- 1Department of Tuina, Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Tuina, Shanghai Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
Objectives: This case demonstrates the efficacy and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine manual therapy (TCMMT) for the treatment of mild to moderate AIS.
Methods: An 10-year-old girl who suffered from low back pain (LBP) with marked shoulder inequality and razorback postural abnormalities, with a clinical diagnosis of idiopathic scoliosis, and the Cobb angle of 20° and angle of trunk rotation (ATR) of the thoracic vertebral segment at 7°, and ATR of the lumbar vertebral segment at 8°, was treated with TCMMT. The patient initially recovered from centralized LBP with repeated TCMMT twice per week for 1 month. Subsequently, the frequency of TCMMT treatment was changed to 1–2 sessions weekly for 6 months. Before treatment, after the first TCMMT, 1 month and 7 months of treatment, and 18 months of follow-up, we used ATR or Cobb angle and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) for assessment. The HRQOL was assessed using the visual analog scale (VAS) scores and the Scoliosis Research Society-22 (SRS-22) patient questionnaire. The minimum clinically important difference (MCID) was used to assess the effectiveness of clinical measures based on a “responder analysis”.
Results: (a) The patient's VAS score was 40/100 before treatment, 25/100 after the first treatment, 15/100 after 1 month of treatment, 12/100 after 7 months of treatment, and 15/100 at follow-up to 18 months. (b) The patient's SRS-22 score was 54/110 before treatment, 61/110 after the first treatment, 79/110 after 1 month of treatment, 106/110 after 7 months of treatment, and 104/110 at follow-up to 18 months. (c) Before treatment, the patient's thoracic ATR angle was 7° and the lumbar ATR angle was 8°, there was no change in the ATR angles of the thoracic and lumbar spine after the first treatment. The thoracic ATR angle was 6° and the lumbar ATR angle was 5° after 1 month of treatment. The thoracic ATR angle was 1.5° and the lumbar ATR angle was 3.5° after 7 months of treatment. The thoracic ATR angle was 2° and the lumbar ATR angle was 4° at the follow up till 18 months. (d) The patient's Cobb angle was 20° before treatment, 7° after the 7 month of treatment, and 8° at follow-up to 18 months. No adverse events during treatment.
Conclusions: TCMMT is a conservative treatment option worthy of consideration when considering a conservative treatment strategy for AIS.
Introduction
Scoliosis is a complex three-dimensional spinal deformity characterized by lateral deviation and vertebral body rotation, with idiopathic scoliosis (IS) being the most common form. Among adolescents, females have a higher prevalence of IS compared to males (1). It is estimated that 1%–3% of adolescents aged 10–16 years exhibit varying degrees of spinal curvature (2). In China, the incidence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is reported to be 5.14% (3). Progressive AIS cases have been observed to demonstrate anterior spinal overgrowth that is disproportionate to longitudinal growth (4, 5). The etiology of AIS remains uncertain, with potential contributing factors including mechanical, metabolic, hormonal, neuromuscular, growth, and genetic abnormalities (6). Despite initially subtle symptoms, AIS can significantly disrupt bone development in adolescents, altering spinal mechanics and adversely impacting both physical and mental well-being. The primary objective of AIS management is to impede curve progression and circumvent the need for surgical intervention (7). Correction of AIS is particularly important, and the early development and implementation of effective and safe interventions for patients with AIS is of great clinical value. Addressing the high financial burden of AIS treatment and exploring novel therapeutic avenues are key areas of research focus in this field (8).
In recent years, with a significant increase in chiropractic studies focusing on the manual treatment of AIS, the stability and recognition of its efficacy have also notably improved. Manual therapy (MT) may be a more conservative treatment option, especially for children who choose to avoid brace therapy as much as possible and are not satisfied with regular observation of their progress (9, 10). In China, traditional Chinese Medicine manual therapy (TCMMT) encompassing soft tissue relaxation techniques and joint adjustment manipulation, is commonly employed for managing AIS. In our previous meta-analysis (11), we concluded that MT should be considered as a complementary and alternative therapy for the effective management of IS patients, especially as it had shown benefits in improving their pain and psychological well-being. The long-term efficacy of treatment of AIS is an important indicator to determine the stability of curative effect, but unfortunately it has been poorly reported, even though TCMMT is a common approach in clinical practice in China (12). For this, we describe a typical case of AIS treated with the TCMMT, aiming to report the long-term efficacy and safety of AIS and to provide physicians with additional therapeutic decisions in the conservative management of scoliosis.
