
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Pediatr. , 17 January 2025
Sec. Pediatric Surgery
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2025.1491520
 Shiqiu Xiong1,†
Shiqiu Xiong1,† Kuku Ge1,†
Kuku Ge1,† Chongzhi Hou2,†
Chongzhi Hou2,† Hongbin Yang1
Hongbin Yang1 Hanhua Zhang1
Hanhua Zhang1 Sheng Zhang2
Sheng Zhang2 Bailing Liu3
Bailing Liu3 Yuewen Hao4
Yuewen Hao4 Ying Fang1*
Ying Fang1* Xiaoxia Ren1*
Xiaoxia Ren1*
Introduction: Anomalous congenital bands are a rare cause of intestinal obstruction, with only five previously reported cases involving duodenal obstruction. We present a fifth case of duodenal obstruction due to two congenital bands and provide a comprehensive literature review summarizing the clinical features of this condition.
Case report: An eight-year-old girl was admitted to our department with recurrent bilious vomiting and abdominal pain lasting six days. She had no significant past medical history, with no previous abdominal surgeries or trauma. Physical examination revealed abdominal tenderness and decreased bowel sounds. Contrast x-ray showed an obstructed passage of contrast through the third part of the duodenum. Abdominal ultrasound identified a strip-like hypoechoic structure compressing the third part of the duodenum. A diagnosis of duodenal obstruction was confirmed, and laparoscopic surgery combined with gastroduodenoscopy was performed. The procedure revealed two congenital bands adjacent to the duodenum: one extending from the duodenum to the transverse colon, and the other from the duodenum to the root of the mesentery. The bands were resected, and gastroduodenoscopy confirmed the resolution of the obstruction.
Discussion: We reviewed 93 cases of anomalous congenital bands, including the present one, comprising 33 adults and 60 children, with 71.0% of the cases involving males. Common symptoms included vomiting and abdominal pain, with physical examinations often showing tenderness and distension. Imaging techniques like plain x-ray, contrast x-ray, ultrasound, and computed tomography often indicated intestinal obstruction but were less effective in directly identifying congenital bands. All cases required abdominal surgery for diagnosis and treatment. Congenital bands were primarily found attached to the ileum or its mesentery and were resected in all cases, with a favorable postoperative prognosis. This case and the literature review provide valuable insights for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Intestinal obstruction is a common acute emergency in children, stemming from both intrinsic and extrinsic causes (1). Typical causes include intussusception, malrotation, ileus, adhesion bands, and Hirschsprung's disease (1, 2). Anomalous congenital bands, which are neither of embryological nor inflammatory origin, are a rare cause of intestinal obstruction, with the ileum being the most commonly affected site (3). To date, over ninety cases have been reported, yet only five cases involving duodenal obstruction due to idiopathic congenital bands have been documented (4–7). This study presents an eight-year-old girl with no prior history of chronic abdominal pain, vomiting, or abdominal surgery who experienced acute duodenal obstruction due to two congenital bands. This case report has received approval from the Ethics Committee of Xi'an Children's Hospital (Approval No: 20240025). Given the rarity of congenital bands, defining their characteristics remains challenging. Therefore, we conducted a comprehensive literature review to summarize the clinical features, imaging findings, treatment strategies, and prognosis associated with intestinal obstruction due to congenital bands.
An eight-year-old girl was admitted to our department with complaints of recurrent bilious vomiting and abdominal pain persisting for six days. Her birth and family histories were unremarkable. There was no history of chronic abdominal pain, vomiting, prior abdominal surgery, or trauma. On physical examination, the patient measured 125 cm in height (25th percentile) and weighed 23 kg (25th percentile). She exhibited moderate tenderness in the upper quadrant of the abdomen, without rebound tenderness. Bowel sounds were notably reduced, with an observed frequency of two per minute.
Laboratory data revealed an increase in serum lipase (140.4 U/L) and amylase (152 U/L), as well as elevated urine amylase (636 U/L). The plain x-ray showed a small fluid-air level with the absence of distal gas (Figure 1A). A barium meal demonstrated an obstructed passage of contrast at the third part (horizontal portion) of the duodenum (Figure 1B). Abdominal ultrasound performed after water intake revealed a strip-like hypoechoic external compression affecting the third part of the duodenum, preventing the passage of contents (Figure 1C). A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen identified distension of the proximal segment of the duodenum with fluid accumulation (Figure 1D). Although the lipase and amylase were slightly increased, no evidence of pancreatitis was identified in imaging modalities. Additionally, none of the imaging studies suggested malrotation. Despite the imaging studies indicating duodenal obstruction, the exact etiology of the obstruction was not confirmed. As a result, we proceeded with gastroduodenoscopy, which revealed that the endoscope could not pass through the distorted intestinal lumen approximately 40 cm distal to the pylorus (Figure 2A).
