- Department of Pediatrics, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, United States
In individuals with cystic fibrosis (CF), lung hyper-inflammation starts early in life and is perpetuated by mucus obstruction and persistent bacterial infections. The continuous tissue damage and scarring caused by non-resolving inflammation leads to bronchiectasis and, ultimately, respiratory failure. Macrophages (MΦs) are key regulators of immune response and host defense. We and others have shown that, in CF, MΦs are hyper-inflammatory and exhibit reduced bactericidal activity. Thus, MΦs contribute to the inability of CF lung tissues to control the inflammatory response or restore tissue homeostasis. The non-resolving hyper-inflammation in CF lungs is attributed to an impairment of several signaling pathways associated with resolution of the inflammatory response, including the heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide (HO-1/CO) pathway. HO-1 is an enzyme that degrades heme groups, leading to the production of potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and bactericidal mediators, such as biliverdin, bilirubin, and CO. This pathway is fundamental to re-establishing cellular homeostasis in response to various insults, such as oxidative stress and infection. Monocytes/MΦs rely on abundant induction of the HO-1/CO pathway for a controlled immune response and for potent bactericidal activity. Here, we discuss studies showing that blunted HO-1 activation in CF-affected cells contributes to hyper-inflammation and defective host defense against bacteria. We dissect potential cellular mechanisms that may lead to decreased HO-1 induction in CF cells. We review literature suggesting that induction of HO-1 may be beneficial for the treatment of CF lung disease. Finally, we discuss recent studies highlighting how endogenous HO-1 can be induced by administration of controlled doses of CO to reduce lung hyper-inflammation, oxidative stress, bacterial infection, and dysfunctional ion transport, which are all hallmarks of CF lung disease.
Introduction
The hallmarks of cystic fibrosis (CF) lung disease are mucus obstruction, chronic hyper-inflammation, chronic infections, and excessive oxidative stress, which severely damage lung tissue over time and ultimately lead to lung failure. Several anti-inflammatory pathways are compromised in CF (Cantin et al., 2015), which further perpetuates lung inflammation. Despite the role of inflammation in CF lung disease, corticosteroids, or high-dose ibuprofen are the only approved long-term treatments for CF airway inflammation. Both treatments are often poorly tolerated (Mogayzel et al., 2013; Cantin et al., 2015). In addition, when treating CF lung disease, a fine balance must be maintained between dampening the pro-inflammatory response and preserving the host defense against microorganisms (Konstan et al., 2014). This situation calls for novel therapeutic targets, which allow a potent anti-inflammatory/antimicrobial host defense followed by restoration of lung tissue homeostasis.
One of the defective anti-inflammatory pathways in CF is the heme-oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide (HO-1/CO) signaling pathway. The stress response enzyme HO-1 catabolizes heme groups to CO and biliverdin, both strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents. CO also has potent bactericidal properties, and acts in a positive feedback loop to increase HO-1 expression. Due to these combined anti-inflammatory and bactericidal properties, modulation of this pathway is an attractive target in CF.
Here, we will discuss: (1) how the shortcomings of CF lung immunity perpetuate inflammatory signaling and poor bacterial clearance; (2) the role of the HO-1/CO signaling pathway; and (3) the potential of CO-based therapy to reduce lung hyper-inflammation, counteract oxidative stress, and improve bacterial clearance, ultimately restoring lung homeostasis in CF lung disease.
CF Lung Disease and Inflammation
Lung hyper-inflammation in CF patients starts early in life and is likely driven by accumulation of viscous mucus in the airways (Montgomery et al., 2017). Mucus airway obstruction and impaired mucociliarly clearance create a favorable environment for respiratory infections (Khan et al., 1995; Brennan et al., 2009; Sturges et al., 2010), which intensify the lung inflammatory response. In the early years, infections by Haemophilus influenza and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) are predominant. Over time, the CF airways become susceptible to chronic infections by the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) (Khan et al., 1995; Brennan et al., 2009; Sturges et al., 2010; Elborn, 2016). In addition to the increased bacterial burden, the epithelial cells and immune cells display altered immune sensing via pathogen- or danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs), which lead to uncontrolled inflammatory responses. This leads to excessive infiltration of neutrophils, which are impaired in clearing the ongoing infection. Furthermore, CF-affected neutrophils have altered apoptosis (Tirouvanziam et al., 2008) and increased neutrophil extracellular trap formation (Gray et al., 2018), which is accompanied by high levels of neutrophil elastase in the airways of CF patients (Garratt et al., 2015; Kanik et al., 2020). This vicious cycle of persistent infections and uncontrolled pro-inflammatory responses also causes severe oxidative stress through the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from neutrophils and CF epithelia, and the irreversible damage of lung tissues (Bonfield et al., 1995; Chmiel and Davis, 2003; Davis, 2006; Cantin et al., 2015; Elborn, 2016; Turnbull et al., 2020). The oxidative stress is worsened by the impaired efflux of chloride, bicarbonate, and other solutes (e.g., glutathione) (Galli et al., 2012).
The failure to efficiently resolve the inflammatory response contributes to the development of chronic hyper-inflammation in CF (Cantin et al., 2015; Roesch et al., 2018; Recchiuti et al., 2019). Indeed, resolution of lung inflammation is an active, tightly coordinated process, whereby counterregulatory mechanisms are induced to clear inflammatory cells from sites of infection or injury in order to restore tissue homeostasis. Successful resolution includes arrest of neutrophil tissue infiltration, apoptosis of neutrophils and their subsequent removal [e.g., via efferocytosis (Yurdagul et al., 2017)], dampening of pro-inflammatory signals, clearance of pathogens and cell debris, and initiation of tissue repair processes (Headland and Norling, 2015).
Macrophages (MΦs) play a critical role in maintaining lung tissue homeostasis. During an inflammatory response, they acquire different pro- or anti-inflammatory properties and tissue-reparative phenotypes. Upon recognition of pathogens, they shift toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype, recruiting other immune cells and initiating inflammation. As the inflammation progresses, MΦs not only phagocytose pathogens, but also clear apoptotic cells and cell debris from the lungs. With other signals from surrounding cells or from the pathogen, this efferocytosis transforms MΦs into an anti-inflammatory phenotype, thus limiting inflammation and promoting the resolution/termination of inflammation (Doran et al., 2020). Furthermore, in the later phases of lung injury, MΦs tightly coordinate parenchymal repair processes, which are essential for reestablishing tissue homeostasis. Due to these key roles, it is not surprising that many chronic lung inflammatory diseases such asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), CF (Bruscia and Bonfield, 2016a; Bruscia and Bonfield, 2016b), and pulmonary fibrosis (Misharin et al., 2017; Reyfman et al., 2019), are associated with abnormal MΦ behavior.
Monocytes/MΦs from CF patients are dysregulated at many levels. In vitro and ex vivo studies from patients with CF and animal models of the disease suggest that both inherited factors (lack of functional CFTR) and acquired factors (CF lung environment) contribute to this dysfunction. As a result, monocytes/MΦs fail to properly handle inflammatory triggers (PAMPs, DAMPs, cytokines, growth factors), struggle to resolve inflammation, and fail to clear dead cells, kill bacteria, and adapt to the environment (reviewed in Bruscia et al. [Bruscia and Bonfield, 2016a; Bruscia and Bonfield, 2016b)].
The exact mechanisms for the exaggerated and dysfunctional inflammatory response observed in CF are not fully understood. However, it appears that the fine balance between the pro- and anti-inflammatory regulatory pathways is disrupted, with heightened pro-inflammatory stimuli and reduced counter-regulatory response, which would ordinarily promote resolution of inflammation. Ibuprofen (Konstan et al., 1995), glucocorticosteroids (Ross et al., 2009), mucolytics (Paul et al., 2004), and antibiotics (Ratjen et al., 2012) are all treatments that have improved CF lung disease and are associated with a reduction in lung inflammation. However, there are concerns about using anti-inflammatory therapies in chronically infected CF patients. Indeed, blocking induction of inflammation may have immunosuppressive effects that compromise the host defense and thus worsen lung infections. This was observed in clinical studies assessing the effect of the LTB4-receptor antagonist BIIL 284, an inhibitor of neutrophil migration, in children and adults with CF. This study was terminated prematurely due to a significant increase in the frequency of pulmonary exacerbations (due to bacterial infections) in adult patients who received the treatment (Doring et al., 2014; Konstan et al., 2014).
The use of CFTR modulators, which correct mutant CFTR trafficking to the plasma membrane (correctors) and enhance its activity (potentiators), are now FDA-approved for most CF patients (Middleton et al., 2019). However, there are few long-term studies of their impact on immune response and monocyte/MΦs function. While Rowe et al. (2014) reported that the CFTR modulator VX-770 (Ivacaftor) did not reverse lung inflammation, other studies showed partial reduction of lung inflammation (Hisert et al., 2017). Ex vivo studies on monocytes and monocyte-derived MΦs from patients with CF suggest that Ivacaftor modulates the inflammatory response (Hisert et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018; Jarosz-Griffiths et al., 2020) and improves bacterial killing (Hisert et al., 2017; Riquelme et al., 2017; Barnaby et al., 2018). The newly approved triple combination CFTR modulator therapy elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) (Middleton et al., 2019) has shown great promise for many CF patients. However, its effect on the abnormal inflammatory response in CF has not been fully elucidated, and it is not known whether it will help control lung hyper-inflammation over the longer life expectancy achieved. Moreover, these therapies are not applicable for all mutations and, therefore, for all patients with CF. Thus, novel therapeutic approaches are needed that, in combination with CFTR modulators, will rescue the abnormal anti-inflammatory regulatory mechanisms and facilitate the resolution of the inflammatory response, while maintaining a potent antimicrobial host defense. Below, we discuss the HO-1/CO pathway, which facilitates anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities while strengthening the host’s bactericidal functions. This pathway is thus an attractive therapeutic target for CF.
HO-1 Function and Regulation
Heme oxygenases (HO) are enzymes that facilitate the degradation of heme, a ubiquitous molecular complex consisting of iron and tetrapyrrole protoporphyrin IX. The heme from the hemoglobin in red blood cells and myoglobin in muscles is involved in the transport and storage of oxygen, respectively. However, many other proteins also use a heme group for fundamental cellular processes. If released from proteins, an excess of free heme is highly toxic because it promotes oxidative stress (Biswas et al., 2014; Wegiel et al., 2015). HO enzymes thus play a crucial role in cells (Gozzelino et al., 2010). HO activity is represented by two separate isoforms: an inducible isoform HO-1 and a constitutively expressed isoform HO-2. A suspected third isozyme, HO-3, turned out to be a pseudogene derived from processed HO-2 transcripts (Mccoubrey et al., 1997). HO-1 and HO-2 are the products of distinct genes, hmox1 and hmox2, respectively. They differ in primary amino acid sequence, biochemical and biophysical properties (Cruse and Maines, 1988; Ryter and Choi, 2016). HO-1 is an integral membrane component of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Gottlieb et al., 2012), but it is also localized in plasma membrane caveolae (Kim et al., 2004), mitochondria (Converso et al., 2006), and nuclei (Biswas et al., 2014). HO-1 is undetectable under physiological conditions but is highly induced after exposure to a broad range of chemical and physical stimuli including heme, ultraviolet-A radiation, hydrogen peroxide, redox cycling compounds, heavy metals, hypoxia, hyperoxia, cytokines, hormones, growth factors, and microorganisms. HO‐1 is mainly induced in hepatic, endothelial, myeloid, and respiratory epithelial cells. One exception is the spleen, where constantly high levels of HO-1 ensure an efficient recycling of iron from senescent erythrocytes (Ryter et al., 2006). Monocytes/MΦs rely on abundant induction of the HO-1 for a controlled immune response and for potent bactericidal activity. In liver endothelial and epithelial cells HO-1 plays a critical anti-oxidant and pro-survival function in response to cellular stressors (Ryter et al., 2006). In contrast to HO-1, HO-2 is constitutively expressed in most tissues, including brain, testis, endothelial, and smooth muscle cells (Zakhary et al., 1996), and is refractory to HO-1 inducers (Maines et al., 1986). The inducible nature of HO-1 makes it an attractive target for drug discovery.
HO-1 catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the oxidative catabolism of heme groups. With the use of cytochrome P-450, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), and molecular oxygen, HO-1 catabolizes heme into equimolar amounts of carbon monoxide (CO), free iron (Fe2+), and biliverdin IXa. The cytoprotective effects of HO-1 are enhanced by its catabolites. Biliverdin is rapidly metabolized to bilirubin (a highly antioxidant compound) by the biliverdin reductase. The free iron, which can stimulate free radical formation, is promptly sequestered by ferritin and recycled for heme synthesis. Degradation of heme is the only mammalian pathway known to produce CO. This gaseous molecule is toxic at higher concentrations because it binds hemoglobin and thus prevents the transport of oxygen. However, at physiological concentrations, CO has strong cytoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and bactericidal properties (Figure 1) (Motterlini and Otterbein, 2010; Ryter et al., 2018).
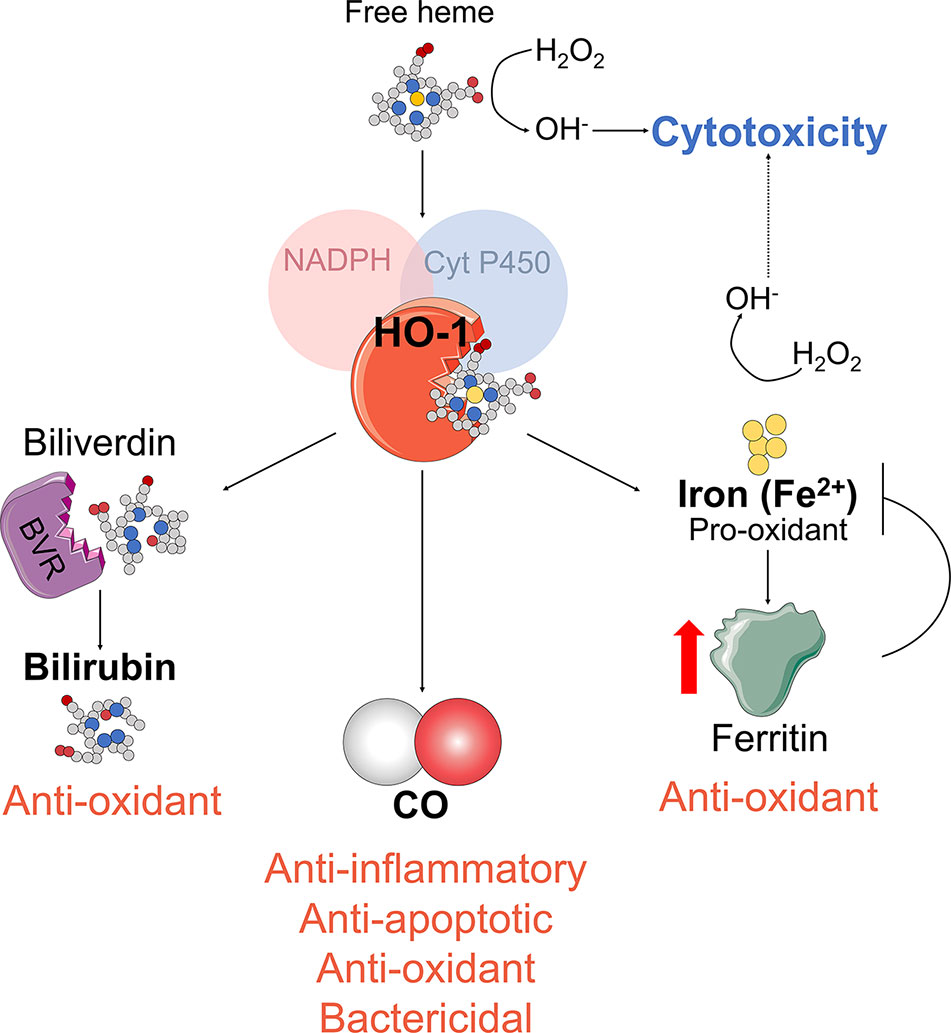
Figure 1 HO-1 enzymatic activity. HO-1 enzymatic activity generates biliverdin and releases carbon monoxide (CO) and Fe2+. Biliverdin is transformed into bilirubin by the biliverdin reductase (BVR). Fe2+ is sequestered by the iron storage protein ferritin.
