
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 02 December 2024
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1425053
Background: Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection (SML) is a type of traditional Chinese medicine injection, which has been considered a promising adjunctive therapy treatment for acute cerebral infarction (ACI). Although there have been positive reports on the treatment of SML, there is still controversy over its exact efficacy and safety in ACI patients. In this study, a systematic review was conducted on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of SML for the treatment of ACI to evaluate its clinical efficacy and safety.
Method: From the establishment of the database until May 2023, all randomized controlled trials related to SML and ACI were collected from the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, Medline, PubMed, CSJD, Wanfang database, CBM and CNKI. This systematic review and meta-analysis were strictly conducted in accordance with the PRISMA statement. The reported outcomes including overall response (ORR), National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), hemorrheology indexes, activity of daily living (ADL) and adverse events were in detail investigated.
Results: An analysis was conducted on the relevant data of 3869 ACI patients from 38 trials. The results indicated that the combination of conventional treatment and SML can significantly improve the ORR of patients (RR = 1.23, 95% CI = 1.20–1.27, P < 0.00001), neurological status (NIHSS, MD = −4.35, 95% CI = −5.15–3.54, P < 0.00001) and ADL (Barthel Index score, MD = 10.27, 95% CI = 7.75–12.79, P < 0.00001) compared with regular treatment alone. After the combined therapy, the hemorheology of ACI patients also significantly improved (P < 0.05). There is no significant difference in the frequency of adverse events between the two groups (RR = 1.49, 95% CI = 0.91–2.46, P = 0.11).
Conclusion: The evidence from the meta-analysis suggested that the combination of conventional therapy and SML is safer and more effective than conventional therapy alone in treating ACI. However, due to the limitations of this analysis, such as regional bias and publication bias, the above conclusions need to be further verified by prospective, high-quality and multicenter clinical trials.
Acute cerebral infarction (ACI) is a common cardiovascular disease caused by partial or extensive cerebral vascular stenosis or occlusion, which can lead to an impaired blood flow to the brain, followed by neurological damage and cerebral ischemia, even death (Liu Y. et al., 2019; Powers et al., 2019; Ma et al., 2017). There are more than 50 million people suffering from cerebral infarction worldwide, and nearly half of stroke survivors leave sequelae (Xue et al., 2019). The annual growth rate of the incidence rate of stroke is 8.7% in China, which is the main cause of death of Chinese people and exceeds the world average (Zhou et al., 2020; Wang W. et al., 2017). The proportion of ACI in stroke cases is 69.6%–70.8%, with a prevalence rate of 2.19%, and an annual death toll of ACI is about 1.96 per million (Li et al., 2020; Wang D. et al., 2017). In addition to seriously affecting the quality of life of patients, it also brings great psychological and economic burden to patients and their families (Zhou et al., 2020; Zeng et al., 2005). In the ultra-early stage of cerebral infarction, thrombolytic therapy is one of the most important method for restoring blood flow, which can improve blood circulation in and around the infarct area to avoid or reduce secondary nerve damage (Powers et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2020). However, a strict time window determines the success or failure of thrombolytic therapy, and it is estimated that only less than 3% of patients have benefited from the treatment (Li et al., 2020; Lyu et al., 2019; Liu H. et al., 2019; Asadi et al., 2015). Reasonable application of antiplatelet drugs and nutritional therapy regimens can contribute to improve symptoms, but may increase the possibility of intracranial hemorrhage (Powers et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020). Therefore, finding an safe and effective adjuvant drug therapy for ACI is urgently needed in clinical practice.
Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection (SML) is a phytochemical agent that synthesized by tanshinol, which is extracted from Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhiae), and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride, which is extracted from Chuanqiong (Rhizoma Chuanqiong) (Ye et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2016). Researches have proved that tanshinol can increase coronary blood flow, improve coronary microcirculation and hemorheology indexes, and reduce the degree of cerebral ischemia (Zhang et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2021; Meim et al., 2019). As the main active ingredient of Chuanqiong, Ligustrazine can inhibit platelet aggregation and fibrosis, promotes vasodilation and eliminates blood stasis (Zhang et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2019; Gao et al., 2015). SML has the pharmacological characteristics of both, and has been used as a supplementary drug in treating ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in numerous hospitals of China (Ye et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2021; Huang W. et al., 2016). The network Meta-analysis by Peng et al. showed combination therapy of SML and conventional treatment can improve the comprehensive efficacy in treating ACI, reduce National Institutes of Health stroke scale (NIHSS) scores and Fibrinogen (FIB) level in the blood, and improve Barthel index levels (Peng et al., 2023). Compared to other traditional Chinese medicine preparations, the combination of SML and western medicine had the best effect on reducing platelet aggregation rate in the blood (Peng et al., 2023). Previous studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of SML in treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, most of the previous studies only evaluated a small number of indicators, and could not comprehensively evaluate the clinical efficacy of SML in treating ACI.
The present study conducted a systematic meta-analysis to fully evaluate the safety and efficacy of the combination of conventional therapy and SML for the treatment of ACI, compared to regular treatment alone, in order to provide scientific references for the design and implementation of future clinical trials (Figure 1. Work flow of the present study).

Figure 1. Work flow of the present study. SMLI, Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection; ACI, Aute cerebral infarction; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; BI, Barthel Index.
This meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Moher et al., 2009). As this project does not require recruiting patients or collecting personal information, further ethical approval is not required. The data were independently extracted from relevant literatures by two researchers, which are completely anonymous with no personal information being collected. All the information collected will be kept confidential and not disclosed to the public. It is necessary for researchers to ensure the privacy of patients while maintaining the accuracy and completeness of the collected data during the data extraction process.
