- 1Department of Pharmacy, Affiliated Children’s Hospital of Jiangnan University (Wuxi Children’s Hospital), Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
- 3Center for ADR Monitoring of Jiangsu, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- 4Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Children’s Hospital of Jiangnan University (Wuxi Children’s Hospital), Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
Objective: This study analyzes the occurrence and characteristics of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) of dupilumab in children in a real-world setting. It aims to enhance clinical practice and minimize medication safety risks in pediatric patients.
Methods: This prospective study included children receiving dupilumab in the hospital between January 2022 and December 2023. Information on ADRs was collected and univariate and multivariate analyses were employed to identify high-risk factors for the occurrence of adverse effects in dupilumab treatment.
Results: A total of 65 ADRs occurred in 1,103 treatments in 127 patients, with an incidence of 27.56% (35/127). A total of 62 patients aged 6 or below participated in this study, accounting for 48.82%. Univariate analysis showed that gender, age, duration of medication, frequency of dupilumab use were risk factors for the occurrence of adverse effects (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age [odds ratio [OR]: 0.071, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.012–0.433; P = 0.004] and frequency of dupilumab use (OR: 3.306, 95% CI: 1.078–10.135; P = 0.036) were risk factors for adverse effects. The outcomes of ADRs were improved in 10 cases (15.38%) and completely recovered in 55 cases (84.62%).
Conclusion: Dupilumab has a good safety profile in Chinese children aged 6 months to 18 years for up to 2 years of treatment, with most adverse reactions being mild to moderate, and no serious ocular adverse reactions were reported. Age and frequency of dupilumab use were risk factors for adverse effects. Younger age and higher frequency of dupilumab use were associated with higher odds of ADRs.
1 Introduction
Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody derived from VelocImmune technology (1, 2) that targets the shared IL-4Rα subunit of IL-4 and IL-13 receptors, thereby inhibiting signaling pathways associated with these cytokines which are key drivers of type 2 inflammation (3–5). Dupilumab is approved in multiple countries, including Europe, the United States, and China, for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in patients aged 6 months and older and asthma in those aged 6 years and older, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis in adults, eosinophilic esophagitis in patients aged 1 year and older weighing at least 15 kg, prurigo nodularis in adults, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults (6–8). The safety of dupilumab has been demonstrated through clinical trials and post-marketing evaluations in adults and adolescents (9–17).
The common ADRs to dupilumab for atopic dermatitis treatment include (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, dry eye, and eosinophilia (6). However, safety data on children particularly Asian infants and those younger than 6 years of age undergoing long-term treatment remain limited (18, 19). Notably, there have been reports of serious adverse events such as uveitis following prolonged dupilumab use (20–22). Data from small cohorts and clinical trials (23–27) suggest that increased rates of dupilumab-related ocular surface disease in patients with atopic dermatitis are linked to more severe baseline disease, prior conjunctivitis, atopic comorbidities, eyelid involvement, elevated thymus and activation-regulated chemokine levels, serum IgE levels, and peripheral blood eosinophilia. However, prospective studies evaluating risk factors for dupilumab-associated ADRs in pediatric patients remain scarce. Real-world safety data on younger children are essential for clinicians to comprehensively assess the risk-benefit profile of dupilumab in China. This study aimed to evaluate the safety of dupilumab in Chinese pediatric patients in a real-world setting.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and eligible participants
A prospective, active monitoring study was conducted for pediatric patients who received dupilumab at least once between January 2022 and December 2023 at the Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Children's Hospital of Jiangnan University.
Inclusion criteria: (1) Children and adolescents aged 6 months to younger than 18 years; (2) Pediatric patients treated with dupilumab injection (300 mg/2.0 ml/vial or 200 mg/1.14 ml/vial pre-filled syringe, Sanofi Winthrop Industrie) administered subcutaneously.
Exclusion criteria: (1) Lack of informed consent from parents or legal guardians; (2) Patients with immunodeficiency, severe systemic diseases (e.g., cardiac, hepatic, renal), or malignancies; (3) Missing electronic medical records.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the hospital (Ethics Approval No: WXCH2021-11-013) and adhered to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki. Standard pediatric clinical procedures and routine treatment protocols were followed by the attending physicians.
2.2 Data collection
Pediatric patient data were extracted from medical records, including demographic information (e.g., gender, age, weight), medication details (e.g., clinical diagnosis, administration time, dosage, route of administration, frequency, concomitant medications). The type, onset, management, and outcomes of ADRs were evaluated and recorded by the MSO (Medication Safety Officer) team during weekly follow-ups or when patients reported ADRs.
2.3 Criteria for adverse reaction evaluation
The causality assessment of all identified ADRs associated with dupilumab was performed using the WHO-Uppsala Monitoring Centre Criteria (WHO-UMC) (28). Two independent reviewers from the MSO team conducted the evaluations, with a third reviewer providing the final assessment in case of disagreement.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS version 26.0. Categorical variables were expressed as numbers (n) and percentages (%), normally distributed continuous variables as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and non-normally distributed continuous variables as medians and interquartile ranges [M (Q1, Q3)]. To identify risk factors associated with dupilumab-related ADRs, each candidate risk factor was initially analyzed using chi-square tests in a univariate model. Variables with statistical significance were then included in a multivariate logistic regression model. The dependent variable was the occurrence of ADRs (0 = No, 1 = Yes), and independent variables were analyzed to identify risk factors. Variables with a P-value < 0.05 in the multivariate logistic regression analysis were considered independent risk factors. A significance level of P < 0.05 was used.
