
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 09 June 2023
Sec. Renal Pharmacology
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1207268
This article is a correction to:
Phyllanthus Niruri L. Exerts Protective Effects Against the Calcium Oxalate-Induced Renal Injury via Ellgic Acid
 Mao-Ting Li1†
Mao-Ting Li1† Lu-Lu Liu1†
Lu-Lu Liu1† Qi Zhou1†
Qi Zhou1† Lin-Xi Huang1
Lin-Xi Huang1 Yu-Xuan Shi1
Yu-Xuan Shi1 Jie-Bin Hou2
Jie-Bin Hou2 Hong-Tao Lu3
Hong-Tao Lu3 Bing Yu4
Bing Yu4 Wei Chen1*
Wei Chen1* Zhi-Yong Guo1*
Zhi-Yong Guo1*A Corrigendum on
Phyllanthus niruri L. exerts protective effects against the calcium oxalate-induced renal injury via ellgic acid
by Li M-T, Liu L-L, Zhou Q, Huang L-X, Shi Y-X, Hou J-B, Lu H-T, Yu B, Chen W and Guo Z-Y (2022). Front. Pharmacol. 13:891788. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.891788
In the published article, there were errors in Figure 4A and Figure 5D as published In Figure 4A, the concentration unit of EA in the column chart is marked as “mM”, while the correct concentration unit in the text is “μM”. In Figure 5D (Con/SQLE) panels, due an error had been made in the labelling of the original images, the immunohistochemical images of the Con/SQLE groups were incorrectly selected. We revised the semi-quantitative histograms of the positive expression area of HMGCS1, SCD and SQLE in Figure 5D in order to present the results more clearly. The corrected Figure 4 and Figure 5 and their caption appear below.
