- 1Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Public Health and Biosafety & Institute for AIDS/STD Control and Prevention, Yunnan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Acute Infectious Diseases Control and Prevention, Yunnan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Background: Rotavirus (RV), norovirus (NoV), human enteric adenovirus (HAdV), human astrovirus (HAstV), and sapovirus (SaV) are important viral causes of acute gastroenteritis (AGE) in children. However, limited information is available regarding AGE in Yunnan, Southwest China.
Methods: To investigate the prevalence of group A rotavirus (RVA), norovirus genogroups I (GI) and II (GII), and HAdV, HAstV, and SaV in children aged <5 years hospitalized with AGE between 2020 and 2022.
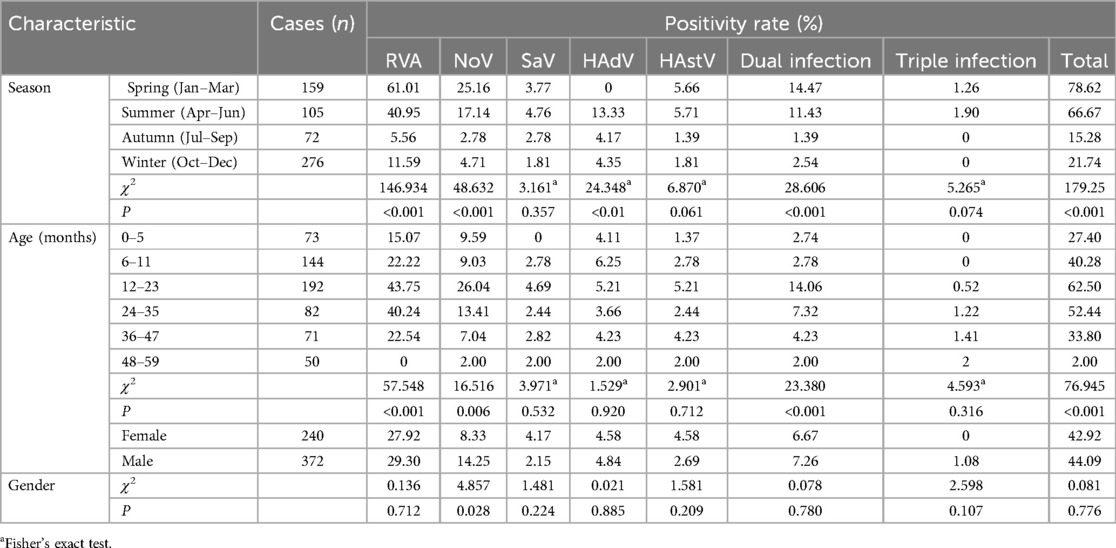
Results: Stool samples were collected from 612 children hospitalized with AGE. A total of 266 of the 612 children presented with AGE (43.46%; 266/612). RVA was detected in 28.76% (176 of 612) of the children. Rotavirus G9P[8] was the most frequent genotype in 2020 and 2021. In 2022, G8P[8] became the dominant genotype combination circulating in Yunnan Province. The norovirus positivity rate was present in 11.93% (73/612) of the 612 samples. Of the 45 GII successfully sequenced samples, GII.4 was the dominant genotype, accounting for 51.11% (23 of 45), followed by GII.3 [P12] (28.89%; 13 of 45). The positivity rates for SaV, HAstV, and HAdV were 2.94% (18/612), 3.43% (21/612), and 4.74% (29/612), respectively. HAdV-F41 was the predominant genotype and non-enteric HAdV-C2 and HAdV-A12 were also observed in Yunnan. Male children had a higher incidence of AGE than female children upon infection with RV, NoV, and HAdV. The highest incidence of AGE was observed among children aged between 12 and 23 months (62.50%; 120/192), followed by children aged between 24 and 35 months (52.44%; 43/82). The incidence rate of the infection peaked (78.62%; 125/159) in the first 3 months of the year, followed by the next 3 months (66.67%; 70/105).
Conclusions: RV and NoV remained the most important agents causing AGE. RV G8P[8] became the dominant circulating genotype instead of G9P[8] in Yunnan in 2022. The authors suggest that monitoring should be strengthened to prevent outbreaks caused by RV G8P[8]. New vaccines, such as the RV G8P[8] genotype, should be considered.
Introduction
Acute gastroenteritis (AGE) is a common illness that affects people of all ages and remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality (1–3). Young children are especially vulnerable to severe disease (4, 5). AGE poses a significant burden on public health (6–8). Bacterial gastroenteritis among children has been decreasing in China (9). Viral etiologies such as group A rotavirus (RVA), norovirus (NoV), human enteric adenovirus (HAdV), human astrovirus (HAstV), and sapovirus (SaV) play a more important role in children aged <5 years, particularly in infants and young children aged <2 years (10), than in children of other age groups (11–13). To better understand the incidence of AGE among children aged <5 years in Yunnan Province, Southwest China, and to characterize the epidemiology of viral gastroenteritis, we analyzed surveillance data collected by AGE sentinel hospitals in Yunnan Province during the period between 2020 and 2022.
Materials and methods
Sample collection
Fecal samples were collected from hospitalized children aged <5 years who sought medical care for AGE at the national viral AGE sentinel hospitals in Yunnan between 2020 and 2022. In total, 612 fecal specimens were collected from these children. In accordance with the National Surveillance Protocol for Viral Diarrhea (2021 version), AGE was defined as more than three episodes of abnormal stools (liquid, watery, mucous, or bloody purulent) in a 24-h period or less than three abnormal stools per day along with vomiting. Information on the fecal specimens, such as the sample collection date, and personal information such as age and gender, were collected from the patients, with the consent of their guardians obtained for the personal information. The stool samples were stored at room temperature for no more than 4 h. All fecal specimens were stored at −70°C before screening.
