
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
METHODS article
Front. Oncol. , 08 April 2025
Sec. Breast Cancer
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1567577
This article is part of the Research Topic Advancing Breast Cancer Care Through Transparent AI and Federated Learning: Integrating Radiological, Histopathological, and Clinical Data for Diagnosis, Recurrence Prediction, and Survivorship View all articles
The segmentation and classification of breast ultrasound (BUS) images are crucial for the early diagnosis of breast cancer and remain a key focus in BUS image processing. Numerous machine learning and deep learning algorithms have shown their effectiveness in the segmentation and diagnosis of BUS images. In this work, we propose a multi-task learning network with an object contextual attention module (MTL-OCA) for the segmentation and classification of BUS images. The proposed method utilizes the object contextual attention module to capture pixel-region relationships, enhancing the quality of segmentation masks. For classification, the model leverages high-level features extracted from unenhanced segmentation masks to improve accuracy. Cross-validation on a public BUS dataset demonstrates that MTL-OCA outperforms several current state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior results in both classification and segmentation tasks.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in females globally (1–3). Therefore, early diagnosis of breast cancer is crucial for reducing mortality, as more than 90% of cases can now be detected at an early stage and treated before becoming metastatic (4). Among these technologies, ultrasound imaging (USI) is one of the most widely used screening methods for early breast cancer detection due to its high convenience, low cost, and high effectiveness. USI uses sound waves to generate images of the body’s internal structures, which are subsequently analyzed by computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems to enhance diagnostic accuracy (5). Automated segmentation and classification are critical steps in CAD systems for interpreting breast ultrasound (BUS) images, forming a foundation for further analysis and treatment planning. In recent years, various image processing tools have been developed for detecting and delineating affected areas in ultrasound images, including segmentation, enhancement, and classification techniques (6–8).
With advancements in computer technology, various machine learning (ML) methods have been proposed Lu et al. (9)Liu et al. (10) and successfully applied to medical image processing and interpretation (11–13). ML methods have also shown great potential in the segmentation and classification of breast ultrasound (BUS) images (14–16). Techniques such as k-nearest neighbors (17), support vector machines (18), and clustering algorithms (19). For example, da Silva et al. applied several ML-based methods, including multilayer perceptrons, k-nearest neighbors, and support vector machines, for breast cancer detection and diagnosis, and compared their performance in BUS image segmentation and classification (20). Lyu and Cheung proposed a hierarchical extreme learning machine (H-ELM) for efficient breast cancer ultrasound analysis (21). Zhu et al. employed random forest regression for the automatic measurement of fetal femur length in ultrasound images (22) and compared their approach with the widely used convolutional neural network (CNN) model, SegNet (23).
Recently, state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms have been proposed for various classification and segmentation tasks (24–28). These algorithms include convolutional neural networks (CNNs) (29, 30), Transformer (31–33), quantum-enhanced deep learning (34–36), and ensemble learning (37, 38). Among these algorithms, CNNs are some of the most widely used methods that is capable of building strong non-linear relationships between training data and labels (39–41). CNN-based architectures have been successfully applied in medical image processing (42–44) and have been employed for interpreting breast ultrasound (BUS) images (45, 46). For instance, Deawon et al. compared the performance of various models in diagnosing breast cancer (47), including image classification models (VGGNet19, ResNet50, DenseNet121, EfficietNet v2) and image segmentation models (UNet, ResUNet++, DeepLab v3). Other notable deep learning algorithms for processing BUS images include generative adversarial networks (GANs) (48), edge enhanced model (49), and probability-based optimal deep learning (50). However, many of these methods follow a two-step approach: first segmenting the BUS images and then classifying them. This two-step approach results in lower computational efficiency and less accurate outcomes. To address these challenges, multi-task learning (MTL) has been introduced, enabling the joint segmentation and classification of BUS images within a unified, end-to-end framework (51, 52). Despite this advancement, most existing MTL methods rely on low-level features learned from the down-sampling path of the network (e.g., UNet’s encoder), which limits their ability to capture high-level semantic information. MTL-COSA utilizes segmentation masks to guide the classification task (53). However, MTL-COSA lacks a segmentation enhancement module to further improve performance.
In this study, we present a novel multi-task learning network (MTL-OCA) that integrates an object contextual attention module for simultaneous segmenting and classifying breast ultrasound (BUS) images. Our key contributions are as follows:
● We propose an innovative multi-task learning architecture that simultaneously handles segmentation and classification tasks for BUS images.
● We introduce an object contextual attention module that refines segmentation masks by learning pixel-region relationships. The high-level features extracted from unenhanced segmentation masks are used to enhance the classification performance.
● Our experimental results demonstrate that MTL-OCA outperforms several state-of-the-art methods in both segmentation and classification tasks.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the deep learning framework, loss functions, and evaluation metrics; Section 3 presents the experimental results and analysis; Section 4 discusses the strengths and limitations of our approach; and Section 5 concludes the paper.
Figure 1 illustrates the architecture of our proposed multi-task learning network (MTL-OCA). MTL-OCA uses Res-UNet as its backbone to learn pixel-region relationships, which enables the generation of highly accurate segmentation masks. The network processes batches of 2D BUS images and produces both segmentation masks and one-hot encoded classification results.
Figure 1 illustrates the architecture of our proposed MTL-OCA, which simultaneously predicts segmentation masks and classification results. The network comprises three main components: the backbone, the object contextual attention module for segmentation, and the classification module for image classification. The backbone is built on a widely used Res-UNet (54), which effectively extracts feature maps from the input images. This Res-UNet employs a three-layer UNet architecture with residual connections, where both the encoder and its symmetric decoder consist of three layers of convolutional blocks (Figure 2). Each block in the encoder includes a Conv2D layer, a GroupNorm layer, and a MaxPooling layer for feature extraction and down-sampling. Similarly, each block in the decoder comprises an Upsample layer, a Conv2D layer, and a GroupNorm layer. Unlike previous multi-task learning approaches that typically rely on features extracted solely from the encoder for classification, our model leverages the complete feature maps from the backbone for both segmentation and classification tasks, thereby enhancing performance in BUS image segmentation and classification.
