
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol., 22 October 2024
Sec. Pharmacoepidemiology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1438292
Background: Amiodarone and dronedarone are both class III antiarrhythmic medications used to treat arrhythmias. The objective of this study was to enhance the current understanding of adverse drug reaction (ADR) associated with amiodarone and dronedarone by employing data mining methods on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), and providing a reference for safe and reasonable clinical use.
Methods: The ADR records were selected by searching the FAERS database from 2011 Q3 to 2023 Q3. The disproportionality analysis algorithms, including Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR), Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR), Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network (BCPNN), and Empirical Bayesian Geometric Mean (EBGM), were used to detect signals of amiodarone-related and dronedarone-related ADRs. The ADR profiles of amiodarone and dronedarone categorized by organ toxicity were compared through the Z-test and the Fisher exact test.
Results: 9,295 reports specifically mentioned the use of amiodarone and 2,485 reports mentioned the use of dronedarone among 9,972,109 reports, with the majority of ADRs occurring in males over 60 years old. The United States was responsible for the highest proportion of reported ADRs. Significant system organ classes (SOC) for both included Cardiac disorders, Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders, and Investigations, etc. At the preferred terms (PTs) level, the more frequent ADR signals for amiodarone were drug interaction (n = 856), hyperthyroidism (n = 758), and dyspnoea (n = 607), while dronedarone were atrial fibrillation (n = 371), dyspnoea (n = 204), and blood creatinine increased (n = 123). Notably, unexpected ADRs, including electrocardiogram T wave alternans (n = 16; EBGM05 = 231.27), accessory cardiac pathway (n = 11; EBGM05 = 140), thyroiditis (n = 178; EBGM05 = 125.91) for amiodarone, and cardiac ablation (n = 11; EBGM05 = 31.86), cardioversion (n = 7; EBGM05 = 22.69), and dysphagia (n = 47; EBGM05 = 3.6) for dronedarone, were uncovered in the instructions. The analysis also revealed significant differences in the ADR profiles of amiodarone and dronedarone, with dronedarone showing higher proportions of cardiac toxicity but lower thyroid toxicity compared to amiodarone.
Conclusion: These findings underscore the significance of vigilantly monitoring and comprehending the potential risks linked to the use of amiodarone and dronedarone. New ADRs discovered and clear ADR profiles of amiodarone and dronedarone enhance a thorough understanding of these drugs, which is essential for clinicians to ensure safe use of amiodarone and dronedarone.
Amiodarone, as a class III antiarrhythmic medication blocking multiple ion channels, has been widely used to treat both supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias (Singh and Vaughan Williams, 1970). However, its extensive use over the years has revealed plenty of adverse effects, ranging from thyroid toxicity to pulmonary toxicity and liver toxicity. These drawbacks have prompted the exploration of alternative treatments with comparable efficacy but fewer adverse reactions. Dronedarone, a structurally similar compound designed to address the limitations of amiodarone by targeting similar cardiac ion channels, aims to provide effective rhythm control while minimizing the risk of systemic toxicities associated with its predecessor (Hohnloser et al., 2009; Torp-Pedersen et al., 2011). Nonetheless, careful monitoring of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and the acquisition of real-world data are crucial for establishing clinically valid drug reference standards, and ensuring both drugs are used optimally to maximize patient benefits and minimize risks.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) is a publicly accessible database specifically designed to assist the FDA in post-market safety monitoring of drugs and therapeutic biologic products (Wang et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). This database allows for the quantitative assessment of reports through signal detection, where a “signal” indicates a drug-related adverse event and is then analyzed to determine if it is an ADR or not. Researchers utilize a variety of particle-based analysis algorithms, such as the Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) (Rothman et al., 2004), Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR) (Evans et al., 2001), Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network (BCPNN) (Bate et al., 1998), and Empirical Bayesian Geometric Mean (EBGM) (Dumouchel, 1999), to evaluate AE risks and detect the signal strength of adverse events associated with medical products. This enables researchers to analyze a wide range of drugs and diseases, identifying potential ADRs of particular concern and thus providing guidance for clinical medication and treatment strategies (Zhao et al., 2024; Du et al., 2024a; Du et al., 2024b).
In this study, we analyzed amiodarone-related and dronedarone-related ADRs reported from Q3 2011 to Q3 2023, utilizing data mining from the FAERS database. We employed the ROR and PRR algorithms to assess the associations between the drugs and adverse events, thereby filtering out ADRs. Subsequently, we constructed a joint probability model linking the drugs to the ADRs identified through ROR and PRR, using the BCPNN algorithm. Lastly, we applied the EBGM algorithm to convert these risk associations into corresponding risk indices, identifying significant high-risk combinations of drugs and ADRs as recognized by the aforementioned algorithms. Additionally, we conducted a comparative analysis of the ADRs associated with both drugs, uncovering new ADR signals. We believe this research will enhance the rational and safe clinical use of amiodarone and dronedarone.
The FAERS is a publicly accessible database designed to facilitate post-marketing surveillance of drugs and therapeutic biologics, capturing all relevant adverse event and medication error information reported by consumers and healthcare professionals. Covering the period from Q3 2011 to Q3 2023, data pertaining to amiodarone and dronedarone ADRs was extracted and preprocessed using MySQL. This clean and standardized data was then meticulously selected and mapped to MedDRA 23.0 to eliminate duplicate case records and precisely identify the adverse events. Significant adverse events were further categorized into preferred terms (PTs) and system organ classes (SOCs) according to the structured hierarchy of MedDRA terminology (Mascolo et al., 2021). Additionally, comprehensive data on clinical characteristics such as gender, age, and reporting countries were systematically compiled for analysis. Severe outcomes, including life-threatening conditions, hospitalization, disability, and death, were also examined. The search terms for amiodarone were “amiodarone” and “amiodarone HYDROCHLORIDE”; for dronedarone, “dronedarone” and “MULTAQ”. ADRs were systematically classified and detailed according to PTs and SOCs in the International MedDRA, version 25.1. This thorough approach ensures an in-depth evaluation of the safety profiles of these medications.