DNA and RNA extraction
The stool samples were suspended in 10% phosphate-buffered saline, mixed for 10 s, and then centrifuged at 8,000×g for 5 min. Viral DNA and RNA were extracted from 200 μl of the supernatant using the Viral Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit (BioPerfectus, Beijing, China, SDK60104) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Detection and phylogenetic analysis of RV, NoV, and HAdV
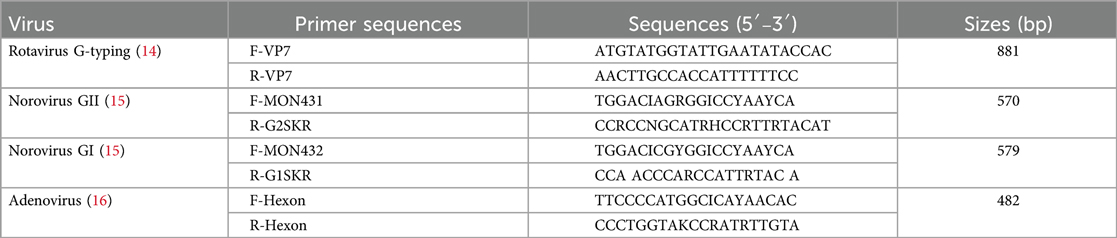
All stool samples were screened for rotavirus (RV), NoV, SaV, HAstV, and HAdV by real-time PCR with the RVA/NoV (GI and GII) Nucleic Acid Testing Kit (ABT Beijing, China) and the Sapovirus/Astrovirus/Enteric Adenovirus Nucleic Acid Testing Kit (ABT, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Both kits contained an internal amplification control. In the PCR assays, an external positive and an external negative control were used to ensure the accuracy of the screening results. Positive RVA, NoV, and HAdV samples with Ct <30 were genotyped by the Sanger sequencing method. The one-step RT-PCR Kit (Qiagen, Germany, 210212) was used to amplify the partial sequences of the VP7/VP4 genes with 881 bp/663 bp RT-PCR products against RVA. The VP7 sequences have been submitted to GenBank (accession numbers: PQ048122-PQ048188). Some positive samples with low nucleic acid load were genotyped using the Rotavirus Fluorescent Genotyping Kit (ABT, China, A9369YH-25T). For norovirus-positive samples, the partial sequences of regions B and C with the primer MON432/G1SKR for GI and the primer MON431/G2SKR for GII yielded 579 and 570 bp RT-PCR products, respectively. The norovirus sequences determined in this study have been deposited in GenBank (accession numbers: PQ044503-PQ044541). In the same way, the hexon gene of HAdV was analyzed to determine the HAdV genotype. The HAdV sequences have been submitted to GenBank under accession number PQ048098-PQ048121. The aforementioned genotype-specific primers are listed in Table 1. Phylogenetic trees of RVA, NoV, and HAdV were constructed using MEGA software (version 11) along with the neighbor-joining and Kimura two-parameter methods. Chi-square tests were used to compare proportions, and p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Basic information
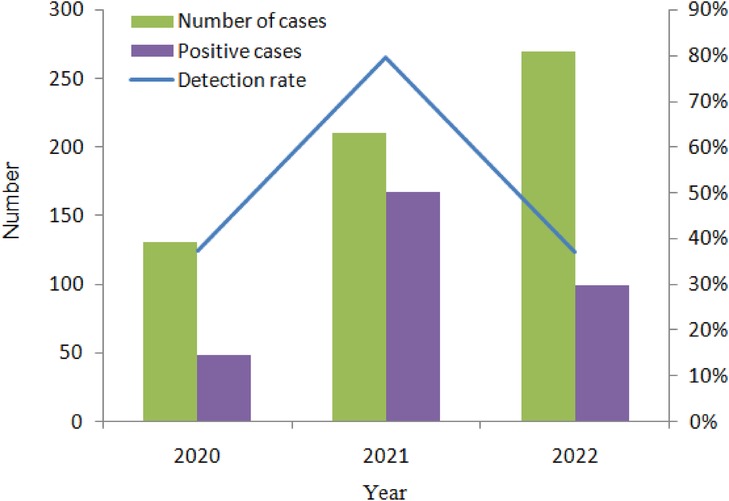
In total, 807 children aged between 0 and 59 months (mean age, 17.35 months) were hospitalized with AGE in Yunnan Province, Southwest China, between January 2020 and December 2022. Of these children, 612 (75.84%) were enrolled in our study, and their stool samples were submitted to the laboratory. The number of stool samples in each year from 2020 to 2022 was 131, 211, and 270, respectively (Figure 1). Of the 612 patients, there were 372 boys and 240 girls, and the count of male patients was 1.55 times more than that of females. The average patient age was 20 months (median age 12 months); 266 samples (43.46%) displayed at least one of the viral etiology positivity rates.
In total, 612 samples were collected for three consecutive monitoring years: 2020, 2021, and 2022. There were 270 samples in 2022 and 131 samples in 2020. The highest viral detection rate was 79.62% in 2021.
