- 1Department of Pediatric Cardiology, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2The Cardiac Development and Early Intervention Unit, West China Institute of Women and Children’s Health, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3West China Clinical Medical College of Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children (Sichuan University), Ministry of Education, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 5Key Laboratory of Development and Diseases of Women and Children of Sichuan Province, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Background: Kawasaki disease (KD) is characterized as an acute febrile inflammatory disorder, which may potentially escalate into a more severe condition termed Kawasaki disease shock syndrome (KDSS). The objective of this research is to understand the clinical attributes of KDSS and to explore the predictive significance of coagulation profiles in the incidence of KDSS.
Method: Patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) were prospectively enrolled and divided into the KDSS group (n = 29) and the non-KDSS group (n = 494). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to ascertain the relationship between coagulation profiles and KDSS. Furthermore, ROC curve analysis was conducted to evaluate the predictive value of the coagulation profile for the occurrence of KDSS.
Result: Among the KDSS patients, the median age was higher and cervical lymph node involvement was greater compared to the non-KDSS group. Additionally pericardial effusion, valve regurgitation, cardiac enlargement, coronary artery lesions (CALs), and Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) resistance were significantly more frequent in the KDSS group than in non-KDSS group. Notably, Prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), D-dimer, and fibrin degradation products (FDP) were significantly elevated in the KDSS group compared to the non-KDSS group. Conversely, total thrombin time (TT), fibrinogen, and antithrombin III (ATIII) activity were significantly reduced. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that PT, APTT, D-dimer, and ATIII were independent risk factors for predicting KDSS occurrence. ROC curve analysis established critical values for PT, D-dimer, FDP, and ATIII as 13.45 s, 2.03 mg/L, 7.45 μg/ml, and 77.5%, respectively. Sensitivity for predicting KDSS occurrence was 76%, 79%, 83%, and 76%, while specificity was 51%, 72%, 63%, and 80%, respectively. When we performed a combined ROC curve analysis of the four indicators, we found that its predictive sensitivity was much higher. Moreover, the Delong test results showed that the AUC of the combined analysis was significantly higher than that of the individual analyses.
Conclusion: Characteristic features of KDSS include older age, a greater likelihood of experiencing pericardial effusion, valve regurgitation, cardiac enlargement, CALs, and IVIG resistance. KD patients with a hypercoagulable state during the acute phase are at a higher risk of developing KDSS.
Introduction
Kawasaki Disease (KD) is an acute, self-limiting febrile illness of unknown etiology, primarily affecting children under the age of five. It is currently the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children in developed countries (1). In recent years, some KD patients have been reported to experience hemodynamic instability during the acute phase of the disease. Sporadic cases of KD with shock syndrome were documented in the mid-1990s (2–5). Kanegaye et al. further defined Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome (KDSS) in 2009 (6), noting that it was associated with more severe laboratory inflammatory markers, larger coronary artery lesions (CALs), mitral valve regurgitation, and an increased risk of prolonged myocardial dysfunction (6–10). Approximately 7% of KD patients develop KDSS (6). Clinical features of KDSS include poor perfusion or shock-like states, which may present early with atypical KD symptoms, making it challenging to diagnose (11). Recent studies have also highlighted difficulties in early recognition, delayed treatment, and an increased need for IVIG retreatment in KDSS cases in North America and Taiwan (5–7, 9, 12). Therefore, early identification and treatment of KDSS patients are crucial to reducing systemic and vascular inflammation.
However, research on predicting KDSS is relatively limited. A case-control study found that KD patients with IL-6 levels higher than 66.7 pg/ml, IL-10 levels higher than 20.85 pg/ml, and IFN-γ levels higher than 8.35 pg/ml are at a higher risk of developing KDSS (13). However, these findings were limited by a small sample size and costly indexes. Moreover, previous studies have summarized the clinical characteristics of KDSS but have not developed a useful predictive model for KDSS. Therefore, an effective and inexpensive predictive indicator is needed to guide clinical work for early KDSS prediction.
It is well-known that acute inflammatory reactions can upregulate cytokine expression and activate the coagulation system (14). In a study of critically ill patients, Ogura et al. found that coagulation abnormalities were associated with an increase in the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score, reflecting systemic inflammatory response syndrome (15). Furthermore, the relationship between immune system activation and the coagulation system is evident in systemic autoimmune or immune-mediated diseases. Encouragingly, our previous studies, along with others, have found that the balance between the coagulation and fibrinolysis systems is disrupted during the acute phase of KD (16–22). Consequently, we speculate that this condition may be more severe in patients with KDSS, and these coagulation-related indicators could serve as predictors for KDSS in clinical settings.
Therefore, in the present study, we prospectively investigated the coagulation profiles in patients with KDSS to test the hypothesis that coagulation-related indicators are valuable for predicting KDSS for the first time.
Material and methods
Subjects
KD patients who visited the West China Second Hospital of Sichuan University between April 2015 and October 2020 were prospectively recruited.