Relevant Literatures were searched in nine electronic databases, including Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, Medline, PubMed, Wanfang database, Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP), Chinese Biological Medicine Database (CBM) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). Chinese and English publications from the establishment of the database until May 2023 were shortlisted using the following search terms: “Danshen Chuanqiongqin” or “Danshen Chuanqiongqin injection” or “Salviae Miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine” or “Radix Salivae Miltiorrhizae Ligustrazine injection” or “Salvia Miltiorrhiza Ligustrazine injection” or “Salviae Miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride injection” combined with “cerebral infarction” or “acute cerebral infarction” or “brain infarction” or “infarction of the brain” or “ischemic stroke” or “ACI”. No other restrictive search criteria were applied (Supplementary Table S1).
• Inclusion criteria
(I) Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving ACI patients were included.
(II) The study subjects (ACI patients) must meet the diagnostic criteria of the World Health Organization for ACI and rule out cerebral hemorrhage through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT).
(III) Articles involving more than 40 ACI patients.
(IV) Literatures comparing the clinical outcomes of conventional treatment with SML adjuvant therapy (experimental group) and conventional single therapy (control group).
(V) Overall response rate (ORR) and NIHSS must be included in every study.
• Exclusion criteria
(I) Unrelated SML studies were excluded.
(II) Inappropriate criteria were excluded in control or experimental group.
(III) Articles with insufficient available data were excluded.
(IV) Non randomized controlled trials, literature reviews, meta-analysis, conference abstracts, repeated studies, case reports, and experimental model researches were excluded.
To ensure the quality of the meta-analysis, the quality of the included randomized controlled trials was assessed using the Cochrane Handbook tool (Zeng et al., 2015). The assessment tool includes the following seven items: (I) random sequence generation, (II) allocation concealment, (III) blinding of participants and personnel, (IV) blinding of outcome assessment, (V) incomplete outcome data, (VI) selective reporting and (VII) other bias. Each item is divided into three levels: low risk, unclear and high risk.
• Main outcomes
(I) ORR
(II) NIHSS
(III) BI score.
• Secondary outcomes
(I) Hemorrheology indexes: Whole blood viscosity (WBV), Plasma viscosity (PV), Whole blood low-shear viscosity (WBLSV), Whole blood high-shear viscosity (WBHSV), FIB, Platelet aggregation rate (PAR) and Hematocrit (HCT).
(II) The level of C-reactive protein (CRP).
(III) Treatment-related adverse events (TRAE).
The data were independently extracted by two researchers (ZYM and HZ) using the inclusion and exclusion criteria mentioned above; The disagreements will be adjudicated by the third reviewer (FZ).
The data were taken from eligible studies:
• Research characteristics, such as first author name, patient ages, publication time, number of cases, and study parameter types.
• Details of the intervention measures, such as intervention techniques, dosage, route of administration, manufacturer information of SML, and duration of SML treatment.
• Outcomes measures and other indicators, such as the ORR, NIHSS, BI, Hemorrheology indexes, CRP, and TRAE.
Missing or incomplete data will be obtained by contacting the authors. If the relevant data could not be obtained, these studies were excluded from the analysis.
The statistical analyses were conducted using Review Manager 5.3 (Nordic Cochran Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark) and Stata 14.0 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, United States). Dichotomous data is represented by risk ratio (RR) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CI), while continuous variables are represented by mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence intervals. P < 0.05 indicates that the difference is statistically significant. Heterogeneity between studies was evaluated using the Cochran’s Q statistic and I2 tests, and I2 > 50% or P < 0.1 indicated a high level of statistical heterogeneity (Jackson et al., 2012). When there is no heterogeneity (I2 < 50%), a fixed-effects model was used to pool the estimates. Otherwise, a random effects model was chosen.
Any publication bias survey was conducted on the parameters reported in more than 10 studies using funnel plots and Begg and Egger tests (Lin and Chu, 2018; Begg and Mazumdar, 1994; Egger et al., 1997). If there is publication bias, a trim-and-fill method was are used to reconcile the estimates of unpublished studies, and the adjusted results were compared with the original pooled RR (Duval and Tweedie, 2000). To investigate the impact of treatment duration and SML manufacturer on clinical efficacy, subgroup analysis was conducted.
After preliminary search, a total of 1,026 articles were identified. 797 papers were excluded from the study due to duplication issues. After reviewing the titles and abstracts, 229 articles were further excluded as they were not unrelated studies (n = 61) or clinical trials (n = 44) or literature review and meta-analysis (n = 5) or case report and meeting abstract (n = 16), and the remaining 103 studies have potential relevance. After a detailed evaluation of the entire text, articles were not RCTs (n = 19), studies with a sample size of less than 40 (n = 4). This study excluded publications with inappropriate standards for the experimental or control group (n = 14) and trials with insufficient data (n = 28). Finally, this analysis included 38 trials (Dai and Wu, 2018; Guo and Guan, 2018; Guo, 2015; Han, 2021; Huang SG. et al., 2016; Ji, 2022; Jiang and Xia, 2019; Lan et al., 2015; Li CL. et al., 2016; Li DQ., 2018; Li, 2021; Li L., 2018; Li and Liu, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Li TD. et al., 2016; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2017; Liu, 2018; Liu, 2014; Mamuti, 2017; Qu and Liu, 2016; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Tan, 2019; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Wu, 2018; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Xu B. et al., 2021; Xu, 2017; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Yan, 2016; Yang et al., 2010; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang and Li, 2013; Zhang, 2019; Zhang and Xiao, 2020; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) involving 3869 ACI patients (Figure 2).
