- Department of Pharmacy, Quanzhou First Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, China
Objectives: Exploring adjustments to the voriconazole dosing program based on therapeutic drug monitoring results to implement individualized therapy.
Methods: PubMed and Embase were systematically searched to obtain study about voriconazole dose adjustment program guided by therapeutic drug monitoring. Quality evaluation and summarization of the obtained studies were performed to obtain program adjustments for voriconazole under therapeutic drug monitoring.
Results: A total of 1,356 and 2,979 studies were searched on PubMed and Embase, respectively, and after removing irrelevant and duplicated studies, a total of 25 studies were included. A loading dose of 5 mg/kg q12 h or 200 mg q12 h and a maintenance dose of 50 mg q12 h or 100 mg q24 h is recommended for patients with Child-Pugh C. And in patients with Child-Pugh C, CYP2C19 genotype had no significant effect on voriconazole blood concentrations. Recommendations for presenting dosing programs based on different CYP2C19 genotypes are inconsistent, and genetic testing is not routinely recommended prior to dosing from a pharmacoeconomic perspective. Additionally, in adult patients, if the voriconazole trough concentration is subtherapeutic, the voriconazole dose should be increased by 25%∼50%. If the voriconazole trough concentration is supratherapeutic,the voriconazole dose should be decreased by 25%∼50%. If a drug-related adverse event occurs, hold 1 dose, decrease subsequent dose by 50%.In pediatric patients, if the voriconazole trough concentration is subtherapeutic, increase the voriconazole dose by 1∼2 mg/kg or increase the voriconazole dose by 50%. If the voriconazole trough concentration is supratherapeutic, reduce the voriconazole dose by 1 mg/kg or hold 1 dose, and decrease the subsequent dose by 25%.
Conclusion: It is recommended that all patients on voriconazole should have their initial dosing program selected on the basis of their hepatic function or other influencing factors (e.g., pathogens, infections, C-reactive protein, albumin, or obesity), and that therapeutic concentrations should be achieved through appropriate dosage adjustments guided by therapeutic drug monitoring. Routine genetic testing for voriconazole application in patients is not considered necessary at this time. However, there has been a great deal of research and partial consensus on individualized dosing of voriconazole, but there are still some critical issues that have not been resolved.
1 Introduction
Voriconazole is a second-generation triazole antifungal drug with broad-spectrum antifungal activity, which is commonly used to treat invasive fungal disease in clinic, and is the first-line drug for invasive aspergillosis. The voriconazole trough concentration has been proved to be related to efficacy and toxicity, but there are still uncertainties in the process of voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) and individualized dosing (Perreault et al., 2019). Yi WM conducted the study in 151 adult patients, 68/151 (45.0%) of whom were critically ill. The study showed that voriconazole blood concentration monitoring is within the target concentration range (1.0∼5.5 mg/L) in only 134/250 (53.6%) of patients, <1.0 mg/L in 65/250 (26.0%), and >5.5 mg/L in 51/250 (20.4%), which suggests that voriconazole blood concentrations were not within the target concentration range in 116/250 (46.4%) of patients (Yi et al., 2017). Moreover, the probability that the trough concentration was within the target concentration range was increased two-fold compared to no dose adjustment when patients outside the target concentration range were dose-adjusted and the trough concentration was later reviewed (Yi et al., 2017). Sarah Perreault conducted a study in 128 adults with hematologic malignancies. The study showed that after 2 dose adjustments, 80% of patients were able to achieve the target concentration range (Perreault et al., 2019). One study based on pediatric patients (1.2∼18.5 years) showed that 55% of patients had voriconazole steady-state trough concentrations outside of the therapeutic concentration range, and 82% of these patients were able to achieve the therapeutic concentration range after dose adjustment (Lempers et al., 2019). Voriconazole exhibits nonlinear pharmacokinetics in vivo when administered at doses recommended in the drug insert for the treatment of invasive Aspergillus infections in adults or pediatrics. Numerous studies have been conducted on the individualized administration of voriconazole, but there are still some key unanswered questions regarding its clinical application. There are also current studies using Model-informed precision dosing (MIPD) to predict and optimize treatment outcomes based on patient characteristics and therapeutic drug monitoring data. In order to improve the clinical efficacy of voriconazole and to achieve individualized dosing of voriconazole, this study explored several aspects of the initial dosing program, the therapeutic concentration range, and the dose-adjustment program to provide a reference for obtaining the optimal clinical treatment program.
2 Materials and quality assessment
2.1 Data sources and searches
The study searched the literatures for voriconazole administered under the guidance of therapeutic drug monitoring. The literatures covered program adjustments or made dose adjustments based on the patient’s liver function profile, genotyping, and body weight. Two researchers independently searched 2 databases (PubMed and Embase) from January 2002 to March 2024 to identify studies on voriconazole dose adjustment program guided by therapeutic drug monitoring (Figure 1). Once duplicates had been removed, the researchers identified studies eligible for analysis by examining titles and abstracts of every record, followed by full-text reviews. Any disagreement between reviewers was resolved by discussion, with arbitration by a third reviewer when required. The search strategy was:
(“voriconazole” OR “VRZ” OR “VRC” OR “VCZ”) AND (“dose adjustment” OR “dosage regimens” OR “dose modification”)
(“voriconazole” OR “VRZ” OR “VRC” OR “VCZ”) AND (“liver failure” OR “liver cirrhosis” OR “liver dysfunction”)
(“voriconazole” OR “VRZ” OR “VRC” OR “VCZ”) AND (“CYP2C19”)
(“voriconazole” OR “VRZ” OR “VRC” OR “VCZ”) AND (“obese” OR “obesity” OR “higher weight” OR “BMI” OR “body mass index”)
(“voriconazole” OR “VRZ” OR “VRC” OR “VCZ”) AND (“software”)
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were decided according to PICOS. Participants (P): 1) patients were administered voriconazole, therapeutic drug monitoring was performed, and a target concentration range for voriconazole was specified, 2) inclusion of pediatric and adult populations. Intervention (I): propose an initial dosing program for special populations, or propose a dosage adjustment program based on a standard dosing program (For patients 12–14 years old and weighing >50 kg or patients ≥15 years old, the loading dose is 400 mg q12 h iv/po, and the maintenance dose is 200 mg q12 h iv/po. For patients aged 2–12 years old or younger, the loading dose is 9 mg/kg q12 h iv/po, and the maintenance dose is 8 mg/kg q12 h iv/po.). Control (C): The initial dosing program for special populations was compared with the standard dosing program, or dose-adjusted was compared with no dose adjustment. Outcome (O): Probability of target attainment (PTA). Study design (S): 1) human study, 2) inclusion of experimental studies (randomized controlled and non-randomized controlled studies), analytical studies (cohort and case-control studies) and pharmacokinetic modeling studies, 3) the study was available in English. Studies have also elaborated on the voriconazole guidelines.
The following studies were excluded: 1) dose adjustment studies for voriconazole in combination with other drugs, 2) studies that did not specify target range concentrations, 3) animal experimentation and laboratory study, 4) non-English studies.
Studies that excluded studies involving switching between different routes of administration were not performed but are labeled in the text.
2.3 Quality assessment
This study used the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (GA Wells et al., 2013) for quality assessment of case-control and cohort studies, MINORS (Slim et al., 2003) for quality assessment of non-randomized controlled interventional studies, and Jadad (Jadad et al., 1996) for quality assessment of randomized controlled interventional studies. For quality evaluation methods of pharmacokinetic modeling studies refer to Niu Wanjie et al. (2018).
The included studies are qualitatively described based on recommendations for initial dosing in specific populations, the implementation of TDM (target concentration ranges, dose recommendations following TDM, timing of repeat TDM), and MIPD.
After a literature search and quality assessment, the contents of the literature were categorized and discussed to derive recommendations for special populations (Child-Pugh C patients, patients with different CYP2C19 genotypes or other special populations) and dose adjustments.
3 Result
3.1 Literature search
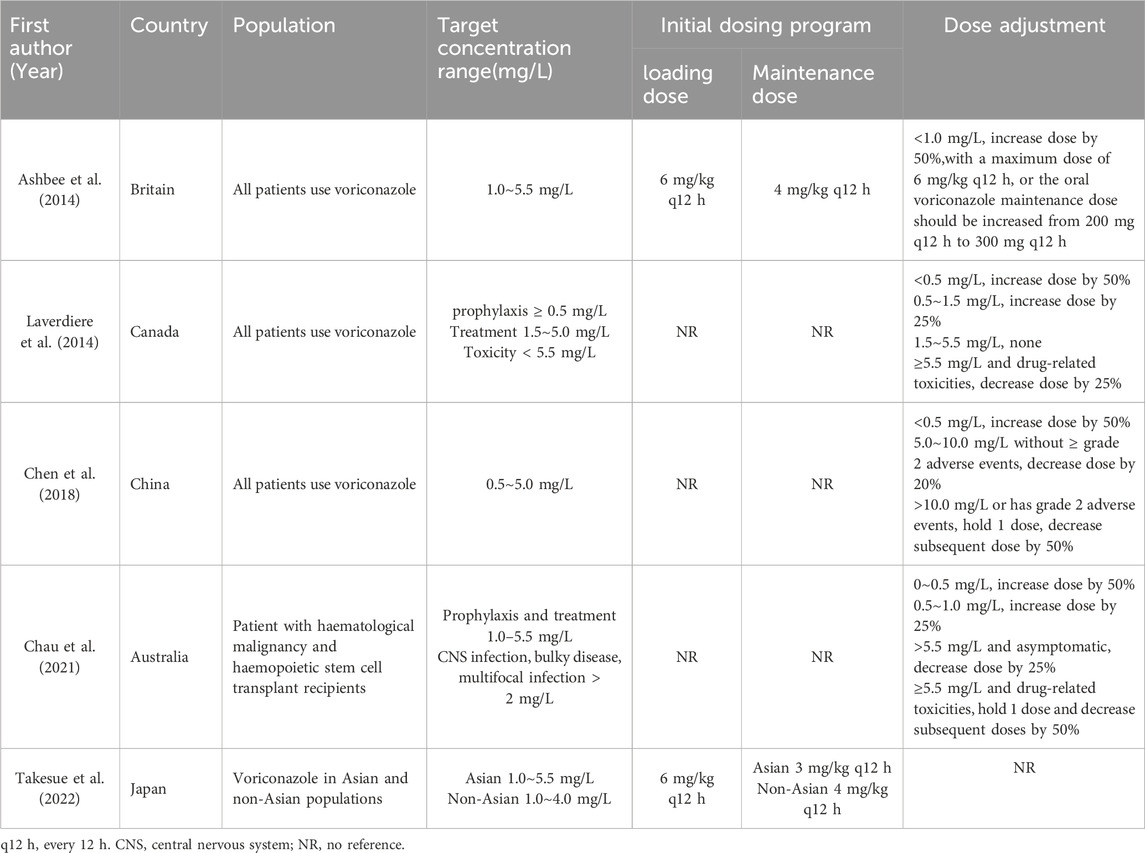
A total of 1,356 and 2,979 studies were searched on PubMed and Embase, respectively, and after removing irrelevant and duplicated studies, a total of 25 studies were included in this paper, of which 4 studies were case-control studies, 4 were cohort studies, 5 were non-randomized controlled studies, 1 was a randomized controlled study and 11 used a modeling program, of which 9 were Population pharmacokinetics (Pop PK), and 3 were Physiologically based pharmacokinetics (PBPK). The study was also described for 5 voriconazole guidelines (Britain, Canada, China, Australia, Japan) (Ashbee et al., 2014; Laverdiere et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018; Chau et al., 2021; Takesue et al., 2022).