Pathogen composition
Rotavirus A
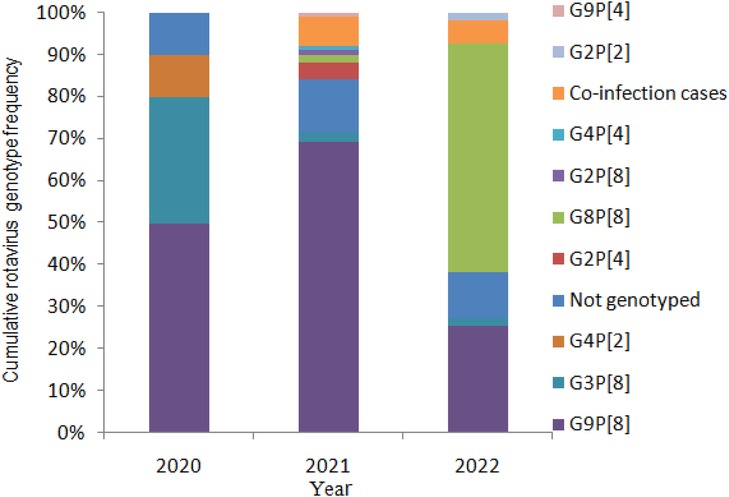
In total, 176 rotaviruses were detected in the 612 stool samples (28.76%). In 2020, 20 cases of patients with a rotavirus positivity rate of 15.27% were reported, including 10 with G9P[8] and 6 with G3P[8]. In 2021, the RV positivity rate was 47.87% (101/211), including 70 patients with G9P[8] and 2 with G8P[8]. In 2022, the rotavirus positivity rate was 20.37% (55/270), including 30 patients with G8P[8] and 14 with G9P[8]. The G8P[8] genotype became the predominant genotype in Yunnan (Figure 2).
Rotavirus genotype diversity was found in children aged <5 years hospitalized with gastroenteritis; RV G9P[8] was the dominant genotype, circulating with G3P[8] before 2022. RV G8P[8] was first detected in Yunnan in 2021, and it became the predominant strain in 2022.
Phylogenetic analysis of RVA
A phylogenetic tree was constructed from the nucleotide sequences of the partial RVA VP7 gene. It showed that G8 and G9 were the prevalent genotypes in Yunnan (Figure 3).
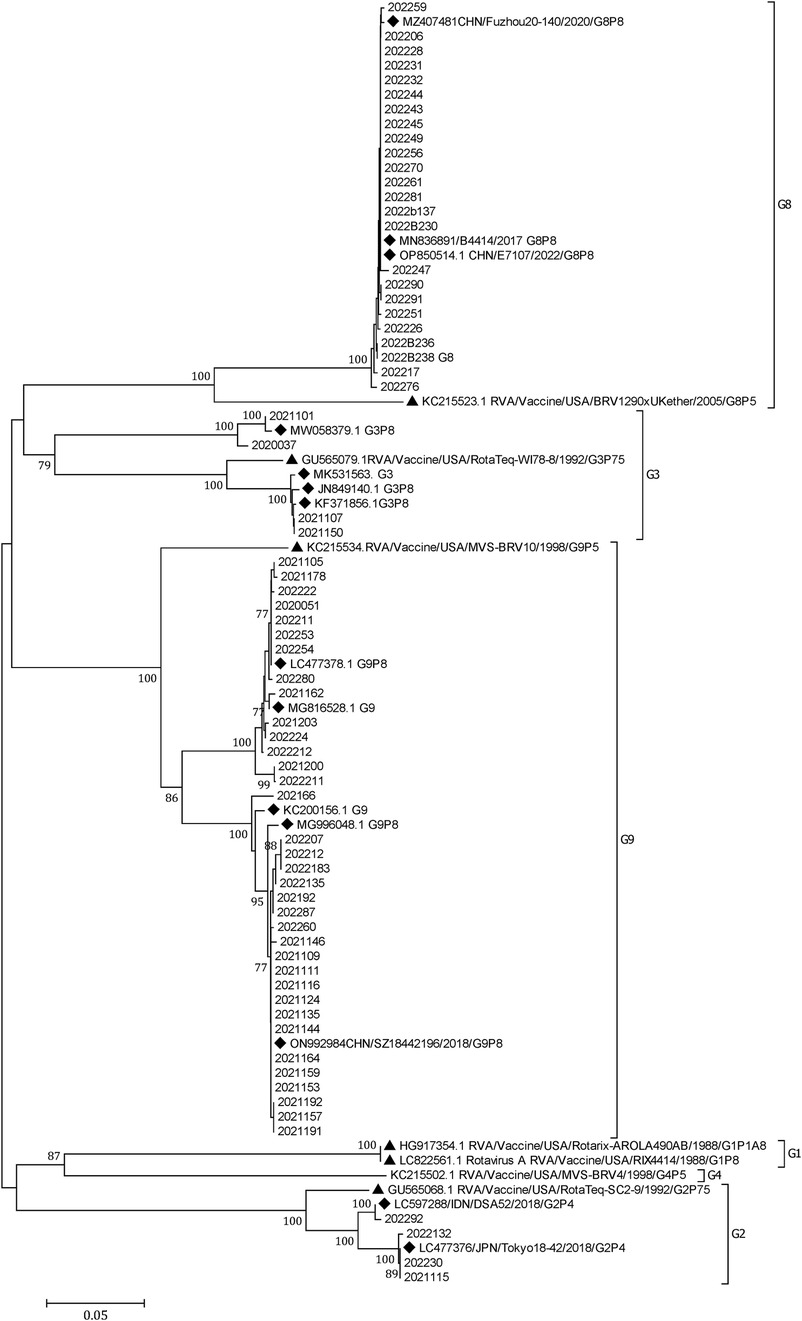
Figure 3. A phylogenetic tree constructed from the nucleotide sequences of the partial RV VP7 gene. A phylogenetic analysis based on the nucleotide sequences of the partial (756 bp) VP7 gene of RVA strains detected in children hospitalized with AGE in Yunnan, 2020–2022. G9 and G8 were the predominant G genotypes. A phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method using the Kimura two-parameter method. Closely related reference strains from GenBank are indicated by accession numbers. Bootstrap support >75% is shown. A GenBank database (reference strains) (◆). Vaccine strains (▴).
