
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Oral. Health , 19 February 2025
Sec. Preventive Dentistry
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/froh.2025.1444399
This article is part of the Research Topic Periodontal Disease and Systemic Health: Preventive Strategies and Management View all articles
Introduction: Periodontitis affects a significant portion of the global population and is associated with systemic health issues. Salivary biomarkers such as salivary matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) and its activated form (aMMP-8) have been studied for their roles in tissue degradation and inflammation in periodontitis. This meta-analysis investigates the association between salivary MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels and periodontitis.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted utilizing PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases up to October 2023, yielding 35 studies that quantified MMP-8 or aMMP-8 in saliva from patients with periodontitis and healthy controls. Data were extracted, and standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. Heterogeneity was assessed, and subgroup analyses were performed based on saliva collection techniques. Meta-regression analysis evaluated the impact of publication year on heterogeneity.
Results: The meta-analysis included 35 studies. Pooled results indicated significantly higher levels of MMP-8 and aMMP-8 in periodontitis cases compared to healthy controls (SMD: 2.71, 95% CI: 1.04–4.38, p = 0.002) with substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 94.5%). No significant difference was found between MMP-8 and aMMP-8 (p = 0.445). Subgroup analyses by saliva collection technique did not reduce heterogeneity significantly. Meta-regression showed that publication year did not impact heterogeneity. Small-study effects and publication bias were present, suggesting caution in interpreting the results.
Discussion: The findings support the potential of MMP-8 and aMMP-8 as biomarkers for periodontitis, although substantial heterogeneity and methodological differences among studies pose challenges. Standardized protocols and larger sample sizes are necessary to enhance the reliability of these biomarkers in clinical practice. Despite limitations, salivary diagnostics hold promise for non-invasive, early detection and monitoring of periodontitis.
Conclusion: Salivary MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels are significantly associated with periodontitis, highlighting their potential as diagnostic biomarkers. However, methodological improvements and standardization are essential for their clinical application. Collaborative efforts and advancements in salivary diagnostics are crucial for improving periodontitis management and patient outcomes.
Periodontitis stands as a significant public health concern, effecting an estimated 20%–50% of the global population (1, 2). This inflammatory disease affects systemic health beyond the oral cavity, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis (3, 4). Key to its pathogenesis are molecular mechanisms involving salivary matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) and its activated form (aMMP-8), which contribute to tissue degradation and inflammation (5).
Salivary matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) constitute a family of zinc-dependent endopeptidases crucial for extracellular matrix remodeling and turnover. Among them, MMP-8, also known as neutrophil collagenase, plays a pivotal role in the degradation of collagen types I, II, and III, key components of periodontal tissues (6, 7). It is predominantly produced by neutrophils, but other cell types, including fibroblasts and macrophages, also contribute to its expression. Activated MMP-8 (aMMP-8) arises from the cleavage of pro-MMP-8 by other proteases, such as serine proteases or other MMPs. This activation process unleashes the proteolytic potential of MMP-8, enhancing its ability to degrade extracellular matrix components (8). The presence of aMMP-8 in periodontal tissues underscores its role as a key mediator of tissue destruction in periodontitis (9, 10).
Periodontitis, characterized by inflammation and destruction of periodontal tissues, represents a complex interplay between microbial pathogens and host immune response. MMP-8 and aMMP-8, with their capacity to degrade collagen and other extracellular matrix components, are implicated in the breakdown of periodontal tissues, leading to clinical manifestations such as gingival inflammation, periodontal pocket formation, irreversible bone loss, and, ultimately, tooth loss. Therefore, the earliest diagnosis will result in better outcomes for an individual at risk for the progression of periodontitis. While clinical and radiological criteria aid in diagnosing periodontitis, detecting it early and tracking its progression can be difficult. MMP-8 shows promise as the top biomarker for predicting, diagnosing, and gauging the progression of periodontitis (11–13).
Saliva has emerged as a pivotal diagnostic medium in dentistry due to its non-invasive collection method and the presence of a plethora of biomarkers. Saliva collection methods are generally categorized as stimulated or unstimulated and have the capability to conduct point-of-care (chairside) testing (14–17). Furthermore, its utility extends beyond traditional clinical assessments, offering insights into various oral and systemic diseases, including periodontits (18). Recent advancements in technologies, such as saliva-based diagnostics approaches, have propelled saliva to the forefront of dental research (19). These methodologies enable the identification of microbial signatures and the quantification of specific protein biomarkers like MMP-8 and aMMP-8, elucidating disease pathogenesis and progression (20, 21). The integration of saliva-based diagnostics into clinical practice holds promise for early disease detection, personalized treatment strategies, and improved patient outcomes (22, 23). It should be noted, to date, there are no FDA approved testing methods or devices for the evaluation of periodontitis risk. The current marketplace features methods and devices categorized within the FDA's Health and Wellness device category. This category correlates to low-risk products that promote a healthy lifestyle (general wellness products) (24).
In our systematic meta-analysis, we investigated the potential association between salivary MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels and periodontitis by examining a total of 35 relevant studies. Our analysis aimed to distinguish any discernible patterns or trends in MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels among individuals with periodontitis compared to those without. Additionally, we explored the utility of saliva as a non-invasive diagnostic medium for periodontitis. The findings from this study provide valuable insights into the potential role of MMP-8 as a biomarker and the broader implications of salivary analysis in periodontitis diagnosis.
We conducted a systematic literature search and meta-analysis to investigate the role of salivary matrix metalloproteinase (MMP8) and activated matrix metalloproteinase (aMMP8) in periodontitis according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) Statement (25). Medical databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, were searched from database inception until October 2023. The comprehensive list of search strategies is presented in Appendix 1. Literature was imported to the EndNote X9 referencing program (The EndNote Team, Clarivate, Philadelphia, PA, USA), and literature was deduplicated using a “Find Duplicates” function. Unique studies were screened based on the inclusion criteria. Original data reporting MMP8 and aMMP8 levels measured in the saliva of patients diagnosed with periodontitis and healthy controls were eligible for the analysis.
Studies excluded during screening included case reports, reviews, non-English publications, unpublished data, those using gingival fluid or serum for MMP8/aMMP8 analysis or mRNA and protein expression data. The remaining studies were screened with full-text information, and extracted data was used in data synthesis. In case of data presented from the same center and overlapping time frame, the latest or the largest dataset was included in the analysis.
Due to the different unit and measurement methods across eligible studies, the effect size was reported in standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) (26). Mean and standard deviations were calculated using Hozo's equation if the data were presented in median, minimum, and maximum values (27). Data were extracted from bar plots using the online tool available at WebPlotDigitizer - Copyright 2010–2023 Ankit Rohatgi (automeris.io), when needed. Studies reporting medians with interquartile ranges (IQR) were excluded due to the precautions in converting IQR to standard deviation according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (version 6.4, 2023) (28). The significance level was set to an alpha value of 0.05. The heterogeneity between studies was measured with I2 values.
The PRISMA flowchart was generated using a Shiny app by Haddaway et al. (29). Statistical analysis and data visualization were performed using RStudio 2023.12.1 (R version 4.3.1) statistical software (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria) (30). Meta-analysis was performed using the meta package (31, 32). The outlier studies were determined using the dmetar package (33, 34). Results of meta-analysis and small study effects were illustrated with Forest and contour-filled Funnel plots, respectively. The Funnel plot asymmetry was analyzed using Egger's asymmetry test (35–38), and the small-study effect was adjusted with Duval and Tweedie trim and fill method (39, 40).
Systematic literature screening of 767 unique studies yielded 148 studies for full-text screening. The largest group of excluded studies was the ones reporting data from periodontitis patients or healthy controls only (n = 68). The following most common reason was the unavailability of reported data required for statistical analysis (n = 39). The PRISMA Flowchart illustrating the screening process is shown in Figure 1.
We found 25 eligible studies published between 2008 and 2022 reporting MMP8 values in periodontitis cases (n = 1317) with matched healthy controls (n = 1,047) (41–65). MMP8 was measured in unstimulated saliva in 68% of included studies (n = 17), and ELISA was the most used method for quantification (Table 1).