3.2 Evaluation of the quality of literatures
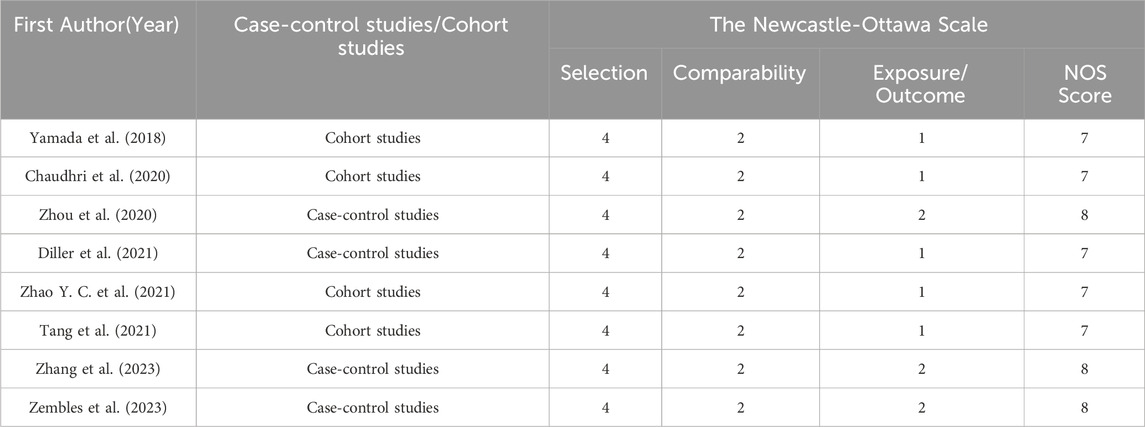
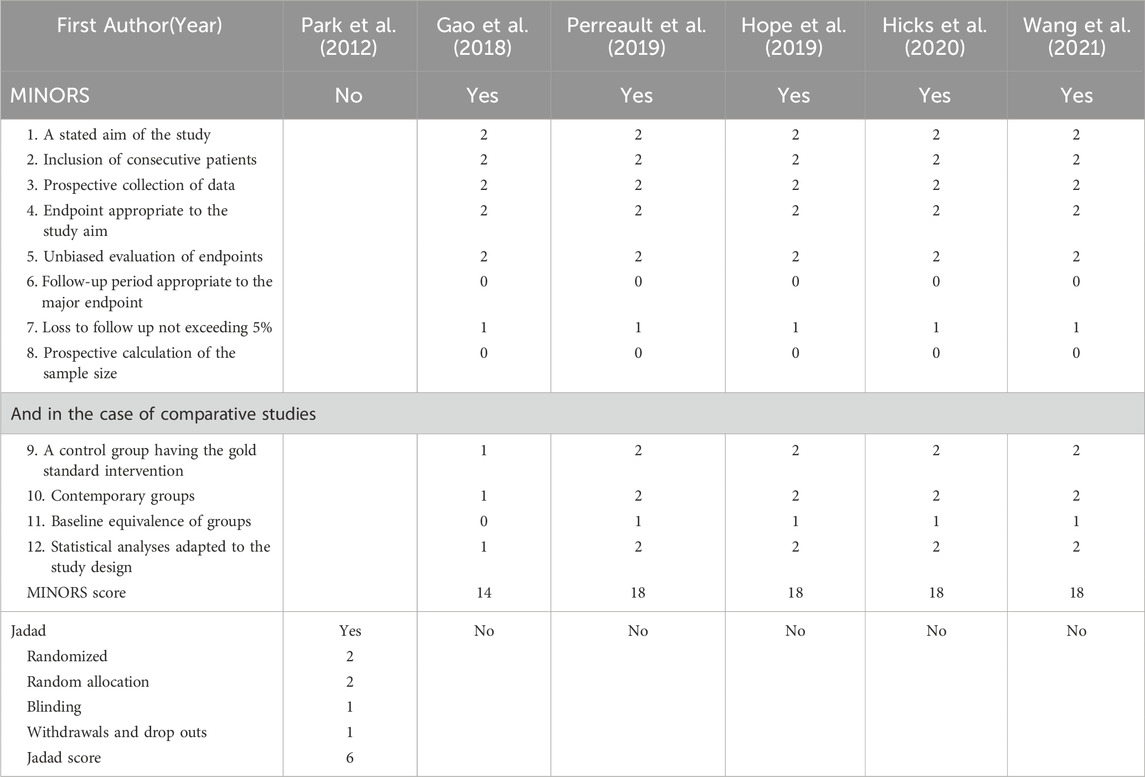
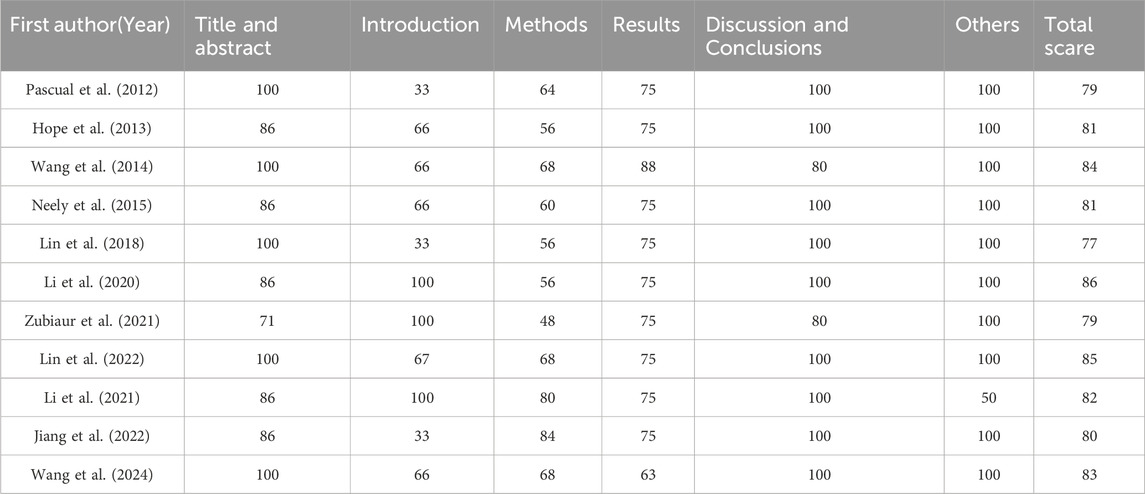
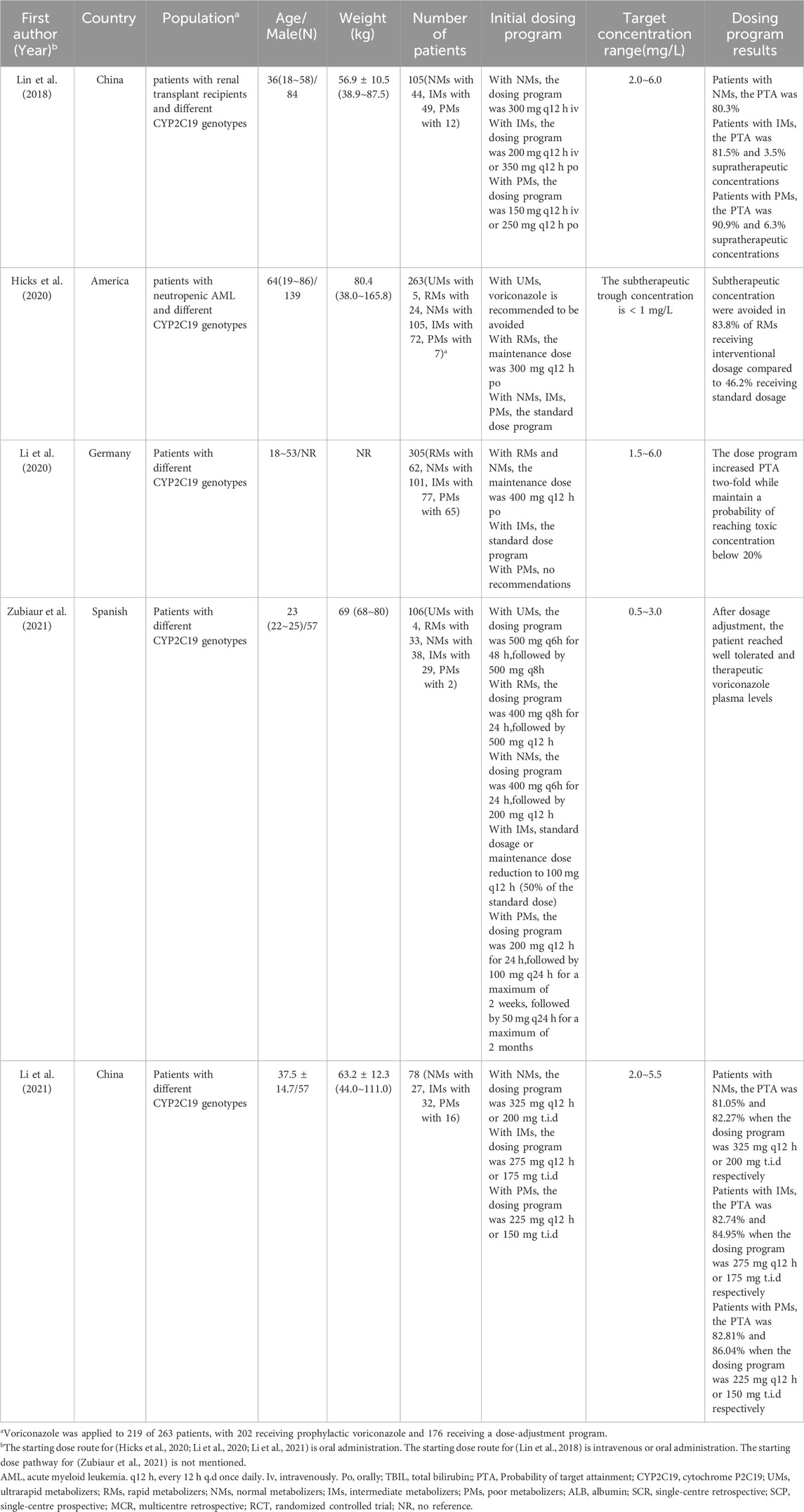
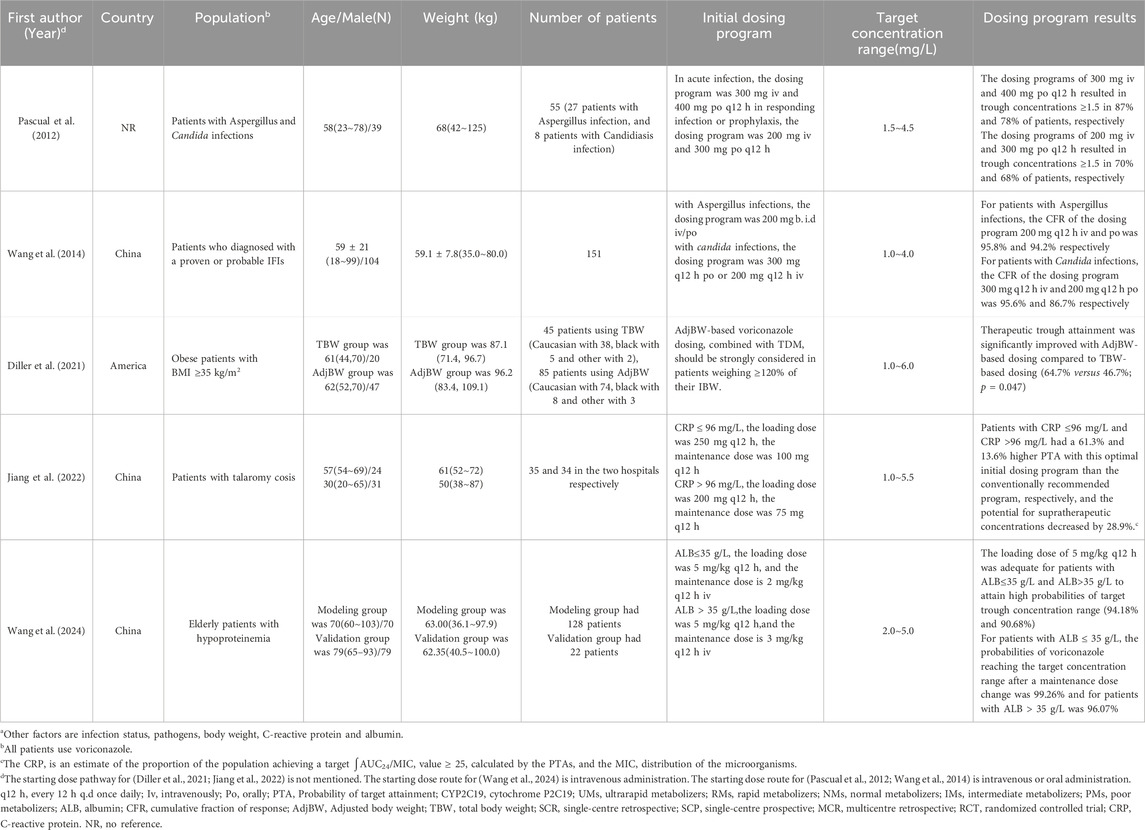
Of the 25 studies, 4 studies (Zhou et al., 2020; Diller et al., 2021; Zembles et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023) were case-control studies and 4 (Yamada et al., 2018; Chaudhri et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2021; Zhao Y. C. et al., 2021) were cohort studies, all of which were evaluated for quality using the NOS (GA Wells et al., 2013), with 5 of them having 7“*” and 3 of them having 8“*”. 5 studies (Perreault et al., 2019; Gao et al., 2018; Hope et al., 2019; Hicks et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021) were non-randomized controlled interventional studies and were evaluated for quality using MINORS (Slim et al., 2003), with four being moderate-quality literatures (scores of 13∼18) and two being high-quality literatures (scores of 19∼24). 1 study (Park et al., 2012) was a randomized controlled interventional study with quality assessment using Jadad (Jadad et al., 1996), which is a high-quality literature (scores of 4∼7). 11 studies (Pascual et al., 2012; Hope et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2014; Neely et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021; Zubiaur et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022; Lin et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024) applied the method of model simulation, and the quality evaluation method was referred to the study of Niu Wanjie et al. (2018). A total of 4 studies scored 77∼80, and a total of 7 studies scored 81∼86. Details are provided in Tables 1– 3.
