- 1Departamento de Ortopedia e Traumatologia, Hospital das Clinicas HCFMUSP, Faculdade de Medicina FMUSP, Universidade de Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil
- 2Instituto de Medicina Fisica e Reabilitacao, IMREA, Hospital das Clínicas HCFMUSP, Faculdade de Medicina FMUSP, Universidade de Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil
- 3Departamento de Patologia, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de Sao Paulo, FMUSP, Sao Paulo, Brazil
- 4Departamento de Medicina Legal, Bioetica, Medicina do Trabalho e Medicina Fisica e Reabilitacao, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de Sao Paulo, FMUSP, Sao Paulo, Brazil
Introduction: Shoulder pain is the third leading cause of musculoskeletal complaints in primary care clinics. Its prevalence varies from 14% to 34%. Among all the structures that can cause shoulder pain, the most vulnerable to injury is the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The ideal management protocol is still unknown. To date, little is known in the literature about the use of ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block as a treatment for supraspinatus muscle tendinitis. Our objective was to assess the effects of the association of a single ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block combined with home-based rotator cuff exercises to reduce pain and improve shoulder functioning in patients with supraspinatus tendinitis.
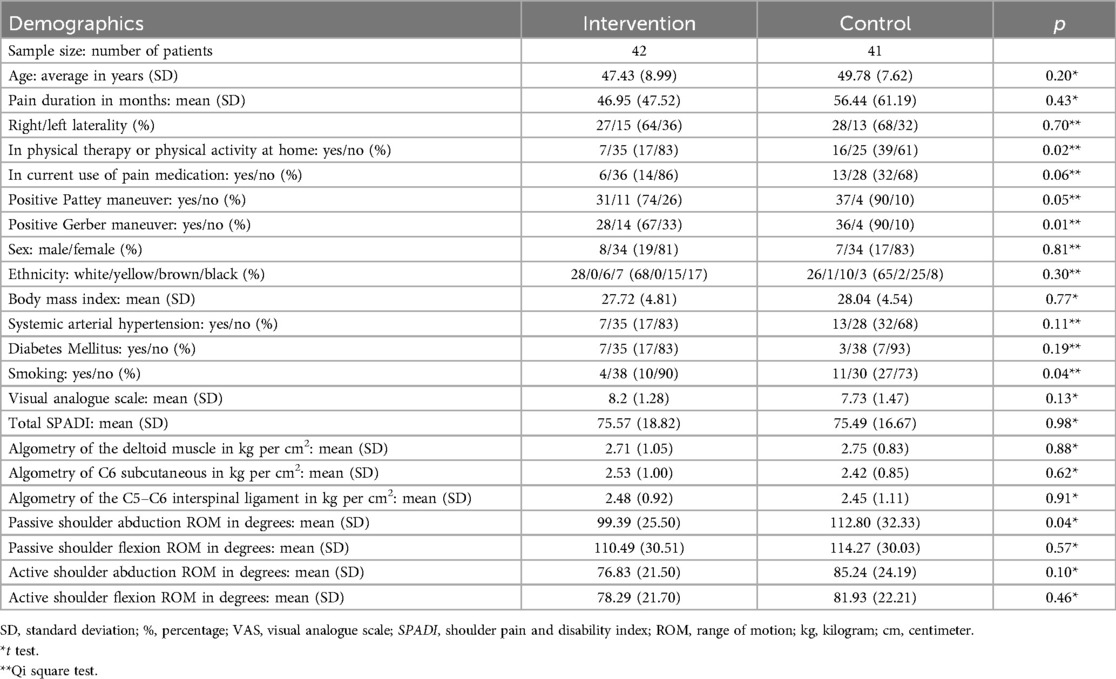
Methods: We evaluated the effect of a single ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block on pain and functioning of people with supraspinatus tendinitis. Diagnosis was performed using the positive Jobe test. Due to large disparity between clinical and radiological findings, only clinical diagnostic criteria were used to select patients. This was a double-blind, randomized, controlled, clinical study in which patients in the intervention group (n = 42) received a single injection of 5 ml of 2% lidocaine, while in the control group (n = 41) patients underwent the same procedure receiving saline solution 0.9%. All patients received face to face instructions by an experienced physiotherapist and a leaflet explaining home-based exercises. Pain and functioning were assessed using the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) questionnaire before the procedure, one week and 12 weeks after the procedure.
Results: Patients in both groups improved significantly since the initial evaluation until the 12th week. Intervention group SPADI (pre, 1 week, 12 weeks): 75.80 ± 18.96, 56.25 ± 31.37, 46.31 ± 31.41 (p < 0.001); Control group SPADI: 75.49 ± 16.67, 50.51 ± 27.58, 49.37 ± 30.90 (p < 0.001). However, there were no significant differences between groups (p = 0.291).
Discussion/conclusion: We concluded that both lidocaine and saline ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve blocks reduce pain and improve shoulder functioning in patients with supraspinatus tendinitis. Unexpectedly, the same block performed with saline showed similar results and effects.
Clinical Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier [NCT02495818].
1 Introduction
Shoulder pain is the third leading cause of musculoskeletal complaints in primary care clinics, behind other prevalent complaints such as low back and knee pain (1, 2). The annual incidence rates varied from 7.7 to 62 per 1,000 person years (1). Its prevalence varies from 14% to 34% (3). Although 40% of the cases of shoulder pain are resolved in six months, after 12 months since the first pain episodes, around 50% of the patients remain with pain, despite undergoing traditional treatments (4). Shoulder pain may persist for one to three years after diagnosis in 20% and 14%, respectively (5). Rotator cuff tears account for 65%–70% of painful shoulders (3) and resulted in 272,148 surgeries in the United States in 2006 (6). Among all the structures that can cause shoulder pain, the most vulnerable to injury is the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle (7). Its impairment causes great pain when performing everyday activities, such as eating and dressing, as well as more complex work-related tasks (8).
The ideal management protocol is still unknown (9). Some interventions, such as physical therapy, exercises (10) and acupuncture (11) may require several weeks to improve symptoms (12). Surgical interventions are recommended in severe cases, however, they are expensive and require a period of post operatory immobilization (13). Moreover, indirect evidence from studies including several painful conditions highlight the disappointing results of oral medications (14) and physiotherapy (15) for managing chronic shoulder pain. Other interventions include extracorporeal shockwaves (16); platelet-rich plasma (17, 18); prolotherapy (18) and hypertonic dextrose injections (19–21). In the review by Lin et al. (19), the combination of extracorporeal shockwave therapy and physiotherapy was the only approach shown to improve both pain and shoulder function. SSNB improved mobility, only (16). The short duration of the analgesic effect of a local anesthetic nerve block can be enhanced by the use of continuous infusion of the anesthetics for weeks or the association of radiofrequency (15).
Suprascapular nerve block (SSNB) is often used to treat severe painful shoulder conditions, such as adhesive capsulitis (9), painful hemiplegic shoulder (9), after rotator cuff surgeries (22) and could be an alternative to treat other shoulder injuries (16, 23–25). The suprascapular nerve provides the sensory innervation of 70% of the shoulder (26). Therefore, the short duration of the effect of a local anesthetic block may allow for the performance of therapeutic exercises that acts in the physiopathology of the supraspinatus tendinitis (27). Suprascapular nerve block is superior to placebo injection of subcutaneous normal saline (23, 24) and convention physiotherapy (28, 29) to reduce pain and improve function in patients with non-specific shoulder pain. Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block seems to be not superior to surface landmark-guided injections (25). However, the use of ultrasound for this procedure is an attractive choice due to its accessibility and portability and the fact that it does not expose patients, operators and doctors to radioactivity (30). Another advantage of using ultrasound is the fact that it allows real-time visualization of the procedure, which besides ensuring the safety of the procedure may also provide valuable diagnostic information about patients anatomy and the procedure as a whole (31). In fact, a meta-analysis (11 studies, 591 patients) evidenced the superiority of the suprascapular nerve block compared with placebo and physical therapy for treatment of chronic shoulder pain (15). However, no previous study assessed the effect of ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block for the management of supraspinatus muscle tendinitis, using a double-blind protocol.
Herein we used intervention with lidocaine as a treatment option for the supraspinatus muscle tendinitis (32). In the control group patients underwent the same procedure, but normal saline solution was used instead. Besides the intervention, patients were instructed by a physiotherapist to perform specific physical exercises at home and received printed material that explained how to perform them (27). Our objective was to assess the effects of the association of a single ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block combined with home-based rotator cuff exercises to reduce pain and improve shoulder functioning in patients with supraspinatus muscle tendinitis.
2 Materials and methods
This was a double-blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial with parallel arms to investigate the efficacy of ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block combined with physical exercises in the treatment of tendinitis of the supraspinatus muscle, as assessed by pain and functionality parameters. The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Clinical Hospital of São Paulo through CAAE 12480513.7.0000.0068 and registered by clinicaltrials.gov under the identifier NCT02495818.