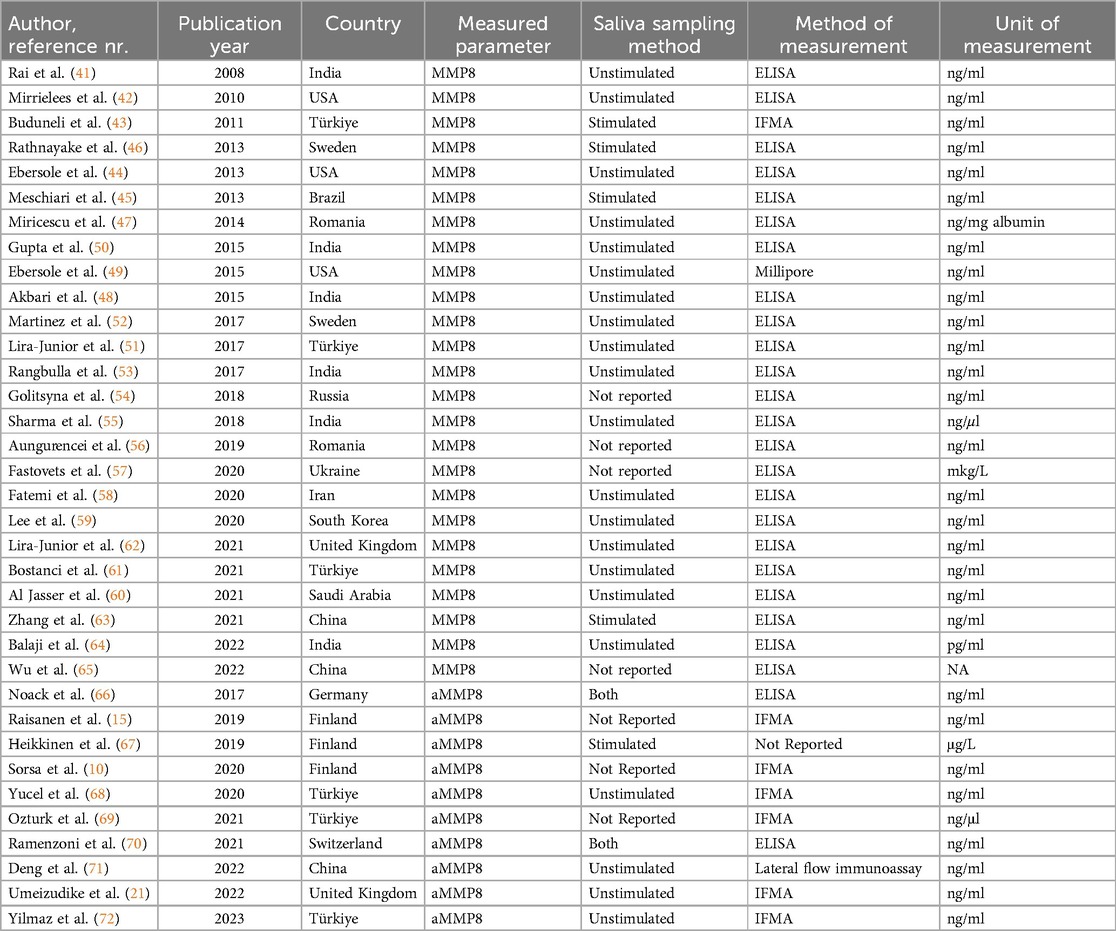
Table 1. Studies included in the meta-analysis analyzing MMP8 and aMMP8 levels in patients with periodontitis and healthy controls.
As the second outcome of interest, we analyzed activated MMP8 (aMMP-8) levels in periodontitis patients (n = 573) and healthy participants (n = 364). The literature review resulted in the inclusion of ten eligible studies reporting aMMP8 levels published between 2017 and 2023. (10, 15, 21, 66–72). Two of these studies reported data from two separate cohorts with stimulated and unstimulated saliva collection (Table 1).
A random effect model meta-analysis of 35 studies with 37 study cohorts quantifying both biomarkers showed significantly high values in periodontitis patients with an overall standardized mean difference of 2.71 (95% CI: 1.04–4.38, p = 0.002), although with a high heterogeneity (I2 = 94.5%) (Figure 2). In a subgroup analysis by the type of the biomarker, studies evaluating MMP8 values showed an overall standardized mean difference of 3.19 (95% CI: 0.38–6.01, p = 0.026, I2 = 95%), while the effect size for aMMP8-quantifying cohorts was 2.02 (95% CI: 0.99–3.05, p < 0.001, I2 = 93.1%) (Figure 2). Overall, no statistical difference was found between studies measuring MMP8 and aMMP8 as a salivary biomarker (p = 0.445).
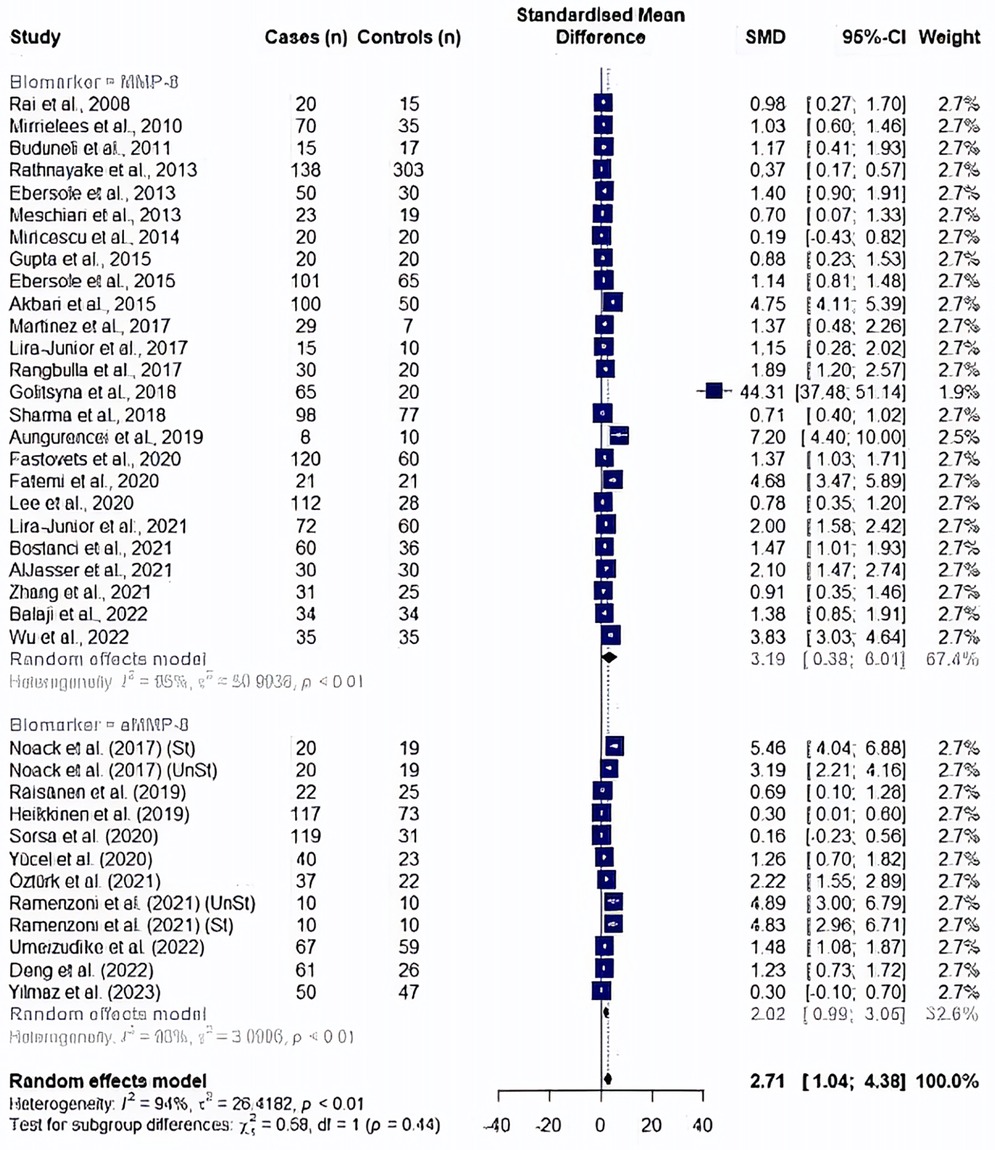
Figure 2. Forest plot illustrating a meta-analysis of MMP8 and aMMP8 values in saliva samples of periodontitis patients and healthy controls. St, stimulated saliva collection; UnSt, unstimulated saliva collection.
In a post hoc analysis, a study by Golitsyna et al. (54) showed an extremely large effect by exceeding the upper bound of the pooled effect and was accepted as an outlier study according to the definition by Viechtbauer et al. (73). An outlier finding function of dmetar package has confirmed the same study as an outlier affecting the random effect analysis results, in addition to seven other studies (10, 46, 47, 55, 56, 67, 72). After the removal of outlier studies (n = 29), a random effect meta-analysis yielded a significantly high MMP8 and aMMP8 levels in periodontitis patients (SMD: 1.97, 95% CI: 1.48–2.46, p < 0.0001, I2 = 90.2%). A subgroup of cohorts showed no difference between two salivary biomarkers (p = 0.147); MMP8: SMD = 1.72, 95% CI: 1.21–2.22, p < 0.0001, I2 = 90.8%) and aMMP8: SMD = 2.65, 95% CI 1.50–3.80, p < 0.0001, I2 = 90%) (Figure 3).