Case presentation
History
A 10-year-old female patient exhibited progressive AIS characterized by a lumbar structural main curve. At the initial visit the patient's height was measured at 136 cm and weight at 31 kg, with no evidence of menarche or sexual development. The chief complaints were chronic low back pain (LBP) persisting for a duration exceeding six months following prolonged periods of sitting, and exacerbation of symptoms following strenuous physical activity. The physical examination revealed the presence of scoliosis, specifically a left curve of the lumbar segment, unequal shoulder height (left lower than right), and unequal length of both lower limbs (left longer than right). The Adam's Forward Bend Test (Adam's test) was operated by doctor who performed the assessment as follow: the patient's legs were erect, feet shoulder-width apart, and hands were folded together as they bent forward to a 90° bow, and the examiner used a scoliometer from the rear to review the patient's back for asymmetrical protuberances and assessed higher protuberances with a scoliometer measurement. The Adam's test of patient was positive, with the angle of trunk rotation (ATR) of 7° in the thoracic vertebral segment and 8° in the lumbar vertebral segment. Anteroposterior radiographs of the entire spine indicated AIS, with a Cobb angle of 20° in the lumbar vertebrae, vertebral rotation, and pelvic inclination. The Risser sign was Grade 0–1.
Method
Intervention
Before the first treatment, we provided patients with health education to clarify the treatment goals of AIS including fully understanding the occurrence, development and prognosis of AIS; correcting bad living habits, such as avoiding crossing legs, correcting improper sitting posture; changing their exercise habits, actively participate in sports activities for muscle building, and avoid competitive unilateral limb sports, etc. The detailed health education content was in Appendix 1.
The treatment plan which the patient received was recommended by the clinician with reference to the scoliosis treatment guidelines. The patient eventually gave up regular observation. The TCMMT was performed by an experienced doctor with over 10 years of clinical practice, ensuring the quality and efficacy of the intervention. The operation process of TCMMT contained two parts: soft tissue relaxation techniques and spinal joint adjustment manipulation. (a) Soft tissue relaxation techniques: The Finger TPS Wireless system of the American PPS company was used to control the quality of the strength and frequency of the manipulation before treatment. The data acquisition frequency was 0.024 S time. The force parameters of the control TCMMT manipulation averaged 45 N, and the frequency was 2 Hz. The patient was in a prone position, and the physiotherapist stood beside the patient. On the convex side of paraspinal muscle ridges, press kneading was used to release the high-tension muscle group. In the paraspinal muscle contracture depression, thumb plucking was used to activate muscle activity. This operation lasted about 10–15 min. (b) Spinal joint adjustment manipulation: For lateral bending of the thoracic vertebrae, the doctor pushed the thenar against the convex side of the vertebral body at the top of the lateral curve with one hand, and the hypothenar against the opposite side of the upper vertebral body (concave side) with the other hand to form a cross. The patient was instructed to take a deep breath. When the patient was at the end of expiration, the doctor rotated her hands and pressed down vertically. Each stage of thoracic scoliosis was performed for this operation following the rhythm of the patient's breathing. For lateral bending of the lumbar segment, the patient was placed in the lateral position (convex side up) with bent the upper leg and straightened lower leg straight. The doctor stood in front of the patient, pushed the shoulder of the patient with one hand, and the other hand pressed against the anterior superior iliac spine of the patient. When the patient's waist was rotated to the maximum, both hands were forced at the same time to obliquely pull in the opposite direction (Figure 1). This operation lasted about 5–8 min.
