- Department of Dermatology, Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing, China
Objective: The purpose of this study is to explore the efficacy and safety of hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether mediated photodynamic therapy (HMME-PDT) in treating children with port-wine stains (PWS).
Method: Literature related to the topic was searched in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang, and China Science Technology Journal Database online databases. The quality of the literature was evaluated using the Effective Public Health Practice Project. The I2 statistic was used to evaluate the consistency of the results.
Results: A total of 19 papers were included. Meta-analysis showed that more than half of the children (56.3%) achieved efficacy I (improvement ≥ 60%). 17% of children achieved efficacy II (improvement ≥ 75%). Regardless of whether the outcome variable was efficacy I or efficacy II, the therapeutic efficacy in children with PWS aged 0–3 years was superior to those aged 3–6 and 6–18 years, and children who underwent a treatment course of ≥3 sessions showed better outcomes compared to those who have only 1 or 2 sessions. After treatment with HMME-PDT, better efficacy was seen in the PWS of the face and neck and pink/red PWS. Additionally, almost all children with PWS treated with HMME-PDT developed edema (99.9%), more than half presented purpura (67.6%), some developed crust (30.8%) and hyperpigmentation (15.0%), and a few occurred scar (2.4%) and hypopigmentation (1.4%).
Conclusion: After HMME-PDT treatment, more than half of the pediatric patients showed an improvement of ≥60%, and no serious adverse reaction events occurred. This study demonstrated that HMME-PDT possessed promising therapeutic efficacy in children with PWS, suggesting that HMME-PDT could be considered a recommended treatment strategy for pediatric PWS. However, future development of standardized assessment guidelines and comparative studies are needed to validate the aforementioned conclusions.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/#loginpage, PROSPERO (CRD42024592367).
Introduction
Port-wine stains (PWS), an alternative name for capillary malformations, is a congenital slow-flow vascular anomaly and one of the most common skin vascular abnormalities (1, 2). PWS usually arises from impaired endothelial cell differentiation and progressive dilation of small venule-like capillaries, with its main characteristic being an increased number of dilated capillaries (3, 4). PWS occurs in 0.1% to 2% of newborns, with no gender predisposition (5). PWS typically manifests in children as flat, light pink, or red macules, which over time may undergo changes such as darkening, thickening, and the development of nodules (6, 7). For instance, the color may intensify and turn purplish in adulthood (8). Throughout the developmental and growth journey, PWS presents a dual harm to affected children. Physiologically, it can result in functional damage, such as hyperplasia of the lips or eyelid thickening that inhibits full closure (9, 10). Additionally, PWS may lead to severe diseases such as glaucoma and delayed visual development, resulting in potential vision loss (6, 11). Psychologically, PWS can instill a sense of stigma in the individuals and inflict distress on the family, profoundly undermining the children's overall well-being and quality of life (12, 13). Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify treatments for children PWS patients to alleviate the disease burden and enhance the overall health of children.
A multitude of treatments for PWS have been employed, such as cryotherapy, surgery, and radioisotope therapy (14). However, these methods often result in noticeable scarring and may even carry a possible risk of skin cancer, leading to their current non-recommendation as the primary treatment option (15). At present, the pulsed dye laser (PDL) is regarded as the gold standard for PWS treatment (16). Yet, with the accumulation of clinical experience, the limitations of PDL have become increasingly evident, characterized by suboptimal therapeutic outcomes and a high likelihood of recurrence (15, 17). An effective and safe treatment approach for PWS remains an unmet need. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) as a promising alternative to PDL has been proposed, particularly with hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether (HMME)-mediated PDT, which has become a primary method for treating PWS in China (15, 18). HMME, also known as hemoporfin, is a new generation of porphyrin photosensitizers (19, 20). Compared to the previous generation of PDT drugs (such as Photofrin® and hematoporphyrin derivative), HMME features a more stable structure, higher photodynamic efficiency, stronger photoactivity, faster clearance rate, and lower toxicity, and it has been widely used in PDT for PWS (21). Nonetheless, there are still inconsistent conclusions regarding the application of HMME-PDT in children. For example, Tan's study suggested HMME-PDT was well-tolerated and effective in Chinese children with PWS, recommending it as the first-line treatment for PWS (22). Whereas Gao et al. concluded that the current evidence was insufficient to support HMME-PDT as a preferred treatment for young children (18).
Based on the above research background, more clinical practice or prospective studies are needed in the future to evaluate and explore the use of HMME-PDT in the children population. To the best of our knowledge, current meta-analyses have mostly focused on comparing different treatment methods for treating PWS in the general population, without simultaneously concentrating on the safety and efficacy of HMME-PDT when applied in children (4, 18, 23). Accordingly, addressing the research gap mentioned, our study aims to comprehensively explore the efficacy and safety of HMME-PDT in treating children with PWS.
Methods
The research was meticulously planned and executed following the guidelines set forth by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework (24).
