- 1Department of Endocrinology, Genetics and Metabolism, Children’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 2Pediatric Clinical Research Centre of Hebei Province, Children’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 3Institute of Pediatric Research, Children’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 4Department of Urology, Children’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 5Department of Ultrasonography, Children’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
Mixed gonadal dysgenesis is caused by a variety of chromosome abnormalities, most commonly Y chromosome mosaicism. An 8-year-old boy presented with short stature for possible treatment with recombinant growth hormone. He had a history of mixed gonadal dysgenesis (hypospadias, bilateral cryptorchidism, processus vaginalis, and dysplastic immature uterus) and a series of corrective surgeries. At 14 months of age, chromosomal karyotyping revealed 46,X,+mar. Upon presentation, lab testing was consistent with the male phenotype at prepuberty. Fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed 45,X[2]/46,X,der(Y).ish psu idic(Y)(q11.2)(SRY++,DYZ3++)[38] karyotype. A literature review identified eight case reports of mixed gonadal dysgenesis associated with 45,X/46,X,idic(Y)(q11.2). Neither sex phenotype nor short stature correlated with the 46,X,idic(Y)(q11.2) mosaic ratio.
1 Introduction
Isodicentric Y chromosomes [idic(Y)] are the most common structural abnormalities of the Y chromosome. The instability of idic(Y) during cell division results in the mosaic 45,X/46,X,idic(Y) karyotype (1). Depending on the different distribution of the 45,X cell line, phenotype varies and may include male infertility, Turner syndrome in females, ambiguous genitalia, gonadal dysgenesis, and short stature (2, 3). Here, we report a case of mixed gonadal dysgenesis in an 8-year-old boy with ambiguous genitalia, ectopic urethral opening, and short stature. Initial chromosomal analysis revealed 46,X,+mar karyotype. Subsequent investigation using fluorescence in situ hybridization demonstrated 45,X[2]/46,X,der(Y).ish psu idic(Y)(q11.2)(SRY++,DYZ3++)[38] karyotype.
2 Case report
An 8-year-old boy presented with short stature (111.4 cm, −3.54 standard deviation; 19.5 kg, −2.11 standard deviation) for possible treatment with recombinant growth hormone. Upon inquiry, the parents disclosed in vitro fertilization birth and a diagnosis of mixed gonadal dysgenesis with a karyotype (46,X,+mar) at 14 months of age and a series of corrective surgeries. Both parents had normal karyotypes. Past medical records documented were as follows: (1) hypospadias and bilateral cryptorchidism; (2) dysplastic immature uterus; (3) surgery to correct hypospadias; (4) high ligation of processus vaginalis; and (5) removal of dysplastic testis on the right side (containing ovarian tissue upon pathological examination; Figure 1) and orchiopexy on the left side.
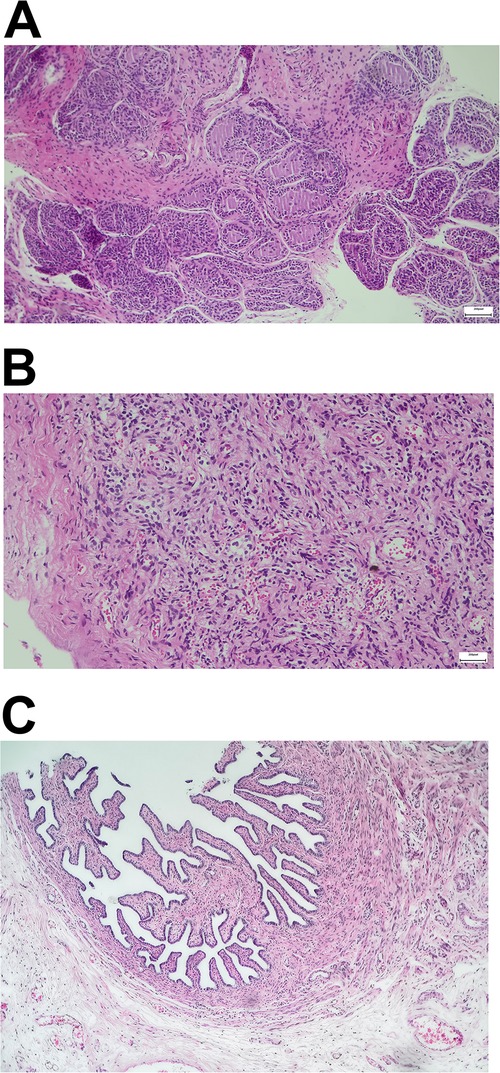
Figure 1. Pathologic examination after laparoscopic exploration. (A) Gonadal dysplasia of the right testis. (B,C) Ovarian stroma and right fallopian tube.