Disproportionality analysis serves as a fundamental technique in pharmacovigilance to identify spontaneous adverse event signals (Zink et al., 2013). In this study, we employed both Frequentist and Bayesian methods to investigate potential correlations between amiodarone or dronedarone and their respective ADRs, using established statistical tools including the ROR, PRR, BCPNN, and EBGM. We limited our analysis to adverse event signals with a minimum of three records. These signals were required to simultaneously meet all four algorithmic criteria, notably a lower limit of the 95% confidence interval (CI) greater than 1.0. To reduce the likelihood of false positives associated with infrequent events with minimal case numbers, we applied a statistical shrinkage technique (Norén et al., 2013). At the PTs level, the number of ADRs and ADR types were then categorized by organ toxicity, and the Z-test and the Fisher exact test for proportions were used to compare the proportions of ADRs and ADR types between amiodarone and dronedarone. All data processing and statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.3.3.
Before calculating the ROR and PRR, it is essential to determine the values of a, b, c, and d. In this context, “a” represents the number of individuals who experienced the target adverse event post-drug exposure, “b” indicates the number of individuals who experienced non-target adverse events post-drug exposure, “c” refers to the number of individuals who experienced the target adverse event post non-drug exposure, and “d” represents the number of individuals who experienced non-target adverse events post non-drug exposure. Consequently, the total number of cases, denoted as “N”, is computed as N = a + b + c + d. This calculation is illustrated in Table 1. The precise formulas for the four algorithms are outlined subsequently:
(i) ROR algorithm
The criteria of positive safety signal detection: the lower limit of 95% CI > 1, N ≥ 3;
(ii) PRR algorithm
The criteria of positive safety signal detection: PRR ≥ 2, χ2 ≥ 4, N ≥ 3;
(iii) BPCNN algorithm
The criteria of positive signals: IC025 > 0 (IC025 represents the lower bound of 95% CI);
(iv) EBGM algorithm
The criteria of positive safety signal detection: EBGM05 > 2 (EBGM05: the lower bound of 95% CI).
From Q3 2011 to Q3 2023, a total of 9,972,109 reports were submitted to the FAERS database. Out of these, 9,295 reports specifically mentioned the use of amiodarone, and 2,485 reports mentioned the use of dronedarone. The clinical characteristics of events with amiodarone and dronedarone are detailed in Table 2. Among all ADRs, a higher percentage of male than female patients (54.23% vs. 34.18%) was reported with the use of amiodarone, while dronedarone showed the opposite trend and had a higher percentage of female than male (47.53% vs. 40.64%). The most significant percentage of reports of amiodarone (39.43%) and dronedarone (41.93%) both occurred in patients aged 60–79 years. The United States is the main drug reporting country for both amiodarone (44.29%) and dronedarone (73.20%), but it is more concentrated for dronedarone. As for severe outcomes, hospitalization was the most frequently reported for amiodarone and dronedarone (49.14% vs. 23.30%), and the incidence of disability was also the lowest for both (3.34% vs. 2.05%).
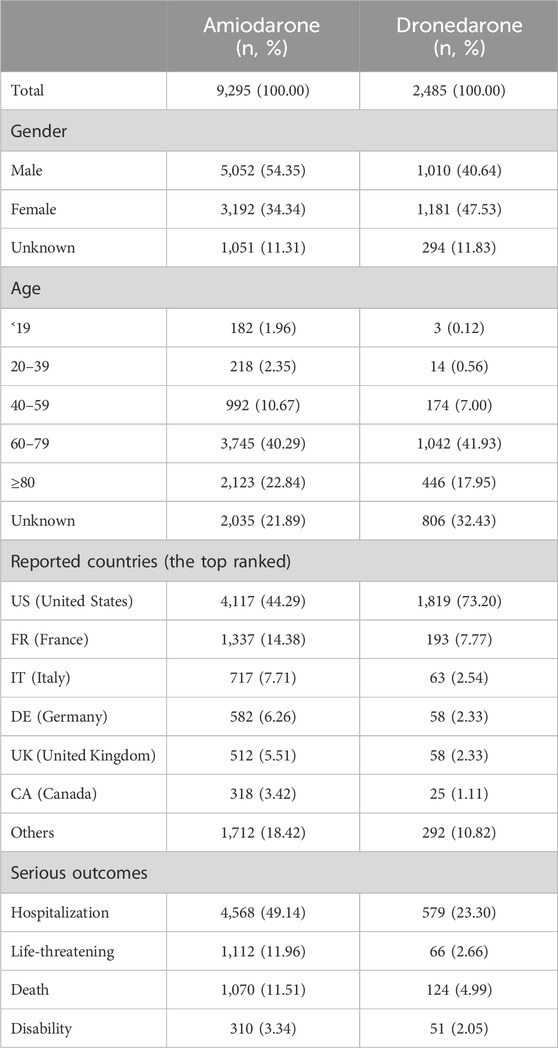
Table 2. The characteristics of reports associated with amiodarone or dronedarone from the FAERS database (2011 Q3 to 2023 Q3).
The signal strengths of reports of amiodarone and dronedarone at the SOC level are outlined in Tables 3, 4 separately. Analyzing the data, amiodarone-associated ADRs affected 27 organ systems, underscoring that ADRs related to amiodarone constitute a relatively common phenomenon. While dronedarone-associated ADRs affected 15 organ systems, these also involved a wide range of aspects. Predominantly, the largest numbers of ADRs were observed in Cardiac disorders in both amiodarone and dronedarone (n = 3,880, EBGM05 = 8.04 vs. n = 825, EBGM05 = 11.3), compliant with drug pharmacology and our expectations. Other large numbers of ADRs for both were observed in Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders (n = 2,876, EBGM05 = 5.93 vs. n = 312, EBGM05 = 4.35), and Investigations (n = 1,795, EBGM05 = 8.31 vs. n = 550, EBGM05 = 7.67). Moreover, it was discovered that Surgical and medical procedures (n = 27, EBGM05 = 9.82), and Infections and infestations (n = 8, EBGM05 = 56.4) at the SOC level represent new ADRs that are not labeled in the instructions for amiodarone, and Surgical and medical procedures (n = 35, EBGM05 = 11.7) represent new ADRs for dronedarone. The 95% CI for the ROR only shows the lower limit of the 95% two-sided CI of the ROR.