Retrieval strategy
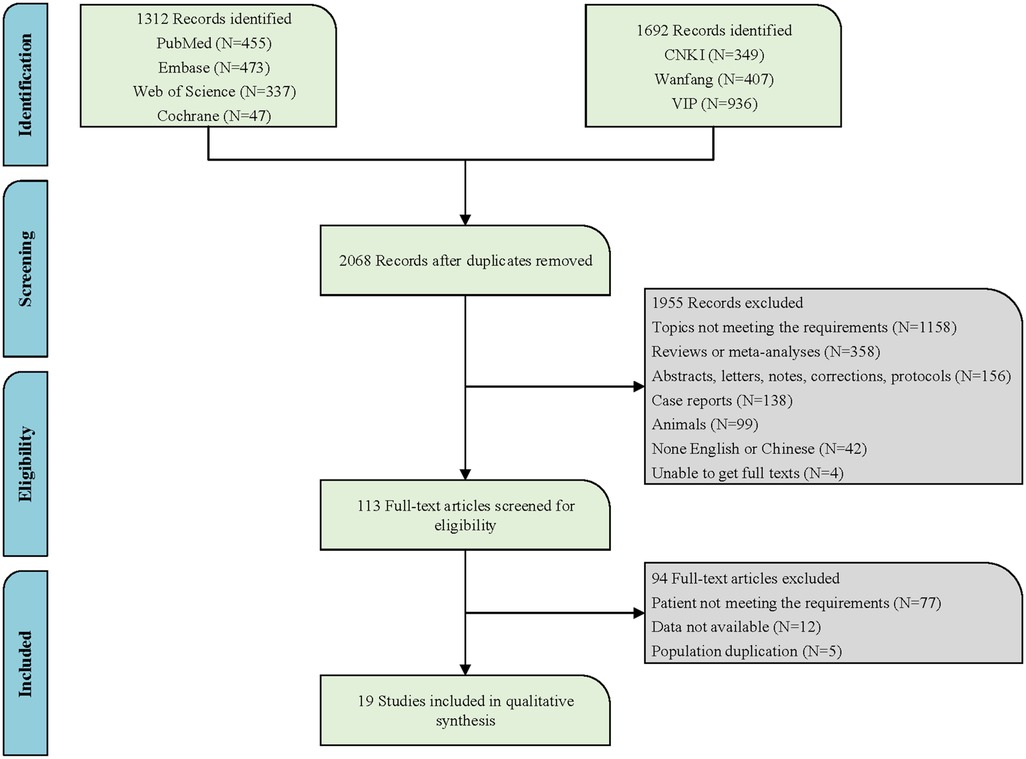
Relevant literature up to May 13, 2024, was searched in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang, and China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP). The primary English search terms were listed below: Port-Wine Stain, Port Wine Stain, Port Wine Stains, Port-Wine Stains, PWS, Nevus Flammeus, Naevus Flammeus, Flame Nevus, Flame Naevus, Nevus Vinosus, Naevus Vinosus, Capillary Malformation, Vascular malformations, Arteriovenous Malformation, Sturge-Weber Syndrome, Sturge Weber Syndrome, Sturge Disease, Sturge Syndrome, Parkes Weber Syndrome, Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis, hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether, HMME, Hemoporfin, Hematoporphyrins, Hematoporphyrin, Hemedonin, Haematoporphyrin, Photochemotherapy, Photochemotherapies, Photodynamic Therap*, PDT, Photodynamic, Photochemo, Phototherapy, Photosensitizing Agent∗, Photosensitising Agent∗. Detailed search information is provided in Figure 1 and specific English search formulas from the PubMed database are shown in the supplementary material (Supplementary Table S1).
Study selection and data extraction
The investigation involved the process of initial curation of the literature by importing identified documents into EndNote X9, followed by an initial selection based on the examination of titles and abstracts. Thereafter, a thorough review of the full texts was conducted in accordance with the specified inclusion and exclusion criteria, leading to the exclusion of documents that did not align with the study's standards. The final corpus of literature that met all criteria was subsequently incorporated into the research. Inclusion criteria were determined based on the PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome) principle to identify articles suitable for this research: (1) Study population: Children (≤18 years) with PWS; (2) Intervention methodology: HMME-PDT; (3) Outcome indicators: Efficacy (or improvement) was the primary outcome, which was quantified as any enhancements to the PWS, such as clearance, fade, and improvement expressed as percentage ranges or alterations of the erythema index (EI); Security evaluation indicators were edema, crust, scar, purpura, hyperpigmentation, and hypopigmentation. Exclusion criteria: (1) The subjects were a mixed age study of children and adults; (2) Data in the literature could not be extracted, e.g., efficacy only qualitatively described, non-60% or 75% cut points; (3) The article was a meta-analysis, review, analysis, case report, conference, letter, errata, program, and was not an English or Chinese article; (4) Where there was overlap in the study population, only the latest or most complete literature was included.
In this survey, information such as the authors of the literature, publication years, countries of publication, types of studies, sample sizes, ages, genders, pretreatment methods, the location and size of the PWS, as well as detailed treatment approaches were collected based on the research requirements. Additional data can be found in Supplementary Table S2.
Outcome measure
To facilitate the meta-analysis, we categorized the improvement effects reported in the literature into two main groups: Efficacy I and Efficacy II. Efficacy I referred to a ≥60% improvement in PWS from before to after treatment. Efficacy II indicated a ≥75% improvement in PWS from before to after treatment. The meta-analysis included percentage ranges that could potentially be translated into categorical scales, as well as other percentage ranges.
The primary outcome measure was assessed by taking photographs of the children before and after each treatment session, based on the regression of the lesions. The methods employed included conventional photography as well as Vein Illumination Skin Analysis (VISIA) skin imaging system. Conventional photography involved taking pictures of the patient before and after each treatment. Three researchers independently evaluated the therapeutic effect based on the pre-and post-treatment photographs, assessing the treatment outcome by the degree of lesion resolution (25). VISIA involved taking standard digital photographs before and after treatment under identical camera settings and lighting conditions from various angles. The images were then analyzed using Image J software to measure the EI within the images, with the treatment efficacy evaluated by the percentage decrease in EI values (25).