2.1 Patients and randomization
Randomization was generated by a computer program that created random blocks of four and six units. Occultation of randomization was maintained through opaque and sealed envelopes. On the day the patient arrived at our institute for the procedure, the research monitor at our center opened the envelope and instructed the nurse to prepare the syringe containing either lidocaine or saline, according to the randomization. The nurse prepared the appropriate syringe, labeled it with the patient's name, and sent it to the physician performing the procedure. The nurse did not disclose the content of the syringe, ensuring blinding of the physician to the administered substance. The patient, the physician, the physiotherapist and the statistician were blinded.
Patients with a clinical diagnosis of supraspinatus tendinitis were selected by the Jobe maneuver, justified by the fact that it is highly sensitive and specific (33). The radiological findings were not considered for including patients in the study due to the high clinical-radiological dissociation (34, 35).
2.1.1 Inclusion criteria
Patients between 30 and 60 years of age, who had symptoms for a month or longer periods and had received a clinical diagnosis of tendinitis of the supraspinatus muscle established by a physiatrist or orthopedist by applying the Jobe maneuver (33, 36). Also, to be included in the study patients had to present a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) ≥4 in rest. We chose a smaller age range because supraspinatus tendinitis prevalence increases with age (37, 38), however, several other comorbidities could have influenced our results in case we included patients over 60 years due to the aging effects. All patients signed the informed consent form and were able to understand and answer the questions.
2.1.2 Exclusion criteria
All patients who had any of the following symptoms, conditions or previous history were excluded: severe osteoarthritis of the shoulder, total rupture of the supraspinatus muscle, active systemic autoimmune disease, fracture of the humerus, fracture of the acromion or clavicle, shoulder dislocation or subluxation, any disease that could lead to spasticity of the upper limbs, such as quadriplegia or stroke, systemic changes that could induce peripheral neuropathy, such as decompensated diabetes or thyroid disease, severe cervical injury previously diagnosed by nuclear magnetic resonance, such as cervical disc herniation or stenosis spinal disorders, which resulted in motor disorders, allergy or hypersensitivity to topical or systemic anesthetics, use of oral or subcutaneous anticoagulation, blood dyscrasias, fibromyalgia according to the 1990 American College of Rheumatology criteria, psychiatric illnesses not controlled or treated by two or more medications, acute or chronic renal failure, hypoxemic respiratory pathologies such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or pulmonary fibrosis, arrhythmias (except isolated supraventricular extrasystoles), coronary insufficiency or heart failure class 2 or higher, pregnant women and patients who could not comply with treatment due to social factors. It is natural and intuitive that myofascial pain syndrome coexists with rotator cuff syndrome, since there is a local inflammatory process and muscle strength imbalance with areas of overload and weakness, which act as trigger points activators (39). Therefore, it was not considered as an exclusion criterion.
2.1.3 Recruitment
Patients who had received medical care or were on the waiting list for rehabilitation treatment at the Lucy Montoro Rehabilitation Medicine Institute in São Paulo, Brazil, and who had a clinical diagnosis of rotator cuff syndrome, as identified in the medical records by the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) code M75.1, were invited for an initial evaluation.
Social agents were responsible for contacting the patient. They applied a quick questionnaire about pathology, age, place of residence and explained the treatment. Patients interested in participating in the study were invited to attend our institution, where they received an explanation about the study and its procedures, including possible complications. Upon agreeing, they signed the informed consent form.
2.1.4 Sample size calculation
To calculate the sample size, we considered the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) questionnaire from a previous published clinical trial performed in patients with a diagnosis of shoulder pain, submitted to a suprascapular nerve block not guided by ultrasound (23). We used this data because there was no similar study in the literature at that time.
The sample size calculation was based on the mean variation (delta) between two independent groups. Assuming a significance level (alpha) of 0.05 (two-tailed test), a statistical power of 80%, and data from the SPADI questionnaire used in this study, the following parameters were applied: the mean delta in the intervention group over 12 weeks was 13.5, and in the control group, 2.6. The standard deviation of the delta in the intervention group was 19.3, and in the control group, 17.4. Based on these values, the calculated sample size was 45 patients per arm. To account for an anticipated 20% loss to follow-up, 11–12 additional patients were included in each group, leading to a total of 113 participants.
2.2 Intervention
A Siemens Sonoline G40 ultrasound device and a linear transducer were used for the ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block, with adjustments according to each patient anatomy (40).
The patient was placed in a sitting position with the hand ipsilateral to the pain resting on the contralateral shoulder. The doctor was positioned behind the patient. Antisepsis of the region was performed with chlorhexidine solution. A thin layer of sterile gel was placed between the ultrasound transducer and the skin. An initial ultrasound evaluation was performed to guide the procedure. Then, the transducer was placed parallel to the spine of the scapula, it was moved superiorly towards the supraspinatus fossa, and then laterally until the scapular notch, where the suprascapular nerve crosses. The nerve is visualized as a round, hyperechoic structure, on average 4–5 cm in depth and lies just below the transverse ligament of the scapula.
The needle used was 10 cm long, 22G thick and had a Quincke tip. It was inserted along the longitudinal axis of the transducer (Figures 1, 2). It was slowly deepened by adjusting the entry angle and the needle path so that 5 ml of 2% lidocaine could be injected close to the suprascapular nerve, in the notch of the scapula. The needle was visualized in its entirety, as well as the injection and local expansion of the anesthetic (Figure 3). Typically, electrical stimulation is employed to locate nerves by eliciting corresponding muscle movements. However, in our study, the nerve was visualized directly using ultrasound imaging, rendering electrical stimulation unnecessary. The patient was observed for 1 h. If there were no complications, the patient was discharged and returned to the outpatient clinic the following week for a new evaluation.
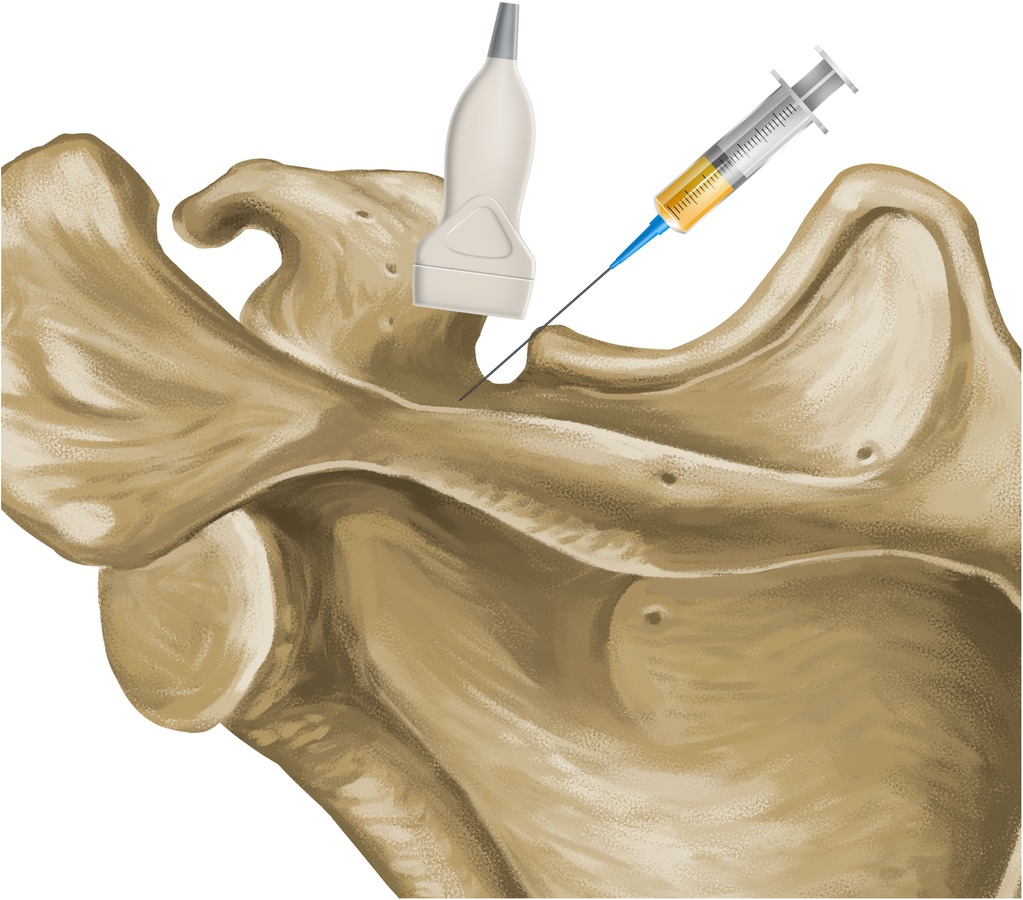
Figure 1. Anatomical relationship between the suprascapular notch, ultrasound transducer and needle.