3 Results
3.1 Analysis of baseline demographic characteristics and adverse reactions
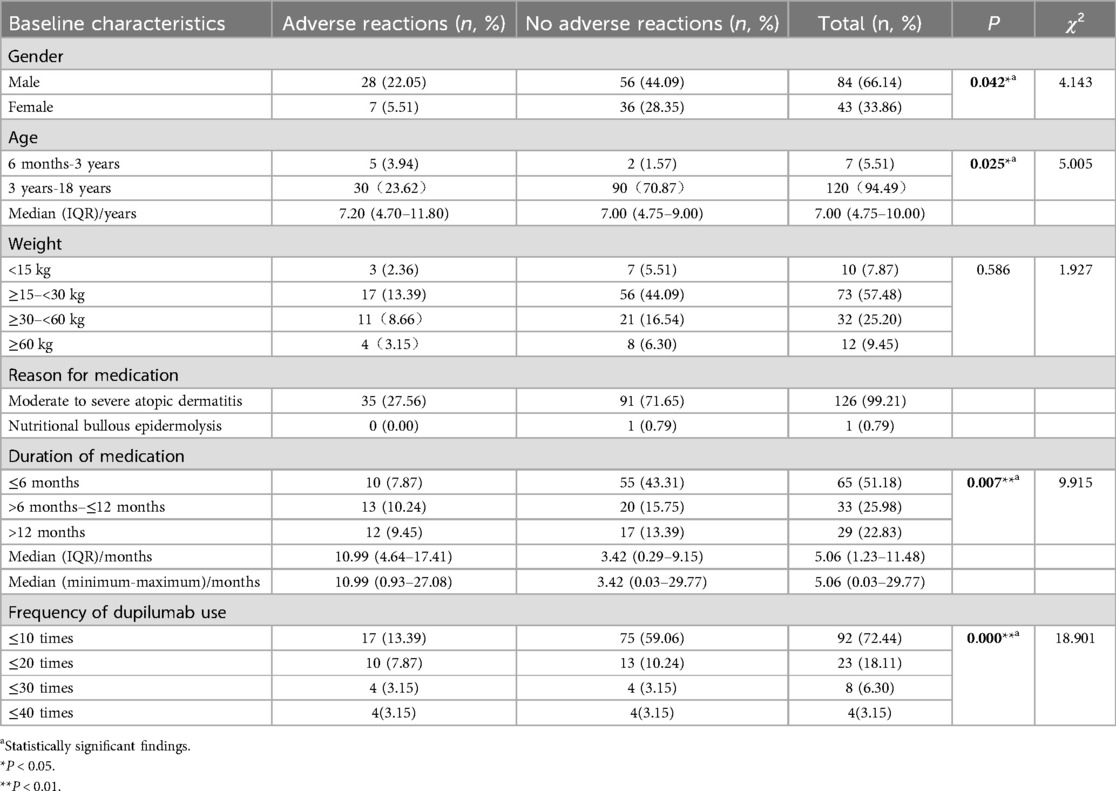
A total of 127 pediatric patients met the inclusion criteria and were included in this study (Table 1). Of these, 84 (66.14%) were boys and 43 (33.86%) were girls. The age range of the patients was between 4.75 and 10 years, with 62 (48.82%) aged 6 years or younger. Nearly all patients (99.21%) were treated for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, except for one patient treated for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Of the 127 patients, 35 experienced ADRs, as shown in Table 1.
To identify risk factors associated with dupilumab-related ADRs, five candidate risk factors were analyzed using chi-square tests in a univariate model, including gender, age, weight, duration of treatment, and frequency of dupilumab use. The results of the univariate analysis were presented in Table 1, and the results of the multivariate analysis were presented in Table 2. In the univariate model, variables that significantly influence the risk of ADRs included gender, age, duration of treatment, and frequency of dupilumab use (P < 0.05). In the multivariate logistic regression model, age [odds ratio [OR]: 0.071, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.012–0.433; P = 0.004] and frequency of dupilumab use (OR: 3.306, 95% CI: 1.078–10.135; P = 0.036) were identified as independent risk factors associated with dupilumab-related ADRs (P < 0.05, Table 2). Younger age was associated with increased ADRs risk (OR <1), while more frequent administration was also linked to a greater likelihood of ADRs (OR >1).
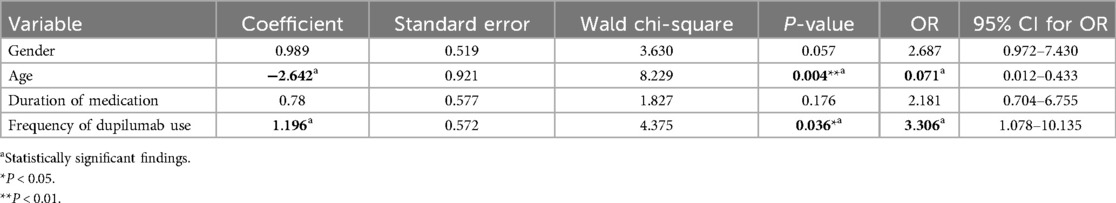
Table 2. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of risk factors for adverse reactions of dupilumab.
