- 1Department of Stomatology, The First People’s Hospital of Kashi Prefecture, Kashi, Xinjiang, China
- 2Department of Pathology, The First People’s Hospital of Kashi Prefecture, Kashi, Xinjiang, China
- 3Kashi Prefecture Cancer Research Institute, The First People’s Hospital of Kashi Prefecture, Kashi, Xinjiang, China
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a prevalent and devastating malignancy of the oral cavity that profoundly affects patient survival and quality of life (QOL). Cleavage Stimulation Factor Subunit 2 (CSTF2) is known to influence tumor development across multiple cancer types. However, its specific association with patient prognosis and immune cell infiltration in OSCC remains insufficiently understood.
Methods: To assess the expression levels and prognostic implications of CSTF2 in OSCC, comprehensive data were acquired from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and subsequently normalized. Immunohistochemical staining of tissue microarrays was performed to analyze CSTF2 expression in the OSCC samples. Differences in CSTF2 expression between OSCC and adjacent non-cancerous samples were evaluated using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Functional enrichment analyses have been performed to identify biological pathways and functions associated with CSTF2. The relationship between the infiltration of various immune cells and CSTF2 expression levels was assessed using single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA). Ultimately, the prognostic significance of CSTF2 was evaluated through Kaplan–Meier survival analysis, in conjunction with univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, as well as receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: High CSTF2 expression was observed in OSCC and associated with unfavorable clinicopathological variables, including histological grade and lymphnode neck dissection. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that CSTF2 plays a role in epidermal development and differentiation, immunoglobulin complexes, peptidases and endopeptidase inhibitor activity, and cytochrome P450 metabolic processes. Additionally, the overexpression of CSTF2 exhibited a negative correlation with the infiltration of immature dendritic cells (iDCs), cytotoxic cells, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). Notably, elevated CSTF2 expression is significantly associated with reduced patient outcomes.
Conclusion: Elevated CSTF2 expression in OSCC is associated with poor prognostic outcomes, highlighting its capacity to function as an innovative prognostic biomarker and a target for therapeutic interventions.
1 Introduction
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a common and devastating malignancy of the oral cavity that severely affects both the quality of life and survival rates of those diagnosed (1). It accounts for a significant proportion of head and neck cancers and is characterized by an aggressive clinical behavior and a propensity for local invasion and regional metastasis (2). Chronic exposure to various risk factors, such as cigarette smoking, alcohol, betel quid (BQ), and human papillomavirus (HPV), may result in the emergence of oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMDs), which are oral mucosal lesions associated with a heightened risk of progressing to OSCC (3–5). Despite improvements in conventional treatment strategies, such as surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, the overall survival rate of individuals diagnosed with OSCC remains approximately 40% (6). Early detection and accurate prognostic assessment are crucial for improving patient outcomes (7). However, current diagnostic approaches, which primarily rely on clinical examination and histopathological evaluation, often fail to identify the disease in its early stages (8). Current research has identified several biomarkers associated with OSCC; however their clinical utility often varies because of the heterogeneity of the disease (9). Furthermore, studies have indicated that other biological markers, such as CD44, may serve as indicators of malignant transformation in oral epithelial dysplasia and provide prognostic information regarding tumor behavior (10). However, the specificity and sensitivity of these markers in predicting clinical outcomes in patients with OSCC remain unclear. Consequently, there is a pressing need for novel research to uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying OSCC, and to identify reliable prognostic biomarkers that could aid clinical decision-making and enhance patient prognostication.
CSTF2, which is located on chromosome 19, is crucial for pre-mRNA processing and polyadenylation (11). As a component of the cleavage and polyadenylation machinery, CSTF2 influences gene expression by regulating mRNA transcript stability and maturation of mRNA transcripts (12). Dysregulation of CSTF2 has been implicated in multiple cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), lung cancer (LUAD), and its expression levels are associated with tumor advancement and unfavorable survival rates (13). Elevated CSTF2 expression levels may contribute to increased cell proliferation and survival, further complicating cancer outcomes (14). However, the clinical significance of CSTF2 and its correlations with immune cell infiltration in OSCC remains unclear.
In the present study, the expression levels and prognostic relevance of CSTF2 in OSCC were elucidated via bioinformatics and tissues microarray techniques. Our results indicated that CSTF2 is substantially overexpressed in OSCC and correlated with negative clinicopathological characteristics, modified immune infiltration and unfavorable prognostic outcomes. In summary, CSTF2 may serve as a promising biomarker for both diagnostic and theraputic strategies for OSCC.
2 Methods
2.1 Data acquisition
Clinical and transcriptomic data from a total of 362 human oral epithelial tissue samples, consisting of 330 OSCC samples and 32 non-tumor tissues, were sourced from TCGA. The Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads (FPKM) format data were transformed into transcripts per million (TPM) for the analytical procedures.
2.2 Tissue microarray
The tissue microarray utilized in this study was provided by Zhongke Guanghua (Xi'an) Intelligent Biological Co., Ltd. (catalog number: HN0580c01), ethics approved by same communicated with number: Csyayj2024081. The array included 39 cancer tissues and 19 adjacent non-cancerous tissues(2 tissues of buccal mucosa, 14 tissues of tongue and 3 tissues of glossooharyngeal mucosa), enabling a comprehensive assessment of CSTF2 expression across differing tumour environments.
2.3 Immunohistochemistry
Tumor and adjacent non-cancerous tissues were preserved using 10% formalin, subsequently paraffin embedded, then sectioned into 4–6 μm slices. Following deparaffinization, rehydration, and microwave antigen retrieval, the slides were incubated with a 1:200 dilution of anti-CSTF2 (Bioss, #A8116) at 4°C. After 12 h, the slides were subjected to a 30 min exposure to a secondary antibody at room temperature, followed by 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) substrate staining and hematoxylin counterstaining.
2.4 Assessment of immunohistochemical staining
Two pathologists, who were not associated with this project, assessed the pathological slides according to the latest literature (15, 16). The diagnosis were based on the criteria defined in the 2022 WHO classification of head and neck tumors (17). The tissues were scored on a scale of 0, 1, 2, and 3, where 0 represented no expression, 1 indicated low expression, 2 represented moderate expression, and 3 indicated high expression. Cohen` kappa test was performed to confirm the results.