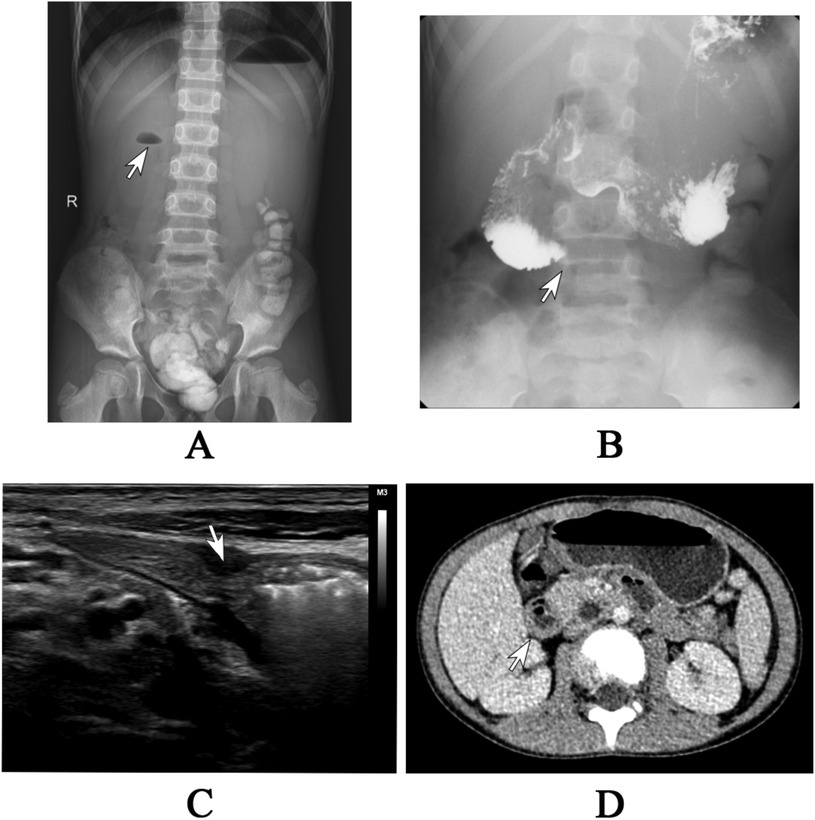
Figure 1. (A) The plain x-ray revealed a small air-fluid level in the upper right quadrant, accompanied by the absence of gas in the distal area. (B) The barium meal study demonstrated an obstructed passage of barium in the third segment of the duodenum. (C) The abdominal ultrasound showed a strip-like hypoechoic external compression affecting the third part of the duodenum, preventing the passage of contents. (D) The abdominal CT scan showed the distension of proximal duodenum with fluid accumulation.
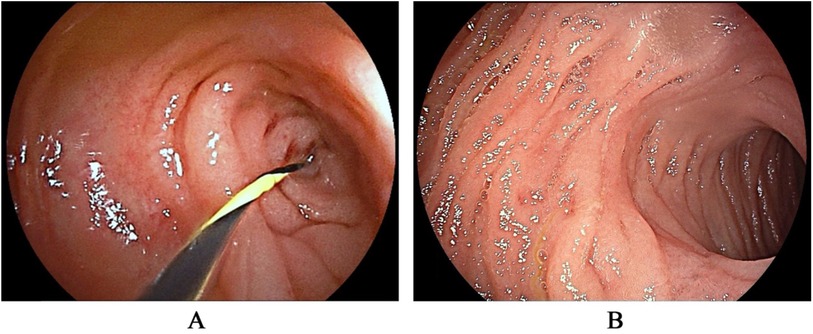
Figure 2. The gastroduodenoscopy revealed a distorted intestinal lumen, preventing the passage of the guidewire (A) after resecting the congenital bands, the distortion of the intestinal lumen was resolved (B).
