- Janssen Research & Development, LLC, San Diego, CA, USA
The histamine H4 receptor (H4R) was first noted as a sequence in genomic databases that had features of a class A G-protein coupled receptor. This putative receptor was found to bind histamine consistent with its homology to other histamine receptors and thus became the fourth member of the histamine receptor family. Due to the previous success of drugs that target the H1 and H2 receptors, an effort was made to understand the function of this new receptor and determine if it represented a viable drug target. Taking advantage of the vast literature on the function of histamine, a search for histamine activity that did not appear to be mediated by the other three histamine receptors was undertaken. From this asthma and pruritus emerged as areas of particular interest. Histamine has long been suspected to play a role in the pathogenesis of asthma, but antihistamines that target the H1 and H2 receptors have not been shown to be effective for this condition. The use of selective ligands in animal models of asthma has now potentially filled this gap by showing a role for the H4R in mediating lung function and inflammation. A similar story exists for chronic pruritus associated with conditions such as atopic dermatitis. Antihistamines that target the H1 receptor are effective in reducing acute pruritus, but are ineffective in pruritus experienced by patients with atopic dermatitis. As for asthma, animal models have now suggested a role for the H4R in mediating pruritic responses, with antagonists of the H4R reducing pruritus in a number of different conditions. The anti-pruritic effect of H4R antagonists has recently been shown in human clinical studies, validating the preclinical findings in the animal models. A selective H4R antagonist inhibited histamine-induced pruritus in health volunteers and reduced pruritus in patients with atopic dermatitis. The history to date of the H4R provides an excellent example of the deorphanization of a novel receptor and the translation of this into clinical efficacy in humans.
Introduction
There are now four known G-coupled protein receptors (GPCRs) that use histamine as a ligand. These receptors were discovered over a span of almost 100 years and each discovery provides excellent examples of the use of state-of-the-art receptor pharmacology to discovery new receptors. The first actions of histamine were noted around 1910 (Barger and Dale, 1910; Dale and Laidlaw, 1911), but this before the idea of receptors was widely accepted. After the development of compounds that blocked the effect of histamine in the 1930–1940s, it was noted that their effects were consistent with a competition for binding at a receptor now known as the histamine H1 receptor (H1R; Wells et al., 1945). These first antihistamines became the basis for very successful drugs, some of which are still in use today. However, they also revealed new questions since there were actions of histamine that were not blocked by these ligands. This led to the proposal that a second histamine receptor existed (Ash and Schild, 1966), and the discovery of selective ligands for this receptor led to its pharmacological characterization and the designation as the H2R (Black et al., 1972). A similar story exist for the discovery of the H3R, where it was noted that various histamine receptor ligands modulated histamine actions in the brain, but that the pharmacology did not match the known H1R and H2R (Arrang et al., 1983).
Discovery of the Histamine H4 Receptor
However, by the 1990s novel receptors were discovered mainly by the identification of their gene sequence and less so by their pharmacology. The cloning of the receptor cDNA for the human H1R and H2R were described in the early 1990s (Gantz et al., 1991; De Backer et al., 1993), but the sequence of the H3R remained elusive despite much work looking for sequences with similarity to the H1R and H2R. The breakthrough came using a different approach where sequences were identified that contained general homologies to GPCR (e.g., predicted seven transmembrane domains and other common residues). These putative orphan GPCR genes were then screened for binding to likely ligands. Using such an approach, a novel sequence was discovered that encoded a GPCR that bound to histamine and had pharmacology that matched that described for the H3R (Lovenberg et al., 1999). The details of the sequence revealed why the gene for the H3R was not found by a homology approach, since it only exhibited ∼20% homology to the H1R and H2R.
While the cloning of the H3R used an orphan GPCR/reverse pharmacology approach, it yielded a receptor that was already known and characterized on a pharmacological basis. The discovery of the H4R truly started with the identification of an orphan GPCR. The discovery of the gene for the H3R provided a tool for additional homology searches of databases for related sequences. This yielded a putative receptor that was ∼35% identical to the H3R and when expressed in heterologous systems was found to have a high affinity for histamine (Liu et al., 2001). These genomic approaches were so prevalent at the time that the identification of this new receptor, now known as the histamine H4 receptor (H4R), was described almost simultaneously by six different laboratories (Nakamura et al., 2000; Oda et al., 2000; Liu et al., 2001; Morse et al., 2001; Nguyen et al., 2001; Zhu et al., 2001). Unlike the H3R, the H4R was completely novel and its function was unknown. However, one hint of function was evident from the expression pattern described in the original cloning papers that showed a fairly selective expression on bone marrow and hematopoietic cells known to be involved in inflammatory and immune responses.
Development of Selective Ligands
The identification of a novel histamine receptor, its expression mainly on cells involved in immune responses coupled with the successful history of drugs that target the H1R and H2R generated immediate interest (Hough, 2001). However, deorphanizing the receptor was only the beginning. Importantly, selective ligands were needed to be able to understand the function of the receptor. The receptor has a relatively high homology to the H3R and thus it is not surprising that many of the compounds previously described as H3R ligands also had affinity for the H4R (Liu et al., 2001). These ligands included (R)-α-methylhistamine, an H3R agonist, and thioperamide, an H3R antagonists, but because these ligands had affinity for both receptors they are not ideal tools for understanding the function of the H4R. The first potent and selective H4R antagonist was JNJ 7777120 (Jablonowski et al., 2003). This compound has a high affinity for the H4R and is highly selective relative to other histamine receptors (Thurmond et al., 2004).
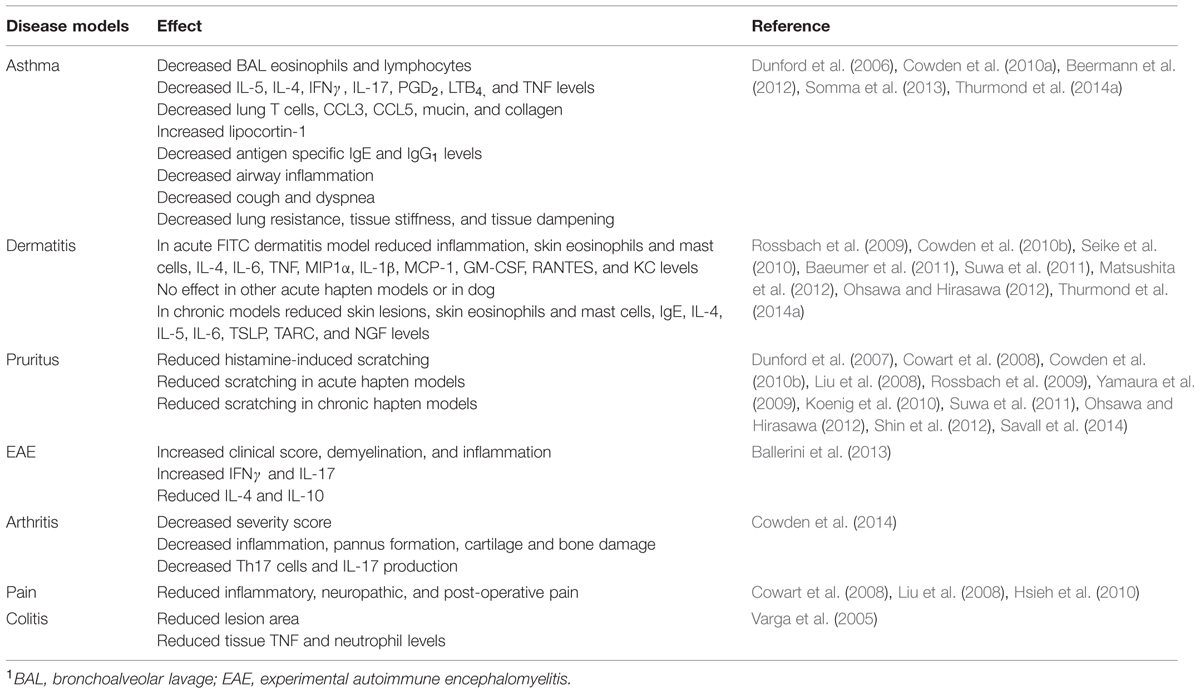
JNJ 7777120 has become an excellent tool for understanding the physiological role of the H4R and has been used extensively in vitro cell models and in animal models. The use of JNJ 7777120 in vivo provided the first evidence that H4R antagonists could have anti-inflammatory properties. Neutrophil influx in a mouse peritonitis model was reduced upon pretreatment with JNJ 7777120 (Thurmond et al., 2004). Early work also showed that JNJ 7777120 and its analog, JNJ 10191584, were also efficacious in a rat colitis model (Varga et al., 2005). This compound along with other H4R antagonists have shown activity in models of asthma, dermatitis, pain, and pruritus among others (Table 1; Dunford et al., 2006, 2007; Cowden et al., 2010b; Hsieh et al., 2010).