Inclusion criteria mandated patients to have a fever and to meet at least 4 out of the 5 diagnostic criteria for KD (rash, bilateral conjunctival injection, cervical lymph node involvement, mucous membrane changes, and limb changes), or at least 3 criteria along with documented coronary artery abnormalities on echocardiography, according to the American Heart Association guidelines (23). Structured questionnaires with pre-coded questions including basic demographic information, clinical manifestations, hematological examination results, treatment and follow-up outcomes, were used for data collection. All questionnaires were pretested and revised accordingly. Data collection was performed by two proficient physicians. The questionnaires were double-checked to assure its completeness. Informed written consent was obtained from parents after the nature of this study had been fully explained to them. The study was approved by the University Ethics Committee on Human Subjects at Sichuan University. All research was performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. During the COVID-19 pandemic, each patient underwent a pre-admission COVID-19 test, with all results indicating negativity prior to hospital admission.
The exclusion criteria encompassed patients with known congenital or chronic hematological disorders affecting the coagulation cascade, end-stage renal disease necessitating dialysis, acute or chronic hepatic failure, and autoimmune diseases. Additionally, individuals who had recently undergone surgery, patients with infectious or inflammatory conditions, and those receiving oral anticoagulants or heparin therapy were also excluded. Ultimately, a total of 523 patients were included in the study. Patients with Kawasaki Disease were categorized into two groups: those with Kawasaki Disease complicated by shock (KDSS group) and those without shock (non-KDSS group). In accordance with previously published guidelines, KDSS is defined as the presence of hypotension and shock (10). We diagnose KDSS if at least one of the following criteria is met: age-specific systolic hypotension (infants 0–28 days, <60 mmHg; infants aged 1–12 months, <70 mmHg; children aged 1–10 years, <70 mmHg + 2 times the age; children >10 years, ≤90 mmHg) (24, 25), a decrease in systolic blood pressure of ≥20% from baseline, or clinical symptoms of poor perfusion (tachycardia, prolonged capillary refill time, cold extremities, decreased pulse, oliguria, or altered mental status), regardless of blood pressure measurements (26).
The following data were collected for all patients: age, gender, typical clinical symptoms of KD, the presence of complete or incomplete KD, and IVIG resistance status. Echocardiographic data, including pericardial effusion, valvular regurgitation, cardiac enlargement, and coronary artery abnormalities, were also recorded. Laboratory parameters assessed in the results included white blood cell count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), hemoglobin levels, platelet count, transaminases, albumin levels, total bilirubin, urea, creatinine, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), and coagulation function assessment. All laboratory parameters were collected prior to the onset of KDSS or IVIG therapy.
All patients received a continuous intravenous infusion of 2 g/kg of IVIG and 30–50 mg/kg/day of aspirin for a period of 24 h, which was continued until the cessation of fever. All KDSS patients received fluid resuscitation and vasoactive agents were given if the fluid resucitation did not work. Initial IVIG resistance was defined as the recurrence or persistence of fever or other clinical symptoms of KD for at least 36 h but not exceeding 7 days after the completion of the first intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment. For patients exhibiting initial IVIG resistance, a second dose of IVIG (2 g/kg as a single intravenous infusion) was administered as per the expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of KD in China. Furthermore, in cases where patients continued to experience recurrent or persistent fever after the second IVIG administration, a pulse intravenous injection of methylprednisolone (10–30 mg/kg/day) was administered for a consecutive 3 days, followed by a gradual transition to oral prednisone (2 mg/kg/day) for a duration of 7 days.
As per the institutional protocol, standardized echocardiograms were obtained by experienced pediatric cardiologists during the acute/subacute phase and at the 6–8-week follow-up assessment in the cardiac outpatient clinic, continuing until coronary artery abnormalities were resolved. Coronary artery abnormalities were defined based on dimension Z-scores (normalized to body surface area) as follows: no involvement (Z-score <2.0), dilatation (Z-score ≥2.0 to <2.5), and aneurysm (Z-score ≥2.5), with giant aneurysms defined as a Z-score ≥10, depending on the maximum internal diameter of the right coronary artery, left anterior descending branch, and left circumflex artery.
Statistics
Data analysis was performed with SPSS 27.0. (IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0, Armonk, NY, IBM Corp.). Descriptive statistics for continuous variables were presented as medians (interquartile range, IQR) or means (standard deviations), while categorical variables were expressed as frequencies (%). Group differences in demographic characteristics, clinical presentations, and laboratory data were assessed using chi-square tests and unpaired Student's t-tests or Mann–Whitney U-tests as appropriate.
In the univariate analysis, key indicators that exhibited differences but lacked correlation with coagulation parameters were subjected to multivariable logistic regression analysis separately in order to identify independent predictive factors for the occurrence of KDSS. The predictive value of PT, d-dimer, FDP, and ATIII for KDSS occurrence was compared, and the optimal cutoff values and their predictive accuracy were determined through ROC analysis. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), diagnostic accuracy, odds ratio (OR), area under the curve (AUC) of the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve, and Youden's Index were evaluated. A significance level of p < .05 was considered statistically significant. The performance differences between different ROC curves were compared using the Delong test.