After conservative treatment, including fasting, gastrointestinal decompression, and nutritional support, the patient's symptoms improved, and she was able to tolerate a liquid diet. The serum lipase, amylase, and urine amylase also decreased. However, a follow-up barium meal revealed persistent obstruction at the third part of the duodenum. One week later, the patient experienced a recurrence of bilious vomiting, with 900 ml of contents. An abdominal laparoscopy combined with gastroduodenoscopy was then performed. During the procedure, two bands were identified: one extending from the duodenum to the transverse colon, crossing over the third part of the duodenum (Figure 3A), and the other attached between the duodenum and the root of the mesentery (Figure 3B). The two bands were resected, allowing contents and gas to pass freely from the duodenum to the jejunum. Additionally, a gastroduodenoscopy was conducted to confirm the resolution of the duodenal obstruction (Figure 2B). The distorted intestinal lumen was found to be unobstructed, and the endoscope passed through smoothly. The histopathological findings revealed that these congenital bands were composed of loose connective tissue.
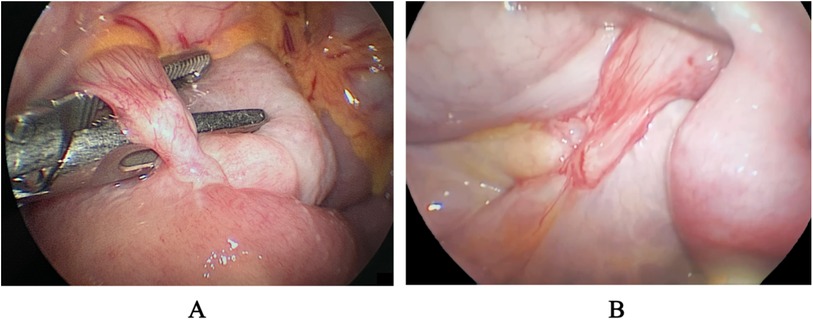
Figure 3. Two congenital bands were identified during the laparoscopy. One extending from the duodenum to the transverse colon, crossing over the third part of the duodenum (A), and the other attached between the duodenum and the root of the mesentery (B).
The child had a fluid diet at the third postoperative day. She was discharged without complications on the fifth postoperative day, and subsequent outpatient follow-ups have been uneventful.
The PubMed database was searched for relevant literature published from the earliest available date up to August 15, 2024. We used the search terms “idiopathic congenital band*”, “congenital peritoneal band*”, “congenital band*”, “anomalous congenital band*”, and “congenital peritoneal belt*”, in titles or abstracts. To ensure thoroughness, we also searched using the terms “congenital band*”, “bowel obstruction”, and “intestinal obstruction” across all fields. Case reports and case series were included, and all references cited in the selected literature were reviewed. Only English-language articles were included. As our focus was specifically on anomalous congenital bands, we excluded literature related to Ladd's bands and the remnants of known structures, such as vitelline arteries or veins, omphalomesenteric ducts, or mesenteric remnants.
All relevant literature was meticulously reviewed, and clinical information was extracted, including demographic details, clinical features, imaging findings, therapeutic methods, and disease prognosis related to idiopathic congenital bands. The extracted data was analyzed using descriptive statistics.
Ultimately, we included 51 papers encompassing a total of 92 cases (3–53). All patients were admitted to emergency or inpatient departments for bowel obstruction due to congenital bands. Of these cases, five involved duodenal obstruction, 67 involved small bowel obstruction, ten involved large bowel obstruction, and ten cases presented with intestinal obstruction without specification of the exact obstruction site.
Among the 93 cases (including the present case in our study), 33 were adults and 60 were children. Within the adult cohort, bowel obstruction primarily affected young and middle-aged adults (ages 18 to <60), comprising 78.8% (26/33) of the cases. In the pediatric group, one-third of the children (20/60) experienced bowel obstruction during infancy, with 13 cases occurring in the neonatal period (Supplementary Material I). The percentage of children affected between toddlerhood and school age was 55.0% (33/60). Only seven cases were reported in adolescents. Regarding gender distribution, the majority of patients were male, comprising 71.0% (66/93) of the cases (Supplementary Material I).
Clinical manifestations were detailed in 75 cases, with abdominal pain (61/75) and vomiting, either bilious or non-bilious (59/75), being the most common symptoms. Constipation was also frequently reported (Supplementary Material I). In infants with bowel obstruction, typical findings included the absence of defecation, refusal of oral intake, and abdominal distension. In terms of past medical history, eight patients had a history of chronic abdominal pain or distension, four had a history of intestinal obstruction, and 10 had undergone abdominal surgeries. The remaining patients were newly diagnosed with bowel obstruction and had no prior history of abdominal symptoms or surgeries. Physical examinations revealed abdominal distension and tenderness as the most commonly described signs. In contrast, six patients had an unremarkable abdominal examination (Supplementary Material I).