The essential cytoprotective role of HO-1 has been demonstrated by the phenotype of HO-1-null mice (HO-1 KO), which display increased embryonic lethality, anemia, and chronic inflammatory disorders. Cells isolated from HO-1 KO animals are also more susceptible to oxidative stress (Poss and Tonegawa, 1997a; Poss and Tonegawa, 1997b). HO-1 KO animals display increased mortality after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration, which supports the importance of HO-1 in mediating protection during bacterial infection (Wiesel et al., 2000). Importantly, the phenotypical alterations in the uniquely observed case of human HO-1 deficiency are similar to those in HO-1 KO mice, with severe hemolytic anemia, endothelial degradation, reduced serum bilirubin, renal and hepatic iron accumulation, and a pro-inflammatory phenotype (Yachie et al., 1999).
The expression of HO-1 is regulated primarily at the transcriptional level via regulatory element sites localized at the 5′-untranslated region of the hmox1 gene promoter. These include binding sites for several prominent transcriptional factors (TFs), such as nuclear factor E2–related factor-2 (Nrf2) (Alam et al., 1999), activator protein-1 (AP-1) family (Alam and Den, 1992; Alam et al., 1999), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) (Lavrovsky et al., 1994), and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) (Lee et al., 1997). For a comprehensive review of HO-1 regulation, please refer to (Alam and Cook, 2007; Waza et al., 2018; Medina et al., 2020). Many of the TFs and signaling pathways involved in modulating HO-1 expression are dysregulated in CF cells, resulting in decreased HO-1 induction (discussed in HO-1 Dysregulation in CF).
Nrf2 is a major transcriptional regulator of HO-1 (Chan and Kan, 1999). At steady state, Nrf2 localizes in the cytoplasm of the cells, where it is inactivated when associated with its cytosolic repressor Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap1). Keap1 actively promotes Nrf2’s rapid degradation by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway to ensure low Nrf2 levels in the cell. Exposure to electrophilic or oxidative stresses causes a conformational change in Keap1, with the subsequent dissociation of Nrf2. Nrf2 then translocates into the nucleus, where it forms a heterodimer with small masculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma (Maf) proteins and binds to the antioxidant response elements (ARE) in the promoter region of genes coding for antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. These include HO-1, NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), and glutathione S transferases (GSTs), which all execute antioxidative functions in cells (Bryan et al., 2013). The Nrf2-mediated HO-1 expression is also finely regulated by TF BTB and CNC Homology 1 (Bach1), which also forms heterodimers with Maf and competes with Nrf2 for the binding sites in the hmox1 promoter region, thus suppressing HO-1 expression (Dhakshinamoorthy et al., 2005). Thus, HO-1 induction is highly regulated and requires the release of Nrf2 from Keap1, the inactivation of its competitor Bach1, and the availability of Maf to initiate transcriptional signaling (Ogawa et al., 2001; Bryan et al., 2013) (Figures 2A, B).
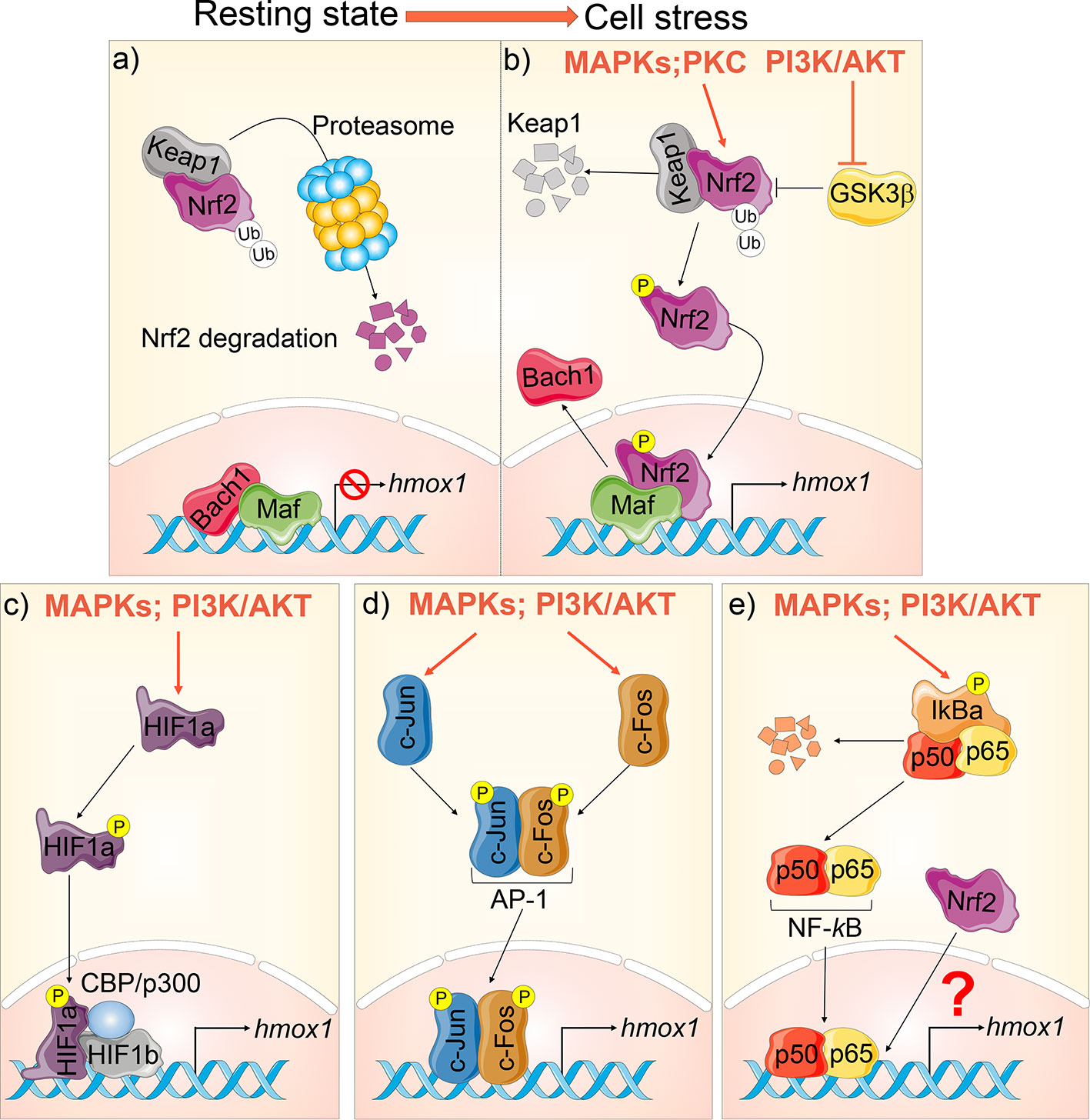
Figure 2 Hmox1 transcriptional regulation. (A) At steady state, Nrf2 is bound to Keap1 in the cytoplasm and targeted for proteasomal degradation. Bach‐1 is bound to Maf at the promoter region of the hmox1, suppressing its transcription. (B) During cellular stress, hmox1 expression is activated in several ways: mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) and protein kinase C (PKC) phosphorylate Nrf2. This stabilizes Nrf2, leading to its translocation into the nucleus. PI3K/AKT inhibits GSK3β. When activated, GSK3β facilitates the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Once in the nucleus, Nrf2 displaces Bach‐1 at the hmox1 promoter leading to transcription. (C) HIF-1 is a heterodimer composed of HIF-1α and HIF-1β. HIF-1α phosphorylation leads to its translocation to the nucleus and association to HIF-1β and CBP/p300, thus inducing hmox1 transcription. (D) Phosphorylation of c-Fos and c-Jun leads to their translocation to the nucleus and formation of the AP-1 complex, which induces hmox1 expression; (E) NF-κB is sequestered in the cytosol under basal conditions by the inhibitor IκB. Phosphorylation results in the proteasomal degradation of IĸB and the consequent release and nuclear translocation of NF-κB dimers (p50/p65) which targets hmox1 activation. A complex crosstalk between NF-κB and Nrf2 can also inhibit hmox1 transcription.
Functional binding sites for AP-1 (Alam et al., 1999), HIF-1α (Lee et al., 1997), and NF-kB (Lee et al., 1997) have been identified within the promoter region of hmox1 gene (details in Figures 2C–E). In response to hypoxia, HIF-1α is phosphorylated by the MAPK p38. This leads to its translocation to the nucleus, where it associates with HIF-1β, the transcriptional co-activator CREB-binding protein (CBP), and p300, thereby leading to transcription of HO-1 (Lee et al., 1997; Medina et al., 2020). Several studies have shown that NF-kB not only positively modulates HO-1 expression by directly binding to its promoter (Naidu et al., 2008; Rushworth et al., 2012), but it may also work as a negative regulator for HO-1 expression. Some of these conflicting data can be reconciled by the complex NF-κB crosstalk with Nrf2 in modulating HO-1 induction during specific cellular responses (Liu et al., 2008; Yu et al., 2011). For instance, NF-kB decreases the availability of CBP/p300 for Nrf2, thus preventing Nrf2 transcriptional activity (Liu et al., 2008). This is relevant for CF, where shifting the competitive binding of CBP/p300 in favor of Nrf2 (over NF-kB) leads to increased expression of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes and decreased cellular inflammation (Ziady et al., 2012). The molecular mechanisms underpinning the dynamic crosstalk between NF-κB and the Nrf2 are extensively reviewed in (Wardyn et al., 2015) and are still under investigation.
Post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications are also potential regulatory mechanisms for controlling HO-1 levels. A number of microRNAs (e.g., miR-24, miR-200c, miR-204, miR-211, miR-155, miR-378, miR-377, miR-217) directly regulate HO-1 levels by decreasing hmox1 messenger RNA stability or translation. Other miRNAs indirectly modulate HO-1 by affecting the expression of upstream regulatory factors, such as Nrf2, Keap1, and Bach1 [Review in (Cheng et al., 2013)]. The GT-microsatellite polymorphism, located in the proximal human hmox1 promoter region, also contributes to the regulation of HO-1 expression. These short GT repetitions increase HO-1 expression, which correlates with a reduced risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, chronic pulmonary emphysema, and other diseases (Exner et al., 2004).
Activation of several signaling cascades mediates induction of HO-1, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) superfamily (p38, ERK, and JNK), protein kinase C (PKC), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) (Figures 2B–E). Protein kinase C facilitates Nrf2 nuclear translocation by phosphorylation of Nrf2 at the Keap1 binding site freeing Nrf2 from Keap1 (Huang et al., 2002). MAPKs and PI3K/AKT can directly (via phosphorylation) or indirectly regulate transcription factors required for the HO-1 induction. The MAPKs and PI3K/AKT signaling cascades have been extensively investigated in the context of Nrf-2-dependent HO-1 activation. PI3K/AKT signaling can indirectly promote HO-1 transcription by inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β)-mediated phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Nrf2 (Bryan et al., 2013). Furthermore, PI3K/AKT signaling activation in response to oxidative stress results in actin polymerization and depolymerization, which promotes translocation of actin-bound Nrf2 into the nucleus (Kang et al., 2002).
HO-1 Dysregulation in CF
In CF, hmox1 has been reported to be a modifier gene, as a specific hmox1 allele correlated with improved lung function in pediatric CF patients chronically infected with P. aeruginosa (Park et al., 2011). On top of genetic variants, studies comparing nasal epithelial cells and blood cells of CF patients with healthy donors have revealed altered epigenetic modifications of the hmox1 gene (Magalhaes et al., 2017). An early study showed that the lungs of patients with CF have increased HO-1 expression compared to control lung resections from patients with cancer (Zhou et al., 2004). This is expected given the inflammatory environment of CF lungs. A better control would be tissues from patients with other lung inflammatory conditions. In the same study, the authors provided the first evidence for the beneficial effect of HO-1 in CF cells. Namely, overexpression of HO-1 in CF human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cell lines (IB3.1) led to potent cytoprotective properties against P. aeruginosa infections (Zhou et al., 2004). HO-1 expression in CF HBE cell lines (CFBE41o-) was decreased at baseline and its induction was hampered following stimulation by LPS or hypoxia compared with a HBE cell line control (Chillappagari et al., 2014; Chillappagari et al., 2020). This suggests that, while HO-1 can still be induced in the absence of CFTR, the amount produced may not be sufficient to provide beneficial effects. The lack of HO-1 correlates with an increased iron load (Chillappagari et al., 2014), that is also observed in lavages and lung tissues of CF patients (Stites et al., 1999; Ghio et al., 2013) and favors P. aeruginosa infections (Reid et al., 2002; Moreau-Marquis et al., 2008).
Several dysfunctional mechanisms may account for the blunted HO-1 induction in CF cells (Figure 3). Our group has demonstrated that HO-1 is inefficiently induced in human and murine CF MΦs in response to inflammatory or infectious triggers, which correlate with exaggerated inflammation and prolonged inflammatory signaling (Zhang et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2015; Di Pietro et al., 2017). We have also shown that the defective induction of HO-1 is due to blunted activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway downstream of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) activation in MΦs from CF mouse models and patients with CF. Alteration of this pathway decreases HO-1 expression and perpetuates the inflammatory response. In addition to decreased induction, the HO-1 cellular distribution is altered in CF-affected MΦs, thus diminishing its beneficial effect. In response to LPS, HO-1 normally translocate to plasma membrane lipid rafts in a caveolin 1 (Cav1)- dependent manner, where it destabilizes the binding between TLR4 and its adapter protein myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) via CO production, thus ending inflammatory signaling (Wang X. et al., 2009). We found that HO-1 does not compartmentalize to the cell surface in CF MΦs, but rather accumulates intracellularly due to decreased Cav1 expression (Zhang et al., 2013). We linked the decreased levels of Cav1 expression to high levels of miR-199a-5p (which targets caveolin 1 3’-UTR) downstream of blunted PI3K/AKT signaling in CF MΦs (Zhang et al., 2015). Importantly, modulation of this pathway via overexpression of HO-1 or treatment with CO-releasing molecules (discussed in the next section) was sufficient to improve the signaling cascade, thus reducing hyper-inflammation in CF MΦs (Zhang et al., 2013). In investigating how loss of CFTR leads to blunted PI3K/AKT signaling, we found that ezrin, an F-actin binding protein that forms a macromolecular complex with CFTR at the plasma membrane (Guggino and Stanton, 2006), links CFTR, TLR4, PI3K/AKT signaling, and HO-1 expression in MΦs (Di Pietro et al., 2017).