3.3 Initial dosing program for special populations
From 2013 to 2022, the relevant guidelines for drug monitoring for voriconazole therapy have been published or updated in Britain (Ashbee et al., 2014), Canada (Laverdiere et al., 2014), China (Chen et al., 2018), Australia (Chau et al., 2021) and Japan (Takesue et al., 2022), and many studies have also put forward suggestions on the initial dosage program for patients of different ages, Child-Pugh C, CYP2C19 genotype, race and Body Mass Index (BMI). Of the five guidelines, only the Britain and Japanese guidelines recommend an initial dosing program, with the British guideline recommending the same initial dosing program as the program in the specification (loading dose of 6 mg/kg q12 h iv or 400 mg q12 h po, and maintenance dose of 4 mg/kg q12 h iv or 200 mg q12 h po). The Japanese guidelines recommend the loading dose to be the same as the instructions, and the maintenance dose to be divided according to different populations and disease types. The maintenance dose is 4 mg/kg q12 h iv for non-Asian populations and 3 mg/kg q12 h iv for Asian populations. The maintenance dose for patients with Candida infections (except for Candida glabrata and Candida krusei) is 200 mg q12 h, and for patients with Aspergillus infections is 300 mg q12 h.
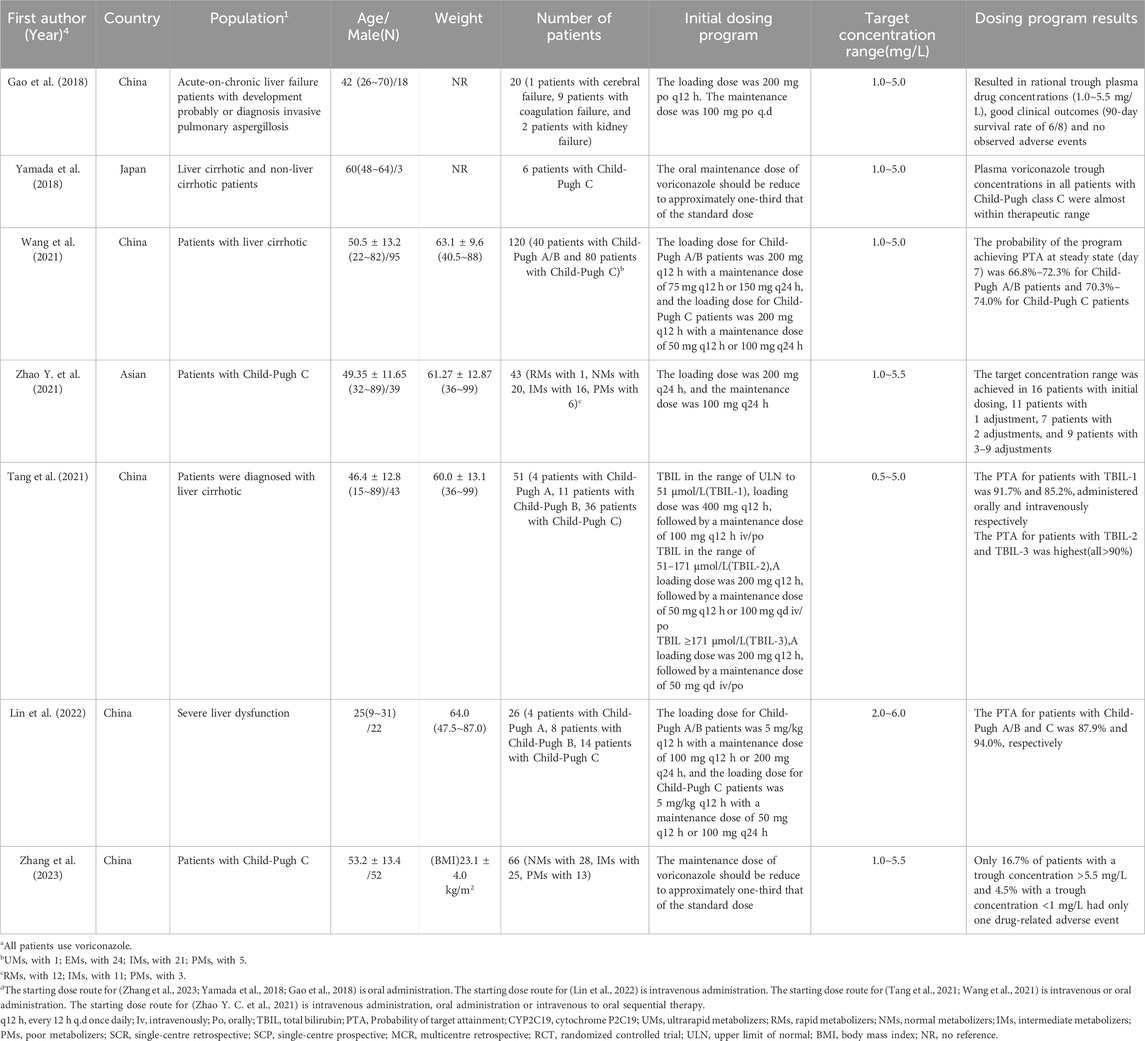
There were 7 studies on Child-Pugh C patients, 3 were prospectives and 4 were retrospectives, and of these 7 studies, 1 was conducted using the pop PK model, in which a loading dose of 5 mg/kg q12 h and a maintenance dose of 50 mg q12 h or 100 mg q24 h were recommended for Child-Pugh C patients (Lin et al., 2022). Of the remaining 6 studies, 2 studies suggested that the maintenance dose of voriconazole in Child-Pugh patients should be reduced to one-third of the standard dose (Zhang et al., 2023; Yamada et al., 2018). 2 studies recommended a loading dose of voriconazole of 200 mg q12 h (Gao et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021), 1 study recommended 200 mg q24 h (Zhao Y. et al., 2021) and all three recommended a maintenance dose of 50 mg q12 h or 100 mg q24 h. In addition, 1 study was a stratified study using Total Bilirubin (TBIL) to determine the dosing program based on patients’ TBIL values (Tang et al., 2021). The specific studies are presented in Table 4.
A total of 5 studies, 4 prospective and 1 retrospective, were conducted in patients with different CYP2C19 genotypes. The recommendations of these 5 studies varied, with only the patients with intermediate metabolizers (IM) being more consistent, with 4 studies (Hicks et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020; Zubiaur et al., 2021) suggesting that standard treatment programs could be used. Modeling methods were used in 4 of these 5 studies (2 for pop PK and 2 for PBPK).For patients with ultrarapid metabolizers (UMs), switching or using the program 500 mg q6 h for 48h, followed by 500 mg q8 h was recommended. For patients with rapid metabolizers (RMs), the maintenance dose was recommended to be 400 mg q12 h or using the program 400 mg q8 h for 24 h, followed by 500 mg q12 h. For patients with normal metabolizers (NMs) For patients with NMs, the recommended maintenance dose is 325–400 mg q12 h po or 200–300 mg q12 h iv or using program 400 mg q6h for 24 h, followed by 200 mg q12 h. For patients with IMs, 3 studies recommend using the standard dose, and 1 study suggests the maintenance dose of 275 mg q12 h or 175 mg t.i.d. For patients with poor metabolizers (PMs), 150∼200 mg q12 h iv or 225∼250 mg q12 h po is recommended, as well as the program 200 mg q12 h for 24 h, followed by 100 mg q24 h for a maximum of 2 weeks, followed by 50 mg q24 h for a maximum of 2 months. The remaining 1 study (Hicks et al., 2020) recommended that voriconazole be avoided in patients with the UMs phenotype, that the maintenance dose for patients with the RMs phenotype could be 300 mg bid po, and that patients with the remaining genotypes could be treated with the standard treatment program. These specific studies are listed in Table 5.
In addition, for overweight and obese patients, the Canadian guideline indicates that dosing based on true body weight (TBW) in obese patients (BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2) may increase the risk of overexposure and toxicity, and therefore recommends that intravenous and oral voriconazole dosing in obese patients should be based on ideal body weight (IBW) or adjusted body weight (AdjBW). The Japanese guidelines recommend the use of IBW or adjusted body weight dosing. It has also been suggested that dosing programs based on TBW are not appropriate for patients with a BMI ≥35 kg/m2, and the use of AdjBW for dosing calculation is recommended (Diller et al., 2021).
