- 1School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an, China
- 2School of Basic Medicine, College of Medicine, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 3Institute of Basic and Translational Medicine, Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an, China
Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a transcription factor responsible for cytoprotection, plays a crucial role in regulating the expression of numerous antioxidant genes, thereby reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and safeguarding cells against oxidative stress. Extensive research has demonstrated the involvement of Nrf2 in various diseases, prompting the exploration of Nrf2 activation as a potential therapeutic approach for a variety of diseases. Consequently, there has been a surge of interest in investigating the Nrf2 signaling pathway and developing compounds that can modulate its activity. Isoliquiritigenin (ISL) (PubChem CID:638278) exhibits a diverse range of pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-tumor properties. Notably, its robust antioxidant activity has garnered significant attention. Furthermore, ISL has been found to possess therapeutic effects on various diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, and cancer, through the activation of the Nrf2 pathway. This review aims to evaluate the potential of ISL in modulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway and summarize the role of ISL in diverse diseases prevention and treatment through modulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
1 Introduction
In recent decades, numerous studies established that oxidative stress contributes to a variety of human diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, neurological disorder, and diabetes (Valko et al., 2007). Oxidative stress denotes the disruption in the equilibrium between oxygen free radicals and antioxidants (Bhimaraj and Tang, 2012). As part of normal physiological processes, ROS (such as superoxide radical, hydroxyl radicals, and hydrogen peroxide) are consistently produced within cells and are counteracted by the antioxidant defense system, thereby preserving a state of dynamic equilibrium and preventing harm to the body. Oxidative stress is caused by the overproduction of ROS, which can trigger the apoptosis of cells by damaging DNA, proteins, and lipids (Valko et al., 2007). Consequently, mitigating oxidative stress has the potential to be an effective therapeutic approach for a range of diseases.
The Nrf2 signaling pathway serves as the primary cellular antioxidative system in response to oxidative stress. As a transcription factor, Nrf2 regulates the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense, thereby reducing ROS levels and safeguarding cells against oxidative damage. Due to its potent antioxidant effects, it has been reported that the Nrf2 signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases including cardiovascular diseases, brain diseases, kidney diseases, cancer et al. (Menegon et al., 2016; Tian et al., 2021; Liu Y. et al., 2022; He et al., 2024; Tang et al., 2024). Specifically, in the context of cardiovascular diseases, activation of Nrf2 has been demonstrated to confer protection against conditions such as myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and atherosclerosis (Tian et al., 2021; He et al., 2024). The study has shown that activation of Nrf2 can decrease infarct size and enhance cardiac function in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, underscoring its therapeutic promise in cardiovascular pathologies (Tian et al., 2021). Similarly, in brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, Nrf2 activation has been associated with neuroprotection (George et al., 2022). The activation of Nrf2 reduces the generation of ROS and improves mitochondrial function, thereby protecting neuronal cells from oxidative stress-induced damage (Brandes et al., 2021). In cancer, the role of Nrf2 is intricate and contingent upon the specific circumstances. While Nrf2 activation can protect normal cells from oxidative damage and reduce cancer risk, its persistent activation in cancer cells can confer resistance to chemotherapy and facilitate the proliferation of tumors. Therefore, the dual roles of Nrf2 inhibition should be taken into consideration in cancer therapy (Cleasby et al., 2014; Torrente et al., 2017; Pouremamali et al., 2022). Nrf2 also plays a crucial role in kidney diseases, where it helps to regulate genes that maintain homeostasis in the kidneys and mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation (Shelton et al., 2015; Liu Y. et al., 2022). Nrf2 has been shown to improve tubular injury and ameliorate kidney dysfunction, making it a promising target for kidney diseases management (Liu Y. et al., 2022). In summary, the Nrf2 signaling pathway is a master regulator of cellular-defense oxidative stress, with significant implications for a wide range of diseases. Moreover, there is presently a significant level of interest in the utilization of small molecular compounds to selectively target the Nrf2 signaling pathway as a means of treating a wide range of diseases (Zhu et al., 2020). Consequently, the quest for efficacious Nrf2 activators represents a promising novel therapeutic approach for the management of these ailments.
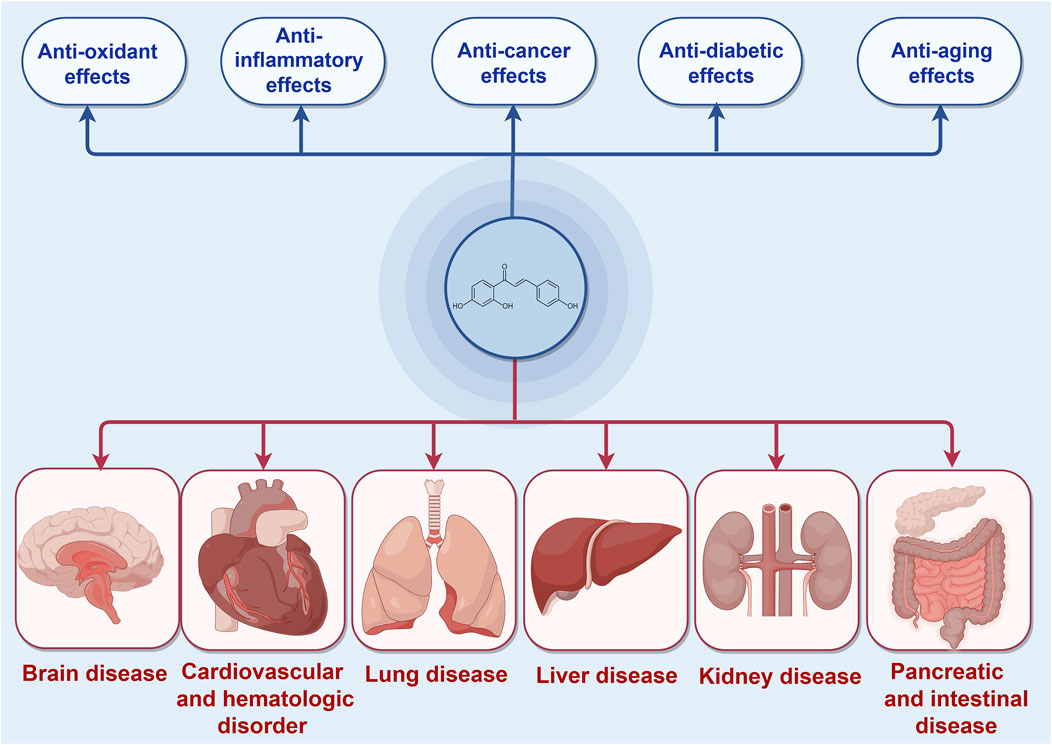
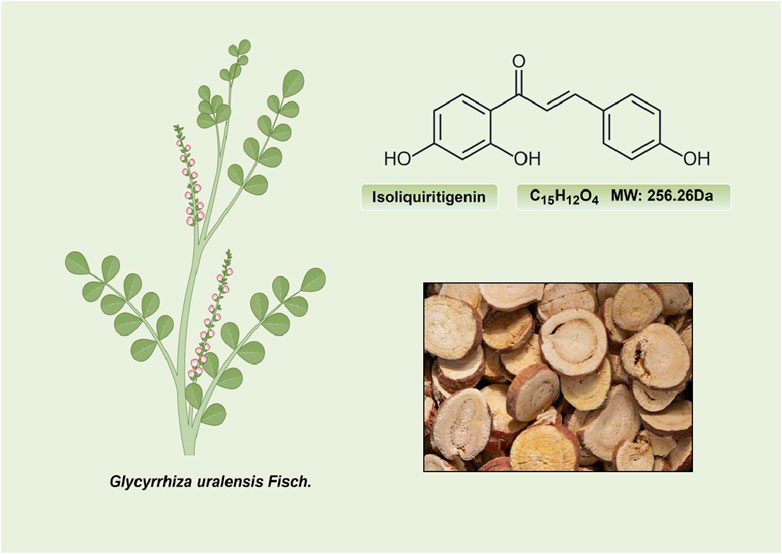
ISL, a chalcone-structured flavonoid derived from Glycyrrhiza uralensis (licorice) species (Li et al., 2010), has been found to possess therapeutic properties in various diseases including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, and cancer through the activation of the Nrf2 pathway (Xiong D. et al., 2018; Gu et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2022). ISL has been reported to exert an endogenous protective effect by facilitating Nrf2 nuclear translocation and modulating the expression of antioxidative enzymes such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate quinone oxidoreductase-1(NQO1), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), superoxide dismutase (SOD) et al. Consequently, the exploration of effective Nrf2 activators may present a novel potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of these diseases. Furthermore, ISL has been widely recognized as a safe phytochemical without any significant toxic, genotoxic, teratogenic properties in treating diseases (Zhao et al., 2019). Numerous studies have demonstrated the diverse pharmacological activities of ISL, including its antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-tumor properties (Iwata et al., 1999; Kwon et al., 2007; Aponte et al., 2008; Feldman et al., 2011; Chen Y. P. et al., 2013; Gaur et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2019). These findings collectively suggest that ISL plays a pivotal role in the prevention and treatment of human diseases (Figure 1). In this context, we specifically explore the therapeutic potential of ISL in targeting the Nrf2 pathway and evaluate its underlying mechanisms, thereby providing valuable insights for future research endeavors in this field.
2 Structure and metabolism of ISL
ISL (C15H12O4; MW: 256.26 Da) is a prominent member of the natural flavonoid compound group, primarily derived from the licorice root and various other plant species including Cicer arietinum L (Zhao et al., 2008), Radix Hedysari (Zhao et al., 2008), and Crinum bulbispermum (Ramadan et al., 2000). ISL (2′4′4-trihydroxychalcone) is classified within the chalcone family of flavonoids and finds application in the food additives and cosmetics industries (Cao et al., 2004; Wang Z. F. et al., 2020). The chemical structure of ISL is depicted in Figure 2. It exhibits limited solubility in water and manifests as a yellow crystalline solid (Wang Z. F. et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2021). The research has determined that the bioavailability of ISL in rats following oral administration ranged from 22.70% to 33.62%, indicating a low level of oral bioavailability. ISL is absorbed in the intestine and is biotransformed through both phases II, in the liver after absorption (Guo et al., 2008). Numerous studies have demonstrated that ISL exhibits favorable uptake and elimination capabilities when administered through various routes, including intraperitoneal, intravenous, and oral inoculations (Han et al., 2011; Qiao et al., 2014). Moreover, it has been observed that orally ingested ISL is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The presence of ISL in plasma can be detected within a 5-min timeframe, with its concentration peaking at 30 min. Following intraperitoneal injection of ISL, the liver exhibited the highest distribution of ISL, followed by the kidney, spleen, blood, lung, brain, and heart. The concentration of ISL in the blood reached its maximum level after 60 min (Han et al., 2011). Intravenous injection resulted in a rapid decrease in ISL concentration in plasma. The distribution half-life of ISL was found to be 0.3 h, while the elimination half-life for ISL doses of 10, 20, and 50 mg/kg were determined to be 4.9, 4.6, and 4.8 h, respectively (Qiao et al., 2014). Additionally, it was observed that intravenous administration of ISL resulted in its predominant distribution within highly vascularized tissues such as the heart, lungs, kidney, and liver. These findings suggest that the distribution pattern of ISL is influenced by the blood flow and perfusion of the respective organs (Qiao et al., 2014). Consequently, these results provide further substantiation for the potential therapeutic efficacy of ISL in treating disorders related to the cardiac, respiratory, and urinary systems. Furthermore, the significant accumulation of ISL in the kidney implies that it may serve as the primary organ for excretion of the compound. Despite its low expression in the brain due to high polarity (Li et al., 2008; Hua et al., 2010), it is intriguing to note that ISL can traverse the blood-brain barriers and exhibit neuroprotective effects in male MCAO-induced focal cerebral ischemic injury (Li et al., 2015). This could be relevant for the blood-brain barrier disruption after stroke (Wang et al., 2011). Presently, several approaches, including self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) and nanoparticles, are being explored to address the challenge of limited oral absorption and bioavailability associated with ISL.