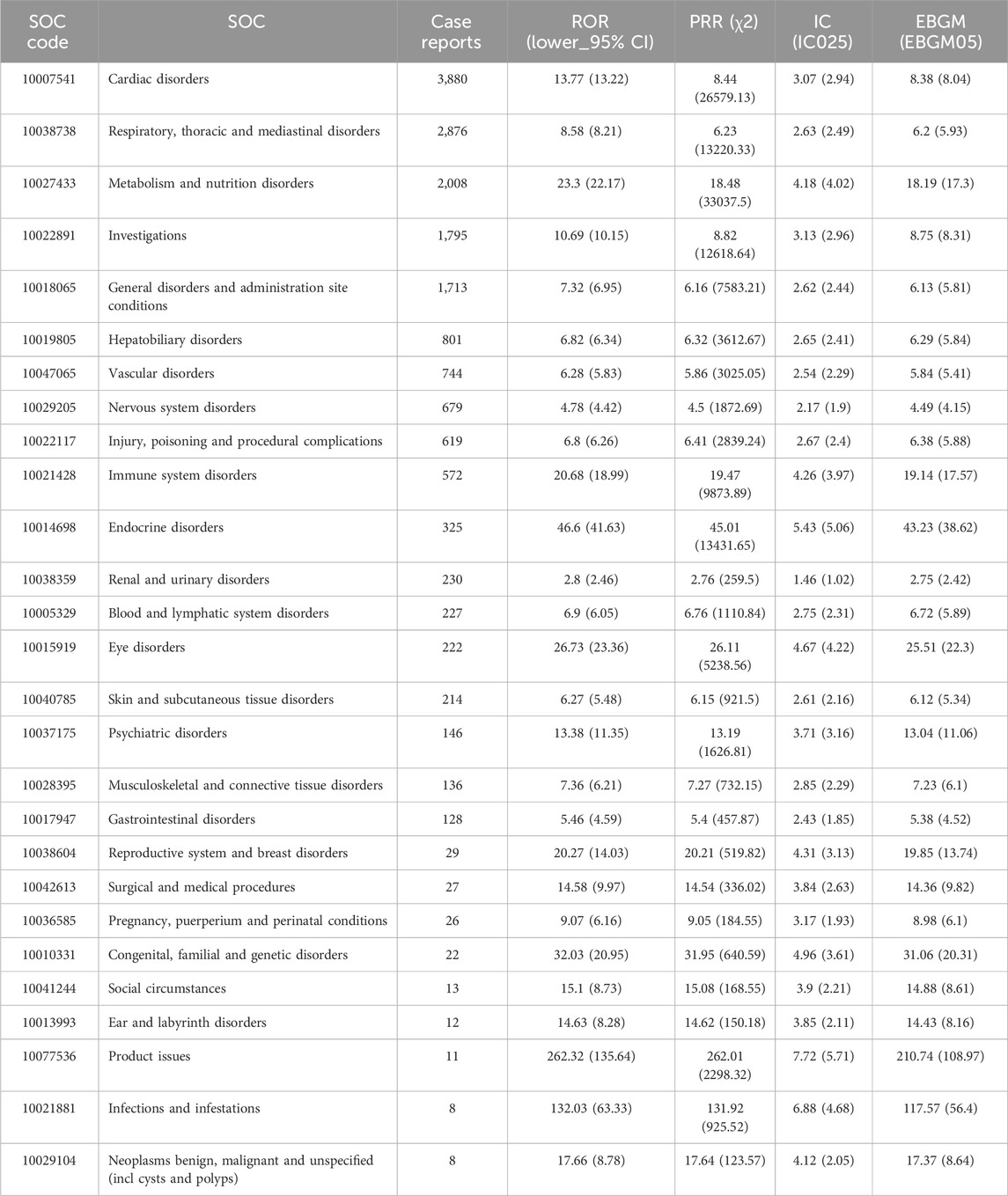
Table 3. Signal strength of AEs of amiodarone at the system organ class (SOC) level in FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) source.