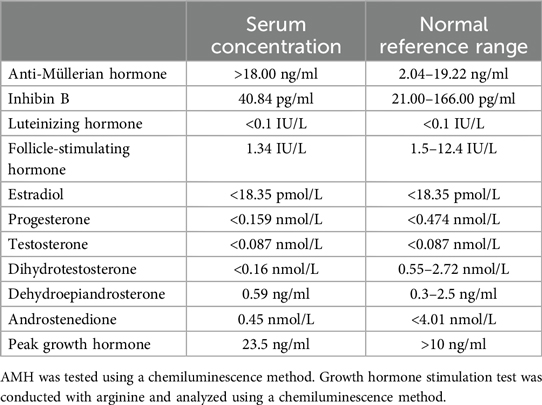
Physical examination is consistent with surgical history and was unremarkable otherwise except for the short stature. Upon ultrasound examination, the remaining testis appeared normal (17 × 11 × 7 mm, +0.17 standard deviation). The results of the laboratory tests were consistent with the male phenotype at prepuberty and excluded idiopathic growth hormone deficiency (Table 1).
Based on these findings, three probes (SRY, DXZ1, and DYZ3) were designed for FISH, which in turn revealed a 45,X[2]/46,X,der(Y).ish psu dic(Y)(q11.2)(SRY++,DYZ3++)[38] karyotype (Figure 2). A schematic diagram of the isodicentric Y chromosome is shown in Figure 3. Considering the normal level of growth hormone and the risk of malignant transformation associated with dysplastic immature uterus, we decided not to initiate treatment with recombinant growth hormone as the parents initially requested. The patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.
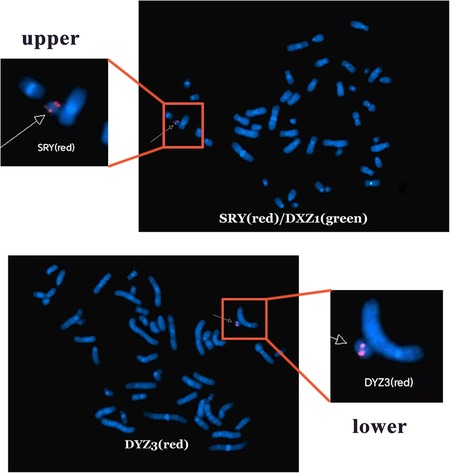
Figure 2. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. SRY shows two red signals, DXZ1 shows one green signal (upper), and DYZ3 shows two red signals (lower).
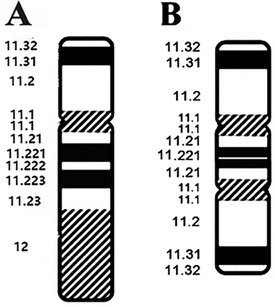
Figure 3. A schematic diagram of the isodicentric Y chromosome. (A) Normal Y chromosome. (B) Dicentric idic(Y) (q11.2) Y chromosome. White lines: breakpoints.
3 Discussion and conclusions
The Y chromosome contains key genes that are critical for male sexual development, including the sex-determining gene SRY and azoospermia factor (4). A deficient SRY gene has been associated with dicentric Y chromosomes (5). Despite the presence of two SRY and two SHOX genes, the index patient had mixed gonadal dysplasia and short stature, respectively (6). Phenotype variation across the patients is caused by different breakpoints and distribution of different tissues of 45,X cell line, especially the gonads. Furthermore, the timing of the mitotic loss of idic(Y) during gonadal ontogenesis and the proportion of SRY-positive pre-Sertoli cells in the gonad is probably more relevant than the postnatal proportion of the different mosaic clones (7). The haplotype duplication involving SHOX in the Yp11.32q11.221 region in the index patient is consistent with a previous study that described isolated SHOX microreplicates with short stature (8). However, the 45,X mosaic karyotype in the index patient could affect linear bone growth due to partial SHOX gene haplo-insufficiency.