As evidenced by the pharmacology of the other histamine receptors, it is important not to rely on the data provided by a single ligand when assigning function to a particular receptor. The reason for this is that despite the best efforts it is almost impossible to completely understand the pharmacology of any ligand and how it may differ in different species, cell types, or conditions. Because of these factors, researchers must use a combination of tools including agonist/antagonist pairs, ligands from different chemical classes, and/or knock-out animals before making conclusions about the function of receptor. The use of a single ligand only gives firm conclusions about the action of that ligand under the given experimental conditions.
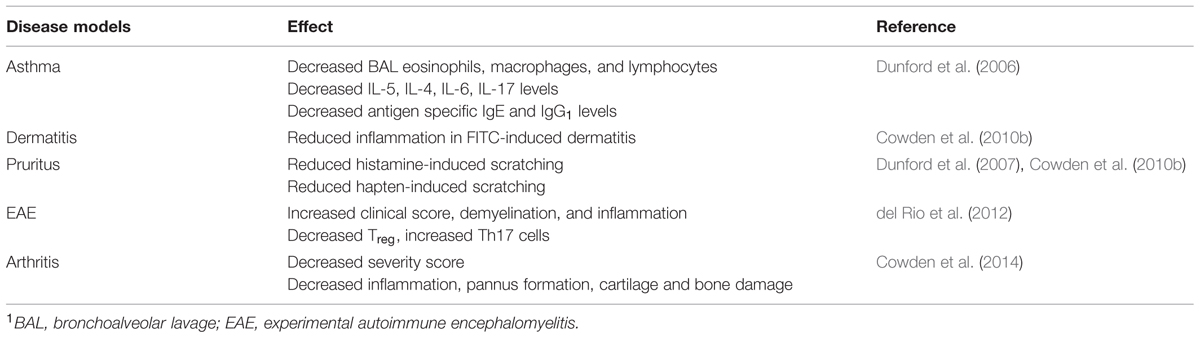
This has been highlighted as a potential issue with JNJ 7777120 as it has been described as having agonistic effects at the H4R of some species in some, but not all, transfected cell models and has been described to drive functional selectivity, i.e., arrestin activation, of the H4R (Seifert et al., 2011). However, while these other pharmacological effects may exist, most of the current data support the fact that JNJ 7777120 is an antagonist in vivo and in primary cells. For example the effects on JNJ 7777120 in models of asthma, dermatitis, arthritis, pain, and peritonitis are consistent to those of other distinct H4R ligands and in H4R-deficient mice (Table 2; Thurmond et al., 2004, 2014a; Dunford et al., 2006; Coruzzi et al., 2007; Altenbach et al., 2008; Cowart et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2008; Cowden et al., 2010b, 2014; Hsieh et al., 2010; Shin et al., 2012; Savall et al., 2014). Perhaps one of the best examples of this is in the role of the receptor in mediating pruritic responses in mice. Dunford et al. (2007) reported that histamine-induced scratching in mice could be blocked by JNJ 77777120 and did not occur in H4R-deficient mice. Furthermore, other H4R agonists also induce scratching that can be blocked by JNJ 7777120, but cannot induce scratching in H4R-deficient mice (Dunford et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2010). Other H4R antagonists with different chemical structure also block this response (Cowart et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2008; Koenig et al., 2010; Shin et al., 2012; Savall et al., 2014). The data then clearly support the role of JNJ 77777120 as an antagonist for this effect. The compound reverses the effect of agonists, mimics the findings in animal lacking the H4R and the results are replicated by other antagonists. However, this cannot be generalized. For example JNJ 7777120 also has been shown to block substance P induced itch (Yamaura et al., 2009) and while is it appropriate to speculate that H4R activation is involved in substance P induced itch based on data in other models, it would take studies in H4R-deficient mice or with other structurally distinct antagonist to firmly conclude this.
Some of the in vivo data also yield insight as to the role of functional selectivity at the H4R. In the models of pruritus, asthma, and dermatitis the phenotype is the same between JNJ 7777120-treated and H4R-deficient mice (Dunford et al., 2006, 2007; Cowden et al., 2010b). This suggests that if the induction of β-arrestin shown by Rosethorne and Charlton (2011) occurs in mice (currently functional selectivity has only been studied for the human receptor), it has little impact on the activity of the compound in these models. For if JNJ 7777120-induced arrestin pathways are anti-inflammatory then they would not exist in the receptor deficient animals. Once again the most likely explanation is that the compound functions as an antagonist of the receptor. This does not mean, however, that the possibility of functional selectivity should be dismissed and it may suggest that antagonists could be created that only block a subset of the pathways activated by the receptor.
Function
Much of the original expression data obtained with the H4R pointed to expression on cells involved in immune responses. In conjunction with this, researchers took advantage that the ligand for this orphan receptor was histamine and thus searched the extensive literature on histamine to find functions mediated by histamine, but where the pharmacology did not clearly point to the H1R, H2R, or H3R. One example of this was in eosinophils. In Clark et al. (1975) showed that histamine could induce chemotaxis of human eosinophils at low concentrations, 10-7 and 10-6 M, but that at 10-5 M chemotaxis was reduced. They showed that neither mepyramine (an H1R antagonist) nor metiamide (an H2R antagonist) had any effect on the enhanced chemotaxis, but that metiamide reversed the inhibition of chemotaxis at 10-5 M. They concluded that the stimulation of chemotaxis by histamine was independent of H1R and H2R and in a later paper concluded that a third histamine receptor existed on eosinophils (this was prior to the discovery of the H3R; Clark et al., 1977). Raible et al. (1992) showed that histamine induced a calcium response in eosinophils and, as observed for chemotaxis, this effect was not inhibited by an H1R antagonist (mepyramine) or an H2R antagonist (cimetidine). The calcium response was inhibited by thioperamide which was described as an antagonist of the newly discovered H3R. In addition (R)-α-methylhistamine, an H3R agonist, induced a calcium response similar to that of histamine. However, the authors commented that the fact that (R)-α-methylhistamine was less potent than histamine suggested that this calcium response was not mediated by a classic H3R since at this receptor histamine is more potent than (R)-α-methylhistamine. In a later study Raible et al. (1994) confirm this unusual pharmacology with a series a different H3R antagonists and agonists. The identity of this novel histamine receptor remained a mystery (or was perhaps ignored) until the discovery of the gene for the H4R. It was noted that the pharmacological profile of the H4R was similar to the receptor described by Raible et al. (1994; Oda et al., 2000; Hough, 2001; Liu et al., 2001; Morse et al., 2001; Zhu et al., 2001; O’Reilly et al., 2002). In particular, burimamide is a weak H4R partial agonist (Zhu et al., 2001; Lim et al., 2005), while (R)-α-methylhistamine and N-methylhistamine are both full agonist (Nakamura et al., 2000; Oda et al., 2000; Liu et al., 2001; Morse et al., 2001; Zhu et al., 2001), but are less potent than histamine thus matching the conflicting pharmacology described by Raible et al. (1992, 1994). The role of the H4R in mediating histamine-induced eosinophil chemotaxis and calcium responses was confirmed once selective ligands became available. Selective H4R antagonists (e.g., JNJ 7777120) have been shown to block histamine-induced chemotaxis and calcium responses (Ling et al., 2004; Strakhova et al., 2009; Reher et al., 2012; Shin et al., 2012). Chemotaxis of eosinophils can also be studied indirectly by measuring shape-change related to actin reorganization that precedes chemotaxis (Sabroe et al., 1999). Histamine and selective H4R agonists such as 4-methylhistamine and others have been shown to induce eosinophil shape change and this can be blocked by H4R selective antagonists (Ling et al., 2004; Lim et al., 2005; Yu et al., 2010; Shin et al., 2012; Thurmond et al., 2014a).