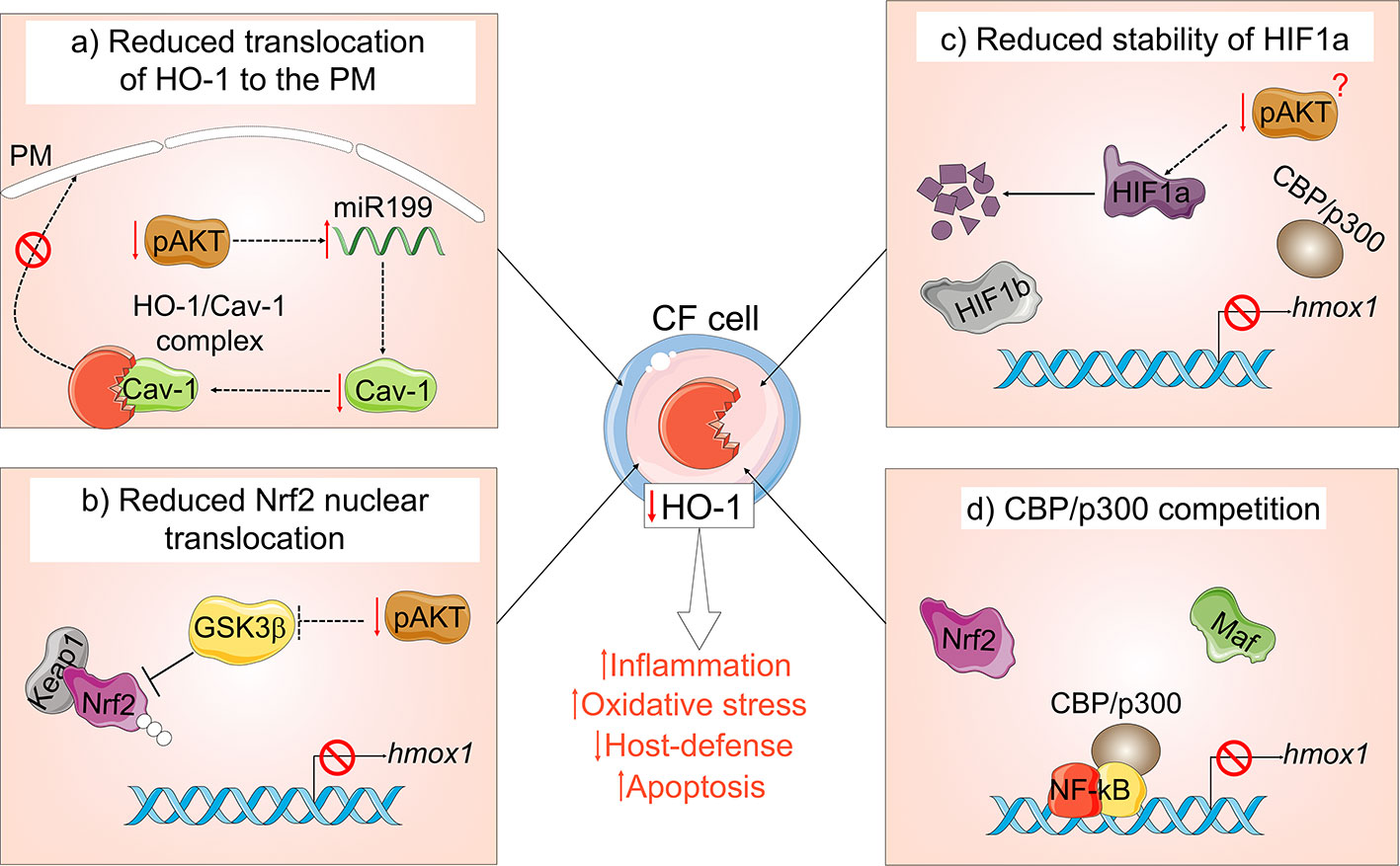
Figure 3 Mechanisms of HO-1 dysregulation in cystic fibrosis (CF). In the absence of functional CFTR: (A) MΦs have a blunted PI3K/AKT signaling in response to TLR4 activation, which leads to accumulation of miR-199a-5p, which reduces Cav1 expression. Loss of Cav1 impairs translocation and compartmentalization of HO-1 at the plasma membrane (PM); (B) blunted PI3K/AKT signaling in CF cells results in elevated levels of active GSK3β, which leads to Nrf2 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation and (C) affects the stability of HIF-1α. (D) NF-kB in CF cells competes for the Nrf2 co-activator CBP/p300, thus preventing Nrf2 transcriptional activity.
Ziady et al. (Chen et al., 2008; Ziady et al., 2012) showed that CFTR deficiency in HBE cells reduces translocation of the transcription factor Nrf2 into the nuclear compartment, thus impairing the transcription of antioxidant genes, including HO-1. This group also found that the co-activator CBP favors the binding to NF-kB (over Nrf2), which increases inflammatory signaling (Chen et al., 2008). Kelley et al. showed that Rp-cAMPS, a cAMP competitor, rescued Nrf2 activity in CF epithelial cells by shifting the CBP association in favor of Nrf2 (over NF-kB), thus decreasing inflammatory signaling and increasing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity (Ziady et al., 2012). In this study HO-1 expression was not tested, however, the rescued Nrf2 activity should result in increased HO-1 expression. Importantly, Ziady’s group recently showed that the broadly used CFTR modulators VX-809 (Lumacaftor) and VX-661 (Tezacaftor) significantly increase Nrf2 activity after correction of CFTR expression in primary epithelial cells of CF patients with homozygous F508del mutations (Borcherding et al., 2019). VX-809 also stabilizes PTEN association with the mutant CFTR protein (upstream regulator of PI3K) (Riquelme et al., 2017) and increases cellular levels and phosphorylation of ezrin (Matos et al., 2019). This helps the mutant CFTR to form a stable macromolecular complex at the plasma membrane, thus improving function (Abbattiscianni et al., 2016). Plasma membrane stabilized mutant CFTR, restores the CFTR downstream signaling transduction events that reestablish the Nrf2-HO-1 axis in VX809-treated cells (Borcherding et al., 2019). In addition to Nrf2, stabilization of HIF-1α is downregulated in unstimulated and hypoxia-stimulated CFTR-deficient HBE cells, which decreases HO-1 expression (Legendre et al., 2011).
While CFTR modulators decreased the inflammatory response (Hisert et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018; Jarosz-Griffiths et al., 2020), and improved their bacterial clearance (Barnaby et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2018) in monocyte/MΦs from patients with CF, these studies did not investigate a possible increase (and thus beneficial effect) of HO-1 levels. In CF patients, CFTR modulators initially decreased the bacterial burden in the lungs, but the bacteria re-emerged over time (Hisert et al., 2017). Thus, to preserve lung function in patients with CF in the long term, we propose that targeting the HO-1/CO pathway can complement existing treatments.
Several trials and studies have indirectly tested HO-1 induction in patients with CF. The first tested candidate was sulphoraphane, an antioxidant compound that induces Nrf2 signaling and improves bacterial clearance by alveolar MΦs (Harvey et al., 2011). The study found no adverse effects of increased dietary sulphoraphane intake. However, larger studies are needed to test sulphoraphane’s efficacy in CF (NCT01315665). GSK Pharmaceuticals have developed a promising small molecule for therapeutically inducing HO-1 (Davies et al., 2016). This molecule activates Nrf2 by binding the Keap1-Nrf2 binding site, favoring their dissociation. It thus improves opsonic phagocytosis in MΦs isolated from COPD patients (Bewley et al., 2018), and may be beneficial for CF patients. As an alternative approach, exogenous delivery of low doses of CO, a potent inducer of HO-1, can be considered to improve CF lung disease. We have proven that exogenous CO delivery can overcome the defective plasma membrane localization of HO-1 in CF MΦs challenged with LPS (Zhang et al., 2013). However, certain epigenetic changes present at the hmox1 gene in CF- affected cells (Magalhaes et al., 2017), may reduce the efficacy of such a therapeutic approach. In the following sections, we discuss the cellular effects of CO administration, and its relevance to CF.
CO Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Functions, and Relevance to CF
Similarly, to nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), CO is a potent gaseous signaling molecule that can freely diffuse through membranes (Fagone et al., 2018). The biological activity of CO depends on its ability to bind with ferrous (Fe2+) ions, thus controlling the activity of several heme-containing proteins (e.g., nitric oxide synthase (NOS), NADPH oxidase, cytochrome C oxidase, guanylate cyclase) (Wang et al., 2014; Ji et al., 2016; Motterlini and Foresti, 2017; Ryter et al., 2018). These proteins activate signaling pathways that are implicated in cell protection/survival against stress, in antioxidant responses, and in regulating inflammation. CO’s downstream targets include p38, HIF-1α, PPARγ, glutathione, nitric oxide, and PI3K/AKT, many of which are altered in CF (Cantin et al., 2015). The current understanding of CO’s biological function derives from studies in which cells and animal models were exposed to non-toxic doses of free CO, or were treated with small molecules able to release controlled amounts of CO, i.e., CO-releasing molecules (CO-RMs). CO-RMs were initially engineered by Motterlini and colleagues (Motterlini et al., 2002). They contain a transition metal (e.g., ruthenium, cobalt, iron) surrounded by carbonyl (CO) groups. Different CO-RMs have been developed to minimize toxicity, improve solubility, and increase control of CO release. Exogenous delivery of low doses of CO mimics the physiological/non-toxic effects elicited by the production of endogenous cellular CO (Motterlini and Otterbein, 2010; Wegiel et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2014; Ji et al., 2016; Motterlini and Foresti, 2017; Ryter et al., 2018).
Several in vivo studies, including ours in CF-affected mice (Zhang et al., 2013), support the notion that exogenous delivery of CO prevents hyper-inflammation and tissue damage in the context of sepsis, sterile inflammation, and hyperoxia (Motterlini and Otterbein, 2010). CO reduces the number of neutrophils in septic lungs by controlling transendothelial migration (Mizuguchi et al., 2009). Moreover, at low concentrations, CO attenuates the lung inflammatory response in mice challenged with LPS or live bacteria (Macgarvey et al., 2012; Wegiel et al., 2014b; Wilson et al., 2017; Kim et al., 2018). It differentially and selectively inhibits LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6), while increasing levels of anti-inflammatory molecules (e.g., IL-10, IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra, PPAR-γ) (Bilban et al., 2006; Haschemi et al., 2011; Piantadosi et al., 2011; Macgarvey et al., 2012; Uddin et al., 2015). This is relevant to CF because CF airway epithelial cells (Perez et al., 2007) and CF MΦs (Bruscia et al., 2009) both secrete more pro-inflammatory cytokines during inflammatory stimuli compared to non-CF cells. Moreover, CO can help reestablish the secretion levels of IL-10, which are lower in CF lungs (Bonfield et al., 1995), and of PPAR-γ, which are lower in CF epithelial cells and MΦs (Andersson et al., 2008; Harmon et al., 2010). Murine (Sawle et al., 2005) and human (Chhikara et al., 2009) MΦs are particularly responsive to CO treatment, which attenuates the inflammatory response to LPS (Sawle et al., 2005).
The anti-inflammatory effect of CO in response to LPS may be mediated by augmenting the caveolin 1(Cav-1)/TLR4 interaction at plasma membrane caveolae by a p38 MAPK-dependent mechanism (Otterbein et al., 2000; Sawle et al., 2005; Bilban et al., 2006; Chhikara et al., 2009; Tsoyi et al., 2009; Wang X. et al., 2009), which favors termination of pro-inflammatory signal transduction events. Importantly, CF MΦs have increased levels of plasma membrane TLR4 receptors (Bruscia et al., 2011) and decreased Cav1 expression in response to LPS (Zhang et al., 2013). We have shown that low levels of Cav1 prevent translocation of HO-1 to the plasma membrane of activated CF MΦs (Zhang et al., 2013), where it normally localizes (Wang X. et al., 2009). CO-RM treatment reversed this dysfunction in CF cells (Zhang et al., 2013).
CO’s anti-inflammatory effects also rely on its ability to strongly induce expression of endogenous HO-1, thus increasing autonomous, cellular CO production. HO-1 expression is driven by several TFs and upstream signaling events (see HO-1 Function and Regulation, Figure 2). Exogenous CO administration can activate all the shown/mentioned TFs to induce HO-1 expression, with activation of preferential pathways depending on the experimental conditions, cell type, and cellular stressors (Piantadosi et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2013) (Figure 4). Mechanistically, low doses of CO transiently increase mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) levels (Wang et al., 2007). This temporary increase in mtROS activates the MKK3/p38 MAPKs and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which ultimately strongly induces HO-1 expression (Otterbein et al., 2000; Otterbein et al., 2003).
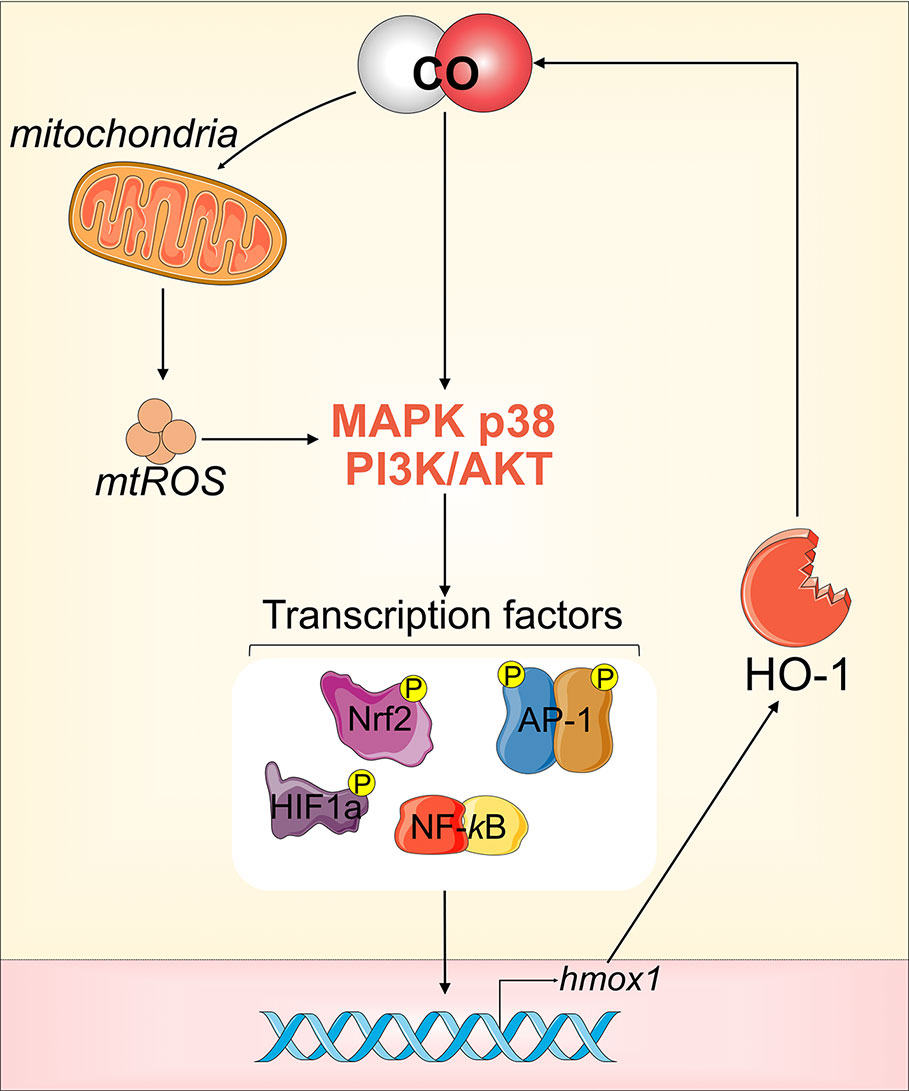
Figure 4 CO-mediated induction of HO-1. Low dose CO can activate all the transcriptional factors (TFs) that drive the expression of HO-1, via either direct or indirect activation of MKK3/p38 MAPKs and PI3K/AKT signaling.