There are many factors that need to be considered in order to establish an individualized voriconazole dosing program, such as the type of infection, severity of infection, inflammation, BMI, and co-medication. The specifics of the 5 relevant studies are listed in Table 6, of which 3 were prospective studies, 2 were retrospective studies.
3.4 Target trough concentration range
In addition to the target concentration ranges recommended by the five guidelines, 5 (Zhou et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024) studies chose different lower concentration limits and 8 (Diller et al., 2021; Zembles et al., 2023; Pascual et al., 2012; Lin et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020; Zubiaur et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2022; John et al., 2019) studies chose different upper concentration limits.
5 studies (Zhou et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024) used 2.0 mg/L as the lower limit of trough concentration. It is based on the study which included 34 patients and the results showed that none of the cases with trough concentration >2 mg/L were ineffective for voriconazole, while two-sixths of the cases with TDM below this threshold were nonresponsive (Dolton and McLachlan, 2014).
The upper limit of trough concentration also varied among studies. 1 study (Zubiaur et al., 2021) used 3.0 mg/L as the upper limit of trough concentration based on the meta-analysis studies. The results of meta-analysis study showed a significantly lower probability of hepatotoxicity at a trough concentration of <3.0 mg/L compared to the control group (RR = 0.37, 95% CI = 0.16∼0.83) (Jin et al., 2016). 1 study (Pascual et al., 2012) used 4.5 mg/L as the upper trough concentration limit, whose result shown that a >15% probability of neurotoxicity at trough concentrations >4.5 mg/L. Six studies (Diller et al., 2021; Zembles et al., 2023; Lin et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2022; John et al., 2019) used 6.0 mg/L as the upper trough concentration limit based on the follow: Firstly, a meta-study consisting of 24 studies included literatures with >10 patients, TDM during voriconazole treatment, and studies that evaluated the relationship between trough concentration and clinical efficacy and/or safety. Literatures were searched from January 1998 through October 2013 and the following keywords were used: “voriconazole”, “triazole”, “vfend”, “drug monitoring”, “pharmacovigilance”, “adverse drug reaction/reporting system”. The meta-analysis showed that patients had an increased probability of adverse effects when trough concentrations ranged was 4.0∼6.0 mg/L (OR = 4.17,95 CI% = 2.08∼8.36) and that a supratherapeutic threshold of 6.0 mg/L was the most predictive of toxicity (OR = 4.60, 95% CI = 1.49–14.16) (Luong et al., 2016). The second is a study whose results show that elevated liver enzymes were frequently observed at voriconazole concentrations >6 mg/L, and this adverse event occurred in 8 of 11 cases at 6 mg/L or higher concentrations (Dolton and McLachlan, 2014). The target concentration ranges for each study are shown in Tables 4–8.
3.5 Dosage adjustment
A total of 4 dose-adjustment literatures were included in the study, 3 (Perreault et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2020; Park et al., 2012) for adults and 1(15) for pediatrics. There is no consistently recommended program for dose adjustment of voriconazole. Of the 4 guidelines (Ashbee et al., 2014; Laverdiere et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018; Chau et al., 2021) that propose a dosing program, details are given in Table 8.
In adult patients, 2 studies (Zhou et al., 2020; Park et al., 2012) recommended that if trough concentrations were much higher than supratherapeutic concentrations or if drug-related adverse events occurred, 1 dose should be reserved, subsequent doses should be reduced by 33% or 50%, and other antifungal drugs should be considered if toxicity was not reversed. In addition, the study by Sarah perreault et al. suggests that when trough concentration was 5.6∼7.9 mg/L, hold dose, and recheck daily through concentration, then restart at 100 mg less when trough concentration was ≤2.5 mg/L. When trough concentration ≥8 mg/L, hold dose, and recheck daily through concentration, then restart at 50% dose reduction when trough is ≤ 2.5 mg/L (PTA = 80%) (Perreault et al., 2019). 3 studies (Perreault et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2020; Park et al., 2012) all recommended that the dose of voriconazole be reduced by 25% ∼ 50% if the trough concentration of voriconazole exceeded the therapeutic concentration and no drug-related adverse effects were observed. And sarah perreault et al. suggested that for trough concentration <0.5∼1.0 mg/L, voriconazole dose increase by 25%∼50%, which made 80% of patients were able to achieve the target concentration range with an adverse reaction rate of only 7.6% (Perreault et al., 2019).The study by WanBeom Park et al. recommended a 100% increase in voriconazole dose at trough concentrations <1 mg/L, with a dose-adjusted probability of target attainment (PTA) of 75% (Park et al., 2012). In addition to the above program, another program was proposed in the study by Pejun Yvonne Zhou et al. When the trough concentration was <0.5 mg/L, re-load voriconazole at a dose of 1.5 times the new maintenance dose for 24 h, followed by a 75% dose increase for the maintenance dose, which increased the level by > 10 times(absolute increment is unknown as 0.5 mg/L was the upper limit of assay detection). When the trough concentration was 1.0∼1.9 mg/L, the increase was 25∼33% or an increase of 67%, which increased the level by 70∼130% or increased the level by 10%. When the trough concentration was 5.5∼7.5 mg/L, reduction of 13% or reduction of 33%, which reduction level by 50% or reduction level by 80%. When the trough concentration was >7.5 mg/L, held off one dose or until neurological symptoms were resolved, followed by 33% reduction in dose, which reduction level by >33% (absolute reduction is unknown as 7.5 mg/L was the upper limit of assay detection) (Zhou et al., 2020).
There are fewer studies on dose adjustment for children and only 1 study by Zembles et al. (2023) was included in this study, which was studied in 59 pediatric patients aged 3.7∼14.7 years old. Of these, the study by Jamie john et al. did not further explore the post-therapeutic efficacy or PTA of dose adjustments, while the study by Tracy N. Zembles et al. showed that after subsequent dose modifications based on TDM, they were able to eventually reach the target in over 80% of patients, though this requires multiple steady-state voriconazole serum trough concentrations measurements. The specifics of the study are represented in Table 7.
3.6 Timing of repeat therapy drug monitoring
The timing of monitoring after application of the initial dosing program of voriconazole has become clearer, but there is still no clear evidence on the timing of re-monitoring after dose adjustment. WanBeom Park et al. argue that if the voriconazole dosage were or administration route was altered or if the interacting drug was introduced or halted, follow-up TDM was repeated on day 4 (Park et al., 2012). The British guideline recommends routine second monitoring to ensure that concentrations are stable and in the effective range, as well as repeat monitoring after dose adjustments and sequential therapy (Ashbee et al., 2014). The timing of repeat monitoring after dose adjustment is mentioned in the Chinese guideline, which thinks the timing of repeated therapy drug monitoring is consistent with the initial sampling time under the circumstance of no voriconazole loading dose, which is expected to be 4∼7 days after adjusting the voriconazole dosing program, or with initiating or withdrawing concomitant drugs that potentially influence voriconazole pharmacokinetic profiles (Chen et al., 2018). The Australian guidelines recommend that repeat testing should be on the fifth day after adjusting the dosing program, but no clear reason is given (Chau et al., 2021). Sarah Perreault et al. argued that trough concentrations should be rechecked on day 5 of the new dosing program (Perreault et al., 2019). Additionally, Tracy N. Zembles et al. suggested that steady state could be reached if voriconazole trough concentrations were repeated on ≥2.5 days after dose adjustment, but most studies chose to repeat monitoring on day 5 (Zembles et al., 2023).
With the exception of the Chinese guidelines, the remaining recommendations are expert opinions. The recommendations of the Chinese guidelines are based on the following 2 studies. Purkins L et al. evaluated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of an intravenous to oral voriconazole program in 41 healthy males. The results showed that after switching from intravenous to oral dosing program, the majority of subjects reached a steady state on day 4, with the mean lowest trough concentration remaining above the clinically important Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) (Purkins et al., 2002). Visual inspection of trough concentration together with statistical analyses of peak concentration and Area under the curve (AUC) values suggest that steady-state levels were achieved by the 4–6 days of multiple dosing (Purkins et al., 2003).
3.7 Dose-prediction software
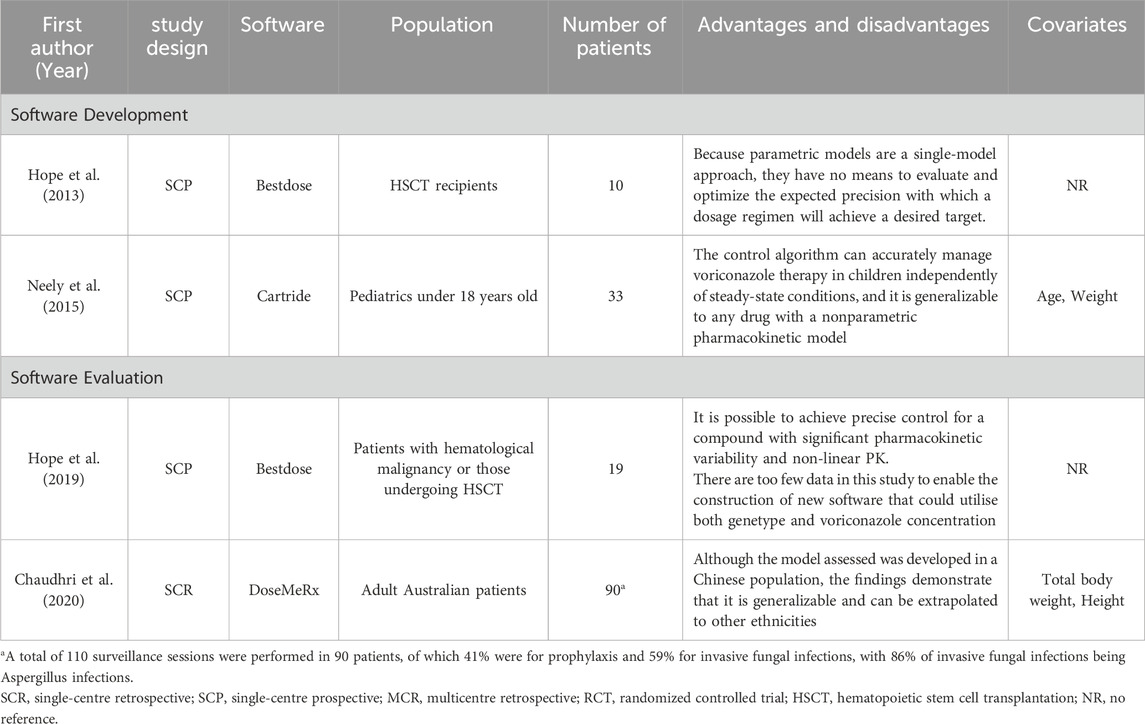
Several studies have used pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling to accurately predict concentrations and dosages based on patient physiological data and drug concentration to guide rational clinical use. This approach is particularly useful for drugs with high pharmacokinetic variability, such as voriconazole. This study included four studies, 2 were software development studies (Hope et al., 2013; Neely et al., 2015) and two (Chaudhri et al., 2020; Hope et al., 2019) were software evaluations. Meanwhile, the two software development studies applied the Pop PK model, 1 of which was evaluated through prospective studies and the other through Monte Carlo simulations. In Table 9 are some of the software evaluations and related content.