After screening, all included trials were conducted in different medical centers in China. The information of the hospitals conducting the relevant research was showed in Supplementary Table S3. A total of 1,962 ACI patients received conventional treatment combined with SML adjuvant therapy, and 1,907 patients received conventional treatment alone. The detailed information on relevant studies and ACI patients is shown in Table 1. Except for one trial (Li and Liu, 2017), all included trials clearly introduced the duration of SML treatment. Twenty-seven studies (Dai and Wu, 2018; Guo and Guan, 2018; Guo, 2015; Han, 2021; Ji, 2022; Jiang and Xia, 2019; Lan et al., 2015; Li CL. et al., 2016; Li DQ., 2018; Li, 2021; Li L., 2018; Li and Liu, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Li TD. et al., 2016; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2014; Qu and Liu, 2016; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Tan, 2019; Wang and Wu, 2018; Xu B. et al., 2021; Xu, 2017; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2010; Zhang and Li, 2013; Zhang and Xiao, 2020; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) specifically describe the manufacturer of SML and the other nine studies (Huang SG. et al., 2016; Liu, 2017; Liu, 2018; Mamuti, 2017; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Yan, 2016; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang, 2019) lacked clear description of production information (Table 1). The SML quality standards used in this study have been approved by Chinese State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA), and have obtained the corresponding production approval number (H52020959 or H22026448). All relevant pharmaceutical companies followed the quality handling procedures specified in the pharmacopoeia.
The risk assessment of bias is shown in Figure 3. The selection, attrition and reporting risks of involved trials were low. There is no clear description provided by all included trials regarding performance and detection risks. Due to the lack of description of key information, Twelve trials (Huang SG. et al., 2016; Jiang and Xia, 2019; Lan et al., 2015; Li and Liu, 2017; Liu, 2017; Liu, 2018; Mamuti, 2017; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Yan, 2016; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang, 2019) were considered that the reported risks are unclear.
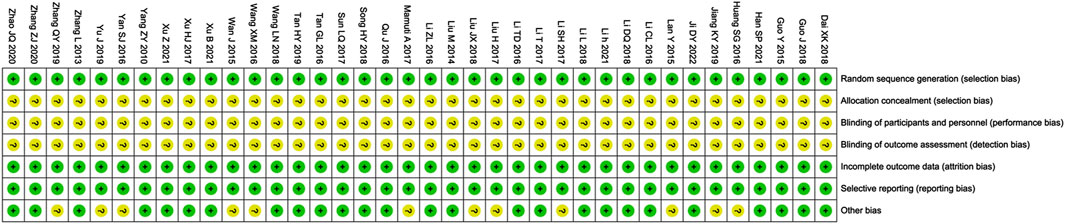
Figure 3. Risk of bias summary. Review of authors’ judgments about each risk of bias item for included studies. Note: Each color represents a different level of bias: red for high-risk, green for low-risk, and yellow for unclear-risk of bias.
Thirty-eight clinical trials (Dai and Wu, 2018; Guo and Guan, 2018; Guo, 2015; Han, 2021; Huang SG. et al., 2016; Ji, 2022; Jiang and Xia, 2019; Lan et al., 2015; Li CL. et al., 2016; Li DQ., 2018; Li, 2021; Li L., 2018; Li and Liu, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Li TD. et al., 2016; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2017; Liu, 2018; Liu, 2014; Mamuti, 2017; Qu and Liu, 2016; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Tan, 2019; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Wu, 2018; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Xu B. et al., 2021; Xu, 2017; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Yan, 2016; Yang et al., 2010; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang and Li, 2013; Zhang, 2019; Zhang and Xiao, 2020; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) involving 3,869 cases compared the ORR between the two groups (Figure 4). Our pooled results showed that compared to conventional treatments alone, patients receiving combined therapy had significantly improved ORR (RR = 1.23, 95% CI = 1.20–1.27, P < 0.00001). There was no heterogeneity, and a fixed-effect model was used for meta-analysis.
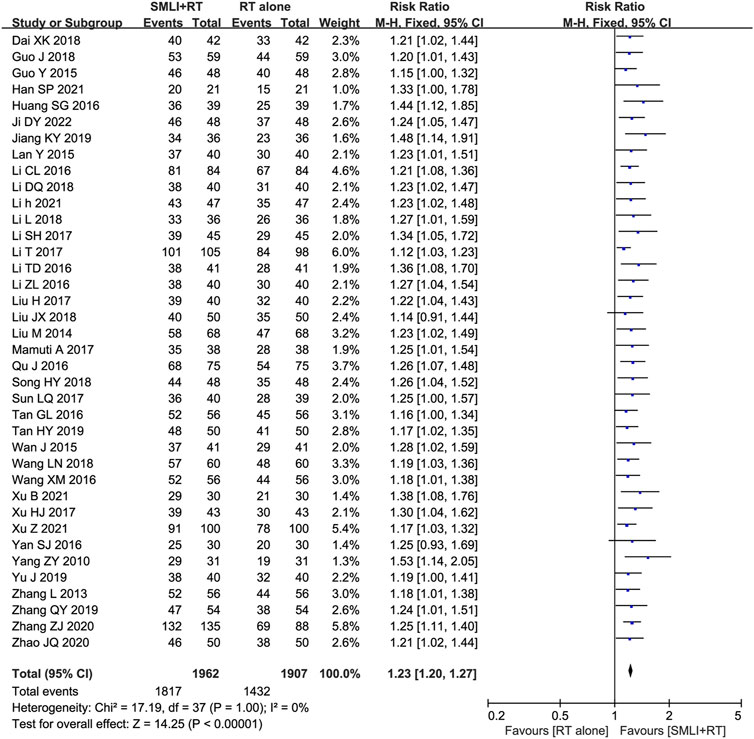
Figure 4. Forest plot of overall response rate in patients treated with RT + SMLT and RT alone. RT, Regular treatment; SMLI, Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection. The fixed effects meta-analysis model (Mantel-Haenszel method) was used.
