
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
EDITORIAL article
Front. Pharmacol. , 16 December 2022
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1074511
This article is part of the Research Topic Edible and Medicinal Plants: From Ethnopharmacological Practices to Interdisciplinary Approaches and Regulations View all 18 articles
Editorial on the Research Topic
Edible and medicinal plants: From ethnopharmacological practices to interdisciplinary approaches and regulations
The investigation on plants that are both medicinal and edible is rooted in different ethno-medicinal systems (Yao et al.) Emerging diseases and health issues, lifestyle and diet changes urge us in seeking novel bioactive substances and formulations from plant sources (Sofowora et al., 2013; Xia et al., 2021). Related study requires interdisciplinary approaches including pharmaceutical, food, medicinal, and plant sciences, and policy study on food and drug administration.
Along with the strong increase in the publication of medicine food homology study (Figure 1), research highlights can be observed from the recent publications, which cover the applications of medicine food homology to modern lifestyle related diseases and health concerns, active substances and groups, mushroom study, increasing strengthening on the concept of nutraceuticals, etc. However, there are still a lack of scientific understanding and investigations for active ingredients and their synergistic and networking effects, lack of clear boundary definition in medicinal use and functional use, lack of clear inclusion criteria and regulation policies in the related studies and products. It could be of interest and needs for the scientific community to consider topics such as the development of proper pharmacological and physiological models, the development of novel and practical active substance delivery systems, holistic evaluation of the short term and long-term effects of the plants and the phytoconstituents. Articles merging these topics and ethnopharmacology may be helpful in reaching an international consensus among scientific and industrial communities.
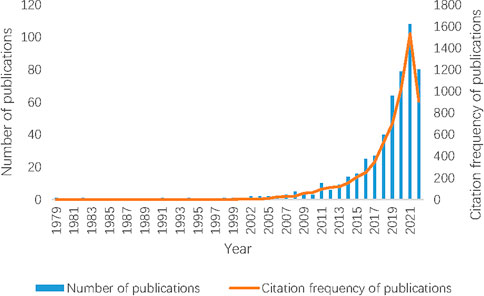
FIGURE 1. Number and citation frequency of medicine food homology related publications. Note: Data were collected from Web of Science Core Research Topic with the following search strategy: Topical Subject = (“Medicinal and Edible” OR “medicine food homology”) OR Title = (“Medicinal and Edible” OR “medicine food homology”) OR Abstract = (“Medicinal and Edible” OR “medicine food homology”), the language was English. A total of 508 papers were obtained, including 53 reviews and 455 articles. Figure only includes studies that met the inclusion criteria of the search strategy (Data as of Jul. 2022).
In this Research Topic, we have provided a discussion forum for the community, and received 47 full length article submissions, with 17 papers published, which covers cultivation and pharmacognosy of medicinal and food plants, ethno-pharmacological practices and pharmacological investigation, food function and safety evaluation of selected plants; identification of novel pharmacological and biological effects of plants, strategy on the development of pharmaceutical, nutraceuticals and functional products, reviews as well as general methodology and research advancement (Tables 1, 2).
This Research Topic provides a platform and community space for sharing and enlightening the state-of-art discovery and scientific understanding in edible and medicinal plants (Table 1). Efforts are expected for further explorations of this Research Topic in a global perspective with stronger networking. Despite of long-standing application in some cultural systems, the understanding and regulation on edible and medicinal plant are still various and in different approaches among food and drug regulatory authorities of different countries. Consensus on the definition and scope, research and evaluation methodology, and rational application and supervision of edible and medicinal plant are anticipated.
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
We would like to thank all the authors, reviewers and frontiers editorial team for their valuable input and contributions.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Sofowora, A., Ogunbodede, E., and Onayade, A. (2013). The role and place of medicinal plants in the strategies for disease prevention. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 10, 210–229. doi:10.4314/ajtcam.v10i5.2
Xia, L., Shi, Y., Su, J., Friedemann, T., Tao, Z., Lu, Y., et al. (2021). Shufeng Jiedu, a promising herbal therapy for moderate COVID-19:Antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, pathways of bioactive compounds, and a clinical real-world pragmatic study. Phytomedicine. 85, 153390. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153390
Keywords: edible plants, medicinal plants, pharmacological effect, health benefit, health product, regulation
Citation: Zhang X, Dias ACP and Lopes NP (2022) Editorial: Edible and medicinal plants: From ethnopharmacological practices to interdisciplinary approaches and regulations. Front. Pharmacol. 13:1074511. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1074511
Received: 19 October 2022; Accepted: 06 December 2022;
Published: 16 December 2022.
Edited by:
Javier Echeverria, University of Santiago, ChileReviewed by:
Dâmaris Silveira, University of Brasilia, BrazilCopyright © 2022 Zhang, Dias and Lopes. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoying Zhang, emhhbmdAYmlvLnVtaW5oby5wdA==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.