Literature quality assessment methodology
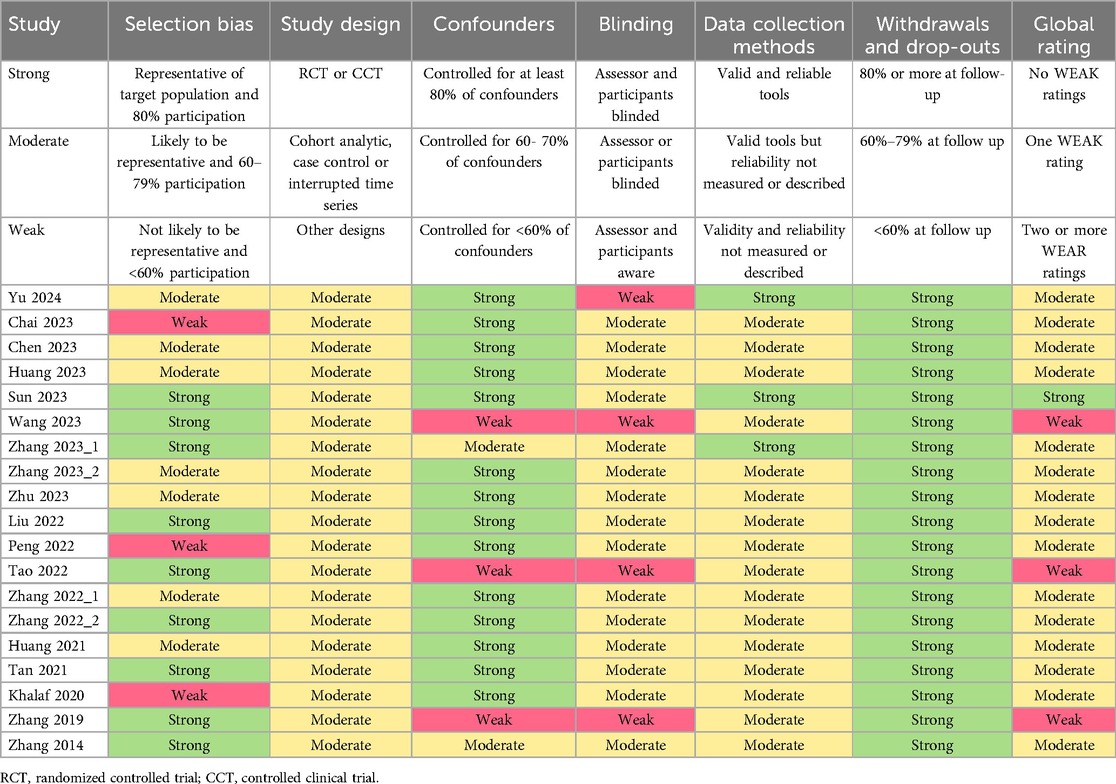
The Effective Public Health Practice Project (EPHPP) tool was employed to evaluate the quality of the literature, assessing selection bias, study design, confounders, blinding, data collection methods, and withdrawals and dropouts—six key areas in total (26). Each area was graded as strong, moderate, or weak, with the overall study rating determined by these assessments. Following the EPHPP guidelines, studies without any weak grades and with four or more strong grades were categorized as “strong”; those with fewer than four strong grades and one weak grade were deemed “moderate”; and those with two or more weak grades were labeled “weak”.
Statistical analysis
The “RATE” was utilized as the effect measure, with the effect size expressed as a 95% confidence interval (CI). Notably, in this article, RATE denoted the pooled estimate of the proportion of patients who achieved the efficacy I (or II) and those who experienced the aforementioned adverse side effects. The 95% CI indicated that if multiple samples were repeatedly drawn from the same population and a confidence interval was calculated for each sample, then approximately 95% of these intervals would contain the true value of the population parameter. Due to the high heterogeneity observed in the majority of outcomes, a random-effects model was employed for all analyses. Improvements were also analyzed stratified by age (0–3/3–6/6–18 years old), sex (male/female), session (1/2/≥3), location (face/neck/trunk or extremities), and type (pink/red/purple or hypertrophic). All studies were statistically analyzed using Stata 15.1 software (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA), with a difference considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
Inclusion of literature and study characteristics
Following the search strategy in both Chinese and English databases, a total of 3,004 articles were retrieved. After removing duplicates, 2,068 articles remained. Based on the review of titles and abstracts, 1,158 articles were excluded due to topics not meeting requirements. A further 358 articles were excluded as they were reviews or meta-analyses. Additionally, 156 records that were merely abstracts, letters, notes, corrections, or protocols were also eliminated. One hundred and thirty-eight case reports, 99 articles of animal experiments, 42 non-English articles, and 4 articles for which the full text could not be obtained were all excluded. After the aforementioned screening process, 113 articles remained. Subsequently, upon reviewing the full texts of the remaining articles, 94 were excluded due to ineligible patient criteria, data not available, and duplicate populations, leaving a final inclusion of 19 articles (17, 20, 22, 25, 27–41). Figure 1 illustrates the specific search flowchart. All studies were conducted in the Chinese population, involving a total of 5,859 children with PWS. Four studies were prospective, and 15 were retrospective. All studies provided specific details regarding the treatment, with 73.68% of the studies (14/19) detailing the exact treatment locations, and 52.63% of the studies (10/19) providing information on the types of PWS. Detailed information is presented in Supplementary Table S2.
Evaluation of bias risk
As shown in Table 1, the quality of the included studies was assessed using the EPHPP tool. According to the tool's guidelines (with strong, moderate, and weak ratings for each item), one study with no weak ratings and four strong ratings was classified as strong. Fifteen studies with fewer than four strong ratings and one weak rating were rated as moderate, and three studies with two or more weak ratings were classified as weak. Overall, the methodological quality is within an acceptable range.