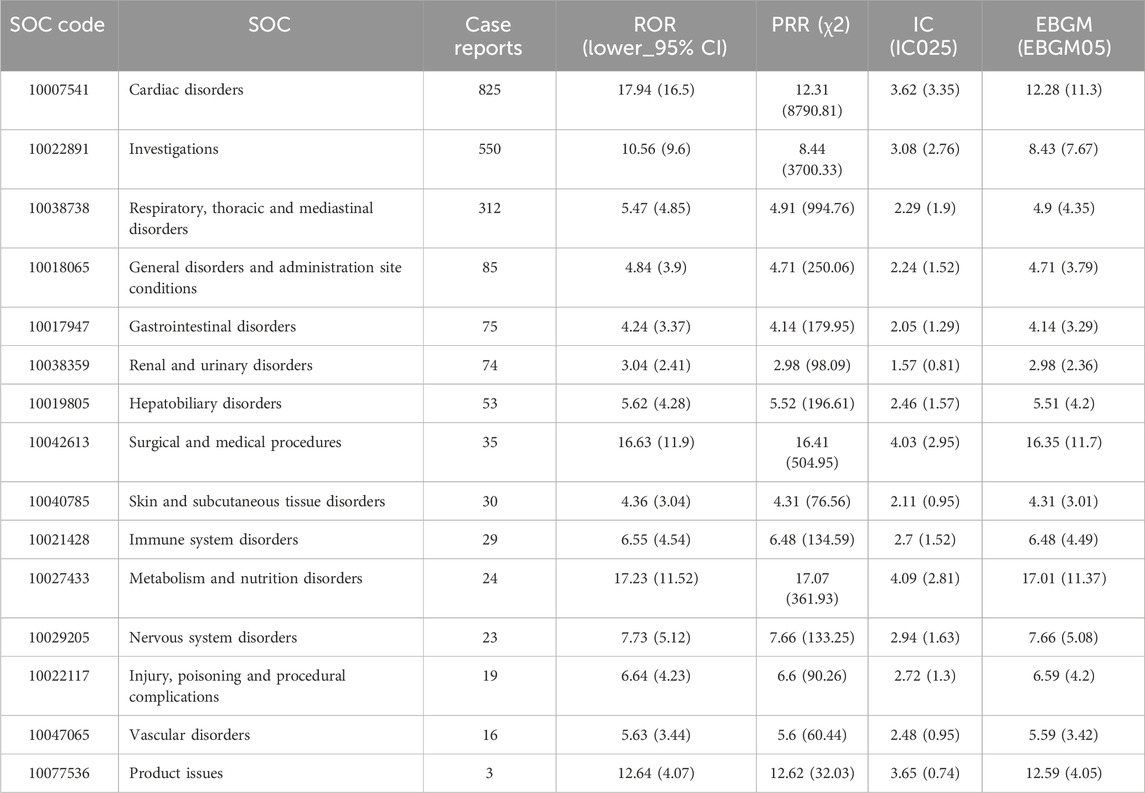
Table 4. Signal strength of AEs of dronedarone at the system organ class (SOC) level in FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) source.
The top 10 signal strengths of ADRs of amiodarone and dronedarone at the PTs level, ranked by frequency and EBGM, are detailed in Table 5, where we compared them with the adverse reactions spelled out in the drug instructions, using * to mark those not mentioned in the instructions. The top 40 signal strengths of ADRs also presented in Supplementary Table S3.
The top 3 frequent adverse safety signals for amiodarone were drug interaction (n = 856), hyperthyroidism (n = 758), and dyspnoea (n = 607); the top 3 largest EBGM05 values were myxoedema coma (EBGM05 = 457.42), electrocardiogram T wave alternans (EBGM05 = 231.27), and mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase increased (EBGM05 = 182.23). The adverse signals not mentioned in the instructions, for example, were electrocardiogram T wave alternans (n = 16, EBGM05 = 231.27), accessory cardiac pathway (n = 11, EBGM05 = 140), and thyroiditis (n = 178, EBGM05 = 125.91). The top 3 frequent adverse safety signals for dronedarone were atrial fibrillation (n = 371), dyspnoea (n = 204), and blood creatinine increased (n = 123); the top 3 largest EBGM05 values were atrial fibrillation (EBGM05 = 35.89), cardiac death (EBGM05 = 35.11), and cardiac ablation (EBGM05 = 31.86). The adverse signals not mentioned in the instructions, for example, were cardiac ablation (n = 11, EBGM05 = 31.86), cardioversion (n = 7, EBGM05 = 22.69), and dysphagia (n = 47, EBGM05 = 3.6). The whole findings are presented in Supplementary Table S1 completely, where 277 newly identified ADRs of amiodarone and 41 newly identified ADRs of dronedarone were marked using *. The analysis of the real-world study based on the FAERS database also provides great reference value for the revision of the instructions for amiodarone and dronedarone.
The main adverse effects of amiodarone are concentrated in cardiac toxicity, pulmonary toxicity, thyroid toxicity, and liver toxicity, while dronedarone was designed to address the limitations of amiodarone. Our deeper comparison assessed their main adverse reactions in Table 6, allowing us to directly compare the strength of the adverse reaction signals. The organ toxicity distributions of the number of ADRs and types of ADRs at the PTs level are shown in Figure 1, and then displayed and compared in Table 7.