3.2 Dupilumab treatment details
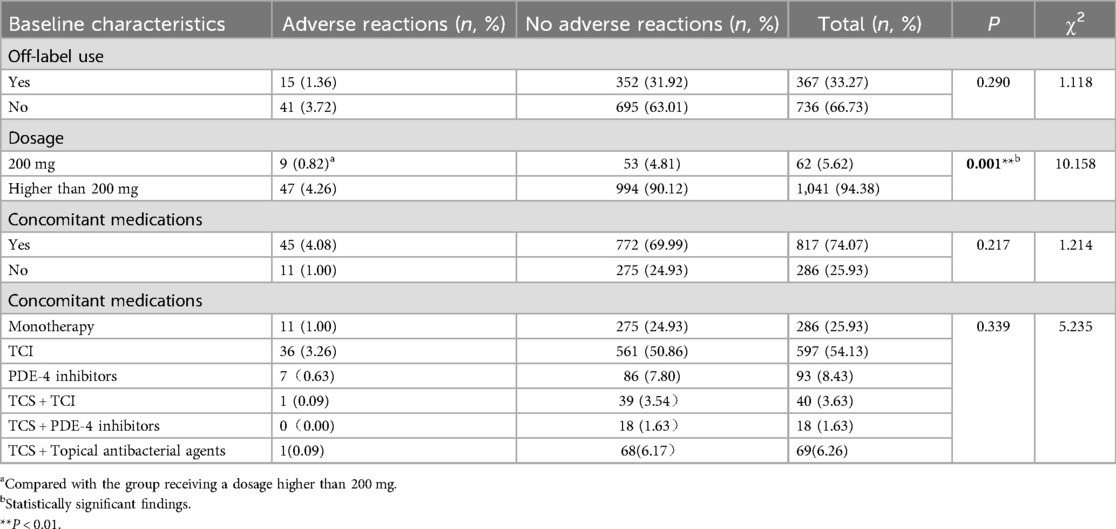
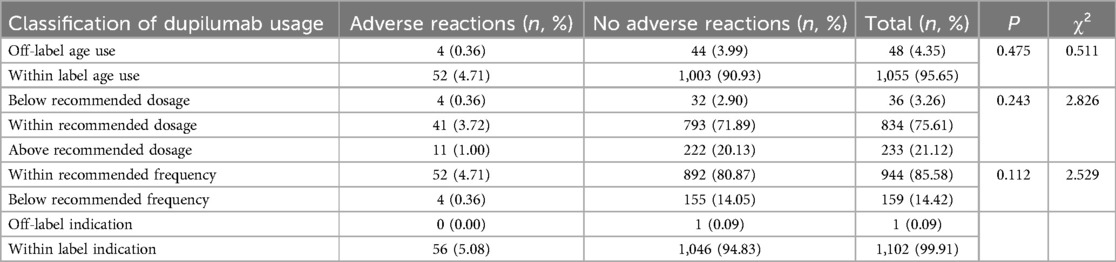
A total of 1,103 dupilumab treatments were administered to 127 patients (Table 3), with doses ranging from 200 to 600 mg via subcutaneous injection. Among these, 367 (33.27%) treatments involved off-label use, including off-age, off-dosage, off-frequency, and off-indication. There was no statistically difference in ADRs incidence between on-label and off-label use (P > 0.05) (Table 3). Then a detailed subgroup analysis of on-label vs. off-label use was conducted and the results were presented in Table 4. Similarly, no significant differences in ADRs incidence were observed between subgroups (P > 0.05). This suggests that off-label use of dupilumab in pediatric populations does not inherently increase the risk of ADRs compared to on-label use.
Concomitant medications were used in 74.07% of treatment regimens, with topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) being the most common combination. Other combination regimens included phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE 4) inhibitors, topical corticosteroids (TCS) combined with TCI or PDE-4 inhibitors, and TCS combined with antibacterial agents. No significant difference in ADRs incidence was found between combination therapy and monotherapy (P > 0.05) (Table 3). No significant differences in ADRs incidence were observed between subgroups (P > 0.05) (Table 3). In contrast, a significant difference in ADRs incidence was observed between the 200 mg and >200 mg dosage groups (P < 0.05).
3.3 Incidence of adverse reactions
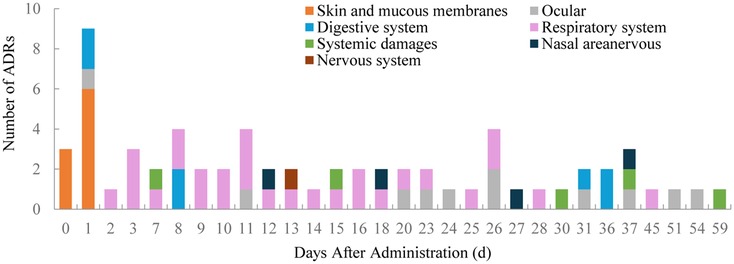
Among the 1,103 treatments, 56 resulted in adverse reactions, totaling 65 ADRs (with some patients experiencing multiple ADRs in one treatment). The most affected systems were the respiratory system (22.05%), eyes (8.66%), skin and mucous membranes (7.09%), and the digestive system (5.51%). Nine ADRs were classified as severe, including herpes simplex virus infection, varicella infection, and prolonged abdominal pain and bloating (Table 5).
3.4 Occurrence and outcomes of ADRs
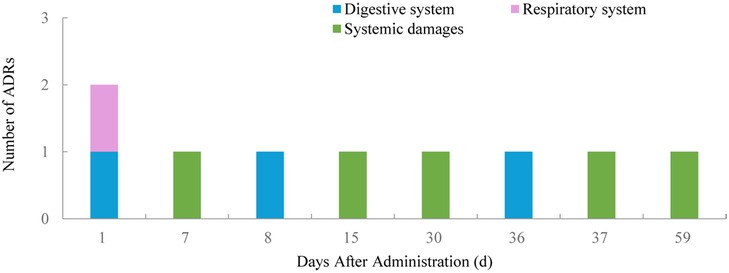
Of the 65 ADRs, 46.15% occurred within the first 11 days after the latest medication (Figure 1). During this period, most skin and mucosal injuries, respiratory diseases, and digestive reactions were observed. Ocular adverse reactions typically occurred 27.6 ± 15.6 days after the latest medication and 5.9 ± 4.6 months following the first dose. No cases led to treatment discontinuation. Distribution of time to occurrence of serious ADRs are presented in Figure 2. The occurrence time of severe ADRs was relatively scattered, with no central trend.