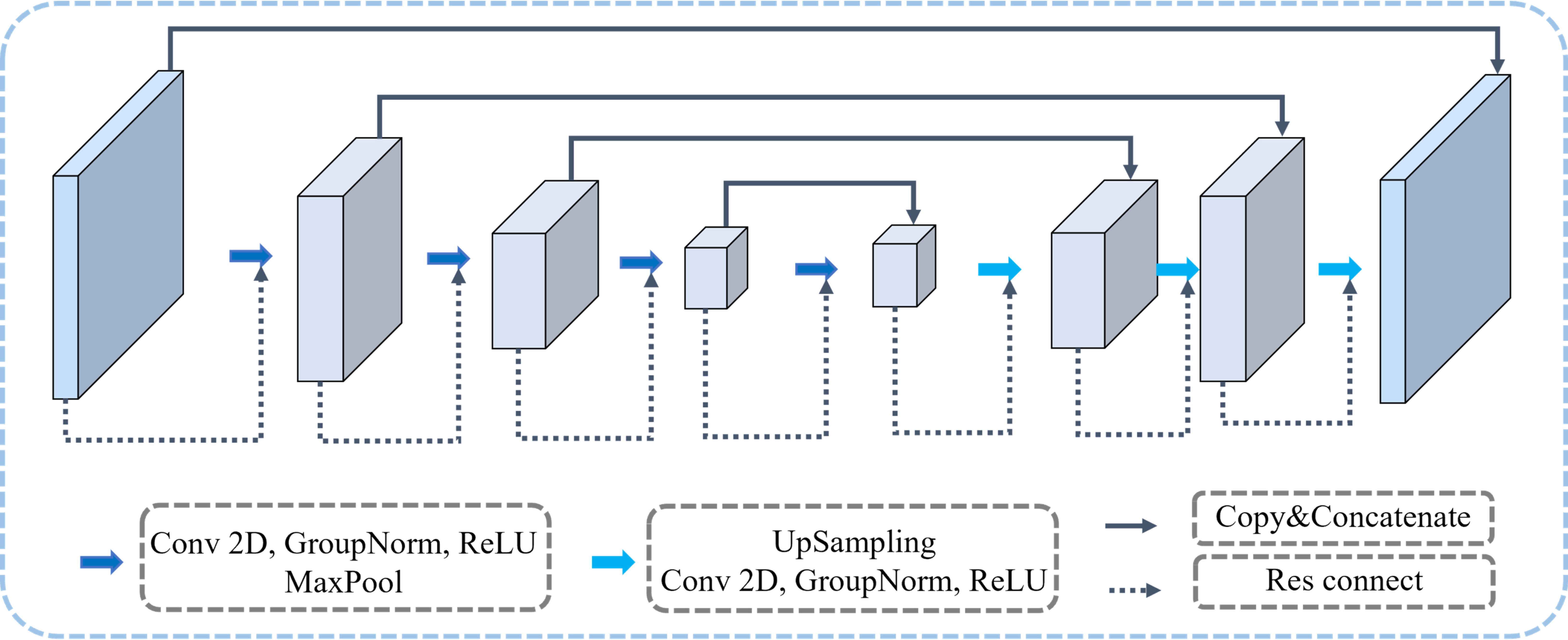
Figure 2. The backbone of our proposed MTL-OCA model. Each rectangular block represents the network’s feature map at varying depths.
The feature maps extracted from the backbone serve as inputs to the object contextual attention module that learns pixel-region relationships to generate enhanced segmentation masks. As illustrated in Figure 1, the contextual pixels are partitioned into K soft object regions, and each corresponds to one of the K segmentation classes. Each soft object region quantifies the degree to which a given pixel belongs to class k, denoted as dk (with K set to 2 in this study). These soft object regions are learned in a supervised manner and essentially serve as coarse segmentation masks. Subsequently, the pixel representations (i.e., the feature maps from the backbone) are multiplied by the soft object regions to produce the object region representations, defined as
where I denotes the set of pixels in the feature maps. xi represents the feature of pixel pi and quantifies the degree to which pixel pi belongs to the kth object region. We obtain the pixel-region relation by multiplying the pixel representations by their corresponding soft object regions as follows
where denotes the nonlinear transformation implemented by the convolutional blocks. Subsequently, the object regions corresponding to the same class are multiplied to enhance the contextual representations, expressed as
where and denote nonlinear transformations implemented by convolutional blocks. Finally, the augmented representations, which produce accurate segmentation masks, are generated by concatenating the contextual and pixel representations. Equation 1 computes the object region representations, Equation 2 establishes the pixel region relations, and their combined outputs serve as inputs to Equation 3 for generating contextual representations. Meanwhile, the classification module performs the classification task on the same feature maps extracted from the backbone. These features, which are derived from the backbone rather than solely from the encoder, contain richer high-level segmentation semantics that guide the classification process. As indicated in the lower half of Figure 1, the classification module is implemented using two layers of a multilayer perceptron (MLP). In this work, the classification results are categorized into three classes: benign, malignant, and normal. So, the final layer consists of three neurons.
Since the proposed network is designed to perform both segmentation and classification simultaneously, the overall loss function is formulated as a combination of the segmentation loss and the classification loss as follows
where and represent the loss functions for the segmentation and classification tasks, respectively. Moreover, the segmentation loss is formulated as a weighted sum of the losses computed on the soft object regions and the augmented representations, written as
where, and are used to supervise the soft object regions and the augmented representations, respectively. α serves as the weighting factor and is set as 0.4 according to the discussions in (55). All the loss functions described in Equations 4, 5 are implemented as cross-entropy.
All deep learning neural networks in this study were implemented and trained on a computer configured with CUDA 11.4, Python 3.7, and PyTorch 1.11, along with other essential libraries. The computer’s hardware setup comprised an Intel 16-core processor, 256 GB of system memory, and two NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPUs (each with 24 GB of dedicated memory). Our MTL-OCA network was trained on the training dataset for 400 epochs with a batch size of 16. Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 1e−3 is adopted in the training process.
In this study, we employ two BUS image datasets to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed model. The first dataset, OASBUD dataset (56), comprises 780 BUS images collected from 600 women aged between 25 and 75. These images are classified into three categories: normal, benign, and malignant (Table 1). The second dataset, UDIAT (57), which consists of 163 ultrasound images, including 110 benign and 53 malignant cases. Due to different image sizes, we resize all the images to 128 × 128 pixels.