Efficacy and stratification analysis of HMME-PDT in the treatment of children with PWS
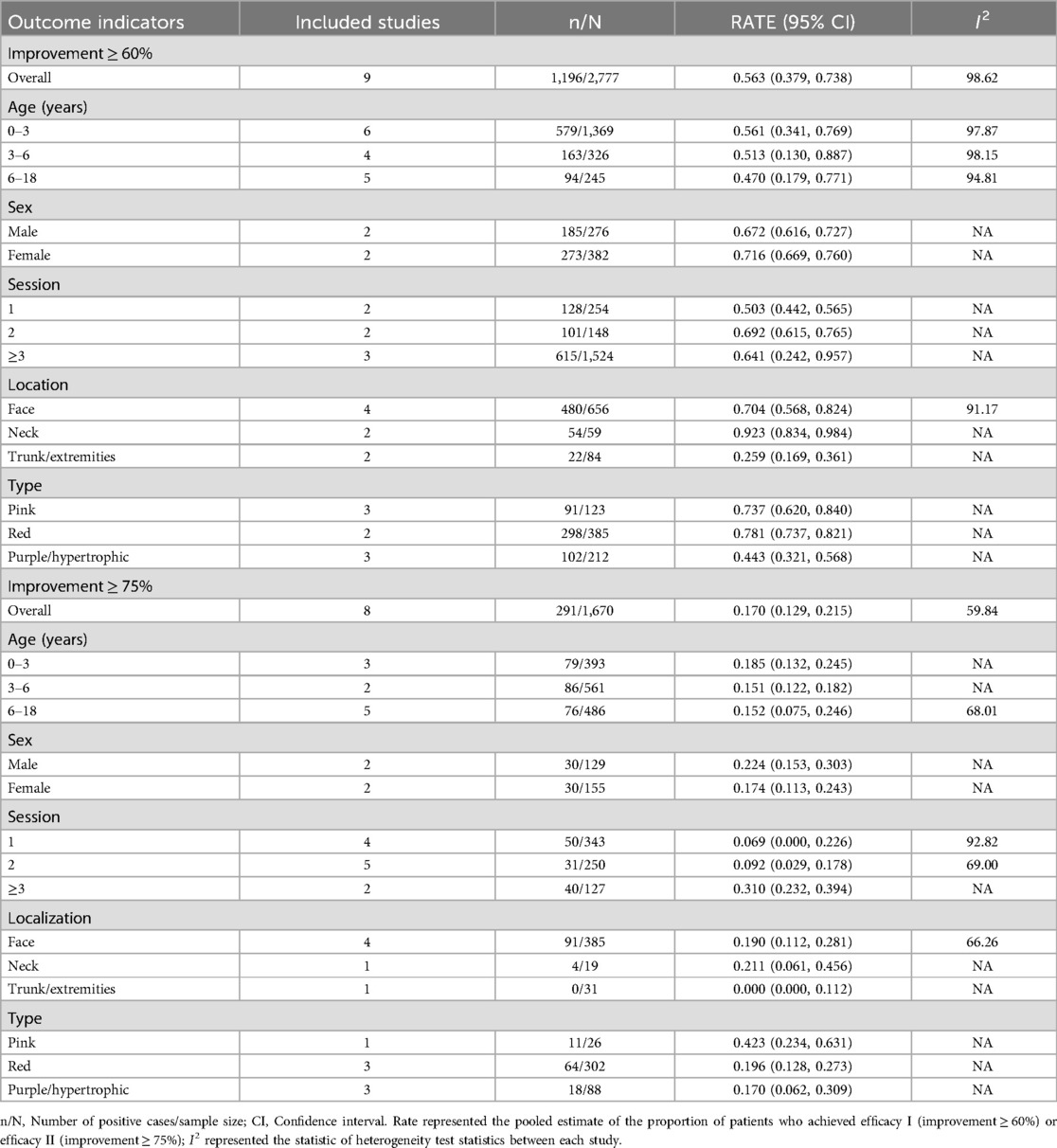
As depicted in Figures 2, 3, the pooled estimate of the proportion of patients achieving efficacy I (improvement ≥ 60%) was 56.3%. The pooled estimate of the proportion of patients achieving efficacy II (improvement ≥ 75%) was 17.0%.

Figure 2. Pooled estimates of the proportion of patients achieving efficacy I (improvement ≥ 60%). ES indicated RATE; CI indicated 95% confidence interval.
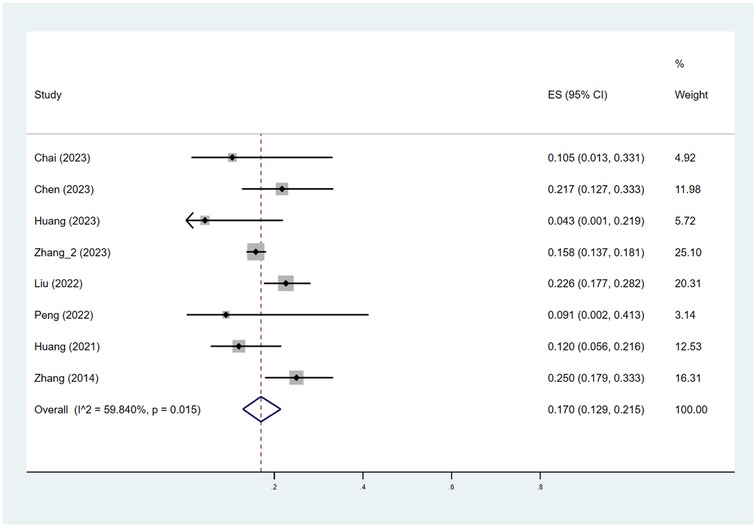
Figure 3. Pooled estimates of the proportion of patients achieving efficacy II (improvement ≥ 75%). ES indicated RATE; CI indicated 95% confidence interval.
A meta-regression analysis was conducted to explore the sources of heterogeneity among groups with efficacy I and efficacy II, stratified by age, gender, treatment course, location, and type. As shown in Supplementary Table S3, among patients achieving efficacy I, the “location” may be a source of study heterogeneity (P < 0.05), while all others were not associated with between-study heterogeneity (P > 0.05).
As shown in Table 2, the pooled estimate proportions of patients achieving efficacy I across the age groups were 56.1% for those aged 0–3 years, 51.3% for those aged 3–6 years, and 47.0% for those aged 6–18 years. The pooled estimated proportions of patients achieving efficacy II were 18.5% for the 0–3 years age group, 15.1% for the 3–6 years age group, and 15.2% for the 6–18 years age group.
Subsequently, a stratified analysis was conducted based on gender. The study found that in the male patients, the pooled estimated proportions of patients achieving efficacy I or efficacy II were 67.2% and 22.4%, respectively. Similarly, in the female, the pooled estimated proportions of patients achieving efficacy I or efficacy II were 71.6% and 17.4%, respectively.
As shown in Table 2, the analysis was conducted by categorizing the treatment courses into three groups: one course, two courses, and three or more courses. The pooled estimated proportions of patients achieving efficacy I or efficacy II after one course of HMME-PDT treatment were 50.3% and 6.9%, respectively. After two courses of treatment, the pooled estimated proportions of patients achieving efficacy I or efficacy II were 69.2% and 9.2%, respectively. After three or more courses of treatment, the pooled estimated proportions of patients achieving efficacy I or efficacy II were 64.1% and 31.0%, respectively.
The data were segmented and analyzed according to the regions of the face, neck, and trunk/extremities. Patients with PWS located on the face, neck, and trunk (or limbs) who underwent HMME-PDT treatment had pooled estimated proportions achieving efficacy I as follows: 70.4%, 92.3%, and 25.9%, respectively. Additionally, the pooled estimated proportions of patients with PWS located on the face, neck, and trunk (or limbs) who achieved efficacy II after HMME-PDT treatment were 19.0%, 21.1%, and 0.0%, respectively.
Finally, a stratified analysis was performed based on the types of PWS, categorizing the study subjects into three groups: pink, red, and purple/hypertrophic PWS. Patients with pink, red, and purple (or hypertrophic) PWS who achieved efficacy I after treatment had pooled estimated proportions of 73.7%, 78.1%, and 44.3%, respectively. Furthermore, the pooled estimate of the proportions of patients with the aforementioned types of PWS who achieved efficacy II after treatment were 42.3%, 19.6%, and 17.0%, respectively.