3 Nrf2 structure and activation
Nrf2, a crucial transcription factor involved in cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative stress, plays a significant role in maintaining equilibrium between free radicals and the body’s antioxidant system (O'Mealey et al., 2017). It is increasingly recognized as a pivotal regulator in various diseases, such as neurological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases, and kidney disorders, among others (Chen et al., 2003; Pietsch et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2006; Rushworth et al., 2008; Kanninen et al., 2009). The NFE2L2 gene encodes Nrf2, a transcription factor belonging to the cap 'n' collar subfamily of basic-region leucine zipper (bZIPs) (Chowdhry et al., 2013). Nrf2 has a molecular weight of about 100 kDa. The protein Nrf2 is composed of seven distinct domains (Neh1-Neh7), each serving a specific function in regulating gene stability and transcriptional activity (Goodfellow et al., 2020; Madden and Itzhaki, 2020; Shaw and Chattopadhyay, 2020) (Figure 3). Nrf2 contains three of these regions at its C-terminus: Neh1, Neh3, and Neh6. Neh1 contains a bZIP domain, which primarily interacts with small Maf proteins for dimerization (Madden and Itzhaki, 2020; Zhou et al., 2020). This interaction allows Nrf2 to recognize and bind to the antioxidant response element (ARE), thereby facilitating the transcription of relevant genes. Neh3, on the other hand, acts as the transactivation domain of Nrf2 and interacts with the transcriptional co-activator chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 6, thereby facilitating the transcription of genes dependent on ARE and exhibiting antioxidant activity (Bellezza et al., 2018; Ooi et al., 2018). Besides, the Neh6 domain, which negatively regulates Nrf2 stability, is a serine-rich domain comprising two motifs (DSGIS and DSAPGS) that bind to β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP) (Panieri et al., 2020). The Neh6 domain plays a role in the degradation of Nrf2 independent of Keap1. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) phosphorylates specific serine amino acid residues (Ser344 and Ser347) within the Neh6 domain, thereby facilitating the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of the Nrf2 protein (Zhang et al., 2020). Conversely, GSK-3β activity is suppressed when it is phosphorylated on Ser21/9 residue, which results in activating Nrf2 and promotes the transcription of its downstream antioxidant and increase the antioxidant capacity (Hayes et al., 2015). The Neh4 and Neh5 domains, situated in the N-terminal halves, are responsible for the transcriptional regulation of downstream target genes. Upon translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus, only the Neh4 and Neh5 domains interact with cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) to activate transcription of the target genes (Bellezza et al., 2018). Furthermore, scholars have also discovered that the Neh4/Neh5 domains engage in interactions with the E3 ubiquitin ligase, hydroxy methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase degradation 1, thereby facilitating the ubiquitylation and subsequent degradation of Nrf2(Wu et al., 2014). The Neh2 domain, which serves as a negative regulatory region and the primary binding site for Keap1, primarily comprises DLG and ETGE motifs (Chowdhry et al., 2013). Elucidating the underlying mechanisms, it has been found that the homodimer double glycine repeat domain (DGR) of Keap1 binds to the DLG and ETGE motifs of Nrf2, leading to the ubiquitination of lysine residues in Nrf2. Consequently, this process results in the inactivation and degradation of Nrf2(Zenkov et al., 2017; Bellezza et al., 2018; Tonelli et al., 2018). Additionally, the investigation revealed that the Neh7 domain engages in an interaction with retinoic X receptor α, resulting in the repression of Nrf2 activity and the transcription of its target genes (Wang et al., 2013). Generally, the activity of Nrf2 is governed by the regulated maintenance of Nrf2 protein levels, which is achieved through both Keap1-dependent and Keap1-independent mechanisms. The subsequent sections provide a comprehensive overview of these two prominent regulatory mechanisms.
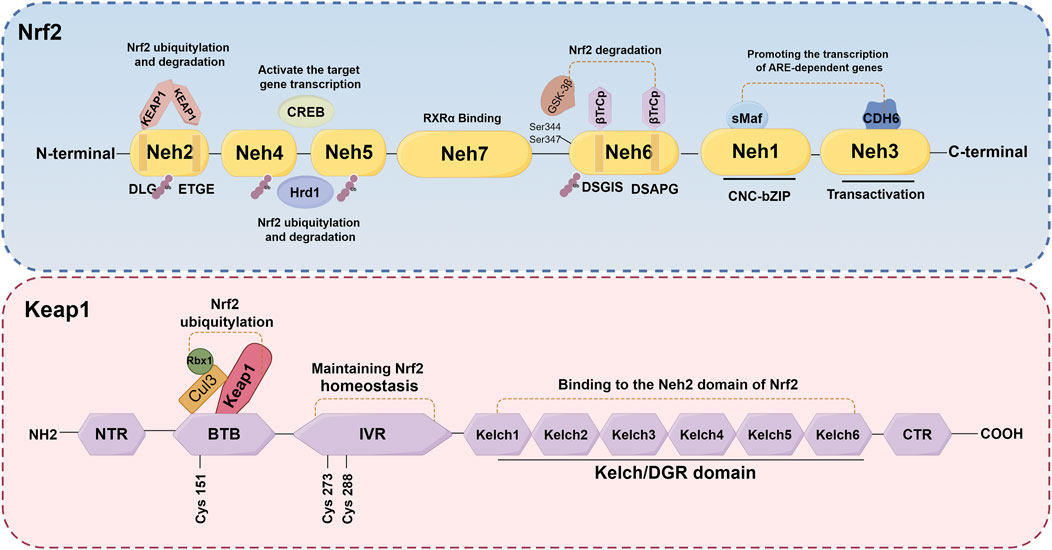
Figure 3. Schematic structures of Nrf2 and Keap1 protein. The protein Nrf2 is composed of seven distinct domains (Neh1-Neh7), each serving a specific function in regulating gene stability and transcriptional activity. The Keap1 protein consists of five distinct domains: NTR, IVR, BTB, DGR and CTR.
3.1 Keap1-dependent regulation
It is widely recognized that the regulation of Nrf2 involves both the Keap1-dependent and Keap1-independent pathways. The Keap1-dependent mechanism serves as the primary pathway for regulating Nrf2. In normal cells, Keap1 acts as a principal negative regulator of Nrf2 by ubiquitinating and degrading it. This negative regulation effectively controls Nrf2 activity and tightly regulates its concentration (Baird and Yamamoto, 2020; Kopacz et al., 2020). The relative molecular weight of Keap1 is 69KD (Canning et al., 2013). The Keap1 protein consists of five distinct domains: the N-terminal domain (NTR), the intervening region (IVR), the Broad complex, Tramtrack and Bric-à-Brac domain (BTB), the DGR, and the C-terminal region (CTR). Among these domains, the DGR domain, also referred to as the Kelch domain, plays a crucial role in the binding of Keap1 to the Neh2 domain of Nrf2(Ooi et al., 2018; Zhou et al., 2020) (Figure 3). Under normal physiological conditions, dimers of Keap1 exist in the cytoplasm and are substrate adapters protein for cullin3 (Cul3) E3 ubiquitin ligases (Suzuki et al., 2019). The additional study has also revealed that the presence of seven lysine residues positioned between the DLG and ETGE motifs in the Neh2 domain renders them susceptible to poly-ubiquitination, thereby facilitating the degradation of Nrf2 by the 26S proteasome system (Shibata et al., 2008; Harder et al., 2015; Mohan and Gupta, 2018) (Figure 4). Furthermore, the IVR domain in Keap1, particularly Cys273 and Cys288, assumes a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the Nrf2-Keap1 complex and ensuring Nrf2 homeostasis. Consequently, in the absence of external stressors, Nrf2 undergoes continuous synthesis and degradation, resulting in minimal net accumulation (Wakabayashi et al., 2004). Notably, Nrf2 exhibits a remarkably short half-life of approximately 10–30 min (Nguyen et al., 2003; Stewart et al., 2003). In contrast, the Cul3-Keap1-E3 ligase’s capacity to ubiquitinate Nrf2 is hindered during periods of stress, causing Nrf2 to relocate to the nucleus and manifest its antioxidative properties. During oxidative stress, it is important to mention that ROS or electrophiles have the ability to cause changes in the structure of the Keap1 domain. Specifically, ROS can modify the reactive cysteine residues within Keap1, such as Cys151 in the BTB domain and Cys273, Cys288 in the IVR domain (Tebay et al., 2015) (Figure 4). This interaction has the potential to disrupt the Keap1/Cul3/RING-box protein 1 (Rbx1) ubiquitin ligase complex and Nrf2 interaction, leading to the dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1 and subsequent suppression of ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Nrf2. When Nrf2 dissociates from Keap1, it translocates into the nucleus where it forms heterodimers with Maf proteins within the Neh1 domain and binds to the coactivator CREB protein, thereby enabling Nrf2 to possess DNA binding capability. In promoter regions, Nrf2 forms a complex with the ARE, thereby enhancing the antioxidant capacity by facilitating transcription of downstream antioxidant genes. Notable examples of these antioxidant genes encompass NQO1, glutathione S-transferase (GST), HO-1, and glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM) (Itoh et al., 1997; Buendia et al., 2016; Tonelli et al., 2018) (Figure 4).
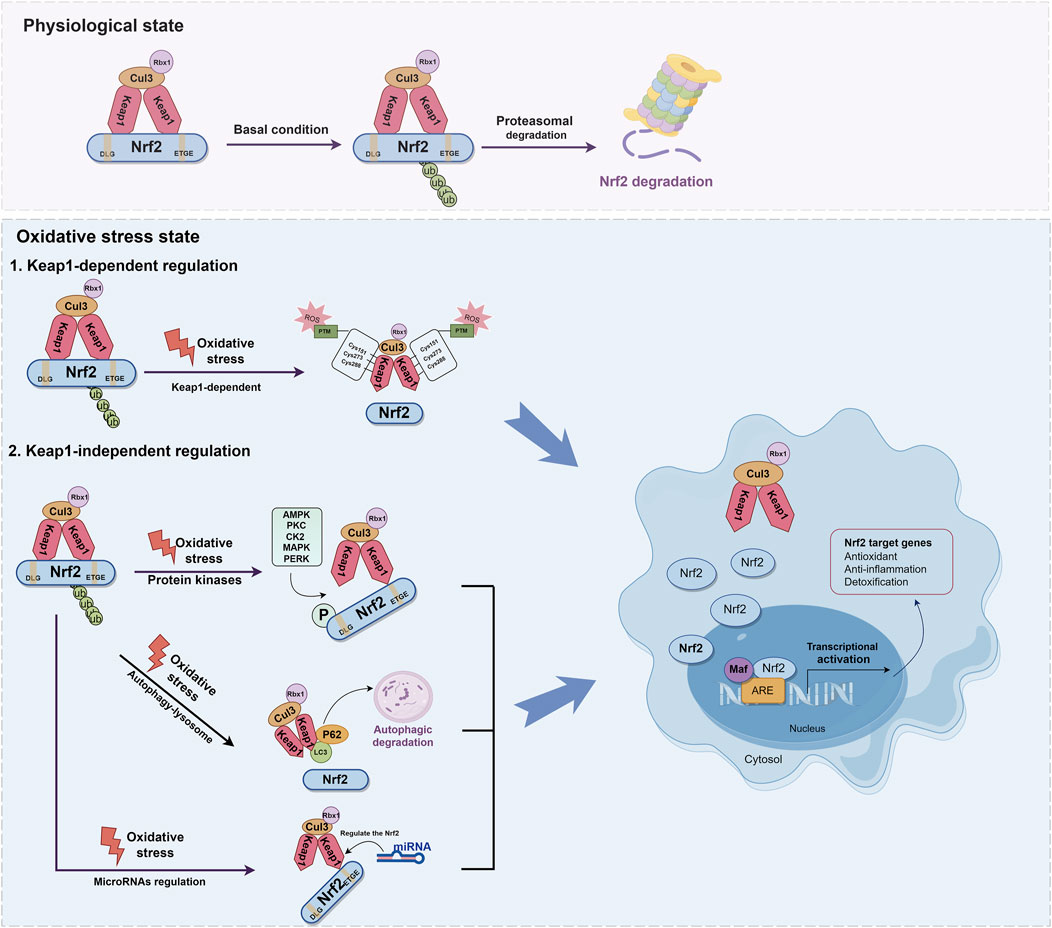
Figure 4. Molecular mechanisms of Keap1-dependent and Keap1-independent modulation of Nrf2. The regulation of Nrf2 involves both the Keap1-dependent and Keap1-independent pathways. Under normal physiological conditions, dimers of Keap1 exist in the cytoplasm and are substrate adapters protein for Cul3 E3 ubiquitin ligases. Nrf2 is ubiquitinated by E3 ubiquitin ligase, and degraded by the 26S proteasome. During oxidative stress, ROS can modify the reactive cysteine residues within Keap1, such as Cys151 in the BTB domain and Cys273, Cys288 in the IVR domain. This interaction disrupt the Keap1-Cul3-Rbx1 ubiquitin ligase complex and Nrf2 interaction, leading to the dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1. When Nrf2 dissociates from Keap1, it translocates into the nucleus where it forms heterodimers with Maf proteins within the Neh1 domain. In promoter regions, Nrf2 forms a complex with the ARE, thereby enhancing the antioxidant capacity by facilitating transcription of downstream antioxidant genes. Nrf2 can also be activated via the autophagy-lysosome pathway. The protein p62 serves as a selective autophagy receptor, facilitating the targeting of ubiquitinated substrates to autophagosomes for degradation. This interaction facilitates the integration of Keap1 into the autophagosome for degradation through the autophagy pathway, resulting in the separation of Nrf2 and Keap1 and thereby promoting the expression of antioxidant enzyme genes. miRNA plays a key role in the regulation of Nrf2 and contributes to its antioxidant capacity.
3.2 Keap1-independent regulation
In addition to the Keap1-dependent Nrf2 regulation pathway, Nrf2 activity is subject to stringent regulation through various mechanisms (Kaspar et al., 2009; Ichimura et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2014; Lin, 2019). Recent research has demonstrated that Nrf2 can also be activated via the autophagy-lysosome pathway, which is a highly regulated process responsible for the removal of damaged proteins and organelles (Ichimura et al., 2013; Zhang L. et al., 2016). The protein sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1/p62) serves as a selective autophagy receptor, facilitating the targeting of ubiquitinated substrates to autophagosomes for degradation. As an adaptor protein, p62 plays a critical role in connecting autophagy with the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway (Mizushima and Hara, 2006). This interaction facilitates the integration of Keap1 into the autophagosome for degradation through the autophagy pathway, resulting in the separation of Nrf2 and Keap1. This facilitates the movement of Nrf2 into the nucleus, thereby promoting the expression of antioxidant enzyme genes (Kageyama et al., 2018). Additionally, p62 is identified as one of the genes regulated by transcription. Nrf2 can activate and induce the production of p62, subsequently reactivating Nrf2, thus establishing a positive feedback loop (Santarino et al., 2017) (Figure 4).