Thirty-eight trials (Dai and Wu, 2018; Guo and Guan, 2018; Guo, 2015; Han, 2021; Huang SG. et al., 2016; Ji, 2022; Jiang and Xia, 2019; Lan et al., 2015; Li CL. et al., 2016; Li DQ., 2018; Li, 2021; Li L., 2018; Li and Liu, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Li TD. et al., 2016; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2017; Liu, 2018; Liu, 2014; Mamuti, 2017; Qu and Liu, 2016; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Tan, 2019; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Wu, 2018; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Xu B. et al., 2021; Xu, 2017; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Yan, 2016; Yang et al., 2010; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang and Li, 2013; Zhang, 2019; Zhang and Xiao, 2020; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) with 3,869 participants measured their neurological status based on NIHSS (Figure 5). The results showed that compared to conventional treatment alone, ACI patients receiving combination therapy had significantly improved neurological status (MD = −4.35, 95% CI = −5.15–3.54, P < 0.00001). There was significant heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 99%, P < 0.00001); Therefore, in order to pool data, we used a random effects model, so any conclusions need to be cautious.
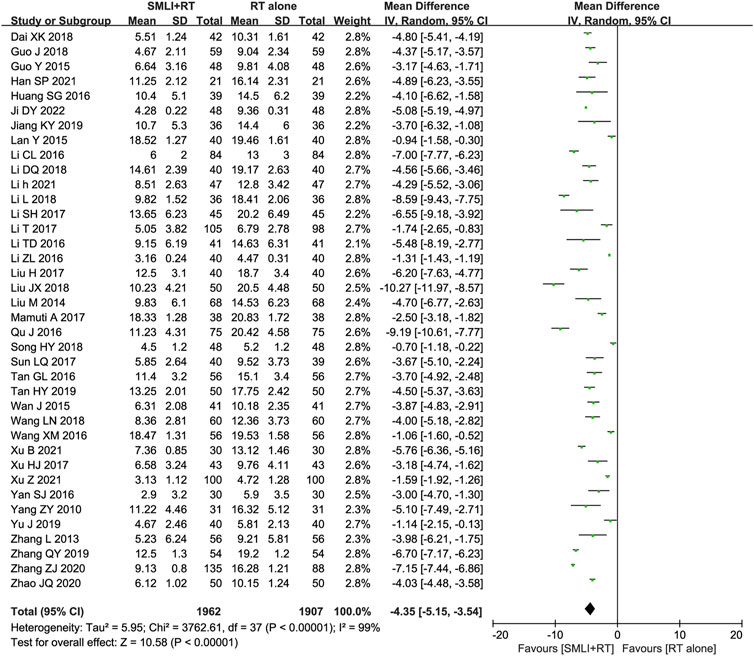
Figure 5. Forest plot of National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale in patients treated with RT + SMLT and RT alone. RT, Regular treatment; SMLI, Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection. The random effects meta-analysis model (Inverse Variance method) was used.
Eighteen-trials (Guo and Guan, 2018; Han, 2021; Ji, 2022; Lan et al., 2015; Li CL. et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017; Mamuti, 2017; Qu and Liu, 2016; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Tan, 2019; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Xu B. et al., 2021; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Yan, 2016; Yu et al., 2019; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) involving 1,918 ACI patient’s ability to perform daily living (ADL) was evaluated based on the BI score. As shown in Figure 6, the BI Score of ACI patients in the combined group were significantly higher than those in the control group (MD = 10.27, 95% CI = 7.75–12.79, P < 0.00001). A P-value <0.00001 and I2 = 96% showed that there was significant heterogeneity between studies; Therefore, a random effect model was adopted.
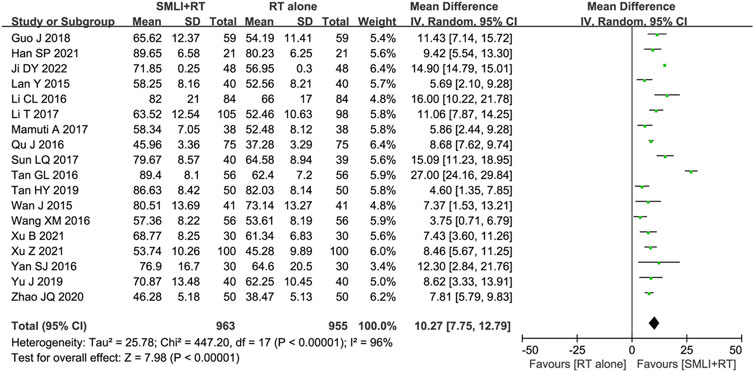
Figure 6. Forest plot of Barthel index score in patients treated with RT + SMLT and RT alone. RT, Regular treatment; SMLI, Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection. The random effects meta-analysis model (Inverse Variance method) was used.
Four studies (Ji, 2022; Li, 2021; Li and Liu, 2017; Xu B. et al., 2021) involved 340 patients and measured CRP levels (Figure 7). The pooled analysis showed that compared with the conventional treatments, the combination of SML could significantly reduce the level of CRP in ACI patients (MD = −4.53, 95% CI = −6.43–2.64, P < 0.00001). According to heterogeneity testing, CRP level exhibits statistical heterogeneity (P < 0.00001, I2 = 98%). Therefore, the random effects model was used for pooling this meta-analysis.
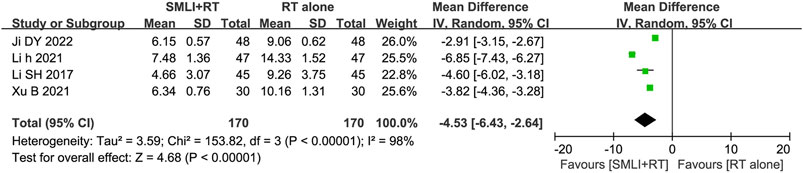
Figure 7. Forest plot of the serum C-reactive protein level in patients treated with RT + SMLT and RT alone. RT, Regular treatment; SMLI, Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection. The random effects meta-analysis model (Inverse Variance method) was used.