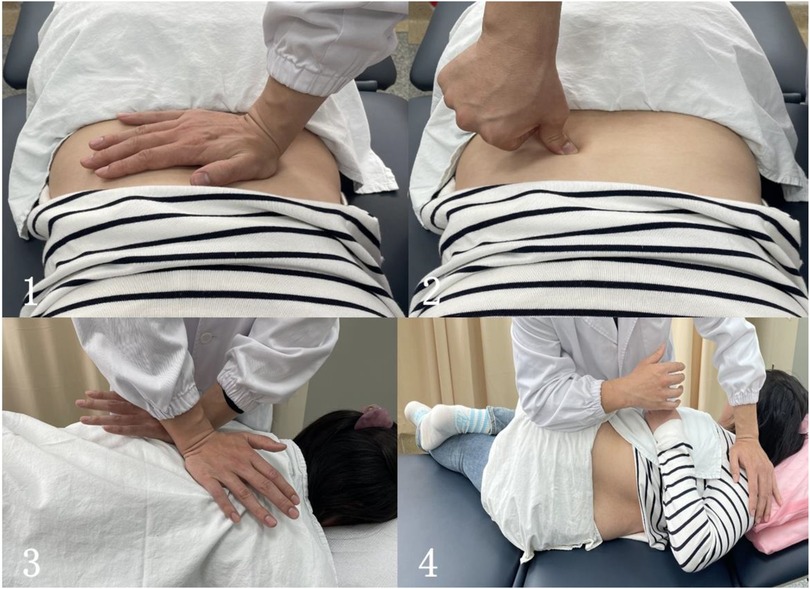
Figure 1. The operation process of TCMMT. (1) The soft tissue relaxation techniques in the convex side of paraspinal muscle ridges; (2) the soft tissue relaxation techniques in the paraspinal muscle contracture depression; (3) the journal joint adjustment manipulation for lateral bending of the thoracic vertebrae; (4) the journal joint adjustment manipulation for lateral bending of the lumbar segment (the subject in the figure was healthy individual and not the case patient reported in this study).
For the first month, treatment was administered twice a week with a 3-day interval and each treatment takes approximately 20 min. After 1 month, the frequency was adjusted to weekly, with an additional weekly session if the pain increased, for 6 months and each treatment takes the same amount of time as before, about 20 min. Treatment was conducted for a total of 7 months.
Outcome measures and follow-up
The patient received a total of 39 TCMMT treatments within 7 months. There were no significant adverse effects during 7 months of treatment.
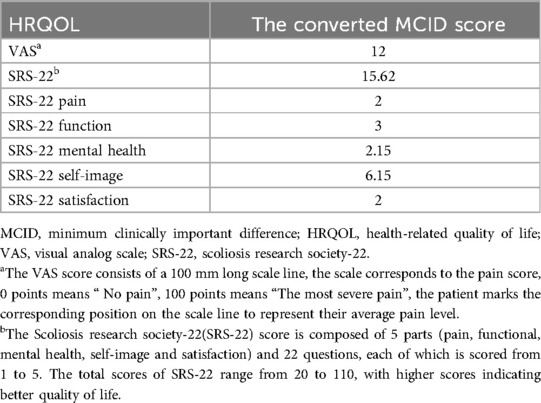
Before treatment, after the first TCMMT, 1 month and 7 months of treatment, and 18 months of follow-up, we used ATR and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) for assessment. The HRQOL was assessed using the visual analog scale (VAS) scores (13) and the Scoliosis Research Society-22 (SRS-22) (14) patient questionnaire. The minimum clinically important difference (MCID) (15) was used to assess the effectiveness of clinical measures based on a “responder analysis”. The converted MCID scores (16, 17) in Table 1 were extrapolated from the literature. After 7 months of treatment and 18 months of follow-up, we re-examined the patient's anteroposterior radiographs of the whole spine to assess Cobb angle changes.
The VAS score decreased from 40 to 25 after the first TCMMT treatment. After 1 month of TCMMT, the VAS score was 15, and the SRS-22 score improved from 54 to 79. The HRQOL results had exceeded MCID values except for the SRS-22 Self-Image scores. The ATR angles for the thoracic and lumbar spine were 6° and 5°, respectively. After 7 months of TCMMT, the patient's VAS score decreased to 12 and the SRS-22 score increased to 106 and the HRQOL results exceeded MCID values. The ATR angle of the thoracic spine decreased to 1.5°, and the ATR of the lumbar spine decreased to 3.5°, and the Cobb angle decreased to 7° from the initial 20°. After 18 months of follow-up, until the patient's first menstrual period was more than 1 year old, and the patient's VAS score was 15 and the SRS-22 score was 104 and the HRQOL results all stayed above the MCID values. The ATR angle at the thoracolumbar segment was maintained at less than 5°, and the Cobb angle was maintained at 10° or less. The results are summarized in Table 2; Figures 2, 3. The Radiograph of changes is in Figure 4.