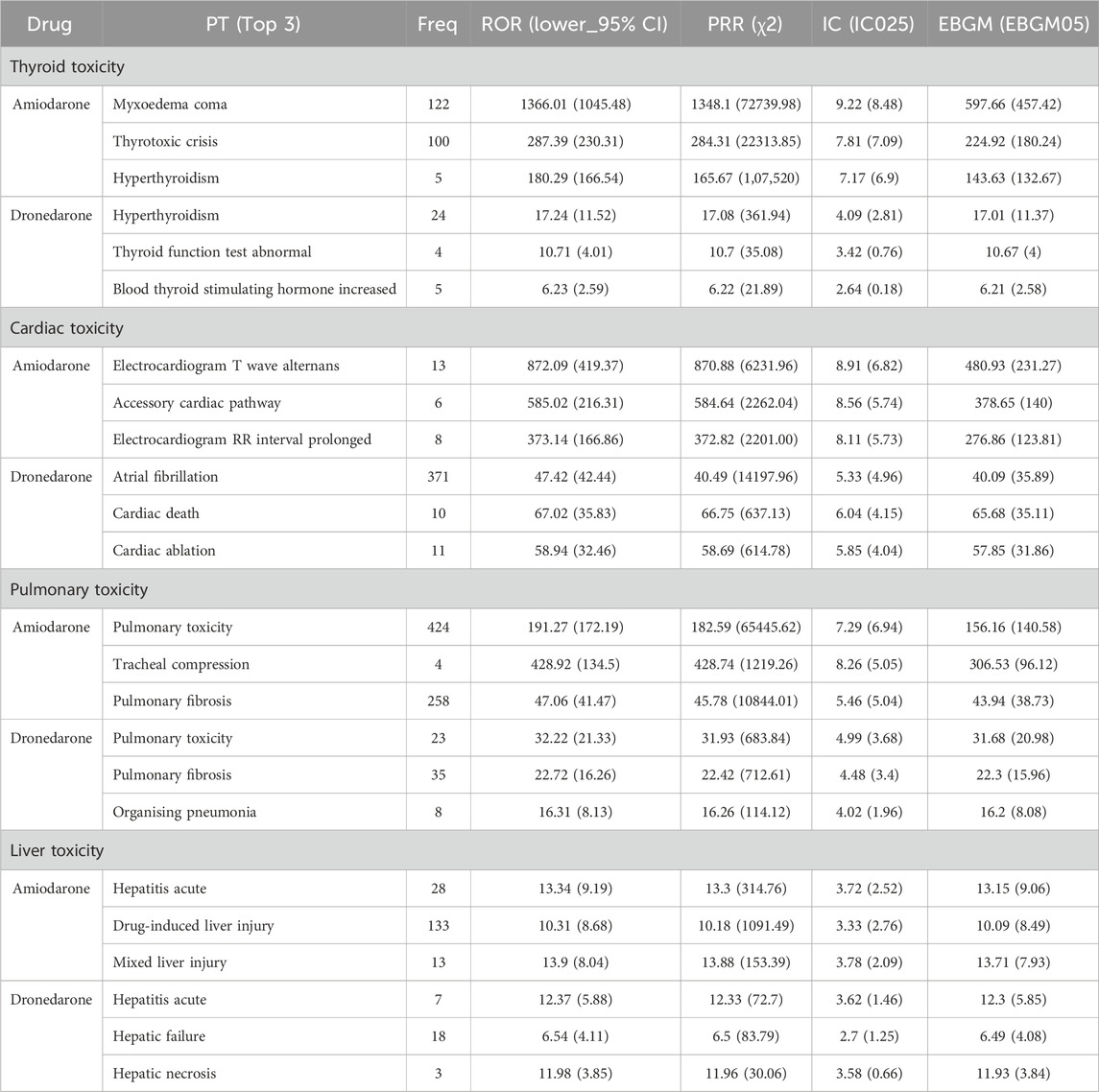
Table 6. Major signals of thyroid toxicity, cardiac toxicity, pulmonary toxicity and liver toxicity sorted by EBGM.
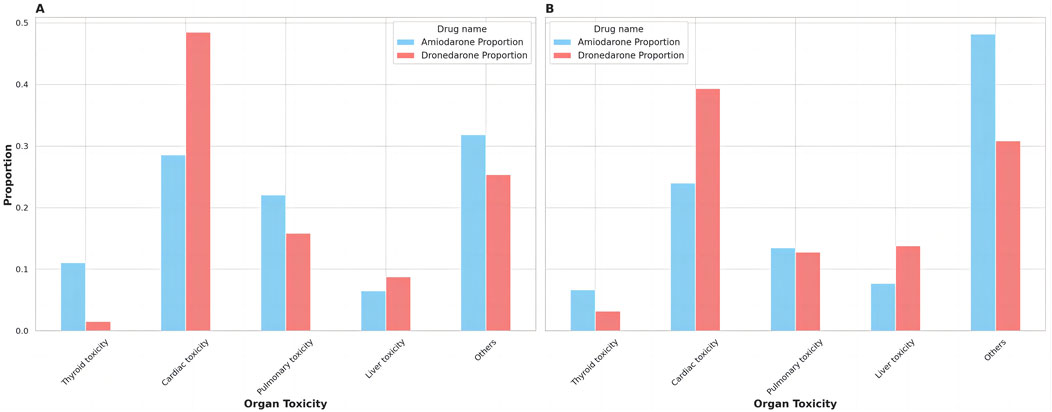
Figure 1. The distribution of organ toxicity for amiodarone and dronedarone. (A) Proportion of ADRs; (B) Proportion of ADR Types.
The top 3 ADRs of thyroid toxicity, cardiac toxicity, pulmonary toxicity, and liver toxicity sorted by EBGM for both amiodarone and dronedarone are shown in Table 6. We could still find thyroid toxicity for dronedarone use, such as hyperthyroidism (n = 24, EBGM05 = 11.37), thyroid function test abnormal (n = 4, EBGM05 = 4) and blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased (n = 4, EBGM05 = 4). The pulmonary toxicity of amiodarone and dronedarone was similar, both have pulmonary toxicity (n = 424, EBGM05 = 140.58 vs. n = 23, EBGM05 = 20.98) and pulmonary fibrosis (n = 258, EBGM05 = 38.73 vs. n = 35, EBGM05 = 15.96). Hepatitis acute (n = 28, EBGM05 = 9.06 vs. n = 7, EBGM05 = 5.85) of liver toxicity was also listed for amiodarone and dronedarone.
There were 467 kinds of ADR types for amiodarone and 94 kinds of ADR types for dronedarone, with 17,471 ADRs for amiodarone and 2,153 ADRs for dronedarone found in the study. We sorted them into different organ toxicity groups in Supplementary Table S2, presented them as Figure 1, and analyzed them in Table 7. Amiodarone had a higher proportion of ADR types compared to dronedarone in thyroid toxicity, pulmonary toxicity, and liver toxicity, but the differences were not significant. Conversely, dronedarone had a significantly higher proportion of ADR types compared to amiodarone in cardiac toxicity (39.36% vs. 23.98%, p ˂ 0.05). Moreover, significant differences in the proportion of ADRs were observed between the two drugs in all categories. Amiodarone had a significantly higher proportion of ADRs compared to dronedarone in thyroid toxicity (11.08% vs. 1.53%, p ˂ 0.001) and pulmonary toxicity (22.03% vs. 15.84%, p ˂ 0.001), while dronedarone had a significantly higher proportion of ADRs compared to amiodarone in cardiac toxicity (48.49% vs. 28.57%, p ˂ 0.001) and liver toxicity (8.78% vs. 6.47%, p ˂ 0.001). These differences highlight the varying organ-specific toxicities of the two drugs, which can inform treatment choices and toxicity management strategies.