The names of the software developed in the two studies are Bestdose and Catrides. The Bestdose was created with data from 64 adults (20 healthy volunteers and 43 patients) and evaluated with pharmacokinetic data from 10 hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) patients. This program can be used to further optimize voriconazole for the treatment of critically immunocompromised patients, but still has many drawbacks for routine application (Hope et al., 2013). This prospective study has several limitations. Catrides, a nonparametric overall model containing 141 patients (85 children and 56 adults) and validated with 33 pediatric patients aged 8 months to 17 years old, showed that the advantages of the procedure are that patients do not have to be at steady state, sample sampling times do not have to be precisely timed, AUCs can be estimated even for a single concentration, and the procedure can be generalized to any drug with a nonparametric pharmacokinetic model, but prospective studies are still needed (Neely et al., 2015).
In a prospective clinical study evaluating Bestdose, results showed that 85.7% of patients had a trough concentration of 1.0–3.0 mg/L at 120 h after the start of treatment, which is above the 33% of the a priori expected proportion (Zembles et al., 2023). Kanika Chaudnri et al. included 90 patients to evaluate DoseMeRx and showed that dose prediction software enhances efficacy, is used to guide clinical decision-making, and can be generalized to other populations, although the model was developed in a Chinese population. However, the software did not monitor clinical outcomes and did not incorporate CYP2C19 genotypes (Chaudhri et al., 2020).
4 Discussion
4.1 Initial dosing program for special populations
There are accepted results for initial dosing programs, but dosing programs for special populations remain to be studied. The Japanese guidelines make different recommendations for maintenance doses for different diseases. The study was conducted by modeling Pop PK on data from 40 patients. The results suggest that transplant recipients receiving voriconazole for the prophylaxis of invasive candidiasis or aspergillosis may achieve target concentrations associated with the desired therapeutic outcome if the maintenance dose is 200 mg q12 h. However, Aspergillus with high minimal inhibitory concentrations may require higher maintenance doses (Perez-Pitarch et al., 2019).
For those with liver cirrhosis, trough concentrations of voriconazole can be affected by hepatic function due to the fact that voriconazole is primarily metabolized by the liver, and severe cholestasis significantly reduces voriconazole clearance, leading to slower metabolism and higher blood concentrations, which can increase the risk of drug-related adverse reactions, thus requiring clinical modification of the initial voriconazole dosing program (Pascual et al., 2012; Grensemann et al., 2021). The dosing program for Child-Pugh A/B is currently clearer, and the dosing program for Child-Pugh C needs further study. Of the 7 studies, 5 (Yamada et al., 2018; Tang et al., 2021; Gao et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2022) were unifactorial and 2 (Zhang et al., 2023; Zhao Y. et al., 2021) were multifactorial. In the 2 multifactorial studies, 1 study first investigated the influencing factors associated with variability in voriconazole trough concentration, performed multivariate bivariate correlation analyses, and developed multivariate linear regression models. The multiple regression linear model explained 34.8% of the variability in voriconazole trough concentration (R2 = 0.348), which implies that there is still a relatively high level of unexplained variability that requires further improvement. The results of another study showed that the mean trough concentration of patients with NMs, IMs, and PMs were 4.34 ± 2.12 mg/L, 4.40 ± 2.29 mg/L, and 4.30 ± 2.14 mg/L, respectively, and there was no significant difference between the three groups (p = 0.990), which ultimately suggests that only Child-Pugh classification affects trough concentration. Both of the 2 multifactorial studies explored the effect of CYP2C19 genotype in Child-Pugh C patients and both concluded that CYP2C19 genotype did not have a significant effect on trough concentration of voriconazole (p > 0.05).
And voriconazole is primarily metabolized in the liver by the CYP2C19 enzyme, with contributions by CYP2C9 and CYP3A4, and CYP2C19 polymorphisms could explain a substantial part of the remarkable inter-individual variability in voriconazole pharmacokinetics (Dean et al., 2012). Patients with CYP2C19 genotypes of IMs and PMs may be at higher risk of supratherapeutic levels and toxicity and the CYP2C19 genotyping as a potential strategy to optimize voriconazole dosing (Zhang et al., 2021). There have also been studies showing that poor metabolizers (most commonly in Asian populations) may experience higher voriconazole concentrations as well as a shift to other metabolic pathways for voriconazole such as 3A4 and 2C9 (McCreary et al., 2023).
It has been suggested that the level of inflammation (expressed as C-reactive protein concentration) can have an impact on voriconazole trough concentrations. Morgan et al. showed that inflammation stimulates the release of cytokines, leading to the regulation of hepatic transcription factor activity. These changes ultimately lead to the downregulation of most cytochrome P450 enzymes, affecting the production of metabolized proteins and thus reducing the clearance of certain drugs. In addition, in vitro studies have shown that pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), downregulate the biosynthesis of a number of CYP450 enzymes involved in the metabolism of voriconazole, such as CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 (Morgan, 2001; Aitken et al., 2006; Morgan et al., 2008). Van Wanrooy MJ et al. studied 128 patients and performed linear regression analyses of patient data unadjusted for covariates (sex, age, dose, route of administration, liver enzymes, and drug-drug interactions) and patient data adjusted for covariates. The results of the multiple linear regression analysis showed that for every 1 mg/L increase in C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration, voriconazole trough concentration increased by 0.015 mg/L (Encalada Ventura et al., 2015). Encalada Ventura MA et al. also correlated metabolic rate (MR) and CRP levels with voriconazole in 19 patients and showed a significant positive correlation between CRP and voriconazole concentration (rho = 0.62; 95% CI, 0.48 to 0.73; p < 0.001) and a negative correlation with MR (rho = −0.64; 95% CI, −0.77∼−0.50; p < 0.001), and voriconazole trough concentration increased with 0.021 mg/L for unit increase in the CRP level, and MR decreased with a −0.010 for every unit increase in the CRP level (p < 0.001 for both results) (Lee et al., 2021). In addition, although no dose adjustment is considered necessary for elderly patients in the voriconazole manual, it has been shown that elderly patients (age ≥ 65 years) have median voriconazole trough concentrations that are 80%–90% higher than those of younger patients after intravenous or oral voriconazole administration (Wang et al., 2014). This may be due to the fact that liver injury occurs in elderly patients and Cytochrome P450 levels decline after age 70 and result in an approximately 30% decrease in drug clearance (Stahl et al., 2018; Abdul-Aziz et al., 2020).
4.2 Target trough concentration range
Voriconazole demonstrates nonlinear saturation pharmacokinetics, resulting in unpredictable change in drug exposure (Abdul-Aziz et al., 2020; Gómez-López, 2020). AUC/MIC is the most predictive pharmacologic parameter, which >25 is closely related to clinical efficacy and patient survival against invasive fungal disease. The relationship between AUC and trough concentration of voriconazole has been demonstrated, and trough concentration/MIC can be used clinically in place of AUC/MIC (Troke et al., 2011; Carmo et al., 2023). Therefore, a defined range of target trough concentrations is of great importance for the clinical application of voriconazole therapy. The evidence for the target concentration ranges for each specific study is described above. In addition, there is evidence that the proportion of drug-resistant fungi has increased in recent years. It is hypothesized that the widespread use of antifungal drugs, the prolonged use of suboptimal concentrations, and the use of fungicides in agriculture have led to the development of genetic mutations that make fungi resistant to the drugs. The fungi most commonly associated with antifungal resistance are Candida, particularly non-albicans Candida and Aspergillus (Kolwijck et al., 2016; Huygens et al., 2023). And it has been shown that the MIC of drugs such as voriconazole has increased due to increased resistance to azoles, which can also have an impact on the target concentration range of voriconazole (Snelders et al., 2015; Pérez-Cantero et al., 2020). Therefore, this suggests that the proposed new target concentration range for voriconazole is meaningful.
There are also studies suggesting different target concentration ranges depending on the type of disease or population. For patients with Aspergillus infections, voriconazole trough concentration should be ≥ 2.0 mg/L. One study compared 107 first samples and 151 subsequent samples from 107 patients. Approximately one-third of the samples had voriconazole trough concentrations that deviated from the target concentration range and were mostly subtherapeutic. After predictive modeling, it was found that voriconazole used for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis had a higher probability of trough concentration >1.0 mg/L in subsequent samples than in first samples (p < 0.05) (Guinea et al., 2016). Another study tested four clinical wild-type and non-wild-type Aspergillus fumigatus isolates in an in vivo pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model with voriconazole Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) MICs ranging from 0.125 to 2.00 mg/L. By correlating trough levels with MICs, the study estimated that the highest MIC of an A. fumigatus isolate that may be treated successfully attaining the PK/PD target of EC50 and avoiding toxic serum trough levels of >5.5 mg/L albeit in a small proportion (<10%) of patients was 2, 4 and 1.5 mg/L for the CLSI, EUCAST and MTS methodologies, respectively. Moreover, considering that >90% of A. fumigatus isolates have CLSI MICs of ≤1 mg/L, the trough concentration of 2 mg/L will be required for PK/PD target attainment (Siopi et al., 2014). In addition, a target trough concentration ≥0.5 mg/L may be applicable for prophylaxis. Data on file at the United States Food and Drug Administration show that success rate in patients with fungal infections, whose mean voriconazole plasma levels were <0.5 g/mL, was 46% compared to 56% with mean plasma levels >0.5 g/mL (Trifilio et al., 2007).
4.3 Dosage adjustment
Four dose-adjustment-related studies (Perreault et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2020; Zembles et al., 2023; Park et al., 2012) were included in this paper. Voriconazole dose adjustments guided by therapeutic drug monitoring are available in the British, Canadian, Chinese and Australian guidelines (Ashbee et al., 2014; Laverdiere et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018; Chau et al., 2021). However, none of the four guidelines mentioned whether it was suitable for adults or pediatrics, and the British guideline did not mention the strength of evidence for the dose-adjustment program. The Canadian guideline stated that the dose-adjustment program was weak recommendation and low level of evidence and the Chinese guideline stated that the dose-adjustment program was conditional recommendation, very low quality of evidence. A dose-adjustment program was also suggested in the Australian guideline, but as the program was modified from the 2019 study by John et al. (2019), it was not included in the study to avoid duplication. Of the 4 studies other than guidelines, 3 studies explored voriconazole dose adjustment programs in adults, 1 study explored voriconazole dose adjustment programs in children.