Measurement of hemorheology in ACI patients was carried out between SML and non-SML groups in ten controlled studies (Guo and Guan, 2018; Han, 2021; Li, 2021; Li L., 2018; Li et al., 2017; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Zhang and Xiao, 2020) (Supplementary Figures S1-S6). In this analysis, our results indicated that ACI patients receiving combination therapy have significantly improved hemorheology compared to those receiving conventional treatment alone, indicated by significantly reduced PV (MD = −0.40, 95% CI = −0.63–0.17, P = 0.0006), WBHSV (MD = −1.17, 95% CI = −1.44–0.89, P < 0.00001), WBLSV (MD = −1.47, 95% CI = −1.74–1.21, P < 0.00001), FIB (MD = −0.94, 95% CI = −1.62–0.26, P = 0.006), HCT (MD = −2.81, 95% CI = −5.50–0.11, P = 0.04) and PAR (MD = −10.46, 95% CI = −12.26–8.65, P < 0.00001). Given the high heterogeneity among studies, a random effects model was used to analyze their RR.
Thirteen trials (Guo, 2015; Huang SG. et al., 2016; Ji, 2022; Lan et al., 2015; Li, 2021; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2014; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Wang and Wu, 2018; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) involving 1,279 ACI patients evaluated the safety of SML mediated therapy. Rash, headache, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting are the most common side effects of SML treatment, and symptoms usually subside after treatment. There was no significant difference in the overall incidence of adverse events between the two groups (Figure 8, RR = 1.49, 95% CI = 0.91–2.46, p = 0.11). Due to low heterogeneity, fixed-effect models were used to analyze the RR rate.
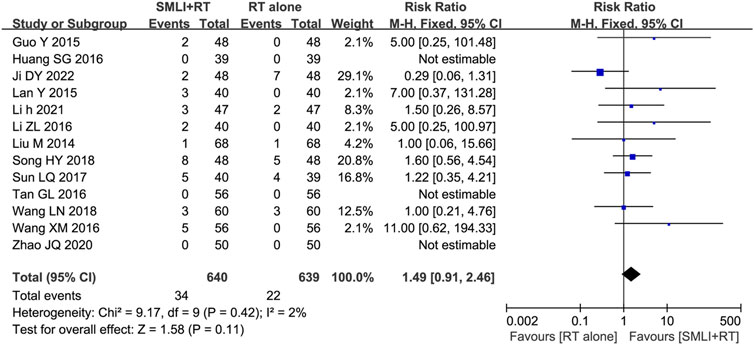
Figure 8. Forest plot of adverse effects in patients treated with RT + SMLT and RT alone. RT, Regular treatment; SMLI, Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection. The fixed effects meta-analysis model (Mantel-Haenszel method) was used.
Publication bias was assessed by Begg’s and Egger’s regression tests (Table 2), and was detected in indicators such as ORR, BI score and WBHSV. A trim-and-fill analysis was carried out to determine whether the publication bias affected the pooled risk. The adjusted RR showed the same trend as the preliminary analysis results (Table 2), reflecting the reliability of our preprimary conclusions.
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to explore the impact of individual studies on the pooled results by removing a separate study from each pooled analysis. As shown in Supplementary Table S2, the results showed that no single study significantly affected the primary outcome measurement, indicating statistically robust results.
We also conducted subgroup analysis to explore the heterogeneity source of ORR and NIHSS in terms of treatment duration and SML manufacturers. As shown in Table 3, our analysis indicated that these variables have no significant impact on the efficacy of SML in treating ACI.
There were 11 important outcomes in this meta-analysis, and the quality was low for ORR, BI, CRP and WBHSV; and moderate for other results (ADE, NIHSS, PV, WBHSV, WBLSV, FIB, HCT and PAR). Risk of bias and publication bias were the common reason for reducing the quality of evidence. Moreover, the total sample size is less than 400 cases for CRP, and their quality was downgraded by one level. No evidence was downgraded because of indirectness and inconsistency (see Table 4 in detail).
ACI is one of the common cerebrovascular diseases, and is a major cause of death and disability with an estimated 77 million people suffering from ACI by 2030 (Liu H. et al., 2019). Many scholars hold the opinion that adjuvant therapy, such as traditional Chinese medicine, will provide benefit for patients with ACI (Lyu et al., 2019; Liu H. et al., 2019; Asadi et al., 2015). SML is a traditional Chinese medicine preparation that has been clinically used as an effective adjuvant to reduce brain injury and promote functional recovery (Zhang et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2021; MEIm et al., 2019). Despite statistical analysis of published literatures, there is still limited comprehensive and systematic evaluation of SML in the treatment of ACI. In this analysis, we conducted extensive online searches based on strict inclusion and exclusion criteria, providing an internationally accessible systematic review of the clinical efficacy and safety of SML in treating ACI.
The meta-analysis was conducted on 38 articles (Dai and Wu, 2018; Guo and Guan, 2018; Guo, 2015; Han, 2021; Huang SG. et al., 2016; Ji, 2022; Jiang and Xia, 2019; Lan et al., 2015; Li CL. et al., 2016; Li DQ., 2018; Li, 2021; Li L., 2018; Li and Liu, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Li TD. et al., 2016; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2017; Liu, 2018; Liu, 2014; Mamuti, 2017; Qu and Liu, 2016; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Tan, 2016; Tan, 2019; Wan et al., 2015; Wang and Wu, 2018; Wang and Zhang, 2016; Xu B. et al., 2021; Xu, 2017; Xu Z. et al., 2021; Yan, 2016; Yang et al., 2010; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang and Li, 2013; Zhang, 2019; Zhang and Xiao, 2020; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) to evaluate the ORR. Compared with conventional treatment alone, the ORR of SML combined with conventional treatment is significantly higher. The combination therapy also significantly improved ADL and the neurological status of ACI patients. CRP is an important indicator in the prediction, prevention and prognosis of ACI (Zhou et al., 2020). Our analysis results indicated that after conventional treatment and combined treatment with SML, the CRP levels of patients significantly decreased. The patient’s hemorheological indicators also showed significant improvement. These results indicated that SML can protect ACI from damage, which may be related to its role in regulating blood viscosity. In order to further eliminate the influence of certain variables on the clinical efficacy of SML in treating ACI, this study conducted a subgroup analysis to determine the effects of different manufacturers of SML and treatment time on ORR and NIHSS. The analysis results showed that the therapeutic effect of SML seems to be unaffected by these variables. However, these analyses involve a limited number of studies and insufficient sample sizes, which may lead to inadequate evaluation. Therefore, these results need to be validated through new evidence and further research.