Among the ADRs outcomes, 10 cases (15.38%) showed improvement (including 2 cases of allergic conjunctivitis, 4 cases of conjunctivitis, 3 cases of epistaxis, and 1 case of allergic rhinitis), while 55 cases (84.62%) achieved total recovery. The ADRs in the eyes improved following the ophthalmologist's prescription of artificial tears, topical corticosteroid preparations, and topical anti-allergic treatments. The herpesvirus infection showed improvement after systemic or topical treatment with open-loop nucleoside antiviral drugs and topical administration of human interferon. The nasal ADRs were alleviated following treatment with vasoconstrictors, topical corticosteroids, and systemic anti-allergic agents. Improvements in respiratory system ADRs were observed after symptomatic treatment with inhaled corticosteroids, antibiotics, and mucus-diluting agents. In children presenting with unexplained abdominal pain, the therapeutic effects of probiotics, traditional Chinese patent medicines were not significant, and the abdominal pain ultimately resolved spontaneously.
3.5 Causality evaluation of adverse reactions
60 (92.31%) ADRs were deemed possible according to WHO-UMC criteria, as the events exhibited reasonable temporal relationships to drug intake; however, these ADRs could also be attributed to underlying diseases or other medications. 5 (7.69%) ADRs were deemed probable according to the WHO-UMC criteria. These events exhibited reasonable time relationships to drug intake, were unlikely to be associated with underlying diseases or other medications, and displayed clinically reasonable responses upon withdrawal. No definite ADRs were identified.
4 Discussion
Our study is among the initial studies to provide prospective real-world evaluations of the safety of dupilumab in Chinese pediatric patients. The findings demonstrate that dupilumab is generally safe for use in children aged 6 months to 18 years, with most ADRs being mild to moderate in severity. Importantly, no serious ocular adverse reactions were reported, which aligns with previously documented safety profiles from other international studies (11–16, 29–32). However, our data underscore the need for vigilance regarding specific patient subgroups that may be at higher risk for ADRs.
The incidence of ADRs in our cohort (27.56%) falls within the range of those observed in other safety studies involving pediatric populations receiving dupilumab (33). ADRs mainly involves the respiratory system, eyes, digestive system, skin and mucous membranes, systemic damage, nose, and nervous system. A systematic review and meta-analysis (34) on the efficacy and safety of dupilumab in children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis, which included 18 studies conducted in Europe, North America, and Asia, reported that most ADRs were mild to moderate and manageable. Common adverse events included exacerbation of atopic dermatitis (12.9%), injection-site reactions (7.3%), nasopharyngitis (10.6%), upper respiratory tract infections (10.1%), headache (7.5%), conjunctivitis (6.6%), eosinophilia (43.5%), and herpes viral infections (7.9%). Although potential biases related to institutional factors existed, the types of ADRs and the incidence of ADRs observed in our study were largely consistent with those reported in the systematic review and meta-analysis. However, there were some differences, for instance, eosinophilia was not observed in our study, as routine blood testing was not conducted during standard treatment in our hospital.
Respiratory related ADRs were the most frequently observed adverse reactions in this study (22.05%), which aligns with findings from other safety studies on dupilumab (35–39). Further investigation of its association with dupilumab is warranted.
Other common ADRs associated with dupilumab included ocular reactions (8.66%), skin and mucous membrane reactions (7.09%), and digestive system reactions (5.51%). Ocular adverse reactions typically occurred 27.6 ± 15.6 days after the latest medication and 5.9 ± 4.6 months following the first dose, consistent with previous reports (27, 40, 41). A Phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial reported similar rates of ocular adverse reactions in patients aged 6 months to under 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: allergic conjunctivitis (1%), conjunctivitis (4%), and stenosing conjunctivitis (5%) (11). A multicenter Canadian case series involving pediatric patients under 12 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis was conducted across six Canadian sites. This study reported that conjunctivitis was diagnosed in 8 out of 96 patients (8.3%), with the first episode occurring on average after 10.5 ± 7.71 weeks. No serious adverse events were recorded, and none of the children discontinued treatment with dupilumab (42). Our findings are largely consistent; however, no cases of stenosing conjunctivitis were observed. At the next follow-up, all ocular reactions had either resolved or were in the process of resolution. The team referred six cases of conjunctivitis and two of allergic conjunctivitis to ophthalmology and showed improvement after treatment with artificial tears, topical corticosteroids, and antiallergic agents. Other studies have noted severe ocular reactions, such as uveitis, occurring 7 months to 2 years post-treatment (39), indicating the need for vigilance regarding delayed-onset ocular ADRs in long-term dupilumab users. The exact pathophysiological mechanisms are not fully understood (43). Some studies indicate that monoclonal antibodies, by binding to IL-4Ra and inhibiting IL-4 and IL-13, can prevent the activation of conjunctival goblet cells. This inhibition results in hypoplasia and a reduction in mucin production, which subsequently affects the stability of the tear film and the functionality of the mucosal epithelial barrier (44, 45). In our study, the longest duration of dupilumab use was 29.8 months, with a median duration of 5.06 months (range 1.23–11.48 months), and no severe ocular ADRs were observed. But this may be attributed to the insufficient follow-up duration. Therefore, extended observational studies are essential for evaluating the long-term safety of dupilumab, especially concerning ocular and systemic effects that may arise with prolonged use. A recent study has demonstrated that the patient's age, history of conjunctivitis, and higher baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score are significantly associated with dupilumab-associated ocular surface disease (46). Previous studies also indicate that the risk of dupilumab-related conjunctivitis is associated with early-onset atopic dermatitis (AD) and eosinophilia (>500/mm3) (11), and that the prophylactic use of artificial tears may mitigate this risk (47, 48). Clinical vigilance is recommended, and some studies suggest restricting dupilumab prescriptions in patients with severe ocular diseases due to known adverse events (29).