Results
The clinical features and serum coagulation profiles of patients with KDSS
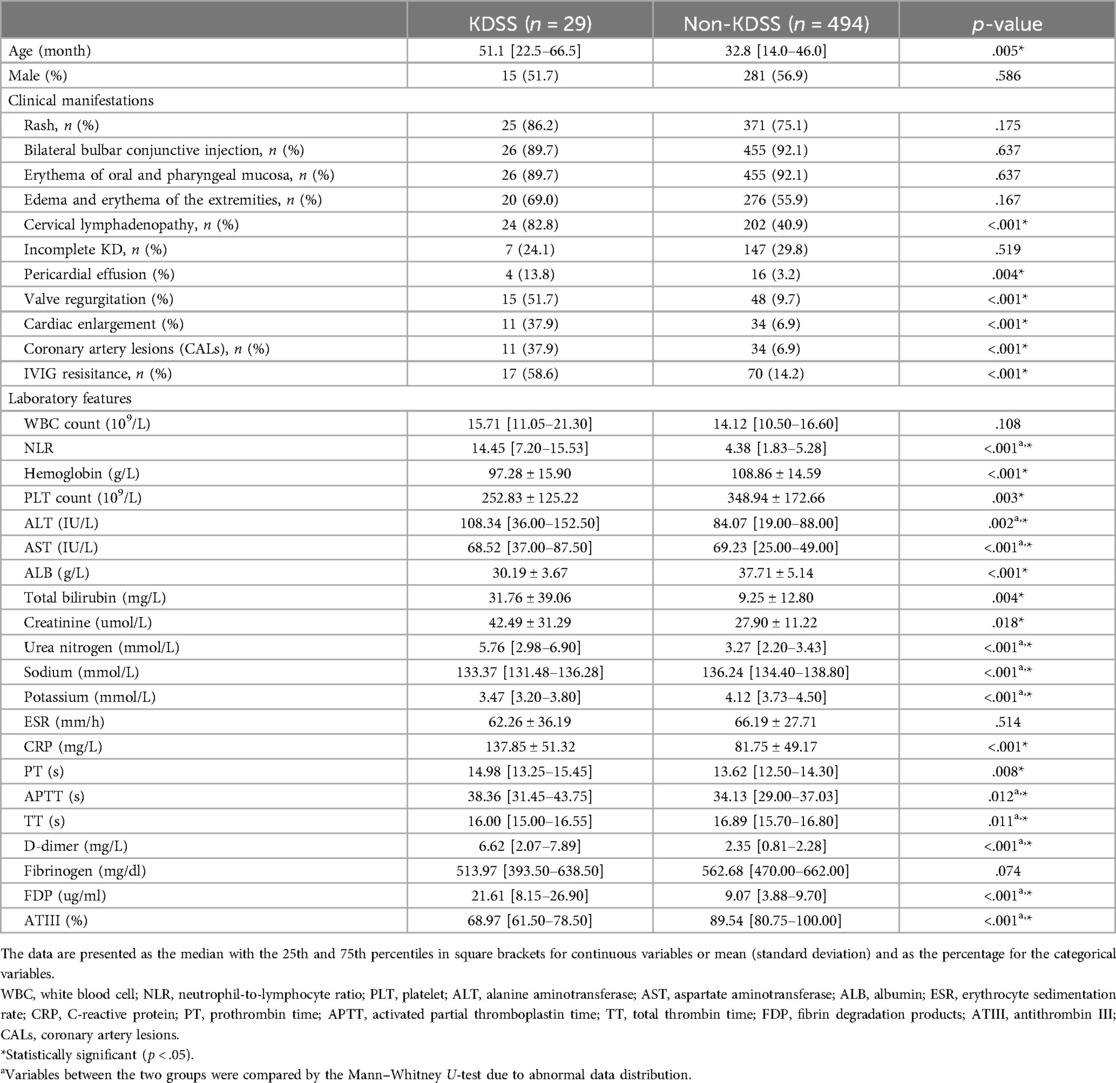
As shown in Table 1, the KDSS group comprised 29 individuals, while the non-KDSS group included 494 individuals. For patients with KDSS, all patients received volume resuscitation, 11 cases (37.9%) received vasoactive infusions. There were no significant differences between the KDSS group and the non-KDSS group regarding gender, typical clinical presentations excluding cervical lymphadenopathy, and the incidence of incomplete Kawasaki disease. However, the KDSS group presented with older age and had a higher proportion with cervical lymphadenopathy. The incidences of pericardial effusion, valvular regurgitation, cardiac enlargement, CALs, and IVIG resisitance in the KDSS group were significantly higher than the non-KDSS group.Children in the KDSS group showed significant elevations in NLR, ALT, Total bilirubin, Creatinine, Urea nitrogen, and CRP, while Hemoglobin, PLT, AST, Sodium, and Potassium were significantly lower (p < .05).
Serum coagulation levels for predicting KDSS
The impact on the coagulation system was assessed by evaluating the coagulation profile of the KDSS group and the non-KDSS group. Children in the KDSS group had significantly longer PT (14.98 [13.25–15.45] s vs. 13.62 [12.50–14.30] s, p = .008), APTT (38.36 [31.45–43.75] s vs. 34.13 [29.00–37.03] s, p = .012), and shorter TT (16.00 [15.00–16.55] s vs. 16.89 [15.70–16.80] s, p = .011). D-dimer (6.62 [2.07–7.89] mg/L vs. 2.35 [0.81–2.28] mg/L, p < .001) and FDP (21.61 [8.15–26.90] ug/ml vs. 9.07 [3.88–9.70] ug/ml, p < .001) were significantly elevated in the KDSS group, while ATIII activity (68.97% [61.50%–78.50%] vs. 89.54% [80.75%–100.00%], p < .001) was significantly decreased. Fibrinogen (513.97 [393.50–638.50] mg/dl vs. 562.68 [470.00–662.00] mg/dl) showed no significant difference (Table 1).