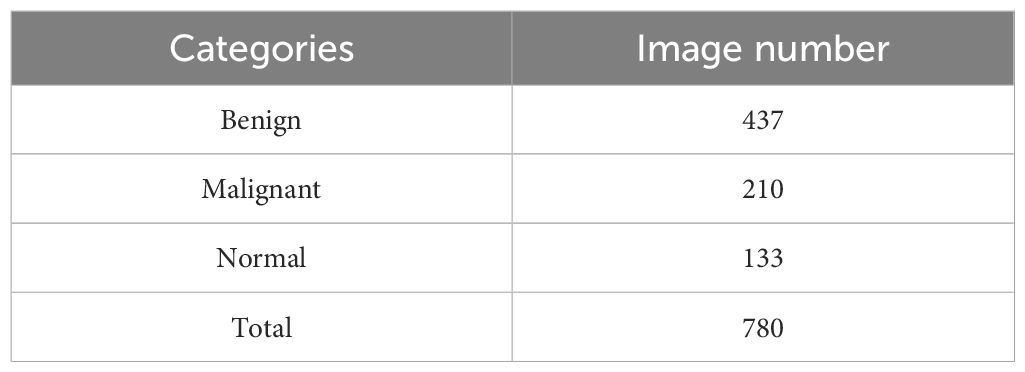
Table 1. Three classes of breast cases and the number of images in each category of the OASBUD dataset.
Note that all input images in both datasets, excluding the labels, are three-channel, which increases the computational cost and load. To reduce this complexity, we convert the BUS images to grayscale prior to the training process. Additionally, we perform 5-fold cross-validation on the datasets. We further augment the training data through various image transformations, including random rotations (ranging from -45° to 45°), random flips, and random center cropping with a 50% probability. Moreover, we apply image contrast enhancement techniques to enrich our dataset, enabling the network to better handle images with varying contrast levels.
To enhance the segmentation results at tumor boundaries, we incorporate the Gaussian derivatives of BUS images, which highlight the edges of tumor boundaries. Let f (x,y) represent a BUS image. The 2D Gaussian kernel function is defined as
where is the standard deviation that determines the width of the Gaussian kernel function. Then Gaussian derivative of BUS images is defined as
The derivative of the Gaussian kernel function respective to and can be expressed as
The magnitude of the Gaussian derivative of the BUS image is given by
Figure 3 displays several BUS images selected from OASBUD detaset. The first row of Figures 3a, b show BUS images featuring an early-stage tumor and a malignant tumor, respectively. Figure 3c shows a normal BUS image. Their corresponding Gaussian derivative magnitude images, calculated using (Equations 6–9), are presented in the second row of Figures 3a-c. Note that the Gaussian derivatives enhance the distinctive features of these BUS images. Notably, we use the computed magnitude as a boundary feature and concatenate it with the original image to create a new input for the network, thereby improving overall task performance.
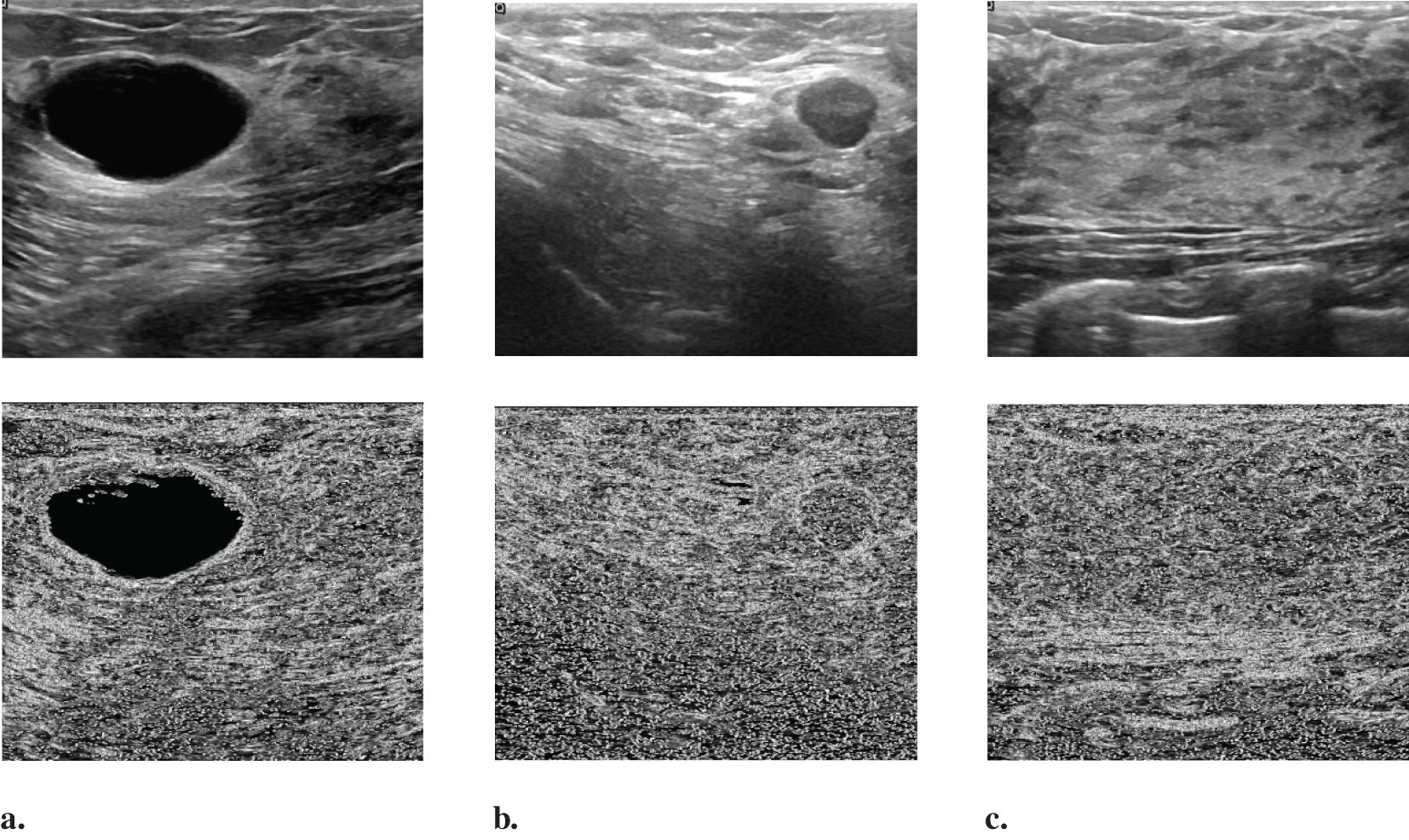
Figure 3. Randomly selected images from the OASBUD dataset and their corresponding Gaussian derivative magnitude images: (a) A representative BUS image with a tumor at an early stage, followed by its Gaussian derivative magnitude image; (b) A representative BUS image with a malignant tumor, followed by its Gaussian derivative magnitude image; (c) A representative BUS image without a tumor, followed by its Gaussian derivative magnitude image.