Digestive related ADRs, involving abdominal pain and bloating, were consistent with previous reports (11, 33). By blocking the activity of IL-4/IL-13 receptors, dupilumab may potentially lead to parasitic infections for users because both cytokines contribute to the elimination of parasites through increased mucus production and eosinophilic mucosal inflammation in the gut (35, 49–52). Thus, if patients present with unexplained abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or severe nocturnal perianal pruritus, examination for parasites in stool or the perianal area is advised. In addition, Yosuke Shimodaira et al. described the case of a 17-year-old Asian male patient with severe AD who had a history of pediatric asthma and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and experienced the occurrence of intermittent abdominal pain, tenesmus, and diarrhea seven times a day after 3 months of dupilumab treatment, subsequently being diagnosed with ulcerative colitis (53). In our study, two cases of abdominal pain were reported, lasting 26 and 10 days, respectively, presenting as paroxysmal dull pain around the umbilicus, without vomiting and with slightly loose stools. The helicobacter pylori test yielded negative results, and the stool routine was normal. An abdominal ultrasound, along with examinations of the liver, gallbladder, spleen, and pancreas, revealed normal findings. Furthermore, fecal examinations were unremarkable, with no parasites detected around the anus. The treatment effects of probiotics and traditional Chinese patent medicines were not significant. These results may be attributed to the local gastrointestinal exposure of the drugs and their limited systemic absorption; however, the specific mechanisms underlying these effects remain unclear and warrant further investigation.
Nine cases of severe ADRs were observed, including abdominal pain, bloating, and infections caused by herpes simplex and varicella, which warrant particular attention. Although the majority of these severe ADRs resolved with appropriate treatment, it is crucial to educate both caregivers and clinicians about the potential for infectious complications, especially when treating children who may have additional risk factors for infection.
Notably, no significant difference was found in ADRs incidence between on-label and off-label uses of dupilumab. In our study, off-label use includes off-age use, off-dosage use, off-frequency use, and off-indication use. For off-age use, dupilumab was administered to children aged 2 years and 11 months to 6 years between January 1, 2022, and May 30, 2023 when dupilumab was only approved for children aged 6 years old and above in China. Off-dosage use includes two types: below the recommended dosage and above the recommended dosage. The doctor's evaluation of the specific condition of the child and the actual availability of drug specifications were common reasons for these deviations. Off-frequency use often involved extending dosing intervals during maintenance therapy for atopic dermatitis due to the high cost of dupilumab. Although off-label use of dupilumab in pediatric populations does not inherently increase the risk of ADRs compared to on-label use, it remains essential to evaluate each case individually, especially given the complex nature of off-label treatment and the lack of long-term data for such uses.
Our multivariate analysis identified younger age and frequency of dupilumab use as independent risk factors for ADRs. Younger age was associated with higher odds of ADRs. This is consistent with the known pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic differences in younger children, whose developing organ systems may lead to altered drug metabolism and increased vulnerability to adverse reactions (54, 55). Based on this finding, here are some recommendations for managing the use of dupilumab in pediatric populations. Healthcare providers should monitor intensively during the initial months of therapy for younger children (≤3 years) to detect ADRs early and focus on mild to moderate ADRs because they are common. In addition, healthcare providers should educate caregivers and parents on recognizing early symptoms such as rash, conjunctivitis, or local injection site reactions, given that young children may have difficulty expressing discomfort or other symptoms (56). Healthcare providers could provide symptomatic management and supportive care for mild reactions. For moderate ADRs, consider temporary dose adjustments or adjunctive treatments. At the same time, monitoring for rare or delayed onset ADRs should still be part of follow-up plans, especially for high-risk groups. And establish protocols for immediate referral to specialists (e.g., dermatologists, ophthalmologists) if severe reactions occur. Caregivers should be able to recognize ADRs such as skin rashes, redness, and mild swelling at the injection site, eye-related symptoms like redness or mild irritation and notify healthcare providers if symptoms persist, worsen, or if new symptoms (e.g., fever or severe rash) occur. It's very important for caregivers to document and report all side effects to the healthcare provider, even if they appear mild. As younger children have a higher likelihood of experiencing ADRs, caregivers should be vigilant in observing their reactions and symptoms after each treatment. Frequent use of dupilumab was another factor that associated with an increased risk of ADRs in this study. The association between frequent dupilumab use and ADRs suggests that cumulative exposure may increase the likelihood of immune modulation leading to adverse events. Clinicians should monito regularly to detect early signs of ADRs, particularly in high-risk organ systems such as the skin, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal system and consider dose intervals and cumulative exposure when tailoring treatment regimens, particularly in younger or more vulnerable pediatric patients.