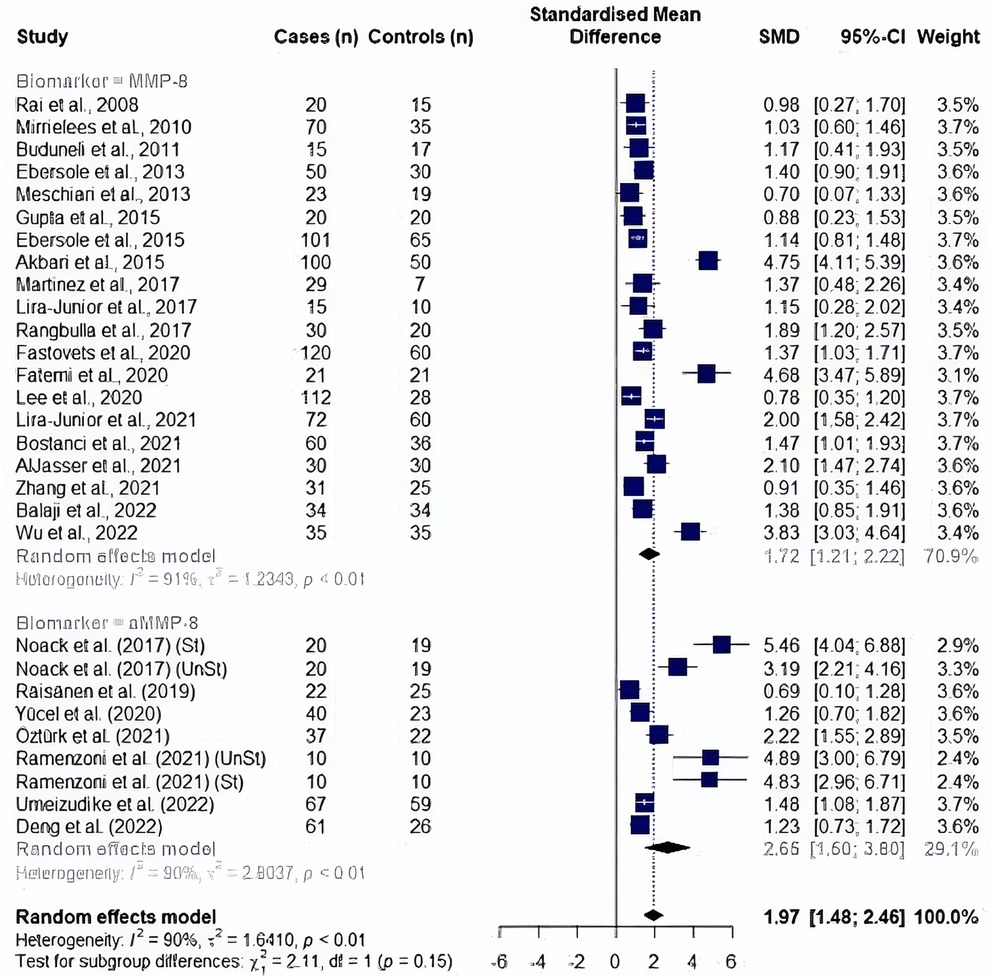
Figure 3. Forest plot illustrating a meta-analysis of MMP8 and aMMP8 values in saliva samples of periodontitis patients and healthy controls after removing outlier studies. St, stimulated saliva collection; UnSt, unstimulated saliva collection.
We analyzed the effects of saliva collection techniques on each biomarker. Studies showed an overall effect favoring high MMP8 levels in periodontitis cases (unstimulated saliva collection: SMD: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.04–2.17, I2 = 92% and stimulated saliva collection: SMD: 0.69, 95% CI: 0.32–1.06, I2 = 57%). Additionally, saliva collected without prior stimulation had significantly higher MMP8 levels than saliva collected upon stimulation (p = 0.007) (Figure 4). In the analysis of aMMP8-quantifying cohorts, both groups showed an overall effect with high aMMP8 levels in periodontitis cases, although the analysis did not improve the heterogeneity (unstimulated: SMD: 1.88, 95% CI: 0.71–3.05, I2 = 90% and stimulated: SMD: 3.45, 95% CI: 0.17–6.72, I2 = 97%). With six and three studies in unstimulated and stimulated subgroups, respectively, group results did not differ statistically (p = 0.379) (Figure 5).
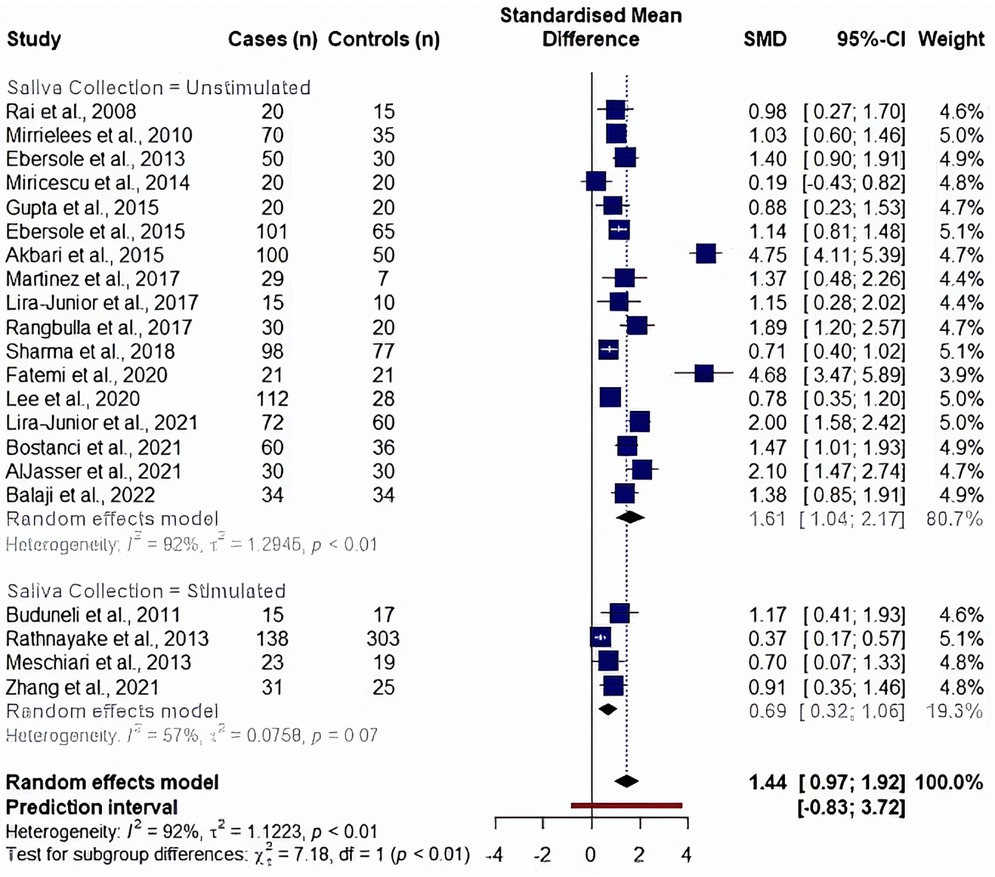
Figure 4. Subgroup analysis by saliva collection method evaluating MMP8 levels. Information on saliva collection method was not reported in studies by Golitsyna et al., 2018 (36), Aungurencei et al., 2019 (38), Fastovets et al., 2020 (39).
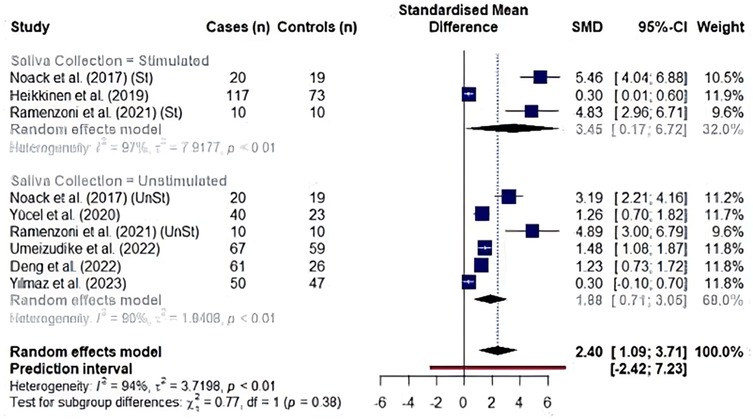
Figure 5. Subgroup analysis by saliva collection technique in studies evaluating aMMP8 levels. St, stimulated saliva collection; UnSt, unstimulated saliva collection. Information on saliva collection method was not reported in studies by Räisänen et al. (2019) (14), Sorsa et al. (2020) (9), Öztürk et al. (2021) (51).
We also conducted a meta-regression analysis adjusting for the effects of publication year. Analysis with all eligible studies (I2 = 99.8%, R2 = 0.0%, p = 0.529) and after exclusion of an outlier study by Golitsyna et al. (54) (I2 = 95.8%, R2 = 6.9%, p = 0.091), showed that publication year was not an affecting predictor of heterogeneity in the studies analyzing MMP8 as a biomarker (Supplementary Figure S1). The same findings were also found in aMMP8-measuring cohorts (I2 = 97.4%, R2 = 3.83%, p = 0.244) (Supplementary Figure S2).