Norovirus
Norovirus was detected in 73 (11.93%) of the 612 patient samples. The positivity rates in 2020, 2021, and 2022 were 9.16% (12/131), 12.80% (27/211), and 12.59% (34/270), respectively. Of the 73 norovirus-positive samples, there were 5 GI and 68 GII. In total, 45 GII samples were successfully genotyped, with the breakup being 20 GII.4 [P16], 13 GII.3 [P12], 3 GII.4 [P31], 3 GII.17 [P17], 3 GII.6 [P7], 2 GII.2 [P16], and 1 GII.7 [P7]. GII.4 [P16] and GII.3 [P12] were the dominant genotypes circulating in Yunnan (Figure 4).
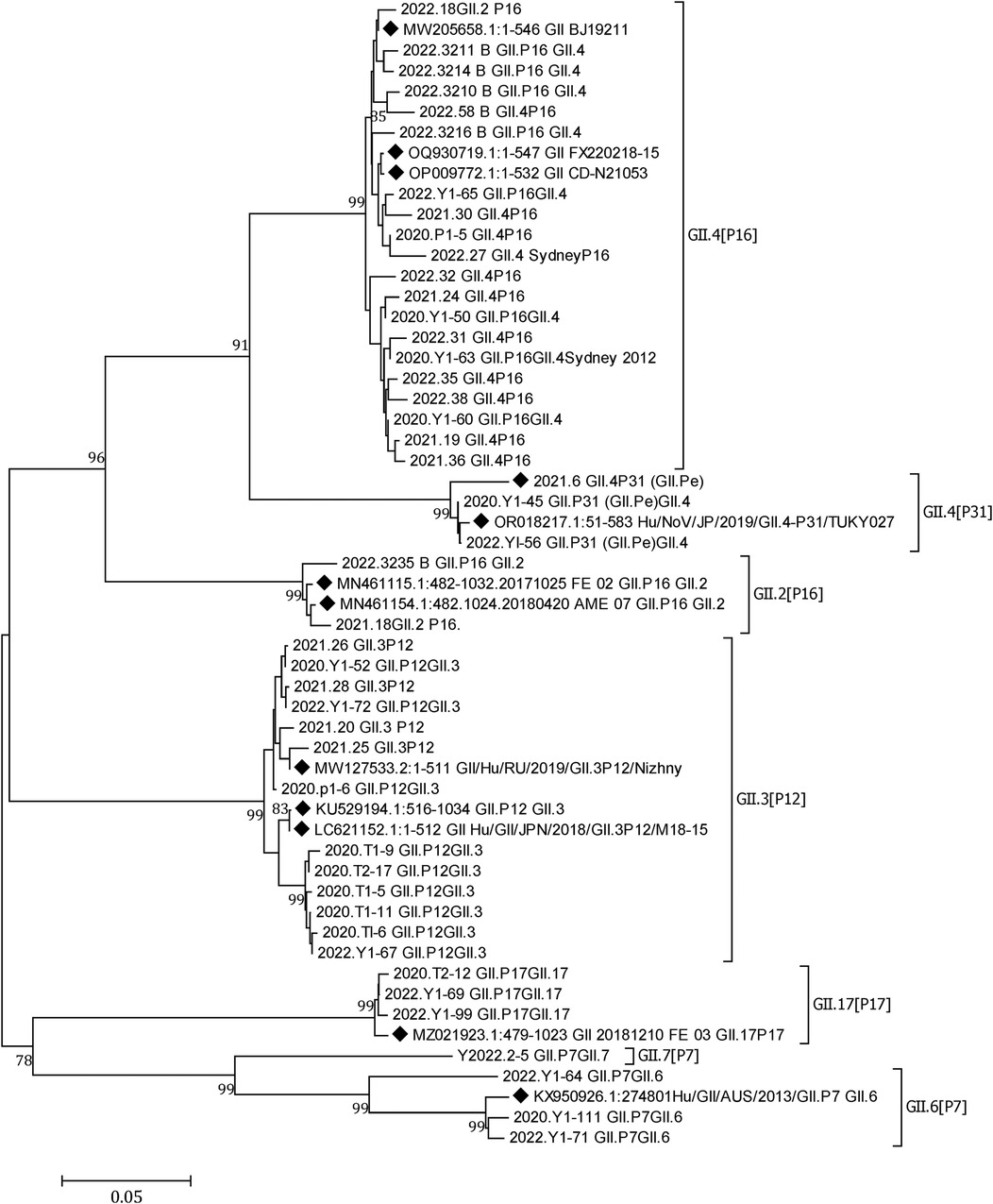
Figure 4. A phylogenetic tree constructed from norovirus GII nucleotide sequences. A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree for the partial capsid gene (GII-576 bp) of NoV strains detected in children hospitalized with AGE in Yunnan, 2020–2022. Closely related reference strains from GenBank are indicated by accession numbers. Bootstrap support >75% is shown. The scale bar represents 0.05 nucleotide substitutions per site across the indicated region. A GenBank database (reference strains) (◆).
SaV, HAstV, and HAdV
A total of 18 SaV, 21 HAstV, and 29 HAdV were detected in the 612 samples; the positivity rates were 2.94% (18/612), 3.43% (21/612), and 4.74% (29/612), respectively. A total of 27 of the 29 HAdVs were successfully sequenced, revealing 21 (77.78%) HAdV-F41, 3 (11.11%) HAdV-C2, 2 (7.41%) HAdV-F40, and 1 (3.70%) HAdV-A12. HAdV-F41 was the predominant genotype circulating in Yunnan (Figure 5).