Safety is one of the key factors affecting the clinical application and further development of drugs. Among the included studies, ten studies (Guo, 2015; Ji, 2022; Lan et al., 2015; Li, 2021; Li ZL. et al., 2016; Liu, 2014; Song, 2018; Sun, 2017; Wang and Wu, 2018; Wang and Zhang, 2016) reported adverse events, and three studies (Huang SG. et al., 2016; Tan, 2016; Zhao and Zhou, 2020) reported no adverse reactions in the two groups. The most common side effects during SML therapy were rash, headache, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. These side effects are not serious, and will disappear after drug withdrawal or symptomatic treatment. However, the combined use of drugs results in incomplete research information and low methodological quality, and its safety needs further research and clarification.
Although we conducted a systematic analysis, our analysis has some limitations. Firstly, the data we have obtained now were not comprehensive. All included trials were conducted in China. SML, as an important herbal preparation, is mainly used in China, which may inevitably lead to regional deviations and affect the clinical application of SML in the world. This regional bias could limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Secondly, current research has detected publication bias in ORR, NIHSS, and adverse events, which may be attributed to some authors tending to publish articles with positive outcomes to editors. Additionally, there is significant heterogeneity in some analyses, particularly in the NIHSS scores (I2 = 99%). Despite subgroup analysis were conducted, the heterogeneity still exists, which could undermine the reliability of the meta-analysis results. These critical issues are all needed to be addressed in future research in order to avoid overestimating the effectiveness and safety of the treatment. Finally, different trials use different outcome measures to evaluate treatment efficacy, thereby reducing the size of statistical samples, which makes summarizing results on the same scale challenging. Given the identified issues with heterogeneity and publication bias, further prospective, high-quality and multicenter clinical trials are needed to confirm these results.
In summary, this meta-analysis indicated that SML combined with conventional therapy was effective for ACI patients. The clinical application of SML not only significantly improved the ORR of conventional treatment, but also effectively improved the blood viscosity of ACI patients. However, due to the increased risk and bias of some included low-quality trials, the clinical efficacy and safety of SML-mediated treatment for ACI still requires rigorous methodological trials to validate.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
ZM: Writing–original draft, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. HZ: Writing–original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. FZ: Writing–original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. KL: Writing–original draft, Project administration, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. ND: Writing–original draft, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. WS: Writing–review and editing, Visualization, Project administration, Methodology, Conceptualization.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1425053/full#supplementary-material
Asadi, H., Dowling, R., Yan, B., Wong, S., and Mitchell, P. (2015). Advances in endovascular treatment of acute ischaemic stroke. Intern Med. J. 45, 798–805. doi:10.1111/imj.12652
Begg, C. B., and Mazumdar, M. (1994). Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50 (4), 1088–1101. doi:10.2307/2533446
Dai, X. K., and Wu, Q. X. (2018). Clinical observation of Salvia miltiorrhiza ligustrazine injection combined with Xuesaitong Injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Guide China Med. 16 (23), 181. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2018.23.138
Deng, Z., Wang, M., Fan, Y., and Liu, M. (2021). Salviae miltiorrhizae and ligustrazine hydrochloride injection combined with mecobalamin for treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 100 (3), e24103. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000024103
Ding, Y., Du, J., Cui, F., Chen, L., and Li, K. (2019). The protective effect of ligustrazine on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 38 (10), 1168–1177. doi:10.1177/0960327119851260
Duval, S., and Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56 (2), 455–463. doi:10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., and Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315 (7109), 629–634. doi:10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Gao, H. J., Liu, P. F., Li, P. W., Huang, Z. Y., Yu, F. B., Lei, T., et al. (2015). Ligustrazine monomer against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen. Res. 10 (5), 832–840. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.156991
Guo, J., and Guan, D. S. (2018). Effects of salvia ligustrazine injection combined with ganglioside on blood viscosity, serum SOD and NIHSS, Barthel function score in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Gerontol. 38 (8), 1804–1806. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.08.006
Guo, Y. (2015). Analysis of curative effect by salviae miltiorrhizae ligustrazine injection combined with edaravone injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl. 9 (21), 20–21. doi:10.14164/j.cnki.cn11-5581/r.2015.21.010
Han, S. P. (2021). Comparison of clinical effects of salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection and Xueshuantong in the treatment of cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 14 (35), 44–46. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2021.35.016
Huang, S. G., Liu, M., and Song, C. J. (2016b). The analysis of treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Psychol. Doct 22 (29), 127–128.
Huang, W., Yang, Y., Zeng, Z., Su, M., Gao, Q., and Zhu, B. (2016a). Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 14 (5), 4537–4544. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5822
Jackson, D., White, I. R., and Riley, R. D. (2012). Quantifying the impact of between-study heterogeneity in multivariate meta-analyses. Stat. Med. 31 (29), 3805–3820. doi:10.1002/sim.5453
Ji, D. Y. (2022). Effects of Danshen ligustrazine injection combined with Urinary kallindinogenase in treatment of patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Med. J. Chin. People’s Health 34 (15), 78–80. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2022.15.023
Jiang, K. Y., and Xia, M. (2019). Treatment of acute cerebral infarction with integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine. Orient. Medicat. Diet. 11, 35–36.