Multivariate logistic regression and ROC curve analysis were used to predict KDSS and validate the model's effectiveness
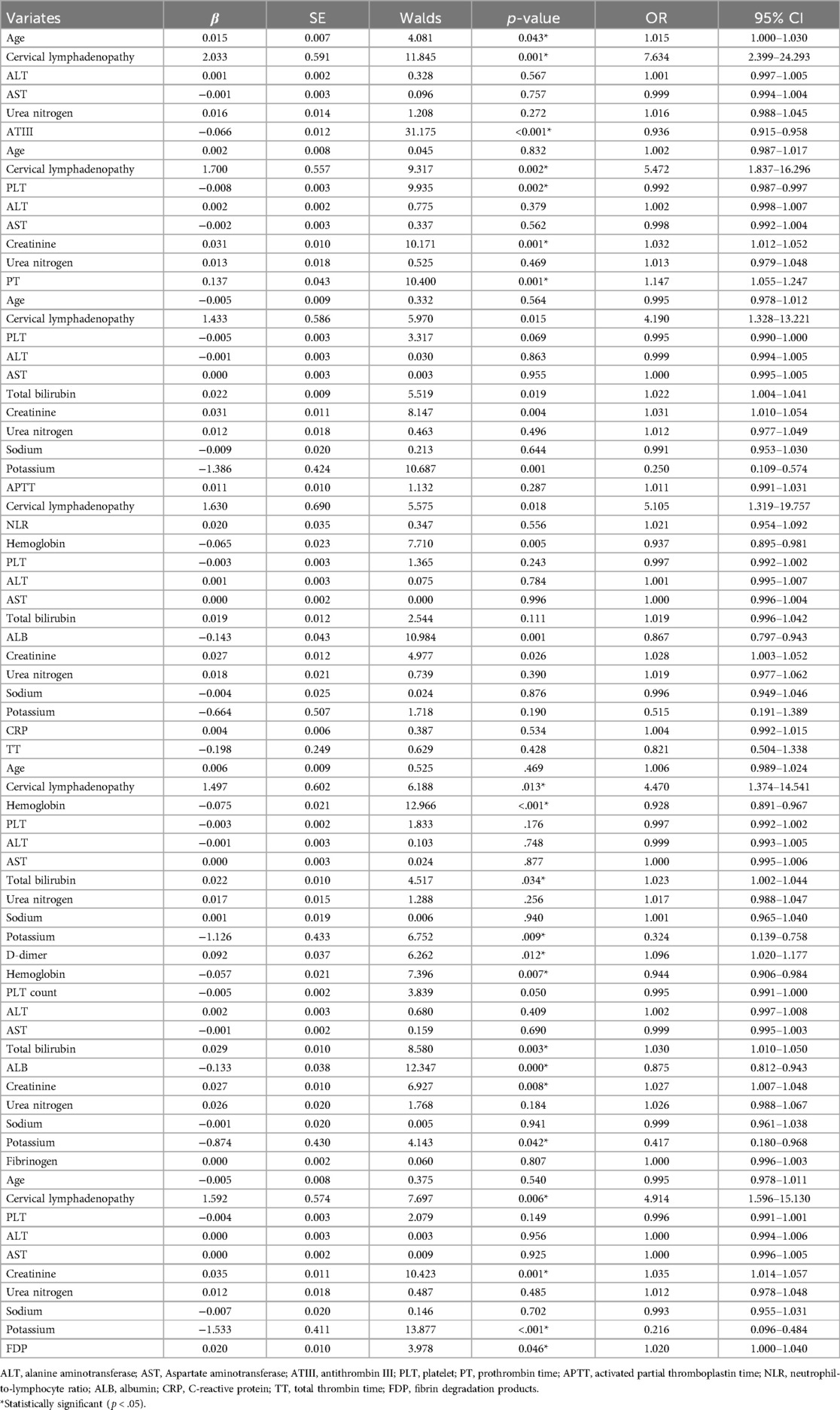
Pearson's correlation was applied to assess the correlation between individual factors and coagulation characteristics. Strong variables were excluded from the model (Supplementary Table S1). Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that longer PT, higher D-dimer and FDP levels, and lower ATIII activity were independent risk factors for the occurrence of KDSS, while APTT and TT did not reach significant differences in the multivariate logistic regression analysis (Table 2).