More recently, it has been proposed that CO promotes resolution of inflammation by inducing expression of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPMs) derived from the metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids (Serhan et al., 2014). In a mouse model of peritonitis (Chiang et al., 2013) and a primate model of pneumonia (Dalli et al., 2015), CO induces expression of a key biosynthetic enzyme (12/15-LOX in mice, and 15-LOX-1 in humans), which induces the production of SPMs. In these models, CO increases levels of Resolvin (Rv)-D1, RvD2, and Lipoxin A4 (LXA4), and reduces levels of pro-inflammatory lipid mediators, such as thromboxane B2 (TXB2), leukotriene B4 (LTB4), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). This is relevant because CF patients have a reduced capacity to biosynthesize SPMs. Clinical studies have shown that the arachidonic-acid-derived LXA4 is reduced in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of patients with CF (Karp et al., 2004; Chiron et al., 2008; Yang et al., 2012; Ringholz et al., 2014). The presence of the omega-3 fatty-acid-derived RvE1 in CF BALF correlates with better lung function compared to patients with undetectable RvE1 (Yang et al., 2012). Moreover, P. aeruginosa infection inhibits 15-epi-LXA4 production in HBE cells, thus promoting mucosal hyper-inflammation (Flitter et al., 2017; Recchiuti et al., 2019)
CO modulates several pathways in a way that may counteract the dysfunctions in the CF epithelium that lead to oxidative stress (Galli et al., 2012). These actions include inducing the aforementioned Nrf2-dependent and Nrf2-independent induction of HO-1, preventing ROS production downstream of NADPH oxidase activity, and rebalancing the defective glutathione homeostasis observed in CF cells (Gao et al., 1999; Velsor et al., 2001; Day et al., 2004; Galli et al., 2012; Yamamoto et al., 2014; De Bari et al., 2018).
CO Stimulates Cellular Host Defense Against Infections: Implications in CF
Activating the HO-1/CO pathway or delivering exogenous CO has a promising additional clinical benefit. Namely, CO enhances MΦ bacterial killing capability and protects the lung epithelium from infection-associated damage (Chin and Otterbein, 2009). Several proposed mechanisms could explain how exposure to CO primes MΦs to better clear bacteria. For example, CO may stimulate bacterial uptake by redistribution of TLR4 at the plasma membrane (Otterbein et al., 2005). Moreover, the uptake of microorganisms such as P. aeruginosa by MΦs requires proper activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway (Araki et al., 2003; Bohdanowicz et al., 2010; Lovewell et al., 2014; Di Pietro et al., 2017; Demirdjian et al., 2018), which is stimulated by CO (Otterbein et al., 2000; Otterbein et al., 2003). TLR4 trafficking and its regulation at the plasma membrane of MΦs is altered in CF (Zhang et al., 2013). CF MΦs also show blunted induction of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in response to LPS or P. aeruginosa (Zhang et al., 2015; Di Pietro et al., 2017).
Wegiel et al. (2014a) have shown that modulation of the HO-1/CO pathway or exogenous delivery of CO increases the efficiency of MΦs in killing bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis. The mechanism relies on CO promoting ATP production from bacteria, which, in turn, activates the Nacht, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NALP3) inflammasome system via binding of the purinergic receptor P2X7 (Wegiel et al., 2014a). An additional in vivo study has shown that CO-driven inflammasome activation facilitates bacterial clearance in a mouse model of polymicrobial infection caused by cecal ligation and puncture (Lancel et al., 2009). This may help macrophages kill P. aeruginosa clinical strains that are adapted to the altered CF environment (Riquelme et al., 2019). However, the effect of CO on inflammasome activation may depend on the type of stimuli, since Nakahira et al. have demonstrated that CO negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in MΦs challenged with LPS but not with live bacteria (Jung et al., 2015).
Autophagy is another cellular mechanism that is fundamental to efficient bacterial clearance by immune cells. CO stimulates autophagy by inducing the expression and activation of the microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) (Lee et al., 2011). Autophagy is impaired in CF HBE (Luciani et al., 2010) and MΦs of CF patients (Abdulrahman et al., 2011). This contributes to the hyper-inflammation (Luciani et al., 2010) and poor bacterial killing of organisms such as Burkholderia cepacia (Abdulrahman et al., 2011) and P. aeruginosa (Ferrari et al., 2017). CO also increases acidification of the phagolysosome (Onyiah et al., 2013). Although controversial (Haggie and Verkman, 2007), this may be an additional dysregulated mechanism in CF MΦs that contributes to the failure to efficiently kill bacteria (Di et al., 2006).
Mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming is a key response by MΦs to efficiently fight pathogens during infection (Mills and O’Neill, 2016). CO affects mitochondrial function by binding to the cytochrome-c oxidase. At high doses, CO damages mitochondria. However, at physiological/non-toxic levels, CO has positive effects on mitochondrial metabolism. CO shifts the cellular energetic metabolism from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation and the pentose phosphate pathway, increasing oxygen consumption and ATP production. This may be a key mechanism in CO’s modulation of the MΦ response to infections. CO also induces mitochondrial and lysosomal biogenesis by activating the guanylate cyclase and the PI3K/AKT pathway, and upregulating transcription factors such as Nrf1, Transcription Factor A, mitochondrial (TFAM), Nrf2, Transcription Factor EB (TFEB), and PGC-1α (Zuckerbraun et al., 2007; Piantadosi et al., 2011; Queiroga et al., 2012; Wegiel et al., 2013; Motterlini and Foresti, 2017; Kim et al., 2018). These data suggest that cellular CO primes MΦs to better respond to cellular stressors. Although CO treatment has been associated with increased bacterial killing (Chin and Otterbein, 2009), caution is required when considering CO as a treatment for infection. This is because CO can inhibit the activity of NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) proteins. However, in other experimental settings, the beneficial effect of CO requires the presence of functional NOX2 (Nakahira et al., 2006; Lin et al., 2019). Thus, the inhibitory effect of CO on NADPH oxidases may depend on the CO dose used, cellular status (steady state or in response to stress), and type of stressor. This must be carefully evaluated when considering CO as a potential CF therapy because MΦs from CF patients may have an intrinsically lower capacity to activate NOX2 in response to bacterial infections (Assani et al., 2017).
A few in vivo studies suggest that administration of CO or CO-RMs protects against mortality after infectious challenge. Systemic delivery of CO-RMs reduced the mortality from 80% to 0% compared with controls in neutropenic mice infected with P. aeruginosa. This correlated with reduced bacterial recovery from the spleen due to either direct CO-mediated killing or enhanced bacterial clearance by the host immune system (Desmard et al., 2009). The authors demonstrate that mitochondrial function was protected in the CO-RM-treated mice and the pro-inflammatory response of sepsis was blunted (Lancel et al., 2009). Similarly, in a mouse peritonitis sepsis model, lower dose of CO-RM (10 mg/kg) resulted in an 80% survival rate. Additionally, upregulation of the HO-1/CO pathway, or delivery of inhaled CO, improved survival of mice in an S. aureus sepsis model. In this model, the mechanism of action relies on mitochondrial energetic metabolism reprogramming and biogenesis, increasing host cell survival, and countering the exuberant pro-inflammatory response in an AKT1-Nrf2 dependent manner (Macgarvey et al., 2012).
Finally, and particularly relevant in the context of CF lung disease, increased cellular levels of CO protect the bronchial epithelium from damage associated with P. aeruginosa infection. Secreted virulence factors from P. aeruginosa (e.g., P. aeruginosa quinolone signaling compound, PQS) decrease levels of HO-1 and Nrf2 expression in lung epithelial cells and primary HBE cells. This increases oxidative stress in epithelial cells, contributing to the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa (Abdalla et al., 2017). In another study by Roussel et al., the P. aeruginosa biofilm-derived quorum sensing molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone (3OC12-HSL) decreased the activation of the Nrf2-HO-1 axis in HBE cells, increasing cellular ROS production (Roussel and Rousseau, 2017). Importantly, we and others have shown that stimulating the HO-1 pathway (with genetic manipulation (Zhou et al., 2004) or exposure to CO-RMs (Murray et al., 2012)) is sufficient to improve HBE cell survival following acute P. aeruginosa infection (Zhou et al., 2004) or exposure to P. aeruginosa biofilms (Murray et al., 2012). Improved CO cellular survival in response to infections may be mediated by stabilization of HIF-1α (Chin et al., 2007) and activation of the PI3K/AKT-driven induction of Bcl-2-mediated protection to apoptotic stimuli (Otterbein et al., 2003; Martin et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2015; Shi et al., 2019).
The Direct Effects of CO on Bacteria and Relevance to CF
Along with the previously discussed stimulation of the host cells, CO treatment has an additional potential clinical benefit in its direct bactericidal activity. Multiple studies have documented that CO and CO-RM treatment results in killing of a variety of pathogenic bacteria including P. aeruginosa, E. coli, Salmonella enterica, S. aureus, and Helicobacter pylori (Nobre et al., 2007; Murray et al., 2012; Bang et al., 2014; Rana et al., 2014; Flanagan et al., 2018). This has generally been true regardless of the carrier molecule used to deliver the CO, which accumulates inside bacterial cells before they release CO (Nobre et al., 2016). CO’s killing efficiency and mechanism of action against microorganisms likely differs based on the CO dose, microorganism, and the metabolic status of the microorganism (Chin and Otterbein, 2009; Chung et al., 2009; Tavares et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 2012). There are many explanations for how CO-RMs induce bacterial cell death (for a comprehensive review, see (Wilson et al., 2012)). One mechanism is that bacterial CO exposure generates reactive oxidative species (ROS) and subsequent DNA damage (Nobre et al., 2009). Another demonstrated mechanism is that CO directly targets respiration by binding to terminal cytochrome oxidases (Desmard et al., 2009; Tavares et al., 2013).
P. aeruginosa demonstrates the promises and limitations of CO and CO-RMs as antimicrobial therapies. We and others have shown that CO-RMs are effective at killing or aiding in the killing of P. aeruginosa clinical strains recovered from CF patients and grown in liquid culture or in biofilms (Murray et al., 2012; Flanagan et al., 2018). However, these studies also show that certain P. aeruginosa clinical isolates are less susceptible to CO (Murray et al., 2012; Flanagan et al., 2018). Moreover, the bacterial growth conditions influence CO’s effectiveness. CO does not effectively kill the common P. aeruginosa strain PAO1 in rich media, but it is highly effective in glucose-based media (Murray et al., 2012). CO-RMs also kill P. aeruginosa in anaerobic conditions (Desmard et al., 2009), similar to those found in the CF lung.
Riquelme & Prince recently pointed out that the metabolic environment is important for CF infections (Riquelme et al., 2019). The CF lung has high levels of succinate, and thus preferentially selects for P. aeruginosa, which efficiently metabolize succinate (Riquelme et al., 2017). This metabolic adaptation drives a transcriptional reprogramming of the bacteria, leading to expression of genes for extracellular molecules that favor bacterial biofilm formation. Interestingly, one study of a novel photo-activated CO-RM demonstrated CO-RM-dependent killing of E. coli when succinate was supplied as the sole carbon source (Nagel et al., 2014). Riquelme & Prince also provide evidence that P. aeruginosa clinical strains adapt to the altered CF environment and change the host immune response to induce recruitment of immune cells (monocytes and neutrophils) to the lungs, while retaining the ability to activate mitochondrial ROS. However, the recruited immune cells display immune dysfunction when challenged with CF-adapted P. aeruginosa, including failure to stabilize HIF-1α and to secrete IL-1β. Thus, CF-adapted bacterial isolates can evade clearance by MΦs (Riquelme et al., 2019). As discussed above (Wegiel et al., 2014a), by stabilizing HIF-1α and restoring IL-1β secretion, CO treatment may enhance the ability of host immune cells to better sense and eradicate P. aeruginosa isolates that are metabolically adapted to the CF lung environment.
CO as a Modulator of Ion Channel Activity: Relevance to CF
CO is also emerging as a modulator of ion channel activity. CO regulates the function of the Ca2+-activated K (BKCa), voltage-activated K+ (Kv), and Ca2+ channel (L-type) families, ligand-gated P2X receptors, tandem P domain K+ channels (TREK1), and the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC). The mechanism/s by which CO modulates their activity is unclear. However, activation of the BKCa channel seems to be directly mediated by CO binding to a metal-based center in BKCa channels (Brazier et al., 2009; Telezhkin et al., 2011). Generation of cGMP by soluble guanylyl cyclase activation (Murad, 2006) and generation of mtROS (Wilkinson and Kemp, 2011; Peers et al., 2015) are two indirect mechanisms that have been proposed to mediate CO‐dependent modulation of ion channel activity.
Relevance to CF
Loss of CFTR function leads to reduced expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase, a target of CO, in CF murine and human airway epithelial cells (Kelley et al., 1997a; Kelley and Drumm, 1998; Elmer et al., 1999; Steagall et al., 2000). This reduces NO production, thus decreasing cGMP levels in CF cells and dysregulating transepithelial sodium and chloride transport (Elmer et al., 1999). Importantly, cGMPs activate CFTR in a PKA-independent manner (Kelley et al., 1997b), and promote trafficking of CFTR to the plasma membrane of the intestinal epithelium (Ahsan et al., 2017). Stimulating this pathway may also correct/potentiate mutant CFTR and thus ameliorate the intestinal fluid deficit in the CF intestine (Arora et al., 2017). Thus, by increasing cGMP cellular levels (Foresti and Motterlini, 1999), CO may help stimulate wild-type and mutant CFTR ion transport. A thought-provoking study by Wang suggests that CO may activate CFTR-dependent Cl- and HCO3- currents across the apical membrane of the rat distal colon. This study reported that the CFTR protein has a high-affinity ferric ion (Fe3+) binding site at the interface between the regulatory domain and intracellular loop 3. The binding of Fe3+ to CFTR prevents channel opening, and CO leads to release of the inhibitive Fe3+ ions, thus activating CFTR (Wang, 2017).
In addition to potentially regulating the CFTR function, CO also modulates the function of ion channels involved in CF lung disease, i.e., the large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (BKCa) and the epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC). The BKCa channels are expressed on the apical membrane of airways. Apical secretion of K+ provides a driving force for Cl− flow, which maintains the airway surface liquid (ASL) volume. Its depletion leads to mucociliary dysfunction (Manzanares et al., 2011; Manzanares et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2020). Importantly, Salathe’s group recently reported that CF HBE cells have reduced BKCa channel activity due to increased lung inflammation, and that restoring BKCa channel activity reduces CF and inflammation-associated mucociliary dysfunction (Kim et al., 2020). Thus, CO’s ability to activate BKCa may reduce inflammation and help re-balance ion secretions in CF.
CO also inhibits the sodium channel ENaC, an established pharmacological target for CF lung disease (Mall, 2009). The ENaC channel absorbs Na+ from the apical side, thus reducing the ASL volume. CO inhibits ENaC in rat cultured alveolar type II cells and human airway epithelial cell line, and it prevents alveolar fluid reabsorption in perfused rabbit lungs (Althaus et al., 2009). Thus, CO can potentially block the hyperabsorption of sodium through the ENaC channel, which may restore ASL volumes (Mall et al., 2004). However, a different study has reported that CO has the opposite effect on ENaC in a mouse kidney cortical collecting duct cell line (Wang S. et al., 2009). These data are not easy to reconcile, but they may reflect tissue-specific differences in ENaC subunit composition, the CO doses, and experimental conditions. More studies are needed to clarify CO’s effect on ENaC in CF epithelium.
In summary, CO targets the signaling cascade associated with NO production and cGMP levels. It also directly targets the activity of ion channels such as BKCa (and potentially CFTR). It may thus help rebalance ion transport across the CF epithelium and restore physiological ASL levels.
Exogenous Delivery of CO and Clinical Applications
Based on encouraging studies in preclinical models, the pharmacological use of CO has been tested in humans. In this rapidly evolving field, the current approaches to delivering controlled levels of CO in humans are: (a) inhalation and (b) a hemoglobin based-CO carrier.