To validate the effectiveness of our proposed model, we compare it against two widely used methods: UNet (58) and MT-DUNet (59). UNet is a popular method for both segmentation and classification tasks, while MT-DUNet is a well-established multi-task learning model specifically designed for BUS image segmentation and classification.
After training our models on the OASBUD dataset, we applied all three models to a blind testing dataset. We randomly selected several images from the blind testing dataset and performed image segmentation using each model (Figure 4). The blue arrows in Figure 4 indicate areas with inaccurate prediction while the red arrows point to regions that are challenging to interpret yet accurately predicted. Figure 4 demonstrates that both our method and MTL-DUNet are more robust than the single-task UNet (denoted as UNet (ST)). This improvement is likely due to the shared features between segmentation and classification tasks (59). We cannot observe the obvious difference between the segmentation results of MTL-OCA and MTL-DUNet. However, their evaluation metrics differ from each other (Table 2). Compared to MTLDUNet, the classification module of MTL-OCA improves classification accuracy by fully leveraging the high-level semantic information from the rough segmentation masks.

Figure 4. Segmentation results for randomly selected images from the OASBUD dataset using different methods. The first and second columns show the original BUS images and the ground truth labels. The third, fourth, and fifth columns display the segmentation results obtained using UNet, MT-DUNet, and our proposed MTL-OCA, respectively. The blue arrows highlight areas with inaccurate interpretations, whereas the red arrows indicate challenging regions that have been accurately predicted.
Figures 5a-c show the confusion matrices for the classification results computed using UNet (ST), MTL-DUNet, and our proposed method, respectively. Note that all models accurately classify the normal class. However, the benign and malignant classification accuracies of our method are notably higher than UNet (ST) and MTL-DUNet. Table 3 summarizes the Precision, Sensitivity, Specificity, and F1-score for these three methods. Table 3 demonstrates that the proposed method outperforms comparative approaches across all evaluation metrics except for those in normal cases. These quantitative parameters indicate the superiority of our model over both UNet (ST) and MTL-DUNet for this classification task. Additionally, to enhance the interpretability of our model, we generated gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) heatmaps (Figure 6). The highlighted regions in these heatmaps correspond well with the key areas of interest in the input images during classification.
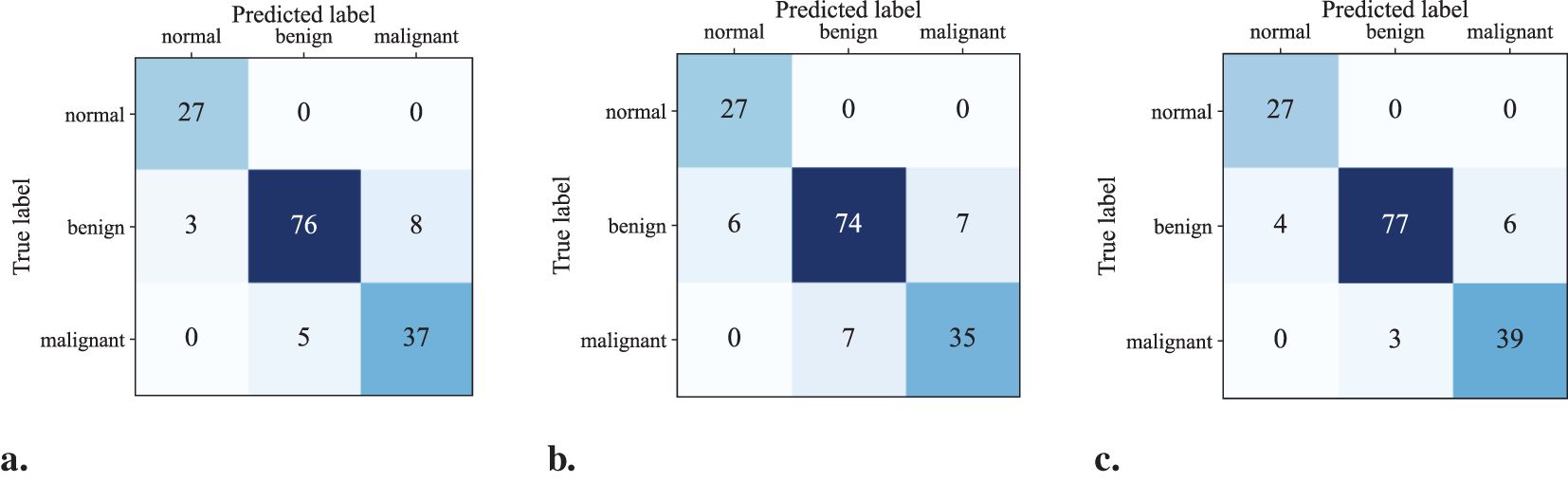
Figure 5. The confusion matrix of the classification results computed using (a) UNet(ST), (b) MTL-DUNet, and (c) our suggested method.
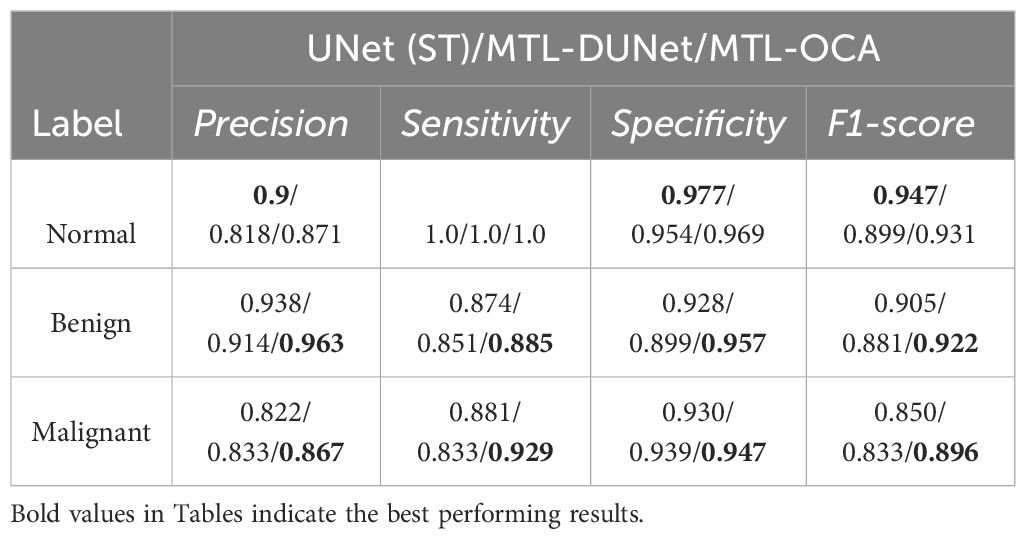
Table 3. The Precision, Sensitivity, Specificity, and F1-score of UNet (ST), MTL-DUNet, and MTL-OCA on the OASBUD dataset.