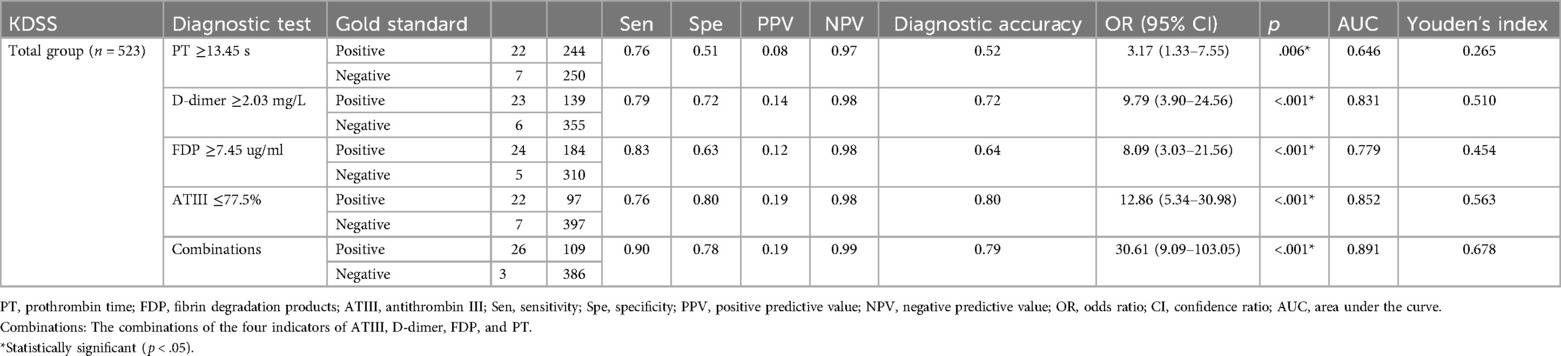
ROC curve analysis was conducted to assess the serum coagulation profile's predictive ability for KDSS occurrence. The areas under the curves (AUC) for PT, D-dimer, FDP, and ATIII in predicting KDSS occurrence were 0.646, 0.831, 0.779, and 0.852, respectively. The cutoff values for PT, D-dimer, FDP, and ATIII were 13.45 s, 2.03 mg/L, 7.45 ug/ml, and 77.5%, respectively, with sensitivities of 76%, 79%, 83%, and 76%, and specificities of 51%, 72%, 63%, and 80%, respectively (Table 3 and Figure 1). When we performed a combined ROC curve analysis of the four indicators, the AUC was 0.891, with a sensitivity of 0.90 and a specificity of 0.78. The Delong test showed that the combined analysis of the four indicators was significantly better than the analysis of each indicator individually (Table 3 and Supplementary Data Sheet S1).
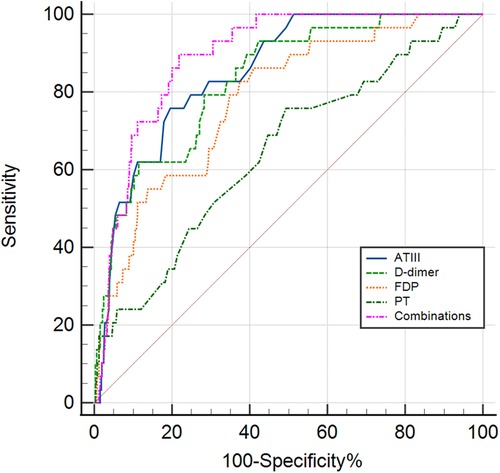
Figure 1. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for coagulation profiles in predicting the KDSS group and non-KDSS group. ATIII, antithrombin III; FDP, fibrin degradation products; PT, prothrombin time; Combinations, the combinations of the four indicators of ATIII, D-dimer, FDP and PT.
Discussion
In this study, we observed a higher incidence of adverse events, including IVIG resistance and cardiac complication (pericardial effusion, valvular regurgitation, cardiac enlargement, coronary artery damage), in patients belonging to the KDSS group. These Patients exhibited significantly extensive inflammatory burden. Notably, our study is the first to comprehensively describe coagulation profiles in KDSS patients and further support the hypothesis of significant differences in their coagulation profile: longer PT and APTT durations, elevated D-dimer and FDP levels, as well as reduced fibrinogen levels and ATIII activity. Additionally, through multivariate logistic regression analysis, we identified longer PT duration, higher D-dimer levels, and lower ATIII activity as independent risk factors for developing KDSS. The ROC curve analysis results showed that D-dimer and ATIII activity had good predictive value for the occurrence of KDSS, and the combined analysis of the four indicators had the best predictive performance. Our study results suggest that patients with impaired coagulation function may require more aggressive treatment to reduce the likelihood of developing KDSS.
Currently, the pathogenesis of KDSS remains elusive; however, it is speculated to involve multiple mechanisms, including severe systemic vasculitis-induced capillary leakage, immune dysregulation, systemic inflammatory responses due to infections, myocardial dysfunction, and abnormal cytokine regulation (27, 28). In a study conducted by Yandie Li et al., significantly higher levels of cytokines such as IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were observed in the serum of KDSS patients compared to the control group consisting of KD patients (14). Our study revealsed that the KDSS group exhibited significantly elevated levels of NLR and CRP along with a more severe degree of anemia. These findings have been closely associated with increased cytokine levels. For instance, the pronounced anemia observed in KDSS patients may result from the upregulation of hepcidin induced by IL-6 (29). CRP levels are positively correlated with IL-6 (30). Elevated IL-6 levels promote chronic inflammation, leading to multi-organ damage and failure. With sustained elevation of IL-6, patients may experience hypoalbuminemia, hyponatremia, and anemia (31). Our study results indicate that KDSS patients in the study group exhibited significantly lower levels of blood sodium, blood potassium, and albumin compared to the KD group, reflecting the substantial elevation of cytokines, including IL-6, in KDSS patients. Furthermore, higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8, were found in patients with elevated D-dimer levels. TNF-α is one of the key cytokines in KD and can induce vascular endothelial cell damage through oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis (19). The vascular endothelium is covered with a network of glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins (glycocalyx), and if the glycocalyx is damaged due to KD vasculitis, endothelial anticoagulant properties are compromised, leading to platelet aggregation abnormalities, a procoagulant state, and increased fibrinolysis (32). In consist with above findings, the present study clinically verified our primary hypothesis that patients with KDSS had significantly decreased PLT levels and elevated D-dimer levels.The condition in children and adolescents associated with COVID-19, known as Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C), is characterized by acute systemic inflammation and multi-organ dysfunction. A significant proportion of MIS-C patients exhibit similar manifestations to those observed in KDSS, with many MIS-C cases presenting signs of coagulation abnormalities (prolonged PT or APTT, elevated D-dimer) (33).