In addition, the identified risk factors emphasize the need for tailored treatment approaches in pediatric populations. Developing risk stratification tools that incorporate age, frequency of use, and other potential factors-such as nutritional status, baseline disease severity, and genetic predispositions can help clinicians predict and mitigate ADRs risks. These findings also highlight the need for longitudinal studies to explore long-term safety profiles and late-onset ADRs, particularly in younger age groups. Investigating genetic, environmental, and cultural factors that may influence susceptibility to ADRs could further enhance the understanding of dupilumab's safety. And collaborative multi-center studies involving diverse patient populations are necessary to validating these findings and developing universal clinical guidelines.
This study has several limitations. In one hand, it was conducted at a single tertiary care institution in China, and the findings may not fully represent broader populations or other healthcare settings. The geographic location of the study could introduce biases due to differences in environmental factors, regional disease prevalence, and healthcare access. The clinical protocols and prescribing practices at our center may not reflect those in other healthcare settings, potentially influencing the observed safety profile of dupilumab. Moreover, cultural factors, such as caregiver reporting tendencies and treatment adherence, may vary across regions and countries. While our study provides valuable real-world safety data, future multi-center studies involving diverse geographic locations are essential to validate these findings and provide a more comprehensive understanding of dupilumab's safety profile in pediatric populations. In the other hand, the maximum follow-up period of 2 years may not capture long-term ADRs or late-onset effects, particularly ocular adverse events like uveitis, reported in other studies. Future studies should extend follow-up duration to evaluate long-term safety, especially for ocular and systemic effects. Additionally, our sample size, while adequate for identifying common ADRs, may not be sufficient to capture rare adverse events.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, our real-life data demonstrated that dupilumab has a good safety profile in Chinese children aged 6 months to 18 years for up to 2 years of treatment, with most adverse reactions being mild to moderate, and no severe ocular reactions were observed. The safety data were consistent with the known safety profile of dupilumab. Age and frequency of dupilumab use were identified as risk factors for the occurrence of adverse effects. Therefore, adverse effects should be closely monitored in patients with these risk factors.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Affiliated Children's Hospital of Jiangnan University (Wuxi Children's Hospital). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
YC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JN: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. ML: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YH: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. KZ: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RH: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LD: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JP: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Science and Technology Development Fund Project of Wuxi Key Medical Disciplines (Grant number: 2024SZD-YXB), and the Projects of the Post-market Safety Reevaluation of Drugs in Jiangsu Province (Grant number: HX-2024DPLYDK).
Acknowledgments
The authors express thanks to the staff of the Children's Hospital of Jiangnan University (Wuxi Children's Hospital) for their technical assistance, and the reviewers for their comments and suggestions that improved this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Macdonald LE, Karow M, Stevens S, Auerbach W, Poueymirou WT, Yasenchak J. Precise and in situ genetic humanization of 6 mb of mouse immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:5147–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323896111
2. Murphy AJ, Macdonald LE, Stevens S, Karow M, Dore AT, Pobursky K. Mice with megabase humanization of their immunoglobulin genes generate antibodies as efficiently as normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:5153–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324022111
3. Le Floc'h A, Allinne J, Nagashima K, Scott G, Birchard D, Asrat S. Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Rα antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation. Allergy. (2020) 75(5):1188–204. doi: 10.1111/all.14151
4. Napolitano M, Maffei M, Patruno C, Leone CA, Di Guida A, Potestio L. Dupilumab effectiveness for the treatment of patients with concomitant atopic dermatitis and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Dermatol Ther. (2021) 34(6):e15120. doi: 10.1111/dth.15120
5. Patruno C, Napolitano M, Argenziano G, Peris K, Ortoncelli M, Girolomoni G. Dupilumab therapy of atopic dermatitis of the elderly: a multicentre, real-life study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2021) 35(4):958–64. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17094
6. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dupixent Package Insert. (2024). Available online at: https://www.regeneron.com/downloads/dupixent_fpi.pdf (Accessed September 10, 2024).
7. European Medicines Agency. Dupixent European Public Assessment Report-Product Information. (2024). Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/dupixent-epar-product-information_en.pdf (Accessed September 10, 2024).
8. Sanofi Winthrop Industrie. Dupixent Package Insert. (2024). Available online at: https://www.sanofi.cn/zh/your-health/products/dupixent (Accessed September 10, 2024).