Imaging findings related to abdominal symptoms were extracted from these cases (Supplementary Material II). Of these, 15 cases underwent abdominal contrast x-ray, revealing common findings such as dilated bowels or bowel loops, with either an abrupt cutoff or restricted contrast passage. In 55 cases that utilized plain x-rays, frequent findings included dilated bowels or bowel loops, multiple air-fluid levels, and reduced bowel gas. Notably, one case involving a 16-year-old girl diagnosed with jejunal obstruction presented with a normal plain x-ray result.
Abdominal CT scan results were reported for 38 patients, typically showing dilated bowels proximal to the compression site, and collapsed bowels distal to it, with detailed documentation of compression sites, levels, and mechanisms. Notably, only two CT scans identified bands responsible for bowel obstruction. In contrast, the current case did not show a narrowing or collapsed bowel lumen on CT. Abdominal ultrasound, performed in several cases, generally demonstrated dilated bowel loops. Remarkably, the abdominal ultrasound in the present case revealed strip-like hypoechoic external compression of the duodenum.
All patients underwent abdominal surgery due to a high suspicion of abdominal obstruction or the failure of conservative treatment (Supplementary Material III). Laparotomy was performed in 80 cases, while laparoscopy was utilized in 13 cases. A total of 87 congenital bands from 85 patients were meticulously documented. The origins of the bands varied, and 38/87 were found to attach to the ileum or its mesentery. Twenty-four were found to be attached to the jejunum, and 17 to the ascending colon. Other attachment sites, including the transverse colon, duodenum, Treitz ligament, and omentum, were observed in a few isolated cases. Three main mechanisms of obstruction due to congenital bands were identified: direct compression of the adjacent bowel by the band, entrapment of a bowel loop between the band and mesentery, and partial volvulus (Supplementary Material III).
All cases underwent band excision or adhesiolysis to relieve bowel obstruction. Additionally, twenty-two patients required bowel resection due to gangrenous, necrotic, non-viable, or perforated segments of the bowel. Postoperative outcomes were documented in 68 cases. Among these, three newborns succumbed to sepsis secondary to peritonitis, and one elderly female patient died from an acute coronary event on the second postoperative day. Two patients experienced intestinal obstructions due to postoperative adhesions, while the remaining patients recovered without complications.
Based on this literature review, among 93 cases of intestinal obstruction due to congenital bands, over two-thirds were children, with the majority (53/60) experiencing their first obstruction before adolescence. Males were disproportionately affected, accounting for 71.0% of the cases. Most studies held the opinion that congenital bands were extremely rare in adults (22, 43, 44), however, we found that approximately one-third affected cases were adults. Considering their embryologic origin, congenital bands are present from birth and typically lead to clinical symptoms early in life (54). However, a portion of cases become symptomatic later in life, and the underlying reasons warrant further exploration. Similar to other congenital malformations, such as Ladd's bands or Meckel's diverticulum, congenital bands might remain asymptomatic in adults due to their specific location or structure (55–57). Occasionally, changes in the body—such as alterations in abdominal pressure, abnormal gastrointestinal motility, or age-related changes in tissue elasticity—may contribute to the onset of symptoms later in life. Moreover, it is possible that some reported “congenital bands” were actually acquired, particularly in adults, where a history of abdominal surgery, trauma, or inflammations could lead to the formation of fibrous bands that mimic congenital bands (15, 58).
Regarding clinical features, common symptoms included abdominal pain, bilious or non-bilious vomiting, and occasionally constipation, which are consistent with those seen in intestinal obstruction from other causes (59). Notably, only probably 20 patients had a history of gastrointestinal disorders, such as chronic abdominal pain, previous intestinal obstructions, or abdominal surgeries. Most patients experienced acute intestinal obstruction for the first time.
Only one study included in the literature reported elevated amylase levels (45). In our case, increased serum lipase, amylase, and urine amylase were observed on the first day of hospitalization. Following gastrointestinal decompression and abdominal laparoscopy, these parameters gradually returned to normal levels. This phenomenon is not uncommon in cases of intestinal obstruction (60, 61). Elevated lipase and amylase levels in intestinal obstruction may arise from several factors. Firstly, the distention of the duodenum during obstruction can lead to blockage of the sphincter of Oddi. Additionally, repeated vomiting may create pressure within the pancreatic duct. These two factors can contribute to the retrograde flow of pancreatic secretions through venous channels (60, 62). Furthermore, increased intestinal permeability may allow more amylase to enter the bloodstream (61, 63). These elevations do not necessarily indicate pancreatitis but are closely linked to the mechanical and physiological changes that occur during obstruction.
