- 1Department of Biochemistry, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India
- 2School of Biomedical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India
A Corrigendum on
Effect of chlorogenic acid supplementation in MPTP-intoxicated mouse
by Singh SS, Rai SN, Birla H, Zahra W, Kumar G, Gedda MR, Tiwari N, Patnaik R, Singh RK, Singh SP (2018). Front Pharmacol. 6:9757. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00757
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 8 as published. The figure panels in Figure 8 were erroneously duplicated. The corrected Figure 8 and its caption appear below.
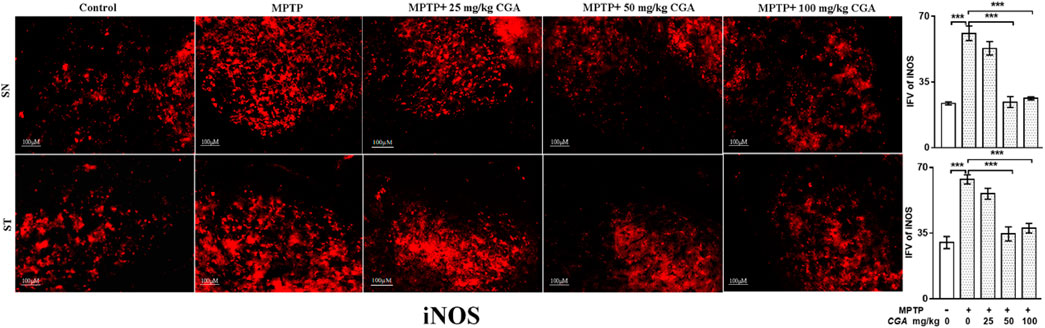
FIGURE 8. IHC of iNOS in the SN and striatum of mice. With 10× magnifications after staining. The increased expression of iNOS in the SN and striatum was found in the MPTP-treated mice compared to control mice, whereas CGA supplementation reduced the expression of iNOS in mice compared with MPTP-intoxicated mice. Values are expressed as mean SEM (n = 3). p < 0.05, ;p < 0.01, and p < 0.001. CGA, chlorogenic acid; MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; SN, substantia nigra; ST, striatum; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; SEM, standard error of mean; IFV, integrated fluorescent value.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: chlorogenic acid, Parkinson’s disease, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, dopaminergic neuron, substania nigra
Citation: Singh SS, Rai SN, Birla H, Zahra W, Kumar G, Gedda MR, Tiwari N, Patnaik R, Singh RK and Singh SP (2023) Corrigendum: Effect of chlorogenic acid supplementation in MPTP-intoxicated mouse. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1145172. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1145172
Received: 15 January 2023; Accepted: 24 January 2023;
Published: 02 February 2023.
Edited by:
Jacob Raber, Oregon Health and Science University, United StatesReviewed by:
Charles K. Meshul, Veterans Hospital Portland, United StatesMuzamil Ahmad, Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (CSIR), India
Copyright © 2023 Singh, Rai, Birla, Zahra, Kumar, Gedda, Tiwari, Patnaik, Singh and Singh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Surya P. Singh, c3VyeWFzaW5naGJodTE2QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†Present addressRanjana Patnaik, School of Biomedical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India
 Saumitra S. Singh1
Saumitra S. Singh1