The amino acid sequence of Nrf2 also provides multiple phosphorylation sites for protein kinases, such as serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues, which play a role in Nrf2 regulation. It has been shown that these modifications to Nrf2 may lead to its degradation, nuclear translocation, and nuclear export (Huang et al., 2002; Cullinan and Diehl, 2004; Keum et al., 2006; Pi et al., 2007). The phosphorylation of Neh2 by protein kinase C (PKC) results in the release of Nrf2 from Keap1 and subsequent enhancement of transcriptional activity of Nrf2. Further supporting the notion that PKC directly phosphorylates Ser40 within Neh2 domain is this finding (Huang et al., 2002). Additionally, it has been reported that GSK-3β phosphorylates the Nrf2 Neh6 domain (DSGIS domain) through β-TrCP, thereby inhibiting Nrf2 activity and exerting a negative regulatory effect (Hayes et al., 2015). The specific mechanism has been reported that β-TrCP has the ability to recognize the phosphorylated DSGIS motif in the Neh6 domain, leading to the formation of the SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein (SCF)β-TrCP E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Ultimately, this complex is involved in Nrf2 ubiquitination and degradation (Latres et al., 1999; Zheng et al., 2002; Hayes et al., 2015). Additionally, it has been reported that casein kinase two is capable of phosphorylating the Neh4 and Neh5 domains of Nrf2(Pi et al., 2007; Apopa et al., 2008). On the other hand, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) directly phosphorylates Nrf2, enhancing Nrf2-Keap1 dissociation and Nrf2 antioxidant pathways (Cullinan et al., 2003). Furthermore, PERK also facilitates the upregulation of the bZIP transcription factor activating transcription factor 4, which interacts with Nrf2 and triggers the activation of Nrf2 targeted genes (He et al., 2001; Ma et al., 2018). The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, known for its involvement in kinase signaling cascades, has been demonstrated that it regulates Nrf2 activity. However, the relationship between MAPK and Nrf2 appears contradictory. For instance, there is evidence that p38 MAPK can both positively and negatively modulate the antioxidant activity of Nrf2(Alam et al., 2000; Yu et al., 2000; Keum et al., 2006; Kocanova et al., 2007; Tsai et al., 2011). On the other hand, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) are more likely to positively regulate Nrf2 activity, as depicted in Figure 4(Keum et al., 2003; Nguyen et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2006; Varì et al., 2011; Choi et al., 2016; Feng et al., 2018).
Moreover, numerous studies have shed light on the correlation between Nrf2 and microRNA (miRNA) (Stachurska et al., 2013; Alural et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2021). miRNA, a crucial type of non-coding single-stranded RNA responsible for gene expression regulation, plays a role in the regulation of Nrf2, with approximately 85 miRNAs potentially involved (Bartel, 2004; Papp et al., 2012). Experimental evidence has previously confirmed that miR-1225-5p directly interacts with Keap1, leading to increased Nrf2 levels and subsequent translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus, resulting in upregulated HO-1 levels (Yang et al., 2021). Additionally, there are reported indications that miR-132 and miR-34a may modulate Nrf2 mRNA expression based on miRNA expression profiles (Stachurska et al., 2013; Alural et al., 2015). The role of miR-141-3p in enhancing the stability of Nrf2 by targeting Keap1 has been demonstrated (van Jaarsveld et al., 2013; Shi et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2021). Overall, Nrf2 is regulated by miRNA as depicted in Figure 4.
4 The role of ISL in targeting different diseases via Nrf2 pathway
4.1 Brain diseases
ISL is recognized as an effective antioxidant and cerebroprotective through the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway (Foresti et al., 2013; Zeng et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2019b). The investigation has revealed that ISL effectively mitigated early brain injury induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage, as evidenced by its ability to inhibit neuronal apoptosis, oxidative stress, and brain edema. Moreover, the administration of ISL augmented the expression of Nrf2, while the inhibition of Nrf2 activity counteracted the antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of ISL (Liu J. Q. et al., 2022). Another study has demonstrated that ISL significantly ameliorated neurological deficits in patients diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease (PD). The underlying mechanism may be attributed to the attenuation of neuro-inflammation through the Nrf2/ARE pathway. The researchers observed that the administration of ISL at a dosage of 20 mg/kg effectively reduced the rotational behavior in PD mice, enhanced the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase, and decreased the expression of α-synuclein. Additionally, ISL not only decreased the expression of ionized calcium bindingadaptor molecule-1 (Iba-1), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), but also upregulated the expression of Nrf2 and NQO1 (Huang et al., 2022). In the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cognitive impairment rat model, ISL also prevented neuronal damage and cognitive impairment by maintaining antioxidant ability and suppressing neuroinflammation. The protective effects of ISL have been shown to be exerted through inhibiting GSK-3β activity through increasing the expression levels of phosphorylated (p)-GSK-3β, thereby disinhibiting Nrf2 and upregulating the gene expression of Nrf2-controlled anti-oxidant genes. Besides, ISL also reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine production (Zhu et al., 2019a). The antioxidant mechanism of ISL is associated with reducing vascular permeability, enhancing neurological functions, and mitigating neuronal apoptosis in order to alleviate traumatic brain injury (TBI). This is achieved through the promotion of nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and the activation of the Nrf2-regulated ARE (Zhang et al., 2018a) (Figure 5). Supplementary Table 1 provides an overview of the Nrf2-related therapeutic effects of ISL in brain injury.
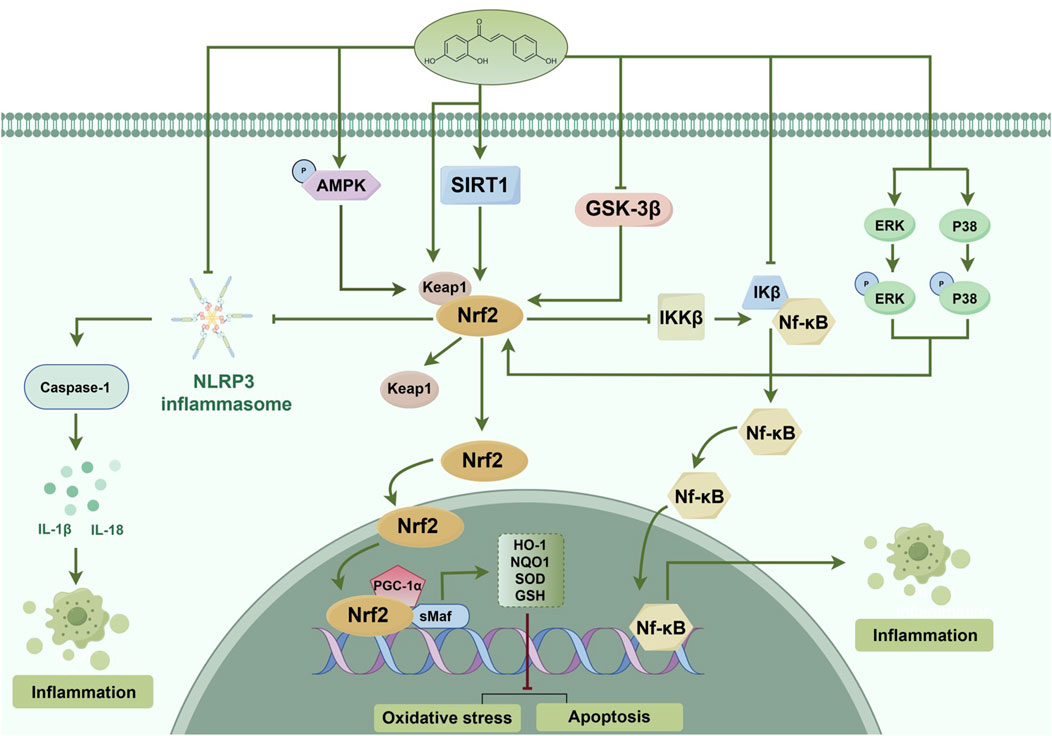
Figure 5. Probable mechanism of action of ISL on the Nrf2 pathway. ISL alleviated oxidative stress, cell apoptosis and inflammation via activating the AMPK/Nrf2 antioxidant signal pathway and inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NF-κB pathway. The inhibitory effect of ISL on NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway may be through both Nrf2 and non-Nrf2-independent signaling events. ISL also phosphorylates MAPKs and upregulates the Keap1, which induces the separation of Nrf2 from Keap1, activation of Nrf2 signaling, and enhancement of detoxification phase II enzymes activity. ISL activates SIRT1 to promote the Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway. Moreover, ISL also increase its antioxidant ability and decrease in inflammatory, cell apoptosis through activating the PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway. Besides, ISL also can inhibit GSK-3β activity by phosphorylation to enhance the Nrf2 related antioxidant gene expression and inhibit the NF-κB induced inflammatory gene. (↑) represent positive effect while (⊥) represent negative effect on the pathway.
4.2 Liver diseases
The prevalence of liver disease has increased significantly in recent years (Zhang et al., 2015). One significant factor contributing to acute liver dysfunction is drug-induced liver toxicity (Rabinowich and Shibolet, 2015). Doxorubicin, a widely utilized cancer chemotherapeutic agent, is commonly employed in the treatment of various tumor types, such as breast cancer, lymphomas, and leukemia, among others (Renu et al., 2019). However, the administration of doxorubicin is associated with adverse effects including cardiotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity (Pugazhendhi et al., 2018). Given that the liver serves as a crucial metabolic organ in the human body, it has been observed that during doxorubicin therapy, the liver is exposed to high concentrations of the drug and experiences the most pronounced impact (Carvalho et al., 2009). Research has demonstrated that doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity is a complex process involving multiple molecules, primarily driven by oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis (Prasanna et al., 2020). There is substantial evidence that doxorubicin inhibits the expression of Nrf2 and reduces the expression of antioxidant enzyme-related genes, thereby intensifying the oxidative stress damage caused by doxorubicin in the liver. As evidenced by the downregulation of serum aminotransferase levels following ISL administration, ISL may mitigate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. This protective effect is achieved through the induction of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling and the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) activity (Al-Qahtani et al., 2022). Furthermore, it has been observed that emodin, the primary constituent of Cassia obtusifolia, Aloe vera, and Polygonum multiflorum, can potentially induce hepatotoxicity, especially when administered in high doses and over an extended period of time (Wang et al., 2009; Panigrahi et al., 2015; Dong et al., 2016). It has been demonstrated that emodin exerts its hepatotoxic effects by generating ROS and activating mitochondria-dependent pathways (Dong et al., 2018). Additionally, another study has revealed that the combination of ISL and emodin exhibits a significant hepatoprotective effect by enhancing cellular activity, reducing the production of ROS, and augmenting antioxidant capacity. Additionally, ISL has been found to promote the separation of Keap1 from Nrf2, resulting in the translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus and subsequent induction of phase-II detoxifying enzyme expression (Ni et al., 2022). Furthermore, ISL has demonstrated significant mitigation of triptolide-induced acute hepatotoxicity by reducing hepatic oxidative stress and the accumulation of both endogenous bile acids and exogenous triptolide and its metabolites (Hou et al., 2018). It has been shown that ISL exerts its protective effects by enhancing Nrf2 expression, its downstream NQO1 expression, and hepatic influx and efflux transporters expression (Hou et al., 2018). As previously mentioned, ISL has demonstrated its potential as a hepatoprotectant and as a means to mitigate the detrimental impacts of other substances on liver function. Additionally, according to studies, ISL protects against acute liver failure caused by LPS/D-galactosamine (LPS/D-GalN), with the extent of this protection being dependent on the dosage administered. This protective mechanism is believed to be mediated through the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator (PGC-1α)/Nrf2 pathway (Wang et al., 2021) (Figure 5). The therapeutic effects of ISL in liver diseases, specifically those related to Nrf2, are summarized in Supplementary Table 1.
4.3 Pancreatic and intestinal diseases
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is a highly prevalent and fatal digestive disorder characterized by an abnormal inflammatory process affecting the pancreas (Lankisch et al., 2015; Lu et al., 2016). The occurrence of severe intestinal dysfunction is closely linked to acute pancreatitis (Karakayali, 2014). It has been suggested that mitigating SAP complications, including intestinal dysfunction, through appropriate interventions can be beneficial (Xiong Y. et al., 2018). Consequently, ameliorating bowel dysfunction may contribute to the improvement of SAP-related injuries. A prior investigation has demonstrated that the restoration of the impaired intestinal barrier is facilitated by the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway (Hu et al., 2018). In a recent study conducted by Zhang et al., it was discovered that mice lacking Nrf2 exhibited heightened vulnerability to injury in the context of SAP. This finding elucidates the crucial reparative function of Nrf2 in maintaining the intestinal barrier intact. Furthermore, the researchers also validated the significant ameliorative effects of ISL on both pancreatic and intestinal damage, as well as its ability to restore intestinal function. These effects were mediated through the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway, which was found to mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation in the animal model of SAP (Zhang et al., 2018b). Furthermore, an additional study has demonstrated that ISL displays substantial antioxidant activity and mitigates pancreatic histopathological damage in a dose-dependent manner by diminishing the levels of serum amylase and lipase. Additionally, ISL has the ability to enhance the Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway’s protein expression. There is evidence that the ML385 (Nrf2 inhibitor) and the zinc protoporphyrin (HO-1 inhibitor) significantly counteract the protective effects of ISL. Collectively, the aforementioned data provide novel evidence that implicates ISL as a protective agent in the experimental model of SAP induced by L-arginine, primarily through its ability to alleviate oxidative stress (Liu et al., 2018). Furthermore, ISL has demonstrated efficacy in preventing inflammatory bowel disease, with its protective effects potentially mediated by activating Nrf2 and its downstream targets (Chi et al., 2017). Consequently, these findings substantiate the potential of ISL as a viable therapeutic option for the clinical management of SAP (Figure 5). Supplementary Table 1 presents a comprehensive overview of the therapeutic effects of ISL on Nrf2-related pathways in both pancreatic and intestinal disorders.