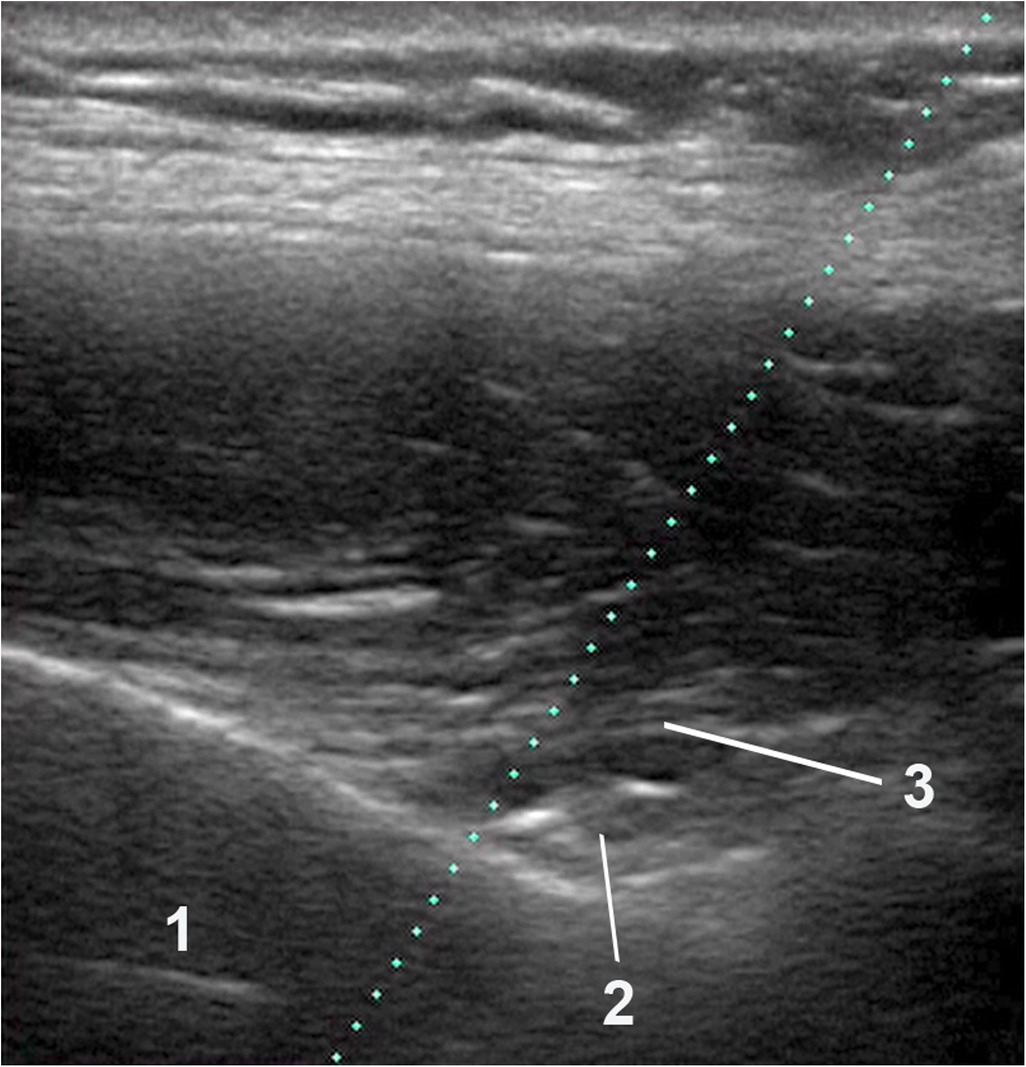
Figure 2. Ultrasound imaging anatomy. Caption: (1) Scapula. (2) Suprascapular nerve. (3) Transverse ligament of the scapula.
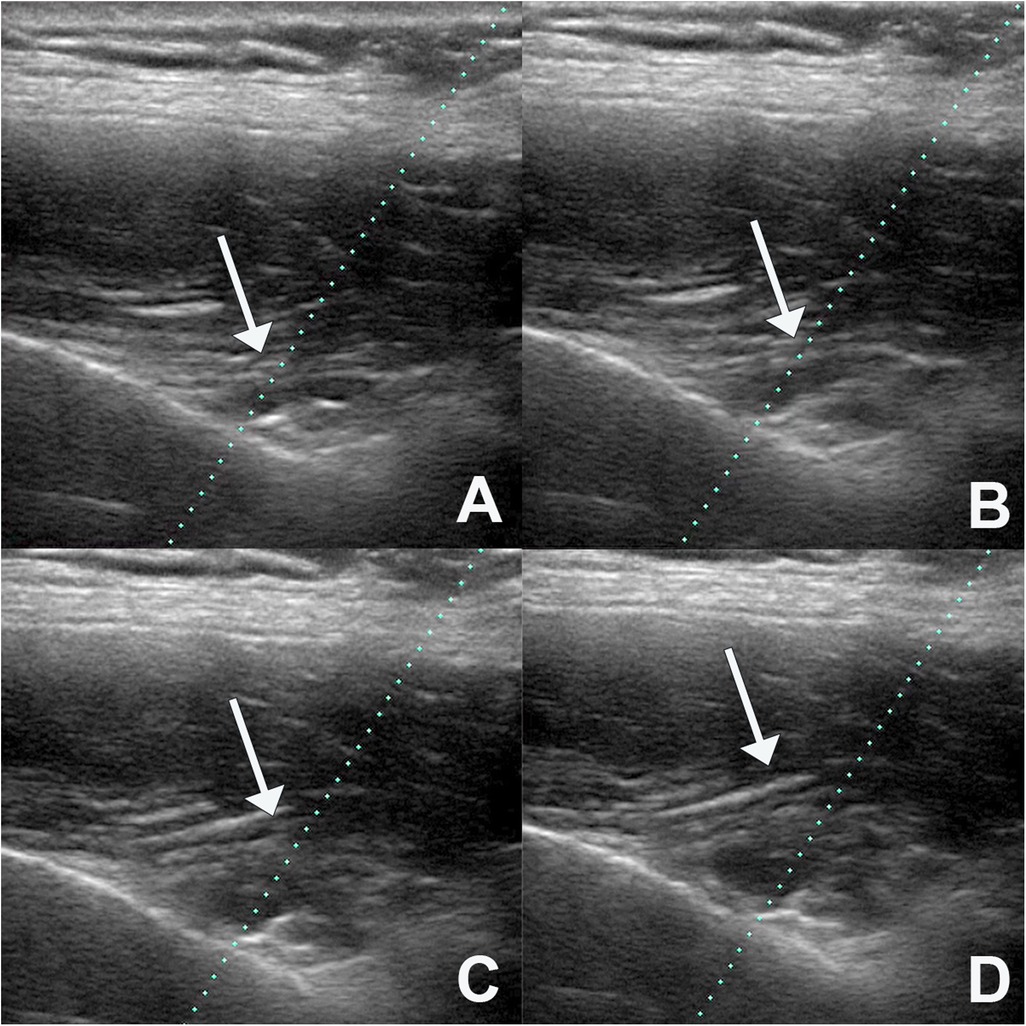
Figure 3. Expansion of the injected fluid, showing that it progressively elevates the transverse ligament of the scapula (A–D).
Patients allocated to the control group received a procedure similar to the intervention group, but instead of lidocaine, they received saline. Neither the patients nor the physician performing the procedure were aware of the substance being administered, as they received a syringe from the nursing staff that was labeled only with the patient's name, without any indication of its contents.
In addition to the procedure, all patients received conservative treatment, which included instructions for home exercise and the use of medication as needed for pain management. The prescribed exercises were introduced by a physical therapist during the first follow-up appointment, one-week post-intervention. The Codman pendulum movements and Hughston exercises were selected due to their simplicity and ease of comprehension (27). Each patient received an instructional booklet containing illustrative figures and detailed educational text. Patients were advised to perform two sets of 12 repetitions for each exercise daily at home. The exercise folder provided to the patients is available as Supplementary Material. If the patient experienced pain during treatment, paracetamol 500 mg every 8 h was indicated. Medications that patients were using prior to the study were not withdrawn.
2.3 Outcome measures
Pain and functioning were assessed using the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) in its validated Portuguese version, since the study was carried out in Brazil (8). Another assessment tool utilized was the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), which consisted of a horizontal line with the left endpoint labeled as “zero,” representing “no pain,” and the right endpoint labeled as “ten,” indicating “maximum pain.” The patient marked the pain level on this line during the evaluation after receiving an explanation. Questionnaires were applied immediately before the procedure, at one-week and 12-week follow-ups.