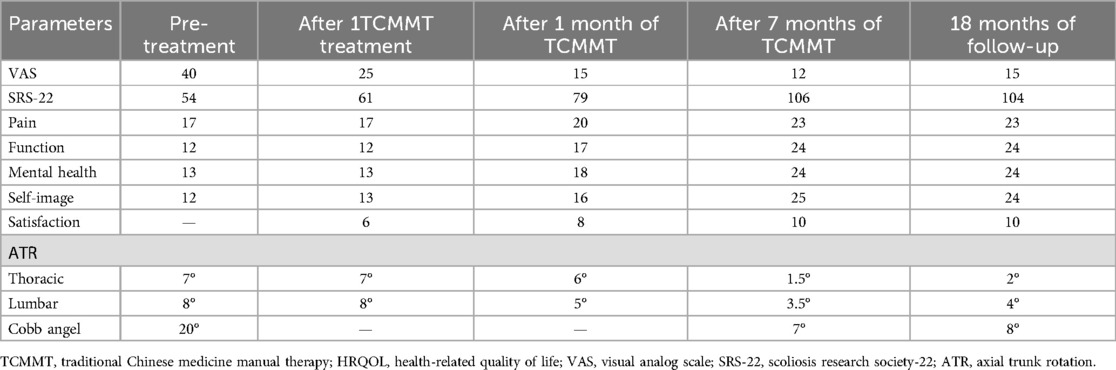
Table 2. Outcomes of HRQOL, ATR and radiographic parameters before and after treatment and follow-up.
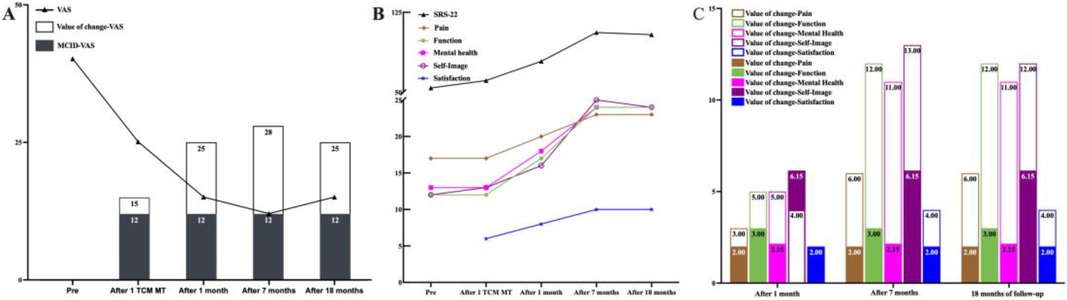
Figure 2. Outcomes of HRQOL before and after treatment and follow-up. (A) The patient's VAS score was 40/100 before treatment, 25/100 after the first treatment, 15/100 after 1 month of treatment, 12/100 after 7 months of treatment, and 15/100 at follow-up to 18 months. From the time of receiving the 1st TCMMT treatment until the 18th month after the follow-up, the patients’ VAS change values were higher than the MCID values. (B) The patient's SRS-22 score was 54/110 before treatment, 61/110 after the first treatment, 79/110 after 1 month of treatment, 106/110 after 7 months of treatment, and 104/110 at follow-up to 18 months. (C) After one month of TCMMT treatment, all SRS-22 results exceeded the preset MCID values, except for SRS-22 Self-Image. At 7 months after treatment and up to 18 months of follow-up, all SRS-22 indices were clinically significant (change values greater than MCID values).
