.3324/haematol.2017.182360
Xu, B. A. O. (2015). An introduction of American OpenFDA of public health Project. China Licens. Pharm. 12 (10), 18–22. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5433.2015.10.005
Yanxin, L., Zou, J., Dong, C., Yamin, S., Xucheng, H., Pen, W., et al. (2022). Research on signal mining of adverse events of GLP-1 receptor agonists based on FAERS. Her. Med. 41 (07), 975–982. doi:10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2022.07.009
Zhou, Q., Du, Z., Qu, K., Shen, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhu, H., et al. (2023). Adverse events of epidiolex: a real-world drug safety surveillance study based on the FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) database. Asian J. Psychiatr. 90, 103828. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2023.103828
Keywords: eculizumab, FAERS, adverse drug events, adverse drug reaction monitoring, ADRM
Citation: Wang X-F, Bao L-R, Hu T-L, Xu R-F, Gao W-N, Wang J-Y, Zhao J-R, Fu Z-L, Wang S-F and Meng Y (2025) Adverse drug events (ADEs) risk signal mining related to eculizumab based on the FARES database. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1440907. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1440907
Received: 30 May 2024; Accepted: 18 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Anick Bérard, Montreal University, CanadaReviewed by:
Daniele Mengato, University Hospital of Padua, ItalyBin Wang, Southeast University, China
Lingran Du, Guangzhou Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Bao, Hu, Xu, Gao, Wang, Zhao, Fu, Wang and Meng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shu-Fang Wang, d3NoZnh5ekAxNjMuY29t; Yan Meng, bWJhbzEyNEBxcS5jb20=
 Xi-Feng Wang
Xi-Feng Wang Lu-Ri Bao2
Lu-Ri Bao2 Jing-Yuan Wang
Jing-Yuan Wang