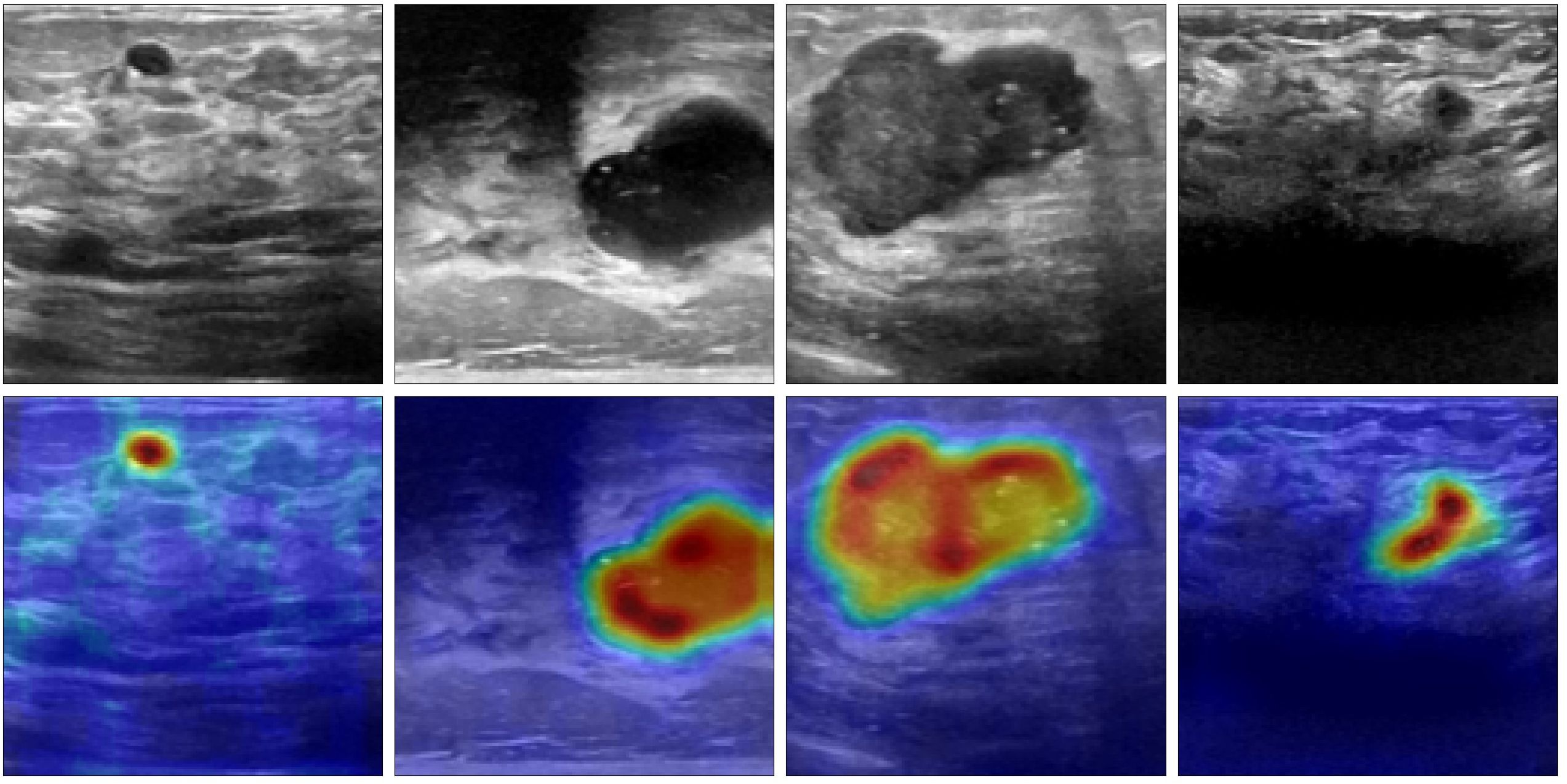
Figure 6. The Grad-CAM heatmaps generated by the proposed method. The first row is the input images and the second row is the corresponding Grad-CAM heatmaps.
In addition, we trained and tested our model on the UDIAT dataset. The first and second columns in Figure 7 show randomly selected BUS images and their corresponding ground truth labels, respectively. The third, fourth, and fifth columns show the segmentation results that are computed using different methods. The blue arrows indicate areas with inaccurate interpretations, and the red arrows point to regions that are challenging to interpret but have been accurately predicted. A visual comparison of these results demonstrates that our proposed method achieves superior segmentation performance compared to UNet and MTL-DUNet, particularly at the boundaries highlighted by the blue and red arrows. Furthermore, we evaluated our method on the UDIAT dataset using the same set of metrics (Tables 4, 5). The experimental findings consistently confirm that our approach outperforms the selected comparative methods across all key indicators.