Lastly, we evaluated eligible studies for small-study effects and publication bias. Visualization with a contour-enhanced Funnel plot identified five studies of small-study effects in the MMP8 cohort (48, 54, 56, 58, 65) (Figure 6A and Supplementary Figure S3). Further, Egger's asymmetry test confirmed the presence of funnel plot asymmetry in the cohort of 25 studies (Intercept = 6.464, 95% CI: 3.66–9.26, t = 4.52, p < 0.001) and the cohort after an outlier study removal (Intercept: 5.161, 95% CI: 2.34–7.98, t = 3.587, p = 0.002). The trim-and-fill procedure added a total of ten studies and provided an estimate of the corrected effect of 0.87 (95%CI: −2.34 to 4.07, p = 0.597) with a heterogeneity of 96.6%. When we applied the adjustment to the study cohorts after an outlier removal (n = 24), after the addition of 10 studies, the corrected effect was 0.84 (95% CI: 0.17–1.51, p = 0.014) with a heterogeneity of 95.4% (Figure 6B and Supplementary Figure S4).
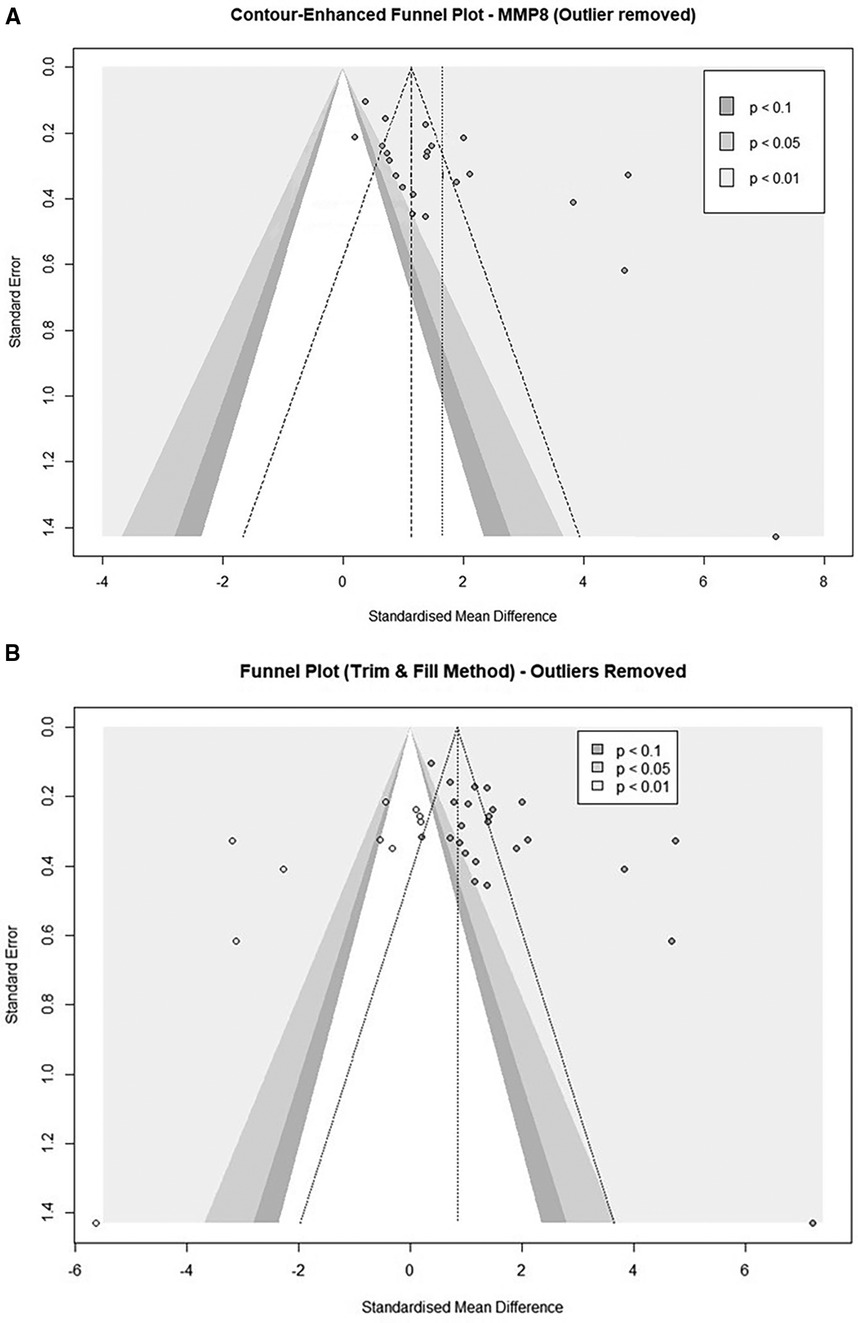
Figure 6. (A) Contour-enhanced funnel plot of MMP8-quantifiying studies evaluating the small-study effects after exclusion of an outlier study (n = 24). (B) Contour-enhanced Funnel plot after a trim and fill analysis (n = 24). (Imputed studies are shown with empty dots).
Funnel plot asymmetry was also observed in five cohorts from three studies using aMMP8 as a biomarker (66, 69, 70) (Figure 7A). An Egger's asymmetry test for small study effects confirmed the funnel plot asymmetry in the general study cohort (Intercept = 6.955, 95% CI: 4.44–9.47, t = 5.427, p < 0.001) and after removal of outlier studies (Intercept = 5.694, 95% CI: 3.09–8.3, t = 4.284, p = 0.004, Supplementary Figure S5). The trim-and-fill-procedure analysis added five studies and provided an estimate of the corrected effect of 0.71 (95%CI: −0.62 to 2.04, p = 0.296) with a heterogeneity of 94.6% (Figure 7B). When applied to nine cohorts after the removal of outliers, after adding three studies, the trim-and-fill analysis found a corrected effect of 1.56 (95%CI: 0.08–3.06, p = 0.039) with heterogeneity of 91.9% (Supplementary Figure S6).
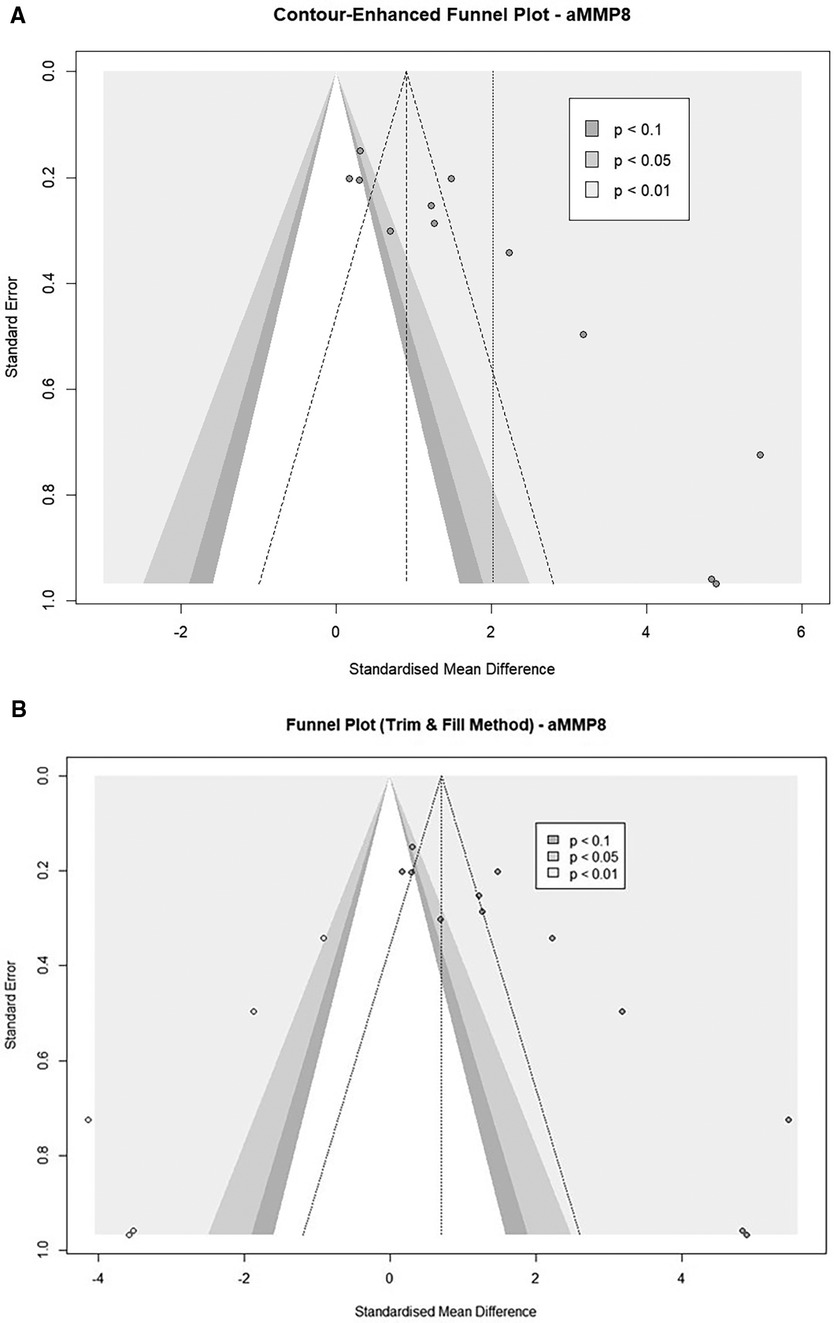
Figure 7. (A) Contour-enhanced funnel plots of aMMP8 cohorts (n = 12). (B) Contour-enhanced Funnel plot after a trim and fill analysis. (Imputed studies are shown with empty dots (n = 12).