In our study, patients in the KDSS group also displayed marked coagulation dysfunction, suggesting that the occurrence of coagulation abnormalities is not incidental and may be associated with the body's excessive inflammatory response. Therefore, coagulation dysfunction can serve as an effective indicator for predicting the development of KDSS. Moreover, prolonged PT and APTT may be attributed to reduced synthesis and/or increased consumption of coagulation factors (34). In clinical practice, it is well known that KD patients often exhibit moderate liver damage accompanied by hepatomegaly. Activation of NK cells by bacterial superantigens can lead to their accumulation in endothelial cells and hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells, contributing to vascular endothelial cell damage and hepatocellular injury associated with KD (35). The significant increase in neutrophils in KD patients results in the substantial production of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which act as procoagulants, creating a prothrombotic environment. Additionally, NETs can stimulate the activation of the complement pathway. Neutrophils, NETs, complement, and thrombus formation all play roles in liver damage (36). The liver, being involved in maintaining coagulation function, contributes to the synthesis and metabolism of clotting factors such as PT and APTT. Therefore, when KD patients experience concomitant liver dysfunction, it can impact coagulation function since most clotting factors are synthesized in the liver, affecting their production. The association between liver damage and alterations in coagulation function highlights the intricate interplay between immune responses, liver function, and coagulation in KD patients. In fact, in our study, patients in the KDSS group had significantly elevated ALT and total bilirubin, hinting liver dysfunction. Overall, the prolongation of PT and APTT may also be partially attributed to more severe liver dysfunction in KDSS patients, reflecting the severe inflammatory reaction.
Due to the higher incidence of IVIG resistance and cardiovascular complications such as CALs in KDSS patients, early identification of KDSS is crucial to mitigate adverse outcomes. However, there is currently limited research on predicting KDSS, with most relevant studies primarily summarizing the epidemiology and certain laboratory or imaging differences in KDSS patients (5–7, 9, 10, 28, 37–42). A case-control study encompassing 27 KDSS patients and 43 KD patients as controls revealed distinct characteristics of KDSS, including heightened cytokine production, a higher likelihood of IVIG unresponsiveness, and an increased incidence of coronary artery abnormalities. These findings align with our study results. The ROC curve analysis demonstrated that the sensitivity and specificity of IL-6 at 66.7 pg/ml, IL-10 at 20.85 pg/ml, and IFN-γ at 8.35 pg/ml for predicting KDSS were 85.2% and 62.8%, 66.7% and 83.7%, and 74.1% and 74.4%, respectively (13). However, these predictive indicators either exhibited lower sensitivity or lower specificity. In another retrospective analysis involving 13 KDSS patients, 35 patients with infectious shock, and 91 control KD patients, ROC curve indicated that the optimal ESR cutoff value for diagnosing KDSS was 56.0 mm/h (sensitivity 75.0%, specificity 100.0%), and the optimal creatinine cutoff value for diagnosing TSS was 0.695 (sensitivity 76.9%, specificity 84.6%). Historically, there has been a lack of relevant research on predicting KDSS occurrence through coagulation profiles. Our study represents the first comprehensive depiction of the coagulation function in KDSS patients, revealing that factors such as antithrombin III (ATIII) can be utilized for predicting KDSS development, exhibiting high predictive efficacy.
The strengths of this study lie in its demonstration of the predictive value of the coagulation profile for KDSS occurrence, along with a relatively large sample size. However, the study has some limitations. First, it was conducted at a single institution, which may introduce selection bias as the hospital is a major pediatric medical center in the southwestern region of China, possibly leading to a higher number of critically ill patients. Despite these limitations, our study is the first to reveal the predictive value of the coagulation profile for the occurrence of KDSS and provides evidence of significant differences in PT, APTT, TT, D-dimer, FDP levels, and ATIII activity between the KDSS group and non-KDSS group. These changes may serve as supplementary laboratory biomarkers for predicting KDSS occurrence. Furthermore, D-dimer and ATIII activity as a single biomarker for predicting KDSS occurrence may have relatively high sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusion
In summary, KDSS is characterized by older age, a higher likelihood of pericardial effusion, valvular regurgitation, cardiac enlargement, coronary artery damage, and IVIG resistance. There is an increased risk of KDSS occurrence in older children with KD who exhibit a procoagulant state during the acute phase.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the University Ethics Committee on Human Subjects at Sichuan University. All research was performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Author contributions
BL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. XL: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. SS: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. PW: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. MW: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. LL: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. YH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. KZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82370236, No. 82070324), Science-Technology Support Plan Projects in Sichuan Province (2023YFH0036).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2024.1450710/full#supplementary-material
References
1. McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2017) 135(17):e927–99. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000484