2.5 Expressed Gene Analysis
Using the median expression levels of CSTF2, patients with OSCC (n = 330) were categorized into two distinct groups to ensure a clear differentiation in biological response. The R package “Limma” was employed to discern differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between cancer and non-cancerous samples, applying thresholds of an adjusted p-value < 0.05 and |log2-fold-change (FC)| >1.5 for significance. The association between CSTF2 and the top ten DEGs was analyzed using Spearman's correlation method. R package “GOplot” (v 1.0.2) was used to applied Gene Ontology (GO) to classify DEGs into various categories. Furthermore, GSEA analysis was executed via the “ClusterProfiler” R package for identifying enriched biological pathways associated with CSTF2.
2.6 Immune infiltration analysis
The levels of immune infiltration for 24 distinct immune cell types were computed, and their relative enrichment scores in OSCC were assessed using single-sample gene set enrichemnt analysis (ssGSEA). The association between CSTF2 expression and the infiltration of various immune cells in OSCC were evaluated via the Spearman's correlation test. Differences in immune infiltration levels between high and low CSTF2 expression groups were evaluated using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, providing insights into the immunological landscape associated with CSTF2 expression in OSCC.
2.7 Prognostic assessment of CSTF2 in OSCC
The influence of CSTF2 expression in OSCC patients was evaluated using the Kaplan–Meier method. The potential independent prognostic value of CSTF2 in OSCC were assessed via univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. The diagnostic and prognostic efficacy CSTF2 in OSCC and various cancer types were assessed via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Furthermore, the univariate Cox regression analysis has been used to explore the interrelations among the variables in the prognostic model. Regplot, survival, and RMS packages were used to analyze clinicopathological features and risk scores.
2.8 Statistical analysis
The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was employed to facilitate comparisons between two distinct groups, whereas the Spearman correlation test was used to investigate the relationships among various variables. Furthermore, both univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analyses were performed to determine the prognostic factors. All statistical analyses were bilateral, with p-values < 0.05 considered statistically significant, thereby guaranteeing the integrity of the results.
3 Results
3.1 CSTF2 is significantly overexpressed in OSCC
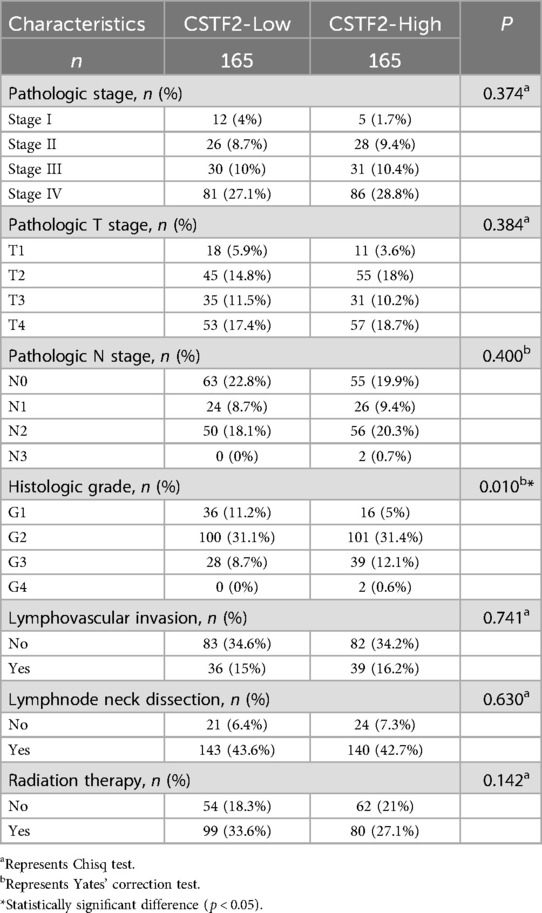
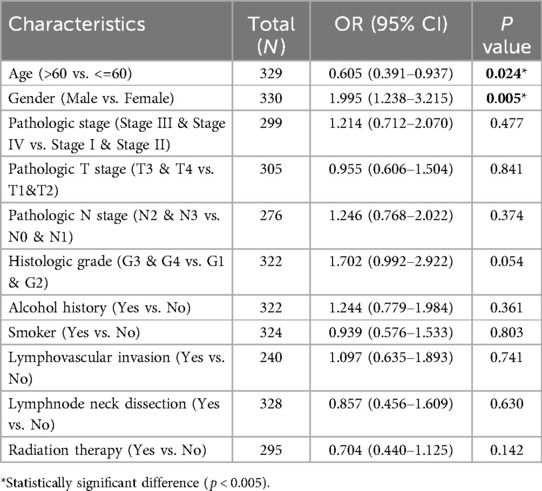
We evaluated the expression levels of the CSTF2 in OSCC tissues relative to those in adjacent non-cancerous tissues. Our Statistical analysis showed high CSTF2 expression in OSCC samples compared to that in the adjacent non-cancerous tissues (Figure 1A). This differential expression was confirmed in 32 paired OSCC samples (Figure 1B). An ROC curve was generated to assess CSTF2's diagnostic potential, resulting in an AUC of 0.717, indicating significant accuracy in distinguishing OSCC from adjacent tissues (Figure 1C). In addition, tissue microarray analysis coupled with immunohistochemistry was performed to validate of CSTF2 expression. Immunohistochemistry results revealed that CSTF2 was predominantly localized in the cell cytoplasm, with partial expression in the nucleus and no expression in the cell membrane. Our analyses further confirmed that the expression levels of CSTF2 were notably elevated in OSCC tissues compared to the adjacent non-cancerous tissues (Figure 1D, Supplementary Figure S1). Quantitative analysis revealed significantly increased staining intensity in OSCC cells, with Cohen's kappa index score of 0.794 (Figure 1E). The correlations between CSTF2 expression and the clinical features of OSCC patients are analyzed (Tables 1a, 1b). Statistical analyses showed that variables, such as age, sex and histological grade were correlated with CSTF2 expression. Logistic regression further identified significant correlations between CSTF2 expression and age and gender (Table 2). Together, these findings suggest that CSTF2 is significantly overexpressed in OSCC and linked to various clinicopathological factors.