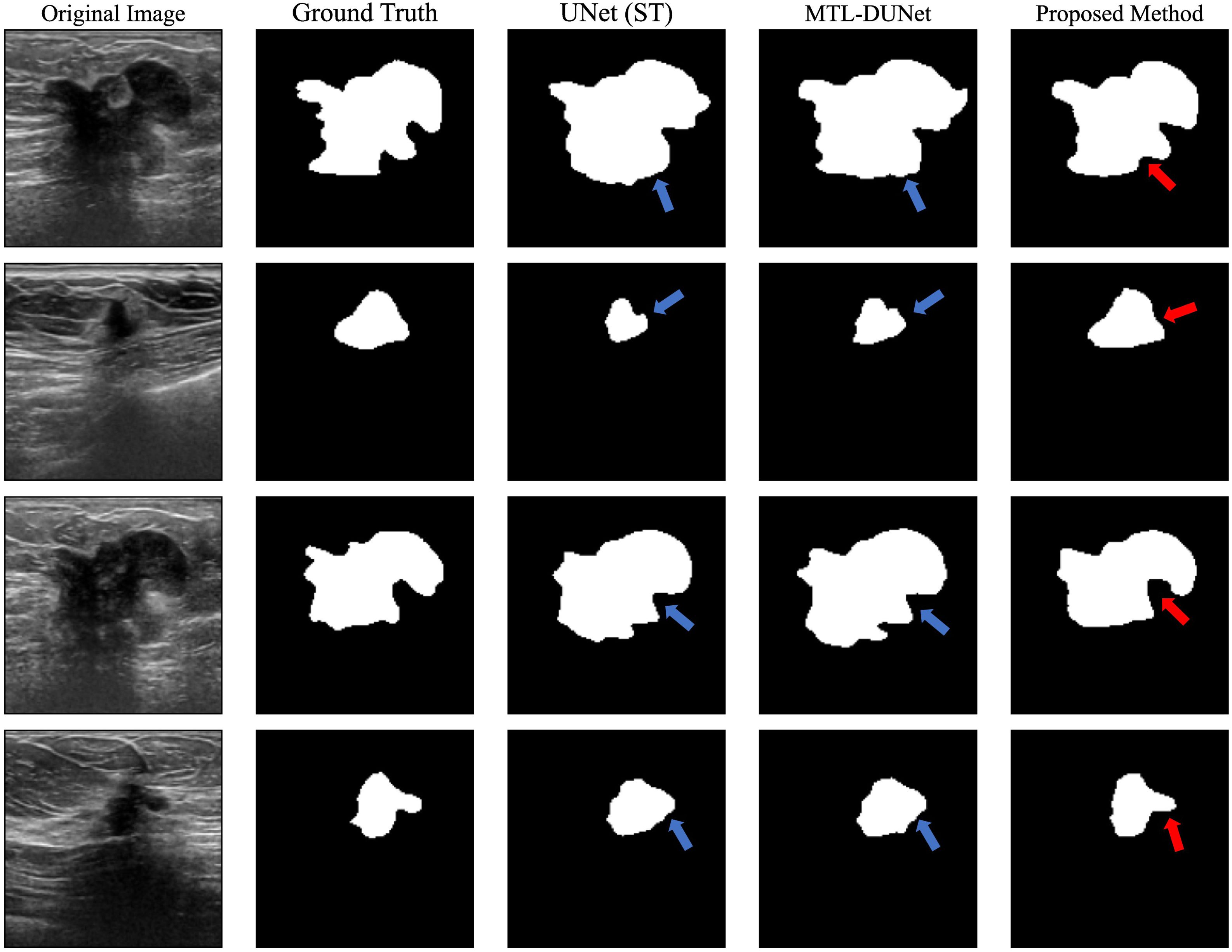
Figure 7. The segmented results for the randomly selected images from the UDIAT dataset using different methods. The first and second columns are the original BUS images and ground truth labels, while the third, fourth, and fifth columns are the segmented results computed using UNet, MTL-DUNet, and our MTL-OCA. The blue arrows highlight areas with inaccurate interpretations, while the red arrows point to regions that are challenging to interpret but have been accurately predicted.
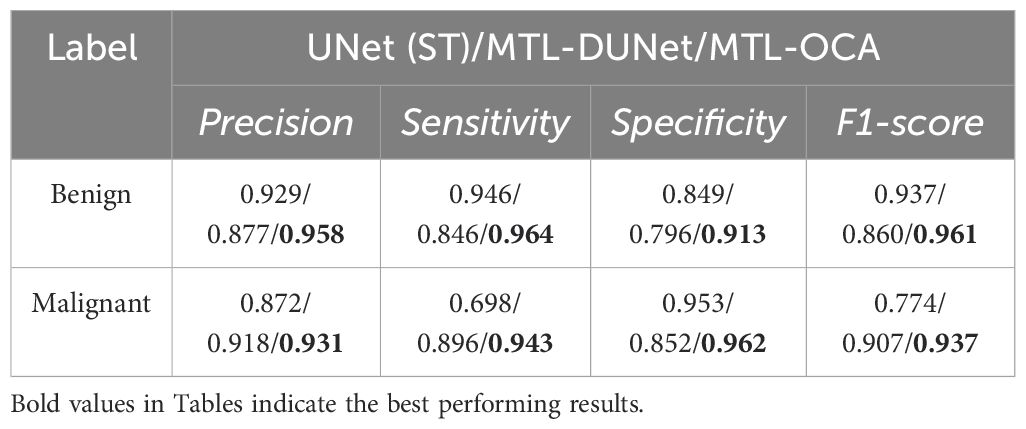
Table 5. The Precision, Sensitivity, Specificity, and F1-score of UNet (ST), MTL-DUNet, and MTL-OCA on the UDIAT dataset.
Based on the OASBUD dataset, we conduct an ablation study on the object contextual attention (OCA) module to evaluate its impact on segmentation and classification performance. We test three different configurations. The first configuration omits the OCA module, which means the backbone generates the final segmentation map. As a result, the classification task relies solely on the results from this segmentation. The second configuration includes the OCA module, and the classification task is based on the enhanced segmentation map produced by the OCA. The third configuration is our proposed architecture in this study. Table 6 presents the results of the ablation study for these three different network architectures when applied to the same testing dataset. Table 6 indicates that integrating the OCA module improves segmentation performance in the second configuration compared to the first. The result of the third configuration shows that both segmentation and classification performance are inferior to our method when the classification model is based solely on the OCA-enhanced segmentation maps. Overall, the proposed MTL-OCA architecture yields the highest Dice coefficient and classification accuracy. The highest accuracy demonstrates that the optimal integration of the OCA module leads to significant performance enhancement.