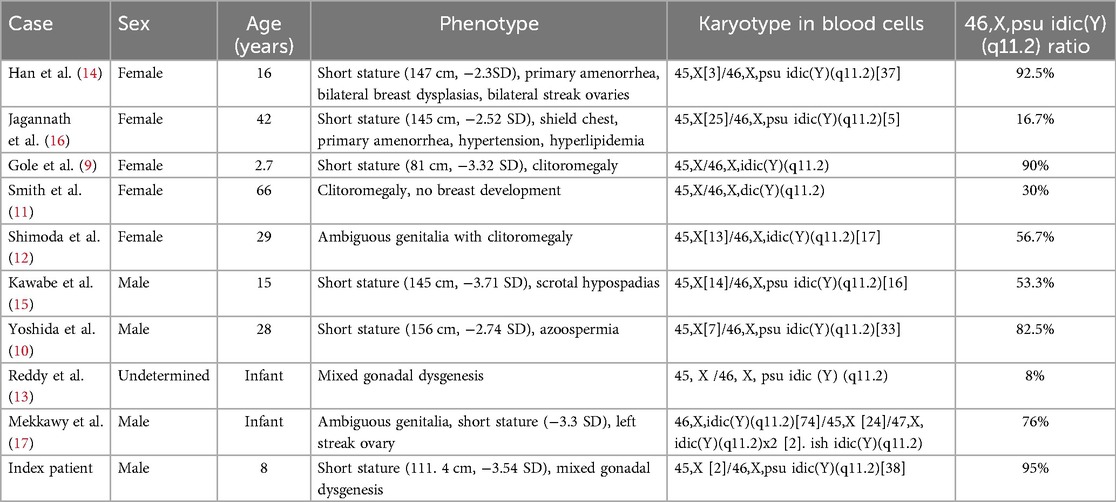
We conducted a literature review of mixed gonadal dysgenesis associated with 45,X/46,X,idic(Y)(q11.2). A search in PubMed identified nine reported cases (9–17). All reported cases were characterized by gonadal dysgenesis, but sexual phenotype varied across the cases: female in five cases, male in three cases, and undetermined in one case (Table 2). Most notably, neither sex phenotype nor short stature correlated with the 46,X,idic(Y)(q11.2) mosaic ratio.
In summary, the mixed gonadal dysgenesis in the index patient was caused by de novo 45,X[2]/46,X,der(Y).ish psu idic(Y)(q11.2)(SRY++,DYZ3++)[38] karyotype. This case represents a valuable addition to the limited collection of Yq11.2 breaks in the literature.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Children's Hospital of Hebei Province. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
QZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XCh: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. LiL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LeL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XCu: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Hebei Provincial Key R&D Program for Health Innovation Special Project (21377710D).
Acknowledgments
We thank the parents for their cooperation in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Tuck-Muller CM, Chen H, Martinez JE, Shen CC, Li S, Kusyk C, et al. Isodicentric Y chromosome: cytogenetic, molecular and clinical studies and review of the literature. Hum Genet. (1995) 96:119–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00214200
2. Dai Y, Li H, Zhang X, Jia M, Gu X. A rare karyotype of nonmosaic isodicentric (Y)(p11.31) with azoospermia and short stature. Andrologia. (2020) 52:e13536. doi: 10.1111/and.13536
3. Beaulieu BM, Brochu P, Lemyre E, Lemieux N. Correlation of intercentromeric distance, mosaicism, and sexual phenotype: molecular localization of breakpoints in isodicentric Y chromosomes. Am J Med Genet A. (2011) 155A(11):2705–12. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34260
4. Disteche CM, Casanova M, Saal H, Friedman C, Sybert V, Graham J, et al. Small deletions of the short arm of the Y chromosome in 46,XY females. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1986) 83:7841–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7841
5. Cui YX, Wang WP, Li TF, Li WW, Wu QY, Li N, et al. Clinical and cytogenomic studies in a case of infertility associated with a nonmosaic dicentric Y chromosome. Andrologia. (2015) 47:477–81. doi: 10.1111/and.12278
6. Rao E, Weiss B, Fukami M, Rump A, Niesler B, Mertz A, et al. Pseudoautosomal deletions encompassing a novel homeobox gene cause growth failure in idiopathic short stature and Turner syndrome. Nat Genet. (1997) 16:54–63. doi: 10.1038/ng0597-54
7. Shinawi M, Cain MP, Vanderbrink BA, Grignon DJ, Mensing D, Cooper ML, et al. Mixed gonadal dysgenesis in a child with isodicentric Y chromosome: does the relative proportion of the 45,X line really matter? Am J Med Genet A. (2010) 152A:1832–7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33475
8. Benito-Sanz S, Barroso E, Heine-Suñer D, et al. Clinical and molecular evaluation of SHOX/PAR1 duplications in Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) and idiopathic short stature (ISS). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 96:E404–12. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1689
9. Gole LA, Lim J, Crolla JA, Loke KY. Gonadal mutations in mosaicism 45,X/46,X,psu dic(Y)(q11.2) resulting in a turner phenotype with mixed gonadal dysgenesis. Singap Med J. (2008) 49:349–51.