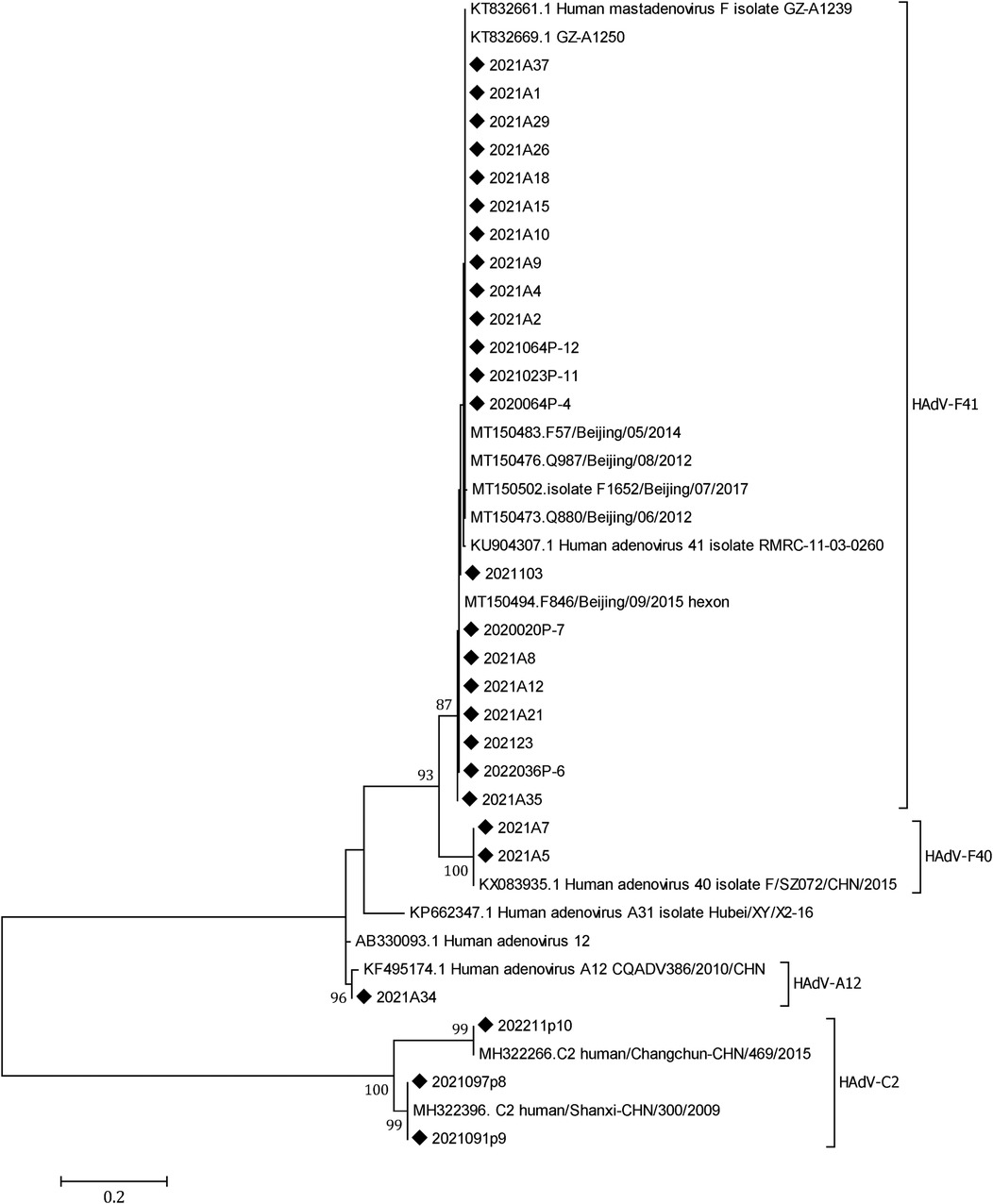
Figure 5. A phylogenetic tree of the HAdV hexon genes. A phylogenetic tree of HAdV hexon gene nucleotide sequences was constructed using the neighbor-joining method. HAdV-F41 was the dominant genotype circulating in Yunnan, 2020–2022. Closely related reference strains from GenBank are indicated by accession numbers. Bootstrap support >75% is shown. The scale bar represents 0.2 nucleotide substitutions per site across the indicated region. The HAdV strains detected in the study (◆).
Prevalence and distribution of coinfection
One virus was detected in 43.46% (266/612) of the samples (i.e., positive samples). Two viruses were present in 43 patients, and three viruses were simultaneously present in 4 patients. Thus, coinfection was detected in 7.68% (47/612) of patients. Both norovirus and rotavirus were screened in 24 samples (51.06%; 24/47).
Epidemiological features
The detection rates of RVA, NoV, SaV, HAdV, and HAstV in male patients were 29.30% (109/372), 14.25% (53/372), 2.15% (8/372), 4.84% (18/372), and 2.69% (10/372), respectively, and the detection rates in female patients were 27.92% (67/240), 8.33% (20/240), 4.17% (10/240), 4.58% (11/240), and 4.58% (11/240), respectively. Except for cases of SaV and HAstV infection, male children had a higher incidence of AGE than their female counterparts; the incidence of AGE significantly differed with respect to NoV infection (χ2 = 4.86, P = 0.028).
The highest rate of incidence of AGE was observed among children aged between 12 and 23 months (62.50%; 120/192), followed by children aged between 24 and 35 months. The lowest incidence rate was observed in children aged between 48 and 59 months (8.00%; 4/50) (Table 2). The detection rates of mixed infections in male and female children were 4.41% (27/612) and 2.61% (16/612), respectively. The detection rates of positive cases significantly differed among seasons (χ2 = 179.25, P < 0.001). The highest detection rate (78.62%; 125/159) was observed in the first quarter of the year, followed by the second quarter (66.67%; 70/105) (Table 2).
