
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Pediatr. , 11 December 2024
Sec. Pediatric Nephrology
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2024.1415064
Background: Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease (ADTKD) caused by REN-causing pathogenic variants (ADTKD-REN) is a rare group of heritable diseases. ADTKD-REN often manifests in childhood with symptoms such as mild hypotension, chronic kidney disease, hyperkalemia, anemia, and acidosis. The diagnosis of ADTKD-REN remains challenging.
Case presentation: We describe a 14-year-old boy with acute kidney injury who was found to have a heterozygous missense mutant c.1085G>A;p.Cys362Tyr (not previously reported in the literature) through Sanger sequencing genetic testing. This confirmed a genetic disorder with a probable autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Notably, despite a family history of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, he was diagnosed with ADTKD.
Conclusion: This case identified a new variant in the REN gene, expanding the known spectrum of REN pathogenic variants. In addition, the importance of family history and genetic testing in confirming the diagnosis is emphasized. Genetic sequencing should be pursued when there are indications for testing.
The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) has risen significantly in recent years, with an increasing number of patients requiring renal replacement therapy (1). The prevention and treatment of CKD have become significant public health challenges worldwide. Research has extensively focused on primary kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, and hypertensive kidney damage. However, with the progress of genetic technology, the proportion of gene nephropathy in the etiology of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) has also gradually increased. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease (ADTKD) is a rare hereditary disorder characterized by progressive loss of kidney function, non-significant urinalysis, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis.
The 2015 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guideline systematically addresses autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial nephropathy (2); five ADTKD-causing genes (MUC1, UMOD, REN, HNF1B, and SEC61A1) and their corresponding genotypes have been identified (3). These genes encode various proteins with renal and extra-renal functions, resulting in distinct clinical manifestations. Among these, pathogenic variants in UMOD, MUC1, and REN are the most prevalent causes of ADTKD. Renin synthesis is a critical step in the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), and in ADTKD-REN, heterozygous REN pathogenic variants lead to reduced renin production. This can result in mild hyperkalemia, anemia, acidemia, and a predisposition to acute kidney injury (4).
In this case report, a 14-year-old male adolescent was genetically tested and found to have a heterozygous missense variant in the REN gene (c.1085G>A; p.Cys362Tyr), a pathogenic variant not previously documented in the literature. The discovery enriches the genetic database of ADTKD and further suggests that genetic testing is the most effective diagnostic tool.
A 14-year-old boy presented with intermittent fever for over a month, elevated blood creatinine for 10 days, and abdominal pain for 3 days. Laboratory tests revealed an influenza A virus infection and right lung pneumonia confirmed by chest CT. Kidney function showed a creatinine level of 137.7 μmol/L (1.56 mg/dl) and uric acid of 732 μmol/L (12.2 mg/dl). The patient was treated with oseltamivir and ceftriaxone sodium on an outpatient basis with no improvement in symptoms. Therefore, he came to our hospital.
The physical examination was unremarkable. Laboratory data showed total protein of 70.4 g/L, albumin of 44.6 g/L, creatinine of 166.3 μmol/L (1.88 mg/dl), uric acid of 796.9 μmol/L (13.28 mg/dl), blood potassium of 4.7 mmol/L, carbon dioxide combining power of 20.2 mmol/L, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 56.02 ml/min/1.73 m2 (Figure 1). Normal or negative findings in routine urinalysis, serum complement, antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA), antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), rheumatoid factor, T-cell testing for tuberculosis infection, and blood sedimentation rate. A kidney ultrasound revealed slightly enhanced echogenicity in the parenchyma of both kidneys and disorganized sinusoidal structures. A cardiac ultrasound suggested a bicuspid aortic valve with increased supravalvular flow velocity and low to moderate regurgitation. An abdominal ultrasound showed multiple gallbladder stones with no apparent abnormalities in the liver, pancreas, and spleen. Due to the sustained elevation of serum creatinine levels from baseline, we considered the patient to be experiencing acute kidney injury. Notably, he had a family history of polycystic kidneys.