Pain threshold was evaluated by algometry in metamer structures related to supraspinatus tendinitis. Measurements were performed on the deltoid muscle, on the lateral region of the arm (parallel algometry using the “rolling pinch” technique) and on the interspinous ligament between the C5 and C6 vertebrae, which correspond, respectively, to the myotome, dermatome and sclerotome. Algometry of metameric structures is exploratory data, but may suggest effects of the procedure on central sensitization of pain in supraspinatus tendinitis. Pain threshold was defined as the minimum pressure needed to induce pain at each point in kg per cm2. Active and passive range of motion for shoulder flexion and abduction was assessed using goniometry. Both algometry and goniometry measures were evaluated immediately before the procedure, at one-week and 12-week follow-ups.
The primary endpoint was measured SPADI, while the secondary endpoint was measured by VAS, algometry and goniometry.
2.4 Statistical analysis
The software used for statistical analysis was JASP Team (2020) version 0.14.1 (University of Amsterdam). The mean SPADI scores of the intervention and control groups over time were compared using repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). The missing data imputation was performed using the Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF) method, where missing data were replaced by the last available observation, ensuring that all patients were included in the subsequent analyses, in line with the intention-to-treat principle. An interim analysis was pre-specified using the O'Brien-Fleming stopping boundary, with a stringent significance threshold set at a p-value of 0.01. This analysis was scheduled to take place at the midpoint of the study to assess whether early termination was warranted based on the accumulated data.
3 Results
3.1 Patients and randomization
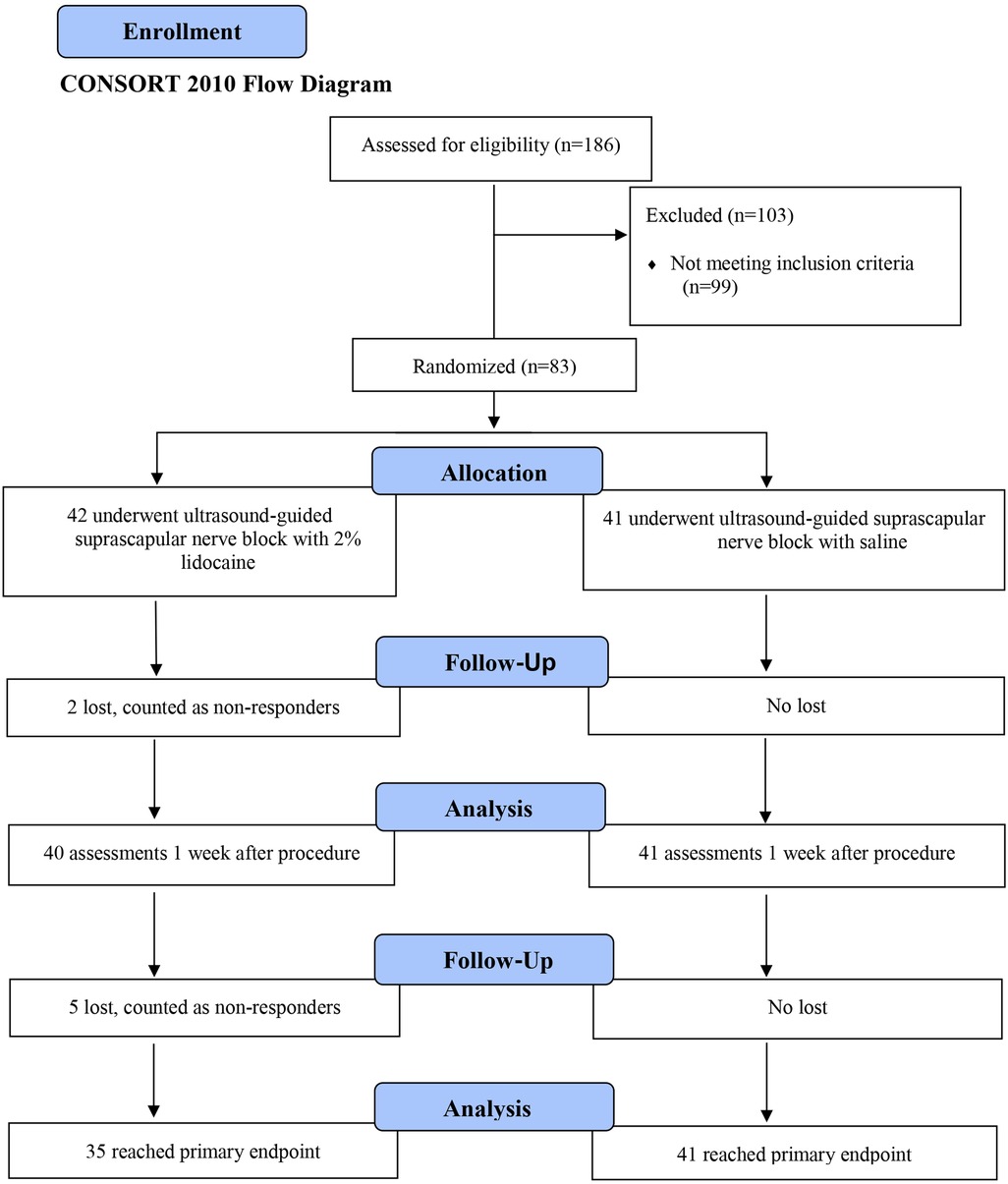
A total of 186 patients were recruited in 3 years; 87 met the inclusion criteria for the screening visit, 4 dropped out for personal reasons before undergoing the procedure and were excluded from the study. The final study included 83 patients. Of these, 76 completed the third and final assessment. Five patients were evaluated twice, and two patients only completed the first assessment. The first patient was included in the study on July 19, 2013 and the last on June 16, 2015.
Table 1 presents the population demographics followed by the study flowchart in Figure 4.
3.1.1 Primary endpoint
The ANOVA test with repeated measures was used to assess the interaction of the intervention over time for the primary outcome, SPADI, using the JASP Team 2020 software version 0.14.1. This statistical analysis is described in Figure 5; Tables 2, 3.
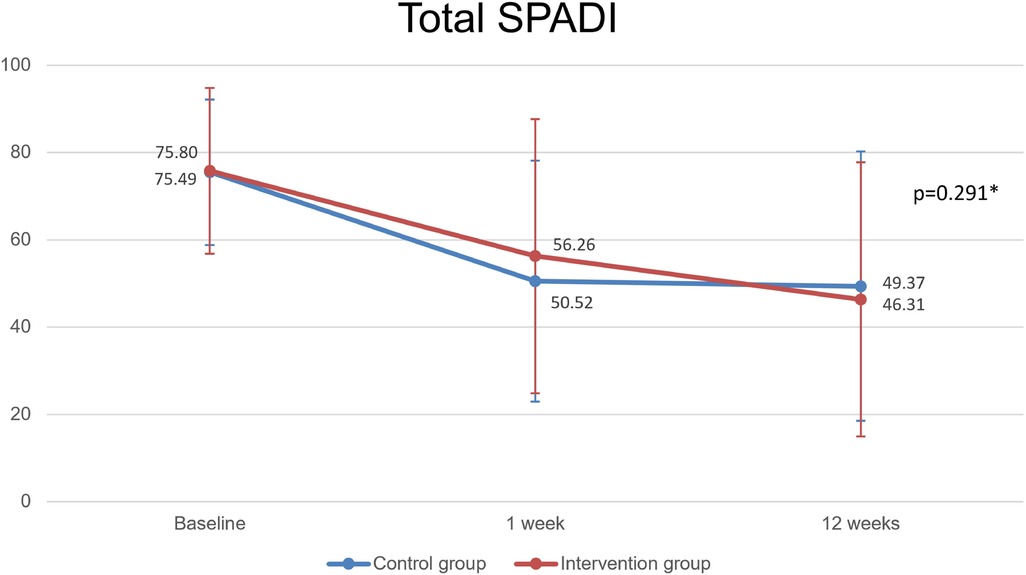
Figure 5. Primary outcome: total SPADI parameter. Caption: SPADI, shoulder pain and disability index; (*): Repeated measures ANOVA.
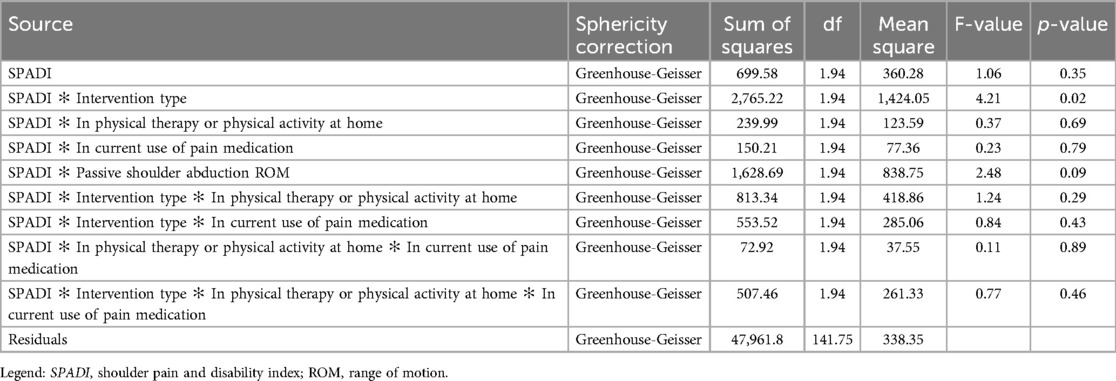
Table 2. Type III Sum of squares for SPADI adjusted for physical therapy, pain medications and passive shoulder abduction range of motion.