Adverse reactions
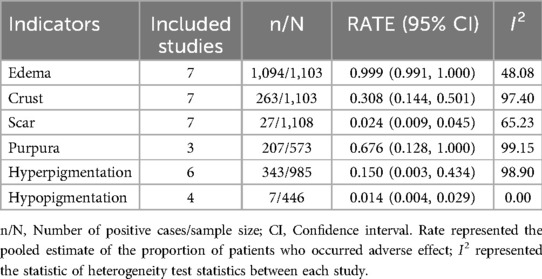
As seen in Table 3, nearly all children (99.9%) presented with edema, over half of the children (67.6%) experienced purpura, 30.8% of children developed crusting and 15.0% of children developed hyperpigmentation. Additionally, a very small number of children exhibited scarring (2.4%) and hypopigmentation (1.4%). Overall, no severe adverse reactions were reported.
Discussion
PWS not only inflicts physical and psychological harm on children but also severely impacts the quality of life of their families (42, 43). Although PDL is considered a first-line treatment for PWS, there is currently no unified international standard for the treatment of children with PWS (44). HMME-PDT, a novel treatment method for PWS recently proposed in China, holds great potential (45). Consequently, this study explored the efficacy and safety of HMME-PDT in the children PWS population, with the main conclusions as follows: (1) More than half of the children had efficacy I (improvement ≥ 60%), but less than 20% of children achieved efficacy II (improvement ≥ 75%). (2) The younger the age at which treatment was administered, the better the therapeutic outcome. Furthermore, a greater number of treatment courses, specifically more than three, may yield improved efficacy. Additionally, treatment of PWS located on the face and neck, as well as those with lighter coloration, may demonstrate better outcomes. (3) After HMME-PDT treatment, virtually all children with PWS exhibited edema, over half developed purpura, some experienced crust and hyperpigmentation, and a minority presented with scar and hypopigmentation.
Over half of the children showed an improvement of more than 60%, demonstrating that HMME-PDT possessed a certain efficacy in the treatment of children with PWS. This was consistent with the findings of Chai and Tan, both of whom concluded that HMME-PDT showed good potential in the treatment of children with PWS (22, 27). Age was closely related to the growth and development of PWS (28). The study found that in both efficacies I and II groups, the proportion of efficacy in children aged 0–3 years was higher than in other age groups. The above result was similar to that of Lin et al., who found that efficacy decreases with age (46). Age has been correlated with the color, thickness, and nodularity of PWS lesions, with children tending to have thinner skin with better irradiation penetration and therefore better treatment outcomes (4, 47). Moreover, when analyzing the data by gender, observing the proportion of females achieving efficacy I (improvement ≥ 60%) was higher than that of males. However, in the efficacy II group (improvement ≥ 75%), a higher proportion of males was noted. Tan's study found that females had better treatment outcomes (22). Yet, in reality, few scholars have focused on the gender differences in HMME-PDT treatment for children with PWS, and conclusions regarding gender differences in efficacy cannot be firmly established. Therefore, future clinical or prospective studies are needed to examine the differences in treatment outcomes related to gender.
Consistent with the research by Huang and Chen et al., our study found that children with PWS who underwent a greater number of HMME-PDT treatment courses experienced better therapeutic outcomes (28, 30). The study by Lin et al. also indicated that the efficacy of 2 consecutive treatments was significantly higher than that of a single one (46). Furthermore, a subgroup analysis was conducted on the efficacy of PWS treatment at different anatomical locations. The results indicated that PWS located on the face and neck responded better than extremities or trunk, with a higher proportion of children showing improved outcomes. It was hypothesized that this may be due to the generally thinner skin on the face and neck, allowing light to penetrate more easily and thus facilitating the resolution of the lesions following treatment (4, 48). Similar to the research by Sun et al., their study found that the therapeutic effect of HMME-PDT was greatly influenced by the location of the PWS (35). But somewhat differently from ours, they believed that the efficacy on the face was not very effective. Furthermore, Zhang's research suggested that there was no significant difference in the therapeutic effect of PWS on the face, neck, and other parts of the body (17). The aforementioned differences were likely attributable to variations in the study populations, and the sample size also exerted a certain degree of influence. Ultimately, stratified analysis based on different types of PWS revealed that, consistent with the research by Zhang et al., purple or hypertrophic PWS types respond less favorably to HMME-PDT compared to pink or red types (17). It is widely acknowledged that the depth and thickness of blood vessels are the most critical factors affecting the treatment outcomes of PWS, with purple PWS often presenting thicker nodules, thus leading to poorer therapeutic results (15, 30).
In this survey, although almost all children experienced edema following HMME-PDT treatment, no severe adverse events were observed. Moreover, minor adverse reactions were likely to occur in most studies. For instance, in the research by Li et al., the side effects following HMME-PDT treatment were primarily manifested as edema, crusting, and excessive pigmentation (49). Besides, edema has been reported to be common in children and adults after PDT (4). In addition, the occurrence of purpura after treatment is also a normal and anticipated reaction, as it typically signifies that the abnormal blood vessels have been damaged and do not require special treatment (50). However, if further reactions occur, such as the skin turning grayish, medical intervention may be necessary (51). Hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation also occurred partially in the children's population in this study, but there was no cause for concern as these reactions usually subsided within 2–6 months (48). Alternatively, concerning the recurrence of PWS, statistical analysis could not be performed due to the absence of data on recurrence in the original literature. In the included literature, studies by Tan (eight weeks after treatment), Zhang (with an average follow-up of 21.3 months), and Yu (with follow-ups ranging from 2–3 years) demonstrated no observed recurrences during the follow-up periods after HMME-PDT treatment (22, 25, 39). This suggested to some extent that the capillaries in PWS may suffer permanent damage that was difficult to repair after HMME-PDT, thereby preventing the recurrence of the condition (22). Although there was a study reporting no recurrences over an 18-year follow-up period post-PDT treatment, long-term follow-up studies specific to HMME-PDT were relatively scarce (52). Future long-term studies are essential to confirm the recurrence and progression of PWS in children patients treated with HMME-PDT. In summary, the aforementioned conclusions indicated that adverse events associated with HMME-PDT treatment for children with PWS were mild and transient. HMME-PDT is relatively safe for children with PWS. However, in the future, clinicians should consider taking appropriate measures early on when applying HMME-PDT to treat children with PWS, in order to address the mentioned reactions and safeguard the satisfaction of the patients as much as possible.