4.4 Cardiovascular diseases and hematologic disorder
Globally, cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality (Sidney et al., 2016). Oxidative stress represents a significant mechanism implicated in the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). In a study utilizing an animal model of AMI, specifically the ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery, researchers observed that ISL exhibited a remarkable ability to reduce myocardial infarct size and enhance the recovery of cardiac function. The mechanism involved the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation, which resulted in the mitigation of myocardial inflammation and oxidative stress in mice with AMI(Yao et al., 2022). Additionally, there is a strong association between diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (Radovits et al., 2009). Pathological changes, including the presence of atheroma plaque, were observed in the aorta of the diabetic group. However, administration of ISL (20 mg/kg) for 8 weeks significantly suppressed endothelin-1 expression in the aortic endothelium of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes and preserved the structural integrity of the aorta. It is noteworthy to mention that ISL has the potential to enhance redox homeostasis in the aorta and prevent the apoptosis of endothelial cells through the Nrf2/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-3 (Caspase-3) pathway (Alzahrani et al., 2021). Additionally, another study demonstrated that ISL can inhibit hypertrophy, fibrosis, and apoptosis in H9c2 cells induced by high glucose, both in vitro and in vivo, by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress. Furthermore, the significant protective effect of ISL was attributed to the inhibition of MAPKs and the induction of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. These aforementioned studies collectively indicate that ISL holds promise for the development of therapeutic interventions against diabetic cardiomyopathy (Gu et al., 2020) (Figure 5). Supplementary Table 1 shows Nrf2-related therapeutic effects of ISL in cardiovascular disease and hematologic disorder.
4.5 Lung diseases
Acute lung injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome is a significant clinical syndrome associated with diffuse inflammation and respiratory failure, resulting in high mortality rates and limited therapeutic interventions (Ware and Matthay, 2000; Baetz et al., 2005; Sarma and Ward, 2011). Previous research has demonstrated that ISL exhibits potent antioxidant properties and has the potential to mitigate lung injury (Liu et al., 2017). To investigate this further, the researchers conducted in vitro studies using a tert-Butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced RAW.264.7 injury model, which mimics lung injury. The findings revealed that treatment with ISL effectively reduced the ROS production and attenuated cellular toxicity in RAW.264.7 cells. In vivo experiments have demonstrated the protective effect of ISL in reducing LPS-induced lung injury in mice with ALI. The role of ISL is primarily emphasized through its impact on lung histopathology, reduction of lung edema, and prevention of protein leakage. Additionally, ISL has been found to inhibit the production of ROS, myeloperoxidase (MPO), and malondialdehyde (MDA). Furthermore, ISL significantly improves the LPS-induced decrease in glutathione (GSH) and SOD levels in vivo. According to the study, activation of the adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway is crucial to effectively protecting against lung injury (Liu et al., 2017). Additionally, a separate study has demonstrated the notable protective effects of ISL against chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke (CS) (Yu et al., 2018). COPD is a highly prevalent disease, with CS being widely recognized as its primary risk factor (Du et al., 2017; Vogelmeier et al., 2017). Prolonged exposure to CS leads to chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, resulting in significant impairment of lung function (Chen et al., 2010; Du et al., 2017). In the aforementioned study, it was observed that ISL effectively mitigated lung pathological injuries induced by CS, as evidenced by the reversal of wet/dry ratio and MPO activity. This notable effect can be attributed to a significant reduction in inflammatory cell infiltration, improvement in the redox state, and modulation of the Nrf2 signal pathway (Yu et al., 2018) (Figure 5). In Supplementary Table 1, we provide an overview of the therapeutic effects of ISL on Nrf2-related mechanisms in lung diseases.
4.6 Kidney diseases
Hypertensive renal injury is a prominent risk factor for renal injury, playing a significant role in developing of end-stage nephropathy and the requirement for dialysis (Dugbartey, 2017). A study conducted on hypertensive renal injury has initially demonstrated that ISL can mitigate the inflammatory cytokine’s production, apoptosis induced by oxidative stress, and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that ISL can effectively safeguard against renal injury by activating the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. These findings indicate the potential preventive and therapeutic benefits of ISL in the context of hypertensive renal injury (Xiong D. et al., 2018) (Figure 5). The therapeutic effects of ISL on kidney diseases, particularly those related to Nrf2, are summarized in Supplementary Table 1.
5 ISL nanoformulations and ISL metabolites
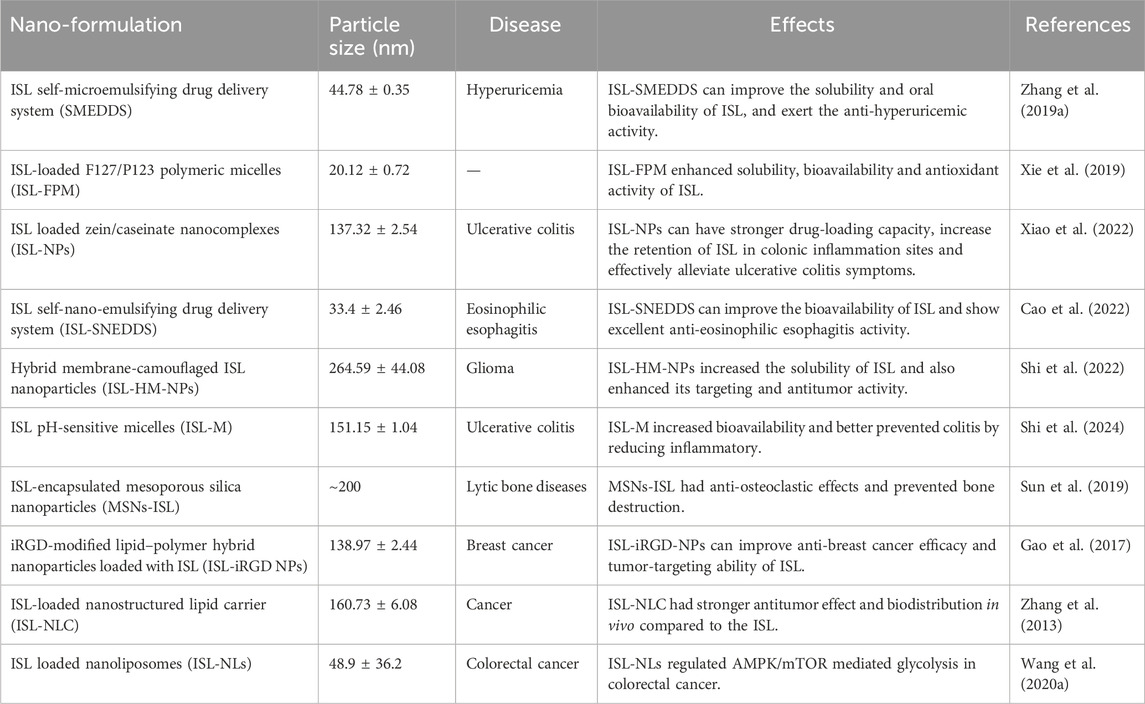
ISL exhibits high solubility in organic solvents but low solubility in water (Xie et al., 2019). ISL has the low bioavailability in vivo due to factors such as its poor solubility, high first-pass metabolism and rapid excretion (Zhang et al., 2013; Qiao et al., 2014). Notably, the term inadequate bioavailability suggests that the desired effects under treatment of ISL are difficult to achieve, thereby hinders its clinical application. To increase the dissolution and improve the oral bioavailability of ISL, encapsulated ISL nanoparticles or nano-ISL have been developed. Next, We have summarized various ISL nanocarriers in preclinical studies and their potential applications in Table 1.
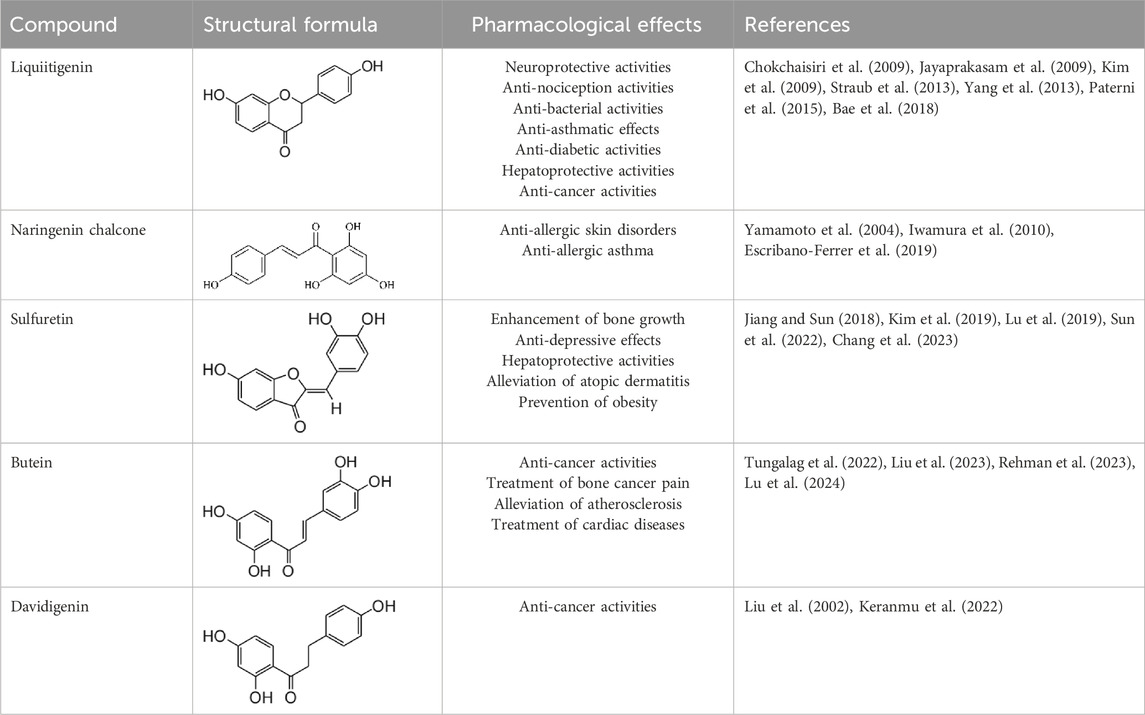
Furthermore, the metabolites of ISL have demonstrated potential pharmacological effects and therapeutic benefits for the treatment of a variety of diseases. These metabolites, including liquiritigenin, naringenin chalcone, sulfuretin, butein, and davidigenin (Yang et al., 2016), have been the subject of numerous studies evaluating their individual pharmacological effects, such as neuroprotection, hepatocyte protection, and anti-cancer properties (Kim et al., 2009; Yang et al., 2013; Lu et al., 2024). A detailed summary of the specific pharmacological effects of each metabolite can be found in Table 2.
6 Limitations and future prospects
All of the above published results suggest that ISL confer protective effects on various disease via Nrf2 signaling pathways. However, due to its low bioavailability and poor delivery characteristics, the big gap between basic research and clinical application still exists. In order to enable ISL available for better therapeutic effects, more trials with ISL either alone or in combination with existing therapies are also needed to fully appreciate its potential. Based on this, the development of ISL formulations may represent a promising avenue for future research. Currently, drug delivery systems such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and micelles has been reported to be applied to enhance drug’s solubility, absorbance, and stability (Zhang et al., 2013; Zhang X. et al., 2016; Xie et al., 2019). Theranostic nanoparticles consisting of ISL and a near-infrared photosensitizer provide a promising delivery platform. It can enhance treatment outcomes, and reduce drug dosage and side effects (Sun et al., 2023). In addition, Studies on the side effects and safety evaluations of this plant are very limited although ISL is widely used in Chinese traditional medicine. In the future, long-term toxicity studies and clinical trials of ISL are still needed.
7 Conclusion
Multiple research studies have shown the considerable role of oxidative stress in the development of various illnesses. Consequently, directing therapeutic interventions towards mitigating oxidative stress may offer a pragmatic approach for treating various ailments. Cells possess multiple antioxidant systems that serve to counteract intracellular ROS. Among these systems, the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway represents a prominent endogenous antioxidant mechanism. Nrf2, as the principal regulator of anti-oxidative stress responses, primarily exerts its influence by stimulating the activation of downstream antioxidant and cellular protective genes. As a result, Nrf2 signal pathway activation may inhibit oxidative stress. In this particular context, ISL exhibits both antioxidant characteristics and minimal toxicity as a natural compound. There are numerous studies suggesting that ISL could be used as a novel therapeutic agent for a variety of diseases by modulating the Nrf2 signal pathway in diverse animal and cellular models. In summary, our review provides new insights for ISL as Nrf2 signaling pathway modulator for treating various diseases.