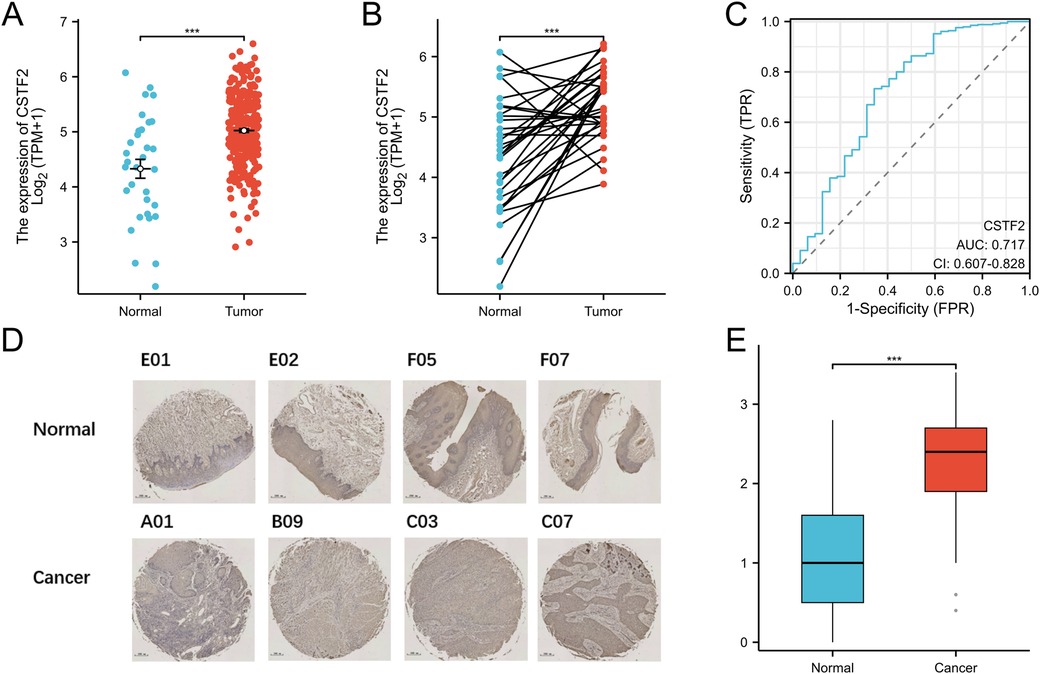
Figure 1. CSTF2 is significantly overexpressed in OSCC. (A) CSTF2 expression in TCGA-OSCC. (B) CSTF2 expression in paired OSCC samples. (C) ROC curve of CSTF2 in OSCC. (D) Immunohistochemical staining of CSTF2 in OSCC tissues chip. (E) Quantification of CSTF2 immunohistochemical staining.
3.2 Functional enrichment analyses of CSTF2-related DEGs in OSCC
CSTF2 related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were examined to further understand the biological significance of CSTF2 in OSCC. A cohort of 330 OSCC patients was stratified into CSTF2-high and CSTF2-low expression groups using the average CSTF2 expression level as a criterion. Comparative analysis identified 895 DEGs, with 496 downregulated genes and 399 upregulated genes, exhibiting an absolute log-fold change exceeding 1.5 and applying thresholds of an adjusted p-value < 0.05. A volcano plot shows the DEGs (Figure 2A). Figure 2B depicts the association between CSTF2 and the top ten DEGs, including SOX14, NOBOX, NKX2–4, SHCBP1l, LINC01224, SMC1B, ZNF541, HMX2, SPINK7 and KRT8P6. Our GO enrichment analysis of biological processes (BP) showed that the primary enriched terms included epidermis development, skin development, epidermal cell differentiation, keratinocyte differentiation and keratinization (Figure 2C). Notable cellular components included immunoglobulin complex, cornified envelope, intermediate filament, keratin filament, and circulating immunoglobulin complex (Figure 2D). The highlighted molecular function (MF) terms included antigen binding, activity of peptidase inhibitor, binding of immunoglobulin receptor, endopeptidase inhibitor activity, and structural constituents of the skin epidermis (Figure 2E). KEGG-related pathways included neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions, Staphylococcus aureus infection, IL-17 signaling, and xenobiotic and drug metabolism by cytochrome P450 (Figure 2F). These findings underscore the unique gene expression patterns that correlate with CSTF2 levels, indicating that these DEGs may be integral to the biological mechanisms involved in OSCC.
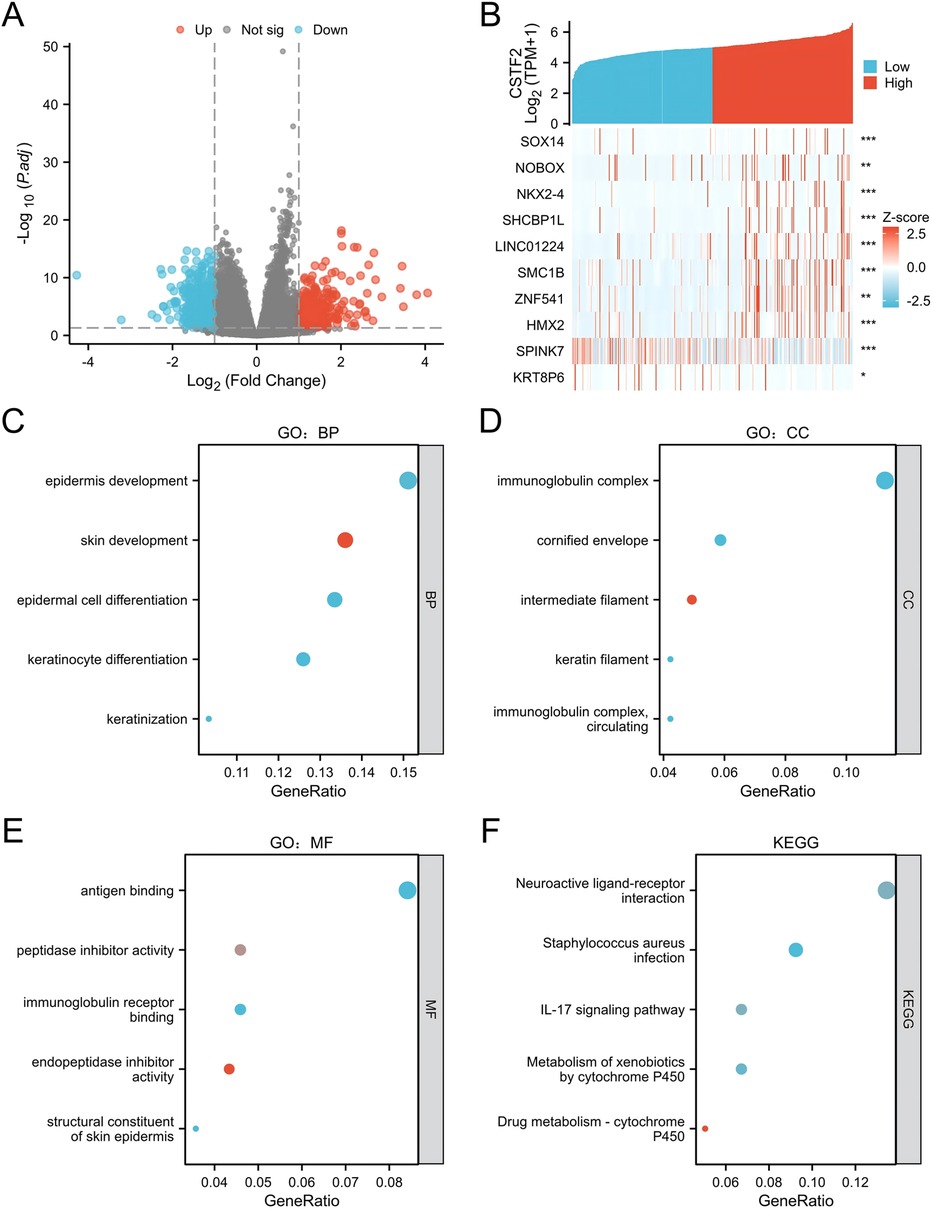
Figure 2. Examination of CSTF2-related DEGs and their functional enrichment in OSCC. (A) Volcano plot illustrating DEGs, with significantly downregulated (blue) and upregulated (red) genes. (B) Heatmap showing the correlation between CSTF2 expression and the top ten DEGs. (C) GO enrichement analysis for biological process (GO-BP) of DEGs. (D) GO enrichement analysis for cellular component (GO-CC) of DEGs. (E) GO enrichement analysis for molecular functions (GO-MF) of DEGs. (F) KEGG analysis of DEGs.