Based on data from the FAERS database from 2011 Q3 to 2023 Q3, the study used ROR and PRR as the primary assays. Then, we used the BCPNN algorithm to construct a joint probability model between topotecan and the AEs identified by ROR and PRR. Next, we applied the EBGM algorithm to convert the risk association into corresponding risk indices and screened for significant high-risk combinations of the drugs and ADRs identified by the above three algorithms. Finally, this study provides a reference for safe and reasonable clinical use of the drugs.
The study analyzed a total of 9,295 reports of ADRs attributed to amiodarone use and 2,485 reports of ADRs attributed to dronedarone use, mainly originating from the United States (44.29% vs. 73.20%). The relatively late initial approval (July, 2009) in the United States may explain why dronedarone is mainly reported in the United States. Both drugs were more frequently reported among the elderly, aligning with the demographic typically at higher risk for atrial fibrillation (Joglar et al., 2023). It’s imperative to highlight that age-related information was absent for nearly a quarter of the patients (21.89% vs. 32.43%), potentially skewing the results. Notably, the proportion of male reports is significantly higher than that of female reports for amiodarone, which is in line with our daily medical practices, while more reports of females than males were found for dronedarone. The restriction of dronedarone use in severe patients may be the explanation (Schweizer et al., 2011). In addition, hospitalization was the most frequently reported serious outcome among both drugs (49.14% vs. 23.30%), but a high proportion of unknown outcomes for dronedarone may have a significant impact on actual outcome analysis.
In the disproportionality analysis of SOC levels, amiodarone focused on Cardiac disorders, respiratory disorders, metabolism disorders (mainly thyroid disorders), investigations and general disorders, which was in agreement with the CAST (Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial) study (Echt et al., 1991), where the common ADRs in patients were thyroid dysfunction, hepatic dysfunction, and pulmonary toxicity, rather than cardiac disorders as the most commonly found ADRs. Dronedarone also focused on cardiac disorders, investigations, and respiratory disorders, and this was not in high agreement with the clinical trials (Hohnloser et al., 2009; Køber et al., 2008; Connolly et al., 2011), where the severity and frequency of ADRs varied instead of concentrating on certain organs or systems. In the SOC level analysis, cardiac disorders were somewhat biased because the applicable disorders were also grouped into PTs level.
After obtaining the results of all PT level ADR signals for amiodarone and dronedarone, the signals were ranked according to their frequency and EBGM. The higher the frequency, the more valuable the excavation, and the higher the EBGM (EBGM05), the higher the risk combinations of the drugs and ADRs were found. After comparing the drug instructions separately, it was found that both showed new ADR signals that were not mentioned in the instructions.
There were 277 ADRs of amiodarone and 41 ADRs of dronedarone not mentioned in the instructions. The top 3 ADR signals not mentioned in the amiodarone label were electrocardiogram T wave alternans (n = 16, EBGM05 = 231.27), accessory cardiac pathway (n = 11, EBGM05 = 140), and thyroiditis (n = 178, EBGM05 = 125.91). Electrocardiogram T wave alternans and accessory cardiac pathways were both additions to the diversity of results in cardiac medical examinations. Thyroiditis is a kind of thyroid toxicity of amiodarone that has been widely reported for years but not officially included in the drug instructions (Ylli et al., 2021). SIADH was identified in association with amiodarone (n = 19, EBGM05 = 3.2), although the signal strength was low, SIADH may be related to amiodarone’s effects on hypothalamic ADH release, possibly due to neurotoxicity or direct renal impact (Hannon and Thompson, 2010). The top 3 ADR signals not mentioned in the dronedarone instructions were cardiac ablation (n = 11, EBGM05 = 31.86), cardioversion (n = 7, EBGM05 = 22.69), and saliva altered (n = 3, EBGM05 = 12.69). The cardiac ablation and the cardioversion both suggested that the use of dronedarone had proarrhythmic side effects that may need medical intervention or surgical procedures (Rizkallah et al., 2016). While saliva altered was not directly highlighted as a common issue with dronedarone, any changes in taste or mouth discomfort could potentially impact saliva production and consistency since some patients report changes in taste, such as a metallic taste or loss of taste, which can indirectly affect saliva production. T-wave alternans could be found in both amiodarone and dronedarone, it may caused by electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia, which disrupt the cardiac action potential and increase the susceptibility to arrhythmias. Additionally, its proarrhythmic effects can exacerbate the heterogeneity of repolarization across the myocardium, contributing to the occurrence of T-wave alternans (Narayan, 2006; Roden, 2008).
A deeper analysis included a summary of all organ toxicity signals for both amiodarone and dronedarone through statistical analysis of the ADR profiles, including the severity of ADRs, the number of ADRs, and the ADR type. According to Figure 1, it can be seen that cardiac toxicity accounted for the largest parts of both, which makes sense as all antiarrhythmic drugs tend to have proarrhythmic side effects at the same time. It should be noted that dronedarone had a higher risk of severe cardiac toxicity events (cardiac death, EBGM05 = 35.11) compared with amiodarone (cardiac arrest, EBGM05 = 6.32), which explains why it is restricted to people who have risk factors for cardiovascular events (Joglar et al., 2023). Moreover, dronedarone showed higher proportions of cardiac toxicity in both ADRs (48.49% vs. 28.57%, p ˂ 0.001) and ADR types (39.36% vs. 23.98%, p ˂ 0.05). Meanwhile, dronedarone reduced the types, numbers, and severity of thyroid toxicity. Unlike amiodarone, which has various types and numbers of thyroid toxic ADRs and even severe ADRs such as myxoedema coma and thyrotoxic crisis, this is consistent with previous research (Hohnloser et al., 2009). Moreover, the liver toxicity of ADRs distribution is higher for dronedarone compared to amiodarone (8.78% vs. 6.47%, p ˂ 0.001), as evidenced by two reported cases of severe liver injury requiring organ transplantation, which prompted the European Medicines Agency to perform a comprehensive review of all available data on potential liver toxicity caused by dronedarone (European Medicines Agency, 1998). Post-marketing data, however, found an association between the use of Class III antiarrhythmics and the onset of acute liver injury, mainly driven by amiodarone (Grimaldi-Bensouda et al., 2018). Pulmonary toxicity of ADRs distribution, however, is higher for amiodarone compared to dronedarone (22.03% vs. 15.84%, p ˂ 0.001), though more and more dronedarone pulmonary toxicity events are being reported (Hernández Voth et al., 2012; Stack et al., 2015; Chen et al., 2024).