2. Gamillscheg A, Zobel G, Karpf EF, Dacar D, Beitzke A, Stein JI, et al. Atypical presentation of Kawasaki disease in an infant. Pediatr Cardiol. (1993) 14(4):223–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00795375
3. Davies HD, Kirk V, Jadavji T, Kotzin BL. Simultaneous presentation of Kawasaki disease and toxic shock syndrome in an adolescent male. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (1996) 15(12):1136–8. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199612000-00021
4. Senzaki H, Suda M, Noma S, Kawaguchi H, Sakakihara Y, Hishi T. Acute heart failure and acute renal failure in Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr Jpn. (1994) 36(4):443–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.1994.tb03220.x
5. Dominguez SR, Friedman K, Seewald R, Anderson MS, Willis L, Glode MP. Kawasaki disease in a pediatric intensive care unit: a case-control study. Pediatrics. (2008) 122(4):e786–90. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-1275
6. Kanegaye JT, Wilder MS, Molkara D, Frazer JR, Pancheri J, Tremoulet AH, et al. Recognition of a Kawasaki disease shock syndrome. Pediatrics. (2009) 123(5):e783–9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-1871
7. Gamez-Gonzalez LB, Murata C, Munoz-Ramirez M, Yamazaki-Nakashimada M. Clinical manifestations associated with Kawasaki disease shock syndrome in Mexican children. Eur J Pediatr. (2013) 172(3):337–42. doi: 10.1007/s00431-012-1879-1
8. Lin MT, Fu CM, Huang SK, Huang SC, Wu MH. Population-based study of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome in Taiwan. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2013) 32(12):1384–6. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31829efae6
9. Chen PS, Chi H, Huang FY, Peng CC, Chen MR, Chiu NC. Clinical manifestations of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: a case-control study. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2015) 48(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2013.06.005
10. Ma L, Zhang YY, Yu HG. Clinical manifestations of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome. Clin Pediatr. (2018) 57(4):428–35. doi: 10.1177/0009922817729483
11. Takahashi K, Oharaseki T, Yokouchi Y, Yamada H, Shibuya K, Naoe S. A halfcentury of autopsy results–incidence of pediatric vasculitis syndromes, especially Kawasaki disease. Circ J. (2012) 76(4):964–70. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-11-0928
12. Taddio A, Rossi ED, Monasta L, Pastore S, Tommasini A, Lepore L, et al. Describing Kawasaki shock syndrome: results from a retrospective study and literature review. Clin Rheumatol. (2017) 36(1):223–8. Li et al. Pediatric Rheumatology. (2019) 17:1 (Page 7 of 9). doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3316-8
13. Li Y, Zheng Q, Zou L, Wu J, Guo L, Teng L, et al. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: clinical characteristics and possible use of IL-6, IL-10 and IFN-γas biomarkers for early recognition. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. (2019) 17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12969-018-0303-4
14. Levi M, van der Poll T, ten Cate H, van Deventer SJ. The cytokinemediated imbalance between coagulant and anticoagulant mechanisms in sepsis and endotoxaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. (1997) 27(1):3–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.1997.570614.x
15. Ogura T, Nakamura Y, Takahashi K, Nishida K, Kobashi D, Matsui S. Treatment of patients with sepsis in a closed intensive care unit is associated with improved survival: a nationwide observational study in Japan. J Intensive Care. (2018) 6:57. doi: 10.1186/s40560-018-0322-8
16. Shao S, Yang L, Liu X, Liu L, Wu M, Deng Y, et al. Predictive value of coagulation profiles for both initial and repeated immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease: a prospective cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2021) 32(6):1349–59. doi: 10.1111/pai.13495
17. Sakurai Y, Takatsuka H, Onaka M, Takada M, Nishino M. Persistent endothelial damage after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Kawasaki disease. Inter Arch Allergy Immunol. (2014) 165(2):111–8. doi: 10.1159/000368402
18. Kong WX, Ma FY, Fu SL, Wang W, Xie CH, Zhang YY, et al. Biomarkers of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. World J Pediatr. (2019) 15(2):168–75. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00234-6
19. Masuzawa Y, Mori M, Hara T, Inaba A, Oba MS, Yokota S. Elevated D-dimer level is a risk factor for coronary artery lesions accompanying intravenous immunoglobulin-unresponsive Kawasaki disease. Therap Apheresis Dia. (2015) 19(2):171–7. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12235
20. Sakai M, Asayama K, Otabe T, Kohri T, Shirahata A. Low tissue plasminogen activator relative to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 as a marker of cardiac complication in children with Kawasaki disease. Clin Appl Throm. (2001) 7(3):214–8. doi: 10.1177/107602960100700306
21. Zhou Y, Wang S, Zhao J, Fang P. Correlations of complication with coronary arterial lesion with VEGF, PLT, D-dimer and inflammatory factor in child patients with Kawasaki disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2018) 22(16):5121–6. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201808_15706
22. Imamura T, Yoshihara T, Yokoi K, Nakai N, Ishida H, Kasubuchi Y. Impact of increased D-dimer concentrations in Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr. (2005) 164(8):526–7. doi: 10.1007/s00431-005-1699-7
23. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the committee on rheumatic fever, endocarditis, and Kawasaki disease, council on cardiovascular disease in the young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics. (2004) 114:1708–33. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-2182
24. Dieckmann RA. Pediatric assessment. In: Gausche-Hill M, Fuchs S, Yamamoto L, editors. APLS: The Pediatric Emergency Medicine Resource. 4th ed. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett (2007). p. 20–51.