HMME, as a second-generation photosensitizer, possesses enhanced photodynamic effects, higher targeting specificity, lower toxicity, and reduced skin phototoxicity (25). In our study, HMME used as a photosensitizer in PDT for pediatric patients with PWS, demonstrated relatively good improvement effects. Most studies also suggested that HMME-PDT was a safe and effective method for the clinical treatment of PWS, indicating that HMME had certain advantages in treating PWS-related lesions to a certain extent (25, 41). There exist photosensitizers with longer absorption wavelengths, such as indocyanine green (ICG) (53). Although studies have shown that ICG may be a promising photosensitizer for PDT, its application in the treatment of PWS is currently very limited in clinical practice and remains in the stage of clinical research and exploration (54). Significantly, while longer wavelengths are more effective in targeting deeper lesions, the current focus on the development and application of photosensitizers is predominantly in oncological treatments, with a scarcity of exploration in the context of PWS (55). Moreover, current research on various photosensitizers and their penetration depth in the treatment of PWS was very limited. Future scholars should focus on this area to promote further advancement in the field of PWS treatment.
Additionally, all cases of HMME-PDT for PWS treatment have been conducted in China, and our study has shown promising efficacy in children (18). Numerous studies have also demonstrated satisfactory outcomes across various populations. For instance, a study by Sun et al., which included 2,952 subjects aged from 8 months to 56 years, indicated that HMME-PDT for PWS is highly effective, with high cure rates and mild local reactions, making it a preferred treatment method (35). Yu et al.'s research similarly confirmed the effectiveness, safety, and good patient tolerance of HMME-PDT for PWS (25). However, Gao et al.'s study suggested that, across all age groups, the clearance rate of PDL was generally higher than that of HMME-PDT (18). PDL exerts its effect by emitting yellow light (such as 585 nm or 595 nm), which is preferentially absorbed by hemoglobin, leading to the selective closure of dilated capillaries in the upper dermis and subsequently causing the color of PWS to gradually lighten (56). Studies have shown that during PDL treatment, while blood vessels are damaged, local hypoxia is also induced, leading to the upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) (19). HIF-1α triggers the transcription of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (57). VEGF, through the VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) signaling pathway, regulates angiogenesis, ultimately leading to the revascularization and reconstitution of blood flow in PWS vessels (58, 59). However, HMME-PDT involves the intravenous administration of the photosensitizer HMME, which accumulates and resides within the dilated capillaries (34). Subsequently, light of an appropriate wavelength is applied to generate oxygen-derived free radicals, selectively destroying the vascular walls of PWS without harming the surrounding tissues, thereby exerting a more effective therapeutic action (60). Therefore, although PDL is currently the standard treatment for PWS, recent studies have pointed out recurrences and patient resistance, leading to suboptimal treatment progress (61). Some studies even recommend HMME-PDT as the first-choice treatment for PWS over PDL (22). Peng et al.'s single-center retrospective study also indicated that HMME-PDT may be more effective in treating purple and red PWS than PDL, with the overall treatment effect for purple PWS being greater than that for red PWS (34). Notably, HMME-PDT requires high technical proficiency from physicians, and precise operation is necessary to avoid suboptimal outcomes. Therefore, HMME-PDT should be applied under the guidance of experienced doctors, adhering to expert consensus (62). In summary, given the ongoing debate about the efficacy and safety of HMME-PDT, larger-scale studies are needed in the future to further verify its exact effects in treating PWS.
This study addresses the efficacy as well as the safety of HMME-PDT for the treatment of PWS in children, for which, according to the search, there are no targeted studies of the mentioned research field for the time being. We expect this review to provide strong evidence for the medical care of children with PWS and to help reduce the physical and psychological damage to children as well as the emotional burden on families. However, our study also has certain limitations. Firstly, previous treatment history and the size of the lesions could potentially affect the therapeutic outcomes, but due to the limitations of the original literature, it was not possible to conduct a detailed analysis. Secondly, the majority of the included studies reported short-term efficacy, with a lack of long-term outcomes. Thirdly, all HMME-PDT studies conducted thus far have been carried out in China, hence caution should be exercised when generalizing these findings to other populations. Hence, more high-quality clinical studies dedicated to exploring the value of HMME-PDT for the treatment of children with PWS are needed in the future.
Conclusion
The meta-analysis discovered that over half of the children treated with HMME-PDT for PWS had an improvement ≥ 60% (efficacy I), with better outcomes observed in younger children who received longer courses of treatment, and facial/neck PWS and pink/red PWS improved better after treatment. Although most patients experienced edema after HMME-PDT therapy, there were no severe adverse reactions. Future large-scale, comprehensive prospective studies could be employed to validate the aforementioned findings, and clinicians should consider a multitude of factors when applying HMME-PDT for the treatment of children with PWS.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
JX: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2024.1501401/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Colletti G, Negrello S, Rozell-Shannon L, Levitin GM, Colletti L, Chiarini L, et al. Surgery for port-wine stains: a systematic review. J Pers Med. (2023) 13(7):1058. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071058
2. Escobar K, Pandher K, Jahnke MN. Capillary malformations. Dermatol Clin. (2022) 40(4):425–33. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2022.06.005
3. Jantarakolica T, Wanitphakdeedecha R, Yan C, Yogya Y, Manuskiatti W, Sudhipongpracha T. Dermatology life quality index in Thai patients with facial port-wine stains. Dermatol Ther. (2023) 13(10):2375–86. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01011-0
4. Wang L, Li L, Huang C. Efficacy of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of port wine stains: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med. (2023) 10:1111234. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1111234
5. Hammill AM, Boscolo E. Capillary malformations. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134(8):e172842. doi: 10.1172/jci172842
6. Bhari N, Agarwal A, Asritha CVV, Panda M, Mahajan R. Vascular malformations. Indian Dermatol Online J. (2024) 15(3):415–30. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_633_23
7. Pellacani A, Rozell-Shannon L, Negrello S, Di Bartolomeo M, Anesi A, Feminò R, et al. The vanishing port-wine stain birthmark—consideration for a rare type of congenital vascular anomaly. Eur J Plast Surg. (2022) 45(6):997–1013. doi: 10.1007/s00238-022-01948-z
8. Hartman E, Balkin DM, See AP. A review of the current state and future directions for management of scalp and facial vascular malformations. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. (2024) 67(3):315–25. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2024.0032