Patients in both groups improved significantly since the initial evaluation until the 12th week. Intervention group SPADI (pre, 1 week, 12 weeks): 75.80 ± 18.96, 56.25 ± 31.37, 46.31 ± 31.41 (p < 0.001); Control group SPADI: 75.49 ± 16.67, 50.51 ± 27.58, 49.37 ± 30.90 (p < 0.001); however, with no significant differences between groups (p = 0.291).
Medication use and physical activity at home was unbalanced within the two groups at baseline. Adjusted statistical analysis revealed that these factors have not influenced or results. The ANOVA for repeated measures for SPADI, considering the combined effect of intervention group, physical therapy/exercise and pain medication, showed no significant difference among the resulting subgroups over time (p > 0.05). Results are described in Table 2.
3.1.2 Secondary endpoint
For exploratory and investigative purposes only, the groups of VAS, goniometry and algometry variables were compared using the ANOVA test with repeated measures using the JASP Team 2020 software version 0.14.1.
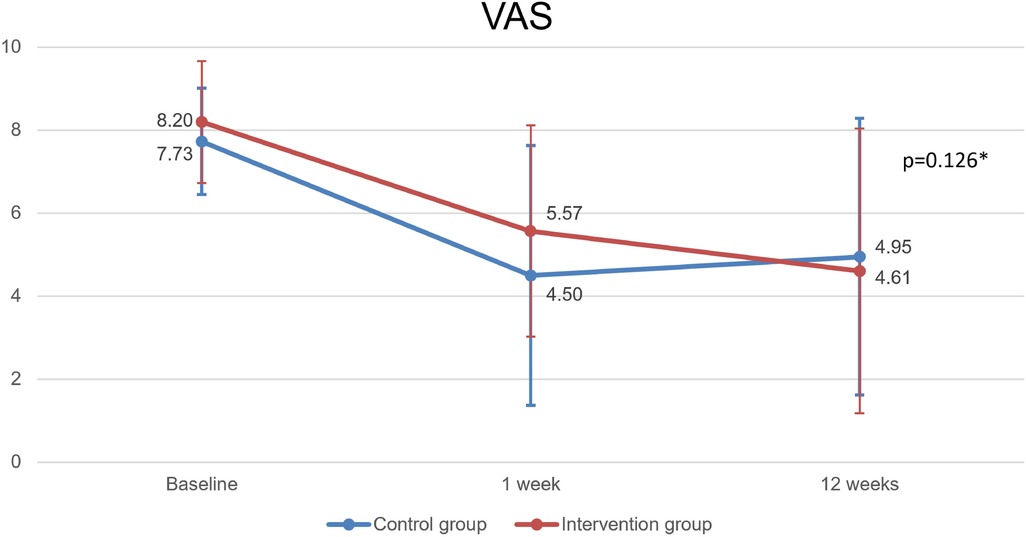
Patients in both groups improved significantly since the initial evaluation until the 12th week. Intervention group VAS (pre, 1 week, 12 weeks): 8.20 ± 1.28, 5.57 ± 3.13, 4.61 ± 3.33 (p < 0.001); Control group: 7.73 ± 1.47, 4.50 ± 2.55, 4.95 ± 3.43 (p < 0.001). However, with no significant differences between groups (p = 0.126). The results are summarized in Figure 6; Tables 3, 4.
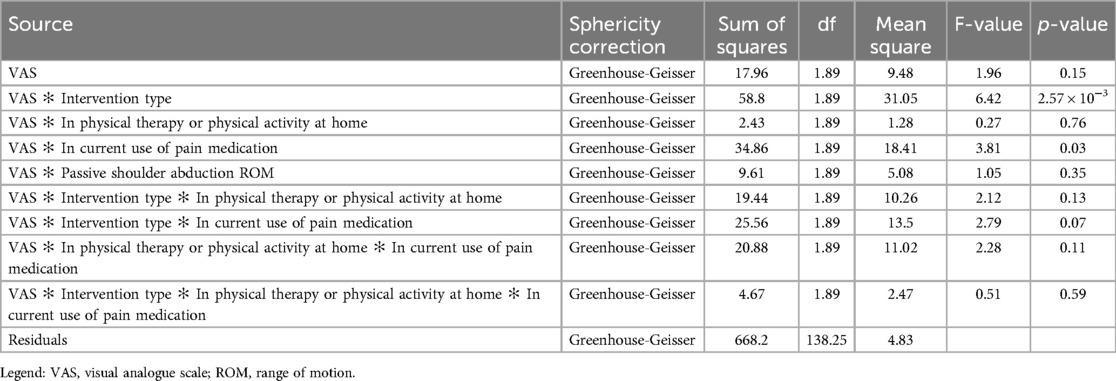
Table 4. Type III Sum of squares for VAS adjusted for physical therapy, pain medications and passive shoulder abduction range of motion.
Medication use and physical activity at home was unbalanced within the two groups at baseline. Adjusted statistical analysis revealed that these factors have not influenced or results. The ANOVA for repeated measures for VAS, considering the combined effect of intervention group, physical therapy/exercise and pain medication, showed no significant difference among the resulting subgroups over time (p > 0.05). Adjustments are described in Table 4.
Some subjects exhibited noteworthy results. At the first-week post-procedure assessment, three patients in the intervention group and none in the control group reported a SPADI score of zero, while three patients in the intervention group and three in the control group recorded a VAS score of zero. At the 12-week post-procedure assessment, five patients in the intervention group and three in the control group had a SPADI score of zero, while four patients in the intervention group and six in the control group reported a VAS score of zero.
The Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) for the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) is reported as 13.2 points (41). In our study, we observed mean reductions of 29.486 (SD: 26.511) in the lidocaine group and 26.121 (SD: 25.617) in the saline group, both significantly exceeding the threshold for clinical relevance. Similarly, for the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), the reported MCID is 1.37 points (42). The mean VAS reductions were 3.586 (SD: 3.116) in the lidocaine group and 2.780 (SD: 3.237) in the saline group, both surpassing the minimum clinically important change. Despite the lack of statistically significant differences between the groups, both procedures produced meaningful clinical improvements, with reductions approximately two to three times higher than the MCID for SPADI and VAS, respectively.
The magnitude of changes for each intervention was assessed by comparing pre-intervention and 12-week post-intervention scores, utilizing intragroup comparisons evaluated with a two-tailed paired t-test. G*Power software and Cohen's d statistic were used to calculate effect sizes. For the intervention group, the SPADI and VAS scores demonstrated large effect sizes, with d = 1.07 and d = 1.06, respectively. Similarly, in the control group, SPADI and VAS scores yielded effect sizes of d = 0.97 and d = 0.93, respectively. Given that Cohen's d values above 0.8 indicate a large effect, both the lidocaine and saline interventions may offer clinically beneficial effects in the treatment of patients.
3.1.3 Adverse events
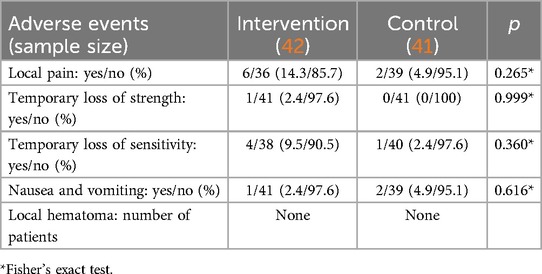
Adverse events are described in Table 5.
3.2 Interim analysis and statistical power
The interim analysis was performed after data collection from 83 patients. Although the significance threshold of p-value < 0.01 was not met, the decision to terminate the study was based on several key considerations. First, the analysis showed that the collected data were sufficiently robust and consistent to allow for conclusive results. Specifically, the statistical power of the study reached 92.2% for the total SPADI and 95.6% for the VAS, suggesting a high probability that the outcomes would remain consistent with those of a full sample size. Given this high level of statistical power and the strength of the evidence, continuing the study was deemed ethically unjustifiable, as it would involve exposing additional patients to an experimental treatment. Consequently, based on the interim analysis, the study was discontinued early, adhering to the pre-specified stopping criteria and ensuring both scientific rigor and ethical responsibility.