The histamine-induced eosinophil shape change was used as a pharmacodynamics readout for a clinical study with JNJ 39758979 (Thurmond et al., 2014a). After oral dosing of the compound to healthy volunteers, blood samples were taken at various timepoints, stimulated with histamine and the shape change of the eosinophils was assessed. At doses and time points where the concentration of JNJ 39758979 was above 100 nM, a statistically significant inhibition was observed. This level of potency was similar to what when the compound was added to blood in vitro (Thurmond et al., 2014a). These results show that in vivo administration of an H4R antagonist in humans can have impact on eosinophil function.
The initial idea that a new histamine receptor was present on eosinophils came about because of differences in the pharmacology of various histamine ligands. Not only were H1R and H2R ligands ineffective, but the potency of H3R ligands was not as expected (Raible et al., 1994). Therefore, it is important to evaluate the pharmacological data with the H4R ligands carefully. First, it has been noted that the potency for eosinophil function of the various H4R ligands (either selective or non-selective) compared to histamine is in general agreement with their relative affinities thus supporting that this is in fact the H4R (Buckland et al., 2003; Ling et al., 2004; Lim et al., 2005; Yu et al., 2010; Reher et al., 2012). Furthermore, the Ki for antagonists can be calculated from studies where the EC50 of histamine is given using modifications of the Cheng and Prusoff (1973) equation. Ling et al. (2004) report IC50 values for JNJ 7777120 and thioperamide for eosinophil shape change and chemotaxis. One can use these values along with the concentration and EC50 for histamine to calculate Ki values of 5 and 4 nM for JNJ 7777120 and 26 and 26 nM for thioperamide for inhibiting histamine-induced eosinophil shape change and chemotaxis, respectively. These numbers are similar to the reported Ki values from recombinant systems for JNJ 7777120 (4 nM) and thioperamide (27 nM; Liu et al., 2001; Thurmond et al., 2004). Consistent with this Barnard et al. (2008) report an IC50 of JNJ 7777120 of 6 nM that corresponds to a calculated Ki value of 2 nM. However, Seifert et al. (2011) have stated incorrectly that the discrepancy in the IC50 values for JNJ 7777120 between the Ling et al. (2004) and Barnard et al. (2008) studies (300 versus 6 nM) support the notion of functional selectivity for the H4R in eosinophils. However, the authors fail to take into account the differences in EC50 for histamine 19 nM for Ling et al. (2004) and 150 nM for Barnard et al. (2008), which when properly accounted for yields almost identical Ki values for JNJ 7777120 (5 nM versus 2 nM). The differences in the EC50 for histamine between the two studies is most likely due to large differences in histamine response related to H4R levels between difference donors as reported by Yu et al. (2010).
The effect of JNJ 7777120 on the histamine calcium response in eosinophils yields the same conclusion with a reported Ki value of 1.3 nM (Reher et al., 2012). However, these same authors report a discrepancy in the Ki values for JNJ 7777120 with respect to chemotaxis. The calculated Ki for JNJ 7777120 was 9.8 nM when histamine was used to induce chemotaxis, but 1.6 nM when a selective H4R agonist was used, UR-PI376 (Reher et al., 2012). They use this data as “evidence for ligand-specific receptor conformation” as the title states. However, the authors fail to account for the role of the H2R in inhibiting chemotaxis. The Ki value of 9.8 nM is calculated using the EC50 of histamine (120 nM), but this is not a true EC50 since the dose response curve is made up of two components – one for the H4R response and one for the H2R response. Indeed when the authors block the H2R with famotidine, the EC50 of histamine is reduced to 39 nM. Recalculating the Ki for JNJ 7777120 using this EC50, which represents the true H4R response, yields a value of 3.2 nM that is completely consistent with the value when using the H4R-selective agonist and the value reported by Ling et al. (2004). Furthermore, this value is similar to the Ki value the authors report for the histamine-induced calcium response because there is no H2R contribution to the calcium signal as shown in the paper (Reher et al., 2012). Therefore, the effects seen by H4R ligands on eosinophil responses are entirely consistent with the known pharmacology of the H4R and no functional selectivity needs to be invoked.
Histamine is largely associated with mast cells since these cells store and secrete large amounts of histamine. Therefore, it was natural early to look for H4R effects in mast cells. One of the major functions of mast cells it to release inflammatory mediators such as histamine upon IgE-mediated degranulation. However, in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells, neither genetic deficiency (mast cells taken from H4R-deficient mice) nor the H3R/H4R antagonist thioperamide had any effect on antigen-mediated degranulation (Hofstra et al., 2003). The H4R does appear to modulate degranulation indirectly by inducing upregulation of high affinity IgE receptors, FcεRI (Mirzahosseini et al., 2013). In addition to this, in human mast cells histamine and 4-methylhistamine on their own were able in induced degranulation and in both cases this could be blocked with JNJ 7777120 (Jemima et al., 2014). As for eosinophils, histamine acting via the H4R can induce increases in intracellular calcium. This histamine-induced calcium response is not present in mast cells from H4R-deficient mice and can be blocked by thioperamide or JNJ 7777120 (Hofstra et al., 2003; Thurmond et al., 2004; Jemima et al., 2014). H4R agonists can also induce calcium responses in these cells (Yu et al., 2010; Jemima et al., 2014). Also similar to eosinophils, histamine-induced chemotaxis can be observed in mast cells. This effect was not observed with mast cells deficient in the H4R and can be blocked by antagonist of the H4R, but not the other histamine receptors (Hofstra et al., 2003; Thurmond et al., 2004, 2014a). As for the eosinophil data the IC50 values for H4R antagonist was consistent with measured values indicating that the effects seen are due to H4R antagonism (Thurmond et al., 2004, 2014a). Changes in cell shape related to chemotaxis can also be measured and blocked by H4R antagonists (Strakhova et al., 2009). Consistent with this, the H4R agonist 4-methylhistamine can induce chemotaxis and this effect is blocked by JNJ 7777120 (Lim et al., 2005). In addition, histamine has also been shown to potentiate the migration of human precursor mast cells to the chemoattractant CXCL12 (Godot et al., 2007). The histamine-induced migration of mast cells may be related to the accumulation of mast cells at sites of inflammation. It has been shown that inhalation of histamine by mice leads to an accumulation of subepithelial mast cells in the trachea and this was reversed upon pretreatment with JNJ 7777120 (Thurmond et al., 2004). The number of mast cells increases in the skin in mouse dermatitis models and in vivo treatment with JNJ 7777120 blocked this accumulation (Cowden et al., 2010b; Seike et al., 2010; Suwa et al., 2011; Matsushita et al., 2012; Ohsawa and Hirasawa, 2012). In addition to inducing chemotaxis, the H4R also enhances inflammatory mediator production from mast cells. In mouse mast cells, histamine and 4-methylhistamine were both able to induce IL-6 production on their own and potentiate the IL-6 production driven by LPS stimulation. These effects were mediated via the H4R since they could be blocked by H4R antagonists and were not present in H4R-deficient mice (Desai and Thurmond, 2011). In human mast cells the H4R mediated the release of leukotrienes, cytokines, and chemokines (Jemima et al., 2014).
The effects on mast cells and eosinophils pointed to allergic diseases such atopic dermatitis and asthma. The FITC-induced dermatitis model in mice is a contact dermatitis model, but unlike other models is characterized by eosinophilia. Mice deficient in the H4R, have reduced inflammation in this model as judged by a reduction in inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the skin and a reduction in swelling at the site of FITC challenge (the ear; Cowden et al., 2010b). Several different H4R antagonists also show the same effect (Cowden et al., 2010b; Thurmond et al., 2014a). At the site of FITC application there is a increase in both the number of eosinophils and mast cells in the skin. Treatment of the mice systemically with JNJ 7777120 was able to reduce, and for mast cells completely block, this increase (Cowden et al., 2010b). The H4R does no play a role in all acute dermatitis models. For example, no effect was observed with H4R antagonists in an acute canine atopic dermatitis model or when 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene or toluene-2,4-diisocyanate were used as the hapten in mice (Rossbach et al., 2009; Baeumer et al., 2011). The same lack of effect was reported with JNJ 7777120 in an acute model using the hapten 2,4,6-trinitro-1-chlorobenzene (TNCB; Seike et al., 2010). However, when TNCB was given chronically the administration of JNJ 7777120 reduced the inflammation, the levels of inflammatory cytokines, and the number of mast cells and eosinophils in the skin (Seike et al., 2010; Suwa et al., 2011; Matsushita et al., 2012). A reduction in inflammation by JNJ 7777120 was also observed in the NC/Nga mouse model of chronic allergic dermatitis (Ohsawa and Hirasawa, 2012). One explanation for the disconnect between some of the acute and chronic hapten models may be accounted for by differences in the cell types involved in the inflammation, i.e., Th1 versus Th2 cells.