Immunofluorescence microscopy revealed negative staining IgA, IgG, IgM, C3, C1q, Fibrin, HbcAg, HbsAg, Kappa, and Lambda. A light microscopic examination of the renal specimen, containing 33 glomeruli, showed global sclerosis in 12 glomeruli and segmental sclerosis in 1 glomerulus. The remaining glomeruli exhibited no remarkable lesions. There was 5% tubular atrophy with few protein casts and red blood cell casts. No interstitial fibrosis was observed, and the renal arterioles appeared normal. Electron microscopy revealed marked vacuolar degeneration of the capillary endothelial cells. The basement membrane was predominantly thin, with a thickness of less than 250 nm, and exhibited segmental effacement of the podocyte foot process. No electron-dense deposits were observed. The findings could not exclude thin basement membrane nephropathy or Alport syndrome (Figure 2). Clinical data and blood samples were collected from the patient and his family for genetic testing using high-throughput sequencing and Sanger sequencing, respectively (Figure 3). A heterozygous missense variant (c.1085G>A;p.Cys362Tyr) was found in the REN gene, and a spontaneous heterozygous missense pathogenic variant was identified in the patient (Figure 4).
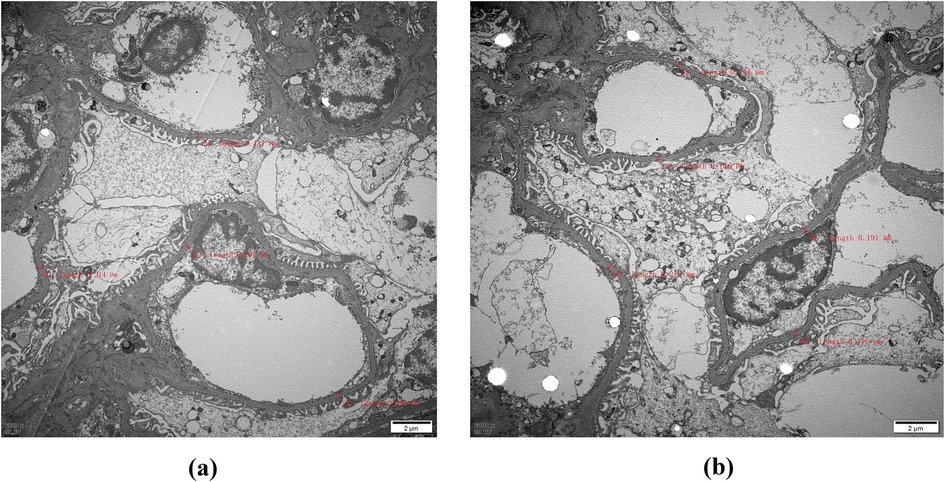
Figure 2. Electron microscopy: The red markings on (a) and (b) indicate that the thickness of the measured substrate film is less than 250 nm, with most samples being classified as thin. Therefore, it is imperative to conduct further investigations into thin basement membrane disease and Alport syndrome (magnification, ×6,000).
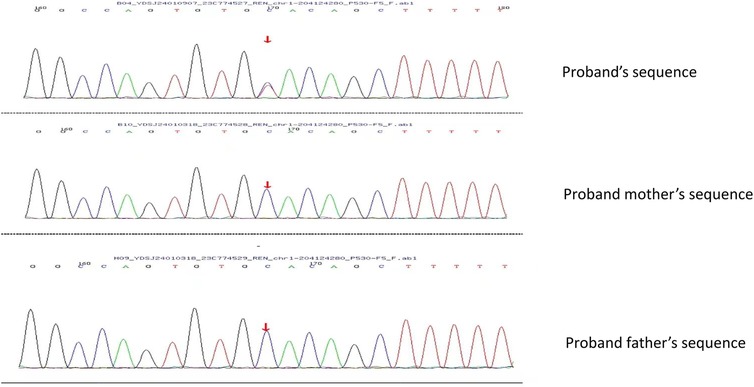
Figure 3. Using Sanger sequencing, it was verified that the bases shown in the peak graph were reverse complementary sequences of the base being tested. The proband had a missense pathogenic variant at nucleotide 1,085 from guanine G to adenine A, which resulted in amino acid 362 being changed from Cys to Tyr. No pathogenic variant was seen in the proband's father and mother at this locus.
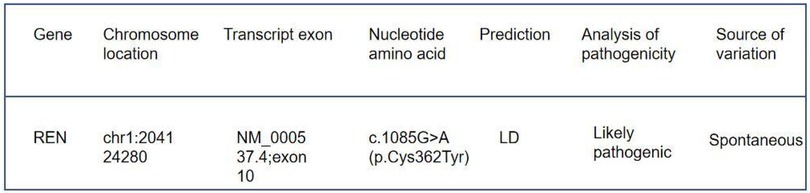
Figure 4. Genetic test results: the detected gene was REN, the pathogenic variant was heterozygous, the origin of the pathogenic variant was spontaneous, and the pathogenic variant was judged to be a suspected pathogenic variant according to American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines.