4 Discussion
In this study, a single ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block combined with home-based rotator cuff exercises improved pain and functionality in people with supraspinatus tendinitis and this effect lasted for at least 12 weeks. This method is usually used in some severe shoulder pathologies, such as adhesive capsulitis (9), painful shoulder of the hemiplegic (9) and after shoulder surgery (22). In addition to these conditions, supraspinatus tendinitis can also compromise shoulder functionality, leading to central sensitization and chronic pain (43). So that, suprascapular nerve block could be considered as an alternative treatment. This method has few adverse events and can be easily included in routine consultations. Our hypothesis is that conventional interventions, such as medication and physiotherapy, could be associated with this procedure to enhance results, which are so desired in difficult-to-treat pathologies.
We have demonstrated that this nerve block can be faster and have immediate results when compared to physical therapy (44) and acupuncture (45). A rotator cuff syndrome rehabilitation exercise program typically lasts from 3 weeks to 6 months, depending on the severity of the injury (44). It is described in the literature that from the fourth week onwards, physical therapy may have a similar effect to some procedures, such as corticosteroid injections, in the treatment of rotator cuff syndrome (46). Sonune (47) demonstrated that the improvement in pain and range of motion with suprascapular nerve block was superior when compared to intra-articular corticosteroid injection on the first day after the procedure, suggesting that, anesthetics should be considered as the preferred substance whenever possible in relation to corticosteroids, as they present faster results and have fewer contraindications and side effects. In Favejee's systematic review (48), the effects of suprascapular nerve block were found to be superior to those of acupuncture in terms of pain reduction and improvements in range of motion, evaluated 30 min after the procedure. Although this data pertains specifically to adhesive capsulitis, it is reasonable to consider that some degree of extrapolation to supraspinatus muscle tendinitis may be applicable.
Suprascapular nerve block becomes important as a possibility to be considered prior to rotator cuff surgical repair in the initial approach. US-guided suprascapular nerve block is not as expensive as surgery (49), which makes it feasible for daily consultations. The biggest cost is the doctor's time, as the health service usually has the ultrasound device. Routine supplies such as syringe, needle, anesthetic, ultrasound gel and gloves are inexpensive. The advantages over surgery are numerous, from low cost (49) to lower risk of complications as it is a less invasive procedure (50). The most common surgery adverse event is failure of tendon healing following rotator cuff repair, which may result in a further procedure (51). Post-surgical infection (51), palsies due to nerve damage (51), as well as post anesthesia cerebrovascular event may be also reported (52).
Our results confirm previous findings from Ryosa's meta-analysis (50) who illustrated that conservative treatment can sometimes have a similar outcome compared to surgical treatment of the rotator cuff tear. Moosmayer (53) and Lambers (54) found better results in favor of surgical treatment, however, the differences were small and, according to the authors themselves, may not represent clinical importance. Despite the shorter follow-up period in our evaluation, we concur with the findings of Kukkonen (55), who reported that physical therapy and surgery may not differ in terms of pain and functionality, as measured by the Constant Score, over the course of one year in patients with supraspinatus tendon injuries.
It is well known that exercise and pain medications can improve pain and function specially in the acute phase of patients suffering from shoulder pain. Our original insight was that the pain relief achieved by the ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block allowed patients to perform their home exercises which allowed for the three-month results observed in our study. We have not anticipated that the saline injection would provide similar improvements in the mid-term follow-up.
On the other hand, it cannot be excluded that normal saline may have independently acted as a perineural space expander, without the involvement of local anesthetic, anti-inflammatory, or nerve repair mechanisms (56). Considering the mechanism of hydrodissection, normal saline may also be considered an injectable for this purpose (56). We cannot rule out the potential mechanical effect of hydrodissection that normal saline may have provided to patients randomized to the control group, potentially facilitating nerve release and improving its gliding under the transverse scapular ligament.
We should also consider that we have only included chronic patients with a mean duration of 46.95 (SD: 47.52) months. It is known that medication and exercises have limited effect for these chronic patients (57). Chronic and long-term use of analgesics, opioids and anti-inflammatory medications should be considered with caution due to their potential side effects and harm. Low adherence to home exercises is also a challenge in the management of chronic musculoskeletal pain conditions (58). In any case, future studies should carefully monitor medication intake and adherence to the home exercise regime. We have included both interventions as the local ethical committee would not allow a group with placebo intervention only.
Part of the placebo effect can be attributed to the Hawthorne effect, in which there is a change in patient's behavior due to the care and attention received during treatment (59, 60). Patients were evaluated by a variety of professionals during the study, including physicians, physical therapists, nurses and social workers, and received care before, during and after the procedure at a renowned institution for a period of three months. All the affection dedicated to the patient may have influenced the response (59, 60). It is described in the literature that placebos present better results as procedures than as oral medications, as they are more invasive (61).
In addition to the psychological and behavioral aspects, the mechanical effect of the procedure, which consists of placing the needle in the patient and injecting the saline solution, can also treat pain (23). Acupuncture and dry needling present consistent results in the literature and may explain part of the response of any procedure that involves needle placement (11, 45, 62). There is a certain therapeutic effect due to local micro bleeding and disruption of the cell membrane, which triggers the beginning of an inflammatory cascade (63). This acute inflammation can lead to tissue repair and growth, with consequent clinical recovery (63). With deep needling and expansion of local fluid, mechanoreceptors of more structures are stimulated, which may contribute to a greater effect (64).
In the 1980s, Mayer (65) demonstrated that the use of naloxone, an opioid antagonist, in high doses could block the needling effect, suggesting analgesia induced by mechanical rather than chemical stimuli. Another study suggested that the endocannabinoid system could also be activated by the dry needling stimuli and may have contribute to pain control (66). Thus, several mechanisms can explain how this procedure works. However, more studies are needed to better understand the reason for the improvement of pain and functioning even in the saline group.
An important factor identified in our study, improvement is pain and shoulder function were statistically significant from baseline data and approximately two times superior than the minimal clinically important difference (MCID), both for SPADI and VAS. Our findings highlight the clinical relevance of the combination of SSNB with home exercises. Previous findings, compiled in a recent systematic review, did not demonstrate significant improvements in SPADI and VAS scores for patients with chronic shoulder pain following SSNB (16). Only mobility improved. Results similar to ours were only identified with the combination of extracorporeal shockwaves and conventional physiotherapy (16). A recent randomized controlled trial compared the effectiveness of ultrasound guided vs. landmark-guided suprascapular nerve block for chronic shoulder pain also using SPADI and VAS as outcome measures. Improvement in pain and shoulder function was similar than those obtained in our study.
Similar to the increase in mobility demonstrated previously (16), we have also identified a significant and superior improvement in passive should abduction, passive and active shoulder flexion in our patients. As a secondary outcome, this is an exploratory finding that should be better explored in future studies. As the body of scientific evidence increases, better understanding of the mechanisms involved on the pathophysiology of complex shoulder conditions will be also elucidated. Improvement in the ROM maybe indirect evidence that patients performed their home exercise regime. Future studies should further investigate the effects of SSNB on the pathophysiology of chronic supraspinatus tendinitis.
Interesting to highlight, is the low attrition observed in our study. The majority of the patients (91.6%) returned for the 12-week evaluation. Another striking benefit was the lack of severe and long-lasting adverse events or complications with the method. Although the absolute numbers of adverse events tended to be higher, local pain, temporary loss of strength and sensitivity and nausea and vomiting were not statistically significantly more frequent in the lidocaine injection group compared with the saline.
4.1 Study limitations
Medication use and physical activity at home was unbalanced within the two groups at baseline. Adjusted statistical analysis revealed that these factors have not influenced our results. On the other hand, a major limitation of our study was the lack of appropriate monitoring of adherence and/or rate at which medication intake and home exercise were carried out during the follow-up period. We have only given face to face instructions of the home exercise regime and given a booklet containing all the exercises. However, we have only included chronic patients with a mean duration of 46.95 (SD: 47.52) months. Medication and exercise have limited effect in these chronic patients (14, 15). Despite no control, we have observed a significant improvement since baseline for both groups. It is important to acknowledge that sex and age may have influenced our results and treatment response. However, due to statistical limitations regarding the number of variables that could be included in the repeated measures ANOVA for SPADI and VAS, we were unable to incorporate these variables in the adjusted analysis. No diagnosis of supraspinatus tendinitis was confirmed through imaging. The well-established clinical-radiological dissociation in the literature, though, supports the validity of clinical examination for diagnostic purposes (67). Other shoulder tendinitis as well as biceps injuries were not excluded, so there are no data on isolated rehabilitation of supraspinatus tendinitis. Another limiting factor is that the follow-up time was only three months, so there is no data on the actual duration of the intervention. On the other hand, this situation reflects the day-to-day of outpatient care.
