
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 21 November 2022
Sec. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Pharmacology
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1075874
This article is a correction to:
Wenshen-Jianpi prescription, a Chinese herbal medicine, improves visceral hypersensitivity in a rat model of IBS-D by regulating the MEK/ERK signal pathway
 Tianyuan Jiang1,2†
Tianyuan Jiang1,2† Ran Niu1,2†
Ran Niu1,2† Qian Liu1,2†
Qian Liu1,2† Yuhan Fu3
Yuhan Fu3 Xiaoying Luo1,2
Xiaoying Luo1,2 Tao Zhang1,2
Tao Zhang1,2 Baoqi Wu1,2
Baoqi Wu1,2 Juan Han4
Juan Han4 Yang Yang1,2
Yang Yang1,2 Xiaolan Su1,2
Xiaolan Su1,2 Jiande D. Z. Chen5
Jiande D. Z. Chen5 Gengqing Song6*
Gengqing Song6* Wei Wei1,2*
Wei Wei1,2*by Jiang T, Niu R, Liu Q, Fu Y, Luo X, Zhang T, Wu B, Han J, Yang Y, Su X, Chen JDZ, Song G and Wei W (2022). Front. Pharmacol. 13:955421. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.955421
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2A as published. The version that was published was an old pre-review version. The corrected Figure 2A appears below:
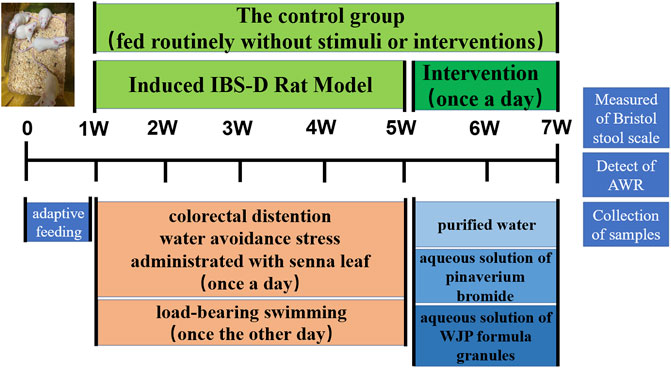
FIGURE 2. Detailed procedures for the experiments and their general conditions. (A) Protocol diagram of the time course involved in the experimental procedures of the IBS-D rat model induced and the intervention.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: rat model of IBS-D, visceral hypersensitivity, Chinese herbal medicine, colon, hippocampus, MEK/ERK signal pathway
Citation: Jiang T, Niu R, Liu Q, Fu Y, Luo X, Zhang T, Wu B, Han J, Yang Y, Su X, Chen JDZ, Song G and Wei W (2022) Corrigendum: Wenshen-Jianpi prescription, a Chinese herbal medicine, improves visceral hypersensitivity in a rat model of IBS-D by regulating the MEK/ERK signal pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13:1075874. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1075874
Received: 21 October 2022; Accepted: 04 November 2022;
Published: 21 November 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Mingyu Sun, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Jiang, Niu, Liu, Fu, Luo, Zhang, Wu, Han, Yang, Su, Chen, Song and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gengqing Song, c29uZ2dhdmluMjAxMEBnbWFpbC5jb20=; Wei Wei, c3h4dHl5QHNpbmEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.