Dose adjustment programs for adults were mentioned in 3 studies. WanBeom Park et al. conducted a randomized, evaluator-blinded, controlled, single-center study. The study was computerized and 108 patients were randomly assigned to either the TDM group (55 patients) or the non-TDM group (53 patients). The TDM group began blood collection on day 4 after voriconazole initiation and, based on the TDM results, adjusted the voriconazole dose according to the given dose adjustment program. dose to bring the trough concentration in line with the target concentration range. The non-TDM group maintained the standard dose of voriconazole. Ultimately, 27 patients in the TDM group had trough concentrations outside the target concentration range, six patients were not given dose adjustments due to discontinuation or death, and 21 patients received dose adjustments, of which 15 reached the target concentration range. The study still has limitations. First, the patients were only from a general hospital in Seoul, Korea, which was a single-center study, and the patients were all of Korean ethnicity. CYP2C19 test results showed that 43% of the patients were NM, 43% were IM, and 14% were PM, with a high percentage of poor metabolizers, which led to high levels of voriconazole concentrations in the study. Also, caution is needed when extrapolating this dose-adjustment program to other ethnic groups or pediatric populations whose pharmacokinetics different from those of adult patients. Second, the use of actual weight-based dosing in the study rather than fixed or ideal weight-based dosing may also have contributed to the high voriconazole levels. Third, the sample size was too small and larger sample sizes are still needed to determine the feasibility of the program (Park et al., 2012). Sarah perreault et al. conducted a prospective study with the primary objective of evaluating a voriconazole dose adjustment program. The study included 128 patients taking oral voriconazole for prophylaxis or treatment, of which 78% were Caucasian, 12% were Hispanic, 7% were black, 1% were Asian, and 2% were other populations. Of these 128 patients, 40% were overweight (BMI ≥ 25–29.99 kg/m2), 21% were obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), and 3.9% were morbidly obese (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2). Dose adjustment was performed in these 128 patients, and 80% were able to achieve the target concentration range at the second dose adjustment. A subgroup analysis of patient-specific characteristics was also performed to obtain a higher percentage of patients >30 years old and BMI > 25 kg/m2 who initially reached the target concentration range, while age ≤30 years old and BMI ≤ 25 kg/m2 were mostly at subtherapeutic levels. The study still has limitations. First, the study was a single-center prospective study with a homogeneous patient population, most of whom were Caucasian and only one Asian, so extrapolation of the dose-adjustment program to other ethnic populations and pediatric populations needs to be done with caution. Second, only 32.8% of patients had a normal BMI, 2.3% had a BMI < 18.5 kg/m2, and 64.9% had a BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, which is a disproportionately large number of patients with abnormal body weights who were administered a fixed dose. Finally, the study did not test the genotype of the patients and voriconazole was used for prophylaxis rather than treatment in 94.8% of patients (Perreault et al., 2019). A single-center retrospective study was also conducted by Pejun Yvonne Zhou et al. Seventy patients were included in the study, 55 of whom were Chinese, 5 Malays, 6 Indians, and 4 from other Asian ethnic groups. And 25 of the patients had probable or confirmed Aspergillus infection and 9 had probable or confirmed Candida infection. The study recommended dose adjustments based on the patients’ voriconazole trough concentration and obtained the effect on subsequent trough concentrations. In this study, only 45.7% of the patients achieved the target concentration range without dose adjustment. For patients with trough concentrations <0.5 mg/L, reloading voriconazole at a dose of 1.5 times the new maintenance dose for 1 day, followed by 75% dose increase for the maintenance dose (n = 1), which increased the level by > 10 times (absolute increment is unknown as 0.5 mg/L was the upper limit of assay detection). For patients with trough concentrations at 1.0∼1.9 mg/L, increasing the dose by 25∼33% (n = 6) and increase the dose by 67%(n = 1), which increased level by 70∼130% and increase level by 10%. For patients with trough concentrations at 5.5∼7.5 mg/L, reduction the dose by 13% (n = 1) and reduction the dose by 33% (n = 3), which reduction level by 50% and reduction level by 80%. For patients with trough concentrations >7.5 mg/L, held off one dose or until neurological symptoms were resolved, followed by 33% reduction in dose (n = 6),which reduction level by >33% absolute reduction is unknown as 7.5 mg/L was the upper limit of assay detection. There are several limitations to the study. First, the patients were all from Southeast Asian populations, 78.6% were Chinese, and only the adult population was included, so extrapolation of this dose adjustment program to other ethnic populations and pediatric populations still requires further study. Second, the study did not perform CYP2C19 genotype testing, so the effect of genetic polymorphisms on voriconazole trough concentration could not be determined. Finally, the sample size was too small, which resulted in the inability to elucidate the inhibitory or inducing effects of the various drugs and corresponding doses on CYP enzymes, and therefore further studies are still needed to recommend a voriconazole dose adjustment program (Zhou et al., 2020).
The incidence of invasive infections in children, although rare, is increasing with the rise of high-risk patients, including preterm infants, pediatric patients treated for hematologic malignancies, or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients (Arrieta et al., 2023). In January 2019, the FDA expanded the indication for voriconazole to include children >2 years of age. Voriconazole pharmacokinetics is different and highly variable in pediatric patients compared to adults, and dosing is difficult, while oral bioavailability is lower (45%). Also, a dose-dependent pharmacokinetic profile of voriconazole was observed in the pediatric population, with a linear pharmacokinetic profile at voriconazole doses of 3∼4 mg/kg q12 h and a non-linear pharmacokinetic profile at 7∼8 mg/kg q12 h. Although the recommended dosage for children is given in the instructions, it has been shown that only 50% of pediatric patients achieve the target concentration at the first steady-state measurement and that children require a larger weight-based dose of voriconazole than adults to achieve the target concentration range, so pediatricians must often extrapolate voriconazole dosages for children from adult data (Zembles et al., 2023). In conclusion, it is challenging to optimize daily dosing to achieve the therapeutic range in pediatric patients (Arrieta et al., 2023; Resztak et al., 2021). A single-center retrospective study was conducted by Tracy N. Zembles et al. The study included 59 pediatric patients with a median age of 10.4 (3.7–14.7) years old. 42 patients had at least 1 measurement of steady-state trough concentration, 21 of whom were ≥12 years old and 21 of whom were <12 years old. Of these 42 patients, 13 patients (31%) had trough concentrations in the target concentration range at the first measurement, and after dose adjustment, 34 (81%) had trough concentrations in the target concentration range. The study included 7 years of longitudinal data collection, but shortcomings remain. First, the sample size was small. Patients were expected to be divided into <2 years old, 2–12 years old, and ≥12 years old subgroups, but because of the small number of patients <2 years old, they were divided into only two groups, <12 years old and ≥12 years old. Second, only 21 patients received a loading dose, which may have led to premature timing of voriconazole TDM in some patients who did not achieve steady-state blood levels. Finally, the study applied both intravenous and enteral administration, which may have resulted in lower voriconazole concentrations (Zembles et al., 2023). In conclusion, all current voriconazole dose-adjustment programs guided by TDM have significant limitations and still require further study and refinement.
4.4 Timing of repeat therapy drug monitoring
TDM should be repeated if the dose or route of administration of voriconazole is changed or if interacting drugs are introduced or discontinued, but the exact timing remains to be determined.
Purkins L et al. conducted 2 studies, one of which was a randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, double-blind study of intravenous escalation and intravenous-to-oral switch study. The study divided 42 patients into 2 cohorts; 28 subjects were enrolled in Cohort 1 (14 on voriconazole, 14 on placebo) and 14 subjects were enrolled in Cohort 2 (7 on voriconazole, 7 on placebo). Patients in cohort 1 were treated with voriconazole 6 mg/kg q12 h iv for 24 h, followed by 3 mg/kg q12h, and then changed to an oral program of 200 mg q12 h po on days 8∼14. After 7 days of elution, switch to a higher maintenance dose (5 mg/kg q12 h iv, then change to an oral program 400 mg q12 h) Cohort 2 used a program of 4 mg/kg q12 h iv, followed by a switch to an oral program of 300 mg q12 h po. The results showed that after switching from intravenous to an oral dosing program, the majority of subjects reached a steady state on day 4, with the mean lowest trough concentration remaining above the clinically important MIC (Purkins et al., 2002). Another study is a single-blind, multiple-dose, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-finding study. The study divided 64 patients into groups of 8 subjects each receiving voriconazole doses of 2 mg/kg q12 h, 4 mg/kg q12 h, 2 mg/kg t.i.d or 3 mg/kg q12 h. Eleven subjects received 1.5 mg/kg t.i.d, and 21 patients received placebo. The study demonstrated by statistical analysis of peak concentrations and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUCτ) from just before dosing to the end of the dosing interval, as well as visual inspection of trough concentrations, that steady state levels were reached on the third or fifth day of multiple dosing (Purkins et al., 2003). However, the former study included only 41 patients and the latter study included only 56 patients. Neither of these two papers were up-to-date. In the future, researchers should pay more attention to the timing of repeat TDM with voriconazole and study it further.
4.5 Dose-prediction software
MIPD is a mathematical modeling and simulation technology that integrates information about the patient, drug, and disease to provide a basis for precise patient dosing. The MIPD often uses nonlinear mixed-effects (NLME) models to predict and optimize treatment outcomes based on patient characteristics and therapeutic drug monitoring data. MIPD is indicated for drugs with narrow therapeutic ranges and complex pharmacokinetics (PK), such as voriconazole (Kluwe et al., 2023). Commonly used models include, but are not limited to, population pharmacokinetic (Pop-PK) models, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) models, population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models, physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBRK) models and artificial intelligence (AI) models, and different modeling and analysis techniques have different characteristics. Voriconazole dose prediction procedures are mostly based on Pop-PK models. Such models should at a minimum contain the most relevant physiological and biological attributes determining the drug’s disposition and enough attributes to explain a substantial portion of observed variability. A pop-PK model can be validated internally, externally, or prospectively to diagnose misspecifications (Darwich et al., 2021; Wicha et al., 2021).
Bestdose was created with data from 64 adults (20 healthy volunteers and 43 patients) and evaluated with pharmacokinetic data from 10 hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) patients. Validation of the performance of the voriconazole controller showed close agreement between the controller-calculated voriconazole dose and the actual dose administered in most cases, but in two patients the controller predicted significantly more medication than was actually administered. This program can be used to further optimize voriconazole for the treatment of critically immunocompromised patients, but still has many drawbacks for routine application (Hope et al., 2013). The procedure needs to be evaluated for accuracy in prospective clinical trials, and the applicability of oral voriconazole to the procedure needs to be tested, as well as other existential issues. In a prospective clinical study of Bestdose, 19 patients (18 Caucasian, 1 other) were included for evaluation of the procedure, but only 14 could be analyzed. 12 of the 14 patients (85.7%; 95% CI, 57.2%–98.2%) had a trough concentration of 1.0∼3.0 mg/L at 120 h after the start of treatment, which is above the 33% of the a priori expected proportion (Hope et al., 2019). This prospective study has several limitations. The sample size of the study was relatively small, containing only patients in the early stages of HSCT rather than those with critical disease leading to potentially more variable and extreme pharmacokinetics, and the duration of the study was relatively short, leaving many issues unexposed. Cartrides, a nonparametric overall model containing 141 patients (85 children and 56 adults) and validated with 33 pediatric patients aged 8 months to 17 years old, showed that the advantages of the procedure are that patients do not have to be at steady state, sample sampling times do not have to be precisely timed, AUCs can be estimated even for a single concentration, and the procedure can be generalized to any drug with a nonparametric pharmacokinetic model, but prospective studies are still needed (Neely et al., 2015). Kanika Chaudnri et al. included 90 patients to evaluate DoseMeRx and showed that dose prediction software enhances efficacy, is used to guide clinical decision-making, and can be generalized to other populations, although the model was developed in a Chinese population. However, the software did not monitor clinical outcomes and did not incorporate CYP2C19 genotypes (Chaudhri et al., 2020).
The study summarized the initial treatment program, target concentration range, and dose adjustment program for voriconazole and identified the following shortcomings in the study. 1) the included studies did not have the same target concentration range, making it difficult to compare studies with the same factors; 2) some of the studies used modeling methods that were not implemented in the clinic, resulting in uncertainty about the clinical efficacy of the programs; and 3) the inclusion of fewer literatures related to dosage adjustments, which made it difficult to draw accurate conclusions.