5 Conclusion
Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block with lidocaine combined with home-based rotator cuff exercises improved the patients’ pain and functionality over the 12 weeks of observation. Unexpectedly, the same block performed with saline showed similar results and effects.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study involving humans was approved by Research Ethics Committee of the Clinical Hospital of São Paulo—University of São Paulo. This study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
PO: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RR: Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FA: Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RA: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WH: Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LB: Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MI: Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
This research was funded by the authors themselves. The author(s) declare that no external financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
To Dr. Margarida Miyazaki, director of the Lucy Montoro Rehabilitation Medicine Institute, Clinical Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, University of São Paulo, who provided all the necessary resources for this study to take place. To the assistant Mr. Artur César Aquino dos Santos, responsible for monitoring and supporting the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpain.2024.1490320/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Lucas J, van Doorn P, Hegedus E, Lewis J, van der Windt D. A systematic review of the global prevalence and incidence of shoulder pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2022) 23(1):1073. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05973-8
2. Urwin M, Symmons D, Allison T, Brammah T, Busby H, Roxby M, et al. Estimating the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in the community: the comparative prevalence of symptoms at different anatomical sites, and the relation to social deprivation. Ann Rheum Dis. (1998) 57(11):649–55. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.11.649
3. Jain NB, Fan R, Higgins LD, Kuhn JE, Ayers GD. Does my patient with shoulder pain have a rotator cuff tear? A predictive model from the ROW cohort. Orthop J Sports Med. (2018) 6(7):2325967118784897. doi: 10.1177/2325967118784897
4. van der Heijden GJ. Shoulder disorders: a state-of-the-art review. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (1999) 13(2):287–309. doi: 10.1053/berh.1999.0021
5. Linsell L, Dawson J, Zondervan K, Rose P, Randall T, Fitzpatrick R, et al. Prevalence and incidence of adults consulting for shoulder conditions in UK primary care; patterns of diagnosis and referral. Rheumatol Oxf Engl. (2006) 45(2):215–21. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei139
6. Jain NB, Higgins LD, Losina E, Collins J, Blazar PE, Katz JN. Epidemiology of musculoskeletal upper extremity ambulatory surgery in the United States. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2014) 15:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-4
7. Opsha O, Malik A, Baltazar R, Primakov D, Beltran S, Miller TT, et al. MRI of the rotator cuff and internal derangement. Eur J Radiol. (2008) 68(1):36–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.02.018
8. Martins J, Napoles BV, Hoffman CB, Oliveira AS. The Brazilian version of shoulder pain and disability index: translation, cultural adaptation and reliability. Rev Bras Fisioter Sao Carlos Sao Paulo Braz. (2010) 14(6):527–36. doi: 10.1590/S1413-35552010000600012
9. Smith N, Liew Z, Johnson S, Ellard DR, Underwood M, Kearney R. A systematic review of the methods and drugs used for performing suprascapular nerve block injections for the non-surgical management of chronic shoulder pain. Br J Pain. (2021) 15(4):460–73. doi: 10.1177/2049463721992091
10. Calis HT, Berberoglu N, Calis M. Are ultrasound, laser and exercise superior to each other in the treatment of subacromial impingement syndrome? A randomized clinical trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. (2011) 47(3):375–80.21946399
11. Molsberger AF, Schneider T, Gotthardt H, Drabik A. German randomized acupuncture trial for chronic shoulder pain (GRASP)—a pragmatic, controlled, patient-blinded, multi-centre trial in an outpatient care environment. Pain. (2010) 151(1):146–54. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.06.036
12. Dominguez-Romero JG, Jiménez-Rejano JJ, Ridao-Fernández C, Chamorro-Moriana G. Exercise-based muscle development programmes and their effectiveness in the functional recovery of rotator cuff tendinopathy: a systematic review. Diagn Basel Switz. (2021) 11(3):529. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030529
13. Haunschild ED, Gilat R, Lavoie-Gagne O, Fu MC, Tauro T, Forsythe B, et al. Return to work after primary rotator cuff repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. (2021) 49(8):2238–47. doi: 10.1177/0363546520975426
14. Zheng XQ, Li K, Wei YD, Tie HT, Yi XY, Huang W. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus corticosteroid for treatment of shoulder pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2014) 95(10):1824–31. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2014.04.024
15. Chang KV, Hung CY, Wu WT, Han DS, Yang RS, Lin CP. Comparison of the effectiveness of suprascapular nerve block with physical therapy, placebo, and intra-articular injection in management of chronic shoulder pain: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2016) 97(8):1366–80. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2015.11.009
16. Yang F, Li X, Wang J, Gao Q, Pan M, Duan Z, et al. Efficacy of different analgesic strategies combined with conventional physiotherapy program for treating chronic shoulder pain: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg. (2024) 19(1):544. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05037-8
17. Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yılmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazıcıoğlu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. (2013) 41(11):2609–16. doi: 10.1177/0363546513496542
18. Karim S A, Hamid MS, Choong A, Ooi MY, Usman J. Effects of platelet-rich plasma and prolotherapy on supraspinatus tendinopathy: a double blind randomized clinical trial. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. (2023) 63(5):674–84. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.22.14376-8
19. Lin CL, Chen YW, Wu CW, Liou TH, Huang SW. Effect of hypertonic dextrose injection on pain and shoulder disability in patients with chronic supraspinatus tendinosis: a randomized double-blind controlled study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2022) 103(2):237–44. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.07.812
20. Lin CL, Huang CC, Huang SW. Effects of hypertonic dextrose injection in chronic supraspinatus tendinopathy of the shoulder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. (2019) 55(4):480–7. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.18.05379-0
21. Kazempour Mofrad M, Rezasoltani Z, Dadarkhah A, Kazempour Mofrad R, Abdorrazaghi F, Azizi S. Periarticular neurofascial dextrose prolotherapy versus physiotherapy for the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: randomized clinical trial. J Clin Rheumatol Pract Rep Rheum Musculoskelet Dis. (2021) 27(4):136–42. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001218
22. Sun C, Ji X, Zhang X, Ma Q, Yu P, Cai X, et al. Suprascapular nerve block is a clinically attractive alternative to interscalene nerve block during arthroscopic shoulder surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg. (2021) 16(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02515-1
23. Shanahan EM, Ahern M, Smith M, Wetherall M, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O. Suprascapular nerve block (using bupivacaine and methylprednisolone acetate) in chronic shoulder pain. Ann Rheum Dis. (2003) 62(5):400–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.5.400
24. Barış Bayram K, Bal S, Safa Satoglu I, Kocyigit H, Gürgan A, Akcay S, et al. Does suprascapular nerve block improve shoulder disability in impingement syndrome? A randomized placebo-contolled study. J Musculoskelet Pain. (2014) 22(2):170–4. doi: 10.3109/10582452.2014.883026
25. Saglam G, Alisar DÇ. A comparison of the effectiveness of ultrasound-guided versus landmark-guided suprascapular nerve block in chronic shoulder pain: a prospective randomized study. Pain Physician. (2020) 23(6):581–8.33185375
26. Fernandes MR, Barbosa MA, Sousa ALL, Ramos GC. Suprascapular nerve block: important procedure in clinical practice. Rev Bras Anestesiol. (2012) 62:100–4. doi: 10.1590/S0034-70942012000100013
27. Ellsworth AA, Mullaney M, Tyler TF, McHugh M, Nicholas S. Electromyography of selected shoulder musculature during un-weighted and weighted Pendulum exercises. North Am J Sports Phys Ther NAJSPT. (2006) 1(2):73–9.
28. Di Lorenzo L, Pappagallo M, Gimigliano R, Palmieri E, Saviano E, Bello A, et al. Pain relief in early rehabilitation of rotator cuff tendinitis: any role for indirect suprascapular nerve block? Eur Medicophysica. (2006) 42(3):195–204.