9. Liu L, Li X, Zhao Q, Yang L, Jiang X. Pathogenesis of port-wine stains: directions for future therapies. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(20):12139. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012139
10. Liu Y, Chen D, Xu J, Tan Y, Wang Y, Zhao H, et al. Quantitative assessment of vascular features in port wine stains through optical coherence tomography angiography. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2021) 36:102607. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102607
11. Ha A, Kim J-S, Baek SU, Park YJ, Jeoung JW, Park KH, et al. Facial port-wine stain phenotypes associated with glaucoma risk in neonates. Am J Ophthalmol. (2020) 220:183–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2020.08.003
12. Raval DM, Rathod VM, Patel AB, Sharma B, Lukhi PD. Sturge-Weber syndrome: a rare case report. Cureus. (2022) 14(9):e28786. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28786
13. Wanitphakdeedecha R, Ng JNC, Yan C, Manuskiatti W, Sudhipongpracha T, Jantarakolica T. Quality of life and psychological effects of port-wine stain: a review of literature. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. (2021) 14:681–90. doi: 10.2147/ccid.S315804
14. Sheng H, Zeng H, Zhang M. Comparing the therapeutic effect of pulsed dye laser and pulsed dye laser plus CO2 in port wine stain. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. (2022) 39(5):923–7. doi: 10.5114/ada.2022.119073
15. Diao P, Han C, Li X, Yang Y, Jiang X. Hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether photodynamic therapy of port wine stain: narrative review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. (2023) 16:1135–44. doi: 10.2147/ccid.S401447
16. Almutairi R, Usmani S, Hussein S, Aldaraji W. The long-pulse potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser: promising treatment for resistant port-wine stains. Cureus. (2024) 16(2):e53994. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53994
17. Zhang X, Yuan C, Xiao X, Yin R, Lei H, Li Y, et al. Hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy for the treatment of port-wine stain: a multicenter, retrospective study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2023) 42:103545. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103545
18. Gao C, Nguyen V, Hochman ML, Gao L, Chen EH, Friedman HI, et al. Current clinical evidence is insufficient to support Hmme-Pdt as the first choice of treatment for young children with port wine birthmarks. Lasers Surg Med. (2024) 56(4):321–33. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23779
19. Mei Y, Xiao X, Fan L, Liu Q, Zheng M, Hamblin MR, et al. In vitro photodynamic therapy of endothelial cells using hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether (hemoporfin): relevance to treatment of port wine stains. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2019) 27:268–75. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.06.003
20. Zhang XY, Al-Odaini N, Zheng WJ, Fan RG, Xiong HD, Huang JC, et al. The relationship between the effectiveness of Hmme-Pdt and the dermoscopic features of port-wine stains in Chinese pediatric patients: a retrospective study. Dermatol Ther. (2022) 12(7):1671–83. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00757-3
21. Pu Y, Chen W, Yu Z. Research progress of hemoporfin–part one: preclinical study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2012) 9(2):180–5. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2011.09.004
22. Chun-Hua T, Li-Qiang G, Hua W, Jian Z, Si-Li N, Li L, et al. Efficacy and safety of hemoporfin photodynamic therapy for port-wine stains in paediatric patients: a retrospective study of 439 cases at a single centre. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2021) 36:102568. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102568
23. Cinkara G, Langbroek GB, van der Horst C, Wolkerstorfer A, Horbach SER, Ubbink DT. Therapeutic strategies for untreated capillary malformations of the head and neck region: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2021) 22(5):603–14. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00616-5
24. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The prisma 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
25. Yu Y, Tang S, Luo Y, Zheng M, He W, Liu Y, et al. Efficacy and influential factors of hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether mediated photodynamic therapy in the treatment for port-wine stains. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2024) 45:103933. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103933
26. Armijo-Olivo S, Stiles CR, Hagen NA, Biondo PD, Cummings GG. Assessment of study quality for systematic reviews: a comparison of the cochrane collaboration risk of bias tool and the effective public health practice project quality assessment tool: methodological research. J Eval Clin Pract. (2012) 18(1):12–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2010.01516.x
27. Chai H, Duan W, Weng J, Liu D, Ma L. Effect of hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy in the treatment of facial port-wine stains on intraocular pressure. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2023) 44:103840. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103840
28. Chen J, Gui Y, Wang S, Huang D, Lyu J, Cheng H, et al. Analysis of related factors affecting hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy for port-wine stain: a retrospective study. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. (2023) 39(5):441–8. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12874
29. Huang Y, Chen B, Yang J, Bi M, Bi L, Fan W. Efficacy of hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy in treating sturge-weber syndrome associated port-wine stains: a retrospective study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. (2023) 90:1–8. doi: 10.25259/ijdvl_1075_2022
30. Huang Y, Yang J, Sun L, Zhang L, Bi M. Efficacy of influential factors in hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy for facial port-wine stains. J Dermatol. (2021) 48(11):1700–8. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16094
31. Khalaf AT, Sun Y, Wang F, Sheng M, Li Y, Liu X. Photodynamic therapy using hmme for port-wine stains: clinical effectiveness and sonographic appearance. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:6030581. doi: 10.1155/2020/6030581
32. Liu J, Zhou J, Hu D, Cui L, Li Y, Ye D, et al. Retrospective analysis of hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy in the treatment of naïve port-wine stains. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2022) 39:103003. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2022.103003
33. Min Z, Jing L, Jun Z, Simeng Q, Zhaoyang W, Zhao W, et al. Influential factors in the efficacy of hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy for port-wine stains. Lasers Med Sci. (2023) 38(1):162. doi: 10.1007/s10103-023-03822-1
34. Peng X, Ye T, Yu B, Liu X, Liu L. Comparing Hmme-Pdt and cynergy dual-wavelength laser in the treatment of facial pws. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2022) 37:102703. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102703
35. Sun J, Zhang Y, Ma T, Liu S, Yue D, Zhang Z, et al. Efficacy of Hemoporfin-Pdt on port-wine stains: a retrospective analysis of 2952 cases. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2023) 44:103837. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103837
36. Tao YY. Summarize the nursing experience of heimpofen photodynamic treatment for children with bright red facial nevus. Med Hyg. (2022) 8:121–4.
37. Wang XJ, Liang XY, Wang Q, Li TN, Qin P, Yao F. Clinical efficacy of hemoporfin photodynamictherapy in treating 67 patients with port-wine stains. Chin J Dermato Venerol Integ Trad W Med. (2023) 22(2):121–4.