Author contributions
MQ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. KM: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. JZ: Funding acquisition, Software, Writing–review and editing. ZZ: Investigation, Software, Writing–review and editing. SW: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. QW: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. HX: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The present work was supported by the Scientific Research Program Funded by Education Department of Shaanxi Provincial Government (23JK0641), Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2020JZ-56), Scientific and Technical Program of Shaanxi Provincial Xi’an Weiyang District (202127), Program for Science and Technology Innovation Team in Xi’an Medical University (2021TD05), the Program funded by Science and Technology and Information Bureau of Shaanxi Provincial Xi’an Weiyang district (202223), the Scientific Research Project of Xi’an Medical University (2023QN04 and 2023QN15), Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2022JQ-814).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1395735/full#supplementary-material
References
Alam, J., Wicks, C., Stewart, D., Gong, P., Touchard, C., Otterbein, S., et al. (2000). Mechanism of heme oxygenase-1 gene activation by cadmium in MCF-7 mammary epithelial cells. Role of p38 kinase and Nrf2 transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 27694–27702. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004729200
Al-Qahtani, W. H., Alshammari, G. M., Ajarem, J. S., Al-Zahrani, A. Y., Alzuwaydi, A., Eid, R., et al. (2022). Isoliquiritigenin prevents Doxorubicin-induced hepatic damage in rats by upregulating and activating SIRT1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 146, 112594. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112594
Alural, B., Ozerdem, A., Allmer, J., Genc, K., and Genc, S. (2015). Lithium protects against paraquat neurotoxicity by NRF2 activation and miR-34a inhibition in SH-SY5Y cells. Front. Cell Neurosci. 9, 209. doi:10.3389/fncel.2015.00209
Alzahrani, S., Said, E., Ajwah, S. M., Alsharif, S. Y., El-Bayoumi, K. S., Zaitone, S. A., et al. (2021). Isoliquiritigenin attenuates inflammation and modulates Nrf2/caspase-3 signalling in STZ-induced aortic injury. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 73, 193–205. doi:10.1093/jpp/rgaa056
Aponte, J. C., Verástegui, M., Málaga, E., Zimic, M., Quiliano, M., Vaisberg, A. J., et al. (2008). Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity of new chalcones. J. Med. Chem. 51, 6230–6234. doi:10.1021/jm800812k
Apopa, P. L., He, X., and Ma, Q. (2008). Phosphorylation of Nrf2 in the transcription activation domain by casein kinase 2 (CK2) is critical for the nuclear translocation and transcription activation function of Nrf2 in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 22, 63–76. doi:10.1002/jbt.20212
Bae, G. D., Park, E. Y., Baek, D. J., Jun, H. S., and Oh, Y. S. (2018). Liquiritigenin prevents palmitate-induced beta-cell apoptosis via estrogen receptor-mediated AKT activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 101, 348–354. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.097
Baetz, D., Shaw, J., and Kirshenbaum, L. A. (2005). Nuclear factor-kappaB decoys suppress endotoxin-induced lung injury. Mol. Pharmacol. 67, 977–979. doi:10.1124/mol.105.011296
Baird, L., and Yamamoto, M. (2020). The molecular mechanisms regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 40. doi:10.1128/MCB.00099-20
Bartel, D. P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5
Bellezza, I., Giambanco, I., Minelli, A., and Donato, R. (2018). Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1865, 721–733. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.02.010
Bhimaraj, A., and Tang, W. H. (2012). Role of oxidative stress in disease progression in Stage B, a pre-cursor of heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 8, 101–111. doi:10.1016/j.hfc.2011.08.003
Brandes, M. S., Zweig, J. A., Tang, A., and Gray, N. E. (2021). NRF2 activation ameliorates oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial function and synaptic plasticity, and in A53T α-synuclein hippocampal neurons. Antioxidants (Basel) 11, 26. doi:10.3390/antiox11010026
Buendia, I., Michalska, P., Navarro, E., Gameiro, I., Egea, J., and León, R. (2016). Nrf2-ARE pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 157, 84–104. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.003
Canning, P., Cooper, C. D. O., Krojer, T., Murray, J. W., Pike, A. C. W., Chaikuad, A., et al. (2013). Structural basis for Cul3 protein assembly with the BTB-Kelch family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 7803–7814. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.437996
Cao, L., Yan, M., Ma, Y. X., Zhang, B. K., Fang, P. F., Xiang, D. X., et al. (2016a). Isoliquiritigenin protects against triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through Nrf2 activation. Pharmazie 71, 394–397. doi:10.1691/ph.2016.6535
Cao, L. J., Li, H. D., Yan, M., Li, Z. H., Gong, H., Jiang, P., et al. (2016b). The protective effects of isoliquiritigenin and glycyrrhetinic acid against triptolide-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells involve Nrf2 activation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 8912184. doi:10.1155/2016/8912184
Cao, M., Wang, Y., Jing, H., Wang, Z., Meng, Y., Geng, Y., et al. (2022). Development of an oral isoliquiritigenin self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery system (ILQ-SNEDDS) for effective treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis induced by food allergy. Pharm. (Basel) 15, 1587. doi:10.3390/ph15121587
Cao, Y., Wang, Y., Ji, C., and Ye, J. (2004). Determination of liquiritigenin and isoliquiritigenin in Glycyrrhiza uralensis and its medicinal preparations by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1042, 203–209. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.05.049
Carvalho, C., Santos, R. X., Cardoso, S., Correia, S., Oliveira, P. J., Santos, M. S., et al. (2009). Doxorubicin: the good, the bad and the ugly effect. Curr. Med. Chem. 16, 3267–3285. doi:10.2174/092986709788803312
Chang, S. H., Giong, H. K., Kim, D. Y., Kim, S., Oh, S., Yun, U. J., et al. (2023). Activation of Nrf2 by sulfuretin stimulates chondrocyte differentiation and increases bone lengths in zebrafish. BMB Rep. 56, 496–501. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0056
Chen, H., Zhang, B., Yuan, X., Yao, Y., Zhao, H., Sun, X., et al. (2013a). Isoliquiritigenin-induced effects on Nrf2 mediated antioxidant defence in the HL-60 cell monocytic differentiation. Cell Biol. Int. 37, 1215–1224. doi:10.1002/cbin.10156
Chen, L., Sun, B. B., Wang, T., Wang, X., Li, J. Q., Wang, H. X., et al. (2010). Cigarette smoke enhances {beta}-defensin 2 expression in rat airways via nuclear factor-{kappa}B activation. Eur. Respir. J. 36, 638–645. doi:10.1183/09031936.00029409
Chen, X. L., Dodd, G., Thomas, S., Zhang, X., Wasserman, M. A., Rovin, B. H., et al. (2006). Activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway protects endothelial cells from oxidant injury and inhibits inflammatory gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290, H1862–H1870. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00651.2005
Chen, X. L., Varner, S. E., Rao, A. S., Grey, J. Y., Thomas, S., Cook, C. K., et al. (2003). Laminar flow induction of antioxidant response element-mediated genes in endothelial cells. A novel anti-inflammatory mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 703–711. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203161200
Chen, Y. P., Zhang, Z. Y., Li, Y. P., Li, D., Huang, S. L., Gu, L. Q., et al. (2013b). Syntheses and evaluation of novel isoliquiritigenin derivatives as potential dual inhibitors for amyloid-beta aggregation and 5-lipoxygenase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 66, 22–31. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.05.015
Cheng, X. R., Yu, B. T., Song, J., Ma, J. H., Chen, Y. Y., Zhang, C. X., et al. (2022). The alleviation of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-Induced colitis correlate with the logP values of food-derived electrophilic compounds. Antioxidants (Basel) 11, 2406. doi:10.3390/antiox11122406
Chi, J. H., Seo, G. S., Cheon, J. H., and Lee, S. H. (2017). Isoliquiritigenin inhibits TNF-α-induced release of high-mobility group box 1 through activation of HDAC in human intestinal epithelial HT-29 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 796, 101–109. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.12.026
Choi, H. Y., Lee, J. H., Jegal, K. H., Cho, I. J., Kim, Y. W., and Kim, S. C. (2016). Oxyresveratrol abrogates oxidative stress by activating ERK-Nrf2 pathway in the liver. Chem. Biol. Interact. 245, 110–121. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2015.06.024
Chokchaisiri, R., Suaisom, C., Sriphota, S., Chindaduang, A., Chuprajob, T., and Suksamrarn, A. (2009). Bioactive flavonoids of the flowers of Butea monosperma. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 57, 428–432. doi:10.1248/cpb.57.428
Chowdhry, S., Zhang, Y., Mcmahon, M., Sutherland, C., Cuadrado, A., and Hayes, J. D. (2013). Nrf2 is controlled by two distinct β-TrCP recognition motifs in its Neh6 domain, one of which can be modulated by GSK-3 activity. Oncogene 32, 3765–3781. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.388
Cleasby, A., Yon, J., Day, P. J., Richardson, C., Tickle, I. J., Williams, P. A., et al. (2014). Structure of the BTB domain of Keap1 and its interaction with the triterpenoid antagonist CDDO. PLoS One 9, e98896. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098896
Cullinan, S. B., and Diehl, J. A. (2004). PERK-dependent activation of Nrf2 contributes to redox homeostasis and cell survival following endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 20108–20117. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314219200
Cullinan, S. B., Zhang, D., Hannink, M., Arvisais, E., Kaufman, R. J., and Diehl, J. A. (2003). Nrf2 is a direct PERK substrate and effector of PERK-dependent cell survival. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 7198–7209. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.20.7198-7209.2003
Dong, X., Fu, J., Yin, X., Cao, S., Li, X., Lin, L., et al. (2016). Emodin: a review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 30, 1207–1218. doi:10.1002/ptr.5631
Dong, X., Ni, B., Fu, J., Yin, X., You, L., Leng, X., et al. (2018). Emodin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepaRG cells via the mitochondrial caspase-dependent pathway. Oncol. Rep. 40, 1985–1993. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6620
Du, Y., Ding, Y., Chen, X., Mei, Z., Ding, H., Wu, Y., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-181c inhibits cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by regulating CCN1 expression. Respir. Res. 18, 155. doi:10.1186/s12931-017-0639-1
Dugbartey, G. J. (2017). H(2)S as a possible therapeutic alternative for the treatment of hypertensive kidney injury. Nitric Oxide 64, 52–60. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2017.01.002
Escribano-Ferrer, E., Queralt Regué, J., Garcia-Sala, X., Boix Montañés, A., and Lamuela-Raventos, R. M. (2019). In vivo anti-inflammatory and antiallergic activity of pure naringenin, naringenin chalcone, and quercetin in mice. J. Nat. Prod. 82, 177–182. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00366
Feldman, M., Santos, J., and Grenier, D. (2011). Comparative evaluation of two structurally related flavonoids, isoliquiritigenin and liquiritigenin, for their oral infection therapeutic potential. J. Nat. Prod. 74, 1862–1867. doi:10.1021/np200174h
Feng, R., Meng, T., Zhao, X., Yu, W., Li, H., Wang, Z., et al. (2024). Isoliquiritigenin reduces experimental autoimmune prostatitis by facilitating Nrf2 activation and suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Mol. Immunol. 169, 37–49. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2024.03.002
Feng, R. B., Wang, Y., He, C., Yang, Y., and Wan, J. B. (2018). Gallic acid, a natural polyphenol, protects against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity by activating ERK-Nrf2-Keap1-mediated antioxidative response. Food Chem. Toxicol. 119, 479–488. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.10.033
Foresti, R., Bains, S. K., Pitchumony, T. S., De Castro Brás, L. E., Drago, F., Dubois-Randé, J. L., et al. (2013). Small molecule activators of the Nrf2-HO-1 antioxidant axis modulate heme metabolism and inflammation in BV2 microglia cells. Pharmacol. Res. 76, 132–148. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.07.010
Fu, Y., and Jia, J. (2021). Isoliquiritigenin confers neuroprotection and alleviates amyloid-β42-induced neuroinflammation in microglia by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB signaling. Front. Neurosci. 15, 638772. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.638772
Gao, F., Zhang, J., Fu, C., Xie, X., Peng, F., You, J., et al. (2017). iRGD-modified lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with isoliquiritigenin to enhance anti-breast cancer effect and tumor-targeting ability. Int. J. Nanomedicine 12, 4147–4162. doi:10.2147/IJN.S134148
Gao, Y., Lv, X., Yang, H., Peng, L., and Ci, X. (2020). Isoliquiritigenin exerts antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects via activating the KEAP-1/Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB and NLRP3 pathways in carrageenan-induced pleurisy. Food Funct. 11, 2522–2534. doi:10.1039/c9fo01984g
Gaur, R., Yadav, K. S., Verma, R. K., Yadav, N. P., and Bhakuni, R. S. (2014). In vivo anti-diabetic activity of derivatives of isoliquiritigenin and liquiritigenin. Phytomedicine 21, 415–422. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2013.10.015
George, M., Tharakan, M., Culberson, J., Reddy, A. P., and Reddy, P. H. (2022). Role of Nrf2 in aging, Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 82, 101756. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101756
Goodfellow, M. J., Borcar, A., Proctor, J. L., Greco, T., Rosenthal, R. E., and Fiskum, G. (2020). Transcriptional activation of antioxidant gene expression by Nrf2 protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal death associated with acute and chronic neurodegeneration. Exp. Neurol. 328, 113247. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113247