MMP-8 plays a central role in extracellular matrix remodeling and turnover, contributing to tissue destruction and inflammation with periodontitis events. A total of 25 and 10 studies, respectively, examining MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels in periodontitis patients compared to healthy controls were included in the current meta-analysis. Our analysis identified significant differences in MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels between periodontitis cases and healthy controls, supporting their potential as diagnostic biomarkers. Additionally, both biomarkers were similar in overall effect sizes and did not differ statistically.
MMP8 is a widely investigated biomarker in saliva, gingival cervical fluid, and serum. aMMP8 is another biomarker used to quantify metalloproteinase. However, aMMP8, as a biomarker, was introduced to practice later, and the most commonly applied method is point-of-care testing. The limitation in the analysis of aMMP-8 investigating studies was the absence of quantified aMMP8 levels, as the salivary testing reports the presence or absence of the condition defined by a threshold specific to the manufacturers. Also, due to its non-invasive collection method and greater accessibility, potentially enhancing study inclusivity and reducing participant burden, we narrowed our focus to studies using saliva samples to maintain consistency across studies and minimize confounding variables, ensuring more reliable and comparable results in the pooled analysis.
The widespread adoption of MMP8 in both clinical and research settings has established it as a predominant biomarker in numerous studies. Although some research suggests that active MMP-8 (aMMP-8) may more effectively distinguish between healthy sites and those affected by periodontitis, MMP-8 has been found to differentiate between mild and severe periodontitis more accurately in certain cases (10, 74–76). In our study, the sample size for MMP8 was notably larger, involving over 2,000 participants, compared to the aMMP-8 cohorts, which included fewer than 1,000 participants. Additionally, MMP8 studies spanned a broader range of publication years compared to those measuring aMMP8. Despite the potential for publication year to influence heterogeneity due to evolving knowledge, our analysis did not identify publication year as a contributing factor to heterogeneity in effect size.
Initially, MMP8 showed a higher overall effect than aMMP8, though they were statistically similar. However, further analysis revealed that this result was inflated due to the large effect of several studies (46, 47, 54–56). Interestingly, while the removal of indicated studies from both biomarker cohorts slightly increased the effect size of aMMP8 in periodontitis, a drastic and opposite effect was observed in MMP8 studies. The drop in the MMP8 effect was affected mainly by a single study (54); even so, the overall effect of MMP8 became slightly lower than that of aMMP8. However, it should be noted that even without outlier studies, both biomarkers did not differ statistically. Nonetheless, the literature underscores the imperative for further exploration with larger sample sizes to elucidate potential divergent advantages between salivary evaluations of aMMP-8 compared to MMP-8. Our analysis corroborated the observation that both MMP-8 and aMMP-8 levels are elevated in the presence of periodontitis, albeit encountering notably high heterogeneity for both biomarker types.
Our analysis revealed challenges posed by heterogeneity and methodological limitations, prompting an exploration of subgroups not previously evaluated in systematic studies of MMP-8. One area of investigation focused on the type of saliva collection technique used, which yielded variations in MMP-8 levels, with unstimulated saliva exhibiting significantly higher levels compared to stimulated saliva. Numerous epidemiological investigations have frequently regarded unstimulated saliva as a reliable proxy for capturing the holistic microbial composition of the oral environment (77–81). Furthermore, variation in research methodologies, particularly in the composition of biomarkers and microbiota, is evident when comparing stimulated and unstimulated saliva collection methods. While a recent analysis found no difference between the two methods (82), others reported distinct bacterial profiles between stimulated and unstimulated saliva samples, with a notable increase in bacterial diversity observed in stimulated samples, potentially due to the removal of bacterial biofilms during chewing (14, 83–85). Despite the higher MMP-8 levels in unstimulated saliva, we could not indicate the saliva collection technique as a factor leading to heterogeneity between study results.
In our study, we categorized testing into two subgroups: laboratory-based and point-of-care (POC). While we aimed to thoroughly evaluate both, the quantity of POC studies was limited, and these studies often lacked the quantified biomarker levels necessary for our analysis (16, 17, 86, 87). Despite these limitations, prior research highlights the potential advantages of POC testing (88–92). It is not only faster but may also yield more accurate results, likely due to minimized salivary degradation (93, 94). Salivary degradation involves the breakdown of saliva's biomolecules, such as proteins and enzymes, which can occur naturally or be influenced by factors like disease, oral hygiene, or medication (93). This degradation can alter saliva's diagnostic utility, which is why some manufacturers add preservatives to maintain sample integrity until testing. However, the effectiveness of these preservatives, particularly for biomarkers like MMP-8 and aMMP-8, remains underexplored, as most studies focus primarily on preserving DNA or RNA (95–97).
The need for more research into POC salivary diagnostics and biomarker stability is underscored by findings from a meta-analysis conducted at Semmelweis University (80). This study revealed significant heterogeneity in MMP-8 research and noted that different measurement methods, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and time-resolved immunofluorometric assay (IFMA), reported varied interval levels of MMP-8, with ELISA showing the most significant disparities (MD = 318.12 n, CI: 205.48; 431.37). Similarly, LUMINEX technology, which can analyze up to 100 analytes simultaneously, also demonstrated significant variation (MD = 183.38, CI: 78.92; 187.84) (92). These findings highlight the critical need for further exploration of POC technologies and the factors affecting the stability of salivary biomarkers to enhance their diagnostic accuracy and utility.
Our meta-analysis makes a significant contribution to the literature by synthesizing the available evidence on salivary MMP-8/aMMP-8 levels during periodontitis events. However, notable limitations, such as the observed high heterogeneity across studies and the potential for bias due to publication bias and small sample sizes, must be acknowledged. Despite efforts to decrease heterogeneity by separating the studies into subgroups based on type of saliva collection method, year of publication, and different study populations, the heterogeneity remained considerable. The impact of study design on heterogeneity and effect estimates cannot be overlooked. Variations in inclusion criteria, sample characteristics, saliva collection methods, and MMP-8/aMMP-8 measurement techniques across studies may contribute to heterogeneity in our meta-analysis (98). While subgroup analyses were performed to explore sources of heterogeneity, residual variability may still exist due to unmeasured confounders or methodological differences not accounted for in our study.
It is crucial to consider the potential for publication bias, where studies with statistically significant results are more likely to be published, leading to an overestimation of effect sizes (99). While efforts were made to include all relevant studies through a comprehensive literature search, the possibility of unpublished or inaccessible data cannot be entirely ruled out. This bias could have influenced our meta-analysis results, particularly in studies reporting small effect sizes or non-significant findings. In addition, selective outcome reporting bias may exist, whereby studies selectively report outcomes based on their statistical significance, leading to an overrepresentation of positive results. To mitigate this bias, we meticulously screened studies for inclusion based on predefined criteria and conducted various analyses to assess the robustness of our findings. However, the potential for selective outcome reporting bias should be considered when interpreting our results.
In reviewing the existing data and additional subgroup analysis, it becomes evident that the observed high heterogeneity within our findings highlights the necessity for standardized protocols. These protocols are essential for ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of results when evaluating salivary biomarkers. Further, it emphasizes the need for consistent calibration of reference intervals across different saliva collection methods, testing devices, and specific biomarkers being assessed. Standardization is particularly vital to ensure accuracy in the diagnosis and monitoring of periodontitis using saliva-based testing. Such standardization typically involves studies that establish biomarker interval ranges in saliva correlated with clinical assessments of disease severity. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) offers guidelines for defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals, which include setting the upper and lower reference limits that are designed to encompass a specific percentage (95%) of the population values from selected reference subjects (100). For most analytes, these limits are calculated as the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles of the distribution of test results in the reference population. Future research should focus on standardizing saliva collection protocols to reduce variability and improve reproducibility, while also exploring MMP-8's diagnostic relevance across diverse populations, including variations by age, ethnicity, and systemic health conditions.