Another disease typically associated with eosinophils and mast cells is asthma. The lack of effect for treating asthma with antagonists that target the H1R and H2R has led many to question the role of histamine in the disease (Thurmond et al., 2008). However, it is possible that histamine acts via the H4R to drive some of the pathophysiology of asthma. In support for a role of the H4R in asthma, polymorphisms in the gene have been associated with infection-induce asthma (Simon et al., 2012). In addition H4R-deficient mice are protected in a mouse asthma model (Dunford et al., 2006). These mice have fewer eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, reduced inflammatory cytokines, and decreased antigen specific IgE and IgG1 levels after allergen challenge (Dunford et al., 2006). Treatment with the H4R antagonists JNJ 7777120, JNJ 10191584, or JNJ 39758979 during allergen challenge also reduced the eosinophilia (Dunford et al., 2006; Cowden et al., 2010a; Beermann et al., 2012; Neumann et al., 2013; Thurmond et al., 2014a). Improvement in lung function has also been shown upon treatment with an H4R antagonist and in H4R-deficient mice (Cowden et al., 2010a; Hartwig et al., 2014). Similar effects have been reported in a guinea pig model, where JNJ 7777120 improved lung function, reduced inflammation, eosinophilia, and inflammatory mediator production in the lung after allergen challenge (Somma et al., 2013). All of these data point to a therapeutic potential for H4R antagonist for the treatment of asthma.
One unexpected finding in the mouse asthma models was that mast cells were not needed for the H4R response. Dunford et al. (2006) showed that the inhibition of lung eosinophilia and inflammatory cytokines levels by an H4R antagonist was still present in mice lacking mast cells. The model used in this case is known to be dependent on T cells and not mast cells (Komai et al., 2003), suggesting that T cells may be the main contributor to the H4R response. To support the effect of the H4R on T cells, JNJ 7777120 was dosed only around the sensitization in the asthma model when antigen specific T cells are being generated. As with the dosing at allergen challenge, treatment with the H4R antagonist at sensitization reduced the number of eosinophils and the inflammatory cytokines (Dunford et al., 2006). These results coupled with the fact that the H4R antagonists worked in models known to be T cell dependent suggested that the receptor was playing a role in the priming and activation of T cells. This effect is reflected in the reduction in Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in BAL fluid or upon restimulation of splenocytes or lymphocytes (Dunford et al., 2006; Cowden et al., 2010a; Somma et al., 2013; Hartwig et al., 2014). The activation of T cells may also be the primary target in the models of atopic dermatitis as reduction in Th2 cytokines have been reported in the skin after treatment with an H4R antagonist (Cowden et al., 2010b; Seike et al., 2010; Matsushita et al., 2012; Ohsawa and Hirasawa, 2012).
There are several possible mechanisms for the H4R effect on T cells. In both asthma and dermatitis models treatment with an H4R antagonist reduced the number of T cells at the site of inflammation (Cowden et al., 2010a; Mahapatra et al., 2014). The reduction may be a result of decreases in the production of chemokines (Cowden et al., 2010a,b) or direct effects of histamine as a chemoattractant for T cells (Bryce et al., 2006; Morgan et al., 2007). Expression of the H4R has been reported on human Th2 cells and H4R agonists increased the expression of IL-31 (Gutzmer et al., 2009). The effects on T cells may also be indirect as there is evidence that the H4R is involved in dendritic cell function and may drive the response in asthma. When H4R-deficient dendritic cells where used to polarize T cells in vitro, these T cells there not able to transfer disease in a mouse adoptive transfer asthma model (Hartwig et al., 2014). This was not the case when H4R-deficient T cells were used. In addition, wild-type T cells could not transfer disease in H4R-deficient mice suggesting that it is the H4R on other cells such as dendritic cells that are important for driving disease (Hartwig et al., 2014). One possible role for the H4R in dendritic cells is in mediating migration of the cells to the site of interaction with T cells, since it has been shown that the migration of antigen positive dendritic cells from the skin to the lymph node was reduced upon treatment with an H4R antagonist (Cowden et al., 2010b). As for T cells, these effects may be a result of H4R directly mediating migration via histamine acting a chemoattractant (Gutzmer et al., 2005; Damaj et al., 2007; Bäumer et al., 2008; Gschwandtner et al., 2010, 2011) or indirectly by reduction in chemokine production (Cowden et al., 2010a,b). The H4R may also impact activation of dendritic cells. Dendritic cells from H4R-deficient mice or treated in vitro with an H4R antagonists were defective in their ability to activate Th2 cells (Dunford et al., 2006). Similarly, when human monocyte derived dendritic cells were treated with JNJ 7777120 the levels of MHC and costimulatory molecules were reduced and these cells were unable to induce allergen-specific proliferation of T cells (Lundberg et al., 2011). In addition to effects on dendritic cell maturation, the H4R modulates cytokine and chemokine production by dendritic cells that may result in defective T cell activation (Gutzmer et al., 2005; Dunford et al., 2006; Dijkstra et al., 2008; Gschwandtner et al., 2010, 2011, 2012). Dendritic cells can be activated by endogenous danger signals action via toll-like receptors (TLRs). Activation of dendritic cells in vitro with TLR ligands leads to the production of cytokines and chemokines and this can be modulated by H4R antagonists (Gutzmer et al., 2005; Dunford et al., 2006; Dijkstra et al., 2008; Gschwandtner et al., 2010, 2011, 2012). In vivo H4R antagonist can inhibit LPS (a TLR ligand) induced production of inflammatory cytokines and this is also reduced in H4R-deficient mice (Cowden et al., 2013). This link between TLR and H4R may important driving asthmatic responses since it has been shown that H4R antagonists are only effective in mouse asthma models when LPS is present (Cowden et al., 2013).
The role for the H4R in T cells pointed to possible roles in other disease that are thought to be T cell mediated. In particular the autoimmune disease rheumatoid arthritis is thought to be driven in part by T cell responses as evidenced by the clinical efficacy of abatacept, that targets the activation of T cells, and the fact that there is a strong genetic association with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DRB1 and the presentation of antigens (Raychaudhuri et al., 2012; Gizinski and Fox, 2014). Based on this, the role of the H4R in preclinical models of rheumatoid arthritis has been explored. H4R-deficient mice and mice treated with the H4R antagonist JNJ 28307474 were protected from disease in both a mouse collagen-induced arthritis and collagen antibody-induced arthritis model (Cowden et al., 2014). This was reflected in an improvement in disease severity score and in the histologic analysis of the joints. The anti-inflammatory effects can be observed either with dosing at the onset of disease or at the peak of disease activity. A second selective H4R antagonist, JNJ 39758979, has also shown activity in the collagen-induced arthritis model (Savall et al., 2014). However, the effect on T cells may not translate into efficacy in all autoimmune diseases. H4R-deficient mice or mice treated with an H4R antagonist had significantly worse disease in mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis models of multiple sclerosis (del Rio et al., 2012; Ballerini et al., 2013).