Image techniques such as plain x-rays, contrast x-rays, CT scans, and abdominal ultrasound demonstrated positive findings of intestinal obstruction. However, identifying the etiology was challenging. Plain x-rays might show air-fluid levels and dilated bowels, but they lacked specificity and might yield negative results at times (5, 25). Contrast x-rays could reveal dilated and narrowed bowel segments but did not provide information on the underlying cause of the obstruction. CT scans were recommended as the primary imaging modality for suspected cases of intestinal obstruction due to their ability to offer comprehensive details on diagnosis, location, level, and etiology (30, 59). However, in this review, only two cases identified congenital bands on CT, characterized by either a hyperdense (on contrast-enhanced CT) or hypodense (on non-contrast-enhanced CT) linear tissue formation (43). Ultrasound imaging also showed distended intestinal loops or signs of peritonitis, but it lacked specificity (14). In the present case, the ultrasound revealed a strip-like hypoechoic structure compressing the nearby bowel. In summary, while various imaging modalities are valuable for diagnosing intestinal obstruction, they may not always lead to a definitive preoperative diagnosis of obstruction caused by a congenital band. For this reason, surgical exploration plays a crucial role in identifying the underlying etiology.
Conservative treatment was always ineffective for managing intestinal obstruction caused by anomalous congenital bands, necessitating abdominal surgery for both diagnosis and treatment in all reviewed cases. While laparotomy has traditionally been the standard approach, laparoscopic surgery has emerged as a safe and effective alternative. Numerous case reports have demonstrated successful outcomes with laparoscopy in both pediatric (13, 25, 29, 40) and adult patients (12, 27, 30, 32), positioning it as a viable first-line surgical option. This emphasizes the importance of considering laparoscopic intervention as a standard approach for timely etiology identification and prompt treatment in cases of intestinal obstruction with an unclear cause. Predominantly, the anomalous congenital bands were identified as attaching to the ileum or its mesentery, followed by the jejunum and colon. Surgical intervention typically involved resecting these bands to alleviate bowel obstruction and, in some cases, excising non-viable or perforated bowel segments. Overall, the prognosis for intestinal obstruction was generally favorable, with most patients recovering without complications. Significantly, four patients—three newborns and one elderly individual—succumbed to severe complications following surgery, highlighting an increased risk of unfavorable outcomes in these particular patient groups.
In this literature review, we have presented a comprehensive summary of the distributions, clinical features, imaging findings, treatment strategies, and overall prognosis associated with intestinal obstruction caused by anomalous congenital bands. However, it is important to acknowledge several limitations. Firstly, our review was limited to English-language papers, potentially excluding relevant cases reported in other languages. This may have resulted in the omission of valuable data that could have provided further insights. Additionally, our review focused solely on cases documented in published databases, overlooking potentially significant cases that were unreported or not indexed. Therefore, the findings and conclusions presented in this study should be interpreted with caution, as they may not capture the full spectrum of possible scenarios.
In conclusion, we presented a rare case of duodenal obstruction caused by two anomalous congenital bands and summarized relevant cases to guide clinicians' attention toward this condition. Our findings offer valuable insights for clinical diagnosis and treatment, highlighting the need for awareness of congenital bands in similar cases.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The studies involving humans were approved by The Ethics Committee of Xi'an Children's Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
SX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KG: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CH: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HY: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. BL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YH: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YF: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. XR: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This case report and literature review was supported by the Xi ‘an Health Committee surface cultivation project (2024ms06) and Xi ‘an Children’s Hospital-Key project - Medical joint project (2022E01).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2025.1491520/full#supplementary-material