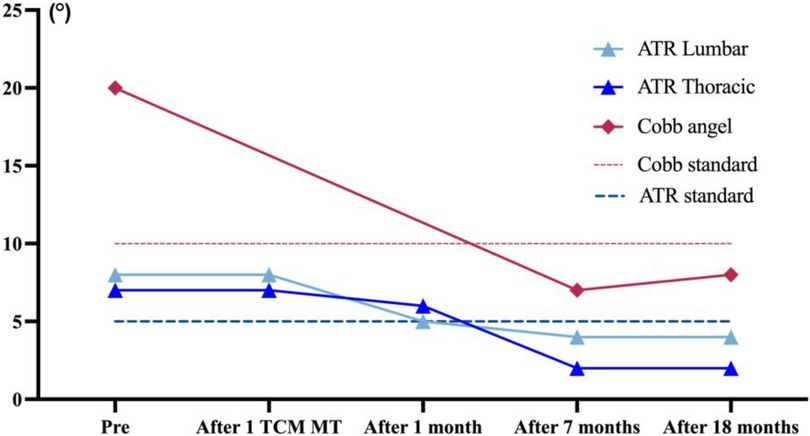
Figure 3. Outcomes of ATR and cobb angle before and after treatment and follow-up. Before treatment, the patient's thoracic ATR angle was 7° and the lumbar ATR angle was 8°, and the Cobb angle was 20°. After 7 months of treatment, the patient's ATR angle and Cobb angle were within the range of normal values until the 18th month of follow-up.
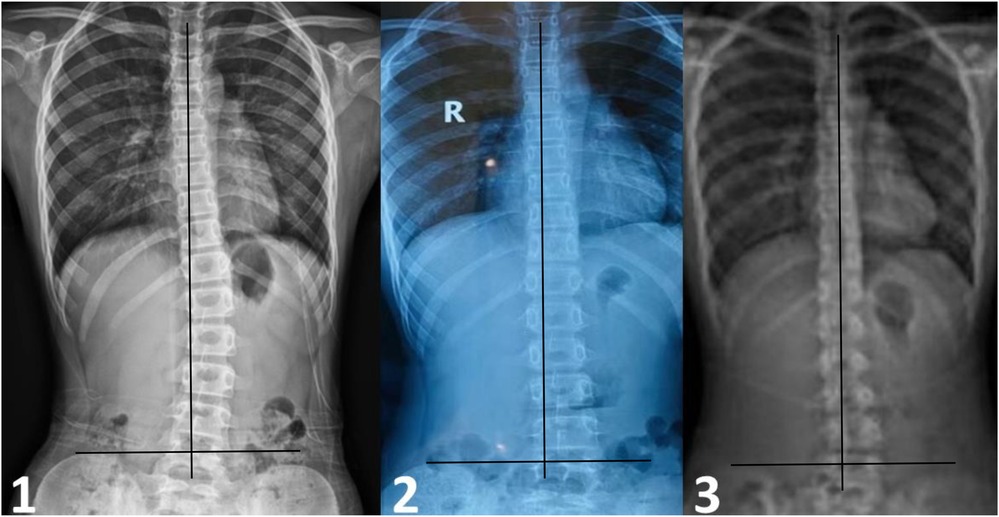
Figure 4. The radiograph of change in the cobb angle during treatment and follow-up. (1) Patient was 10 years old. At the first visit, radiographs showed the 20° to the left in lumbar spine scoliosis. (2) After 7 months TCMMT treatment, anteroposterior radiographs showing that the Cobb angle was less than 10°, the lumbar spine scoliosis reduced obviously. (3) The correction of scoliosis was maintenance stable at 18 months follow-up.
Discussion
The treatment of MT to solve patients' spine-related pain and negative emotions has its advantages and limitations have been widely described (11). The correction technique for adolescent spinal deformities has achieved considerable methodological support, but the efforts to achieve such correction through the method of TCMMT are relatively silent (18). In our report, TCMMT could reverse the patient's Cobb angle, adjust the patient's back posture, relieve pain, improve quality of life, and achieve more reliable patient satisfaction. Cobb and ATR angle reductions were demonstrated in the results that could be maintained from after 7 months of treatment to 18 months of follow-up. The cost of TCMMT treatment on AIS is far less than the cost of surgery and braces (19, 20). Comparison with MICD through the value of HRQOL changes after treatment can provide patients and policymakers with clearer insights into treatment efficacy, potentially guiding them towards choosing TCMMT. As a safe and effective complementary and alternative therapy, TCMMT may be a new treatment option for patients who choose conservative treatment with benefits for AIS patients. We hope that these findings will offer valuable insights for improving the conservative treatment of AIS in clinical practice.