Lan, Y., Xiao, J. X., Zheng, T. Y., and Liu, Z. X. (2015). Effect of Danshin Chuanqiong injection on lysophosphatidic acid and p-selectin in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Mod. J. Integ Trad. Chin. West Med. 24 (8), 840–842. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2015.08.016
Li, C. L., Za, X. C., and Sun, Y. H. (2016a). Effect of Danshen Chuanqiongqin injection on serum VCAM-1, ICAM-1, ET-1 and NO in elderly patients with acute cerebral infraction. Mod. J. Integ Trad. Chin. West Med. 25 (19), 2088–2090. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.19.011
Li, D. Q. (2018a). Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Ligustrazine injection on SOD, Hcy, and the recovery of neurological function in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Asia-Pacific Trad. Med. 14 (6), 175–176. doi:10.11954/ytctyy.201806067
Li, H. (2021). Clinical effect of salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection combined with alteplase in the treatment of elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction. Women's Health Res. 7, 25–26.
Li, L. (2018b). Effect of Danshen Ligustrazine injection on neurological function and hemorheology in patients with acute cerebral infarction. J. Imag. Res. Med. Appl. 2 (2), 225–227. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2096-3807.2018.02.148
Li, R., Li, Y., Li, B., Sun, H., Liu, X., Ge, X., et al. (2020). Effectiveness comparisons of different Chinese herbal injection therapies for acute cerebral infarction: a protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine 99 (32), e21584. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000021584
Li, S. H., and Liu, S. J. (2017). Clinical observation of Danshen Ligustrazine injection for treatment of cerebral infarction. Health Lit. 8, 33. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-5217.2017.08.031
Li, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Xie, W. Q., Pei, X., and Fan, Y. G. (2017). Clinical observation of Salviae Miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride injection combined with atorvastatin in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Drug Clin. 32 (10), 1872–1875. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2017.10.013
Li, T. D., He, X. Y., Chen, H. X., and Jiang, M. J. (2016b). Clinical observation of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Ligustrazine injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. World Clin. Med. 10 (16), 81–86.
Li, Z. L., Yao, D. M., and Yao, G. L. (2016c). Clinical observation of Salviae Miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride injection combined with combined with low molecular weight heparin in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Drug Clin. 31 (8), 1184–1187. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2016.08.014
Lin, L., and Chu, H. (2018). Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 74 (3), 785–794. doi:10.1111/biom.12817
Liu, H. (2017). Study on the application effect of alprostadil and Salvia miltiorrhiza Ligustrazine injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. China rural. health, 75–76. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-361X.2017.z1.038
Liu, H., Yan, Y., Pang, P., Mao, J., Hu, X., Li, D., et al. (2019b). Angong Niuhuang pill as adjuvant therapy for treating acute cerebral infarction and intracerebral hemorrhage: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 237, 307–313. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.043
Liu, J. X. (2018). Clinical effect of edaravone combined with Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Diet. Health 5 (25), 76. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8439.2018.25.093
Liu, M. (2014). Efficacy and safety of edaravone alone or combined with Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Mod. J. Integ Trad. Chin. West Med. 23 (19), 2105–2107. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2014.19.022
Liu, Y., Wu, X., and Yu, Z. (2019a). Ginkgo leaf extract and dipyridamole injection as adjuvant treatment for acute cerebral infarction: protocol for systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 98 (8), e14643. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000014643
Lyu, J., Xie, Y., Wang, Z., and Wang, L. (2019). Salvianolic Acids for injection combined with conventional treatment for patients with acute cerebral infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 7914–7927. doi:10.12659/msm.917421
Ma, X., Yang, Y. X., Chen, N., Xie, Q., Wang, T., He, X., et al. (2017). Meta-analysis for clinical evaluation of Xingnaojing injection for the treatment of cerebral infarction. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 485. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00485
Mamuti, A. (2017). Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Ligustrazine injection intravenous on cerebral infarction. China Health Care Nutr. 27 (24), 213–214. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7484.2017.24.321
Meim, X. D., Cao, Y. F., Che, Y. Y., Li, J., Shang, Z. P., Zhao, W. J., et al. (2019). Danshen: a phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 17, 59–80. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(19)30010-x
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G.PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 62 (10), e1000097–e1001012. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Peng, S. X., Wei, C., Lei, J. Y., Zhang, T., and Ding, Y. B. (2023). Network Meta-analysis of Chinese medicine injections for activating blood and resolving stasis in adjuvant treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 48 (15), 4215–4230. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230425.501
Powers, W. J., Rabinstein, A. A., Ackerson, T., Adeoye, O. M., Bambakidis, N. C., Becker, K., et al. (2019). Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 50 (12), e344–e418. doi:10.1161/str.0000000000000211
Qu, J., and Liu, F. C. (2016). The clinical effect of edaravone combined with salvia ligustrazine in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Clin. Res. Pract. 1 (24), 112–113. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2096-1413.2016.24.055
Song, H. Y. (2018). Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza ligustrazine injection combined with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on NIHSS score and serum neuron specific enolase myelin basic protein level in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chin. Remed Clin. 18 (11), 2023–2025. doi:10.11655/zgywylc2018.11.073
Sun, L. Q. (2017). Clinical observation of Salviae Miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride injection combined with urinary kallidinogenase in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Drug Clin. 32 (11), 2091–2094. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2017.11.008
