
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol., 31 August 2023
Sec. Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1274075
This article is part of the Research TopicEditor's Feature: Negative findings in Pharmacogenetics and PharmacogenomicsView all 8 articles
This article is a correction to:
CYP3A genetic variation and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and candidate gene study
A Corrigendum on
CYP3A genetic variation and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and candidate gene study
by McEvoy L, Cliff J, Carr DF, Jorgensen A, Lord R and Pirmohamed M (2023). Front. Pharmacol. 14:1178421. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1178421
In the published article, there was an error in the legend and artwork for Figure 2 as published. Additional information relating to variant carriage or non-carriage needed. Forest Plot data was incorrectly reported. The corrected Figure 2 and its caption appears below.
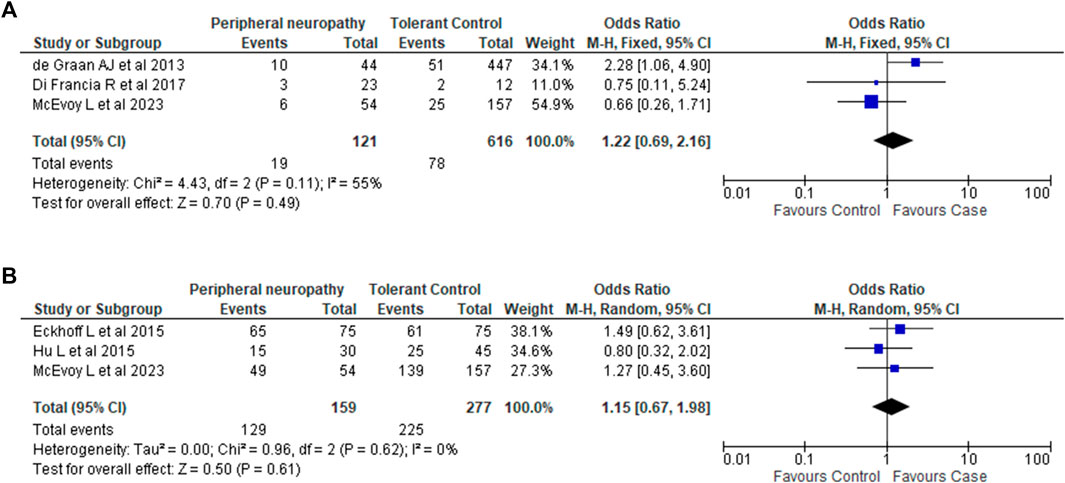
FIGURE 2. Association between CYP3A4*22 and CYP3A5*3 variants and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy. (A). Association between CYP3A4*22 and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy. Analysis of *22 carriage (*1/*22 and *22/*22) vs. non-carriage (*1/*1). Note: The phenotype definition for cases in Di Francia et al. (2017) differed from our phenotype definition of Grade 2 PN and above. Di Francia et al. (2017) considered Grade 1 and above as cases. (B). Association between CYP3A5*3 and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy. Analysis of *3 homozygous carriage (*3/*3) vs. non-carriage and heterozygous carriage (*1/*1 and *1/*3).
In the published article, there was an error. Meta-analysis data from Figure 2 was incorrectly reported in the Results.
A correction has been made to 3 Results, 3.4 Meta-analysis, paragraphs 2 and 3. These sentences previously stated:
“For CYP3A4*22, sufficient data was available from 2 studies (de Graan et al., 2013; Di Francia et al., 2017). Combining this with the data we generated showed that there was no association between CYP3A4*22 and PN (OR 1.1; 95% CI 0.62-1.97; I2 42%; p = 0.74).
For CYP3A5*3, sufficient data was available from 2 studies (Eckhoff et al., 2015a; Hu et al., 2016). Combining these two studies with the data from our candidate gene analysis again showed no association between CYP3A5*3 and PN (OR 0.99; 95% CI 0.57-1.71; I2 = 0%; p = 0.97).”
The corrected sentences appear below:
“For CYP3A4*22, sufficient data was available from 2 studies (de Graan et al., 2013; Di Francia et al., 2017). Combining this with the data we generated showed that there was no association between CYP3A4*22 and PN (OR 1.22; 95% CI 0.69–2.16; I2 55%; p = 0.49).
For CYP3A5*3, sufficient data was available from 2 studies (Eckhoff et al., 2015a; Hu et al., 2016). Combining these two studies with the data from our candidate gene analysis again showed no association between CYP3A5*3 and PN (OR 1.15; 95% CI 0.67–1.98; I2 = 0%; p = 0.61).”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: chemotherapy, cytochrome P450, peripheral neuropathy, personalised medicine, pharmacogenetics
Citation: McEvoy L, Cliff J, Carr DF, Jorgensen A, Lord R and Pirmohamed M (2023) Corrigendum: CYP3A genetic variation and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and candidate gene study. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1274075. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1274075
Received: 07 August 2023; Accepted: 15 August 2023;
Published: 31 August 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Luis Abel Quiñones, University of Chile, ChileCopyright © 2023 McEvoy, Cliff, Carr, Jorgensen, Lord and Pirmohamed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Laurence McEvoy, bC5tY2V2b3lAbGl2ZXJwb29sLmFjLnVr; Munir Pirmohamed, bXVuaXJwQGxpdmVycG9vbC5hYy51aw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.