38. Zhang B, Zhang TH, Huang Z, Li Q, Yuan KH, Hu ZQ. Comparison of pulsed dye laser (Pdl) and photodynamic therapy (Pdt) for treatment of facial port-wine stain (Pws) birthmarks in pediatric patients. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2014) 11(4):491–7. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2014.06.004
39. Zhang LC, Yang J, Huang YB, Bi MY. Efficacy of hemoporfin photodynamic therapy for pulsed dye laser-resistant facial port-wine stains in 107 children: a retrospective study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. (2021) 88(2):275. doi: 10.25259/ijdvl_976_20
40. Zhang S, Wang X, Chen H, Cao H, Zhang H, Yang M, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of two different hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether-mediated photodynamic therapy regimen in Chinese children with port-wine stain. Exp Dermatol. (2023) 32(9):1371–82. doi: 10.1111/exd.14834
41. Zhang Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Qiu M, Chen H, et al. Clinical study on hemoporfin pdt for infant facial port-wine stains. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2019) 25:106–10. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2018.09.012
42. Jiang F, Shao J, Chen L, Yang N, Liu J, Li Z. Influence of port-wine stains on quality of life of children and their parents. Acta Derm-Venereol. (2021) 101(8):adv00516. doi: 10.2340/00015555-3883
43. Mohamed SA, Sidow NO, Adam BA, Hassan MS, Ibrahim AA, Osman MF, et al. Undiagnosed epileptic case since childhood of Sturge-Weber syndrome: first case report from Somalia. Int Med Case Rep J. (2024) 17:621–5. doi: 10.2147/imcrj.S463858
44. Snast I, Lapidoth M, Kaftory R, Nosrati A, Hodak E, Mimouni D, et al. Does interval time between pulsed dye laser treatments for port-wine stains influence outcome? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci. (2021) 36(9):1909–16. doi: 10.1007/s10103-021-03264-7
45. Mazur A, Koziorowska K, Dynarowicz K, Aebisher D, Bartusik-Aebisher D. Photodynamic therapy for treatment of disease in children-a review of the literature. Children. (2022) 9(5):695. doi: 10.3390/children9050695
46. Lin Y, Gong W, Kang J, Fang Y, Liu J, Lin L, et al. Hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy for port-wine stains: multivariate analysis of clinical efficacy and optical coherence tomography appearance. Front Med. (2022) 9:800836. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.800836
47. Kang J, Liu JJ, Fang YH, Lin YY, Gong W, Wang HY, et al. Hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy for port-wine stains on extremities. Dermatol Ther. (2023) 13(8):1857–71. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-00970-8
48. Li-Qiang G, Hua W, Si-Li N, Chun-Hua T. A clinical study of Hmme-Pdt therapy in Chinese pediatric patients with port-wine stain. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2018) 23:102–5. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2018.06.006
49. Li DC, Nong X, Hu ZY, Fang TW, Zhao TT, Sun SH, et al. Efficacy and related factors analysis in Hmme-Pdt in the treatment of port wine stains. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2020) 29:101649. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101649
50. Tang Y, Xie H, Li J, Jian D. The association between treatment reactions and treatment efficiency of hemoporfin-photodynamic therapy on port wine stains: a prospective double blind randomized controlled trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2017) 18:171–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.02.005
51. Zhang LC, Yang J, Huang YB, Huang Z, Bi MY. Post treatment care in photodynamic therapy (Pdt) of large facial port-wine stain (Pws) birthmarks. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2021) 36:102604. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102604
52. Yu W, Ma G, Qiu Y, Chen H, Jin Y, Yang X, et al. 18 years long-term results of facial port-wine stain (Pws) after photodynamic therapy (Pdt)–a case report. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2015) 12(1):143–5. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2014.09.004
53. Klein A, Szeimies RM, Bäumler W, Zeman F, Schreml S, Hohenleutner U, et al. Indocyanine green-augmented diode laser treatment of port-wine stains: clinical and histological evidence for a new treatment option from a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. (2012) 167(2):333–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10950.x
54. Burns JM, Jia W, Nelson JS, Majaron B, Anvari B. Photothermal treatment of port-wine stains using erythrocyte-derived particles doped with indocyanine green: a theoretical study. J Biomed Opt. (2018) 23(12):1–10. doi: 10.1117/1.Jbo.23.12.121616
55. Liu WT, Wang HT, Yeh YH, Wong TW. An update on recent advances of photodynamic therapy for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15(5):1328. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051328
56. Gao K, Huang Z, Yuan KH, Zhang B, Hu ZQ. Side-by-Side comparison of photodynamic therapy and pulsed-dye Laser treatment of port-wine stain birthmarks. Br J Dermatol. (2013) 168(5):1040–6. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12130
57. Kowalska M, Dębek W, Matuszczak E. Infantile hemangiomas: an update on pathogenesis and treatment. J Clin Med. (2021) 10(20):4631. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204631
58. Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. (2011) 473(7347):298–307. doi: 10.1038/nature10144
59. Nguyen V, Hochman M, Mihm MC, Nelson JS Jr., Tan W. The pathogenesis of port wine stain and Sturge Weber syndrome: complex interactions between genetic alterations and Aberrant Mapk and Pi3k activation. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(9):2243. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092243
60. Chen D, Wang Y, Zhao H, Qiu H, Wang Y, Yang J, et al. Monitoring perfusion and oxygen saturation in port-wine stains during vascular targeted photodynamic therapy. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9(3):214. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3210
61. Han Y, Ying H, Zhang X, Yu W, Cen Q, Chen X, et al. Retrospective study of photodynamic therapy for pulsed dye laser-resistant port-wine stains. J Dermatol. (2020) 47(4):348–55. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15238
Keywords: port-wine stains, hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether, photodynamic therapy, children, meta-analysis
Citation: Xu J and Li H (2025) Efficacy and safety of hemoporfin photodynamic therapy in treating port-wine stains in Chinese children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pediatr. 12:1501401. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1501401
Received: 25 September 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Shahper Nazeer Khan, University of Manitoba, CanadaReviewed by:
David Kessel, Wayne State University, United StatesXuemin Xiao, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, China
Samira Syed, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust, United Kingdom
Copyright: © 2025 Xu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Xu, ZHJ4dWppbmc4ODY2QDEyNi5jb20=
 Jing Xu
Jing Xu Hongxin Li
Hongxin Li