For AIS patients who choose conservative treatment options, the guidelines (7) may still have room for additional refinement. As patients' demands for aesthetic body shape and spinal health continue to increase, regular observation intervals of several months are likely to make them miss the best treatment window period. Studies have shown that without effective intervention for advanced AIS patients, the curve Angle may increase by an average of 9.6° within 6 months (21, 22). Although bracing and physiotherapeutic scoliosis specific exercise (PSSE) are also the main non-surgical treatments recommended by the guidelines for the treatment of IS, they also limit their use in many cases. For example, wearing braces can affect the patients' appearance, resulting in local skin lesions or pigmentation (23). It is very easy for patients to give up treatment because PSSE requires long periods of daily training for long periods to be effective (24). For those patients who resist PSSE, observation or braces, TCMMT may serve as a viable option to complement the alternative therapies.
There are still areas that need attention in the operation of TCMMT. Firstly, AIS patients whose primary curvature is in the lumbar spine may be more likely to be corrected by TCMMT than those with thoracic curves. For the thoracic spine, the lateral force transmission is more easily absorbed by the costal arch. Since the lumbar spine doesn't have the transverse support of the costal arch, the force will be applied to the lumbar spine directly and produce effectiveness. Secondly, the high frequency and long period of continuous treatment are the keys to the qualitative change in curative effect. Despite reports suggesting, MT can be recommended to improve forward head posture, thoracic kyphosis and pelvic alignment in the short and medium term, but not shoulder posture and scoliosis (25). But our findings suggest otherwise. In our view, by repeatedly adjusting the paraspinal muscle strength and spinal stress on both sides of the spine, TCMMT continuously produces slow remodeling and change of the spine under the effect of reducing the muscle tension on the convex side and increasing it on the concave side. The TCMMT gradually improves the mechanical imbalance of the spine and eventually restores the relative balance of the mechanical properties of the spine and restores the strength of the paravertebral muscles and achieves the treatment goal of delaying the development of scoliosis and correcting the deformity of scoliosis. Finally, it's worth noting that the TCMMT technique may be suitable for correcting mild AIS patients with the Risser sign less than grade 3. This is possibly due to the softer vertebrae of these AIS patients, along with their bones having good growth potential and plasticity.
The evidence of manipulation in the treatment of spinal deformities is still limited (26). Whether TCMMT will show more therapeutic advantages compared with PSSE therapy still needs to be carefully observed. Without enough evidence, clinicians need to be cautious when giving diagnoses and treatment recommendations. We believe that TCMMT remains a recommended alternative treatment option to try for considering conservative treatment strategies. We advocate for future studies that conduct more RCTs to increase the strength of clinical evidence.
Limitation
The case we reported of scoliosis in which the predominant curvature is in the lumbar segments and is a unilateral curvature of the scoliosis. We are of the opinion that these patients are more amenable to the use of massage therapy. However, in patients with scoliosis in both the thoracic and lumbar spine, the efficacy of manipulative therapy still needs to be carefully observed to ensure robustness of efficacy. In addition, the patient has good treatment compliance and completes all treatments in the course of therapy in this case. The TCMMT requires prolonged and constant stimulation of the paravertebral musculature, and the efficacy of the therapy will probably be inhibited in patients with poor compliance, which is another drawback. Finally, according to the original plan, the patient should be followed up after 6 months, but due to the patient's personal reasons (busy revising for exams), the follow-up is postponed to 7 months after treatment which may lead to potential bias in the results.
Conclusion
This typical case demonstrates the safe and effective use of TCMMT in the treatment of AIS with LBP and postural abnormalities. After 7 months of TCMMT, the Cobb angle of the main curve was reduced by 13° in AIS patients, which was maintained until the 18-month follow-up. More research is needed to justify its use in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
This case report was agreed upon with ethical approval from the Medical Ethics Committee of Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (NO.193 2024-1420-003-01). Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the legal guardian of the participant. Written informed consent was obtained from individuals and legal guardians of minors for the reporting of any potentially identifiable images or data results included in this article.