3.3 GSEA analysis of CSTF2 in OSCC
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was conducted to identify significant enrichment in diverse biological processes and signaling pathways. The results showed enrichment in processes hallmark datasets, including E2F targets, G2m checkpoints, Mitotic spindle, MYC targets V2 and Hedgehog Signaling. The Biological Processes section highlightes DNA-templated replication, meiotic cell cycle, and regulation of DNA replication. The cellular composition comprised condensed chromosomes, nuclear Chromosomes, chromosomal regions, and replication forks. Molecular functions included ATP-dependent activity on DNA, helicase activity, DNA helicase activity, single-stranded DNA helicase activity, and catalytic activity on DNA (Figure 3). Collectively, these results suggest a potential role for CSTF2 as a tumour promoter in OSCC through the activation of various signaling pathways.
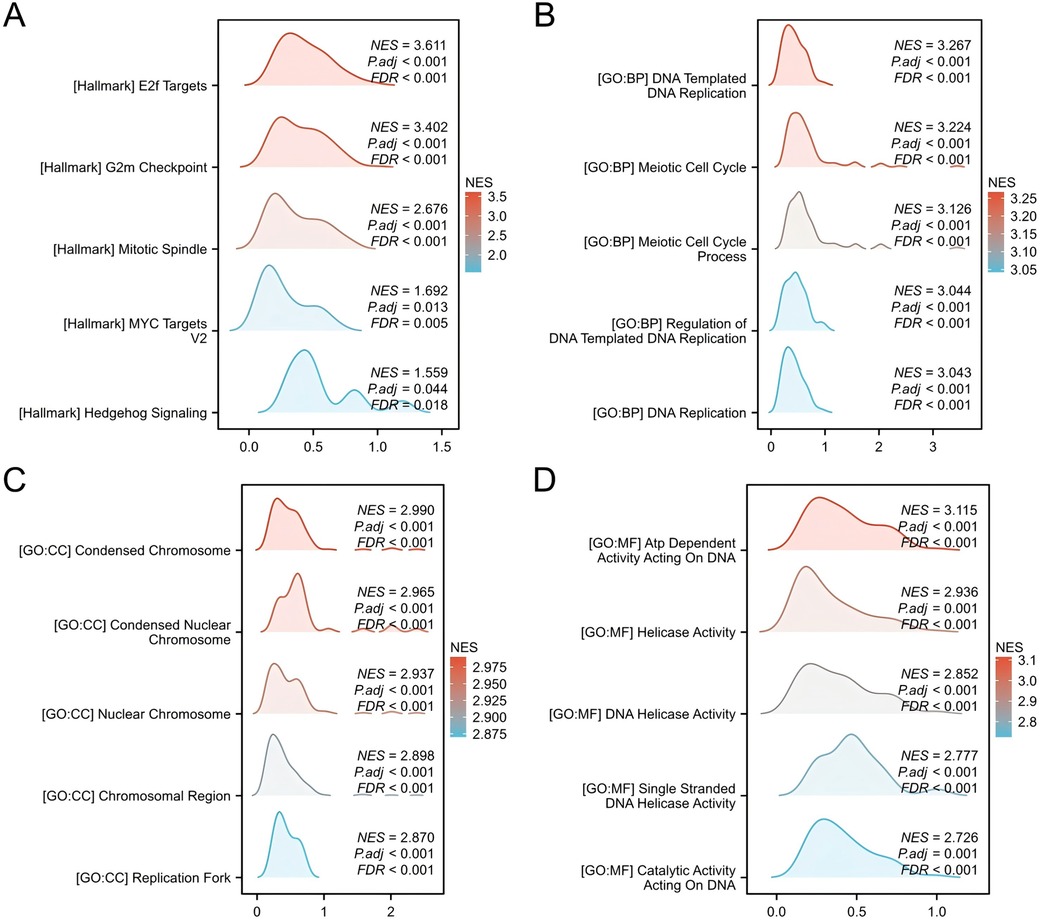
Figure 3. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of DEGs. GSEA enrichment results for (A) Hallmark genesets, (B) BP genesets, (C) CC genesets. (D) MF genesets.
3.4 Tumor immune signature analysis
The association between CSTF2 expression and the infiltration of diverse immune cell types was examined utilizing ssGSEA (Figure 4A). The analysis revealed a negative correlation between CSTF2 expression and the presence of immature dendritic cells (iDC), cytotoxic cells, and plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) (Figures 4B–G). Conversely, a positive correlation was observed among Helper T cell 2 (Th2), T helper cells, and Central memory T cell (Tcm) (Supplementary Figures S2A–F). These results imply that CSTF2 may modulate the immune cell composition within the OSCC tumour microenvironment.