5 Conclusion
There has been a great deal of research and partial consensus on individualized dosing of voriconazole, but there are still some critical issues that have not been resolved. Recently updated guidelines for TDM of voriconazole or antifungals focus on key issues that need to be addressed. The 2021 edition of the Australian guideline focuses on 9 issues regarding TDM of antifungals. The 2022 edition of the Japanese guideline focuses on 5 issues regarding TDM of voriconazole. There is still no clear and uniform program for dose adjustment of voriconazole guided by TDM. Based on the results of the study, it is recommended that all patients on voriconazole should have their initial dosing program selected on the basis of their hepatic function or other influencing factors (e.g., pathogens, infections, C-reactive protein, albumin, or obesity), and that therapeutic concentrations should be achieved through appropriate dosage adjustments guided by therapeutic drug monitoring. Routine genetic testing for voriconazole application in patients is not considered necessary at this time. In terms of dose adjustment, in adult patients, if the voriconazole trough concentration is subtherapeutic, the voriconazole dose should be increased by 25%∼50%. If the voriconazole trough concentration is supratherapeutic,the voriconazole dose should be decreased by 25%∼50%. If a drug-related adverse event occurs, hold 1 dose, decrease subsequent dose by 50%.In pediatric patients, if the voriconazole trough concentration is subtherapeutic, increase the voriconazole dose by 1∼2 mg/kg or increase the voriconazole dose by 50%. If the voriconazole trough concentration is supratherapeutic, reduce the voriconazole dose by 1 mg/kg or hold 1 dose, and decrease the subsequent dose by 25%. Most of the previous clinical studies have a low level of evidence-based medicine evidence, and more prospective, multicenter clinical studies are needed to promote individualized dosing of voriconazole.
Author contributions
LJ: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review & editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing–review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Quanzhou City Science & Technology Program of China, High-level Talent Innovation Project of Quanzhou (2021C036R).
Acknowledgments
This article was completed under the guidance of my tutor ZL. I would like to express my heartfelt thanks to him for his guidance and help!
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
q12 h, every 12 h; q.d, once daily; Iv, intravenously; Po, orally; TBIL, total bilirubin; PTA, Probability of target attainment; CYP2C19, cytochrome P2C19; UMs, ultrarapid metabolizers; RMs, rapid metabolizers; NMs, normal metabolizers; IMs, intermediate metabolizers; PMs, poor metabolizers; SCR, single-centre retrospective; SCP, single-centre prospective; MCR, multicentre retrospective; RCT, randomized controlled trial; ULN, upper limit of normal; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ALB, albumin; CFR, cumulative fraction of response; AdjBW, adjusted body weight; TBW, total body weight; CRP, c-reactive protein; TDM, therapeutic drug monitoring; CAP, chronic pulmonary aspergillosis; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; NR, no reference; MIPD, model-informed precision dosing; NLME, nonlinear mixed-effects; CNS, central nervous system.
References
Abdul-Aziz, M. H., Alffenaar, J. C., Bassetti, M., Bracht, H., Dimopoulos, G., Marriott, D., et al. (2020). Antimicrobial therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill adult patients: a Position Paper. Intensive care Med. 46 (6), 1127–1153. doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06050-1
Aitken, A. E., Richardson, T. A., and Morgan, E. T. (2006). Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 46, 123–149. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141059
Arrieta, A. C., Lee, A., and Tran, M. T. (2023). Invasive Mold infections in children: Navigating Troubled Waters with a Broken Compass. Infect. Dis. Ther. 12 (6), 1465–1485. doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00819-9
Ashbee, H. R., Barnes, R. A., Johnson, E. M., Richardson, M. D., Gorton, R., and Hope, W. W. (2014). Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of antifungal agents: guidelines from the British Society for Medical Mycology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69 (5), 1162–1176. doi:10.1093/jac/dkt508
Carmo, A., Rocha, M., Pereirinha, P., Tomé, R., and Costa, E. (2023). Antifungals: from pharmacokinetics to clinical Practice. Antibiot. Basel, Switz. 12 (5), 884. doi:10.3390/antibiotics12050884
Chau, M. M., Daveson, K., Alffenaar, J. C., Gwee, A., Ho, S. A., Marriott, D. J. E., et al. (2021). Consensus guidelines for optimising antifungal drug delivery and monitoring to avoid toxicity and improve outcomes in patients with haematological malignancy and haemopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2021. Intern. Med. J. 51 (Suppl. 7), 37–66. doi:10.1111/imj.15587
Chaudhri, K., Stocker, S. L., Williams, K. M., McLeay, R. C., Marriott, D. J. E., Di Tanna, G. L., et al. (2020). Voriconazole: an audit of hospital-based dosing and monitoring and evaluation of the predictive performance of a dose-prediction software package. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75 (7), 1981–1984. doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa098
Chen, K., Zhang, X., Ke, X., Du, G., Yang, K., and Zhai, S. (2018). Individualized medication of voriconazole: a Practice guideline of the Division of therapeutic drug monitoring, Chinese pharmacological Society. Ther. drug Monit. 40 (6), 663–674. doi:10.1097/ftd.0000000000000561
Darwich, A. S., Polasek, T. M., Aronson, J. K., Ogungbenro, K., Wright, D. F. B., Achour, B., et al. (2021). Model-informed precision dosing: Background, Requirements, validation, implementation, and forward Trajectory of individualizing drug therapy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 61, 225–245. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-033020-113257
Dean, L. (2012). “Voriconazole therapy and CYP2C19 genotype,” in Medical genetics Summaries. Editors V. M. Pratt, S. A. Scott, M. Pirmohamed, B. Esquivel, B. L. Kattman, and A. J. Malheiro (Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information). (US).
Diller, E., Krekel, T., Spec, A., and Klaus, J. (2021). Evaluation of total body weight versus adjusted body weight voriconazole dosing in obese patients. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 65 (7), e0246020. doi:10.1128/aac.02460-20
Dolton, M. J., and McLachlan, A. J. (2014). Voriconazole pharmacokinetics and exposure-response relationships: assessing the links between exposure, efficacy and toxicity. Int. J. Antimicrob. agents 44 (3), 183–193. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.05.019
Encalada Ventura, M. A., Span, L. F., van den Heuvel, E. R., Groothuis, G. M. M., and Alffenaar, J. W. C. (2015). Influence of inflammation on voriconazole metabolism. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 59 (5), 2942–2943. doi:10.1128/aac.04789-14
Gao, J., Zhang, Q., Wu, Y., Li, Y., Qi, T., Zhu, C., et al. (2018). Improving survival of acute-on-chronic liver failure patients complicated with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 876. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-19320-2
Ga Wells, B. S., O'Connell, D., Peterson, J., Welch, V., Losos, M., and Tugwell, P. (2013). The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available at: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (Accessed August 10, 2024).
Gómez-López, A. (2020). Antifungal therapeutic drug monitoring: focus on drugs without a clear recommendation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. official Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 26 (11), 1481–1487. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.037
Grensemann, J., Pfaffendorf, C., Wicha, S. G., König, C., Roedl, K., Jarczak, D., et al. (2021). Voriconazole pharmacokinetics are not altered in critically ill patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure and Continuous renal Replacement therapy: an observational study. Microorganisms 9 (10), 2087. doi:10.3390/microorganisms9102087
Guinea, J., Escribano, P., Marcos-Zambrano, L. J., Peláez, T., Kestler, M., Muñoz, P., et al. (2016). Therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole helps to decrease the percentage of patients with off-target trough serum levels. Med. Mycol. 54 (4), 353–360. doi:10.1093/mmy/myv099
Hicks, J. K., Quilitz, R. E., Komrokji, R. S., Kubal, T. E., Lancet, J. E., Pasikhova, Y., et al. (2020). Prospective CYP2C19-guided voriconazole prophylaxis in patients with Neutropenic acute myeloid leukemia reduces the incidence of subtherapeutic antifungal plasma concentrations. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 107 (3), 563–570. doi:10.1002/cpt.1641
Hope, W., Johnstone, G., Cicconi, S., Felton, T., Goodwin, J., Whalley, S., et al. (2019). Software for dosage individualization of voriconazole: a prospective clinical study. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 63 (4), e02353. doi:10.1128/aac.02353-18
Hope, W. W., Vanguilder, M., Donnelly, J. P., Blijlevens, N. M. A., Brüggemann, R. J. M., Jelliffe, R. W., et al. (2013). Software for dosage individualization of voriconazole for immunocompromised patients. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 57 (4), 1888–1894. doi:10.1128/aac.02025-12
Huygens, S., Dunbar, A., Buil, J. B., Klaassen, C. H. W., Verweij, P. E., van Dijk, K., et al. (2023). Clinical impact of Polymerase Chain reaction-based Aspergillus and azole resistance detection in invasive aspergillosis: a prospective multicenter study. Clin. Infect. Dis. official Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 77 (1), 38–45. doi:10.1093/cid/ciad141
Jadad, A. R., Moore, R. A., Carroll, D., Jenkinson, C., Reynolds, D. J., Gavaghan, D. J., et al. (1996). Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control. Clin. trials 17 (1), 1–12. doi:10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4
Jiang, Z., Wei, Y., Huang, W., Li, B., Zhou, S., Liao, L., et al. (2022). Population pharmacokinetics of voriconazole and initial dosage optimization in patients with talaromycosis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 982981. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.982981
Jin, H., Wang, T., Falcione, B. A., Olsen, K. M., Chen, K., Tang, H., et al. (2016). Trough concentration of voriconazole and its relationship with efficacy and safety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71 (7), 1772–1785. doi:10.1093/jac/dkw045
John, J., Loo, A., Mazur, S., and Walsh, T. J. (2019). Therapeutic drug monitoring of systemic antifungal agents: a pragmatic approach for adult and pediatric patients. Expert Opin. drug metabolism & Toxicol. 15 (11), 881–895. doi:10.1080/17425255.2019.1671971
Kluwe, F., Michelet, R., Huisinga, W., Zeitlinger, M., Mikus, G., and Kloft, C. (2023). Towards model-informed precision dosing of voriconazole: challenging published voriconazole nonlinear mixed-effects models with Real-World clinical data. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 62 (10), 1461–1477. doi:10.1007/s40262-023-01274-y
Kolwijck, E., van der Hoeven, H., de Sévaux, R. G., ten Oever, J., Rijstenberg, L. L., van der Lee, H. A. L., et al. (2016). Voriconazole-susceptible and voriconazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus Coinfection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. care Med. 193 (8), 927–929. doi:10.1164/rccm.201510-2104LE
Laverdiere, M., Bow, E. J., Rotstein, C., Autmizguine, J., Broady, R., Garber, G., et al. (2014). Therapeutic drug monitoring for triazoles: a needs assessment review and recommendations from a Canadian perspective. Can. J. Infect. Dis. & Med. Microbiol. = J. Can. des maladies Infect. de Microbiol. medicale 25 (6), 327–343. doi:10.1155/2014/340586
Lee, Y., Puumala, E., Robbins, N., and Cowen, L. E. (2021). Antifungal drug resistance: Molecular mechanisms in Candida albicans and beyond. Chem. Rev. 121 (6), 3390–3411. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00199
Lempers, V. J., Meuwese, E., Mavinkurve-Groothuis, A. M., Henriet, S., van der Sluis, I. M., Hanff, L. M., et al. (2019). Impact of dose adaptations following voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring in pediatric patients. Med. Mycol. 57 (8), 937–943. doi:10.1093/mmy/myz006
Li, S., Wu, S., Gong, W., Cao, P., Chen, X., Liu, W., et al. (2021). Application of population pharmacokinetic analysis to characterize CYP2C19 Mediated metabolic mechanism of voriconazole and support dose optimization. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 730826. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.730826
Li, X., Frechen, S., Moj, D., Lehr, T., Taubert, M., Hsin, C. H., et al. (2020). A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of voriconazole integrating time-dependent inhibition of CYP3A4, genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19 and predictions of drug-drug interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 59 (6), 781–808. doi:10.1007/s40262-019-00856-z
Lin, X. B., Li, Z. W., Yan, M., Zhang, B. K., Liang, W., Wang, F., et al. (2018). Population pharmacokinetics of voriconazole and CYP2C19 polymorphisms for optimizing dosing regimens in renal transplant recipients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 84 (7), 1587–1597. doi:10.1111/bcp.13595
Lin, X. B., Lui, K. Y., Guo, P. H., Liu, X. M., Liang, T., Hu, X. G., et al. (2022). Population pharmacokinetic model-guided optimization of intravenous voriconazole dosing regimens in critically ill patients with liver dysfunction. Pharmacotherapy 42 (1), 23–33. doi:10.1002/phar.2634
Luong, M. L., Al-Dabbagh, M., Groll, A. H., Racil, Z., Nannya, Y., Mitsani, D., et al. (2016). Utility of voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring: a meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71 (7), 1786–1799. doi:10.1093/jac/dkw099
McCreary, E. K., Davis, M. R., Narayanan, N., Andes, D. R., Cattaneo, D., Christian, R., et al. (2023). Utility of triazole antifungal therapeutic drug monitoring: Insights from the Society of infectious diseases Pharmacists: endorsed by the Mycoses study group Education and research Consortium. Pharmacotherapy 43 (10), 1043–1050. doi:10.1002/phar.2850
Morgan, E. T. (2001). Regulation of cytochrome p450 by inflammatory mediators: why and how? Drug metabolism Dispos. Biol. fate Chem. 29 (3), 207–212.