The qualitative analysis of the results validates the effectiveness of our proposed multi-task deep learning architecture for the automatic joint segmentation and classification of BUS images. However, we believe that special attention should be paid to three key aspects of the implementation. First, the choice of backbone is crucial for the successful application of a multi-task learning model. In our research, we selected the widely used ResUNet as the backbone. While we have not gone into extensive detail on this choice, prior research has emphasized the importance of selecting suitable neural network architecture. Several advanced models that address various challenges could also serve as viable options for the backbone. Exploring alternative architecture presents a promising avenue for future work. Second, to address the class imbalance in the dataset, we employed data augmentation techniques to modify the class distribution in the training set. For future studies, we may consider using specialized loss functions, such as focal loss (60), to mitigate the issue of class imbalance more effectively. Lastly, while our model performs well on the two datasets used in this study, its performance may be constrained by the size and variety of the training data. Future research will focus on expanding and diversifying the dataset to improve the robustness and generalizability of our approach.
We propose a multi-task learning network with an object contextual attention module (MTL-OCA) for simultaneous segmentation and classification of BUS images. Numerical experiments on two widely used datasets, namely OASBUD and UDIAT, demonstrate that the object contextual attention module enhances segmentation masks by effectively learning the pixel-region relationships within BUS images. Additionally, the Grad-CAM heatmaps demonstrate that high-level information extracted from the unenhanced segmentation masks can improve classification performance. The comparisons with UNet and MT-DUNet confirm the effectiveness of our model for the joint segmentation and classification of BUS images.
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://github.com/hugofigueiras/Breast-Cancer-Imaging-Datasets/tree/main.
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. FS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. KY: Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors thank Dr. Aly Fahmy at Cairo University and the UDIAT Diagnostic Centre in Sabadell (Spain) for the open datasets.
Author KY was employed by the company Beijing Smartmore Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Zhou X, Li C, Rahaman MM, Yao Y, Ai S, Sun C, et al. A comprehensive review for breast histopathology image analysis using classical and deep neural networks. IEEE Access. (2020) 8:90931–56. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2993788
2. Zhou Y, Chen H, Li Y, Liu Q, Xu X, Wang S, et al. Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of tumors in 3d automated breast ultrasound images. Med Image Anal. (2021) 70:101918. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101918
3. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21609
4. Bleicher RJ, Ruth K, Sigurdson ER, Beck JR, Ross E, Wong Y, et al. Time to surgery and breast cancer survival in the United States. JAMA Oncol. (2016) 2:330–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.4508
5. Yang S, Gao X, Liu L, Shu R, Yan J, Zhang G, et al. Performance and reading time of automated breast us with or without computer-aided detection. Radiology. (2019) 292:540–9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019181816
6. Mojabi P, Khoshdel V, Lovetri J. Tissue-type classification with uncertainty quantification of microwave and ultrasound breast imaging: A deep learning approach. IEEE Access. (2020) 8:182092–104. doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639
7. Wang Y, Ge X, Ma H, Qi S, Zhang G, Yao Y. Deep learning in medical ultrasound image analysis: a review. IEEE Access. (2021) 9:54310–24. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3071301
8. Rezaei Z. A review on image-based approaches for breast cancer detection, segmentation, and classification. Expert Syst Appl. (2021) 182:115204. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115204
9. Lu M, Duan G, Zhang T, Liu N, Song Y, Zhang Z, et al. Influences of paleoclimatic changes on organic matter enrichment mechanisms in freshwater and saline lacustrine oil shales in China: A machine learning approach. Earth-Science Rev. (2025) 262:105061. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2025.105061
10. Liu N, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Wang Z, Gao J, Liu R, et al. Multiple-frequency attribute blending via adaptive uniform manifold approximation and projection and its application on hydrocarbon reservoir delineation. Geophysics. (2024) 89:WA195–206. doi: 10.1190/geo2023-0111.1
11. Saber A, Sakr M, Abo-Seida OM, Keshk A, Chen H. A novel deep-learning model for automatic detection and classification of breast cancer using the transfer-learning technique. IEEE Access. (2021) 9:71194–209. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079204
12. Chang S, Gao Y, Pomeroy MJ, Bai T, Zhang H, Liang Z. (2022). Fully utilizing contrast enhancement on lung tissue as a novel basis material for lung nodule characterization by multi-energy ct, in: 7th International Conference on Image Formation in X-Ray Computed Tomography, Baltimore, United States, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering. 12304:500–4. Bellingham, Washington, USA: SPIE Digital Library.
13. Chang S, Gao Y, Pomeroy MJ, Bai T, Zhang H, Liang Z. (2022). Using tissue-energy response to generate virtual monoenergetic images from conventional ct for computer-aided diagnosis of lesions, in: 7th International Conference on Image Formation in X-Ray Computed Tomography, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, Baltimore, United States, Vol. 12304. pp. 348–52. Bellingham, Washington, USA: SPIE Digital Library.
14. Rahmawaty M, Nugroho HA, Triyani Y, Ardiyanto I, Soesanti I. (2016). Classification of breast ultrasound images based on texture analysis, in: 2016 1st International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (IBIOMED), Yogyakarta, Indonesia. 2016 1st International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (IBIOMED 2016) pp. 1–6. New York, USA: IEEE.
15. Wang Z, Li M, Wang H, Jiang H, Yao Y, Zhang H, et al. Breast cancer detection using extreme learning machine based on feature fusion with cnn deep features. IEEE Access. (2019) 7:105146–58. doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639
16. Xian M, Zhang Y, Cheng H, Xu F, Zhang B, Ding J. Automatic breast ultrasound image segmentation: A survey. Pattern Recognition. (2018) 79:340–55. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.02.012
17. Priya K, Senthilkumar V, Isaac JS, Kottu S, Ramakrishna V, Kumar MJ. (2022). Breast cancer segmentation by k-means and classification by machine learning, in: 2022 International Conference on Automation, Computing and Renewable Systems (ICACRS), Pudukkottai, India. pp. 651–6. New York, USA: IEEE.