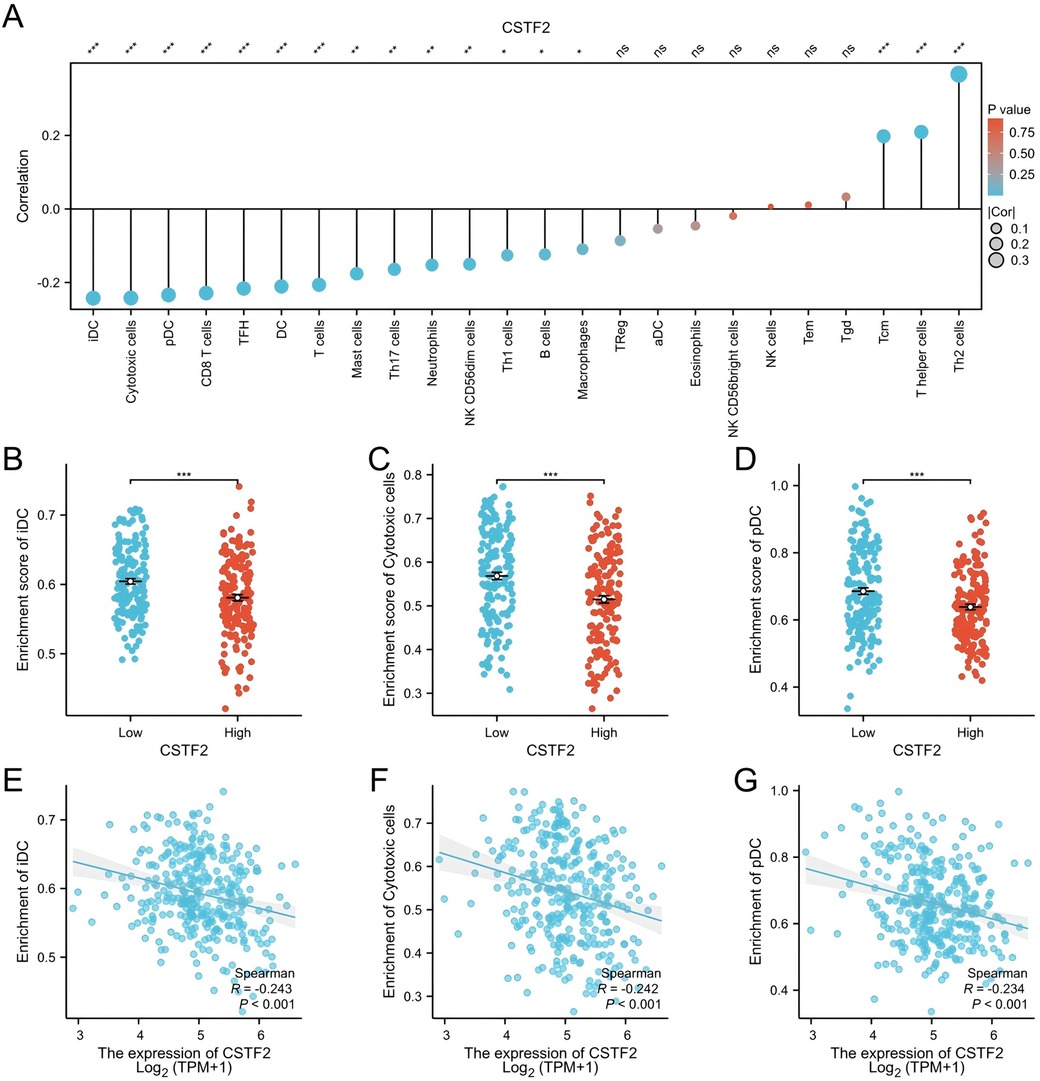
Figure 4. Correlation between CSTF2 expression and infiltration of immune cells in OSCC. (A) Overview of the correlation between CSTF2 expression level and different types of immune cells. (B) Impact of CSTF2 expression on iDC infiltration. (C) Impact of CSTF2 expression on Cytotoxic cell infiltration. (D) Connection between CSTF2 and infiltration of pDC cell. (E) Association between CSTF2 and iDC. (F) The correlation between CSTF2 and Cytotoxic cells. (G) Association between CSTF2 expression levels and plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) infiltration.
3.5 CSTF2 expression correlates with poor prognosis in OSCC
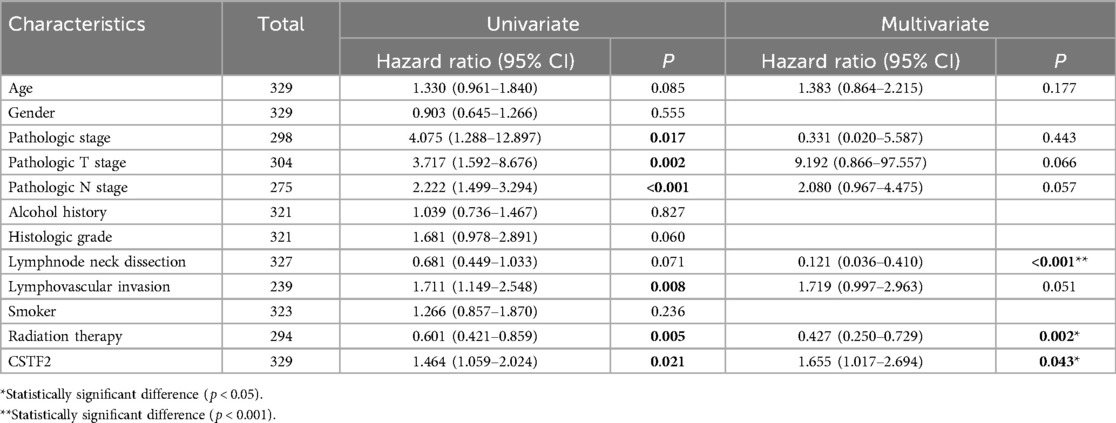
We conducted the Kaplan–Meier analysis to evaluated whether CSTF2 expression was correlated with the survival rates of OSCC patients. Our analysis showed that elevated CSTF2 expression was correlated with poor OS (P = 0.021) and DSS (P = 0.020) outcomes (Figures 5A,B). However, CSTF2 expression did not correlate with PFI (P = 0.296, Figure 5C). Additionally, we explored whether the overexpression of CSTF2 could assess patient survival in multiple cancer types other than OSCC. Elevated CSTF2 expression levels were markedly correlated with diminished OS in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC), pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD), and sarcoma (SARC) (Supplementary Figure S2). Further ROC analysis indicated that PADD (AUC = 0.929) and SARC (AUC = 0.903) had higher AUC values than 0.7 (Supplementary Figure S3). Table 3 presents the Cox univariate and multivariate analyses of CSTF2 expression in OSCC patients. Multivariate analysis identified lymphovascular invasion (P < 0.001), radiation therapy (P = 0.002), and expression of CSTF2 expression (P = 0.043) as independent variables for OSCC prognosis.