1. Saliakellis E, Borrelli O, Thapar N. Paediatric GI emergencies. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. (2013) 27(5):799–817. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2013.08.013
2. Peyvasteh M, Askarpour S, Javaherizadeh H, Taghizadeh S. Ileus and intestinal obstruction–comparison between children and adults. Pol Przegl Chir. (2011) 83(7):367–71. doi: 10.2478/v10035-011-0058-9
3. Akgür FM, Tanyel FC, Büyükpamukçu N, Hiçsönmez A. Anomalous congenital bands causing intestinal obstruction in children. J Pediatr Surg. (1992) 27(4):471–3. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(92)90340-D
4. Nair SK, Chawla S. Congenital peritoneal band causing partial duodenal obstruction. A case report. Indian J Pediatr. (1962) 29:351–4. doi: 10.1007/BF02748287
5. Crankson SJ, Al-Mane KA, Al-Zaben A, Al-Dhafian A. Extrinsic duodenal obstruction from anomalous congenital band. Ann Saudi Med. (2000) 20(5-6):443–4. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2000.443
6. Liu C, Wu TC, Tsai HL, Chin T, Wei C. Obstruction of the proximal jejunum by an anomalous congenital band–a case report. J Pediatr Surg. (2005) 40(3):E27–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2004.11.008
7. Naous A, Itani R, Itani MK, Naja Z, Rajab M. Congenital adhesion band: a rare case in a neonate. Radiol Case Rep. (2024) 19(2):499–502. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.10.076
8. Asano S, Konuma K, Rikimaru S, Inoue K. Volvulus of the transverse colon in a four-year-old boy. Z Kinderchir. (1982) 35(1):21–3.7064578
9. Lin DS, Wang NL, Huang FY, Shih SL. Sigmoid adhesion caused by a congenital mesocolic band. J Gastroenterol. (1999) 34(5):626–8. doi: 10.1007/s005350050384
10. Maeda A, Yokoi S, Kunou T, Tsuboi S, Niinomi N, Horisawa M, et al. Intestinal obstruction in the terminal ileum caused by an anomalous congenital vascular band between the mesoappendix and the mesentery: report of a case. Surg Today. (2004) 34(9):793–5. doi: 10.1007/s00595-004-2821-6
11. Etensel B, Ozkisacik S, Döger F, Yazici M, Gürsoy H. Anomalous congenital band: a rare cause of intestinal obstruction and failure to thrive. Pediatr Surg Int. (2005) 21(12):1018–20. doi: 10.1007/s00383-005-1563-x
12. Wu JM, Lin HF, Chen KH, Tseng LM, Huang SH. Laparoscopic diagnosis and treatment of acute small bowel obstruction resulting from a congenital band. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. (2005) 15(5):294–6. doi: 10.1097/01.sle.0000183258.34926.59
13. Itagaki MW, Lema R, Gregory JS. Small bowel obstruction caused by a congenital jejuno-jejuno band in a child. Pediatr Emerg Care. (2005) 21(10):673–4. doi: 10.1097/01.pec.0000181416.64353.4b
14. Dimitrios C, George AA, Dimosthenis Z, Nikolaos X. Intestinal obstruction due to an anomalous congenital band. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2008) 14(1):36–7. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.37806
15. Hunter IA, Sarkar R, Smith AM. Small bowel obstruction complicating colonoscopy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2008) 2:179. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-2-179
16. Kumar A, Ramakrishnan TS, Sahu S. Large bowel obstruction by anomalous congenital band. Med J Armed Forces India. (2009) 65(4):378–9. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(09)80110-X
17. Mansoor K, Al Hamidi S, Khan AM, Samujh R. Rare case of pediatric cecal volvulus. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. (2009) 14(3):110–2. doi: 10.4103/0971-9261.57707
18. Kumar A, Ramakrishnan TS, Behl A, Sahu S, Singh G. Intestinal obstruction in a child: internal hernia caused by an anomalous congenital band. Trop Gastroenterol. (2010) 31(3):219–21.21560529
19. Fang AC, Carnell J, Stein JC. Constipation in a 7-year-old boy: congenital band causing a strangulated small bowel and pulseless electrical activity. J Emerg Med. (2012) 42(3):283–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.05.092
20. Sarkar D, Gongidi P, Presenza T, Scattergood E. Intestinal obstruction from congenital bands at the proximal jejunum: a case report and literature review. J Clin Imaging Sci. (2012) 2:78. doi: 10.4103/2156-7514.105130
21. Nouira F, Sarrai N, Charieg A, Jlidi S, Chaouachi B. Small bowel obstruction by an anomalous congenital band. Acta Chir Belg. (2012) 112(1):77–8. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2012.11680801
22. Sozen S, Emir S, Yazar FM, Altinsoy HK, Topuz O, Vurdem UE, et al. Small bowel obstruction due to anomalous congenital peritoneal bands—case series in adults. Bratisl Lek Listy. (2012) 113(3):186–9. doi: 10.4149/bll_2012_043
23. Catania VD, Olivieri C, Nanni L, Pintus C. Extrinsic colonic obstruction by congenital fibrous band in an infant. BMJ Case Rep. (2013) 2013:bcr2012007897. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007897