CO Inhalation
At high concentrations (10,000 ppm), inhalation of CO is toxic. However, at controlled low concentrations (10–200 ppm), exogenous CO delivery is safe in humans [NCT00531856 (Mayr et al., 2005) (Bathoorn et al., 2007)] and is beneficial against numerous diseases and pathological conditions featuring hyper-inflammation, tissue damage, pulmonary arterial hypertension, and ischemic conditions (Motterlini and Otterbein, 2010; Ji et al., 2016; Ryter and Choi, 2016; Ryter et al., 2018). Inhalation of 100–125 ppm CO by patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is safe, reduces sputum eosinophil levels and improves responsiveness to methacholine [NCT00122694 (Bathoorn et al., 2007)]. Results from a multicenter, double-blinded, clinical trial of inhaled CO in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis show that CO inhalation (100-200 ppm) was not associated with adverse events, but also did not result in significant changes in the study end points. These end points included differences in matrix metalloproteinase-7 serum concentration and pulmonary function test measures [NCT01214187 (Rosas et al., 2018)]. However, treatment with CO lead to a change in the expression profile of peripheral blood mononuclear cells dominated by oxidative phosphorylation-related genes (Casanova et al., 2019). Clinical implications for such transcriptional changes are not clear. Following successful preclinical studies in primates (Dalli et al., 2015; Fredenburgh et al., 2015), CO inhalation was tested in an initial safety study with patients with sepsis induced by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Subjects were administered inhaled CO (100 ppm or 200 ppm) or placebo for 90 min for up to 5 consecutive days. The treatment was well-tolerated and appeared to be safe (Fredenburgh et al., 2018). A multi-center Phase II clinical trial of inhaled CO for the treatment of ARDS involving 5 US-based medical centers is currently ongoing (NCT03799874).
Hemoglobin-Based CO Carrier
Prolong Pharmaceuticals has developed PP-007 (formerly known as Sanguinate), a polyethylene-glycol-modified (PEGylated) form of bovine hemoglobin loaded with CO. CO is released within 2 h of infusion and exchanged for oxygen, which is then delivered to areas of low oxygen tension (Abuchowski, 2017). This dual mode of action targets inflammation (CO) and hypoxia (O2), two complications in the CF lung. PP-007 is also PEGylated, which ensures stability and prolongs retention of the molecules in the circulation. PP-007 is being studied for several clinical situations to treat hypoxia and/or inflammation, including sickle cell disease (SCD), reperfusion injury, and cerebral hemorrhage (Misra et al., 2014; Abuchowski, 2016; Abuchowski, 2017; Dhar et al., 2017; Misra et al., 2017; Abu Jawdeh et al., 2018). PP-007 is safe in a phase I clinical trials in both healthy controls and patients with SCD. After a single intravenous dose (80, 120, or 160 mg/kg) in a randomized phase I single-blinded placebo-controlled study, the only observed adverse effect was a transient trend toward increased blood pressure, likely due to temporary intravascular volume expansion, which resolved within 24 h. In addition, a dose-dependent decrease in serum haptoglobin was observed, which binds to PP-007, forming a complex that is cleared from the circulation. Importantly, no Hb was detected in the urine, and no signs of nephrotoxicity were found (Abuchowski, 2016; Abuchowski, 2017). A second Phase I study in SCD patients also showed the transient increase in blood pressure, as well as an asymptomatic increase in troponin. Currently, PP-007 is being tested in several Phase II clinical trials in SCD (NCT02672540; NCT02600390). PP-007 is also well-tolerated in patients with other diseases, such as subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) (NCT02323685). PP-007 is FDA-approved for compassionate care, and has been successfully used as an artificial oxygen transfusion agent in two patients undergoing surgery, a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and a woman with postpartum hemorrhage (Holzner et al., 2018; Brotman et al., 2019). Patients were eventually stabilized, and no adverse events were reported (Sam et al., 2017; Thenuwara et al., 2017). Given PP-007’s cytoprotective effects and its use in ischemia-reperfusion injury in renal transplant patients (clinicaltrials.gov, ID: NCT02490202; Phase II/III), PP-007 may be able to prevent/reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury in CF patients after lung transplant (Porteous et al., 2015). The anti-inflammatory effects of PP-007 in preclinical mouse models of CF lung disease are currently being tested by our laboratory.
Concluding Remarks
Modulating the HO-1/CO pathway, e.g., via CO administration, can attenuate hyper-inflammation, counteract oxidative stress, improve bacterial clearance by strengthening the host defense mechanisms or by direct killing, and rehydrate the airways (Figure 5). We therefore propose that the HO-1/CO pathway may be targeted as an adjuvant therapy to minimize lung disease in CF.
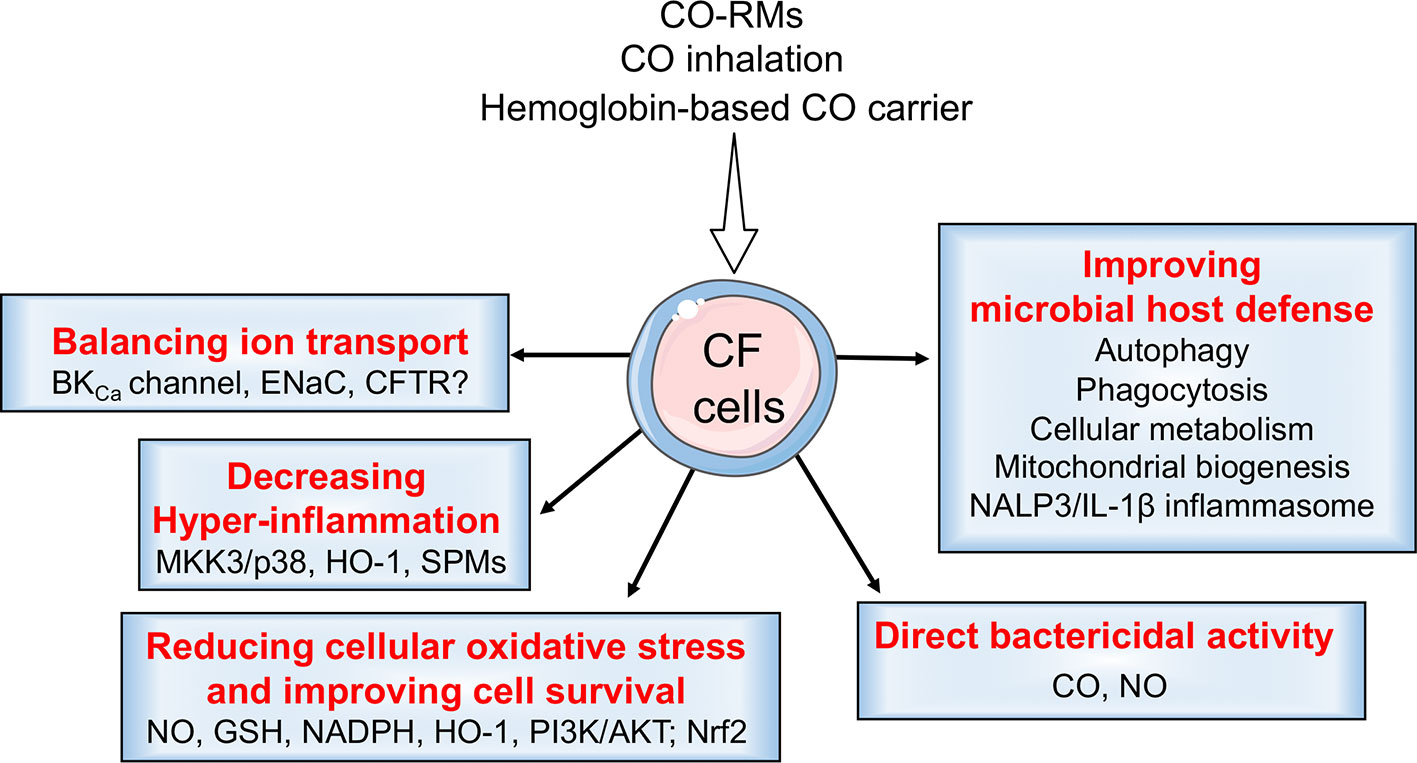
Figure 5 CO beneficial effects in cystic fibrosis (CF). CO may have several beneficial effects in CF. In addition to transcriptional induction of HO-1, CO helps to rebalance ion transport in bronchial epithelial cells by modulating the activity of BKCa channels, ENaC, and, possibly, CFTR. It has direct bactericidal activity and also primes the macrophages. It thus improves the host defense mechanisms by modulating autophagy, phagocytosis, the inflammasome, and immunometabolic responses. CO reduces cellular oxidative stress and improves cell survival by activating/inducing NO, GSH, NADPH, HO-1, PI3K/AKT, and Nrf2. CO also decreases hyper-inflammation by increasing levels of anti-inflammatory mediators, HO-1 and SPMs.
Author Contributions
CP, HÖ, TM, and EB wrote the manuscript. CP designed the figures. EB initiated and overseen the work. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The Bruscia lab has been supported by a grant from Prolong Pharmaceuticals.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Yale CF Research Center and Dr. Marie Egan for the continuous support, and Drs. Diane Krause, Roberto Motterlini, and Roberta Foresti for helpful discussions. We acknowledge that there is a vast amount of literature on the topic. Due to limitations in the space and scope, this review represents only a selection of this literature. This work was supported by The American Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (BRUSCHI18G0 and OZ18F0), and by NIH/NHLBI (5R01HL123851-04).
References
Abbattiscianni, A. C., Favia, M., Mancini, M. T., Cardone, R. A., Guerra, L., Monterisi, S., et al. (2016). Correctors of mutant CFTR enhance subcortical cAMP-PKA signaling through modulating ezrin phosphorylation and cytoskeleton organization. J. Cell Sci. 129, 1128–1140. doi: 10.1242/jcs.177907
Abdalla, M. Y., Hoke, T., Seravalli, J., Switzer, B. L., Bavitz, M., Fliege, J. D., et al. (2017). Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Induces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in Lung Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00176-17
Abdulrahman, B. A., Khweek, A. A., Akhter, A., Caution, K., Kotrange, S., Abdelaziz, D. H., et al. (2011). Autophagy stimulation by rapamycin suppresses lung inflammation and infection by Burkholderia cenocepacia in a model of cystic fibrosis. Autophagy 7, 1359–1370. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.11.17660
Abu Jawdeh, B. G., Woodle, E. S., Leino, A. D., Brailey, P., Tremblay, S., Dorst, T., et al. (2018). A phase Ib, open-label, single arm study to assess the safety, pharmacokinetics, and impact on humoral sensitization of SANGUINATE infusion in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin. Transplant. 32. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13155
Abuchowski, A. (2016). PEGylated Bovine Carboxyhemoglobin (SANGUINATE): Results of Clinical Safety Testing and Use in Patients. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 876, 461–467. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3023-4_58
Abuchowski, A. (2017). SANGUINATE (PEGylated Carboxyhemoglobin Bovine): Mechanism of Action and Clinical Update. Artif. Organs 41, 346–350. doi: 10.1111/aor.12934
Ahsan, M. K., Tchernychev, B., Kessler, M. M., Solinga, R. M., Arthur, D., Linde, C. I., et al (2017). Linaclotide activates guanylate cyclase-C/cGMP/protein kinase-II-dependent trafficking of CFTR in the intestine. Physiol. Rep. 5. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13299
Alam, J., Cook, J. L. (2007). How many transcription factors does it take to turn on the heme oxygenase-1 gene? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 36, 166–174. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0340TR
Alam, J., Den, Z.(1992). Distal AP-1 binding sites mediate basal level enhancement and TPA induction of the mouse heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 21894–21900.