Discussion
This 3-year investigation systematically explored viral agents causing AGE among children aged <5 in Yunnan Province, southwest China, between the years 2020 and 2022. The surveillance showed that RVA, NoV, and HAdV were the most common causes of AGE. It ' reported that approximately 60% of hospital admissions for AGE worldwide are attributed to RVA infection, which tends to have a more severe course and is even significantly associated with mortality (17–19). RVA genotypes vary in different regions (20–22). It has been reported that rotavirus G1 is the most widespread genotype globally and constitutes the dominant genotype in many regions (20, 22, 23). G9P[8] was the predominant RVA genotype in China in 2016–2018 (24). In our study, 73 of 612 (11.92%) stool specimens demonstrated RVA positivity. Rotavirus G9P[8] was the dominant epidemic genotype, circulating with G3P[8] in 2020–2021 in Yunnan. RVA G8P[8] became the predominant epidemic strain in 2022. The tourism industry in Yunnan is well-developed due to the unique geographical conditions and excellent climate. In combination with a large population (48 million), these factors enable the new strain to circulate easily. Vaccination is an effective method against RVA infection, and the authors suggest that a vaccine that includes G8P[8] should be developed as early as possible against a potential rotavirus outbreak. China's National Immunization Program has achieved remarkable success, but it does not include the rotavirus vaccine; moreover, Yunnan is a relatively underdeveloped province. Both factors contribute to the low vaccination rate.
NoV and SaV are members of the Caliciviridae family. NoV is the most common cause of sporadic viral AGE and gastroenteritis outbreaks (25–27) and exhibits a highly diverse genotype, which is divided into 10 distinct geno groups (GI-GX). These groups are subclassified into genetic clusters or genotypes (28). In our study, 73 (11.93%) NoVs and 18 (2.94%) SaVs were detected in 612 patients, and NoV GII was the most prevalent geno group (93.15%; 68/73). GII.4 was identified as the predominant genotype in all settings (29–33). In this study, we obtained similar results: GII.4 [P16] was predominant in Yunnan during 2020–2022, followed by GII.3[P12]. No norovirus-targeting medications are available, and vaccines are still in development. Currently, the prevention of NoV infection relies on frequent hand hygiene, limited contact with virus-infected individuals, and disinfection of contaminated environmental surfaces (34).
HAdVs, one of the major etiologic agents associated with AGE in young children (35, 36), are classified into six subgenera (A–G). Types 40 (HAdV-F40) and 41 (HAdV-F41) in subgenus F are causative agents of enteric infections (37). Non-enteric genotypes are significantly associated with AGE among children aged <5 years of age (38). Two non-enteric HAdV serotypes were detected in our study, HAdV-C2 and HAdV-A12. HAdV infection was identified in 4.74% of the 612 tested children. Among the 27 sequenced HAdVs, HAdV-F41 was the predominant genotype (77.78%), followed by HAdV-C2 (11.11%), HAdV-F40 (7.41%), and HAdV-A12 (3.70%). There is a need to closely monitor AGE caused by non-enteric HAdV genotypes other than HAdV-F40 and HAdV-F41.
In terms of coinfection, RVA and NoV were the main pathogens of AGE in hospitalized children with a significant difference (χ2 = 28.61, P < 0.05). Three pathogens were even observed in four patients. Because of the limited number of cases, the clinical data were insufficient to establish a direct relationship with the severity of clinical symptoms. Viral infections are more common during the cold season (4, 39), but the seasonality differs among regions (40, 41). The highest detection rate (78.62%; 125/159) in Yunnan was observed during the first 3 months of the year (χ2 = 179.25, P < 0.001), followed by the next 3 months (66.67%; 70/105). Perhaps this is related to Yunnan's unique geographical environment and climate.
Children <5 years of age are susceptible to AGE, especially those aged between 12 and 23 months (χ2 = 76.945, P < 0.001), and the incidence rate of AGE was 62.50% (120/192) in this age group, followed by 52.44% (43/82) in the 24–35-month age group.
In this study, only a statistically significant association related to gender was determined for NoV infection (p = 0.028). Table 2 shows that NoVs were detected in 14.25% of the boys and 8.33% of the girls. For RVA infection, it was observed that boys were more infected than girls (29.30% and 27.92%, respectively), with no statistical significance, while for HAstV and SaV infections, it was observed that girls were infected more frequently than boys; however, these results were not statistically significant (p = 0.209 and p = 0.224, respectively).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, China adopted strict prevention and control policies, which objectively contributed to a reduction in diarrhea cases. In 2020, there were only 131 patients with a relatively low positivity rate (37.40%; 49/131). However, in 2021, the number of AGE cases rose rapidly. There were 211 samples with the highest incidence rate of 79.62% (168/211). In 2022, a total of 270 samples were tested, and the detection rate was 37.04% (100/270), which showed that the incidence rate decreased almost to the same level as in 2020.
Conclusions
This study provides baseline data concerning the possible role of gastroenteritis-causing viruses in children. The results offer valuable information that may alert healthcare providers to periods of increased likelihood of community infection. Caution should be exercised when outbreaks are caused by the new G8[P8] RVA strains and it is recommended that susceptible children actively get vaccinated against RVAs. Further long-term and large-scale epidemiological surveys are recommended to better understand the disease burden, etiologic agents, and clinical impact in Yunnan Province.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Yunnan Center for Disease Control and Prevention. This study was conducted with residual clinical samples. Written informed consent was not required because the enrolled patients and their information were fully anonymized during data analysis. Verbal informed consent was obtained from the patients’ parents or guardians.