9. Napolitano M, Fabbrocini G, Potestio L, Fontanella G, Picone V, Bennardo L. A 24-weeks real-world experience of dupilumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. (2022) 35(8):e15588. doi: 10.1111/dth.15588
10. Wang M, Gao XH, Zhang L. A review of dupilumab in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants and children. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2024) 18:941–51. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S457761
11. Paller AS, Simpson EL, Siegfried EC, Cork MJ, Wollenberg A, Arkwright PD. Dupilumab in children aged 6 months to younger than 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2022) 400(10356):908–19. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01539-2
12. Stingeni L, Bianchi L, Antonelli E, Caroppo ES, Ferrucci SM, Gurioli C. A 52-week update of a multicentre Italian real-world experience on effectiveness and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2023) 37(3):e384–8. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18648
13. Napolitano M, Fabbrocini G, Neri I, Stingeni L, Boccaletti V, Piccolo V. Dupilumab treatment in children aged 6–11 years with atopic dermatitis: a multicentre, real-life study. Paediatr Drugs. (2022) 24(6):671–8. doi: 10.1007/s40272-022-00531-0
14. Paller AS, Pinter A, Wine Lee L, Aschoff R, Zdybski J, Schnopp C. Dupilumab for children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis: an Asian perspective. Dermatol Ther. (2021) 34(3):e14933. doi: 10.1111/dth.14933
15. Paller AS, Pinter A, Wine Lee L, Aschoff R, Zdybski J, Schnopp C. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab treatment with concomitant topical corticosteroids in children aged 6 months to 5 years with severe atopic dermatitis. Adv Ther. (2024) 41(3):1046–61. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02753-1
16. Bacharier LB, Maspero JF, Katelaris CH, Fiocchi AG, Gagnon R, de Mir I. Assessment of long-term safety and efficacy of dupilumab in children with asthma (LIBERTY ASTHMA EXCURSION): an open-label extension study. Lancet Respir Med. (2024) 12(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00303-X
17. Cather J, Young M, DiRuggiero DC, Tofte S, Williams L, Gonzalez T. A review of phase 3 trials of dupilumab for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults, adolescents, and children aged 6 and up. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). (2022) 12(9):2013–38. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00778-y
18. Wang A, Zhou Y, Luo Y, Gao Y, Chen J, Li W. High loading-dose of dupilumab resulted in rapid disease control in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1160710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1160710
19. Zhou B, Peng C, Cao Q, Wang J, Chen X, Li J. Dupilumab therapy in children aged 2–12 years with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a Chinese real-world study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2024) 38(1):e35–8. doi: 10.1111/jdv.19409
20. Padidam S, Raiji V, Moorthy R, Oliver A, Do B. Association of dupilumab with intraocular inflammation. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. (2022) 30(5):1068–73. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2020.1861305
21. Ayasse M, Lockshin B, Do BK, Kaiser R, Silverberg JI. A case report of uveitis secondary to dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. (2021) 7:98–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.11.012
22. Achten R, van Luijk C, Thijs J, Drylewicz J, Delemarre E, Nierkens S. Non-infectious uveitis secondary to dupilumab treatment in atopic dermatitis patients shows a pro-inflammatory molecular profile. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. (2024) 32(7):1150–4. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2023.2182325
23. Akinlade B, Guttman-Yassky E, de Bruin-Weller M, Simpson EL, Blauvelt A, Cork MJ. Conjunctivitis in dupilumab clinical trials. Br J Dermatol. (2019) 181(3):459–73. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17869
24. Treister AD, Kraff-Cooper C, Lio PA. Risk factors for dupilumab-associated conjunctivitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. (2018) 154(10):1208–11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.2690
25. Nettis E, Bonzano L, Patella V, Detoraki A, Trerotoli P, Lombardo C. Dupilumab-associated conjunctivitis in patients with atopic dermatitis: a multicenter real-life experience. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2020) 30(3):201–4. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0481
26. Touhouche AT, Cassagne M, Bérard E, Giordano-Labadie F, Didier A, Fournié P. Incidence and risk factors for dupilumab associated ocular adverse events: a real-life prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2021) 35(1):172–9. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16724
27. Achten RE, Van Luijk C, Van der Rijst L, Bakker D, Spekhorst L, Zuithoff N. Identification of risk factors for dupilumab-associated ocular surface disease in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. (2022) 102:adv00666. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v102.1128
28. World Health Organization (WHO)-Uppsala Monitoring Centre. The Use of the WHO-UMC System for Standardized Case Causality Assessment. (2013). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/WHO-causality-assessment (Accessed December 04,2024)
29. Halling AS, Loft N, Silverberg JI, Guttman-Yassky E, Thyssen JP. Real-world evidence of dupilumab efficacy and risk of adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2021) 84(1):139–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.051
30. Simpson EL, Paller AS, Siegfried EC, Boguniewicz M, Sher L, Gooderham MJ. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with uncontrolled moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. (2020) 156(1):44–56. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3336
31. Paller AS, Siegfried EC, Thaçi D, Wollenberg A, Cork MJ, Arkwright PD. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab with concomitant topical corticosteroids in children 6 to 11 years old with severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2020) 83(5):1282–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.054
32. Cork MJ, Thaçi D, Eichenfield LF, Arkwright PD, Hultsch T, Davis JD. Dupilumab in adolescents with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: results from a phase IIa open-label trial and subsequent phase III open-label extension. Br J Dermatol. (2020) 182(1):85–96. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18476
33. Alexander H, Malek R, Prieto-Merino D, Gribaleva E, Baden M, Beattie P. A prospective observational cohort study comparing the treatment effectiveness and safety of ciclosporin, dupilumab and methotrexate in adult and paediatric patients with atopic dermatitis: results from the UK-Irish A-STAR register. Br J Dermatol. (2024) 191:988. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae287