The collagen-induced arthritis model is known to be driven by the production of IL-17 from Th17 cells (Lubberts et al., 2001; Nakae et al., 2003; Lubberts et al., 2004). Treatment with the H4R antagonist in this model decreased the production of IL-17 from lymphocytes and reduced the number of IL-17 positive CD4 cells (Th17 cells) in the inguinal lymph node, but had no effect on the production of IFNγ. H4R antagonists also blocked the differentiation of Th17 cells in vitro and reduction in IL-17 production has also been reported in models of asthma and dermatitis (Dunford et al., 2006; Cowden et al., 2010b, 2014). As for the asthma model, the effects on T cells could be direct or indirect. For the collagen antibody-induced model, adoptive transfer of wild-type dendritic cells (splenic CD11c+ cells) restored disease in H4R-deficient animals suggesting that the H4R on antigen presenting cells was crucial for disease activity (Cowden et al., 2014). This is also suggested when Th17 development was studied directly in vivo using an adoptive transfer model. The H4R antagonist blocked the Th17 differentiation of transgenic T cells in vivo. In addition the transfer of wild-type transgenic T cells into H4R-deficient host mice also resulted in a reduction in Th17 cells supporting the conclusion that the H4R on host antigen presenting cells is important (Cowden et al., 2014). However, this may not be the complete story as transfer of H4R-deficient transgenic T cells into wild-type host also lead to a reduction in Th17 cells indicating that the H4R on T cells is also important. Expression the H4R has been reported on human and mouse Th17 cells (Mommert et al., 2012; Cowden et al., 2014). In isolated human Th17 cells H4R agonist increased the production of IL-17 and this was reduced by an H4R antagonist suggesting that the receptor can have a direct effect on Th17 cells (Mommert et al., 2012).
Pruritus is another process that has long been associated with histamine (for a review see Thurmond et al., 2014b). In fact, injection of histamine into the skin of humans causes the sensation of itching. Antihistamines that target the H1R have exhibited efficacy in reducing itch in a number of conditions such as acute urticaria and allergic rhinitis. However, the itch associated with other pruritic diseases such as atopic dermatitis is not well-controlled by these drugs. The discovery of the H4R prompted the exploration as to whether this receptor could be responsible for pruritic responses not driven by the H1R. Injection of histamine into the skin of mice causes a scratching response. This response can be inhibited by the administration of H4R antagonists (Bell et al., 2004; Dunford et al., 2007; Yamaura et al., 2009; Shin et al., 2012; Savall et al., 2014). Histamine-induced scratching is also reduced in H4R-deficient mice (Dunford et al., 2007). Injection of H4R agonists can induce scratching and this is inhibited with H4R antagonists or in H4R-deficient mice (Dunford et al., 2007; Cowart et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2008; Koenig et al., 2010; Yu et al., 2010). H4R antagonists can also inhibit scratching in mice induced by substance P, haptens, and in models of dermatitis (Rossbach et al., 2009; Yamaura et al., 2009; Cowden et al., 2010b; Suwa et al., 2011; Ohsawa and Hirasawa, 2012). These data have prompted the study of the anti-pruritic effects of H4R antagonists in humans.
Clinical Data
There have only been a few reports of clinical data with H4R antagonists. The compound with the most published information is JNJ 39758979. JNJ 39758979 is a potent and selective H4R antagonist that has efficacy in preclinical models of pruritus, dermatitis, asthma, and arthritis (Savall et al., 2014; Thurmond et al., 2014a). This H4R antagonist has been used to explore the role of the receptor in mediating histamine-induced pruritus in humans (NCT01068223). Over three periods subjects received either a single dose of JNJ 39758979, the H1R antagonist cetirizine, or placebo. At 2 and 6 h after dosing, histamine was injected intradermally into the skin of the forearm of each subject and the pruritic response was assessed by having the subject rate the itch sensation on 1–10 scale over a 10 min period (Kollmeier et al., 2014). JNJ 39758979 reduced the itch sensation induced by histamine at both 2 and 6 h after dosing, whereas placebo had no effects. Cetirizine was used as a positive control and it reduced the pruritic response at 6 h post-dose as expected. This data validates the preclinical findings in mice and shows that the H4R is involved in mediating pruritic responses in humans. This suggests that H4R antagonists will have utility in humans in treating pruritic conditions known to be mediated by histamine such as acute urticaria and allergic rhinitis. Of potential interest is the drug alcaftadine that is a topical ophthalmic solution indicated for the prevention of itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. This compound has weak activity at the H4R as well as being a potent H1R antagonist and this differentiates it from other topical treatments such as olopatadine that has no H4R activity (Gallois-Bernos and Thurmond, 2012). Preclinical data indicate that the combination of H4R and H1R may yield better efficacy against pruritus than an H1R alone (Dunford et al., 2007; Nakano et al., 2009; Rossbach et al., 2009; Cowden et al., 2010b; Ohsawa and Hirasawa, 2012). This may also be true in humans as an analysis across two clinical efficacy studies indicated that alcaftadine exhibited greater efficacy in reducing ocular itch compared to olopatadine after conjunctival allergen challenge (McLaurin et al., 2014).
One pruritic condition where the itch is not well controlled by H1R antagonists is atopic dermatitis, which is a common inflammatory pruritic skin disease. Pruritus is one of the most common and characteristic symptoms of atopic dermatitis (Williams, 2005). Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of H1R antagonists for the reduction of pruritus associated with atopic dermatitis, with limited evidence for efficacy (Klein and Clark, 1999; Akdis et al., 2006; Saeki et al., 2009). These observations prompted the study of H4R antagonists in preclinical dermatology models and indicated that such antagonists could be efficacious (Cowden et al., 2010b; Seike et al., 2010; Suwa et al., 2011; Matsushita et al., 2012; Ohsawa and Hirasawa, 2012). Evidence that H4R can be efficacious against atopic dermatitis in humans has been provided in the clinical with JNJ 39758979. A phase 2a study in adults with moderate atopic dermatitis compared two doses of JNJ 39758979 versus placebo (Murata et al., 2015). Unfortunately, the study was terminated before all subjects completed the treatment period due to two cases of agranulocytosis that was most likely related to reactive metabolites of the compound and not to H4R antagonism (Murata et al., 2015). Post hoc analysis indicated evidence of efficacy. The primary efficacy was assessed at week 6 using eczema area and severity index (EASI) scores. There was a numerical reduction in the EASI score for both 100 and 300 mg JNJ 39758979 compared to placebo, but these changes were not statically significant. The EASI score does not include any direct measurements of pruritus, which is the most common and characteristic symptom of atopic dermatitis, and therefore several secondary endpoints were include to assess pruritus. Across all of these endpoints there was a strong and nominally statistically significant reduction in the pruritus sensed by patients on JNJ 39758979 (Murata et al., 2015). Therefore although there are caveats with the interpretation of the results and issues with the safety of JNJ 39758979, it appears that other safer H4R antagonists could have utility in the treatment of atopic dermatitis especially with respect to reducing pruritus.
In addition to the published studies a study with JNJ 39758979 in patients with persistent asthma (NCT00946569) has been completed, but no data has been reported. In addition to this other H4R antagonists have been reported to be in the clinic such as UR-63325, PF-3893787, and toreforant (JNJ 38518168), the first H4R antagonist with a generic name. ClinicalTrials.gov indicates that UR-63325 has completed a nasal allergen challenge study in patients with allergic rhinitis (NCT01260753) and PF-3893787 a bronchial allergen challenge study in patients with asthma (NCT00856687), but no results have been reported. Toreforant has completed efficacy studies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (NCT01679951, NCT00941707, and NCT01862224). Results for these studies have not been reported, but it was noted that a dose range finding study in rheumatoid arthritis (NCT01679951) was terminated for lack of efficacy. Studies with toreforant in patients with asthma (NCT01823016) and psoriasis (NCT02295865) were ongoing as of February 2015.
Conclusion
The story of the H4R provides an excellent case study for the deorphanization of a novel receptor and the translation of this into clinical efficacy in humans. The gene for the receptor was discovered via genomic homology searches and reverse pharmacology led to the identification of its role in immune and pruritic responses. This work has now resulted in the first reports of clinical efficacy for H4R antagonists and point to the potential of these ligands as future drugs for the treatment of a variety of indications.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Author is an employee and stock holder of Johnson and Johnson, the parent company of Janssen Research & Development.
References
Akdis, C. A., Akdis, M., Bieber, T., Bindslev-Jensen, C., Boguniewicz, M., Eigenmann, P., et al. (2006). Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults: European academy of allergology and clinical immunology/American academy of allergy, asthma and immunology/PRACTALL consensus report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 118, 152–169. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.03.045
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Altenbach, R. J., Adair, R. M., Bettencourt, B. M., Black, L. A., Fix-Stenzel, S. R., Gopalakrishnan, S. M., et al. (2008). Structure-activity studies on a series of a 2-aminopyrimidine-containing histamine H4 receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 51, 6571–6580. doi: 10.1021/jm8005959
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Arrang, J. M., Garbarg, M., and Schwartz, J. C. (1983). Autoinhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature 302, 832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0
Ash, A. S. F., and Schild, J. O. (1966). Receptors mediating some action of histamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 27, 427–439.