24. Low SF, Ngiu CS, Sridharan R, Lee YL. Midgut malrotation with congenital peritoneal band: a rare cause of small bowel obstruction in adulthood. BMJ Case Rep. (2014) 2014:bcr2013202690. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-202690
25. Jerraya H, Khalfallah M, Gaja A, Dziri C. Laparoscopic treatment of intestinal obstruction caused by an uncommon congenital band. BMJ Case Rep. (2015) 2015:bcr2015212536. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2015-212536
26. Aydin E. A rare cause of intestinal obstruction in a newborn: congenital band compression. North Clin Istanb. (2016) 3(1):75–8. doi: 10.14744/nci.2015.26349
27. Nicolas G, Kfoury T, Shimlati R, Koury E, Tohmeh M, Gharios E, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of small bowel strangulation due to congenital band: three cases of congenital band in adults lacking a history of trauma or surgery. Am J Case Rep. (2016) 17:712–9. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.899664
28. Erginel B, Soysal FG, Ozbey H, Keskin E, Celik A, Karadag A, et al. Small bowel obstruction due to anomalous congenital bands in children. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2016) 2016:7364329. doi: 10.1155/2016/7364329
29. Miyao M, Takahashi T, Uchida E. A case of anomalous congenital band that was difficult to differentiate from omphalomesenteric duct anomaly. J Nippon Med Sch. (2017) 84(6):304–7. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.304
30. Abdelwahed Y, Saber R, Imen BI, Hakim Z, Ayoub Z. A case report of small bowel obstruction secondary to congenital peritoneal band in adult. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2017) 30:23–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.11.007
31. Vishnoi V, Park SW, Martin P. Acute chylous peritonitis as a result of jejunal volvulus and small bowel obstruction from a congenital band adhesion. ANZ J Surg. (2019) 89(7-8):E345–e6. doi: 10.1111/ans.14462
32. Cruise DA, Goddard K. Congenital band adhesion causing a proximal jejunal obstruction: an uncommon presentation and diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. (2019) 12(7):e229235. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229235
33. Kerkeni Y, Aicha B, Hamzaoui M. Idiopathic congenital anomalous bands: about ten cases with systematic review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Adolesc Med. (2020) 7(4):157–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpam.2020.03.006
34. Hadded D, Mesbahi M, Zouaghi A, Marouani M, Chamekhi C, Ben Maamer A. Adult small bowel obstruction due to congenital peritoneal belt: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2021) 84:106016. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.106016
35. Guillen J, Ramey S, Parimi PS. Congenital adhesion band presenting as intestinal perforation in an extremely low birth weight infant. AJP Rep. (2021) 11(1):e1–4. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1722729
36. Parrado RH, Rubalcava NS, Davenport KP. From the cecum to the sigmoid: twisted colon in the pediatric population. Cureus. (2021) 13(9):e17974. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17974
37. Tepelenis K, Stefanou SK, Stefanou CK, Tepelenis N, Margariti P, Christopoulou A, et al. Small bowel obstruction due to a congenital adhesion: a rare case report. J Surg Case Rep. (2021) 2021(7):rjab282. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjab282
38. Maree G, Alelayan A, Hemi F, Shater W, Ghuzlan A, Ali W. Jejunal obstruction due to jejunocolic congenital band in a 12-year-old child: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2022) 16(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03546-w
39. Sarraf K, Newman O, Mirkazemi M, Serena T. Laparoscopic enterolysis of congenital band precipitating pathogenic heterotopic mesenteric ossification requiring hemicolectomy: a case report. Am J Case Rep. (2022) 23:e934910. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.934910
40. Figueroa LM, Escobar G, Osorno J, Acuña M, Solarte J. Peritonealized urachal remnant and obstructive congenital peritoneal band. A case report. Cir Pediatr. (2022) 35(1):46–9. doi: 10.54847/cp.2022.01.19
41. Machino K, Kondo K, Sato K, Imamura T, Ohsawa Y. Strangulated bowel obstruction by idiopathic congenital band in very low birthweight infant. Pediatr Int. (2023) 65(1):e15408. doi: 10.1111/ped.15408
42. Arambepola D, Blades H, Sinha R, Sarma D. Therapeutic emergency laparoscopy for small bowel obstruction secondary to a congenital peritoneal band. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). (2022) 83(4):1–3. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2021.0505
43. Niang FG, Nsia RE, Faye I, Ndong A, Tendeng JN, Diedhiou M, et al. Small bowel obstruction due to congenital band in an adult: radio-surgical correlation. Radiol Case Rep. (2024) 19(1):400–2. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.10.052