Tan, G. L. (2016). Clinical effect of danshen ligustrazin injection in treating acute cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 9 (6C), 16–18. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2016.18.007
Tan, H. Y. (2019). Clinical effect of edaravone combined with salvia ligustrazine on patients with acute cerebral infarction. Acta Med. Sin. 32 (5), 68–71. doi:10.19296/j.cnki.1008-2409.2019-05-018
Wan, J., Yang, X. H., and Zhu, L. L. (2015). Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Ligustrazine injection on the degree of neurological deficit and activities of daily living in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica Res. 26 (3), 659–660. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2015.03.058
Wang, D., Liu, J., Liu, M., Lu, C., Brainin, M., and Zhang, J. (2017b). Patterns of stroke between university hospitals and nonuniversity hospitals in mainland China: prospective multicenter hospital-based registry study. World Neurosurg. 98, 258–265. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2016.11.006
Wang, L. N., and Wu, X. L. (2018). Clinical observation of Salviae miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride injection combined with alteplase in treatment of acute cerebral infarction in elderly patients. Drug Clin. 33 (10), 2511–2514. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2018.10.009
Wang, W., Jiang, B., Sun, H., Ru, X., Sun, D., Wang, L., et al. (2017a). Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation 135 (8), 759–771. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.116.025250
Wang, X. M., and Zhang, M. (2016). Effect of Danshen Ligustrazine injection on lysophosphatidic acid, plasma endothelin and p-selectin in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Mod. J. Integ Trad. Chin. West Med. 25 (19), 2118–2120. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.19.023
Xu, B., Dai, W. P., and Feng, J. (2021a). Clinical study on danshen chuanxiongqin injection assisting routine western medicine for acute ischemic stroke. J. New Chin. Med. 53 (21), 96–100. doi:10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2021.21.023
Xu, H. J. (2017). Clinical observation of 43 cases of acute cerebral infarction treated with Salviae Miltiorrhizae and Ligustrazine Hydrochloride injection. Cardiov Dis. J. Integ Trad. Chin. West Med. 5 (10), 41–42. doi:10.16282/j.cnki.cn11-9336/r.2017.10.028
Xu, Z., Liu, Y., and Liang, F. (2021b). Clinical efficacy of Danshen Chuanxiongqin Injection and its effect on serum levels of LPA,Hcy and MCP-1 in patients with ischemic stroke. J. Chang. Univ. Chin. Med. 37 (1), 84–87. doi:10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2021.01.023
Xue, P., Ma, Z., and Liu, S. (2019). Efficacy and safety of Ginkgo leaf extract and dipyridamole injection for ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 1403. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01403
Yan, S. J. (2016). Clinical study of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Ligustrazine injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. J. New Chin. Med. 48 (2), 19–21. doi:10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2016.02.008
Yang, Z. Y., Zhang, H. L., and Luo, X. H. (2010). Therapeutic effect observation on combination of Salvia miltiorrhiza Ligustrazine and cerebroprotein hydrolysate for the treatment of 31 cases of acute cerebral infarction. Yunnan J. Trad. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica 31 (3), 21–22. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2349.2010.03.012
Ye, T., Li, Y., Xiong, D., Gong, S., Zhang, L., Li, B., et al. (2021). Combination of Danshen and ligustrazine has dual anti-inflammatory effect on macrophages and endothelial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 266, 113425. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113425
Yu, J., Hu, Y., Gao, J., and Pang, H. B. (2019). Effects of Salvia Miltiorrhiza Ligustrazine combined with rosuvastatin on plasma brain natriuretic peptide, miR-223 and short-term prognosis in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Eval. Anal. Drug-Use Hosp. China 19 (11), 1335–1338. doi:10.14009/j.issn.1672-2124.2019.11.016
Zeng, X., Liu, M., Yang, Y., Li, Y., and Asplund, K. (2005). Ginkgo biloba for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005 (4), CD003691. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003691.pub2
Zeng, X., Zhang, Y., Kwong, J. S., Zhang, C., Li, S., Sun, F., et al. (2015). The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: a systematic review. J. Evid. Based Med. 8 (1), 2–10. doi:10.1111/jebm.12141
Zhang, L., and Li, L. (2013). Clinical observation of Salvia miltiorrhiza ligustrazine injection combined with Xueshuantong injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Conval. Med. 22 (6), 528–529. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-619X.2013.06.032
Zhang, Q. Y. (2019). Clinical value of Danshen ligustrazine injection combined with edaravone in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. World Latest Med. Infor 19 (3), 174. doi:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2019.03.145
Zhang, X., Wu, J., Zhang, B., and Zhou, W. (2016). Danshenchuanxiongqin injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 36 (2), 144–150. doi:10.1016/s0254-6272(16)30020-6
Zhang, Z. J., and Xiao, X. L. (2020). Study on the curative effect of radix salivae miltiorrhizae and ligustrazine combined with Xueshuantong in the treatment of cerebral infarction and its influence on hemodynamics. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl. 14 (7), 15–17. doi:10.14164/j.cnki.cn11-5581/r.2020.07.006
Zhao, J. Q., and Zhou, C. J. (2020). Effect of Danshen and Ligustrazine Injection on acute ischemic stroke and its influence on nerve function defect and inflammatory factors. Hainan Med. J. 31 (11), 1369–1372. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2020.11.003
Keywords: Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection, traditional Chinese herbal medicine injection, acute cerebral infarction, regular treatments, meta-analysis
Citation: Ma Z, Zhang H, Zhao F, Li K, Dong N and Sang W (2024) Safety and effectiveness of Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection for acute cerebral infarction in Chinese population: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1425053. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1425053
Received: 29 May 2024; Accepted: 18 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited by:
Javier Echeverria, University of Santiago, ChileReviewed by:
Qinwei Fu, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Ma, Zhang, Zhao, Li, Dong and Sang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nanhai Dong, MTM1NjMwMTY4OTdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Wenwen Sang, c2FuZ3d3bGNybXl5QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.