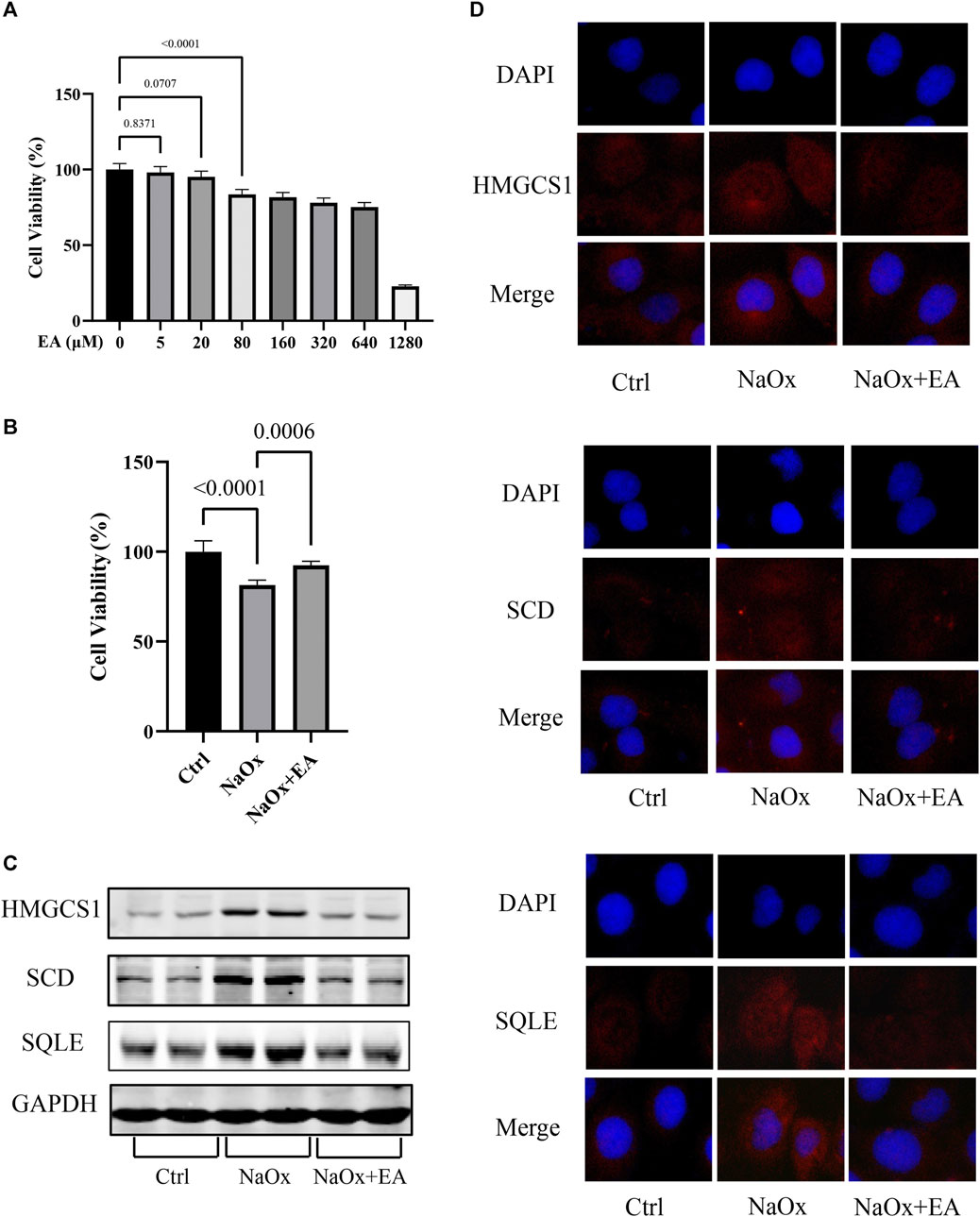
FIGURE 4. Ellagic acid protects NaOx-induced injury in cells and reduces the expression of SQLE, HMGCS1, and SCD (A) The cytotoxicity of ellagic acid on HK-2 cells determined by the CCK8 assay (B) The cytotoxicity of ellagic acid on NaOx treated HK-2 cells determined by the CCK8 assay (C) The expression of SQLE, HMGCS1, and SCD by Western blot in the control group (Ctrl), sodium oxalate group (NaOx), and ellagic acid treatment group (NaOx + EA) (D) Cells were analyzed by immunocytochemistry (100X) in the control group (Ctrl), sodium oxalate group (NaOx), and ellagic acid treatment group (NaOx + EA).
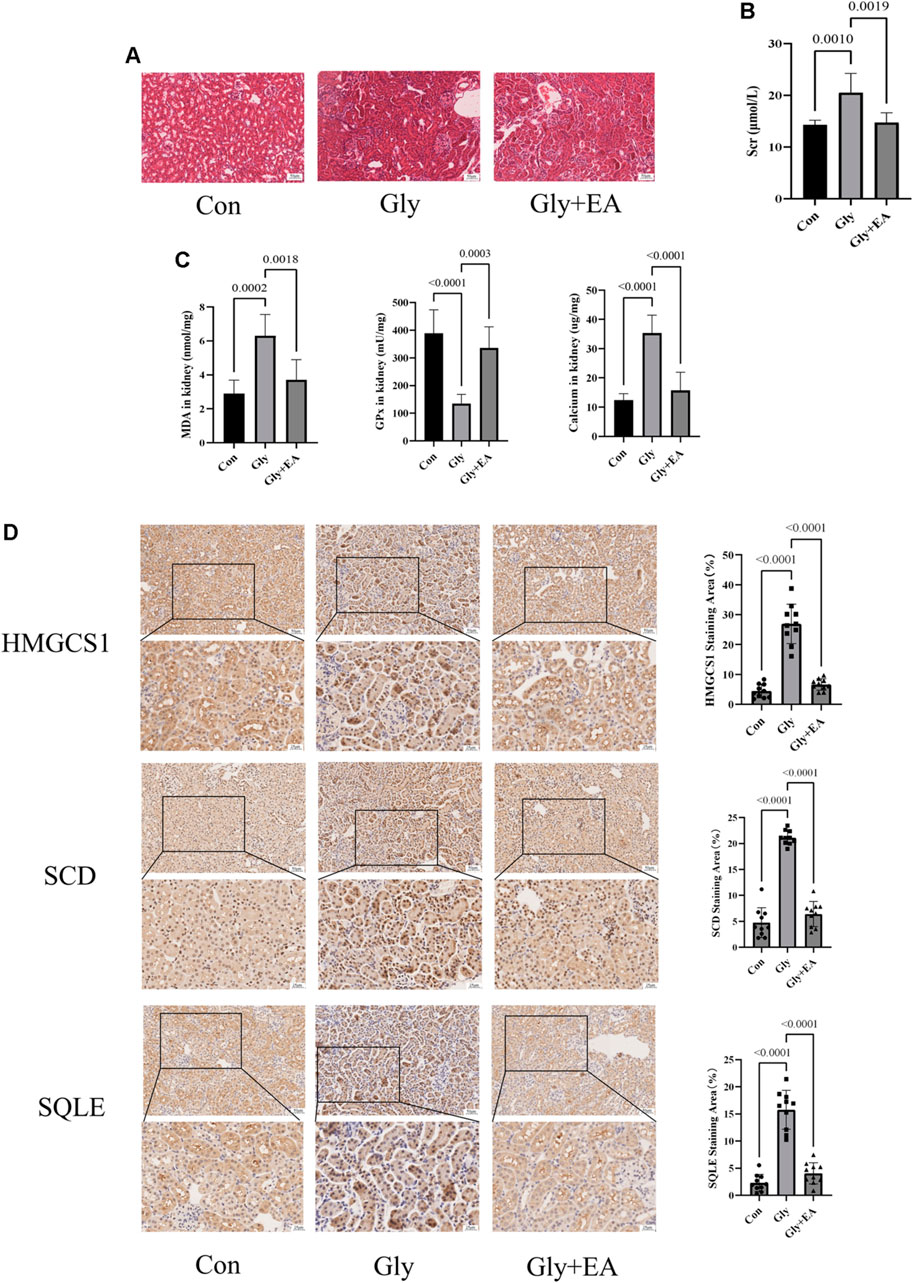
FIGURE 5. Ellagic acid protects calcium oxalate-induced renal injury in mice and reduces the expression of SQLE, HMGCS1, and SCD (A) Representative light microscopy images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidneys from the control group (Con), glyoxylate-induced CaOx group (Gly), and ellagic acid treatment group (Gly + EA) (magnification, ×200; scale bar = 50 μm) (B) Serum creatinine level in control group (Con), glyoxylate-induced CaOx group (Gly), and ellagic acid treatment group (Gly + EA) (C) The GPx activities, MDA, and total calcium content in control group (Con), glyoxylate-induced CaOx group (Gly), and ellagic acid treatment group (Gly + EA) (D) Expression of SCD, HMGCS1, and SQLE were analyzed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) (left) Representative light microscopy images of IHC staining of kidney of mice (magnification, ×200; scale bar = 50 μm (up) and 25 μm (down)) (right) Semi-quantitative score of SCD, HMGCS1, and SQLE.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Phyllanthus niruri L., calcium oxalate-induced renal injury, network pharmacology, ellagic acid, lipid nephrotoxicity
Citation: Li M-T, Liu L-L, Zhou Q, Huang L-X, Shi Y-X, Hou J-B, Lu H-T, Yu B, Chen W and Guo Z-Y (2023) Corrigendum: Phyllanthus niruri L. exerts protective effects against the calcium oxalate-induced renal injury via ellgic acid. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1207268. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1207268
Received: 17 April 2023; Accepted: 01 June 2023;
Published: 09 June 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Ying-Yong Zhao, Northwest University, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Li, Liu, Zhou, Huang, Shi, Hou, Lu, Yu, Chen and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Chen, d3VqaWFuZzAyQDE2My5jb20=; Zhi-Yong Guo, ZHJndW96aGl5b25nQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.