Alam, J., Stewart, D., Touchard, C., Boinapally, S., Choi, A. M., Cook, J. L. (1999). Nrf2, a Cap’n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26071–26078. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.37.26071
Althaus, M., Fronius, M., Buchackert, Y., Vadasz, I., Clauss, W. G., Seeger, W., et al. (2009). Carbon monoxide rapidly impairs alveolar fluid clearance by inhibiting epithelial sodium channels. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 41, 639–650. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0458OC
Andersson, C., Zaman, M. M., Jones, A. B., Freedman, S. D. (2008). Alterations in immune response and PPAR/LXR regulation in cystic fibrosis macrophages. J. Cyst. Fibros 7, 68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2007.05.004
Araki, N., Hatae, T., Furukawa, A., Swanson, J. A. (2003). Phosphoinositide-3-kinase-independent contractile activities associated with Fcgamma-receptor-mediated phagocytosis and macropinocytosis in macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 116, 247–257. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00235
Arora, K., Huang, Y., Mun, K., Yarlagadda, S., Sundaram, N., Kessler, M. M., et al. (2017). Guanylate cyclase 2C agonism corrects CFTR mutants. JCI Insight 2. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.93686
Assani, K., Shrestha, C. L., Robledo-Avila, F., Rajaram, M. V., Partida-Sanchez, S., Schlesinger, L. S., et al. (2017). Human Cystic Fibrosis Macrophages Have Defective Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase C Activation of the NADPH Oxidase, an Effect Augmented by Burkholderia cenocepacia. J. Immunol. 198, 1985–1994. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502609
Bang, C. S., Kruse, R., Demirel, I., Onnberg, A., Soderquist, B., Persson, K. (2014). Multiresistant uropathogenic extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli are susceptible to the carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 (CORM-2). Microb. Pathog. 66, 29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2013.12.003
Barnaby, R., Koeppen, K., Nymon, A., Hampton, T. H., Berwin, B., Ashare, A., et al. (2018). Lumacaftor (VX-809) restores the ability of CF macrophages to phagocytose and kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 314, L432–L438. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00461.2017
Bathoorn, E., Slebos, D. J., Postma, D. S., Koeter, G. H., Van Oosterhout, A. J., Van Der Toorn, M., et al. (2007). Anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled carbon monoxide in patients with COPD: a pilot study. Eur. Respir. J. 30, 1131–1137. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00163206
Bewley, M. A., Budd, R. C., Ryan, E., Cole, J., Collini, P., Marshall, J., et al. (2018). Opsonic Phagocytosis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Is Enhanced by Nrf2 Agonists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 198, 739–750. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201705-0903OC
Bilban, M., Bach, F. H., Otterbein, S. L., Ifedigbo, E., D’avila, J. C., Esterbauer, H., et al. (2006). Carbon monoxide orchestrates a protective response through PPARgamma. Immunity 24, 601–610. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.03.012
Biswas, C., Shah, N., Muthu, M., La, P., Fernando, A. P., Sengupta, S., et al. (2014). Nuclear heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) modulates subcellular distribution and activation of Nrf2, impacting metabolic and anti-oxidant defenses. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 26882–26894. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.567685
Bohdanowicz, M., Cosio, G., Backer, J. M., Grinstein, S. (2010). Class I and class III phosphoinositide 3-kinases are required for actin polymerization that propels phagosomes. J. Cell Biol. 191, 999–1012. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201004005
Bonfield, T. L., Panuska, J. R., Konstan, M. W., Hilliard, K. A., Hilliard, J. B., Ghnaim, H., et al. (1995). Inflammatory cytokines in cystic fibrosis lungs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 152, 2111–2118. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.6.8520783
Borcherding, D. C., Siefert, M. E., Lin, S., Brewington, J., Sadek, H., Clancy, J. P., et al. (2019). Clinically-approved CFTR modulators rescue Nrf2 dysfunction in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J. Clin. Invest. 129, 3448–3463. doi: 10.1172/JCI96273
Brazier, S. P., Telezhkin, V., Mears, R., Muller, C. T., Riccardi, D., Kemp, P. J. (2009). Cysteine residues in the C-terminal tail of the human BK(Ca)alpha subunit are important for channel sensitivity to carbon monoxide. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 648, 49–56. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-2259-2_5
Brennan, S., Sly, P. D., Gangell, C. L., Sturges, N., Winfield, K., Wikstrom, M., et al. (2009). Alveolar macrophages and CC chemokines are increased in children with cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 34, 655–661. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00178508
Brotman, I., Kocher, M., Mchugh, S. (2019). Bovine Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carrier Treatment in a Severely Anemic Jehovah’s Witness Patient After Cystoprostatectomy and Nephrectomy: A Case Report. A. A. Pract. 12, 243–245. doi: 10.1213/XAA.0000000000000901
Bruscia, E. M., Bonfield, T. L. (2016a). Cystic Fibrosis Lung Immunity: The Role of the Macrophage. J. Innate Immun. 8, 550–563. doi: 10.1159/000446825
Bruscia, E. M., Bonfield, T. L. (2016b). Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Chest Med. 37, 17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2015.11.010
Bruscia, E. M., Zhang, P. X., Ferreira, E., Caputo, C., Emerson, J. W., Tuck, D., et al. (2009). Macrophages directly contribute to the exaggerated inflammatory response in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-/- mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 40, 295–304. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0170OC
Bruscia, E. M., Zhang, P. X., Satoh, A., Caputo, C., Medzhitov, R., Shenoy, A., et al. (2011). Abnormal trafficking and degradation of TLR4 underlie the elevated inflammatory response in cystic fibrosis. J. Immunol. 186, 6990–6998. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100396
Bryan, H. K., Olayanju, A., Goldring, C. E., Park, B. K. (2013). The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms of regulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 85, 705–717. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.11.016
Cantin, A. M., Hartl, D., Konstan, M. W., Chmiel, J. F. (2015). Inflammation in cystic fibrosis lung disease: Pathogenesis and therapy. J. Cyst. Fibros 14, 419–430. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.03.003
Casanova, N., Zhou, T., Gonzalez-Garay, M. L., Rosas, I. O., Goldberg, H. J., Ryter, S. W., et al. (2019). Low Dose Carbon Monoxide Exposure in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Produces a CO Signature Comprised of Oxidative Phosphorylation Genes. Sci. Rep. 9, 14802. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50585-3
Chan, K., Kan, Y. W. (1999). Nrf2 is essential for protection against acute pulmonary injury in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 12731–12736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12731
Chen, J., Kinter, M., Shank, S., Cotton, C., Kelley, T. J., Ziady, A. G. (2008). Dysfunction of Nrf-2 in CF epithelia leads to excess intracellular H2O2 and inflammatory cytokine production. PloS One 3, e3367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003367
Cheng, X., Ku, C. H., Siow, R. C. (2013). Regulation of the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway by microRNAs: New players in micromanaging redox homeostasis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 64, 4–11. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.025
Chhikara, M., Wang, S., Kern, S. J., Ferreyra, G. A., Barb, J. J., Munson, P. J., et al. (2009). Carbon monoxide blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced gene expression by interfering with proximal TLR4 to NF-kappaB signal transduction in human monocytes. PloS One 4, e8139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008139
Chiang, N., Shinohara, M., Dalli, J., Mirakaj, V., Kibi, M., Choi, A. M., et al. (2013). Inhaled carbon monoxide accelerates resolution of inflammation via unique proresolving mediator-heme oxygenase-1 circuits. J. Immunol. 190, 6378–6388. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202969
Chillappagari, S., Venkatesan, S., Garapati, V., Mahavadi, P., Munder, A., Seubert, A., et al. (2014). Impaired TLR4 and HIF expression in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells downregulates hemeoxygenase-1 and alters iron homeostasis in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 307, L791–L799. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00167.2014
Chillappagari, S., Garapati, V., Mahavadi, P., Naehrlich, L., Schmeck, B. T., Schmitz, M. L., et al. (2020). Defective BACH1/HO-1 regulatory circuits in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. J. Cyst. Fibros. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2020.05.006
Chin, B. Y., Otterbein, L. E. (2009). Carbon monoxide is a poison... to microbes! CO as a bactericidal molecule. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 9, 490–500. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.06.025
Chin, B. Y., Jiang, G., Wegiel, B., Wang, H. J., Macdonald, T., Zhang, X. C., et al. (2007). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha stabilization by carbon monoxide results in cytoprotective preconditioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 5109–5114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609611104
Chiron, R., Grumbach, Y. Y., Quynh, N. V., Verriere, V., Urbach, V. (2008). Lipoxin A(4) and interleukin-8 levels in cystic fibrosis sputum after antibiotherapy. J. Cyst. Fibros 7, 463–468. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2008.04.002
Chmiel, J. F., Davis, P. B. (2003). State of the art: why do the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis become infected and why can’t they clear the infection? Respir. Res. 4, 8. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-4-8
Chung, S. W., Hall, S. R., Perrella, M. A. (2009). Role of haem oxygenase-1 in microbial host defence. Cell Microbiol. 11, 199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01261.x
Converso, D. P., Taille, C., Carreras, M. C., Jaitovich, A., Poderoso, J. J., Boczkowski, J. (2006). HO-1 is located in liver mitochondria and modulates mitochondrial heme content and metabolism. FASEB J. 20, 1236–1238. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4204fje
Cruse, I., Maines, M. D. (1988). Evidence suggesting that the two forms of heme oxygenase are products of different genes. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 3348–3353.
Dalli, J., Kraft, B. D., Colas, R. A., Shinohara, M., Fredenburgh, L. E., Hess, D. R., et al. (2015). The Regulation of Proresolving Lipid Mediator Profiles in Baboon Pneumonia by Inhaled Carbon Monoxide. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 53, 314–325. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0299OC
Davies, T. G., Wixted, W. E., Coyle, J. E., Griffiths-Jones, C., Hearn, K., Mcmenamin, R., et al. (2016). Monoacidic Inhibitors of the Kelch-like ECH-Associated Protein 1: Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (KEAP1:NRF2) Protein-Protein Interaction with High Cell Potency Identified by Fragment-Based Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 59, 3991–4006. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00228
Davis, P. B. (2006). Cystic fibrosis since 1938. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 173, 475–482. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200505-840OE
Day, B. J., Van Heeckeren, A. M., Min, E., Velsor, L. W. (2004). Role for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein in a glutathione response to bronchopulmonary pseudomonas infection. Infect. Immun. 72, 2045–2051. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.2045-2051.2004
De Bari, L., Favia, M., Bobba, A., Lassandro, R., Guerra, L., Atlante, A. (2018). Aberrant GSH reductase and NOX activities concur with defective CFTR to pro-oxidative imbalance in cystic fibrosis airways. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 50, 117–129. doi: 10.1007/s10863-018-9748-x
Demirdjian, S., Hopkins, D., Sanchez, H., Libre, M., Gerber, S. A., Berwin, B. (2018). Phosphatidylinositol-(3,4,5)-Trisphosphate Induces Phagocytosis of Nonmotile Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 86. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00215-18
Desmard, M., Davidge, K. S., Bouvet, O., Morin, D., Roux, D., Foresti, R., et al. (2009). A carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM-3) exerts bactericidal activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and improves survival in an animal model of bacteraemia. FASEB J. 23, 1023–1031. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-122804
Dhakshinamoorthy, S., Jain, A. K., Bloom, D. A., Jaiswal, A. K. (2005). Bach1 competes with Nrf2 leading to negative regulation of the antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene expression and induction in response to antioxidants. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 16891–16900. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500166200
Dhar, R., Misra, H., Diringer, M. N. (2017). SANGUINATE (PEGylated Carboxyhemoglobin Bovine) Improves Cerebral Blood Flow to Vulnerable Brain Regions at Risk of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 27, 341–349. doi: 10.1007/s12028-017-0418-3
Di, A., Brown, M. E., Deriy, L. V., Li, C., Szeto, F. L., Chen, Y., et al. (2006). CFTR regulates phagosome acidification in macrophages and alters bactericidal activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 933–944. doi: 10.1038/ncb1456
Di Pietro, C., Zhang, P. X., O’rourke, T. K., Murray, T. S., Wang, L., Britto, C. J., et al. (2017). Ezrin links CFTR to TLR4 signaling to orchestrate anti-bacterial immune response in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 7, 10882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11012-7
Doran, A. C., Yurdagul, A., Jr., Tabas, I. (2020). Efferocytosis in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 20, 254–267. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0240-6
Doring, G., Bragonzi, A., Paroni, M., Akturk, F. F., Cigana, C., Schmidt, A., et al. (2014). BIIL 284 reduces neutrophil numbers but increases P. aeruginosa bacteremia and inflammation in mouse lungs. J. Cyst. Fibros 13, 156–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2013.10.007
Elmer, H. L., Brady, K. G., Drumm, M. L., Kelley, T. J. (1999). Nitric oxide-mediated regulation of transepithelial sodium and chloride transport in murine nasal epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. 276, L466–L473. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1999.276.3.L466
Exner, M., Minar, E., Wagner, O., Schillinger, M. (2004). The role of heme oxygenase-1 promoter polymorphisms in human disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 37, 1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.07.008
Fagone, P., Mazzon, E., Bramanti, P., Bendtzen, K., Nicoletti, F. (2018). Gasotransmitters and the immune system: Mode of action and novel therapeutic targets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 834, 92–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.026
Ferrari, E., Monzani, R., Villella, V. R., Esposito, S., Saluzzo, F., Rossin, F., et al. (2017). Cysteamine re-establishes the clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages bearing the cystic fibrosis-relevant F508del-CFTR mutation. Cell Death Dis. 8, e2544. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.476
Flanagan, L., Steen, R. R., Saxby, K., Klatter, M., Aucott, B. J., Winstanley, C., et al. (2018). The Antimicrobial Activity of a Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecule (EBOR-CORM-1) Is Shaped by Intraspecific Variation within Pseudomonas aeruginosa Populations. Front. Microbiol. 9, 195. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00195
Flitter, B. A., Hvorecny, K. L., Ono, E., Eddens, T., Yang, J., Kwak, D. H., et al. (2017). Pseudomonas aeruginosa sabotages the generation of host proresolving lipid mediators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, 136–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610242114
Foresti, R., Motterlini, R. (1999). The heme oxygenase pathway and its interaction with nitric oxide in the control of cellular homeostasis. Free Radic. Res. 31, 459–475. doi: 10.1080/10715769900301031
Fredenburgh, L. E., Kraft, B. D., Hess, D. R., Harris, R. S., Wolf, M. A., Suliman, H. B., et al. (2015). Effects of inhaled CO administration on acute lung injury in baboons with pneumococcal pneumonia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 309, L834–L846. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00240.2015
Fredenburgh, L. E., Perrella, M. A., Barragan-Bradford, D., Hess, D. R., Peters, E., Welty-Wolf, K. E., et al. (2018). A phase I trial of low-dose inhaled carbon monoxide in sepsis-induced ARDS. JCI Insight 3. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.124039
Galli, F., Battistoni, A., Gambari, R., Pompella, A., Bragonzi, A., Pilolli, F., et al. (2012). Oxidative stress and antioxidant therapy in cystic fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1822, 690–713. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.12.012
Gao, L., Kim, K. J., Yankaskas, J. R., Forman, H. J. (1999). Abnormal glutathione transport in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 277, L113–L118. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1999.277.1.L113
Garratt, L. W., Sutanto, E. N., Ling, K. M., Looi, K., Iosifidis, T., Martinovich, K. M., et al. (2015). Matrix metalloproteinase activation by free neutrophil elastase contributes to bronchiectasis progression in early cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 46, 384–394. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00212114
Ghio, A. J., Roggli, V. L., Soukup, J. M., Richards, J. H., Randell, S. H., Muhlebach, M. S. (2013). Iron accumulates in the lavage and explanted lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros 12, 390–398. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2012.10.010
Gottlieb, Y., Truman, M., Cohen, L. A., Leichtmann-Bardoogo, Y., Meyron-Holtz, E. G. (2012). Endoplasmic reticulum anchored heme-oxygenase 1 faces the cytosol. Haematologica 97, 1489–1493. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.063651
Gozzelino, R., Jeney, V., Soares, M. P. (2010). Mechanisms of cell protection by heme oxygenase-1. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 50, 323–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105600
Gray, R. D., Hardisty, G., Regan, K. H., Smith, M., Robb, C. T., Duffin, R., et al. (2018). Delayed neutrophil apoptosis enhances NET formation in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 73, 134–144. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2017-210134
Guggino, W. B., Stanton, B. A. (2006). New insights into cystic fibrosis: molecular switches that regulate CFTR. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 426–436. doi: 10.1038/nrm1949