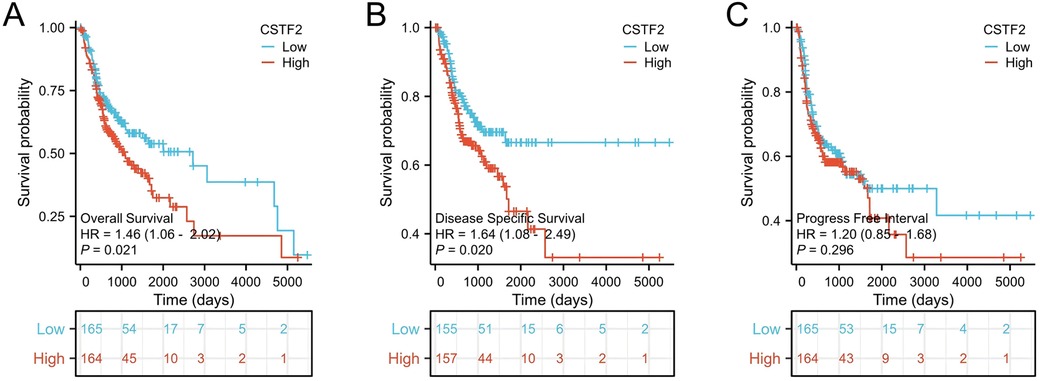
Figure 5. CSTF2 expression is linked to unfavorable survival in OSCC patients. (A) OS, (B) DSS. (C) PFI.
3.6 The creation and validation of a nomogram for OSCC patient prognosis
We developed a prognostic nomogram that incorporated independent prognostic factors to predict OS in OSCC patients. In the nomogram, elevated scores suggested worse prognosis (Figure 6A). Calibration curves were employed to assess the predictive accuracy of the nomogram (Figures 6B–D). The nomogram's bootstrap resampling consistency index (C-index) score was 0.734 (95% CI: 0.678–0.765), demonstrating a moderate level of accuracy in predicting overall survival rates of OSCC patient.
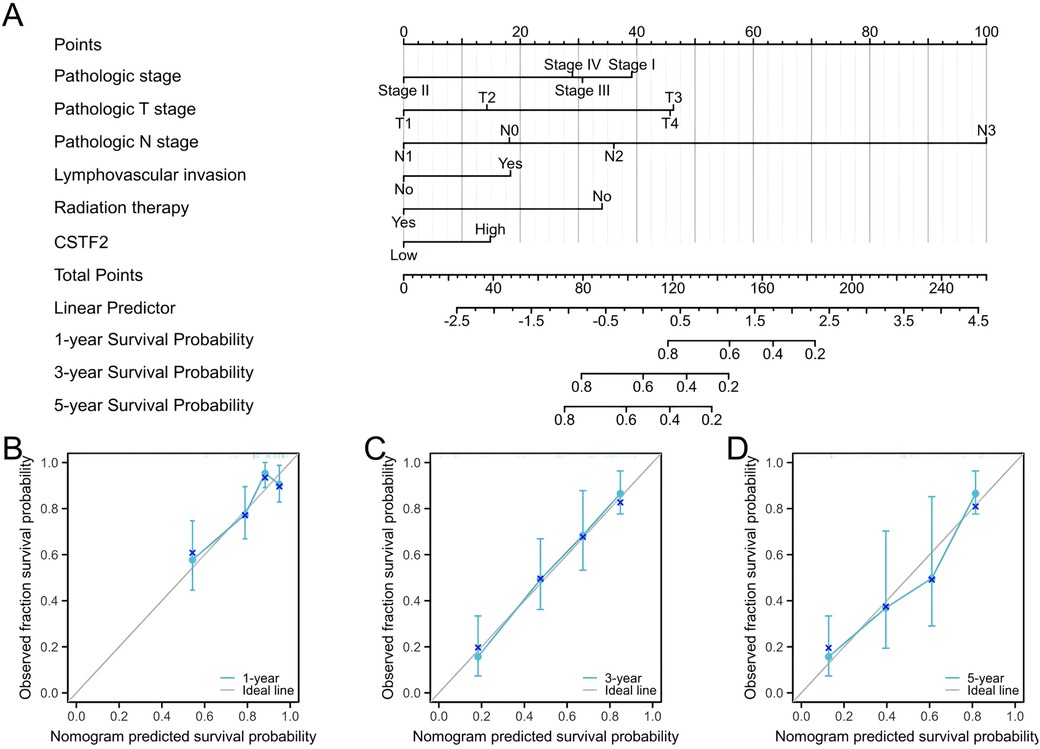
Figure 6. Prognostic diagnostic plots for predicting overall survival in OSCC patients. (A) A prognostic plot was created to forecast overall survival at intervals of 1, 3, 5 years. (B) Calibration curve demonstrating prediction accuracy for 1-year. (C) Prediction accuracy for 3-year. (D) Prediction accuracy for 5-year.
4 Discussion
As a prevalent malignancy in the oral cavity, OSCC substantially affects the quality of life and survival rates globally (18). In china, the incidence of OSCC is increasing, and is influenced by life style factors, such as cigarette smoking, alcohol abuse, betel quid and certain viral infections (19, 20). Recent data reveal an alarming increase in the incidence rate of OSCC within this area, coupled with a disturbing tendency for the disease to manifest at a younger age (21). Despite advancements in treatment approaches, including surgical intervention, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, the prognosis of OSCC is unfavorable, primarily because of late-stage diagnoses, as symptoms are often subtle and nonspecific (22). Therefore, new molecular biomarkers are urgently needed to enhance the early detection and improve the prognostic assessments of patients with OSCC.