34. Xu Y, Guo L, Li Z, Wu S, Jiang X. Efficacy and safety profile of dupilumab for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Dermatol. (2023) 40(5):841–50. doi: 10.1111/pde.15398
35. Klion AD, Nutman TB. The role of eosinophils in host defense against helminth parasites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2004) 113(1):30–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.10.050
36. Li J, Yan S, Wang H, Luo X. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis among children aged 6–17: a single-center, prospective, open-label study. Chin J Allergy Clin Immuno. (2022) 16(6):581–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8705.2022.06.003
37. Beck LA, Deleuran M, Bissonnette R, de Bruin-Weller M, Galus R, Nakahara T. Dupilumab provides acceptable safety and sustained efficacy for up to 4 years in an open-label study of adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2022) 23(3):393–408. doi: 10.1007/s40257-022-00685-0
38. Beck LA, Thaçi D, Deleuran M, Blauvelt A, Bissonnette R, de Bruin-Weller M. Dupilumab provides favorable safety and sustained efficacy for up to 3 years in an open-label study of adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2020) 21(4):567–77. doi: 10.1007/s40257-020-00527-x
39. Ariëns LFM, van der Schaft J, Bakker DS, Balak D, Romeijn MLE, Kouwenhoven T. Dupilumab is very effective in a large cohort of difficult-to-treat adult atopic dermatitis patients: first clinical and biomarker results from the BioDay registry. Allergy. (2020) 75(1):116–26. doi: 10.1111/all.14080
40. Iznardo H, Roé E, Vicente A, Prat C, Casals M, Martín-Santiago A. Dupilumab treatment in paediatric atopic dermatitis (2 to 18 years): Spanish multicentre retrospective real-life study. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2024) 50(1):104–12. doi: 10.1093/ced/llae300
41. Fu ZY, Xie TT, Guo DH. Literature analysis of ocular adverse drug reactions related to dupilumab. China Pharm. (2023) 34(14):1744–7. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2023.14.16
42. Martinez-Cabriales S, Marcoux D, Liy-Wong C, Prajapati VH, Sibbald C, Cunningham N. Multicenter Canadian case series of pediatric patients less than 12 years of age with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. Pediatr Dermatol. (2024) 41(1):5–11. doi: 10.1111/pde.15418
43. Mickevicius T, Pink AE, Bhogal M, O'Brart D, Robbie SJ. Dupilumab-induced, tralokinumab-induced, and belantamab mafodotin-induced adverse ocular events-incidence, etiology, and management. Cornea. (2023) 42(4):507–19. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000003162
44. Francuzik W, Alexiou A, Worm M. Safety of dupilumab in patients with atopic dermatitis: expert opinion. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2021) 20:997–1004. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1939673
45. Bakker DS, Ariens LFM, van Luijk C, van der Schaft J, Thijs JL, Schuttelaar MLA. Goblet cell scarcity and conjunctival inflammation during treatment with dupilumab in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. (2019) 180:1248–9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17538
46. Shim S, Kim JS, Yee J, Gwak HS. A risk-scoring system to predict dupilumab-associated ocular surface disease in patients with atopic dermatitis. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1425550. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1425550
47. Thyssen JP, de Bruin-Weller MS, Paller AS, Leshem YA, Vestergaard C, Deleuran M. Conjunctivitis in atopic dermatitis patients with and without dupilumab therapy-international eczema council survey and opinion. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2019) 33(7):1224–31. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15608
48. Agnihotri G, Shi K, Lio PA. A clinician’s guide to the recognition and management of dupilumab-associated conjunctivitis. Drugs R D. (2019) 19(4):311–8. doi: 10.1007/s40268-019-00288-x
49. Brusselle GG, Koppelman GH. Biologic therapies for severe asthma. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386(2):157–71. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2032506
50. Braddock M, Hanania NA, Sharafkhaneh A, Colice G, Carlsson M. Potential risks related to modulating interleukin-13 and interleukin-4 signalling: a systematic review. Drug Saf. (2018) 41(5):489–509. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0636-9
51. Bernstein ZJ, Shenoy A, Chen A, Heller NM, Spangler JB. Engineering the IL-4/IL-13 axis for targeted immune modulation. Immunol Rev. (2023) 320(1):29–57. doi: 10.1111/imr.13230
52. Working Group for Atopic Dermatitis Chinese Society of Dermatology, Working Group for Children’s Diseases Chinese Society of Dermatology. Treatment of atopic dermatitis with dupilumab: an expert consensus. Chin J Dermatol. (2022) 55(6):465–70. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115797-20210615-00456
53. Shimodaira Y, Takahashi S, Iijima K. Anti-IL-4Ralpha monoclonal antibody dupilumab mimics ulcerative colitis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. (2021) 21(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01803-8
54. Kearns GL, Abdel-Rahman SM, Alander SW, Blowey DL, Leeder JS, Kauffman RE. Developmental pharmacology–drug disposition, action, and therapy in infants and children. N Engl J Med. (2003) 349(12):1157–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra035092
55. Nogueira Guerra L, Herdeiro MT, Ribeiro-Vaz I, Clérigo MI, Rocha C, Araújo A. Adverse drug reactions in children: a ten-year review of reporting to the Portuguese pharmacovigilance system. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2015) 14(12):1805–13. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2015.1105214
Keywords: children, dupilumab, real world, safety, adverse drug reactions
Citation: Chen Y, Ni J, Li M, Hong Y, Zhu K, Hong R, Deng L, Li Z, Pu J, Yang T and Wang Y (2025) Safety of dupilumab in Chinese pediatric patients aged 6 months and older: a prospective real-world study. Front. Pediatr. 12:1524962. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1524962
Received: 8 November 2024; Accepted: 17 December 2024;
Published: 17 January 2025.
Edited by:
Vito Di Lernia, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, ItalyReviewed by:
Catherine M. T. Sherwin, University of Western Australia, AustraliaBenedetta Pessina, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Meyer IRCCS—Firenze, Italy
Copyright: © 2025 Chen, Ni, Li, Hong, Zhu, Hong, Deng, Li, Pu, Yang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ting Yang, MTUxNjE1MTUxMDBAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yan Wang, OTg2MjAyMzI5MkBqaWFuZ25hbi5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yanhua Chen
Yanhua Chen Jiang Ni2,†
Jiang Ni2,† Kouzhu Zhu
Kouzhu Zhu