25. Haque IU, Zaritsky AL. Analysis of the evidence for the lower limit of systolic and mean arterial pressure in children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2007) 8:138–44. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000257039.32593.DC
26. Fitzmaurice L, Gerardi JM. Cardiovascular system. In: Gausche-Hill M, Fuchs S, Yamamoto L, editors. APLS: The Pediatricemergency Medicine Resource. 4th ed. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett (2007). p. 106–45.
27. Taddio A, Rossi ED, Monasta L, Pastore S, Tommasini A, Lepore L, et al. Describing Kawasaki shock syndrome: results from a retrospective study and literature review. Clin Rheumatol. (2016) 36(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3316-8
28. Natterer J, Perez M-H, Di Bernardo S. Capillary leak leading to shock in Kawasaki disease without myocardial dysfunction. Cardiol Young. (2012) 22(3):349–52. doi: 10.1017/S1047951111001314
29. Kuo HC, Yang YL, Chuang JH, Tiao MM, Yu HR, Huang LT, et al. Inflammation-induced hepcidin is associated with the development of anemia and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. J Clin Immunol. (2012) 32(4):746–52. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9668-1
30. Mitani Y, Sawada H, Hayakawa H, Aoki K, Ohashi H, Matsumura M, et al. Elevated levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and serum amyloid-a late after Kawasaki disease: association between inflammation and late coronary sequelae in Kawasaki disease. Circulation. (2005) 111(1):38–43. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000151311.38708.29
31. Schmidt-Arras D, Rose-John S. IL-6 Pathway in the liver: from physiopathology to therapy. J Hepatol. (2016) 64:1403–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.004
32. Selleri C, Sato T, Anderson S, Young NS, Maciejewski JP. Interferongamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppress both early and late stages of hematopoiesis and induce programmed cell death. J Cell Physiol. (1995) 165(3):538–46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041650312
33. Jiang L, Tang K, Levin M, Irfan O, Morris SK, Wilson K, et al. COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents. Lancet Infect Dis. (2020) 20(11):e276–88. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30651-4
34. Tripodi A, Mannucci PM. The coagulopathy of chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. (2011) 365(2):147–56. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1011170
35. Seki S, Habu Y, Kawamura T, Takeda K, Dobashi H, Ohkawa T, et al. The liver as a crucial organ in the first line of host defense: the roles of Kupffer cells, natural killer (NK) cells and NK1.1 Ag+ T cells in T helper 1 immune responses. Immunol Rev. (2000) 174:35–46. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2002.017404.x
36. Maxwell AJ, Ding J, You Y, Dong Z, Chehade H, Alvero A, et al. Identification of key signaling pathways induced by SARS-CoV2 that underlie thrombosis and vascular injury in COVID-19 patients. J Leukoc Biol. (2021) 109(1):35–47. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4COVR0920-552RR
37. Liang YC, Chang CH, Lin MT, Kao FY, Huang SK, Wu MH. Shock and unresponsiveness to repeated courses of intravenous immunoglobulin in Kawasaki disease: a nationwide database study. Pediatr Res. (2020) 87(5):961–6. doi: 10.1038/s41390-019-0668-1
38. Yang HF, Chen WL, Chang CN, Chen SJ, Fan HC. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: case report. Paediatr Int Child Health. (2016) 36(1):76–8. doi: 10.1179/2046905515Y.0000000002
39. Lamrani L, Manlhiot C, Elias MD, Choueiter NF, Dionne A, Harahsheh AS, et al. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome vs classical Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis and comparison with SARS-CoV-2 multisystem inflammatory syndrome. Can J Cardiol. (2021) 37(10):1619–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2021.05.014
40. Schuster JE, Palac HL, Innocentini N, Rowley AH, Young LT, Shulman ST. Hyponatremia is a feature of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: a case-control study. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. (2017) 6(4):386–8. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piw081
41. Lin YJ, Cheng MC, Lo MH, Chien SJ. Early differentiation of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome and toxic shock syndrome in a pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2015) 34(11):1163–7. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000852
Keywords: Kawasaki disease, coronary artery lesions, antithrombin III, D-dimer, coagulation profile
Citation: Li B, Liu X, Shao S, Wu P, Wu M, Liu L, Hua Y, Duan H, Zhou K and Wang C (2024) Predictive value of coagulation profiles for Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: a prospective cohort study. Front. Pediatr. 12:1450710. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1450710
Received: 18 June 2024; Accepted: 5 August 2024;
Published: 16 August 2024.
Edited by:
Nazmi Narin, Izmir Katip Celebi University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Silin Pan, Qingdao University, ChinaSertac Hanedan Onan, University of Health Sciences, Türkiye
Copyright: © 2024 Li, Liu, Shao, Wu, Wu, Liu, Hua, Duan, Zhou and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongyu Duan, NDk1NDI5OTc4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Kaiyu Zhou, a2FpeXV6aG91MzEzQDE2My5jb20=; Chuan Wang, V2FuZ2NodWFuMTMwOEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Bowen Li1,2,3,4,5,†
Bowen Li1,2,3,4,5,† Xiaoliang Liu
Xiaoliang Liu Lei Liu
Lei Liu Hongyu Duan
Hongyu Duan Kaiyu Zhou
Kaiyu Zhou Chuan Wang
Chuan Wang