Our study also underscores the importance of future research to mitigate these issues by implementing standardized methodologies and expanding sample sizes. This approach is crucial to improve diagnostic precision and the clinical application of saliva-based tests in evaluating periodontitis. Additionally, it is important to consider diverse patient populations characterized by various factors such as smoking habits, diabetes status, and dietary practices, including snacking frequency, all of which may influence MMP-8 levels (101–104). Conducting studies in real-world settings with larger, diverse cohorts and standardized methods will help address current limitations and provide strong evidence that supports the integration of saliva-based diagnostics into standard dental care practices. This advancement will significantly enhance the understanding and management of periodontitis.
The current meta-analysis provides compelling evidence of the association between salivary MMP-8/aMMP-8 levels and periodontitis. These findings underscore the utility of saliva as a non-invasive diagnostic tool and highlight the intricate role of MMP-8 in the pathophysiology of periodontitis.
Our results highlight the promising role of saliva-based diagnostics in enhancing the management of periodontitis. Despite encountering challenges such as heterogeneity and methodological limitations, the accessibility and convenience of saliva collection make it a valuable tool for routine screening and monitoring. Collaborative efforts, standardized protocols, and larger studies are needed to validate salivary biomarkers and improve oral health.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
SB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TS: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. VN: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LP: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
SB was employed by GameShift Healthcare Solutions, LLC, Harmony Health, Inc. TS was employed by Harmony Health, Inc and Oral Genome, Corp.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/froh.2025.1444399/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Bubble plot of meta-regression analysis evaluating MMP8 values adjusted for the publication year illustrating the estimated regression slope and effect size of included studies. [The outlier study by Golitsyna et al. (36) has been excluded].
Supplementary Figure S2 | Bubble plot of meta-regression analysis evaluating aMMP8 values adjusted for the publication year illustrating the estimated regression slope and effect size of included studies.
Supplementary Figure S3 | Funnel plot of MMP8-quantifying studies with all eligible studies (n = 25).
Supplementary Figure S4 | Funnel plot after a trim and fill analysis. (Imputed studies are shown with empty dots) (n = 25).
Supplementary Figure S5 | Funnel plot of aMMP8 studies after exclusion of outlier cohorts (n = 9).
Supplementary Figure S6 | Contour-enhanced Funnel plot after a trim and fill analysis. (Imputed studies are shown with empty dots) (n = 9).
1. Nazir M, Al-Ansari A, Al-Khalifa K, Alhareky M, Gaffar B, Almas K. Global prevalence of periodontal disease and lack of its surveillance. Sci World J. (2020): 2146160. doi: 10.1155/2020/2146160
2. Sanz M, D'Aiuto F, Deanfield J, Fernandez-Avilés F. European Workshop in periodontal health and cardiovascular disease—scientific evidence on the association between periodontal and cardiovascular diseases: a review of the literature. Eur Heart J Suppl. (2010) 12(suppl_B):B3–B12. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/suq003
3. Peng X, Cheng L, You Y, Tang C, Ren B, Li Y, et al. Oral microbiota in human systematic diseases. Int J Oral Sci. (2022) 14(1):14. doi: 10.1038/s41368-022-00163-7
4. Boynes SG, Davis L, Adams G, Mills M, Deutchman M. MORE Care: narrowing the rural interprofessional oral health care gap. Denta Quest Institute. (2017) 1:8–13.
5. Atanasova T, Stankova T, Bivolarska A, Vlaykova T. Matrix metalloproteinases in oral health-special attention on MMP-8. Biomedicines. (2023) 11(6):1514–20. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061514
6. Schubert-Unkmeir A, Konrad C, Slanina H, Czapek F, Hebling S, Frosch M. Neisseria meningitidis induces brain microvascular endothelial cell detachment from the matrix and cleavage of occludin: a role for MMP-8. PLoS Pathog. (2010) 6(4):e1000874. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000874
7. Wang X, Rojas-Quintero J, Wilder J, Tesfaigzi Y, Zhang D, Owen CA. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 promotes polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) pericellular proteolysis by anchoring matrix metalloproteinase-8 and -9 to PMN surfaces. J Immunol. (2019) 202(11):3267–81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801466
8. Di Stefano M, Polizzi A, Santonocito S, Romano A, Lombardi T, Isola G. Impact of oral microbiome in periodontal health and periodontitis: a critical review on prevention and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(9):5142. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095142
9. Zhang L, Li X, Yan H, Huang L. Salivary matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8 as a biomarker for periodontitis: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2018) 97(3):e9642. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009642
10. Sorsa T, Alassiri S, Grigoriadis A, Räisänen IT, Pärnänen P, Nwhator SO, et al. Active MMP-8 (aMMP-8) as a grading and staging biomarker in the periodontitis classification. Diagnostics (Basel). (2020) 10(2):61–70. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10020061
11. Ghiabi E, Weerasinghe S. The periodontal examination profile of general dentists in Nova Scotia, Canada. J Periodontol. (2011) 82(1):33–40. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.100348
12. Luchian I, Goriuc A, Sandu D, Covasa M. The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13) in periodontal and peri-implant pathological processes. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(3):1806–12. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031806
13. Sorsa T, Gursoy UK, Nwhator S, Hernandez M, Tervahartiala T, Leppilahti J, et al. Analysis of matrix metalloproteinases, especially MMP-8, in gingival creviclular fluid, mouthrinse and saliva for monitoring periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. (2016) 70(1):142–63. doi: 10.1111/prd.12101
14. Gomar-Vercher S, Simón-Soro A, Montiel-Company JM, Almerich-Silla JM, Mira A. Stimulated and unstimulated saliva samples have significantly different bacterial profiles. PLoS One. (2018) 13(6):e0198021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198021
15. Räisänen IT, Heikkinen AM, Nwhator SO, Umeizudike KA, Tervahartiala T, Sorsa T. On the diagnostic discrimination ability of mouthrinse and salivary aMMP-8 point-of-care testing regarding periodontal health and disease. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. (2019) 95(4):114871. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.114871
16. Heikkinen AM, Raivisto T, Räisänen I, Tervahartiala T, Bostanci N, Sorsa T. Implementing of aMMP-8 point-of-care test with a modified new disease classification in Finnish adolescent cohorts. Clin Exp Dent Res. (2022) 8(5):1142–8. doi: 10.1002/cre2.603
17. Deng K, Pelekos G, Jin L, Tonetti MS. Diagnostic accuracy of a point-of-care aMMP-8 test in the discrimination of periodontal health and disease. J Clin Periodontol. (2021) 48(8):1051–65. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13485
18. Nonaka T, Wong DTW. Saliva diagnostics: salivaomics, saliva exosomics, and saliva liquid biopsy. J Am Dent Assoc. (2023) 154(8):696–704. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2023.05.006
19. Dongiovanni P, Meroni M, Casati S, Goldoni R, Thomaz DV, Kehr NS, et al. Salivary biomarkers: novel noninvasive tools to diagnose chronic inflammation. Int J Oral Sci. (2023) 15(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00231-6
20. Letra A, Silva RM, Rylands RJ, Silveira EM, de Souza AP, Wendell SK, et al. MMP3 And TIMP1 variants contribute to chronic periodontitis and may be implicated in disease progression. J Clin Periodontol. (2012) 39(8):707–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01902.x
21. Umeizudike KA, Lähteenmäki H, Räisänen IT, Taylor JJ, Preshaw PM, Bissett SM, et al. Ability of matrix metalloproteinase-8 biosensor, IFMA, and ELISA immunoassays to differentiate between periodontal health, gingivitis, and periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. (2022) 57(3):558–67. doi: 10.1111/jre.12985
22. Korte DL, Kinney J. Personalized medicine: an update of salivary biomarkers for periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. (2016) 70(1):26–37. doi: 10.1111/prd.12103
23. Karayasheva D, Glushkova M, Boteva E, Mitev V, Kadiyska T. Association study for the role of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 3 gene polymorphisms in dental caries susceptibility. Arch Oral Biol. (2016) 68:9–12. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2016.03.007
24. Administration USFaD. General Wellness: Policy for Low Risk Devices Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff. In: Health CfDaR, editor. (2019).
25. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Br Med J. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
26. Murad MH, Wang Z, Chu H, Lin L. When continuous outcomes are measured using different scales: guide for meta-analysis and interpretation. Br Med J. (2019) 364:k4817. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4817
27. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2005) 5(1):13–9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
28. Higgins J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, Welch VA. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 6.4;(updated August 2023). Melbourne: Cochrane (2023).
29. Haddaway NR, Page MJ, Pritchard CC, McGuinness LA. PRISMA2020: an R package and shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and open synthesis. Campbell Syst Rev. (2022) 18(2):e1230. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1230
32. Wallace BC, Schmid CH, Lau J, Trikalinos TA. Meta-Analyst: software for meta-analysis of binary, continuous and diagnostic data. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2009) 9:1–2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-9-80
33. Harrer M, Cuijpers P, Furukawa T, Ebert DD. Dmetar: companion R package for the guide'Doing meta-analysis in R’. R package version 00. 9000 (2019).