Several limitations of this real-world observational study with large-sample data must be acknowledged. Firstly, the voluntary nature of reporting to the FAERS database makes it vulnerable to underreporting, potentially leading to incomplete data. This might result in less severe or common adverse events being underrepresented, while more serious or rare events could be disproportionately reported, introducing a risk of data omission or information bias (Yang et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2023; Du et al., 2024c). This selective reporting can lead to an overrepresentation of severe adverse events and an underrepresentation of less severe ones. Secondly, explicit causality isn’t mandatorily required for data submission, meaning the reports can highlight safety signal strengths without necessarily indicating actual risk levels. Thirdly, the absence of comprehensive data on the total number of patients treated with amiodarone or dronedarone precludes accurate calculation of ADRs’ true incidence from FAERS data. In signal detection, a strong signal might result from high reporting rates rather than a high true incidence, potentially leading to misinterpretation of the drug’s safety profile. Additionally, the clinical interpretation of the ADR signals, particularly for cardiac ablation and cardioversion, may be confounded by the drug’s lower efficacy, which necessitates more aggressive treatments rather than reflecting direct toxicities. This highlights the importance of cautious clinical interpretation and the need for future research to further explore the relationship between drug efficacy and ADR reporting. Finally, our analysis predominantly focused on exploring the correlation between amiodarone or dronedarone and ADRs, designating the drug’s role as a “preferred suspect.” This approach implies a focus on the direct correlation between the drug and ADRs without delving into the potential effects of multi-factorial confounding factors, such as secondary suspect drugs, concomitant medications, and multi-drug interactions.
The study applied pharmacovigilance analysis methods to the FAERS database to detect safety signals of ADRs linked to amiodarone and dronedarone treatment and provided some complementary ADR signals that were not mentioned in the instructions. Through further analysis of organ toxicity, it was found that dronedarone had a higher proportion of ADR types and ADRs for cardiac toxicity but a lower proportion of ADR types and ADRs for thyroid toxicity compared to amiodarone. Given these findings, clinicians should implement tailored monitoring strategies, focusing on thyroid and pulmonary health for amiodarone users and cardiac toxicity for those on dronedarone. Long-term follow-up and regular assessments are crucial to detect delayed adverse events. Additionally, informed discussions with patients about the specific risks of each drug are essential for shared decision-making. It’s imperative to closely monitor for new and unforeseen ADRs upon administering the medication, as certain life-threatening adverse events necessitate prompt detection and intervention. Overall, this study provides a reference for the reasonable and safe clinical use of amiodarone and dronedarone.
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://fis.fda.gov/extensions/FPD-QDE-FAERS/FPD-QDE-FAERS.html.
YX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. BZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Software, Writing–review and editing. LH: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1438292/full#supplementary-material
Bate, A., Lindquist, M., Edwards, I. R., Olsson, S., Orre, R., Lansner, A., et al. (1998). A Bayesian neural network method for adverse drug reaction signal generation. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 54 (4), 315–321. doi:10.1007/s002280050466
Chen, Y., Fu, Z., Wen, X., Zhang, M., Min, Q., Wang, P., et al. (2024). Analysis of a serious adverse reaction of pulmonary fibrosis caused by dronedarone. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 100, 100743. doi:10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100743
Connolly, S. J., Camm, A. J., Halperin, J. L., Joyner, C., Alings, M., Amerena, J., et al. (2011). Dronedarone in high-risk permanent atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 365 (24), 2268–2276. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1109867
Du, Y., Guo, Z., Xu, B., Yang, Y., Hu, M., Hu, Y., et al. (2024a). A real-world disproportionality analysis of the FDA adverse event reporting system events for ibuprofen. Expert Opin. Drug Saf., 1–11. doi:10.1080/14740338.2024.2348556
Du, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, Z., Hu, M., Xie, D., Wang, X., et al. (2024b). A real-world disproportionality analysis of semaglutide: post-marketing pharmacovigilance data. J. Diabetes Investig. 15, 1422–1433. doi:10.1111/jdi.14229
Du, Y., Zhu, J., Guo, Z., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Hu, M., et al. (2024c). Metformin adverse event profile: a pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) from 2004 to 2022. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 17 (2), 189–201. doi:10.1080/17512433.2024.2306223
Dumouchel, W. (1999). Bayesian data mining in large frequency Tables, with an application to the FDA spontaneous reporting system. Am. Statistician 53 (3), 177–190. doi:10.1080/00031305.1999.10474456
Echt, D. S., Liebson, P. R., Mitchell, L. B., Peters, R. W., Obias-Manno, D., Barker, A. H., et al. (1991). Mortality and morbidity in patients receiving encainide, flecainide, or placebo. The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 324 (12), 781–788. doi:10.1056/NEJM199103213241201
European Medicines Agency (1998). Assessment report for MULTAQ. London, United Kingdom: European Medicines Agency. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/variation-report/multaq-h-c-1043-a20-05-epar-assessment-report-variation_en.pdf.