Author contributions
BZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ML: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JR: Writing – review & editing. TH: Writing – review & editing. XZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SW: Writing – review & editing. LK: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. MF: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Pilot Project on Chinese Medicine Intervention for Scoliosis in Children and Adolescents (Huangpu District, Shanghai) and Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center Emerging Frontier Technology Joint Research Project (SHDC12024110) and Shanghai Innovative Medical Device Application Demonstration Project “Surface Electromyography Application Demonstration” (23SHS05400).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the patient for being willing to share this case to improve understanding of related fields of medicine and improve patient care.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Faldini C, Manzetti M, Neri S, Barile F, Viroli G, Geraci G, et al. Epigenetic and genetic factors related to curve progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic scoping review of the current literature. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(11):5914. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115914
2. Altaf F, Gibson A, Dannawi Z, Noordeen H. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Br Med J. (2013) 346:f2508. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f2508
3. Yan B, Lu X, Qiu Q, Nie G, Huang Y. Predicting adolescent idiopathic scoliosis among Chinese children and adolescents. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:1784360. doi: 10.1155/2020/1784360
4. Chu WC, Lam WW, Chan YL, Ng BK, Lam TP, Lee KM, et al. Relative shortening and functional tethering of spinal cord in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis?: Study with multiplanar reformat magnetic resonance imaging and somatosensory evoked potential. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2006) 31(1):E19–25. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000193892.20764.51
5. Rajwani T, Bagnall KM, Lambert R, Videman T, Kautz J, Moreau M, et al. Using magnetic resonance imaging to characterize pedicle asymmetry in both normal patients and patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2004) 29(7):E145–52. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000120507.36611.8D
6. Wang S, Qiu Y, Zhu Z, Ma Z, Xia C, Zhu F. Histomorphological study of the spinal growth plates from the convex side and the concave side in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2007) 2:19. doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-2-19
7. Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, Czaprowski D, Schreiber S, de Mauroy JC, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. (2018) 13:3. doi: 10.1186/s13013-017-0145-8
8. Gill PJ, Anwar MR, Thavam T, Hall M, Rodean J, Kaiser SV, et al. Identifying conditions with high prevalence, cost, and variation in cost in US children’s hospitals. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4(7):e2117816. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17816
9. Pu Chu EC, Chakkaravarthy DM, Huang KHK, Ho VWK, Lo FS, Bhaumik A. Changes in radiographic parameters following chiropractic treatment in 10 patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a retrospective chart review. Clin Pract. (2020) 10(3):1258. doi: 10.4081/cp.2020.1258
10. Chu EC, Lee WT, Tam DMY, Ng NY, Nur AB. Scoliosis causing cervical dystonia in a chiropractic office. Cureus. (2023) 15(3):e35802. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35802
11. Ren J, Kong L, Wu Z, Zhou X, Huang Q, He T, et al. Benefits on pain and mental health of manual therapy for idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1038973. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1038973
12. Sun Y, Zhang Y, Ma H, Tan M, Zhang Z. Spinal manual therapy for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Biomed Res Int. (2023) 2023:7928429. doi: 10.1155/2023/7928429
13. Ma K, Wang C, Huang Y, Wang Y, Li D, He G. The effects of physiotherapeutic scoliosis-specific exercise on idiopathic scoliosis in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy. (2023) 121:46–57. doi: 10.1016/j.physio.2023.07.005
14. Qiu G, Qiu Y, Zhu Z, Liu Z, Song Y, Hai Y, et al. Re-evaluation of reliability and validity of simplified Chinese version of SRS-22 patient questionnaire: a multicenter study of 333 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2011) 36(8):E545–50. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181e0485e
15. Chung AS, Copay AG, Olmscheid N, Campbell D, Walker JB, Chutkan N. Minimum clinically important difference: current trends in the spine literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2017) 42(14):1096–105. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001990