The patient was treated with intravenous methylprednisolone at 40 mg for 10 days, followed by a reduction in dose at 20 mg for 6 days. His renal function improved, with his creatinine levels decreasing to 100.3 μmol/L (1.13 mg/dl) and uric acid levels to 374.5 μmol/L (6.2 mg/dl). He was discharged from hospital on 16 mg of oral methylprednisolone, which was tapered off in the outpatient clinic.
ADTKD was first introduced in 1945 by Smith and Graham (5). It was originally named medullary cystic nephropathy based on imaging owing to a limited understanding of genetic diseases at the time. Currently, ADTKD, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), and Alport syndrome are considered the three major hereditary kidney diseases (6). Clinical manifestations of ADTKD tend to be non-specific and may not be evident on urinary examination and renal ultrasonography, yet the disease progresses slowly and inevitably to end-stage renal disease. ADTKD is associated with at least five pathogenic variants: UMOD, MUC1, REN, HNF1B, and the rare SEC61A1. As of the end of November 2022, 35 reports of pathogenic variants in the REN gene are documented in the Global Variome shared LOVD database, with 16 identified disease-causing variants (7).
The REN gene encodes prorenin, which is hydrolyzed to form renin, a key enzyme involved in the breakdown of angiotensinogen (8). Pathogenic variants in the REN gene lead to the production of aberrant renin that accumulates in cells, inducing apoptosis. These pathogenic variants manifest in two ways: the more common childhood or adolescent onset, often associated with acute kidney injury, anemia, gout, and hyperkalemia, and the adult onset, which resembles CKD (9). In this paper, we report the case of a male adolescent with acute kidney injury. We considered various factors, including primary kidney disease, drugs, infection, and metabolism disturbance. Combined with his family history, we speculated he might also have a polycystic kidney, prompting us to conduct a genetic examination. The result was surprising: despite a family history of polycystic kidney disease, the patient was confirmed to have ADTKD with a previously unreported pathogenic variant site. It remains unclear whether this missense pathogenic variant is entirely independent.
In summary, the patient presented with hyperuricemia and acute kidney injury at the age of 14 years. His urinary sediment was bland, and there was no hyperkalemia, anemia, or acidosis. There were no uric acid kidney stones present, suggesting that the patient did not have an overproduction of uric acid. Genetic testing revealed a p.Cys362Tyr variant in the REN gene. Neither of his parents had this variant. The renal biopsy revealed glomerulosclerosis in 12/33 glomeruli, with limited tubular atrophy and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. After treatment for acute kidney injury, the patient had baseline mild chronic kidney disease, with serum creatinine of 1.13 mg/dl. Based on the patient's clinical presentation, laboratory findings, and the results of the renal biopsy, we diagnosed the patient with chronic kidney disease. The viral infection resulted in AKI, which was identified as the causative factor for the patient's renal insufficiency rather than an etiological one. Consequently, we promptly withdrew hormone therapy at a later stage.
The finding of a new genetic variant in the REN gene (p.Cys362Tyr) requires further investigation to determine if this variant is causative or simply a non-pathogenic variant. In silico (computer-generated) scores can be calculated to determine if this amino acid change would result in a likely pathogenic or non-pathogenic pathogenic variant. In this case, the variant has a Rare Exome Variant Ensemble Learner (REVEL) score of 0.74, which is supportive of the variant being deleterious. The variant was not found in any other individuals in the gnomAD database, which is also supportive. In addition, the cysteine residue at 362 forms a disulfide bond with the cysteine residue at 325. A family has been reported with a similar phenotype and a pathogenic variant at p.Cys325Arg (11). Thus, in silico evidence would suggest that the pathogenic variant is causative. One must then compare the clinical findings in other patients with similar pathogenic changes. Rampoldi was the first to describe a pathogenic variant in the REN gene (p.L381P) as a cause of ADTKD. Živná et al. then described 15 individuals with pathogenic variants in the mature REN gene. All patients reported with REN pathogenic variants have presented after the age of 20 years, often with gout. They have experienced slowly progressive chronic kidney disease, leading to end-stage kidney disease at a mean age of 64 years (10). The patients have a bland urinary sediment and no hematuria.
Thus, there is strong evidence to suggest that the patient has ADTKD-REN. He has chronic kidney disease, bland urinary sediment, and hyperuricemia. An in silico examination suggests that the REN variant is causative. The patient presented earlier than other patients with a pathogenic variant in the mature REN variant. It is likely that the patient developed AKI from his viral illness and this led to the detection of his baseline mild chronic kidney disease. It is likely that the REN pathogenic variant predisposed him to acute kidney injury.