Gu, X., Shi, Y., Chen, X., Sun, Z., Luo, W., Hu, X., et al. (2020). Isoliquiritigenin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibition of hyperglycemia-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Phytomedicine 78, 153319. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153319
Guo, J., Liu, A., Cao, H., Luo, Y., Pezzuto, J. M., and Van Breemen, R. B. (2008). Biotransformation of the chemopreventive agent 2',4',4-trihydroxychalcone (isoliquiritigenin) by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 36, 2104–2112. doi:10.1124/dmd.108.021857
Han, B., Chen, W., Zheng, Q., Wang, X., Yan, H., Li, L., et al. (2011). Determination of isoliquiritigenin and its distribution in mice by synchronous fluorescence spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 27, 1115–1119. doi:10.2116/analsci.27.1115
Harder, B., Jiang, T., Wu, T., Tao, S., Rojo De La Vega, M., Tian, W., et al. (2015). Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2 regulation and how these influence chemical modulation for disease intervention. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 43, 680–686. doi:10.1042/BST20150020
Hayes, J. D., Chowdhry, S., Dinkova-Kostova, A. T., and Sutherland, C. (2015). Dual regulation of transcription factor Nrf2 by Keap1 and by the combined actions of β-TrCP and GSK-3. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 43, 611–620. doi:10.1042/BST20150011
He, C. H., Gong, P., Hu, B., Stewart, D., Choi, M. E., Choi, A. M., et al. (2001). Identification of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) as an Nrf2-interacting protein. Implication for heme oxygenase-1 gene regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 20858–20865. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101198200
He, L., Chen, Q., Wang, L., Pu, Y., Huang, J., Cheng, C. K., et al. (2024). Activation of Nrf2 inhibits atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice through suppressing endothelial cell inflammation and lipid peroxidation. Redox Biol. 74, 103229. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2024.103229
Hou, Z., Chen, L., Fang, P., Cai, H., Tang, H., Peng, Y., et al. (2018). Mechanisms of triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity and protective effect of combined use of isoliquiritigenin: possible roles of Nrf2 and hepatic transporters. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 226. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00226
Hu, Q., Ren, J., Li, G., Wu, J., Wu, X., Wang, G., et al. (2018). The mitochondrially targeted antioxidant MitoQ protects the intestinal barrier by ameliorating mitochondrial DNA damage via the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9, 403. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0436-x
Hua, X., Fu, Y. J., Zu, Y. G., Wu, N., Kong, Y., Li, J., et al. (2010). Plasma pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of cajaninstilbene acid in rats by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 52, 273–279. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2010.01.004
Huang, H. C., Nguyen, T., and Pickett, C. B. (2002). Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at Ser-40 by protein kinase C regulates antioxidant response element-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 42769–42774. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206911200
Huang, L., Han, Y., Zhou, Q., Sun, Z., and Yan, J. (2022). Isoliquiritigenin attenuates neuroinflammation in mice model of Parkinson's disease by promoting Nrf2/NQO-1 pathway. Transl. Neurosci. 13, 301–308. doi:10.1515/tnsci-2022-0239
Huang, X., Gao, Y., Qin, J., and Lu, S. (2014). The role of miR-34a in the hepatoprotective effect of hydrogen sulfide on ischemia/reperfusion injury in young and old rats. PLoS One 9, e113305. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113305
Huang, X., Shi, Y., Chen, H., Le, R., Gong, X., Xu, K., et al. (2020). Isoliquiritigenin prevents hyperglycemia-induced renal injuries by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via SIRT1-dependent mechanism. Cell Death Dis. 11, 1040. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03260-9
Hung, S. Y., Chen, J. L., Tu, Y. K., Tsai, H. Y., Lu, P. H., Jou, I. M., et al. (2024). Isoliquiritigenin inhibits apoptosis and ameliorates oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis chondrocytes through the Nrf2/HO-1-mediated pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 170, 116006. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116006
Ichimura, Y., Waguri, S., Sou, Y. S., Kageyama, S., Hasegawa, J., Ishimura, R., et al. (2013). Phosphorylation of p62 activates the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway during selective autophagy. Mol. Cell 51, 618–631. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.003
Itoh, K., Chiba, T., Takahashi, S., Ishii, T., Igarashi, K., Katoh, Y., et al. (1997). An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 236, 313–322. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6943
Iwamura, C., Shinoda, K., Yoshimura, M., Watanabe, Y., Obata, A., and Nakayama, T. (2010). Naringenin chalcone suppresses allergic asthma by inhibiting the type-2 function of CD4 T cells. Allergol. Int. 59, 67–73. doi:10.2332/allergolint.09-OA-0118
Iwata, S., Nagata, N., Omae, A., Yamaguchi, S., Okada, Y., Shibata, S., et al. (1999). Inhibitory effect of chalcone derivatives on recombinant human aldose reductase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 22, 323–325. doi:10.1248/bpb.22.323
Jayaprakasam, B., Doddaga, S., Wang, R., Holmes, D., Goldfarb, J., and Li, X. M. (2009). Licorice flavonoids inhibit eotaxin-1 secretion by human fetal lung fibroblasts in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 820–825. doi:10.1021/jf802601j
Jiang, P., and Sun, H. (2018). Sulfuretin alleviates atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice via suppressing Th2 cell activity. Immunol. Res. 66, 611–619. doi:10.1007/s12026-018-9025-4
Kageyama, S., Saito, T., Obata, M., Koide, R. H., Ichimura, Y., and Komatsu, M. (2018). Negative regulation of the keap1-nrf2 pathway by a p62/sqstm1 splicing variant. Mol. Cell Biol. 38. doi:10.1128/MCB.00642-17
Kanninen, K., Heikkinen, R., Malm, T., Rolova, T., Kuhmonen, S., Leinonen, H., et al. (2009). Intrahippocampal injection of a lentiviral vector expressing Nrf2 improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 16505–16510. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908397106
Karakayali, F. Y. (2014). Surgical and interventional management of complications caused by acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 20, 13412–13423. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13412
Kaspar, J. W., Niture, S. K., and Jaiswal, A. K. (2009). Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 47, 1304–1309. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.035
Keranmu, A., Pan, L. B., Fu, J., Han, P., Yu, H., Zhang, Z. W., et al. (2022). Biotransformation of liquiritigenin into characteristic metabolites by the gut microbiota. Molecules 27, 3057. doi:10.3390/molecules27103057
Keum, Y. S., Owuor, E. D., Kim, B. R., Hu, R., and Kong, A. N. (2003). Involvement of Nrf2 and JNK1 in the activation of antioxidant responsive element (ARE) by chemopreventive agent phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC). Pharm. Res. 20, 1351–1356. doi:10.1023/a:1025737622815
Keum, Y. S., Yu, S., Chang, P. P., Yuan, X., Kim, J. H., Xu, C., et al. (2006). Mechanism of action of sulforaphane: inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms contributing to the induction of antioxidant response element-mediated heme oxygenase-1 in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Cancer Res. 66, 8804–8813. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3513
Kim, S., Song, N. J., Chang, S. H., Bahn, G., Choi, Y., Rhee, D. K., et al. (2019). Sulfuretin prevents obesity and metabolic diseases in diet induced obese mice. Biomol. Ther. Seoul. 27, 107–116. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2018.090
Kim, Y. W., Kang, H. E., Lee, M. G., Hwang, S. J., Kim, S. C., Lee, C. H., et al. (2009). Liquiritigenin, a flavonoid aglycone from licorice, has a choleretic effect and the ability to induce hepatic transporters and phase-II enzymes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 296, G372–G381. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.90524.2008
Kocanova, S., Buytaert, E., Matroule, J. Y., Piette, J., Golab, J., De Witte, P., et al. (2007). Induction of heme-oxygenase 1 requires the p38MAPK and PI3K pathways and suppresses apoptotic cell death following hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Apoptosis 12, 731–741. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-0016-x
Kopacz, A., Kloska, D., Forman, H. J., Jozkowicz, A., and Grochot-Przeczek, A. (2020). Beyond repression of Nrf2: an update on Keap1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 157, 63–74. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.03.023
Kwon, H. M., Choi, Y. J., Choi, J. S., Kang, S. W., Bae, J. Y., Kang, I. J., et al. (2007). Blockade of cytokine-induced endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression by licorice isoliquiritigenin through NF-kappaB signal disruption. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 232, 235–245.
Lankisch, P. G., Apte, M., and Banks, P. A. (2015). Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 386, 85–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60649-8
Latres, E., Chiaur, D. S., and Pagano, M. (1999). The human F box protein beta-Trcp associates with the Cul1/Skp1 complex and regulates the stability of beta-catenin. Oncogene 18, 849–854. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202653
Li, D., Wang, Q., Yuan, Z. F., Zhang, L., Xu, L., Cui, Y., et al. (2008). Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of orientin in rat by liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 47, 429–434. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2008.01.035
Li, H., Ye, M., Zhang, Y., Huang, M., Xu, W., Chu, K., et al. (2015). Blood-brain barrier permeability of Gualou Guizhi granules and neuroprotective effects in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 12, 1272–1278. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.3520
Li, S., Li, W., Wang, Y., Asada, Y., and Koike, K. (2010). Prenylflavonoids from Glycyrrhiza uralensis and their protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B inhibitory activities. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 5398–5401. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.110
Lin, Y. H. (2019). MicroRNA networks modulate oxidative stress in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 4497. doi:10.3390/ijms20184497
Liu, J. Q., Zhao, X. T., Qin, F. Y., Zhou, J. W., Ding, F., Zhou, G., et al. (2022a). Isoliquiritigenin mitigates oxidative damage after subarachnoid hemorrhage in vivo and in vitro by regulating Nrf2-dependent Signaling Pathway via Targeting of SIRT1. Phytomedicine 105, 154262. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154262
Liu, Q., Lv, H., Wen, Z., Ci, X., and Peng, L. (2017). Isoliquiritigenin activates nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 to suppress the NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome and inhibits the NF-κB pathway in macrophages and in acute lung injury. Front. Immunol. 8, 1518. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01518
Liu, X., Zhao, S., Zhao, Q., Chen, Y., Jia, S., Xiang, R., et al. (2023). Butein, a potential drug for the treatment of bone cancer pain through bioinformatic and network pharmacology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 472, 116570. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2023.116570
Liu, X., Zhu, Q., Zhang, M., Yin, T., Xu, R., Xiao, W., et al. (2018). Isoliquiritigenin ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice via inhibition of oxidative stress and modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 7161592. doi:10.1155/2018/7161592
Liu, Y., Uruno, A., Saito, R., Matsukawa, N., Hishinuma, E., Saigusa, D., et al. (2022b). Nrf2 deficiency deteriorates diabetic kidney disease in Akita model mice. Redox Biol. 58, 102525. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102525
Liu, Z. L., Tanaka, S., Horigome, H., Hirano, T., and Oka, K. (2002). Induction of apoptosis in human lung fibroblasts and peripheral lymphocytes in vitro by Shosaiko-to derived phenolic metabolites. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25, 37–41. doi:10.1248/bpb.25.37
Lu, G., Tong, Z., Ding, Y., Liu, J., Pan, Y., Gao, L., et al. (2016). Aspirin protects against acinar cells necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis in mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 6089430. doi:10.1155/2016/6089430
Lu, Y., Shan, L., Cheng, X., and Zhu, X. L. (2024). Exploring the mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of butein in colorectal cancer using network pharmacology and single-cell RNA sequencing data. J. Gene Med. 26, e3628. doi:10.1002/jgm.3628
Lu, Y. T., Xiao, Y. F., Li, Y. F., Li, J., Nan, F. J., and Li, J. Y. (2019). Sulfuretin protects hepatic cells through regulation of ROS levels and autophagic flux. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 40, 908–918. doi:10.1038/s41401-018-0193-5
Ma, T. J., Lan, D. H., He, S. Z., Ye, Z., Li, P., Zhai, W., et al. (2018). Nrf2 protects human lens epithelial cells against H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative and ER stress: the ATF4 may be involved. Exp. Eye Res. 169, 28–37. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2018.01.018
Madden, S. K., and Itzhaki, L. S. (2020). Structural and mechanistic insights into the Keap1-Nrf2 system as a route to drug discovery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom 1868, 140405. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140405
Menegon, S., Columbano, A., and Giordano, S. (2016). The dual roles of NRF2 in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 22, 578–593. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2016.05.002
Mizushima, N., and Hara, T. (2006). Intracellular quality control by autophagy: how does autophagy prevent neurodegeneration? Autophagy 2, 302–304. doi:10.4161/auto.2945
Mohan, S., and Gupta, D. (2018). Crosstalk of toll-like receptors signaling and Nrf2 pathway for regulation of inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 108, 1866–1878. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.019