Haggie, P. M., Verkman, A. S. (2007). Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-independent phagosomal acidification in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 31422–31428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705296200
Harmon, G. S., Dumlao, D. S., Ng, D. T., Barrett, K. E., Dennis, E. A., Dong, H., et al. (2010). Pharmacological correction of a defect in PPAR-gamma signaling ameliorates disease severity in Cftr-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 16, 313–318. doi: 10.1038/nm.2101
Harvey, C. J., Thimmulappa, R. K., Sethi, S., Kong, X., Yarmus, L., Brown, R. H., et al. (2011). Targeting Nrf2 signaling improves bacterial clearance by alveolar macrophages in patients with COPD and in a mouse model. Sci. Transl. Med. 3, 78ra32. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002042
Haschemi, A., Chin, B. Y., Jeitler, M., Esterbauer, H., Wagner, O., Bilban, M., et al. (2011). Carbon monoxide induced PPARgamma SUMOylation and UCP2 block inflammatory gene expression in macrophages. PloS One 6, e26376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026376
Headland, S. E., Norling, L. V. (2015). The resolution of inflammation: Principles and challenges. Semin. Immunol. 27, 149–160. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2015.03.014
Hisert, K. B., Heltshe, S. L., Pope, C., Jorth, P., Wu, X., Edwards, R. M., et al. (2017). Restoring Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Function Reduces Airway Bacteria and Inflammation in People with Cystic Fibrosis and Chronic Lung Infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 195, 1617–1628. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201609-1954OC
Holzner, M. L., Demaria, S., Haydel, B., Smith, N., Flaherty, D., Florman, S. (2018). Pegylated Bovine Carboxyhemoglobin (SANGUINATE) in a Jehovah’s Witness Undergoing Liver Transplant: A Case Report. Transplant. Proc. 50, 4012–4014. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.09.006
Huang, H. C., Nguyen, T., Pickett, C. B. (2002). Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at Ser-40 by protein kinase C regulates antioxidant response element-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 42769–42774. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206911200
Jarosz-Griffiths, H. H., Scambler, T., Wong, C. H., Lara-Reyna, S., Holbrook, J., Martinon, F., et al. (2020). Different CFTR modulator combinations downregulate inflammation differently in cystic fibrosis. Elife 9. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54556
Ji, X., Damera, K., Zheng, Y., Yu, B., Otterbein, L. E., Wang, B. (2016). Toward Carbon Monoxide-Based Therapeutics: Critical Drug Delivery and Developability Issues. J. Pharm. Sci. 105, 406–416. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2015.10.018
Jung, S. S., Moon, J. S., Xu, J. F., Ifedigbo, E., Ryter, S. W., Choi, A. M., et al. (2015). Carbon monoxide negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 308, L1058–L1067. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00400.2014
Kang, K. W., Lee, S. J., Park, J. W., Kim, S. G. (2002). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulates nuclear translocation of NF-E2-related factor 2 through actin rearrangement in response to oxidative stress. Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 1001–1010. doi: 10.1124/mol.62.5.1001
Kanik, E. T., Yilmaz, O., Ozdogru, E., Alper, H., Ulman, C., Kanik, A., et al. (2020). Relevance between clinical status and exhaled molecules related to neutrophilic inflammation in pediatric cystic fibrosis. J. Breath Res. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/ab670d
Karp, C. L., Flick, L. M., Park, K. W., Softic, S., Greer, T. M., Keledjian, R., et al. (2004). Defective lipoxin-mediated anti-inflammatory activity in the cystic fibrosis airway. Nat. Immunol. 5, 388–392. doi: 10.1038/ni1056
Kelley, T. J., Drumm, M. L. (1998). Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression is reduced in cystic fibrosis murine and human airway epithelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 102, 1200–1207. doi: 10.1172/JCI2357
Kelley, T. J., Al-Nakkash, L., Drumm, M. L. (1997a). C-type natriuretic peptide increases chloride permeability in normal and cystic fibrosis airway cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 16, 464–470. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.16.4.9115758
Kelley, T. J., Cotton, C. U., Drumm, M. L. (1997b). In vivo activation of CFTR-dependent chloride transport in murine airway epithelium by CNP. Am. J. Physiol. 273, L1065–L1072. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1997.273.5.L1065
Khan, T. Z., Wagener, J. S., Bost, T., Martinez, J., Accurso, F. J., Riches, D. W. (1995). Early pulmonary inflammation in infants with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 151, 1075–1082. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.4.7697234
Kim, H. P., Wang, X., Galbiati, F., Ryter, S. W., Choi, A. M. (2004). Caveolae compartmentalization of heme oxygenase-1 in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 18, 1080–1089. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1391com
Kim, H. J., Joe, Y., Rah, S. Y., Kim, S. K., Park, S. U., Park, J., et al. (2018). Carbon monoxide-induced TFEB nuclear translocation enhances mitophagy/mitochondrial biogenesis in hepatocytes and ameliorates inflammatory liver injury. Cell Death Dis. 9, 1060. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1112-x
Kim, M. D., Baumlin, N., Yoshida, M., Polineni, D., Salathe, S. F., David, J. K., et al. (2020). Losartan Rescues Inflammation-related Mucociliary Dysfunction in Relevant Models of Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 201, 313–324. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201905-0990OC
Konstan, M. W., Byard, P. J., Hoppel, C. L., Davis, P. B. (1995). Effect of high-dose ibuprofen in patients with cystic fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 848–854. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503303321303
Konstan, M. W., Doring, G., Heltshe, S. L., Lands, L. C., Hilliard, K. A., Koker, P., et al. (2014). A randomized double blind, placebo controlled phase 2 trial of BIIL 284 BS (an LTB4 receptor antagonist) for the treatment of lung disease in children and adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros 13, 148–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2013.12.009
Lancel, S., Hassoun, S. M., Favory, R., Decoster, B., Motterlini, R., Neviere, R. (2009). Carbon monoxide rescues mice from lethal sepsis by supporting mitochondrial energetic metabolism and activating mitochondrial biogenesis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 329, 641–648. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.148049
Lavrovsky, Y., Schwartzman, M. L., Levere, R. D., Kappas, A., Abraham, N. G. (1994). Identification of binding sites for transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-2 in the promoter region of the human heme oxygenase 1 gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 5987–5991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5987
Lee, P. J., Jiang, B. H., Chin, B. Y., Iyer, N. V., Alam, J., Semenza, G. L., et al. (1997). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates transcriptional activation of the heme oxygenase-1 gene in response to hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 5375–5381. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5375
Lee, S. J., Ryter, S. W., Xu, J. F., Nakahira, K., Kim, H. P., Choi, A. M., et al. (2011). Carbon monoxide activates autophagy via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species formation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 45, 867–873. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0352OC
Legendre, C., Mooij, M. J., Adams, C., O’gara, F. (2011). Impaired expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells - a role for HIF-1 in the pathophysiology of CF? J. Cyst. Fibros 10, 286–290. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2011.02.005
Lin, C. C., Hsiao, L. D., Cho, R. L., Yang, C. M. (2019). CO-Releasing Molecule-2 Induces Nrf2/ARE-Dependent Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression Suppressing TNF-alpha-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 8. doi: 10.3390/jcm8040436
Liu, G. H., Qu, J., Shen, X. (2008). NF-kappaB/p65 antagonizes Nrf2-ARE pathway by depriving CBP from Nrf2 and facilitating recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1783, 713–727. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.002
Lovewell, R. R., Hayes, S. M., O’toole, G. A., Berwin, B. (2014). Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellar motility activates the phagocyte PI3K/Akt pathway to induce phagocytic engulfment. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 306, L698–L707. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00319.2013
Luciani, A., Villella, V. R., Esposito, S., Brunetti-Pierri, N., Medina, D., Settembre, C., et al. (2010). Defective CFTR induces aggresome formation and lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis through ROS-mediated autophagy inhibition. Nat. Cell Biol. 12, 863–875. doi: 10.1038/ncb2090
Macgarvey, N. C., Suliman, H. B., Bartz, R. R., Fu, P., Withers, C. M., Welty-Wolf, K. E., et al. (2012). Activation of mitochondrial biogenesis by heme oxygenase-1-mediated NF-E2-related factor-2 induction rescues mice from lethal Staphylococcus aureus sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 185, 851–861. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201106-1152OC
Magalhaes, M., Rivals, I., Claustres, M., Varilh, J., Thomasset, M., Bergougnoux, A., et al. (2017). DNA methylation at modifier genes of lung disease severity is altered in cystic fibrosis. Clin. Epigenet. 9, 19. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0300-8
Maines, M. D., Trakshel, G. M., Kutty, R. K. (1986). Characterization of two constitutive forms of rat liver microsomal heme oxygenase. Only one molecular species of the enzyme is inducible. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 411–419.
Mall, M., Grubb, B. R., Harkema, J. R., O’neal, W. K., Boucher, R. C. (2004). Increased airway epithelial Na+ absorption produces cystic fibrosis-like lung disease in mice. Nat. Med. 10, 487–493. doi: 10.1038/nm1028
Mall, M. A. (2009). Role of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel in the pathogenesis and as a therapeutic target for cystic fibrosis lung disease. Exp. Physiol. 94, 171–174. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2008.042994
Manzanares, D., Gonzalez, C., Ivonnet, P., Chen, R. S., Valencia-Gattas, M., Conner, G. E., et al. (2011). Functional apical large conductance, Ca2+-activated, and voltage-dependent K+ channels are required for maintenance of airway surface liquid volume. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 19830–19839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.185074
Manzanares, D., Krick, S., Baumlin, N., Dennis, J. S., Tyrrell, J., Tarran, R., et al. (2015). Airway Surface Dehydration by Transforming Growth Factor beta (TGF-beta) in Cystic Fibrosis Is Due to Decreased Function of a Voltage-dependent Potassium Channel and Can Be Rescued by the Drug Pirfenidone. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 25710–25716. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.670885
Martin, D., Rojo, A. I., Salinas, M., Diaz, R., Gallardo, G., Alam, J., et al. (2004). Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and the Nrf2 transcription factor in response to the antioxidant phytochemical carnosol. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 8919–8929. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309660200
Matos, A. M., Pinto, F. R., Barros, P., Amaral, M. D., Pepperkok, R., Matos, P. (2019). Inhibition of calpain 1 restores plasma membrane stability to pharmacologically rescued Phe508del-CFTR variant. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 13396–13410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008738
Mayr, F. B., Spiel, A., Leitner, J., Marsik, C., Germann, P., Ullrich, R., et al. (2005). Effects of carbon monoxide inhalation during experimental endotoxemia in humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 171, 354–360. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200404-446OC
Mccoubrey, W. K., Jr., Huang, T. J., Maines, M. D. (1997). Isolation and characterization of a cDNA from the rat brain that encodes hemoprotein heme oxygenase-3. Eur. J. Biochem. 247, 725–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00725.x
Medina, M. V., Sapochnik, D., Garcia Sola, M., Coso, O. (2020). Regulation of the Expression of Heme Oxygenase-1: Signal Transduction, Gene Promoter Activation, and Beyond. Antioxid. Redox Signal 32, 1033–1044. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7991
Middleton, P. G., Mall, M. A., Drevinek, P., Lands, L. C., Mckone, E. F., Polineni, D., et al. (2019). Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor for Cystic Fibrosis with a Single Phe508del Allele. N. Engl. J. Med. 381, 1809–1819. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908639
Mills, E. L., O’Neill, L. A. (2016). Reprogramming mitochondrial metabolism in macrophages as an anti-inflammatory signal. Eur. J. Immunol. 46, 13–21. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445427
Misharin, A. V., Morales-Nebreda, L., Reyfman, P. A., Cuda, C. M., Walter, J. M., Mcquattie-Pimentel, A. C., et al. (2017). Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages drive lung fibrosis and persist in the lung over the life span. J. Exp. Med. 214, 2387–2404. doi: 10.1084/jem.20162152
Misra, H., Lickliter, J., Kazo, F., Abuchowski, A. (2014). PEGylated carboxyhemoglobin bovine (SANGUINATE): results of a phase I clinical trial. Artif. Organs 38, 702–707. doi: 10.1111/aor.12341
Misra, H., Bainbridge, J., Berryman, J., Abuchowski, A., Galvez, K. M., Uribe, L. F., et al. (2017). A Phase Ib open label, randomized, safety study of SANGUINATE in patients with sickle cell anemia. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 39, 20–27. doi: 10.1016/j.bjhh.2016.08.004
Mizuguchi, S., Stephen, J., Bihari, R., Markovic, N., Suehiro, S., Capretta, A., et al. (2009). CORM-3-derived CO modulates polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration across the vascular endothelium by reducing levels of cell surface-bound elastase. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 297, H920–H929. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00305.2009
Mogayzel, P. J., Jr., Naureckas, E. T., Robinson, K. A., Mueller, G., Hadjiliadis, D., Hoag, J. B., et al. (2013). Cystic fibrosis pulmonary guidelines. Chronic medications for maintenance of lung health. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 187, 680–689. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201207-1160OE
Montgomery, S. T., Mall, M. A., Kicic, A., Stick, S. M., Arest, C. F. (2017). Hypoxia and sterile inflammation in cystic fibrosis airways: mechanisms and potential therapies. Eur. Respir. J. 49. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00903-2016
Moreau-Marquis, S., Bomberger, J. M., Anderson, G. G., Swiatecka-Urban, A., Ye, S., O’toole, G. A., et al. (2008). The DeltaF508-CFTR mutation results in increased biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa by increasing iron availability. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 295, L25–L37. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00391.2007
Motterlini, R., Foresti, R. (2017). Biological signaling by carbon monoxide and carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 312, C302–C313. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00360.2016
Motterlini, R., Otterbein, L. E. (2010). The therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 9, 728–743. doi: 10.1038/nrd3228
Motterlini, R., Clark, J. E., Foresti, R., Sarathchandra, P., Mann, B. E., Green, C. J. (2002). Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules: characterization of biochemical and vascular activities. Circ. Res. 90, E17–E24. doi: 10.1161/hh0202.104530
Murad, F. (2006). Shattuck Lecture. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in cell signaling and drug development. N. Engl. J. Med. 355, 2003–2011. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa063904
Murray, T. S., Okegbe, C., Gao, Y., Kazmierczak, B. I., Motterlini, R., Dietrich, L. E., et al. (2012). The carbon monoxide releasing molecule CORM-2 attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. PloS One 7, e35499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035499
Nagel, C., Mclean, S., Poole, R. K., Braunschweig, H., Kramer, T., Schatzschneider, U. (2014). Introducing [Mn(CO)3(tpa-kappa(3)N)](+) as a novel photoactivatable CO-releasing molecule with well-defined iCORM intermediates - synthesis, spectroscopy, and antibacterial activity. Dalton. Trans. 43, 9986–9997. doi: 10.1039/c3dt51848e
Naidu, S., Wijayanti, N., Santoso, S., Kietzmann, T., Immenschuh, S. (2008). An atypical NF-kappa B-regulated pathway mediates phorbol ester-dependent heme oxygenase-1 gene activation in monocytes. J. Immunol. 181, 4113–4123. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.4113
Nakahira, K., Kim, H. P., Geng, X. H., Nakao, A., Wang, X., Murase, N., et al. (2006). Carbon monoxide differentially inhibits TLR signaling pathways by regulating ROS-induced trafficking of TLRs to lipid rafts. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2377–2389. doi: 10.1084/jem.20060845
Nobre, L. S., Seixas, J. D., Romao, C. C., Saraiva, L. M. (2007). Antimicrobial action of carbon monoxide-releasing compounds. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 4303–4307. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00802-07
Nobre, L. S., Al-Shahrour, F., Dopazo, J., Saraiva, L. M. (2009). Exploring the antimicrobial action of a carbon monoxide-releasing compound through whole-genome transcription profiling of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 155, 813–824. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.023911-0
Nobre, L. S., Jeremias, H., Romao, C. C., Saraiva, L. M. (2016). Examining the antimicrobial activity and toxicity to animal cells of different types of CO-releasing molecules. Dalton. Trans. 45, 1455–1466. doi: 10.1039/C5DT02238J
Ogawa, K., Sun, J., Taketani, S., Nakajima, O., Nishitani, C., Sassa, S., et al. (2001). Heme mediates derepression of Maf recognition element through direct binding to transcription repressor Bach1. EMBO J. 20, 2835–2843. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.11.2835
Onyiah, J. C., Sheikh, S. Z., Maharshak, N., Steinbach, E. C., Russo, S. M., Kobayashi, T., et al. (2013). Carbon monoxide and heme oxygenase-1 prevent intestinal inflammation in mice by promoting bacterial clearance. Gastroenterology 144, 789–798. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.025
Otterbein, L. E., Bach, F. H., Alam, J., Soares, M., Tao Lu, H., Wysk, M., et al. (2000). Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat. Med. 6, 422–428. doi: 10.1038/74680
Otterbein, L. E., Otterbein, S. L., Ifedigbo, E., Liu, F., Morse, D. E., Fearns, C., et al. (2003). MKK3 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates carbon monoxide-induced protection against oxidant-induced lung injury. Am. J. Pathol. 163, 2555–2563. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63610-3
Otterbein, L. E., May, A., Chin, B. Y. (2005). Carbon monoxide increases macrophage bacterial clearance through Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 expression. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 51, 433–440.