This study aimed to explore CSTF2 expression in OSCC tissues and its potential as a prognostic biomarker. Initially identified as a candidate oncogene in human T-cell lymphoma, high expression of CSTF2 has been observed in various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (23–26). However, its contribution to OSCC remains unclear. Using comprehensive bioinformatics analyses along with tissue microarray immunohistochemistry, our results suggest that CSTF2 expression is significantly high in OSCC. Furthermore, high CSTF2 expression was correlated with unfavorable clinicopathological factors, including patient age and gender. CSTF2 is known to promote cancer progression by affecting various signaling pathways such as c-Myc translation, IL-6/IL-6R, and Src/p190B (27, 28). However, CSTF2 mediated biological roles and signaling pathways require further investigation. In the current study, our GO/KEGG and GSEA analyses revealed that CSTF2 related expression group showed significant enrichment in pathways related to epidermal development and differentiation, immunoglobulin complex, peptidase and endopeptidase inhibitor activity, and cytochrome p450 metabolism. These findings requires additional experimental validation and could improve our understanding of CSTF2-related biological functions in OSCC.
Tumor cells exist within a complex microenvironment that includes not only cancer cells but also immune cells and various stromal components (29, 30). In malignant tumors, including OSCC, the tumor cells are typically surrounded by infiltrating immune cells (31). The prognostic impact of immune cell infiltration in solid tumors is determined by factors such as the immune cell type, density, and spatial distribution (32). Assessing infiltrating immune cells in OSCC may enhance ICI treatment and serve as a potential predictor of treatment outcomes (33). Notably, the elevated CSTF2 expression exhibited significant enrichment of the IL-17 signaling pathway. We examined the correlation between CSTF2 expression levels and the infiltration of various immune cells. Our study demonstrated that CSTF2 overexpression is inversely associated with the infiltration of iDC, cytotoxic cells, and pDCs, whereas it is positively associated with Th2 cells, T helper cells, and Tcm cells. These findings indicate that overexpression of CSTF2 could potentially affect the progression and prognosis of OSCC through the levels its modulation of infiltrating immune cell levels.
Prior studies have established an association between CSTF2 expression and decreased survival rates across various cancers (34, 35). Our survival analysis indicated that high CSTF2 expression independently predicted poor OS and DSS in OSCC patients. Therefore, CSTF2 may serve as a potential molecular biomarker of OSCC.
While the insights gained from this study are significant, it is crucial to recognize its limitations. The findings are primarily derived from assessments of data obtained from public databases, supplemented by immunohistochemical validation using tissue microarrays, which lack extensive validation through comprehensive clinical sample analyses. Furthermore, although we have proposed potential mechanisms that clarify the role of CSTF2 in OSCC, additional experimental studies are necessary to confirm the specific molecular pathways involved.
In conclusion, this study identified high CSTF2 expression as an independent negative prognostic indicator of OSCC, which was linked to aggressive clinical characteristics and immune regulatory mechanisms. CSTF2 may play a critical role in OSCC development through various signaling pathways. Nonetheless, the mechanism by which CSTF2 influences OSCC tumorigenesis and progression necessitate further investigation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Zhongke Guanghua (Xi'an) Intelligent Biological Co., Ltd. Ethics approval number: Csyayj2024081. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by- product of routine care or industry. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
AA: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZA: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology, Validation. MM: Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Software, Supervision. ZL: Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work supported by Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, number 2023D01F12. State key laboratory of pathogenesis, prevention, treatment of central Asian high incidence diseases fund, number SKL-HIDCA-2024-KS3. Sponsed by The First People’s Hospital of Kashi Prefecture, Science Research Project Fund, number KDYY202405.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/froh.2025.1548829/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Positive correlation between CSTF2 expression and various immune cells. (A) Differential infiltration levels of Th2 cells in relation to CSTF2 expression. (B) T helper cells infiltration in relation to CSTF2 expression. (C) Tcm cell infiltration levels in relation to CSTF2 expression. (D) Correlation between CSTF2 and Th2 cell infiltration. (E) Relationship between CSTF2 and T helper cell infiltration. (F) Correlation between CSTF2 expression and Tcm cell infiltration.
Supplementary Figure S2 | Prognostic values of CSTF2 expression in pan-cancer. (A) OS; (B) DSS; (C) PFI.
Supplementary Figure S3 | ROC curves of CSTF2 in various cancer types. (A) HNSC; (B) KIRC; (C) PAAD; (D) LIHC; (E) SARC.
Supplementary Figure S4 | Prognostic values of CSTF2 expression in patients with OSCC evaluated by the Kaplan–Meier method in different subgroups. (A–K) OS survival curves of Age >60 years; Male; Female; Pathologic stage III and IV; Pathologic stage T3 and T4; Pathologic stage N0 and N1; Histologic grade G1 and G2; Lymphovascular invasion, NO; Lymphnode neck dissection; Radiation therapy; Smoker and Alcohol history.