This case illustrates the importance of genetic testing in making a genetic diagnosis (11). Patients with pathogenic variants in the mature REN peptide, in general, have a good prognosis and only require symptomatic treatment (12). The patient should have close follow-up, though the literature would suggest that he should not require renal replacement therapy for many years.
The discovery of this case further expands the ADTKD-REN pathogenic variant database with a new missense pathogenic variant type. In conclusion, the clinical presentation of ADTKD is often unremarkable, leading to potential misdiagnosis. Nephrologists are encouraged to take a thorough patient history when suspecting the disease and to perform gene sequencing early.
The datasets generated and analyzed in this case report are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical concerns, as the study involves a single patient. Requests to access the datasets can be directed to the corresponding author, Zhijuan Hu, ataHV6aGlqdWFuMTk3MkAxNjMuY29t.
The studies involving humans were approved by Department of Nephrology, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang, China. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)' legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
JM: Writing – original draft. ZH: Writing – review & editing. QL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JinL: Writing – review & editing. JieL: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
ADTKD, autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease; ADPKD, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; RAS, renin–angiotensin system.
1. Bleyer AJ, Kmoch S. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease: of names and genes. Kidney Int. (2014) 86(3):459–61. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.125
2. Eckardt KU, Alper SL, Antignac C, Bleyer AJ, Chauveau D, Dahan K, et al. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease: diagnosis, classification, and management–A KDIGO consensus report. Kidney Int. (2015) 88(4):676–83. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.28
3. Devuyst O, Olinger E, Weber S, Eckardt K, Kmoch S, Rampoldi L, et al. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2019) 5:60. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0109-9
4. Clissold RL, Clarke HC, Spasic-Boskovic O, Brugger K, Abbs S, Bingham C, et al. Discovery of a novel dominant mutation in the REN gene after forty years of renal disease: a case report. BMC Nephrol. (2017) 18(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0631-5
5. Smith CH, Graham JB. Congenital medullary cysts of the kidneys with severe refractory anemia. Am J Dis Child. (1945) 69:369–77. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1945.02020180033006
6. Kidd K, Vylet'al P, Schaeffer C, Olinger E, Živná M, Hodaňová K, et al. Genetic and clinical predictors of age of ESKD in individuals with autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease due to UMOD mutations. Kidney Int Rep. (2020) 5(9):1472–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.06.029
7. Econimo L, Schaeffer C, Zeni L, Cortinovis R, Alberici F, Rampoldi L, et al. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease: an emerging cause of genetic CKD. Kidney Int Rep. (2022) 7(11):2332–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.08.012
8. Zivná M, Hůlková H, Matignon M, Hodanová K, Vylet'al P, Kalbácová M, et al. Dominant renin gene mutations associated with early-onset hyperuricemia, anemia, and chronic kidney failure. Am J Hum Genet. (2009) 85(2):204–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.07.010
9. Živná M, Kidd K, Kmoch S, Bleyer AJ. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease – REN. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews®. Seattle, WA: University of Washington (2011).
10. Živná M, Kidd K, Zaidan M, Vyleťal P, Barešová V, Hodaňová K, et al. An international cohort study of autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease due to REN mutations identifies distinct clinical subtypes. Kidney Int. (2020) 98(6):1589–604. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.06.041
11. Ottlewski I, Münch J, Wagner T, Schönauer R, Bachmann A, Weimann A, et al. Value of renal gene panel diagnostics in adults waiting for kidney transplantation due to undetermined end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. (2019) 96(1):222–30. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.01.038
12. Živná M, Kidd K, Kmoch S, Bleyer AJ. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease – REN. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A. editors. GeneReviews®. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2024 (2011). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53700/
Keywords: ADTKD, acute kidney injury, hyperuricemia, REN, renal insufficiency
Citation: Ma J, Hu Z, Liu Q, Li J and Li J (2024) Case Report: A potentially pathogenic new variant of the REN gene found in a family experiencing autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease. Front. Pediatr. 12:1415064. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1415064
Received: 9 April 2024; Accepted: 8 October 2024;
Published: 11 December 2024.
Edited by:
Mohammad Al-bataineh, University of Pittsburgh, United StatesReviewed by:
Anthony Bleyer, Wake Forest University, United StatesCopyright: © 2024 Ma, Hu, Liu, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhijuan Hu, aHV6aGlqdWFuMTk3MkAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.