Baeumer, W., Stahl, J., Sander, K., Petersen, L. J., Paps, J., Stark, H., et al. (2011). Lack of preventing effect of systemically and topically administered histamine H1 or H4 receptor antagonists in a dog model of acute atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 20, 577–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01268.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ballerini, C., Aldinucci, A., Luccarini, I., Galante, A., Manuelli, C., Blandina, P., et al. (2013). Antagonism of histamine H4 receptors exacerbates clinical and pathological signs of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 170, 67–77. doi: 10.1111/bph.12263
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Barger, G., and Dale, H. H. (1910). 4-β-Aminoethylglyoxaline (β-Aminazolylethylamine) and the other active principles of ergot. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 97, 2592–2595. doi: 10.1039/ct9109702592
Barnard, R., Barnard, A., Salmon, G., Liu, W., and Sreckovic, S. (2008). Histamine-induced actin polymerization in human eosinophils: an imaging approach for histamine H4 receptor. Cytometry A 73, 299–304. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20514
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bäumer, W., Wendorff, S., Gutzmer, R., Werfel, T., Dijkstra, D., Chazot, P., et al. (2008). Histamine H4 receptors modulate dendritic cell migration through skin – immunomodulatory role of histamine. Allergy 63, 1387–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01720.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Beermann, S., Glage, S., Jonigk, D., Seifert, R., and Neumann, D. (2012). Opposite effects of mepyramine on JNJ 7777120-induced amelioration of experimentally induced asthma in mice in sensitization and provocation. PLoS ONE 7:e30285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030285
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bell, J. K., McQueen, D. S., and Rees, J. L. (2004). Involvement of histamine H4 and H1 receptors in scratching induced by histamine receptor agonists in BalbC mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 142, 374–380. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705754
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Black, J. W., Duncan, W. A. M., Durant, C. J., Ganellin, C. R., and Parsons, E. M. (1972). Definition and antagonism of histamine H2-receptors. Nature 236 385–390. doi: 10.1038/236385a0
Bryce, P. J., Mathias, C. B., Harrison, K. L., Watanabe, T., Geha, R. S., and Oettgen, H. C. (2006). The H1 histamine receptor regulates allergic lung responses. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1624–1632. doi: 10.1172/JCI26150
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Buckland, K. F., Williams, T. J., and Conroy, D. M. (2003). Histamine induces cytoskeletal changes in human eosinophils via the H4 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 140, 1117–1127. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705530
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cheng, Y., and Prusoff, W. H. (1973). Relation between the inhibition constant K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes fifty per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2
Clark, R. A. F., Gallin, J. I., and Kaplan, A. P. (1975). Selective eosinophil chemotactic activity of histamine. J. Exp. Med. 142, 1462–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1462
Clark, R. A. F., Sandler, J. A., Gallin, J. I., and Kaplan, A. P. (1977). Histamine modulation of eosinophil migration. J. Immunol. 118, 137–145.
Coruzzi, G., Adami, M., Guaita, E., de Esch, I. J. P., and Leurs, R. (2007). Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the selective histamine H4-receptor antagonists JNJ7777120 and VUF6002 in a rat model of carrageenan-induced acute inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 563, 240–244. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.026
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cowart, M. D., Altenbach, R. J., Liu, H., Hsieh, G. C., Drizin, I., Milicic, I., et al. (2008). Rotationally constrained 2,4-Diamino-5,6-disubstituted pyrimidines: a new class of histamine H4 receptor antagonists with improved druglikeness and in vivo efficacy in pain and inflammation models. J. Med. Chem. 51, 6547–6557. doi: 10.1021/jm800670r
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cowden, J. M., Riley, J. P., Ma, J. Y., Thurmond, R. L., and Dunford, P. J. (2010a). Histamine H4 receptor antagonism diminishes existing airway inflammation and dysfunction via modulation of Th2 cytokines. Respir. Res. 11:86. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-86
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cowden, J. M., Zhang, M., Dunford, P. J., and Thurmond, R. L. (2010b). The histamine H4 receptor mediates inflammation and pruritus in Th2-dependent dermal inflammation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 130, 1023–1033. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.358
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cowden, J. M., Yu, F., Banie, H., Farahani, M., Ling, P., Nguyen, S., et al. (2014). The histamine H4 receptor mediates inflammation and Th17 responses in preclinical models of arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 600–608. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203832
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cowden, J. M., Yu, F., Challapalli, M., Huang, J. F., Kim, S., Fung-Leung, W. P., et al. (2013). Antagonism of the histamine H4 receptor reduces LPS-induced TNF production in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 62, 599–607. doi: 10.1007/s00011-013-0612-5
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dale, H. H., and Laidlaw, P. P. (1911). The physiological action of β-Iminazolylethylamine. J. Physiol. 41, 318–344. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001406
Damaj, B. B., Becerra, C. B., Esber, H. J., Wen, Y., and Maghazachi, A. A. (2007). Functional expression of H4 histamine receptor in human natural killer cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 179, 7907–7915. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.11.7907
De Backer, M. D., Gommeren, W., Moereels, H., Nobels, G., Van Gompel, P., Leysen, J. E., et al. (1993). Genomic cloning, heterologous expression and pharmacological characterization of a human histamine H1 receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197, 1601–1608. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2662
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
del Rio, R., Noubade, R., Saligrama, N., Wall, E. H., Krementsov, D. N., Poynter, M. E., et al. (2012). Histamine H4 receptor optimizes T regulatory cell frequency and facilitates anti-inflammatory responses within the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 188, 541–547. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101498
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Desai, P., and Thurmond, R. L. (2011). Histamine H4 receptor activation enhances LPS-induced IL-6 production in mast cells via ERK and PI3K activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 41, 1764–1773. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040932
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dijkstra, D., Stark, H., Chazot, P. L., Shenton, F. C., Leurs, R., Werfel, T., et al. (2008). Human inflammatory dendritic epidermal cells express a functional histamine H4 receptor. J. Invest. Dermatol. 128, 1696–1703. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701250
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dunford, P. J., O’Donnell, N., Riley, J. P., Williams, K. N., Karlsson, L., and Thurmond, R. L. (2006). The histamine H4 receptor mediates allergic airway inflammation by regulating the activation of CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 176, 7062–7070. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.7062
Dunford, P. J., Williams, K. N., Desai, P. J., Karlsson, L., McQueen, D., and Thurmond, R. L. (2007). Histamine H4 receptor antagonists are superior to traditional antihistamines in the attenuation of experimental pruritus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119, 176–183. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.08.034
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gallois-Bernos, A. C., and Thurmond, R. L. (2012). Alcaftadine, a new antihistamine with combined antagonist activity at histamine H1, H2, and H4 receptors. J. Recept. Ligand Channel Res. 5, 9–20. doi: 10.2147/JRLCR.S39369
Gantz, I., Munzert, G., Tashiro, T., Schaffer, M., Wang, L., DelValle, J., et al. (1991). Molecular cloning of the human histamine H2 receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 178, 1386–1392. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(91)91047-G
Gizinski, A. M., and Fox, D. A. (2014). T cell subsets and their role in the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 26, 204–210. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000036
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Godot, V., Arock, M., Garcia, G., Capel, F., Flys, C., Dy, M., et al. (2007). H4 histamine receptor mediates optimal migration of mast cell precursors to CXCL12. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 120, 827–834. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.05.046
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gschwandtner, M., Bunk, H., Koether, B., Thurmond, R. L., Kietzmann, M., Werfel, T., et al. (2012). Histamine down-regulates IL-27 production in antigen-presenting cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 92, 21–29. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0111017
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gschwandtner, M., Mommert, S., Koether, B., Werfel, T., and Gutzmer, R. (2011). The histamine H4 receptor is highly expressed on plasmacytoid dendritic cells in psoriasis and histamine regulates their cytokine production and migration. J. Invest. Dermatol. 131, 1668–1676. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.72
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gschwandtner, M., Rossbach, K., Dijkstra, D., Baeumer, W., Kietzmann, M., Stark, H., et al. (2010). Murine and human Langerhans cells express a functional histamine H4 receptor: modulation of cell migration and function. Allergy 65, 840–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02279.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gutzmer, R., Diestel, C., Mommert, S., Koether, B., Stark, H., Wittmann, M., et al. (2005). Histamine H4 receptor stimulation suppresses IL-12p70 production and mediates chemotaxis in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 174, 5224–5232. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5224
Gutzmer, R., Mommert, S., Gschwandtner, M., Zwingmann, K., Stark, H., and Werfel, T. (2009). The histamine H4 receptor is functionally expressed on TH2 cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 123, 619–625. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.12.1110
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Hartwig, C., Munder, A., Glage, S., Wedekind, D., Schenk, H., Seifert, R., et al. (2014). The histamine H4-receptor (H4R) regulates eosinophilic inflammation in ovalbumin-induced experimental allergic asthma in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445179 [Epub ahead of print].