References
1. Tan Y, Wang Z, Xu M, Li B, Huang Z, Qin S, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinomas: state of the field and emerging directions. Int J Oral Sci. (2023) 15:44. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00249-w
2. Khijmatgar S, Yong J, Rübsamen N, Lorusso F, Rai P, Cenzato N, et al. Salivary biomarkers for early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma (oscc) and head/neck squamous cell carcinoma (hnscc): a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. (2024) 60:32–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2023.10.003
3. Kumari P, Debta P, Dixit A. Oral potentially malignant disorders: etiology, pathogenesis, and transformation into oral cancer. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:825266. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.825266
4. Chamoli A, Gosavi AS, Shirwadkar UP, Wangdale KV, Behera SK, Kurrey NK, et al. Overview of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: risk factors, mechanisms, and diagnostics. Oral Oncol. (2021) 121:105451. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105451
5. Purwanto DJ, Soedarsono N, Reuwpassa JO, Adisasmita AC, Ramli M, Djuwita R. The prevalence of oral high-risk hpv infection in Indonesian oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oral Dis. (2020) 26:72–80. doi: 10.1111/odi.13221
6. Tajmirriahi N, Razavi SM, Shirani S, Homayooni S, Gasemzadeh G. Evaluation of metastasis and 5-year survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients in isfahan (2001–2015). Dent Res J. (2019) 16:117–21. doi: 10.4103/1735-3327.250974
7. Ghaderi H, Roshan-Zamir M, Jafarinia M, Kruger E. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: focus on biomarkers for screening. J Dent. (2024) 25:1–16. doi: 10.30476/dentjods.2023.96159.1924
8. Nguyen TTH, Sodnom-Ish B, Choi SW, Jung H, Cho J, Hwang I, et al. Salivary biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. (2020) 46:301–12. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.5.301
9. Radaic A, Kamarajan P, Cho A, Wang S, Hung GC, Najarzadegan F, et al. Biological biomarkers of oral cancer. Periodontol 2000. (2024) 96:250–80. doi: 10.1111/prd.12542
10. Poothakulath Krishnan R, Pandiar D, Ramani P, Ramalingam K, Jayaraman S. Utility of cd44/cd24 in the outcome and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Cureus. (2023) 15(8):e42899. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42899
11. Masoumzadeh E, Grozdanov PN, Jetly A, MacDonald CC, Latham MP. Electrostatic interactions between cstf2 and pre-mrna drive cleavage and polyadenylation. Biophys J. (2022) 121:607–19. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.01.005
12. Ding J, Su Y, Liu Y, Xu Y, Yang D, Wang X, et al. The role of cstf2 in cancer: from technology to clinical application. Cell Cycle. (2023) 22:2622–36. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2299624
13. Zhang S, Zhang X, Lei W, Liang J, Xu Y, Liu H, et al. Genome-wide profiling reveals alternative polyadenylation of mrna in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. (2019) 17:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1986-0
14. Feng L, Jing F, Qin X, Zhou L, Ning Y, Hou J, et al. Cleavage stimulation factor subunit 2: function across cancers and potential target for chemotherapeutic drugs. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:852469. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.852469
15. Pekarek L, Garrido-Gil MJ, Sanchez-Cendra A, Cassinello J, Pekarek T, Fraile-Martinez O, et al. Emerging histological and serological biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma: applications in diagnosis, prognosis evaluation and personalized therapeutics (review). Oncol Rep. (2023) 50:852469. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8650
16. Almangush A, Mäkitie AA, Triantafyllou A, de Bree R, Strojan P, Rinaldo A, et al. Staging and grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma: an update. Oral Oncol. (2020) 107:104799. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104799
17. Muller S, Tilakaratne WM. Update from the 5th edition of the world health organization classification of head and neck tumors: tumours of the oral cavity and mobile tongue. Head Neck Pathol. (2022) 16:54–62. doi: 10.1007/s12105-021-01402-9
18. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
19. Bugshan A, Farooq I. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: metastasis, potentially associated malignant disorders, etiology and recent advancements in diagnosis. F1000Research. (2020) 9:229. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.22941.1
20. Eloranta R, Vilen S, Keinanen A, Salo T, Qannam A, Bello IO, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: effect of tobacco and alcohol on cancer location. Tob Induc Dis. (2024) 22:1–9. doi: 10.18332/tid/189303
21. Wu N, Li Y, Ma X, Huang Z, Chen Z, Chen W, et al. High incidence of hpv infection in minors with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. (2024) 19:51. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01470-9
22. Caruntu A, Yang S, Acero J. New insights for an advanced understanding of the molecular mechanisms in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6964. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136964
23. Chen Z, Hao W, Tang J, Gao W, Xu H. Cstf2 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma progression via aerobic glycolysis. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:897804. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.897804
24. Yang F, He Y, Ge N, Guo J, Yang F, Sun S. Exploring kras-mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a model validation study. Front Immunol. (2024) 14:1203459. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1203459
25. Curinha A, Oliveira Braz S, Pereira-Castro I, Cruz A, Moreira A. Implications of polyadenylation in health and disease. Nucleus. (2014) 5:508–19. doi: 10.4161/nucl.36360
26. Zheng Y, Li X, Deng S, Zhao H, Ye Y, Zhang S, et al. Cstf2 mediated mrna n6-methyladenosine modification drives pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma m6a subtypes. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:6334. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41861-y
27. Chen X, Zhang J, Luo J, Wu S, Yuan G, Ma N, et al. Cstf2-induced shortening of therac1 3′utr promotes the pathogenesis of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:5848–62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0822
28. Zhang M, Liu J. Cleavage stimulation factor 2 promotes malignant progression of liver hepatocellular carcinoma by activating phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/protein kinase b/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:10047–60. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2063100
29. Eckert AW, Wickenhauser C, Salins PC, Kappler M, Bukur J, Seliger B. Clinical relevance of the tumor microenvironment and immune escape of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. (2016) 14:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0828-6
30. Xue Y, Song X, Fan S, Deng R. The role of tumor-associated macrophages in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:959747. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.959747
31. Wu J, Zhang T, Xiong H, Zeng L, Wang Z, Peng Y, et al. Tumor-infiltrating cd4(+) central memory t cells correlated with favorable prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Inflamm Res. (2022) 15:141–52. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S343432
32. Kurkalang S, Roy S, Acharya A, Mazumder P, Mazumder S, Patra S, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of gingivo-buccal oral cancer reveals two dominant cellular programs. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:4732–46. doi: 10.1111/cas.15979
33. Liu R, Yang F, Yin J, Liu Y, Zhang W, Zhou H. Influence of tumor immune infiltration on immune checkpoint inhibitor therapeutic efficacy: a computational retrospective study. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:685370. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685370
34. Huang Y, Xu J, Xie C, Liao Y, Lin R, Zeng Y, et al. A novel gene pair cstf2/dpe2a impacts prognosis and cell cycle of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2023) 10:1639–57. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S413935
Keywords: oral squamous cell carcinoma, CSTF2, prognosis, immune infiltration, differential expression, biomarker
Citation: Aierken Z, Muhetaer M, Lei Z and Abudourousuli A (2025) Expression of CSTF2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its relationship with immune infiltration and poor prognosis. Front. Oral. Health 6:1548829. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1548829
Received: 20 December 2024; Accepted: 23 January 2025;
Published: 7 February 2025.
Edited by:
Mariana Villarroel-Dorrego, Central University of Venezuela, VenezuelaReviewed by:
Jessica Maldonado-Mendoza, Metropolitan Autonomous University, MexicoRosana Morelatto, National University of Cordoba, Argentina
Yamely Ruiz Vázquez, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Copyright: © 2025 Aierken, Muhetaer, Lei and Abudourousuli. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ainiwaerjiang Abudourousuli, QWJ1ZHVyc2xpQG1haWwyLnN5c3UuZWR1LmNu
 Zumulaiti Aierken1
Zumulaiti Aierken1 Ainiwaerjiang Abudourousuli
Ainiwaerjiang Abudourousuli