Nguyen, T., Sherratt, P. J., Huang, H. C., Yang, C. S., and Pickett, C. B. (2003). Increased protein stability as a mechanism that enhances Nrf2-mediated transcriptional activation of the antioxidant response element. Degradation of Nrf2 by the 26 S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 4536–4541. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207293200
Ni, B., Liu, Y., Gao, X., Cai, M., Fu, J., Yin, X., et al. (2022). Isoliquiritigenin attenuates emodin-induced hepatotoxicity in vivo and in vitro through Nrf2 pathway. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 261, 109430. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109430
O'mealey, G. B., Plafker, K. S., Berry, W. L., Janknecht, R., Chan, J. Y., and Plafker, S. M. (2017). A PGAM5-KEAP1-Nrf2 complex is required for stress-induced mitochondrial retrograde trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 130, 3467–3480. doi:10.1242/jcs.203216
Ooi, B. K., Chan, K. G., Goh, B. H., and Yap, W. H. (2018). The role of natural products in targeting cardiovascular diseases via Nrf2 pathway: novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1308. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01308
Panieri, E., Buha, A., Telkoparan-Akillilar, P., Cevik, D., Kouretas, D., Veskoukis, A., et al. (2020). Potential applications of NRF2 modulators in cancer therapy. Antioxidants (Basel) 9, 193. doi:10.3390/antiox9030193
Panigrahi, G. K., Suthar, M. K., Verma, N., Asthana, S., Tripathi, A., Gupta, S. K., et al. (2015). Investigation of the interaction of anthraquinones of Cassia occidentalis seeds with bovine serum albumin by molecular docking and spectroscopic analysis: correlation to their in vitro cytotoxic potential. Food Res. Int. 77, 368–377. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2015.08.022
Papp, D., Lenti, K., Módos, D., Fazekas, D., Dúl, Z., Türei, D., et al. (2012). The NRF2-related interactome and regulome contain multifunctional proteins and fine-tuned autoregulatory loops. FEBS Lett. 586, 1795–1802. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.016
Park, S. M., Lee, J. R., Ku, S. K., Cho, I. J., Byun, S. H., Kim, S. C., et al. (2016). Isoliquiritigenin in licorice functions as a hepatic protectant by induction of antioxidant genes through extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated NF-E2-related factor-2 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Nutr. 55, 2431–2444. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1051-6
Paterni, I., Bertini, S., Granchi, C., Tuccinardi, T., Macchia, M., Martinelli, A., et al. (2015). Highly selective salicylketoxime-based estrogen receptor β agonists display antiproliferative activities in a glioma model. J. Med. Chem. 58, 1184–1194. doi:10.1021/jm501829f
Pi, J., Bai, Y., Reece, J. M., Williams, J., Liu, D., Freeman, M. L., et al. (2007). Molecular mechanism of human Nrf2 activation and degradation: role of sequential phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 42, 1797–1806. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.001
Pietsch, E. C., Chan, J. Y., Torti, F. M., and Torti, S. V. (2003). Nrf2 mediates the induction of ferritin H in response to xenobiotics and cancer chemopreventive dithiolethiones. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 2361–2369. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210664200
Pouremamali, F., Pouremamali, A., Dadashpour, M., Soozangar, N., and Jeddi, F. (2022). An update of Nrf2 activators and inhibitors in cancer prevention/promotion. Cell Commun. Signal 20, 100. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-00906-3
Prasanna, P. L., Renu, K., and Valsala Gopalakrishnan, A. (2020). New molecular and biochemical insights of doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 250, 117599. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117599
Pugazhendhi, A., Edison, T., Velmurugan, B. K., Jacob, J. A., and Karuppusamy, I. (2018). Toxicity of Doxorubicin (Dox) to different experimental organ systems. Life Sci. 200, 26–30. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.023
Qiao, H., Zhang, X., Wang, T., Liang, L., Chang, W., and Xia, H. (2014). Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and bioavailability of isoliquiritigenin after intravenous and oral administration. Pharm. Biol. 52, 228–236. doi:10.3109/13880209.2013.832334
Rabinowich, L., and Shibolet, O. (2015). Drug induced steatohepatitis: an uncommon culprit of a common disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 168905. doi:10.1155/2015/168905
Radovits, T., Bömicke, T., Kökény, G., Arif, R., Loganathan, S., Kécsán, K., et al. (2009). The phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor vardenafil improves cardiovascular dysfunction in experimental diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 156, 909–919. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00098.x
Ramadan, M. A., Kamel, M. S., Ohtani, K., Kasai, R., and Yamasaki, K. (2000). Minor phenolics from Crinum bulbispermum bulbs. Phytochemistry 54, 891–896. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)00184-9
Rehman, M., Chaudhary, R., Rajput, S., Agarwal, V., Kaushik, A. S., Srivastava, S., et al. (2023). Butein ameliorates chronic stress induced atherosclerosis via targeting anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic and BDNF pathways. Physiol. Behav. 267, 114207. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2023.114207
Renu, K., K, B. S., Parthiban, S., S, S., George, A., P, B. T., et al. (2019). Elevated lipolysis in adipose tissue by doxorubicin via PPARα activation associated with hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 843, 162–176. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.11.018
Rushworth, S. A., Macewan, D. J., and O'connell, M. A. (2008). Lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 and heme oxygenase-1 protects against excessive inflammatory responses in human monocytes. J. Immunol. 181, 6730–6737. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.6730
Santarino, I. B., Viegas, M. S., Domingues, N. S., Ribeiro, A. M., Soares, M. P., and Vieira, O. V. (2017). Involvement of the p62/NRF2 signal transduction pathway on erythrophagocytosis. Sci. Rep. 7, 5812. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-05687-1
Sarma, J. V., and Ward, P. A. (2011). Oxidants and redox signaling in acute lung injury. Compr. Physiol. 1, 1365–1381. doi:10.1002/cphy.c100068
Shaw, P., and Chattopadhyay, A. (2020). Nrf2-ARE signaling in cellular protection: mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms. J. Cell Physiol. 235, 3119–3130. doi:10.1002/jcp.29219
Shelton, L. M., Lister, A., Walsh, J., Jenkins, R. E., Wong, M. H., Rowe, C., et al. (2015). Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analyses uncover regulatory roles of Nrf2 in the kidney. Kidney Int. 88, 1261–1273. doi:10.1038/ki.2015.286
Shi, F., Du, M., Wang, Q., Adu-Frimpong, M., Li, C., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Isoliquiritigenin containing PH sensitive micelles for enhanced anti-colitis activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 113, 918–929. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2023.09.020
Shi, L., Wu, L., Chen, Z., Yang, J., Chen, X., Yu, F., et al. (2015). MiR-141 activates nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway via down-regulating the expression of Keap1 conferring the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 35, 2333–2348. doi:10.1159/000374036
Shi, W., Cao, X., Liu, Q., Zhu, Q., Liu, K., Deng, T., et al. (2022). Hybrid membrane-derived nanoparticles for isoliquiritin enhanced glioma therapy. Pharm. (Basel) 15, 1059. doi:10.3390/ph15091059
Shibata, T., Ohta, T., Tong, K. I., Kokubu, A., Odogawa, R., Tsuta, K., et al. (2008). Cancer related mutations in NRF2 impair its recognition by Keap1-Cul3 E3 ligase and promote malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 13568–13573. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806268105
Sidney, S., Quesenberry, C. P., Jaffe, M. G., Sorel, M., Nguyen-Huynh, M. N., Kushi, L. H., et al. (2016). Recent trends in cardiovascular mortality in the United States and public Health goals. JAMA Cardiol. 1, 594–599. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2016.1326
Stachurska, A., Ciesla, M., Kozakowska, M., Wolffram, S., Boesch-Saadatmandi, C., Rimbach, G., et al. (2013). Cross-talk between microRNAs, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2, and heme oxygenase-1 in ochratoxin A-induced toxic effects in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 57, 504–515. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201200456
Stewart, D., Killeen, E., Naquin, R., Alam, S., and Alam, J. (2003). Degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and stabilization by cadmium. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 2396–2402. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209195200
Straub, I., Krügel, U., Mohr, F., Teichert, J., Rizun, O., Konrad, M., et al. (2013). Flavanones that selectively inhibit TRPM3 attenuate thermal nociception in vivo. Mol. Pharmacol. 84, 736–750. doi:10.1124/mol.113.086843
Sun, F., Shen, H., Liu, Q., Chen, Y., Guo, W., Du, W., et al. (2023). Powerful synergy of traditional Chinese medicine and aggregation-induced emission-active photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 17, 18952–18964. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c04342
Sun, X., Jiang, X., Li, X., Qi, Z., and Lu, Y. (2022). Sulfuretin exerts anti-depressive effects in the lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive mouse models. Physiol. Behav. 250, 113800. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2022.113800
Sun, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Liu, B., Zhu, S., Zhu, L., et al. (2019). Licorice isoliquiritigenin-encapsulated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for osteoclast inhibition and bone loss prevention. Theranostics 9, 5183–5199. doi:10.7150/thno.33376
Suzuki, T., Muramatsu, A., Saito, R., Iso, T., Shibata, T., Kuwata, K., et al. (2019). Molecular mechanism of cellular oxidative stress sensing by Keap1. Cell Rep. 28, 746–758. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.047
Tang, Z., Chen, Z., Guo, M., Peng, Y., Xiao, Y., Guan, Z., et al. (2024). NRF2 deficiency promotes ferroptosis of astrocytes mediated by oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 7517–7533. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04023-9
Tebay, L. E., Robertson, H., Durant, S. T., Vitale, S. R., Penning, T. M., Dinkova-Kostova, A. T., et al. (2015). Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 88, 108–146. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.021
Tian, H., Xiong, Y., Zhang, Y., Leng, Y., Tao, J., Li, L., et al. (2021). Activation of NRF2/FPN1 pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by regulating iron homeostasis and ferroptosis. Cell Stress Chaperones 27, 149–164. doi:10.1007/s12192-022-01257-1
Tonelli, C., Chio, I. I. C., and Tuveson, D. A. (2018). Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal 29, 1727–1745. doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7342
Torrente, L., Sanchez, C., Moreno, R., Chowdhry, S., Cabello, P., Isono, K., et al. (2017). Crosstalk between NRF2 and HIPK2 shapes cytoprotective responses. Oncogene 36, 6204–6212. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.221
Tsai, C. W., Lin, C. Y., and Wang, Y. J. (2011). Carnosic acid induces the NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 expression in rat clone 9 cells through the p38/nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 pathway. J. Nutr. 141, 2119–2125. doi:10.3945/jn.111.146779
Tungalag, T., Park, K. W., and Yang, D. K. (2022). Butein ameliorates oxidative stress in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts through activation of the NRF2 signaling pathway. Antioxidants (Basel) 11, 1430. doi:10.3390/antiox11081430
Valko, M., Leibfritz, D., Moncol, J., Cronin, M. T., Mazur, M., and Telser, J. (2007). Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 39, 44–84. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001
Van Jaarsveld, M. T., Helleman, J., Boersma, A. W., Van Kuijk, P. F., Van Ijcken, W. F., Despierre, E., et al. (2013). miR-141 regulates KEAP1 and modulates cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 32, 4284–4293. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.433
Varì, R., D'archivio, M., Filesi, C., Carotenuto, S., Scazzocchio, B., Santangelo, C., et al. (2011). Protocatechuic acid induces antioxidant/detoxifying enzyme expression through JNK-mediated Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. J. Nutr. Biochem. 22, 409–417. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.03.008
Vogelmeier, C. F., Criner, G. J., Martinez, F. J., Anzueto, A., Barnes, P. J., Bourbeau, J., et al. (2017). Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report. GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 195, 557–582. doi:10.1164/rccm.201701-0218PP
Wakabayashi, N., Dinkova-Kostova, A. T., Holtzclaw, W. D., Kang, M. I., Kobayashi, A., Yamamoto, M., et al. (2004). Protection against electrophile and oxidant stress by induction of the phase 2 response: fate of cysteines of the Keap1 sensor modified by inducers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 2040–2045. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307301101
Wang, G., Yu, Y., Wang, Y. Z., Yin, P. H., Xu, K., and Zhang, H. (2020a). The effects and mechanisms of isoliquiritigenin loaded nanoliposomes regulated AMPK/mTOR mediated glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 48, 1231–1249. doi:10.1080/21691401.2020.1825092
Wang, H., Jia, X., Zhang, M., Cheng, C., Liang, X., Wang, X., et al. (2023a). Isoliquiritigenin inhibits virus replication and virus-mediated inflammation via NRF2 signaling. Phytomedicine 114, 154786. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154786
Wang, H., Liu, K., Geng, M., Gao, P., Wu, X., Hai, Y., et al. (2013). RXRα inhibits the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the Neh7 domain of NRF2. Cancer Res. 73, 3097–3108. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3386
Wang, J. B., Ma, Y. G., Zhang, P., Jin, C., Sun, Y. Q., Xiao, X. H., et al. (2009). Effect of processing on the chemical contents and hepatic and renal toxicity of rhubarb studied by canonical correlation analysis. Yao Xue Xue Bao 44, 885–890.