Author contributions
NL: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Investigation. EQ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Validation. ZD: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Visualization. LL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. LJ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Software. JC: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. XZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZW: Writing – original draft, Data curation. YZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Open Research Fund Program of Yunnan Key Laboratory of Vaccine research & Development on severe Infections Diseases (2020KF001).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Yunnan Provincial viral diarrhea monitoring units for their valuable contributions. Dr. Wenpeng Gu and Dr. Duo Li are very much appreciated for rendering their assistance in the writing of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2024.1497467/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392(10159):1736–88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7
2. Burke RM, Mattison CP, Pindyck T, Dahl RM, Rudd J, Bi D, et al. Burden of norovirus in the United States, as estimated based on administrative data: updates for medically attended illness and mortality, 2001–2015. Clin Infect Dis. (2021) 73(1):e1–8. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa438
3. Lian Y, Wu S, Luo L, Lv B, Liao Q, Li Z, et al. Epidemiology of norovirus outbreaks reported to the public health emergency event surveillance system, China, 2014–2017. Viruses. (2019) 11(4):1–12. doi: 10.3390/v11040342
4. Li F, Guo L, Li Q, Xu H, Fu Y, Huang L, et al. Changes in the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of viral gastroenteritis among hospitalized children in the mainland of China: a retrospective study from 2016 to 2020. BMC Pediatr. (2024) 24(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04776-1
5. Mandolo JJ, Henrion MYR, Mhango C, Chinyama E, Wachepa R, Kanjerwa O, et al. Reduction in severity of all-cause gastroenteritis requiring hospitalisation in children vaccinated against rotavirus in Malawi. Viruses. (2021) 13(12):1–12. doi: 10.3390/v13122491
6. Dickerson JF, Salas SB, Donald J, Groom HC, Lee MH, Mattison CP, et al. Economic burden of acute gastroenteritis among members of integrated healthcare delivery system, United States, 2014–2016. Emerg Infect Dis. (2024) 30(5):968–73. doi: 10.3201/eid3005.230356
7. Huo Y, Gao F, Wang J, Liu Z, Zhou L, Gu B, et al. Economic burden and influencing factors of acute gastroenteritis in China: a population-based face to face survey in 2018. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:905458. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.905458
8. Bartsch SM, Lopman BA, Ozawa S, Hall AJ, Lee BY. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PLoS One. (2016) 11(4):e0151219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151219
9. Gong X, Wu H, Xiao W, Li J, Lin S, Chen M, et al. Surveillance of infectious diarrhea patients in Shanghai during 2013–2016,based on establishment of diarrhea public health comprehensive surveillance system. Chin J Infect Dis. (2018) 036(006):327–32. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2018.06.002
10. Chang H, Guo J, Wei Z, Huang Z, Wang C, Qiu Y, et al. Aetiology of acute diarrhoea in children in Shanghai, 2015–2018. PLoS One. (2021) 16(4):e0249888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249888
11. Wilhelmi I, Roman E, Sánchez-Fauquier A. Viruses causing gastroenteritis. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2003) 9(4):247–62. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0691.2003.00560.x
12. Wang LP, Zhou SX, Wang X, Lu QB, Shi LS, Ren X, et al. Etiological, epidemiological, and clinical features of acute diarrhea in China. Nat Commun. (2021) 12(1):2464. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22551-z
13. do Socorro Fôro Ramos E, de Oliveira Ribeiro G, Villanova F, de Padua Milagres FA, Brustulin R, Araújo ELL, et al. Composition of eukaryotic viruses and bacteriophages in individuals with acute gastroenteritis. Viruses. (2021) 13(12):1–12. doi: 10.3390/v13122365
14. Iturriza-Gómara M, Auchterlonie IA, Zaw W, Molyneaux P, Desselberger U, Gray J. Rotavirus gastroenteritis and central nervous system (CNS) infection: characterization of the VP7 and VP4 genes of rotavirus strains isolated from paired fecal and cerebrospinal fluid samples from a child with CNS disease. J Clin Microbiol. (2002) 40(12):4797–9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.12.4797-4799.2002
15. Cannon JL, Barclay L, Collins NR, Wikswo ME, Castro CJ, Magaña LC, et al. Genetic and epidemiologic trends of norovirus outbreaks in the United States from 2013 to 2016 demonstrated emergence of novel GII.4 recombinant viruses. J Clin Microbiol. (2017) 55(7):2208–21. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00455-17
16. Yihui C, Enfa Q, Jianping C, Lili J, Jianping C, Yibin X. Molecular biological characteristics of adenovirus infection in children with diarrhea in two medical institutions in Yunnan province. Chin J Virol. (2020) 36(06):1133–7. doi: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003793
17. Jiang H, Zhang Y, Xu X, Li X, Sun Y, Fan X, et al. Clinical, epidemiological, and genotypic characteristics of rotavirus infection in hospitalized infants and young children in Yunnan province. Arch Virol. (2023) 168(9):229. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05849-9
18. Digwo D, Chidebelu P, Ugwu K, Adediji A, Farkas K, Chigor V. Prevalence and relative risk of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children under five years in Nigeria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pathog Glob Health. (2023) 117(1):24–35. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2022.2043223
19. Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet. (2013) 382(9888):209–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2
20. Esona MD, Ward ML, Wikswo ME, Rustempasic SM, Gautam R, Perkins C, et al. Rotavirus genotype trends and gastrointestinal pathogen detection in the United States, 2014–2016: results from the new vaccine surveillance network. J Infect Dis. (2021) 224(9):1539–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab177