Park, J. E., Yung, R., Stefanowicz, D., Shumansky, K., Akhabir, L., Durie, P. R., et al. (2011). Cystic fibrosis modifier genes related to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Genes Immun. 12, 370–377. doi: 10.1038/gene.2011.5
Paul, K., Rietschel, E., Ballmann, M., Griese, M., Worlitzsch, D., Shute, J., et al. (2004). Effect of treatment with dornase alpha on airway inflammation in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 169, 719–725. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200307-959OC
Peers, C., Boyle, J. P., Scragg, J. L., Dallas, M. L., Al-Owais, M. M., Hettiarachichi, N. T., et al. (2015). Diverse mechanisms underlying the regulation of ion channels by carbon monoxide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 172, 1546–1556. doi: 10.1111/bph.12760
Perez, A., Issler, A. C., Cotton, C. U., Kelley, T. J., Verkman, A. S., Davis, P. B. (2007). CFTR inhibition mimics the cystic fibrosis inflammatory profile. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 292, L383–L395. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00403.2005
Piantadosi, C. A., Carraway, M. S., Babiker, A., Suliman, H. B. (2008). Heme oxygenase-1 regulates cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2-mediated transcriptional control of nuclear respiratory factor-1. Circ. Res. 103, 1232–1240. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000338597.71702.ad
Piantadosi, C. A., Withers, C. M., Bartz, R. R., Macgarvey, N. C., Fu, P., Sweeney, T. E., et al. (2011). Heme oxygenase-1 couples activation of mitochondrial biogenesis to anti-inflammatory cytokine expression. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 16374–16385. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.207738
Porteous, M. K., Diamond, J. M., Christie, J. D. (2015). Primary graft dysfunction: lessons learned about the first 72 h after lung transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 20, 506–514. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000232
Poss, K. D., Tonegawa, S. (1997a). Heme oxygenase 1 is required for mammalian iron reutilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 10919–10924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10919
Poss, K. D., Tonegawa, S. (1997b). Reduced stress defense in heme oxygenase 1-deficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 10925–10930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10925
Queiroga, C. S., Almeida, A. S., Vieira, H. L. (2012). Carbon monoxide targeting mitochondria. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 749845. doi: 10.1155/2012/749845
Rana, N., Mclean, S., Mann, B. E., Poole, R. K. (2014). Interaction of the carbon monoxide-releasing molecule Ru(CO)3Cl(glycinate) (CORM-3) with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium: in situ measurements of carbon monoxide binding by integrating cavity dual-beam spectrophotometry. Microbiology 160, 2771–2779. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.081042-0
Ratjen, F., Saiman, L., Mayer-Hamblett, N., Lands, L. C., Kloster, M., Thompson, V., et al. (2012). Effect of azithromycin on systemic markers of inflammation in patients with cystic fibrosis uninfected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chest 142, 1259–1266. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0628
Recchiuti, A., Mattoscio, D., Isopi, E. (2019). Roles, Actions, and Therapeutic Potential of Specialized Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators for the Treatment of Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 252. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00252
Reid, D. W., Withers, N. J., Francis, L., Wilson, J. W., Kotsimbos, T. C. (2002). Iron deficiency in cystic fibrosis: relationship to lung disease severity and chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Chest 121, 48–54. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.1.48
Reyfman, P. A., Walter, J. M., Joshi, N., Anekalla, K. R., Mcquattie-Pimentel, A. C., Chiu, S., et al. (2019). Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 199, 1517–1536. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2410OC
Ringholz, F. C., Buchanan, P. J., Clarke, D. T., Millar, R. G., Mcdermott, M., Linnane, B., et al. (2014). Reduced 15-lipoxygenase 2 and lipoxin A4/leukotriene B4 ratio in children with cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 44, 394–404. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00106013
Riquelme, S. A., Hopkins, B. D., Wolfe, A. L., Dimango, E., Kitur, K., Parsons, R., et al. (2017). Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Attaches Tumor Suppressor PTEN to the Membrane and Promotes Anti Pseudomonas aeruginosa Immunity. Immunity 47, 1169–1181 e1167. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.11.010
Riquelme, S. A., Lozano, C., Moustafa, A. M., Liimatta, K., Tomlinson, K. L., Britto, C., et al. (2019). CFTR-PTEN-dependent mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav4634
Roesch, E. A., Nichols, D. P., Chmiel, J. F. (2018). Inflammation in cystic fibrosis: An update. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 53, S30–S50. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24129
Rosas, I. O., Goldberg, H. J., Collard, H. R., El-Chemaly, S., Flaherty, K., Hunninghake, G. M., et al. (2018). A Phase II Clinical Trial of Low-Dose Inhaled Carbon Monoxide in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 153, 94–104. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.09.052
Ross, K. R., Chmiel, J. F., Konstan, M. W. (2009). The role of inhaled corticosteroids in the management of cystic fibrosis. Paediatr. Drugs 11, 101–113. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200911020-00002
Roussel, L., Rousseau, S. (2017). Exposure of airway epithelial cells to Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm-derived quorum sensing molecules decrease the activity of the anti-oxidant response element bound by NRF2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 483, 829–833. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.009
Rowe, S. M., Heltshe, S. L., Gonska, T., Donaldson, S. H., Borowitz, D., Gelfond, D., et al. (2014). Clinical mechanism of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator potentiator ivacaftor in G551D-mediated cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 190, 175–184. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201404-0703OC
Rushworth, S. A., Zaitseva, L., Murray, M. Y., Shah, N. M., Bowles, K. M., Macewan, D. J. (2012). The high Nrf2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-kappaB and underlies its chemo-resistance. Blood 120, 5188–5198. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-422121
Ryter, S. W., Choi, A. M. (2016). Targeting heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide for therapeutic modulation of inflammation. Transl. Res. 167, 7–34. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2015.06.011
Ryter, S. W., Alam, J., Choi, A. M. (2006). Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: from basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 86, 583–650. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2005
Ryter, S. W., Ma, K. C., Choi, A. M. K. (2018). Carbon monoxide in lung cell physiology and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 314, C211–C227. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00022.2017
Sam, C., Desai, P., Laber, D., Patel, A., Visweshwar, N., Jaglal, M. (2017). Pegylated bovine carboxyhaemoglobin utilisation in a thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura patient. Transfus. Med. 27, 300–302. doi: 10.1111/tme.12407
Sawle, P., Foresti, R., Mann, B. E., Johnson, T. R., Green, C. J., Motterlini, R. (2005). Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CO-RMs) attenuate the inflammatory response elicited by lipopolysaccharide in RAW264.7 murine macrophages. Br. J. Pharmacol. 145, 800–810. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706241
Serhan, C. N., Chiang, N., Dalli, J., Levy, B. D. (2014). Lipid mediators in the resolution of inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7, a016311. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016311
Shi, J., Yu, J., Zhang, Y., Wu, L., Dong, S., Wu, L., et al. (2019). PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated HO-1 induction regulates mitochondrial quality control and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Lab. Invest. 99, 1795–1809. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0286-x
Steagall, W. K., Elmer, H. L., Brady, K. G., Kelley, T. J. (2000). Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-dependent regulation of epithelial inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 22, 45–50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.22.1.3789
Stites, S. W., Plautz, M. W., Bailey, K., O’brien-Ladner, A. R., Wesselius, L. J. (1999). Increased concentrations of iron and isoferritins in the lower respiratory tract of patients with stable cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 160, 796–801. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.160.3.9811018
Sturges, N. C., Wikstrom, M. E., Winfield, K. R., Gard, S. E., Brennan, S., Sly, P. D., et al. (2010). Monocytes from children with clinically stable cystic fibrosis show enhanced expression of Toll-like receptor 4. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 45, 883–889. doi: 10.1002/ppul.21230
Tavares, A. F., Nobre, L. S., Saraiva, L. M. (2012). A role for reactive oxygen species in the antibacterial properties of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 336, 1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02633.x
Tavares, A. F., Parente, M. R., Justino, M. C., Oleastro, M., Nobre, L. S., Saraiva, L. M. (2013). The bactericidal activity of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules against Helicobacter pylori. PloS One 8, e83157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083157
Telezhkin, V., Brazier, S. P., Mears, R., Muller, C. T., Riccardi, D., Kemp, P. J. (2011). Cysteine residue 911 in C-terminal tail of human BK(Ca)alpha channel subunit is crucial for its activation by carbon monoxide. Pflugers Arch. 461, 665–675. doi: 10.1007/s00424-011-0924-7
Thenuwara, K., Thomas, J., Ibsen, M., Ituk, U., Choi, K., Nickel, E., et al. (2017). Use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy and PEGylated carboxyhemoglobin bovine in a Jehovah’s Witness with life-threatening anemia following postpartum hemorrhage. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 29, 73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2016.10.006
Tirouvanziam, R., Gernez, Y., Conrad, C. K., Moss, R. B., Schrijver, I., Dunn, C. E., et al. (2008). Profound functional and signaling changes in viable inflammatory neutrophils homing to cystic fibrosis airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 4335–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712386105
Tsoyi, K., Ha, Y. M., Kim, Y. M., Lee, Y. S., Kim, H. J., Kim, H. J., et al. (2009). Activation of PPAR-gamma by carbon monoxide from CORM-2 leads to the inhibition of iNOS but not COX-2 expression in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Inflammation 32, 364–371. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9144-0
Turnbull, A. R., Pyle, C. J., Patel, D. F., Jackson, P. L., Hilliard, T. N., Regamey, N., et al. (2020). Abnormal pro-gly-pro pathway and airway neutrophilia in pediatric cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros 19, 40–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.017
Uddin, M. J., Li, C. S., Joe, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, Q., Ryter, S. W., et al. (2015). Carbon Monoxide Inhibits Tenascin-C Mediated Inflammation via IL-10 Expression in a Septic Mouse Model. Mediators Inflammation 2015, 613249. doi: 10.1155/2015/613249
Velsor, L. W., Van Heeckeren, A., Day, B. J. (2001). Antioxidant imbalance in the lungs of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein mutant mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 281, L31–L38. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.281.1.L31
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Kim, H. P., Nakahira, K., Ryter, S. W., Choi, A. M. (2007). Carbon monoxide protects against hyperoxia-induced endothelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting reactive oxygen species formation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 1718–1726. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607610200
Wang, S., Publicover, S., Gu, Y. (2009). An oxygen-sensitive mechanism in regulation of epithelial sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 2957–2962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809100106
Wang, X. M., Kim, H. P., Nakahira, K., Ryter, S. W., Choi, A. M. (2009). The heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide pathway suppresses TLR4 signaling by regulating the interaction of TLR4 with caveolin-1. J. Immunol. 182, 3809–3818. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0712437
Wang, D., Viennois, E., Ji, K., Damera, K., Draganov, A., Zheng, Y., et al. (2014). A click-and-release approach to CO prodrugs. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 50, 15890–15893. doi: 10.1039/C4CC07748B
Wang, G. (2017). Mechanistic insight into the heme-independent interplay between iron and carbon monoxide in CFTR and Slo1 BKCa channels. Metallomics 9, 634–645. doi: 10.1039/C7MT00065K
Wardyn, J. D., Ponsford, A. H., Sanderson, C. M. (2015). Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-kappaB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 43, 621–626. doi: 10.1042/BST20150014
Waza, A. A., Hamid, Z., Ali, S., Bhat, S. A., Bhat, M. A. (2018). A review on heme oxygenase-1 induction: is it a necessary evil. Inflammation Res. 67, 579–588. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1151-x
Wegiel, B., Hanto, D. W., Otterbein, L. E. (2013). The social network of carbon monoxide in medicine. Trends Mol. Med. 19, 3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.10.001
Wegiel, B., Larsen, R., Gallo, D., Chin, B. Y., Harris, C., Mannam, P., et al. (2014a). Macrophages sense and kill bacteria through carbon monoxide-dependent inflammasome activation. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 4926–4940. doi: 10.1172/JCI72853
Wegiel, B., Nemeth, Z., Correa-Costa, M., Bulmer, A. C., Otterbein, L. E. (2014b). Heme oxygenase-1: a metabolic nike. Antioxid. Redox Signal 20, 1709–1722. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5667
Wegiel, B., Hauser, C. J., Otterbein, L. E. (2015). Heme as a danger molecule in pathogen recognition. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 89, 651–661. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.08.020
Wiesel, P., Patel, A. P., Difonzo, N., Marria, P. B., Sim, C. U., Pellacani, A., et al. (2000). Endotoxin-induced mortality is related to increased oxidative stress and end-organ dysfunction, not refractory hypotension, in heme oxygenase-1-deficient mice. Circulation 102, 3015–3022. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.24.3015
Wilkinson, W. J., Kemp, P. J. (2011). Carbon monoxide: an emerging regulator of ion channels. J. Physiol. 589, 3055–3062. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.206706
Wilson, J. L., Jesse, H. E., Poole, R. K., Davidge, K. S. (2012). Antibacterial effects of carbon monoxide. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 13, 760–768. doi: 10.2174/138920112800399329
Wilson, J. L., Bouillaud, F., Almeida, A. S., Vieira, H. L., Ouidja, M. O., Dubois-Rande, J. L., et al. (2017). Carbon monoxide reverses the metabolic adaptation of microglia cells to an inflammatory stimulus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 104, 311–323. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.022
Yachie, A., Niida, Y., Wada, T., Igarashi, N., Kaneda, H., Toma, T., et al. (1999). Oxidative stress causes enhanced endothelial cell injury in human heme oxygenase-1 deficiency. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 129–135. doi: 10.1172/JCI4165
Yamamoto, T., Takano, N., Ishiwata, K., Ohmura, M., Nagahata, Y., Matsuura, T., et al. (2014). Reduced methylation of PFKFB3 in cancer cells shunts glucose towards the pentose phosphate pathway. Nat. Commun. 5, 3480. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4480
Yang, J., Eiserich, J. P., Cross, C. E., Morrissey, B. M., Hammock, B. D. (2012). Metabolomic profiling of regulatory lipid mediators in sputum from adult cystic fibrosis patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 53, 160–171. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.05.001
Yu, M., Li, H., Liu, Q., Liu, F., Tang, L., Li, C., et al. (2011). Nuclear factor p65 interacts with Keap1 to repress the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Cell Signal 23, 883–892. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.01.014
Yurdagul, A., Jr., Doran, A. C., Cai, B., Fredman, G., Tabas, I. A. (2017). Mechanisms and Consequences of Defective Efferocytosis in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 4, 86. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00086
Zakhary, R., Gaine, S. P., Dinerman, J. L., Ruat, M., Flavahan, N. A., Snyder, S. H. (1996). Heme oxygenase 2: endothelial and neuronal localization and role in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 795–798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.2.795
Zhang, P. X., Murray, T. S., Villella, V. R., Ferrari, E., Esposito, S., D’souza, A., et al. (2013). Reduced caveolin-1 promotes hyperinflammation due to abnormal heme oxygenase-1 localization in lipopolysaccharide-challenged macrophages with dysfunctional cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J. Immunol. 190, 5196–5206. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201607
Zhang, P. X., Cheng, J., Zou, S., D’souza, A. D., Koff, J. L., Lu, J., et al. (2015). Pharmacological modulation of the AKT/microRNA-199a-5p/CAV1 pathway ameliorates cystic fibrosis lung hyper-inflammation. Nat. Commun. 6, 6221. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7221
Zhang, S., Shrestha, C. L., Kopp, B. T. (2018). Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators have differential effects on cystic fibrosis macrophage function. Sci. Rep. 8, 17066. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35151-7
Zhou, H., Lu, F., Latham, C., Zander, D. S., Visner, G. A. (2004). Heme oxygenase-1 expression in human lungs with cystic fibrosis and cytoprotective effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 170, 633–640. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200311-1607OC
Ziady, A. G., Sokolow, A., Shank, S., Corey, D., Myers, R., Plafker, S., et al. (2012). Interaction with CREB binding protein modulates the activities of Nrf2 and NF-kappaB in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 302, L1221–L1231. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00156.2011
Keywords: monocyte/macrophages, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), carbon monoxide (CO), CO-releasing molecules, lung inflammation, cystic fibrosis (CF)
Citation: Di Pietro C, Öz HH, Murray TS and Bruscia EM (2020) Targeting the Heme Oxygenase 1/Carbon Monoxide Pathway to Resolve Lung Hyper-Inflammation and Restore a Regulated Immune Response in Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 11:1059. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01059
Received: 01 May 2020; Accepted: 30 June 2020;
Published: 14 July 2020.
Edited by:
Carla Maria Pedrosa Ribeiro, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, United StatesReviewed by:
Judith Voynow, Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU, United StatesCarole L. Wilson, University of Wisconsin-Madison, United States
Copyright © 2020 Di Pietro, Öz, Murray and Bruscia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Emanuela M. Bruscia, ZW1hbnVlbGEuYnJ1c2NpYUB5YWxlLmVkdQ==
 Caterina Di Pietro
Caterina Di Pietro Hasan H. Öz
Hasan H. Öz Thomas S. Murray
Thomas S. Murray Emanuela M. Bruscia
Emanuela M. Bruscia