10. Yoshida A, Nakahori Y, Kuroki Y, Motoyama M, Araki Y, Miura K, et al. Dicentric Y chromosome in an azoospermic male. Mol Hum Reprod. (1997) 3:709–12. doi: 10.1093/molehr/3.8.709
11. Smith YR, Stetten G, Charity L, Isacson C, Gearhart JP, Namnoum AB. Ambiguous genitalia in an elderly woman with a mosaic 45,X/46,X,dic(Y) (Q11.2) karyotype. Urology. (1996) 47:259–62. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(99)80431-2
12. Shimoda N, Sato K, Satoh S, Ogawa O, Ito S, Kato T. Atypical true hermaphroditism with a mosaic 45,X/46,X,dic(Y)(q11.2) karyotype. J Urol. (1998) 160:1434–5. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)62565-5
13. Reddy KS, Sulcova V, Ho CK, Conner ED, Khurana A. An infant with a mosaic 45,X/46,X,psu dic(Y)(pter–>q11.2::q11.2–>pter) karyotype and mixed gonadal dysgenesis studied for extent of mosaicism in the gonads. Am J Med Gene. (1996) 66:441–4. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19961230)66:4<441:: AID-AJMG11>3.0.CO;2-U
14. Han Y, Wu J, Tan F, Sha J, Zhang B, Zhai JF, et al. 45,X/46,X,psu Idic(Y)(q11.2) mosaicism in a primary amenorrhea girl with Swyer syndrome. Case Rep Genet. (2023) 9:9127512. doi: 10.1155/2023/9127512
15. Kawabe Y, Yamaguchi M, Miyagaki S, Ota T, Morimoto H, Hattori A, et al. 45,X/46,X,psu Idic(Y)(q11.2) in a phenotypically normal male with short stature: a case report. Clin Ped Endo. (2020) 29:189–93. doi: 10.1297/cpe.29.189
16. Jagannath AD, Rastogi U, Spooner AE, Lin AE, Agnihotri AK. Aortic dissection and moyamoya disease in turner syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. (2010) 152A:2085–9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33539
Keywords: isodicentric Y chromosome, mosaicism, Yq11.2 breaks, mixed gonadal dysgenesis, karyotyping, fluorescence in situ hybridization
Citation: Zhang Q, Chen X, Cao Y, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Liu L, Liu L and Cui X (2024) 45,X[2]/46,X,der(Y).ish Psu idic(Y)(q11.2)[38] mosaic karyotype in mixed gonadal dysgenesis: a case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 12:1460174. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1460174
Received: 5 July 2024; Accepted: 26 September 2024;
Published: 16 October 2024.
Edited by:
Nagwa Elsayed Afify Gaboon, Ain Shams University, EgyptReviewed by:
Mona Kamal Mekkawy, National Research Centre, EgyptHeba Elsedfy, Ain Shams University, Egypt
Copyright: © 2024 Zhang, Chen, Cao, Zhou, Liu, Liu, Liu and Cui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaowei Cui, Y3VpeGlhb3dlaTY4QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qiang Zhang
Qiang Zhang Xiaoxiao Chen1,†
Xiaoxiao Chen1,† Yanyan Cao
Yanyan Cao Yingye Liu
Yingye Liu