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Hofstra, C. L., Desai, P. J., Thurmond, R. L., and Fung-Leung, W.-P. (2003). Histamine H4 receptor mediates chemotaxis and calcium mobilization of mast cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 305, 1212–1221. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.046581
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Hough, L. B. (2001). Genomics meets histamine receptors: new subtypes, new receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 415–419.
Hsieh, G. C., Chandran, P., Salyers, A. K., Pai, M., Zhu, C. Z., Wensink, E. J., et al. (2010). H4 receptor antagonism exhibits anti-nociceptive effects in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 95, 41–50. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.12.004
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Jablonowski, J. A., Grice, C. A., Chai, W., Dvorak, C. A., Venable, J. D., Kwok, A. K., et al. (2003). The first potent and selective non-imidazole human histamine H4 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 46, 3957–3960. doi: 10.1021/jm0341047
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Jemima, E. A., Prema, A., and Thangam, E. B. (2014). Functional characterization of histamine H4 receptor on human mast cells. Mol. Immunol. 62, 19–28. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.05.007
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Klein, P. A., and Clark, R. A. F. (1999). An evidence-based review of the efficacy of antihistamines in relieving pruritus in atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. 135, 1522–1525. doi: 10.1001/archderm.135.12.1522
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Koenig, J. R., Liu, H., Drizin, I., Witte, D. G., Carr, T. L., Manelli, A. M., et al. (2010). Rigidified 2-aminopyrimidines as histamine H4 receptor antagonists: effects of substitution about the rigidifying ring. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 1900–1904. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.01.131
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Kollmeier, A., Francke, K., Chen, B., Dunford, P. J., Greenspan, A. J., Xia, Y., et al. (2014). The H4 receptor antagonist, JNJ 39758979, is effective in reducing histamine-induced pruritus in a randomized clinical study in healthy subjects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 350, 181–187. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.215749
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Komai, M., Tanaka, H., Masuda, T., Nagao, K., Ishizaki, M., Sawada, M., et al. (2003). Role of Th2 responses in the development of allergen-induced airway remodelling in a murine model of allergic asthma. Br. J. Pharmacol. 138, 912–920. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705105
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Lim, H. D., van Rijn, R. M., Ling, P., Bakker, R. A., Thurmond, R. L., and Leurs, R. (2005). Evaluation of histamine H1-, H2-, and H3-receptor ligands at the human histamine H4 receptor: identification of 4-methylhistamine as the first potent and selective H4 receptor agonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 314, 1310–1321. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.087965
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ling, P., Ngo, K., Nguyen, S., Thurmond, R. L., Edwards, J. P., Karlsson, L., et al. (2004). Histamine H4 receptor mediates eosinophil chemotaxis with cell shape change and adhesion molecule upregulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 142, 161–171. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705729
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Liu, C., Ma, X.-J., Jiang, X., Wilson, S. J., Hofstra, C. L., Blevitt, J., et al. (2001). Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H4) expressed in bone marrow. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 420–426.
Liu, H., Altenbach, R. J., Carr, T. L., Chandran, P., Hsieh, G. C., Lewis, L. G. R., et al. (2008). cis-4-(Piperazin-1-yl)-5,6,7a,8,9,10,11,11a-octahydrobenzofuro[2,3-h]quinazolin-2-amine (A-987306), a new histamine H4R antagonist that blocks pain responses against Carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia. J. Med. Chem. 51, 7094–7098. doi: 10.1021/jm8007618
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Lovenberg, T. W., Roland, B. L., Wilson, S. J., Jiang, X., Pyati, J., Huvar, A., et al. (1999). Cloning and functional expression of the human histamine H3 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 55, 1101–1107.
Lubberts, E., Joosten, L. A., Oppers, B., van den Bersselaar, L., Coenen-de Roo, C. J., Kolls, J. K., et al. (2001). IL-1-independent role of IL-17 in synovial inflammation and joint destruction during collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 167, 1004–1013. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.1004
Lubberts, E., Koenders, M. I., Oppers-Walgreen, B., van den Bersselaar, L., Coenen-de, R. C. J., Joosten, L. A., et al. (2004). Treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine interleukin-17 antibody after the onset of collagen-induced arthritis reduces joint inflammation, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 650–659. doi: 10.1002/art.20001
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Lundberg, K., Broos, S., Greiff, L., Borrebaeck, C. A. K., and Lindstedt, M. (2011). Histamine H4 receptor antagonism inhibits allergen-specific T-cell responses mediated by human dendritic cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 651, 197–204. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.10.065
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Mahapatra, S., Albrecht, M., Behrens, B., A.-Dittrich, M., Jirmo, A., Behrens, G., et al. (2014). Delineating the role of histamine-1-and -4-receptors in a mouse model of th2-dependent antigen-specific skin inflammation. PLoS ONE 9:e87296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087296
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Matsushita, A., Seike, M., Okawa, H., Kadawaki, Y., and Ohtsu, H. (2012). Advantages of histamine H4 receptor antagonist usage with H1 receptor antagonist for the treatment of murine allergic contact dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 21, 714–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01559.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
McLaurin, E. B., Marsico, N. P., Ackerman, S. L., Ciolino, J. B., Williams, J. M., Villanueva, L., et al. (2014). Ocular itch relief with alcaftadine 0.25% versus olopatadine 0.2% in allergic conjunctivitis: pooled analysis of two multicenter randomized clinical trials. Adv. Ther. 31, 1059–1071. doi: 10.1007/s12325-014-0155-3
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Mirzahosseini, A., Dalmadi, B., and Csutora, P. (2013). Histamine receptor H4 regulates mast cell degranulation and IgE induced FcεRI upregulation in murine bone marrow-derived mast cells. Cell. Immunol. 283, 38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2013.05.006
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Mommert, S., Gschwandtner, M., Koether, B., Gutzmer, R., and Werfel, T. (2012). Human memory Th17 cells express a functional histamine H4 receptor. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 177–185. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.09.028
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Morgan, R. K., McAllister, B., Cross, L., Green, D. S., Kornfeld, H., Center, D. M., et al. (2007). Histamine 4 receptor activation induces recruitment of FoxP3+ T cells and inhibits allergic asthma in a murine model. J. Immunol. 178, 8081–8089. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.8081
Morse, K. L., Behan, J., Laz, T. M., West, R. E. Jr., Greenfeder, S. A., Anthes, J. C., et al. (2001). Cloning and characterization of a novel human histamine receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296, 1058–1066.
Murata, Y., Song, M., Kikuchi, H., Hisamichi, K., Xu, X. L., Greenspan, A., et al. (2015). Phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group study of a H4R-antagonist (JNJ-39758979) in Japanese adults with moderate atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 42, 129–139. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12726
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Nakae, S., Saijo, S., Horai, R., Sudo, K., Mori, S., and Iwakura, Y. (2003). IL-17 production from activated T cells is required for the spontaneous development of destructive arthritis in mice deficient in IL-1 receptor antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1035999100
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Nakamura, T., Itadani, H., Hidaka, Y., Ohta, M., and Tanaka, K. (2000). Molecular cloning and characterization of a new human histamine receptor, HH4R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 279, 615–620. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.4008
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Nakano, Y., Takahashi, Y., Ono, R., Kurata, Y., Kagawa, Y., and Kamei, C. (2009). Role of histamine H4 receptor in allergic conjunctivitis in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 608, 71–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.02.035
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Neumann, D., Beermann, S., Burhenne, H., Glage, S., Hartwig, C., and Seifert, R. (2013). The dual H3/4R antagonist thioperamide does not fully mimic the effects of the ‘standard’ H4R antagonist JNJ 7777120 in experimental murine asthma. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 386, 983–990. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0898-4
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Nguyen, T., Shapiro, D. A., George, S. R., Setola, V., Lee, D. K., Cheng, R., et al. (2001). Discovery of a novel member of the histamine receptor family. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 427–433.