44. Sleiay M, Sleiay B, Albaroudi D, Alsmoudi H, Abshi MA, Alaswad M, et al. Small bowel obstruction in a 29-year-old male with congenital peritoneal bands: a rare case report from Syria. Clin Case Rep. (2024) 12(3):e8663. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.8663
45. Just JD, Bailey RJ. Duodenal obstruction from congenital bands: an unusual cause of pancreatitis. Can J Gastroenterol. (1996) 10(7):449–50. doi: 10.1155/1996/738106
46. Attaallah W, Mokhtare S, Özden G, Yeğen C. Intestinal obstruction due to congenital mesenteric band in an adult patient. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2013) 24(4):356–8. doi: 10.4318/tjg.2013.0611
47. Kostic A, Krstic M, Slavkovic A, Vacic N. Intestinal obstruction in children: could it be congenital abdominal bands? Pediatr Emerg Care. (2013) 29(4):500–1. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e31828a388f
48. Sharma D, Parameshwaran R, Dani T, Shetty P. Malrotation with transverse colon volvulus in early pregnancy: a rare cause for acute intestinal obstruction. BMJ Case Rep. (2013) 2013:bcr2013200820. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200820
49. Leung AA, Yamamoto J, Luca P, Beaudry P, McKeen J. Congenital bands with intestinal malrotation after propylthiouracil exposure in early pregnancy. Case Rep Endocrinol. (2015) 2015:789762. doi: 10.1155/2015/789762
50. Aranovich D, Schrier I. Reversed intestinal rotation presented as bowel obstruction in a pregnant woman. Case Rep Surg. (2015) 2015:870437. doi: 10.1155/2015/870437
51. Wang Y, Gowing S, Arena G. Adult colo-colonic intussusception caused by congenital bands: a case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2016) 26:88–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.07.019
52. Menconi G, Schembari E, Randazzo V, Mattone E, Coco O, Mannino M, et al. Intestinal obstruction due to congenital bands in adults who have never had abdominal surgery two case reports and a review of the literature. Ann Ital Chir. (2019) 90:524–31.31929177
53. Guragai M, Bhusal S, Bhatta A. Intestinal obstruction of congenital origin: a case report. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. (2020) 58(221):59–61. doi: 10.31729/jnma.4708
54. Yang KH, Lee TB, Lee SH, Kim SH, Cho YH, Kim HY. Congenital adhesion band causing small bowel obstruction: what’s the difference in various age groups, pediatric and adult patients? BMC Surg. (2016) 16(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12893-016-0196-4
55. Naddouri J, Khouah R, Sekkat H, Bakali Y, El Alaoui MM, Raiss M, et al. Small bowel obstruction in adults, Ladd’s band is an exceptional cause: a case report. Pan Afr Med J. (2024) 47:34. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.47.34.36435
56. Grassi C, Conti L, Palmieri G, Banchini F, Dacco MD, Cattaneo GM, et al. Ladd’s band in the adult, an unusual case of occlusion: case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2020) 71:45–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.04.046
57. Bani-Hani KE, Shatnawi NJ. Meckel’s diverticulum: comparison of incidental and symptomatic cases. World J Surg. (2004) 28(9):917–20. doi: 10.1007/s00268-004-7512-3
58. Weibel MA, Majno G. Peritoneal adhesions and their relation to abdominal surgery. A postmortem study. Am J Surg. (1973) 126(3):345–53. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(73)80123-0
59. Jackson PG, Raiji MT. Evaluation and management of intestinal obstruction. Am Fam Physician. (2011) 83(2):159–65.21243991
60. Byrne JJ, Boyd TF. Serum amylase levels in experimental intestinal obstruction. N Engl J Med. (1957) 256(25):1176–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195706202562503
61. Spector D, Perry Z, Shah S, Kim JJ, Tarnoff ME, Shikora SA. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: hyperamylasemia is associated with small bowel obstruction. Surg Obes Relat Dis. (2015) 11(1):38–43. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2014.04.030
62. Byrne JJ, Boyd TF. Hyperamylasemia in intestinal obstruction and its relationship to pancreatitis. Am J Surg. (1963) 105:720–9. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(63)90484-7
Keywords: intestinal obstruction, anomalous congenital band, clinical features, case report, literature review
Citation: Xiong S, Ge K, Hou C, Yang H, Zhang H, Zhang S, Liu B, Hao Y, Fang Y and Ren X (2025) Duodenal obstruction due to two congenital bands: a case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 13:1491520. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1491520
Received: 5 September 2024; Accepted: 2 January 2025;
Published: 17 January 2025.
Edited by:
Lovenish Bains, University of Delhi, IndiaReviewed by:
Heba Taher, Cairo University, EgyptCopyright: © 2025 Xiong, Ge, Hou, Yang, Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Hao, Fang and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Fang, ZmFuZ3lpbmc1MjZAdmlwLjE2My5jb20=; Xiaoxia Ren, MjQxMjY2MjM4M0BxcS5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.