29. Korkmaz OK, Capaci K, Eyigor C, Eyigor S. Pulsed radiofrequency versus conventional transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in painful shoulder: a prospective, randomized study. Clin Rehabil. (2010) 24(11):1000–8. doi: 10.1177/0269215510371417
30. Hackworth RJ. A new and simplified approach to target the suprascapular nerve with ultrasound. J Clin Anesth. (2013) 25(4):347–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2013.01.006
31. Strakowski JA. Ultrasound-Guided peripheral nerve procedures. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. (2016) 27(3):687–715. doi: 10.1016/j.pmr.2016.04.006
32. Abdelshafi ME, Yosry M, Elmulla AF, Al-Shahawy EAD, Adou Aly M, Eliewa EAK. Relief of chronic shoulder pain: a comparative study of three approaches. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. (2011) 21(1):83–92.21991738
33. Jain NB, Wilcox RB, Katz JN, Higgins LD. Clinical examination of the rotator cuff. PM R. (2013) 5(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.08.019
34. Milgrom C, Schaffler M, Gilbert S, van Holsbeeck M. Rotator-cuff changes in asymptomatic adults. The effect of age, hand dominance and gender. J Bone Joint Surg Br. (1995) 77(2):296–8. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.77B2.7706351
35. Tempelhof S, Rupp S, Seil R. Age-related prevalence of rotator cuff tears in asymptomatic shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. (1999) 8(4):296–9. doi: 10.1016/S1058-2746(99)90148-9
36. Gillooly JJ, Chidambaram R, Mok D. The lateral jobe test: a more reliable method of diagnosing rotator cuff tears. Int J Shoulder Surg. (2010) 4(2):41–3. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.70822
37. Whittle S, Buchbinder R. In the clinic. Rotator cuff disease. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162(1):ITC1–15. doi: 10.7326/AITC201501060
38. Varacallo M, El Bitar Y, Sina RE, Mair SD. Rotator cuff syndrome. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing (2024). Available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531506/ (cited October 8, 2024)
39. Imamura ST, Riberto M, Fischer AA, Imamura M, Kaziyama HHS, Teixeira MJ. Successful pain relief by treatment of myofascial components in patients with hip pathology scheduled for total hip replacement. J Musculoskelet Pain. (1998) 6(1):73–89. doi: 10.1300/J094v06n01_06
40. Harmon D, Hearty C. Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block technique. Pain Physician. (2007) 10(6):743–6.17987095
41. Williams JW, Holleman DR, Simel DL. Measuring shoulder function with the shoulder pain and disability Index. J Rheumatol. (1995) 22(4):727–32.7791172
42. Paul A, Lewis M, Shadforth MF, Croft PR, Van Der Windt DAWM, Hay EM. A comparison of four shoulder-specific questionnaires in primary care. Ann Rheum Dis. (2004) 63(10):1293–9. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.012088
43. Noten S, Struyf F, Lluch E, D’Hoore M, Van Looveren E, Meeus M. Central pain processing in patients with shoulder pain: a review of the literature. Pain Pract. (2017) 17(2):267–80. doi: 10.1111/papr.12502
44. Roy JS, Moffet H, Hébert LJ, Lirette R. Effect of motor control and strengthening exercises on shoulder function in persons with impingement syndrome: a single-subject study design. Man Ther. (2009) 14(2):180–8. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2008.01.010
45. Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Maschino AC, Lewith G, MacPherson H, Foster NE, et al. Acupuncture for chronic pain: individual patient data meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. (2012) 172(19):1444–53. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3654
46. Page MJ, Green S, McBain B, Surace SJ, Deitch J, Lyttle N, et al. Manual therapy and exercise for rotator cuff disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2016) 2016(6):CD012224. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012224
47. Sonune S, Gaur A, Gupta S. Comparative study of ultrasound guided supra-scapular nerve block versus intra-articular steroid injection in frozen shoulder. Int J Res Orthop. (2016) 2:387. doi: 10.18203/issn.2455-4510.IntJResOrthop20164174
48. Favejee MM, Huisstede BMA, Koes BW. Frozen shoulder: the effectiveness of conservative and surgical interventions–systematic review. Br J Sports Med. (2011) 45(1):49–56. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2010.071431
49. Carr AJ, Cooper CD, Campbell MK, Rees JL, Moser J, Beard DJ, et al. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of open and arthroscopic rotator cuff repair [the UK rotator cuff surgery (UKUFF) randomised trial]. Health Technol Assess. (2015) 19(80):1–218. doi: 10.3310/hta19800
50. Ryösä A, Laimi K, Äärimaa V, Lehtimäki K, Kukkonen J, Saltychev M. Surgery or conservative treatment for rotator cuff tear: a meta-analysis. Disabil Rehabil. (2017) 39(14):1357–63. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2016.1198431
51. Chamberlain AM, Aleem A, Keener JD. What’s new in shoulder and elbow surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2017) 99(20):1780–6. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.17.00756
52. Paxton ES, Backus J, Keener J, Brophy RH. Shoulder arthroscopy: basic principles of positioning, anesthesia, and portal anatomy. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. (2013) 21(6):332–42. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-21-06-332
53. Moosmayer S, Lund G, Seljom US, Haldorsen B, Svege IC, Hennig T, et al. Tendon repair compared with physiotherapy in the treatment of rotator cuff tears: a randomized controlled study in 103 cases with a five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2014) 96(18):1504–14. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.M.01393
54. Lambers Heerspink FO, van Raay JJAM, Koorevaar RCT, van Eerden PJM, Westerbeek RE, van ‘t Riet E, et al. Comparing surgical repair with conservative treatment for degenerative rotator cuff tears: a randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. (2015) 24(8):1274–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.05.040
55. Kukkonen J, Joukainen A, Lehtinen J, Mattila KT, Tuominen EKJ, Kauko T, et al. Treatment of non-traumatic rotator cuff tears: a randomised controlled trial with one-year clinical results. Bone Joint J. (2014) 96-B(1):75–81. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.96B1.32168
56. Buntragulpoontawee M, Chang KV, Vitoonpong T, Pornjaksawan S, Kitisak K, Saokaew S, et al. The effectiveness and safety of commonly used injectates for ultrasound-guided hydrodissection treatment of peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes: a systematic review. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:621150. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.621150
57. Andres BM, Murrell GAC. Treatment of tendinopathy: what works, what does not, and what is on the horizon. Clin Orthop. (2008) 466(7):1539–54. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0260-1
58. Francisco IM, Tozzo MC, Martins J, de Oliveira AS. Adherence of individuals with shoulder pain to home exercise booklets: barriers, facilitators, and the impact of disability, self-efficacy, and treatment expectations. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. (2024) 72:102956. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2024.102956
59. Fernald DH, Coombs L, DeAlleaume L, West D, Parnes B. An assessment of the hawthorne effect in practice-based research. J Am Board Fam Med JABFM. (2012) 25(1):83–6. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2012.01.110019
60. Sedgwick P, Greenwood N. Understanding the hawthorne effect. Br Med J. (2015) 351:h4672. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h4672
61. Kaptchuk TJ. The placebo effect in alternative medicine: can the performance of a healing ritual have clinical significance? Ann Intern Med. (2002) 136(11):817–25. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-11-200206040-00011
62. Stoychev V, Finestone AS, Kalichman L. Dry needling as a treatment modality for tendinopathy: a narrative review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. (2020) 13(1):133–40. doi: 10.1007/s12178-020-09608-0
63. Bertrand H, Reeves KD, Bennett CJ, Bicknell S, Cheng AL. Dextrose prolotherapy versus control injections in painful rotator cuff tendinopathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2016) 97(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2015.08.412
64. Ceccheerelli F, Bordin M, Gagliardi G, Caravello M. Comparison between superficial and deep acupuncture in the treatment of the shoulder’s myofascial pain: a randomized and controlled study. Acupunct Electrother Res. (2001) 26(4):229–38. doi: 10.3727/036012901816355938
65. Mayer DJ, Price DD, Rafii A. Antagonism of acupuncture analgesia in man by the narcotic antagonist naloxone. Brain Res. (1977) 121(2):368–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90161-5
66. Hesselink JMK, Kopsky DJ. Enhancing acupuncture by low dose naltrexone. Acupunct Med J Br Med Acupunct Soc. (2011) 29(2):127–30. doi: 10.1136/aim.2010.003566
Keywords: rotator cuff, rotator cuff injuries, supraspinatus tendinopathy, nervous block, pain management
Citation: Otani PT, Rached RDVA, Alfieri FM, Azevedo RS, Hsing WT, Battistella LR and Imamura M (2024) Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block with lidocaine vs. saline combined with physical exercises for the rehabilitation of supraspinatus tendinitis: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. Front. Pain Res. 5:1490320. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2024.1490320
Received: 3 September 2024; Accepted: 21 October 2024;
Published: 12 November 2024.
Edited by:
Sanjeev Kumar, University of Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Hayk Petrosyan, JFK Johnson Rehabilitation Institute, United StatesMaria Paço, Cooperativa de Ensino Superior Politécnico e Universitário, Portugal
Copyright: © 2024 Otani, Rached, Alfieri, Azevedo, Hsing, Battistella and Imamura. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pericles Tey Otani, dGV5b3RhbmlAZ21haWwuY29t
†ORCID:
Pericles Tey Otani
orcid.org/0000-0003-1655-6823
Roberto Del Valhe Abi Rached
orcid.org/0000-0001-6906-4975
Fabio Marcon Alfieri
orcid.org/0000-0002-5242-3246
Raymundo Soares de Azevedo Neto
orcid.org/0000-0003-0660-2371
Wu Tu Hsing
orcid.org/0000-0002-7019-7342
Linamara Rizzo Battistella
orcid.org/0000-0001-5275-0733
Marta Imamura
orcid.org/0000-0003-0355-9697
 Pericles Tey Otani
Pericles Tey Otani Roberto Del Valhe Abi Rached
Roberto Del Valhe Abi Rached Fabio Marcon Alfieri
Fabio Marcon Alfieri Raymundo Soares de Azevedo Neto
Raymundo Soares de Azevedo Neto Wu Tu Hsing
Wu Tu Hsing Linamara Rizzo Battistella
Linamara Rizzo Battistella Marta Imamura
Marta Imamura