Morgan, E. T., Goralski, K. B., Piquette-Miller, M., Renton, K. W., Robertson, G. R., Chaluvadi, M. R., et al. (2008). Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in infection, inflammation, and cancer. Drug metabolism Dispos. Biol. fate Chem. 36 (2), 205–216. doi:10.1124/dmd.107.018747
Neely, M., Margol, A., Fu, X., van Guilder, M., Bayard, D., Schumitzky, A., et al. (2015). Achieving target voriconazole concentrations more accurately in children and adolescents. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 59 (6), 3090–3097. doi:10.1128/aac.00032-15
Niu Wanjie, J. Z., Yu, E., Wu, S., Jia, S., and Qin, W. (2018). Quality assessment of research papers on population pharmacokinetics in China. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 38 (13), 1345–1349. doi:10.13286/j.cnki.chinhosppharmacyj.2018.13.01
Park, W. B., Kim, N. H., Kim, K. H., Lee, S. H., Nam, W. S., Yoon, S. H., et al. (2012). The effect of therapeutic drug monitoring on safety and efficacy of voriconazole in invasive fungal infections: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. official Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 55 (8), 1080–1087. doi:10.1093/cid/cis599
Pascual, A., Csajka, C., Buclin, T., Bolay, S., Bille, J., Calandra, T., et al. (2012). Challenging recommended oral and intravenous voriconazole doses for improved efficacy and safety: population pharmacokinetics-based analysis of adult patients with invasive fungal infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. official Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 55 (3), 381–390. doi:10.1093/cid/cis437
Pérez-Cantero, A., López-Fernández, L., Guarro, J., and Capilla, J. (2020). Azole resistance mechanisms in Aspergillus: update and recent advances. Int. J. Antimicrob. agents 55 (1), 105807. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.09.011
Perez-Pitarch, A., Guglieri-Lopez, B., Ferriols-Lisart, R., Pérez, A., Ezquer-Garín, C., Hernández-Boluda, J. C., et al. (2019). Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of voriconazole against Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp. in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Ther. drug Monit. 41 (6), 740–747. doi:10.1097/ftd.0000000000000657
Perreault, S., McManus, D., Anderson, A., Lin, T., Ruggero, M., and Topal, J. E. (2019). Evaluating a voriconazole dose modification guideline to optimize dosing in patients with hematologic malignancies. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. official Publ. Int. Soc. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 25 (6), 1305–1311. doi:10.1177/1078155218786028
Purkins, L., Wood, N., Ghahramani, P., Greenhalgh, K., Allen, M. J., and Kleinermans, D. (2002). Pharmacokinetics and safety of voriconazole following intravenous-to oral-dose escalation regimens. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 46 (8), 2546–2553. doi:10.1128/aac.46.8.2546-2553.2002
Purkins, L., Wood, N., Greenhalgh, K., Allen, M. J., and Oliver, S. D. (2003). Voriconazole, a novel wide-spectrum triazole: oral pharmacokinetics and safety. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 56 (Suppl. 1), 10–16. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01993.x
Resztak, M., Sobiak, J., and Czyrski, A. (2021). Recent advances in therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole, Mycophenolic Acid, and Vancomycin: a literature review of pediatric studies. Pharmaceutics 13 (12), 1991. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13121991
Siopi, M., Mavridou, E., Mouton, J. W., Verweij, P. E., Zerva, L., and Meletiadis, J. (2014). Susceptibility breakpoints and target values for therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole and Aspergillus fumigatus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69 (6), 1611–1619. doi:10.1093/jac/dku023
Slim, K., Nini, E., Forestier, D., Kwiatkowski, F., Panis, Y., and Chipponi, J. (2003). Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 73 (9), 712–716. doi:10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
Snelders, E., Camps, S. M., Karawajczyk, A., Rijs, A. J. M. M., Zoll, J., Verweij, P. E., et al. (2015). Genotype-phenotype complexity of the TR46/Y121F/T289A cyp51A azole resistance mechanism in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG & B 82, 129–135. doi:10.1016/j.fgb.2015.06.001
Stahl, E. C., Haschak, M. J., Popovic, B., and Brown, B. N. (2018). Macrophages in the aging liver and age-related liver disease. Front. Immunol. 9, 2795. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02795
Takesue, Y., Hanai, Y., Oda, K., Hamada, Y., Ueda, T., Mayumi, T., et al. (2022). Clinical Practice guideline for the therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole in non-Asian and Asian adult patients: consensus review by the Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and the Japanese Society of therapeutic drug monitoring. Clin. Ther. 44 (12), 1604–1623. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.10.005
Tang, D., Yan, M., Song, B. L., Zhao, Y. C., Xiao, Y. W., Wang, F., et al. (2021). Population pharmacokinetics, safety and dosing optimization of voriconazole in patients with liver dysfunction: a prospective observational study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 87 (4), 1890–1902. doi:10.1111/bcp.14578
Trifilio, S., Singhal, S., Williams, S., Frankfurt, O., Gordon, L., Evens, A., et al. (2007). Breakthrough fungal infections after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients on prophylactic voriconazole. Bone marrow Transplant. 40 (5), 451–456. doi:10.1038/sj.bmt.1705754
Troke, P. F., Hockey, H. P., and Hope, W. W. (2011). Observational study of the clinical efficacy of voriconazole and its relationship to plasma concentrations in patients. Antimicrob. agents Chemother. 55 (10), 4782–4788. doi:10.1128/aac.01083-10
Wang, J., Shen, Y., Wu, Z., and Ge, W. (2024). Population pharmacokinetics of voriconazole and dose optimization in elderly Chinese patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64 (2), 253–263. doi:10.1002/jcph.2357
Wang, T., Chen, S., Sun, J., Cai, J., Cheng, X., Dong, H., et al. (2014). Identification of factors influencing the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole and the optimization of dosage regimens based on Monte Carlo simulation in patients with invasive fungal infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69 (2), 463–470. doi:10.1093/jac/dkt369
Wang, T., Yan, M., Tang, D., Dong, Y., Zhu, L., Du, Q., et al. (2021). Using Child-Pugh Class to optimize voriconazole dosage regimens and improve safety in patients with liver cirrhosis: Insights from a population pharmacokinetic model-based analysis. Pharmacotherapy 41 (2), 172–183. doi:10.1002/phar.2474
Wicha, S. G., Märtson, A. G., Nielsen, E. I., Koch, B. C. P., Friberg, L. E., Alffenaar, J. W., et al. (2021). From therapeutic drug monitoring to model-informed precision dosing for Antibiotics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 109 (4), 928–941. doi:10.1002/cpt.2202
Yamada, T., Imai, S., Koshizuka, Y., Tazawa, Y., Kagami, K., Tomiyama, N., et al. (2018). Necessity for a significant maintenance dosage reduction of voriconazole in patients with severe liver cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class C). Biol. & Pharm. Bull. 41 (7), 1112–1118. doi:10.1248/bpb.b18-00164
Yi, W. M., Schoeppler, K. E., Jaeger, J., Mueller, S. W., MacLaren, R., Fish, D. N., et al. (2017). Voriconazole and posaconazole therapeutic drug monitoring: a retrospective study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 16 (1), 60. doi:10.1186/s12941-017-0235-8
Zembles, T. N., Dasgupta, M., Kenkel, T. J., Lehrer, B., Simpson, P., Havens, P. L., et al. (2023). Higher weight-based doses are required to achieve and Maintain therapeutic voriconazole serum trough concentrations in children. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. JPPT official J. PPAG 28 (3), 247–254. doi:10.5863/1551-6776-28.3.247
Zhang, Y., Hou, K., Liu, F., Luo, X., He, S., Hu, L., et al. (2021). The influence of CYP2C19 polymorphisms on voriconazole trough concentrations: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mycoses 64 (8), 860–873. doi:10.1111/myc.13293
Zhang, Y., Wu, R., Liu, F., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Ji, C., et al. (2023). Factors influencing blood concentration of voriconazole and therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with Child–Pugh Class C cirrhosis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther., 2023, 1, 10. doi:10.1155/2023/4240869
Zhao, Y., Hou, J., Xiao, Y., Wang, F., Zhang, B., Zhang, M., et al. (2021). Predictors of voriconazole trough concentrations in patients with Child-Pugh Class C cirrhosis: a prospective study. Antibiot. Basel, Switz. 10 (9), 1130. doi:10.3390/antibiotics10091130
Zhao, Y. C., Zou, Y., Hou, J. J., Xiao, C. L., Zhang, B. K., Li, J. K., et al. (2021). Factors affecting voriconazole trough concentration and optimal maintenance voriconazole dose in Chinese children. Antibiot. Basel, Switz. 10 (12), 1542. doi:10.3390/antibiotics10121542
Zhou, P. Y., Lim, T. P., Tang, S. L. S., Liew, Y., Chua, S. G. N., Lim, L. L. C., et al. (2020). The utility of voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring in a multi-racial cohort in Southeast Asia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 21, 427–433. doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2019.12.004
Keywords: voriconazole, therapeutic drug monitoring, dose adjustment, individualized medication, concentration range
Citation: Jiang L and Lin Z (2024) Voriconazole: a review of adjustment programs guided by therapeutic drug monitoring. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1439586. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1439586
Received: 28 May 2024; Accepted: 12 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Yao Liu, Daping Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Suodi Zhai, Peking University Third Hospital, ChinaKhalid Waleed Taher, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2024 Jiang and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiqiang Lin, bGluLXpoaXFpYW5nQDE2My5jb20=
 Li Jiang
Li Jiang Zhiqiang Lin*
Zhiqiang Lin*