16. Crawford CH 3rd, Glassman SD, Bridwell KH, Berven SH, Carreon LY. The minimum clinically important difference in SRS-22R total score, appearance, activity and pain domains after surgical treatment of adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2015) 40(6):377–81. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000761
17. Ma C, Wu S, Xiao L, Xue Y. Responsiveness of the Chinese version of the Oswestry disability index in patients with chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. (2011) 20(3):475–81. doi: 10.1007/s00586-010-1624-2
18. Hung HY, Kong WC, Tam TH, Leung PC, Zheng Y, Wong AYL, et al. Efficacy and safety of the orthopaedic manipulation techniques of the Lin school of Lingnan region in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: protocol of a participant-and-assessor-blinded randomized controlled study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2024) 25(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-07152-9
19. Bozzio AE, Hu X, Lieberman IH. Cost and clinical outcome of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgeries-experience from a nonprofit community hospital. Int J Spine Surg. (2019) 13(5):474–8. doi: 10.14444/6063
20. Ikwuezunma I, Wang K, Margalit A, Sponseller P, Jain A. Cost-utility analysis comparing bracing versus observation for skeletally immature patients with thoracic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2021) 46(23):1653–9. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004189
21. Sanders JO, Browne RH, McConnell SJ, Margraf SA, Cooney TE, Finegold DN. Maturity assessment and curve progression in girls with idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2007) 89(1):64–73. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.F.00067
22. Rigo M. Patient evaluation in idiopathic scoliosis: radiographic assessment, trunk deformity and back asymmetry. Physiother Theory Pract. (2011) 27(1):7–25. doi: 10.3109/09593985.2010.503990
23. Wang H, Tetteroo D, Arts JJC, Markopoulos P, Ito K. Quality of life of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients under brace treatment: a brief communication of literature review. Qual Life Res. (2021) 30(3):703–11. doi: 10.1007/s11136-020-02671-7
24. Schreiber S, Parent EC, Hedden DM, Moreau M, Hill D, Lou E. Effect of Schroth exercises on curve characteristics and clinical outcomes in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. J Physiother. (2014) 60(4):234. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2014.08.005
25. Santos TS, Oliveira KKB, Martins LV, Vidal APC. Effects of manual therapy on body posture: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gait Posture. (2022) 96:280–94. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2022.06.010
26. Posadzki P, Lee MS, Ernst E. Osteopathic manipulative treatment for pediatric conditions: a systematic review. Pediatrics. (2013) 132(1):140–52. doi: 10.1542/peds.2012-3959
Appendix 1
Health Education Content for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
1. To educate children and adolescents about the onset, prognosis and progression of scoliosis, to reduce their anxiety and fear of the unknown about scoliosis, and to reduce the psychosocial impact of scoliosis on children and adolescents.
2. Adopt correct body postures, develop good habits of standing, sitting, lying down and writing postures in daily life and study, and avoid prolonged one-shoulder loads and prolonged sitting.
3. Enhance exercise management and exercise the low back muscles. Ensure daily exercise hours and avoid regular exercise programs that are unilaterally dominated or unilaterally powered.
4. Cultivate healthy eating habits among children and adolescents and provide nutritionally balanced meals that are beneficial to bone development.
5. Avoid over-exertion: Patients are advised to avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time, and to get up and move around at regular intervals to relax the body.
Keywords: adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, manual therapy, traditional Chinese medicine, low back pain, case report
Citation: Zhu B, Li M, Ren J, He T, Zhou X, Wang S, Kong L and Fang M (2025) Traditional Chinese medicine manual therapy for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a case report. Front. Pediatr. 12:1500373. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1500373
Received: 23 September 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 21 January 2025.
Edited by:
Ching-Mao Chang, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, TaiwanReviewed by:
Elena Amaricai, Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaEric Chun-Pu Chu, EC Healthcare, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright: © 2025 Zhu, Li, Ren, He, Zhou, Wang, Kong and Fang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lingjun Kong, Y2h1bnlvbmcwMUAxNjMuY29t; Min Fang, Zm0tdG4wNTEwQHNodXRjbS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Bowen Zhu
Bowen Zhu Miaoxiu Li
Miaoxiu Li Jun Ren
Jun Ren Tianxiang He
Tianxiang He Xin Zhou
Xin Zhou Shoujian Wang
Shoujian Wang Lingjun Kong
Lingjun Kong Min Fang
Min Fang