Wang, L., Wang, X., Kong, L., Wang, S., Huang, K., Wu, J., et al. (2021). Isoliquiritigenin alleviates LPS/D-GalN-induced acute liver failure by activating the PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway to reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 100, 108159. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108159
Wang, Z., Leng, Y., Tsai, L. K., Leeds, P., and Chuang, D. M. (2011). Valproic acid attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia: the roles of HDAC and MMP-9 inhibition. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 31, 52–57. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.195
Wang, Z., Li, W., Wang, X., Zhu, Q., Liu, L., Qiu, S., et al. (2023b). Isoliquiritigenin induces HMOX1 and GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in gallbladder cancer cells. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 136, 2210–2220. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000002675
Wang, Z. F., Liu, J., Yang, Y. A., and Zhu, H. L. (2020b). A review: the anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antibacterial properties of four kinds of licorice flavonoids isolated from licorice. Curr. Med. Chem. 27, 1997–2011. doi:10.2174/0929867325666181001104550
Ware, L. B., and Matthay, M. A. (2000). The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 342, 1334–1349. doi:10.1056/NEJM200005043421806
Wu, T., Zhao, F., Gao, B., Tan, C., Yagishita, N., Nakajima, T., et al. (2014). Hrd1 suppresses Nrf2-mediated cellular protection during liver cirrhosis. Genes Dev. 28, 708–722. doi:10.1101/gad.238246.114
Xiao, M., Wu, S., Cheng, Y., Ma, J., Luo, X., Chang, L., et al. (2022). Colon-specific delivery of isoliquiritigenin by oral edible zein/caseate nanocomplex for ulcerative colitis treatment. Front. Chem. 10, 981055. doi:10.3389/fchem.2022.981055
Xie, Y. J., Wang, Q. L., Adu-Frimpong, M., Liu, J., Zhang, K. Y., Xu, X. M., et al. (2019). Preparation and evaluation of isoliquiritigenin-loaded F127/P123 polymeric micelles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 45, 1224–1232. doi:10.1080/03639045.2019.1574812
Xiong, D., Hu, W., Ye, S. T., and Tan, Y. S. (2018a). Isoliquiritigenin alleviated the Ang II-induced hypertensive renal injury through suppressing inflammation cytokines and oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 506, 161–168. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.013
Xiong, Y., Chen, L., Fan, L., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., Qin, D., et al. (2018b). Free total rhubarb anthraquinones protect intestinal injury via regulation of the intestinal immune response in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 75. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00075
Xu, C., Yuan, X., Pan, Z., Shen, G., Kim, J. H., Yu, S., et al. (2006). Mechanism of action of isothiocyanates: the induction of ARE-regulated genes is associated with activation of ERK and JNK and the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 1918–1926. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0497
Xu, J., Xie, G., Yang, W., Wang, W., Zuo, Z., and Wang, W. (2021). Platelet-rich plasma attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via delivering miR-141-3p-containing exosomes. Cell Cycle 20, 1487–1499. doi:10.1080/15384101.2021.1949839
Yamamoto, T., Yoshimura, M., Yamaguchi, F., Kouchi, T., Tsuji, R., Saito, M., et al. (2004). Anti-allergic activity of naringenin chalcone from a tomato skin extract. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 68, 1706–1711. doi:10.1271/bbb.68.1706
Yang, E. J., Kim, M., Woo, J. E., Lee, T., Jung, J. W., and Song, K. S. (2016). The comparison of neuroprotective effects of isoliquiritigenin and its Phase I metabolites against glutamate-induced HT22 cell death. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 5639–5643. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.10.072
Yang, E. J., Park, G. H., and Song, K. S. (2013). Neuroprotective effects of liquiritigenin isolated from licorice roots on glutamate-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neuronal cells. Neurotoxicology 39, 114–123. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2013.08.012
Yang, K., Shen, Z., Zou, Y., and Gao, K. (2021). Rosmarinic acid inhibits migration, invasion, and p38/AP-1 signaling via miR-1225-5p in colorectal cancer cells. J. Recept Signal Transduct. Res. 41, 284–293. doi:10.1080/10799893.2020.1808674
Yao, D., Bao, L., Wang, S., Tan, M., Xu, Y., Wu, T., et al. (2024). Isoliquiritigenin alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1/SLC7a11/GPX4 axis in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 221, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.05.012
Yao, D., Shi, B., Wang, S., Bao, L., Tan, M., Shen, H., et al. (2022). Isoliquiritigenin ameliorates ischemia-induced myocardial injury via modulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 16, 1273–1287. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S362754
Yerra, V. G., Kalvala, A. K., and Kumar, A. (2017). Isoliquiritigenin reduces oxidative damage and alleviates mitochondrial impairment by SIRT1 activation in experimental diabetic neuropathy. J. Nutr. Biochem. 47, 41–52. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.05.001
Yu, D., Liu, X., Zhang, G., Ming, Z., and Wang, T. (2018). Isoliquiritigenin inhibits cigarette smoke-induced COPD by attenuating inflammation and oxidative stress via the regulation of the Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1001. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01001
Yu, R., Mandlekar, S., Lei, W., Fahl, W. E., Tan, T. H., and Kong, A. N. (2000). p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase negatively regulates the induction of phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes that detoxify carcinogens. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2322–2327. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.4.2322
Zeng, J., Chen, Y., Ding, R., Feng, L., Fu, Z., Yang, S., et al. (2017). Isoliquiritigenin alleviates early brain injury after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage via suppressing ROS- and/or NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. J. Neuroinflammation 14, 119. doi:10.1186/s12974-017-0895-5
Zenkov, N. K., Kozhin, P. M., Chechushkov, A. V., Martinovich, G. G., Kandalintseva, N. V., and Menshchikova, E. B. (2017). Mazes of Nrf2 regulation. Biochem. (Mosc) 82, 556–564. doi:10.1134/S0006297917050030
Zhang, K., Wang, Q., Yang, Q., Wei, Q., Man, N., Adu-Frimpong, M., et al. (2019a). Enhancement of oral bioavailability and anti-hyperuricemic activity of isoliquiritigenin via self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 218. doi:10.1208/s12249-019-1421-0
Zhang, L., Li, J., Ma, J., Chen, X., Chen, K., Jiang, Z., et al. (2016a). The relevance of Nrf2 pathway and autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells upon stimulation of reactive oxygen species. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 3897250. doi:10.1155/2016/3897250
Zhang, M., Huang, L., Teng, C., Wu, F., Ge, L., Shi, Y., et al. (2018a). Isoliquiritigenin provides protection and attenuates oxidative stress-induced injuries via the nrf2-ARE signaling pathway after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Res. 43, 2435–2445. doi:10.1007/s11064-018-2671-z
Zhang, M., Huang, L. L., Teng, C. H., Wu, F. F., Ge, L. Y., Shi, Y. J., et al. (2019b). Correction to: isoliquiritigenin provides protection and attenuates oxidative stress-induced injuries via the nrf2-ARE signaling pathway after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Res. 44, 510–511. doi:10.1007/s11064-019-02718-3
Zhang, M., Wu, Y. Q., Xie, L., Wu, J., Xu, K., Xiao, J., et al. (2018b). Isoliquiritigenin protects against pancreatic injury and intestinal dysfunction after severe acute pancreatitis via Nrf2 signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 936. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00936
Zhang, X., Hu, C., Kong, C. Y., Song, P., Wu, H. M., Xu, S. C., et al. (2020). FNDC5 alleviates oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via activating AKT. Cell Death Differ. 27, 540–555. doi:10.1038/s41418-019-0372-z
Zhang, X., Qiao, H., Chen, Y., Li, L., Xia, H., and Shi, Y. (2016b). Preparation, properties and preclinical pharmacokinetics of low molecular weight heparin-modified isoliquiritigenin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 15, 269–282.
Zhang, X. Y., Qiao, H., Ni, J. M., Shi, Y. B., and Qiang, Y. (2013). Preparation of isoliquiritigenin-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier and the in vivo evaluation in tumor-bearing mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 49, 411–422. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2013.04.020
Zhang, Y., Ren, J. S., Shi, J. F., Li, N., Wang, Y. T., Qu, C., et al. (2015). International trends in primary liver cancer incidence from 1973 to 2007. BMC Cancer 15, 94. doi:10.1186/s12885-015-1113-4
Zhao, J., Yu, Q. T., Li, P., Zhou, P., Zhang, Y. J., and Wang, W. (2008). Determination of nine active components in Radix Hedysari and Radix Astragali using capillary HPLC with diode array detection and MS detection. J. Sep. Sci. 31, 255–261. doi:10.1002/jssc.200700379
Zhao, Q. Q., Zhang, X. Y., Tang, X. F., and Qiao, H. (2021). A novel and oral colon targeted isoliquiritigenin delivery system: development, optimization, characterization and in vitro evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 66, 102777. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102777
Zhao, T. T., Xu, Y. Q., Hu, H. M., Gong, H. B., and Zhu, H. L. (2019). Isoliquiritigenin (ISL) and its formulations: potential antitumor agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 26, 6786–6796. doi:10.2174/0929867325666181112091700
Zheng, N., Schulman, B. A., Song, L., Miller, J. J., Jeffrey, P. D., Wang, P., et al. (2002). Structure of the Cul1-Rbx1-Skp1-F boxSkp2 SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. Nature 416, 703–709. doi:10.1038/416703a
Zhou, H., Wang, Y., You, Q., and Jiang, Z. (2020). Recent progress in the development of small molecule Nrf2 activators: a patent review (2017-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 30, 209–225. doi:10.1080/13543776.2020.1715365
Zhu, X., Liu, J., Chen, S., Xue, J., Huang, S., Wang, Y., et al. (2019a). Isoliquiritigenin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. BMC Neurosci. 20, 41. doi:10.1186/s12868-019-0520-x
Zhu, X., Liu, J., Huang, S., Zhu, W., Wang, Y., Chen, O., et al. (2019b). Neuroprotective effects of isoliquiritigenin against cognitive impairment via suppression of synaptic dysfunction, neuronal injury, and neuroinflammation in rats with kainic acid-induced seizures. Int. Immunopharmacol. 72, 358–366. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.028
Zhu, Y., Yang, Q., Liu, H., Song, Z., and Chen, W. (2020). Phytochemical compounds targeting on Nrf2 for chemoprevention in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 887, 173588. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173588
Glossary
ACSL4 Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4
ALF acute liver failure
ALI acute lung injury
AMI acute myocardial infarction
AMPK adenosine 5‘-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase
ARE antioxidant response element
Bax Bcl-2-associated X
Bcl-2 B-cell lymphoma-2
BTB Broad complex, Tramtrack and Bric-à-Brac domain
bZIP basic-region leucine zipper
Caspase-3 cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-3
CAT catalase
COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
COX-2 cyclooxygenase-2
CREB cAMP response element-binding protein
CS cigarette smoke
CTR C-terminal region
Cul3 cullin3
DGR double glycine repeat domain
ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase
FPM F127/P123 polymeric micelles
GBC Gallbladder cancer
GCLC glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit
GCLM glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit
GPX4 gluta thione peroxidase 4
GSH glutathione
GSH-PX glutathione peroxidase
GSK-3β glycogen synthase kinase-3β
GST glutathione S-transferase
HDAC histone deacetylase
HMGB1 high mobility group box 1 protein
HMOX1 haem oxygenase-1
HO-1 heme oxygenase-1
Iba-1 ionized calcium bindingadaptor molecule-1
IL-1β interleukin-1β
iNOS inducible nitric oxidesynthzase
ISL Isoliquiritigenin
ISL-HM-NPs Hybrid membrane-camouflaged Isoliquiritigenin nanoparticles
ISL-M Isoliquiritigenin pH-sensitive micelles
MSNs-ISL Isoliquiritigenin-encapsulated mesoporous silica nanoparticles
ISL-iRGD-NPs iRGD-modified lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with Isoliquiritigenin
ISL-NLC Isoliquiritigenin-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier
ISL-NLs Isoliquiritigenin loaded nanoliposomes
IVR intervening region
IκBα I-kappa-B-alpha
JNK c-Jun N-terminal kinase
Keap1 Kelch-like epichlorohydrin associated protein 1
LPS lipopolysaccharide
LPS/D-GalN LPS/D-galactosamine
MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase
MDA malondialdehyde
miRNA microRNA
MPO myeloperoxidase
MRP4 multidrug resistance protein 4
NF-κB nuclear factor kappa-B
NLRP3 NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3
NPs nanocomplexes
NQO1 nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate(NADPH) quinone oxidoreductase-1
NOX2 NADPH oxidase 2
Nrf2 nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2
NTR N-terminal domain
PD Parkinson’s disease
PERK protein kinase RNA–like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
PGC-1α peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator
PKC protein kinase C
RA rheumatoid arthritis
Rbx1 RING box protein 1
ROS reactive oxygen species
SAP severe acute pancreatitis
SCF SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein
SLC7A11 solute carrier family 7 member 11
SIRT1 silent information regulator 1
SMEDDS self-microemulsifying drug delivery system
SNEDDS self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems
SOD superoxide dismutase
SQSTM1 sequestosome 1
t-BHP tert-Butyl hydroperoxide
TBI traumatic brain injury
TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α
TGF-β transforming growth factor-β
VCAM-1 vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
β-TrCP β-transducin repeat-containing protein
4-HNE 4-hydroxynonenal
Keywords: Nrf2, Isoliquiritigenin, disorders, anti-oxidant, natural compound
Citation: Qiu M, Ma K, Zhang J, Zhao Z, Wang S, Wang Q and Xu H (2024) Isoliquiritigenin as a modulator of the Nrf2 signaling pathway: potential therapeutic implications. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1395735. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1395735
Received: 04 March 2024; Accepted: 24 September 2024;
Published: 09 October 2024.
Edited by:
Ping-Jyun Sung, National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium, TaiwanReviewed by:
Zeba Farooqui, University of Illinois Chicago, United StatesNaureen Fatima, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, United States
Copyright © 2024 Qiu, Ma, Zhang, Zhao, Wang, Wang and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing Wang, cV93YW5ncGhhQHhpeWkuZWR1LmNu; Hao Xu, eHVoYW9AeGl5aS5lZHUuY24=
†Present addresses: Hao Xu, Shaanxi Second Provincial People's Hospital, Xi'an, China
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Mangmang Qiu
Mangmang Qiu Kang Ma
Kang Ma Junfeng Zhang
Junfeng Zhang Zhaohua Zhao1
Zhaohua Zhao1 Qing Wang
Qing Wang