34. Kadlec D, Sainani KL, Nimphius S. With great power comes great responsibility: common errors in meta-analyses and meta-regressions in strength & conditioning research. Sports Med. (2013) 53(2):313–25. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01766-0
35. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br Med J. (1997) 315(7109):629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
36. Pustejovsky JE, Rodgers MA. Testing for funnel plot asymmetry of standardized mean differences. Res Synth Methods. (2019) 10(1):57–71. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1332
37. Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J, Sutton AJ. Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. Int J Epidemiol. (2002) 31(1):88–95. doi: 10.1093/ije/31.1.88
38. Stuck AE, Rubenstein LZ, Wieland D. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Asymmetry detected in funnel plot was probably due to true heterogeneity. BMJ Br Med J. (1998) 316(7129):469. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7129.469
39. Papageorgiou SN, Dimitraki D, Coolidge T, Kotsanos N. Publication bias & small-study effects in pediatric dentistry meta-analyses. Journal of Evidence Based Dental Practice. (2015) 15(1):8–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jebdp.2014.09.001
40. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. (2000) 56(2):455–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x
41. Rai B, Kharb S, Jain R, Anand SC. Biomarkers of periodontitis in oral fluids. J Oral Sci. (2008) 50(1):53–6. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.50.53
42. Mirrielees J, Crofford LJ, Lin Y, Kryscio RJ, Dawson DR 3rd, Ebersole JL, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and salivary biomarkers of periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. (2010) 37(12):1068–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01625.x
43. Buduneli E, Mäntylä P, Emingil G, Tervahartiala T, Pussinen P, Barış N, et al. Acute myocardial infarction is reflected in salivary matrix metalloproteinase-8 activation level. J Periodontol. (2011) 82(5):716–25. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.100492
44. Ebersole JL, Schuster JL, Stevens J, Dawson D 3rd, Kryscio RJ, Lin Y, et al. Patterns of salivary analytes provide diagnostic capacity for distinguishing chronic adult periodontitis from health. J Clin Immunol. (2013) 33(1):271–9. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9771-3
45. Meschiari CA, Marcaccini AM, Santos Moura BC, Zuardi LR, Tanus-Santos JE, Gerlach RF. Salivary MMPs, TIMPs, and MPO levels in periodontal disease patients and controls. Clin Chim Acta. (2013) 421:140–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.03.008
46. Rathnayake N, Akerman S, Klinge B, Lundegren N, Jansson H, Tryselius Y, et al. Salivary biomarkers of oral health: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40(2):140–7. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12038
47. Miricescu D, Totan A, Calenic B, Mocanu B, Didilescu A, Mohora M, et al. Salivary biomarkers: relationship between oxidative stress and alveolar bone loss in chronic periodontitis. Acta Odontol Scand. (2014) 72(1):42–7. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2013.795659
48. Akbari G, Prabhuji ML, Karthikeyan BV, Raghunatha K, Narayanan R. Analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-8 levels in gingival crevicular fluid and whole mouth fluid among smokers and nonsmokers using enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay and a novel chair-side test. J Indian Soc Periodontol. (2015) 19(5):525–30. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.162201
49. Ebersole JL, Nagarajan R, Akers D, Miller CS. Targeted salivary biomarkers for discrimination of periodontal health and disease(s). Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2015) 5:62–70. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00062
50. Gupta N, Gupta ND, Gupta A, Khan S, Bansal N. Role of salivary matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) in chronic periodontitis diagnosis. Front Med. (2015) 9(1):72–6. doi: 10.1007/s11684-014-0347-x
51. Lira-Junior R, Öztürk V, Emingil G, Bostanci N, Boström EA. Salivary and serum markers related to innate immunity in generalized aggressive periodontitis. J Periodontol. (2017) 88(12):1339–47. doi: 10.1902/jop.2017.170287
52. Martinez GL, Majster M, Bjurshammar N, Johannsen A, Figueredo CM, Boström EA. Salivary colony stimulating factor-1 and interleukin-34 in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. (2017) 88(8):e140–9. doi: 10.1902/jop.2017.170081
53. Rangbulla V, Nirola A, Gupta M, Batra P, Gupta M. Salivary IgA, interleukin-1β and MMP-8 as salivary biomarkers in chronic periodontitis patients. Chin J Dent Res. (2017) 20(1):43–51. doi: 10.3290/j.cjdr.a37741
54. Golitsyna AA, Yugay YV, Markelova EV. Analysis of MMP-8, MMP-9 indicators and their TIMP-1 inhibitor in periodontitis among patients with diabetes mellitus type II. Res J Pharmaceut Biol Chem Sci. (2018) 9(4):821–5.
55. Sharma N, Bansal Y. Effect of asparagus curillus on levels of matrix metallo proteinases in GCF and saliva of periodontal patients. Int J Pharm Sci Res. (2018) 9(10):4422–9.
56. Aungurencei A, Luchian I, Goriuc A, Constantinescu D, Martu I, Popa DD, et al. Collagenase-2-(MMP-8) as a poimt - of- care biomerker in periodontal disease in patients with or without fixed prosthesis therapeutic response to doxycycline. Rev Chim. (2019) 70(11):4068–72. doi: 10.37358/RC.19.11.7703
57. Fastovets OO, Masheiko IV, Lucash AY. Evaluation of bone resorptive potential in the treatment of generalized periodontitis. Wiad Lek. (2020) 73(11):2396–402. doi: 10.36740/WLek202011112
58. Fatemi K, Rezaee SA, Banihashem SA, Keyvanfar S, Eslami M. Importance of MMP-8 in salivary and gingival crevicular fluids of periodontitis patients. Iran J Immunol. (2020) 17(3):236–43. doi: 10.22034/iji.2020.81170.1512
59. Lee J, Lee JB, Song HY, Son MJ, Li L, Rhyu IC, et al. Diagnostic models for screening of periodontitis with inflammatory mediators and microbial profiles in Saliva. Diagnostics (Basel). (2020) 10(10):820–5. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100820
60. AlJasser RN, Alaqeely RS, Al-Hoqail IA, Al-Haddab M, AlQahtani SS, AlKenani ME, et al. Association between isotretinoin (roaccutanne) use and changes in periodontal clinical parameters and MMP-8 and MMP-9 salivary levels. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2021) 26(7):191–7. doi: 10.52586/4933
61. Bostanci N, Mitsakakis K, Afacan B, Bao K, Johannsen B, Baumgartner D, et al. Validation and verification of predictive salivary biomarkers for oral health. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):6406–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85120-w
62. Lira-Junior R, Bissett SM, Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ, Boström EA. Levels of myeloid-related proteins in saliva for screening and monitoring of periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. (2021) 48(11):1430–40. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13534
63. Zhang Y, Kang N, Xue F, Qiao J, Duan J, Chen F, et al. Evaluation of salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis of periodontitis. BMC Oral Health. (2021) 21(1):266–70. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01600-5
64. Balaji S, Cholan PK, Victor DJ. Evaluation of “soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1), interleukin-1β, and matrix metalloproteinase-8” as a short panel of salivary biomarkers in patients with and without stage III/IV periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. (2022) 12(1):33–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.10.003
65. Wu S, Li Z, Wang J, Liu L, Pang Y. Correlation analysis of miR-1246 expression in Saliva of patients with chronic periodontitis and periodontal indexes, inflammatory cytokines, and protease molecules. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:1949159. doi: 10.1155/2022/1949159
66. Noack B, Kipping T, Tervahartiala T, Sorsa T, Hoffmann T, Lorenz K. Association between serum and oral matrix metalloproteinase-8 levels and periodontal health status. J Periodontal Res. (2017) 52(5):824–31. doi: 10.1111/jre.12450
67. Heikkinen AM, Räisänen IT, Tervahartiala T, Sorsa T. Cross-sectional analysis of risk factors for subclinical periodontitis; active matrix metalloproteinase-8 as a potential indicator in initial periodontitis in adolescents. J Periodontol. (2019) 90(5):484–92. doi: 10.1002/JPER.18-0450
68. Yucel ZPK, Afacan B, Emingil G, Tervahartiala T, Kose T, Sorsa T. Local and systemic levels of aMMP-8 in gingivitis and stage 3 grade C periodontitis. J Periodont Res. (2020) 55(6):887–94. doi: 10.1111/jre.12781
69. Öztürk V, Emingil G, Umeizudike K, Tervahartiala T, Gieselmann DR, Maier K, et al. Evaluation of active matrix metalloproteinase-8 (aMMP-8) chair-side test as a diagnostic biomarker in the staging of periodontal diseases. Arch Oral Biol. (2021) 124:104955. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104955
70. Ramenzoni LL, Hofer D, Solderer A, Wiedemeier D, Attin T, Schmidlin PR. Origin of MMP-8 and lactoferrin levels from gingival crevicular fluid, salivary glands and whole saliva. BMC Oral Health. (2021) 21(1):385–90. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01743-5