Evans, S. J., Waller, P. C., and Davis, S. (2001). Use of proportional reporting ratios (PRRs) for signal generation from spontaneous adverse drug reaction reports. Pharmacoepidemiol. drug Saf. 10 (6), 483–486. doi:10.1002/pds.677
Grimaldi-Bensouda, L., Wedemeyer, H., Wiegand, J., Lohse, A. W., Benichou, J., Rossignol, M., et al. (2018). Dronedarone, amiodarone and other antiarrhythmic drugs, and acute liver injuries: a case-referent study. Int. J. Cardiol. 266, 100–105. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.04.007
Hannon, M. J., and Thompson, C. J. (2010). The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone: prevalence, causes and consequences. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 162 (Suppl. 1), S5–S12. doi:10.1530/EJE-09-1063
Hernández Voth, A. R., Catalán, J. S., Benavides Mañas, P. D., Avila Martínez, R. J., Peñalver Paolini, C. L., and Díaz de Atauri Rodríguez, M. J. (2012). A 73-year-old man with interstitial lung disease due to dronedarone. Am. J. Respir. Crit. care Med. 186 (2), 201–202. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.186.2.201
Hohnloser, S. H., Crijns, H. J., van Eickels, M., Gaudin, C., Page, R. L., Torp-Pedersen, C., et al. (2009). Effect of dronedarone on cardiovascular events in atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 360 (7), 668–678. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0803778
Joglar, J. A., Chung, M. K., Armbruster, A. L., Benjamin, E. J., Chyou, J. Y., Cronin, E. M., et al. (2023). 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 149, e1–e156. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001193
Køber, L., Torp-Pedersen, C., McMurray, J. J., Gøtzsche, O., Lévy, S., Crijns, H., et al. (2008). Increased mortality after dronedarone therapy for severe heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 358 (25), 2678–2687. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0800456
Mascolo, A., Scavone, C., Ferrajolo, C., Rafaniello, C., Danesi, R., Del Re, M., et al. (2021). Immune checkpoint inhibitors and cardiotoxicity: an analysis of spontaneous reports in eudravigilance. Drug Saf. 44 (9), 957–971. doi:10.1007/s40264-021-01086-8
Narayan, S. M. (2006). T-wave alternans and the susceptibility to ventricular arrhythmias. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 47 (2), 269–281. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.066
Norén, G. N., Hopstadius, J., and Bate, A. (2013). Shrinkage observed-to-expected ratios for robust and transparent large-scale pattern discovery. Stat. methods Med. Res. 22 (1), 57–69. doi:10.1177/0962280211403604
Rizkallah, J., Kuriachan, V., and Brent Mitchell, L. (2016). The use of dronedarone for recurrent ventricular tachycardia: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Res. notes 9, 370. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-2116-1
Roden, D. M. (2008). Cellular basis of drug-induced torsades de pointes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 154 (7), 1502–1507. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.238
Rothman, K. J., Lanes, S., and Sacks, S. T. (2004). The reporting odds ratio and its advantages over the proportional reporting ratio. Pharmacoepidemiol. drug Saf. 13 (8), 519–523. doi:10.1002/pds.1001
Schweizer, P. A., Becker, R., Katus, H. A., and Thomas, D. (2011). Dronedarone: current evidence for its safety and efficacy in the management of atrial fibrillation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 5, 27–39. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S10315
Singh, B. N., and Vaughan Williams, E. M. (1970). The effect of amiodarone, a new anti-anginal drug, on cardiac muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 39 (4), 657–667. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09891.x
Stack, S., Nguyen, D. V., Casto, A., and Ahuja, N. (2015). Diffuse alveolar damage in a patient receiving dronedarone. Chest 147 (4), e131–e133. doi:10.1378/chest.14-1849
Torp-Pedersen, C., Crijns, H. J., Gaudin, C., Page, R. L., Connolly, S. J., Hohnloser, S. H., et al. (2011). Impact of dronedarone on hospitalization burden in patients with atrial fibrillation: results from the ATHENA study. Eur. Soc. Cardiol. 13 (8), 1118–1126. doi:10.1093/europace/eur102
Wang, Y., Zhao, B., Yang, H., and Wan, Z. (2024). A real-world pharmacovigilance study of FDA adverse event reporting system events for sildenafil. Andrology 12 (4), 785–792. doi:10.1111/andr.13533
Yang, H., Wan, Z., Chen, M., Zhang, X., Cui, W., and Zhao, B. (2023). A real-world data analysis of topotecan in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 19 (4), 217–223. doi:10.1080/17425255.2023.2219390
Ylli, D., Wartofsky, L., and Burman, K. D. (2021). Evaluation and treatment of amiodarone-induced thyroid disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. metabolism 106 (1), 226–236. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa686
Zhang, W., Chen, M., Cai, X., Zhang, M., Hu, M., Hu, Y., et al. (2024). Detection and analysis of signals of adverse events of memantine based on the US food and drug administration adverse event reporting system. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 23 (5), 617–625. doi:10.1080/14740338.2024.2338251
Zhao, B., Fu, Y., Cui, S., Chen, X., Liu, S., and Luo, L. (2024). A real-world disproportionality analysis of Everolimus: data mining of the public version of FDA adverse event reporting system. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1333662. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1333662
Zhao, B., Zhang, X., Chen, M., and Wang, Y. (2023). A real-world data analysis of acetylsalicylic acid in FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 19 (6), 381–387. doi:10.1080/17425255.2023.2235267
Keywords: amiodarone, dronedarone, data mining, FAERS, pharmacovigilance, adverse drug reaction
Citation: Xu Y, Zhao B and He L (2024) Adverse drug reaction signals mining comparison of amiodarone and dronedarone: a pharmacovigilance study based on FAERS. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1438292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438292
Received: 25 May 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 22 October 2024.
Edited by:
Christos Kontogiorgis, Democritus University of Thrace, GreeceReviewed by:
Kristen Campbell, Duke University Hospital, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Xu, Zhao and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ye Xu, eHkxNTUwMTExMzA5OUAxMjYuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.