21. Rakau KG, Nyaga MM, Gededzha MP, Mwenda JM, Mphahlele MJ, Seheri LM, et al. Genetic characterization of G12P[6] and G12P[8] rotavirus strains collected in six African countries between 2010 and 2014. BMC Infect Dis. (2021) 21(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05745-6
22. Koukou DM, Michos A, Chatzichristou P, Trimis G, Tatsi EB, Dellis C, et al. Rotavirus epidemiology and genotype distribution in hospitalised children, Greece, 2008 to 2020: a prospective multicentre study. Euro Surveill. (2022) 27(47):1–12. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.Es.2022.27.47.2101133
23. Giri S, Kumar CPG, Khakha SA, Chawla-Sarkar M, Gopalkrishna V, Chitambar SD, et al. Diversity of rotavirus genotypes circulating in children <5 years of age hospitalized for acute gastroenteritis in India from 2005 to 2016: analysis of temporal and regional genotype variation. BMC Infect Dis. (2020) 20(1):740. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05448-y
24. Liu X, Wang M, Li S, Li J, Xiao J, Li H, et al. Genomic and evolutionary characteristics of G9P[8], the dominant group a rotavirus in China (2016–2018). Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:997957. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.997957
25. Torner N, Martinez A, Broner S, Moreno A, Camps N, Domínguez A, et al. Epidemiology of acute gastroenteritis outbreaks caused by human calicivirus (norovirus and sapovirus) in Catalonia: a two year prospective study, 2010–2011. PLoS One. (2016) 11(4):e0152503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152503
26. Parikh MP, Vandekar S, Moore C, Thomas L, Britt N, Piya B, et al. Temporal and genotypic associations of sporadic norovirus gastroenteritis and reported norovirus outbreaks in middle Tennessee, 2012–2016. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 71(9):2398–404. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1106
27. Hofmann FM, Olawumi E, Michaelis M, Stößel U, Hofmann F. Significance of norovirus in occupational health: a review of published norovirus outbreaks in central and Northern Europe. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. (2020) 93(8):911–23. doi: 10.1007/s00420-020-01543-4
28. Chhabra P, de Graaf M, Parra GI, Chan MC, Green K, Martella V, et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J Gen Virol. (2019) 100(10):1393–406. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001318
29. Mans J. Norovirus infections and disease in lower-middle and low-income countries, 1997–2018. Viruses. (2019) 11(4):1–19. doi: 10.3390/v11040341
30. Duan L, Yang X, Xie J, Zhan W, Zhang C, Liu H, et al. Prevalence of GII.4 Sydney norovirus strains and associated factors of acute gastroenteritis in children: 2019/2020 season in Guangzhou, China. Food Environ Virol. (2021) 13(3):357–67. doi: 10.1007/s12560-021-09482-0
31. Bucardo F, Reyes Y, Becker-Dreps S, Bowman N, Gruber JF, Vinjé J, et al. Pediatric norovirus GII.4 infections in Nicaragua, 1999–2015. Infect Genet Evol. (2017) 55:305–12. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.10.001
32. Hoa Tran TN, Trainor E, Nakagomi T, Cunliffe NA, Nakagomi O. Molecular epidemiology of noroviruses associated with acute sporadic gastroenteritis in children: global distribution of genogroups, genotypes and GII.4 variants. J Clin Virol. (2013) 56(3):269–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2012.11.011
33. Kendra JA, Tohma K, Parra GI. Global and regional circulation trends of norovirus genotypes and recombinants, 1995–2019: a comprehensive review of sequences from public databases. Rev Med Virol. (2022) 32(5):e2354. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2354
34. Bányai K, Estes MK, Martella V, Parashar UD. Viral gastroenteritis. Lancet (London, England). (2018) 392(10142):175–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31128-0
35. Khan NU, Shamsullah , Shahidullah , Shah AA, Zaidi SSZ, Chen Z. Epidemiology of human adenovirus in Pakistani children hospitalized with community-acquired gastroenteritis under the age of five years. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19(19):1–11. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912534
36. Qiu Y, Freedman SB, Williamson-Urquhart S, Farion KJ, Gouin S, Poonai N, et al. Significantly Longer shedding of norovirus compared to rotavirus and adenovirus in children with acute gastroenteritis. Viruses. (2023) 15(7):1541. doi: 10.3390/v15071541
37. Uhnoo I, Svensson L, Wadell G. Enteric adenoviruses. Bailliere’s Clinical Gastroenterology. (1990) 4(3):627–42. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(90)90053-J
38. do Nascimento LG, Fialho AM, de Andrade JdSR, de Assis RMS, Fumian TM. Human enteric adenovirus F40/41 as a major cause of acute gastroenteritis in children in Brazil, 2018 to 2020. Sci Rep. (2022) 12(1):11220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15413-1
39. Yang L, Shi S, Na C, Li B, Zhao Z, Yang T, et al. Rotavirus and norovirus infections in children under 5 years old with acute gastroenteritis in southwestern China, 2018–2020. J Epidemiol Glob Health. (2022) 12(3):292–303. doi: 10.1007/s44197-022-00050-8
40. Ouedraogo N, Ngangas SM, Bonkoungou IJ, Tiendrebeogo AB, Traore KA, Sanou I, et al. Temporal distribution of gastroenteritis viruses in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso: seasonality of rotavirus. BMC Public Health. (2017) 17(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4161-7
Keywords: acute gastroenteritis, rotavirus, norovirus, human enteric adenovirus, human astrovirus, sapovirus
Citation: Li N, Qiao E, Duan Z, Li L, Jiang L, Cun J, Zhou X, Wang ZC, Zhou Y and Cao Y (2025) Prevalence and genetic characterization of viral gastroenteritis in hospitalized children aged <5 years in Yunnan Province, China, 2020–2022. Front. Pediatr. 12:1497467. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1497467
Received: 19 September 2024; Accepted: 13 December 2024;
Published: 8 January 2025.
Edited by:
Tung Phan, University of Pittsburgh, United StatesReviewed by:
Kentaro Tohma, United States Food and Drug Administration, United StatesKarina Gomes, Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Infecciosas Dr. Carlos G. Malbrán (INEI), Argentina
Copyright: © 2025 Li, Qiao, Duan, Li, Jiang, Cun, Zhou, Wang, Zhou and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yihui Cao, NTI2NTA1Nzc5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Yongming Zhou, enltOTE3MThAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Nan Li1,†
Nan Li1,† Yihui Cao
Yihui Cao