71. Deng K, Wei S, Xu M, Shi J, Lai H, Tonetti MS. Diagnostic accuracy of active matrix metalloproteinase-8 point-of-care test for the discrimination of periodontal health status: comparison of saliva and oral rinse samples. J Periodontal Res. (2022) 57(4):768–79. doi: 10.1111/jre.12999
72. Yilmaz D, Niskanen K, Gonullu E, Tervahartiala T, Gürsoy UK, Sorsa T. Salivary and serum levels of neutrophil proteases in periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Oral Dis. (2024) 30(3):1660–8. doi: 10.1111/odi.14574
73. Viechtbauer W, Cheung MW. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2010) 1(2):112–25. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.11
74. Hernández M, Baeza M, Räisänen IT, Contreras J, Tervahartiala T, Chaparro A, et al. Active MMP-8 quantitative test as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of periodontitis. Diagnostics (Basel). (2021) 11(8):1503–10. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081503
75. Keskin M, Rintamarttunen J, Gülçiçek E, Räisänen IT, Gupta S, Tervahartiala T, et al. A comparative analysis of treatment-related changes in the diagnostic biomarker active metalloproteinase-8 levels in patients with periodontitis. Diagnostics (Basel). (2023) 13(5):903–9. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050903
76. Räisänen IT, Aji N, Sakellari D, Grigoriadis A, Rantala I, Pätilä T, et al. Active matrix metalloproteinase-8 (aMMP-8) versus total MMP-8 in periodontal and peri-implant disease point-of-care diagnostics. Biomedicines. (2023) 11(11):2885–92. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11112885
77. Lozupone C, Hamady M, Knight R. Unifrac–an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinformatics. (2006) 7:371–9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-371
78. Aas JA, Paster BJ, Stokes LN, Olsen I, Dewhirst FE. Defining the normal bacterial flora of the oral cavity. J Clin Microbiol. (2005) 43(11):5721–32. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.11.5721-5732.2005
79. Jiang Q, Liu J, Chen L, Gan N, Yang D. The oral microbiome in the elderly with dental caries and health. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2018) 8:442–9. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00442
80. Merglova V, Polenik P. Early colonization of the oral cavity in 6-and 12-month-old infants by cariogenic and periodontal pathogens: a case-control study. Folia Microbiol. (2016) 61:423–9. doi: 10.1007/s12223-016-0453-z
81. Foratori-Junior GA, Ventura TMO, Grizzo LT, Jesuino BG, Castilho A, Buzalaf MAR, et al. Is there a difference in the proteomic profile of stimulated and unstimulated saliva samples from pregnant women with/without obesity and periodontitis? Cells. (2023) 12(10):2885–91. doi: 10.3390/cells12101389
82. Al Habobe H, Haverkort EB, Nazmi K, Van Splunter AP, Pieters RHH, Bikker FJ. The impact of saliva collection methods on measured salivary biomarker levels. Clin Chim Acta. (2024) 552:117628. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117628
83. Figueira J, Gouveia-Figueira S, Öhman C, Lif Holgerson P, Nording ML, Öhman A. Metabolite quantification by NMR and LC-MS/MS reveals differences between unstimulated, stimulated, and pure parotid saliva. J Pharm Biomed Anal. (2017) 140:295–300. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.03.037
84. Belstrøm D, Holmstrup P, Bardow A, Kokaras A, Fiehn NE, Paster BJ. Comparative analysis of bacterial profiles in unstimulated and stimulated saliva samples. J Oral Microbiol. (2016) 8:30112. doi: 10.3402/jom.v8.30112
85. Simón-Soro A, Tomás I, Cabrera-Rubio R, Catalan MD, Nyvad B, Mira A. Microbial geography of the oral cavity. J Dent Res. (2013) 92(7):616–21. doi: 10.1177/0022034513488119
86. Lorenz K, Keller T, Noack B, Freitag A, Netuschil L, Hoffmann T. Evaluation of a novel point-of-care test for active matrix metalloproteinase-8: agreement between qualitative and quantitative measurements and relation to periodontal inflammation. J Periodontal Res. (2017) 52(2):277–84. doi: 10.1111/jre.12392
87. Izadi Borujeni S, Mayer M, Eickholz P. Activated matrix metalloproteinase-8 in saliva as diagnostic test for periodontal disease? A case-control study. Med Microbiol Immunol. (2015) 204(6):665–72. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0413-2
88. Rogozinska M, Biesaga M. Decomposition of flavonols in the presence of Saliva. Appl Sci. (2020) 10(21):7511. doi: 10.3390/app10217511
89. Liu J, Geng Z, Fan Z, Liu J, Chen H. Point-of-care testing based on smartphone: the current state-of-the-art (2017–2018). Biosens Bioelectron. (2019) 132:17–37. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.068
90. von Lode P. Point-of-care immunotesting: approaching the analytical performance of central laboratory methods. Clin Biochem. (2005) 38(7):591–606. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2005.03.008
91. Johnson AJ, Zhou S, Hoops SL, Hillmann B, Schomaker M, Kincaid R, et al. Saliva testing is accurate for early-stage and presymptomatic COVID-19. Microbiol Spectr. (2021) 9(1):e0008621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00086-21
92. Miočević O, Cole CR, Laughlin MJ, Buck RL, Slowey PD, Shirtcliff EA. Quantitative lateral flow assays for salivary biomarker assessment: a review. Front Public Health. (2017) 5:133–9. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00133
93. Chiappin S, Antonelli G, Gatti R, De Palo EF. Saliva specimen: a new laboratory tool for diagnostic and basic investigation. Clin Chim Acta. (2007) 383(1-2):30–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2007.04.011
94. Pittman TW, Decsi DB, Punyadeera C, Henry CS. Saliva-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic. Theranostics. (2023) 13(3):1091–108. doi: 10.7150/thno.78872
95. Irwin SV, Deardorff LM, Deng Y, Fisher P, Gould M, June J, et al. Sulfite preservatives effects on the mouth microbiome: changes in viability, diversity and composition of microbiota. PLoS One. (2022) 17(4):e0265249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265249
96. d'Amone L, Matzeu G, Omenetto FG. Stabilization of salivary biomarkers. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. (2021) 7(12):5451–73. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c01138
97. Sullivan R, Heavey S, Graham DG, Wellman R, Khan S, Thrumurthy S, et al. An optimised saliva collection method to produce high-yield, high-quality RNA for translational research. PLoS One. (2020) 15(3):e0229791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229791
98. Domokos Z, Simon F, Uhrin E, Szabó B, Váncsa S, Varga G, et al. Salivary MMP-8 in early periodontitis diagnosis and prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Available at SSRN 4625540 (2023).
99. Shaver A, Megally H, Boynes SG, Zokaie T, Puttige Ramesh N, Clermont D, et al. Illustrating the Role of Dental Journals in the Translational Science Process. Chicago, IL: American Institute of Dental Public Health (2022).
100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals, 3 ed. Available at Available online at: https://clsi.org/media/1421/ep28a3c_sample.pdf (accessed on June 5, 2024).
101. Leite FRM, Nascimento GG, Scheutz F, López R. Effect of smoking on periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-regression. Am J Prev Med. (2018) 54(6):831–41. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2018.02.014
102. Zappacosta B, Martorana GE, Papini S, Gervasoni J, Iavarone F, Fasanella S, et al. Morpho-functional modifications of human neutrophils induced by aqueous cigarette smoke extract: comparison with chemiluminescence activity. Luminescence. (2011) 26(5):331–5. doi: 10.1002/bio.1233
103. Costa PP, Trevisan GL, Macedo GO, Palioto DB, Souza SL, Grisi MF, et al. Salivary interleukin-6, matrix metalloproteinase-8, and osteoprotegerin in patients with periodontitis and diabetes. J Periodontol. (2010) 81(3):384–91. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090510
104. Nardi GM, Cesarano F, Papa G, Chiavistelli L, Ardan R, Jedlinski M, et al. Evaluation of salivary matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-8) in periodontal patients undergoing non-surgical periodontal therapy and mouthwash based on ozonated olive oil: a randomized clinical trial.”. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17(18):6619. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186619
Keywords: salivary diagnostics, periodontitis, biomarkers, matrix metalloproteinase 8 (MMP-8), metaanalysis, saliva, disease progression, oral health
Citation: Boynes SG, Sofiyeva N, Saw T, Nieto V and Palomo L (2025) Assessment of salivary matrix metalloproteinase (MMP8) and activated salivary matrix metalloproteinase (aMMP8) in periodontitis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oral. Health 6:1444399. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1444399
Received: 5 June 2024; Accepted: 28 January 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited by:
Chun Hung Chu, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Marta Mazur, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyCopyright: © 2025 Boynes, Sofiyeva, Saw, Nieto and Palomo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sean G. Boynes, ZHJzZWFuYm95bmVzQGhhcm1vbnloZWFsdGhmb3VuZGF0aW9uLm9yZw==
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.