Oda, T., Morikawa, N., Saito, Y., Masuho, Y., and Matsumoto, S. (2000). Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of histamine receptor preferentially expressed in leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36781–36786. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006480200
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ohsawa, Y., and Hirasawa, N. (2012). The antagonism of histamine H1 and H4 receptors ameliorates chronic allergic dermatitis via anti-pruritic and anti-inflammatory effects in NC/Nga mice. Allergy 67, 1014–1022. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2012.02854.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
O’Reilly, M., Alpert, R., Jenkinson, S., Gladue, R. P., Foo, S., Trim, S., et al. (2002). Identification of a histamine H4 receptor on human eosinophils-role in eosinophil chemotaxis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 22, 431–448. doi: 10.1081/RRS-120014612
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Raible, D. G., Lenahan, T., Fayvilevich, Y., Kosinski, R., and Schulman, E. S. (1994). Pharmacologic characterization of a novel histamine receptor on human eosinophils. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 149, 1506–1511. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.6.8004306
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Raible, D. G., Schulman, E. S., DiMuzio, J., Cardillo, R., and Post, T. J. (1992). Mast cell mediators prostaglandin-D2 and histamine activate human eosinophils. J. Immunol. 148, 3536–3542.
Raychaudhuri, S., Sandor, C., Stahl, E. A., Freudenberg, J., Lee, H. S., Jia, X., et al. (2012). Five amino acids in three HLA proteins explain most of the association between MHC and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 44, 291–296. doi: 10.1038/ng.1076
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Reher, T. M., Neumann, D., Buschauer, A., and Seifert, R. (2012). Incomplete activation of human eosinophils via the histamine H4-receptor: evidence for ligand-specific receptor conformations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 84, 192–203. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.04.004
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Rosethorne, E. M., and Charlton, S. J. (2011). Agonist-biased signaling at the histamine H4 receptor: JNJ7777120 recruits β -arrestin without activating G proteins. Mol. Pharmacol. 79, 749–757. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.068395
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Rossbach, K., Wendorff, S., Sander, K., Stark, H., Gutzmer, R., Werfel, T., et al. (2009). Histamine H4 receptor antagonism reduces hapten-induced scratching behaviour but not inflammation. Exp. Dermatol. 18, 57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00762.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Sabroe, I., Hartnell, A., Jopling, L. A., Bel, S., Ponath, P. D., Pease, J. E., et al. (1999). Differential regulation of eosinophil chemokine signaling via CCR3 and non-CCR3 pathways. J. Immunol. 162, 2946–2955.
Saeki, H., Furue, M., Furukawa, F., Hide, M., Ohtsuki, M., Katayama, I., et al. (2009). Guidelines for management of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 36, 563–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00706.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Savall, B. M., Chavez, F., Tays, K., Dunford, P., Cowden, J., Hack, M. D., et al. (2014). Discovery and SAR of 6-Alkyl-2,4-diaminopyrimidines as H4 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 57, 2429–2439. doi: 10.1021/jm401727m
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Seifert, R., Schneider, E. H., Dove, S., Brunskole, I., Neumann, D., Strasser, A., et al. (2011). Paradoxical stimulatory effects of the “standard” histamine H4-receptor antagonist JNJ7777120: the H4-receptor joins the club of 7TM receptors exhibiting functional selectivity. Mol. Pharmacol. 79, 631–638. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.071266
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Seike, M., Furuya, K., Omura, M., Hamada-Watanabe, K., Matsushita, A., and Ohtsu, H. (2010). Histamine H4 receptor antagonist ameliorates chronic allergic contact dermatitis induced by repeated challenge. Allergy 65, 319–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02240.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Shin, N., Covington, M., Bian, D., Zhuo, J., Bowman, K., Li, Y., et al. (2012). INCB38579, a novel and potent histamine H4 receptor small molecule antagonist with anti-inflammatory pain and anti-pruritic functions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 675, 47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.11.027
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Simon, T., Semsei, A. F., Ungvari, I., Hadadi, E., Virag, V., Nagy, A., et al. (2012). Asthma endophenotypes and polymorphisms in the histamine receptor HRH4 gene. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 159, 109–120. doi: 10.1159/000335919
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Somma, T., Cinci, L., Formicola, G., Pini, A., Thurmond, R., Ennis, M., et al. (2013). A selective antagonist of histamine H4 receptors prevents antigen-induced airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs: involvement of lipocortin-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 170, 200–213. doi: 10.1111/bph.12264
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Strakhova, M. I., Cuff, C. A., Manelli, A. M., Carr, T. L., Witte, D. G., Baranowski, J. L., et al. (2009). In vitro and in vivo characterization of A-940894: a potent histamine H4 receptor antagonist with anti-inflammatory properties. Br. J. Pharmacol. 157, 44–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00236.x
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Suwa, E., Yamaura, K., Oda, M., Namiki, T., and Ueno, K. (2011). Histamine H4 receptor antagonist reduces dermal inflammation and pruritus in a hapten-induced experimental model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 667, 383–388. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.037
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Thurmond, R. L., Chen, B., Dunford, P. J., Greenspan, A. J., Karlsson, L., La, D., et al. (2014a). Clinical and preclinical characterization of the histamine H4 receptor antagonist JNJ-39758979. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 349, 176–184. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.211714
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Thurmond, R. L., Kazerouni, K., Chaplan, S. R., and Greenspan, A. J. (2014b). “Peripheral neuronal mechanism of itch: histamine and itch,” in Itch: Mechanisms and Treatment, Chap. 10, eds E. Carstens and T. Akiyama (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press), 143–192.
Thurmond, R. L., Desai, P. J., Dunford, P. J., Fung-Leung, W.-P., Hofstra, C. L., Jiang, W., et al. (2004). A potent and selective histamine H4 receptor antagonist with anti-inflammatory properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 309, 404–413. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.061754
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Thurmond, R. L., Gelfand, E. W., and Dunford, P. J. (2008). The role of histamine H1 and H4 receptors in allergic inflammation: the search for new antihistamines. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7, 41–53. doi: 10.1038/nrd2465
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Varga, C., Horvath, K., Berko, A., Thurmond, R. L., Dunford, P. J., and Whittle, B. J. R. (2005). Inhibitory effects of histamine H4 receptor antagonists on experimental colitis in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 522, 130–138. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.08.045
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Wells, J. A., Morris, H. C., Bull, H. B., and Dragstedt, C. A. (1945). Observations on the nature of the antagonism of histamine by β-dimethylaminoethyl benzhydryl ether (benadryl). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 85, 122–128.
Williams, H. C. (2005). Clinical practice. Atopic dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 2314–2324. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp042803
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Yamaura, K., Oda, M., Suwa, E., Suzuki, M., Sato, H., and Ueno, K. (2009). Expression of histamine H4 receptor in human epidermal tissues and attenuation of experimental pruritus using H4 receptor antagonist. J. Toxicol. Sci. 34, 427–431. doi: 10.2131/jts.34.427
PubMed Abstract | Full Text | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Yu, F., Wolin, R. L., Wei, J., Desai, P. J., McGovern, P. M., Dunford, P. J., et al. (2010). Pharmacological characterization of oxime agonists of the histamine H4 receptor. J. Receptor Ligand Channel Res. 3, 37–49. doi: 10.2147/JRLCR.S6468
Keywords: histamine, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, asthma, arthritis
Citation: Thurmond RL (2015) The histamine H4 receptor: from orphan to the clinic. Front. Pharmacol. 6:65. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00065
Received: 14 January 2015; Paper pending published 12 February 2015;
Accepted: 12 March 2015; Published online: 31 March 2015.
Edited by:
Ye Fang, Corning Incorporated, USAReviewed by:
Nora Ibargoyen, Basque Office for Health Technology Assessment, SpainDomenico Criscuolo, Genovax, Italy
Copyright © 2015 Thurmond. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Robin L. Thurmond, Janssen Research & Development, LLC, 3210 Merryfield Row, San Diego, CA 92121, USAcnRodXJtb25AaXRzLmpuai5jb20=
 Robin L. Thurmond
Robin L. Thurmond