18. Wu W, Lin S, Moon WK. Combining support vector machine with genetic algorithm to classify ultrasound breast tumor images. Computerized Med Imaging Graphics. (2012) 36:627–33. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2012.07.004
19. Moon WK, Lo C-M, Chen R-T, Shen Y-W, Chang JM, Huang C-S, et al. Tumor detection in automated breast ultrasound images using quantitative tissue clustering. Med Phys. (2014) 41:042901. doi: 10.1118/1.4869264
20. da Silva DS, Nascimento CS, Jagatheesaperumal SK, Albuquerque VHC d. Mammogram image enhancement techniques for online breast cancer detection and diagnosis. Sensors. (2022) 22:8818. doi: 10.3390/s22228818
21. Lyu S, Cheung RC. Efficient and automatic breast cancer early diagnosis system based on the hierarchical extreme learning machine. Sensors. (2023) 23:7772. doi: 10.3390/s23187772
22. Zhu F, Liu M, Wang F, Qiu D, Li R, Dai C. Automatic measurement of fetal femur length in ultrasound images: a comparison of random forest regression model and segnet. Math Biosci Eng. (2021) 18:7790–805. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021387
23. Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. (2017) 39:2481–95. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.34
24. Wang Z, Gao X, Zhang Y, Zhao G. Mslwenet: A novel deep learning network for lake water body extraction of google remote sensing images. Remote Sens. (2020) 12:4140. doi: 10.3390/rs12244140
25. Li S, Liu N, Li F, Gao J, Ding J. Automatic fault delineation in 3-d seismic images with deep learning: Data augmentation or ensemble learning? IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. (2022) 60:1–14. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3150353
26. Wang S, Chen W, Xie SM, Azzari G, Lobell DB. Weakly supervised deep learning for segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. (2020) 12:207. doi: 10.3390/rs12020207
27. Maxwell AE, Warner TA, Guillén LA. Accuracy assessment in convolutional neural network-based deep learning remote sensing studies—part 1: Literature review. Remote Sens. (2021) 13:2450. doi: 10.3390/rs13132450
28. Chen X, Zhang C, Bai T, Chang S. Improving spectral ct image quality based on channel correlation and self-supervised learning. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging. (2023) 9:1084–97. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2023.3334488
29. Umer MJ, Sharif M, Wang S-H. Breast cancer classification and segmentation framework using multiscale cnn and u-shaped dual decoded attention network. Expert Syst. (2022):e13192. doi: 10.1111/exsy.13192
30. Deepak GD, Bhat SK. A comparative study of breast tumour detection using a semantic segmentation network coupled with different pretrained cnns. Comput Methods Biomechanics Biomed Engineering: Imaging Visualization. (2024) 12:2373996. doi: 10.1080/21681163.2024.2373996
31. Liu N, Li Z, Liu R, Zhang H, Gao J, Wei T, et al. Ashformer: axial and sliding window based attention with high-resolution transformer for automatic stratigraphic correlation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. (2023) 61:1–10. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3334492
32. Xiao H, Li L, Liu Q, Zhu X, Zhang Q. Transformers in medical image segmentation: A review. Biomed Signal Process Control. (2023) 84:104791. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104791
33. Liu N, Huo J, Li Z, Wu H, Lou Y, Gao J. Seismic attributes aided horizon interpretation using an ensemble dense inception transformer network. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. (2024) 62:1–10. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3349687
34. Wei L, Liu H, Xu J, Shi L, Shan Z, Zhao B, et al. Quantum machine learning in medical image analysis: A survey. Neurocomputing. (2023) 525:42–53. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.049
35. Yan F, Huang H, Pedrycz W, Hirota K. Review of medical image processing using quantum-enabled algorithms. Artif Intell Rev. (2024) 57:300. doi: 10.1007/s10462-024-10932-x
36. Liu N, Huang T, Gao J, Xu Z, Wang D, Li F. Quantum-enhanced deep learning-based lithology interpretation from well logs. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. (2021) 60:1–13. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3085340
37. Dang T, Nguyen TT, McCall J, Elyan E, Moreno-Garc´ıa CF. Two-layer ensemble of deep learning models for medical image segmentation. Cogn Comput. (2024) 1–20:1141–60. doi: 10.1007/s12559-024-10257-5
38. Podda AS, Balia R, Barra S, Carta S, Fenu G, Piano L. Fully-automated deep learning pipeline for segmentation and classification of breast ultrasound images. J Comput Sci. (2022) 63:101816. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2022.101816
39. Liu N, Wu L, Wang J, Wu H, Gao J, Wang D. Seismic data reconstruction via wavelet-based residual deep learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. (2022) 60:1–13. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3152984
40. Pires de Lima R, Marfurt K. Convolutional neural network for remote-sensing scene classification: Transfer learning analysis. Remote Sens. (2019) 12:86. doi: 10.3390/rs12010086
41. Hu F, Xia G-S, Hu J, Zhang L. Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. (2015) 7:14680–707. doi: 10.3390/rs71114680
42. Chang S, Chen X, Duan J, Mou X. A cnn-based hybrid ring artifact reduction algorithm for ct images. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. (2020) 5:253–60. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS
43. Xu Y, Wang Y, Yuan J, Cheng Q, Wang X, Carson PL. Medical breast ultrasound image segmentation by machine learning. Ultrasonics. (2019) 91:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2018.07.006
44. Ma J, He Y, Li F, Han L, You C, Wang B. Segment anything in medical images. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:654. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44824-z
45. Alruily M, Said W, Mostafa AM, Ezz M, Elmezain M. Breast ultrasound images augmentation and segmentation using gan with identity block and modified u-net 3+. Sensors. (2023) 23:8599. doi: 10.3390/s23208599
46. Xie X, Shi F, Niu J, Tang X. (2018). Breast ultrasound image classification and segmentation using convolutional neural networks, in: Advances in Multimedia Information Processing — PCM 2018, pp. 200–11. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
47. Kwak D, Choi J, Lee S. Rethinking breast cancer diagnosis through deep learning based image recognition. Sensors. (2023) 23:2307. doi: 10.3390/s23042307
48. Luo J, Zhang H, Zhuang Y, Han L, Chen K, Hua Z, et al. 2s-busgan: A novel generative adversarial network for realistic breast ultrasound image with corresponding tumor contour based on small datasets. Sensors. (2023) 23:8614. doi: 10.3390/s23208614
49. Daoud MI, Al-Ali A, Alazrai R, Al-Najar MS, Alsaify BA, Ali MZ, et al. An edge-based selection method for improving regions-of-interest localizations obtained using multiple deep learning object-detection models in breast ultrasound images. Sensors. (2022) 22:6721. doi: 10.3390/s22186721
50. Jabeen K, Khan MA, Alhaisoni M, Tariq U, Zhang Y-D, Hamza A, et al. Breast cancer classification from ultrasound images using probability-based optimal deep learning feature fusion. Sensors. (2022) 22:807. doi: 10.3390/s22030807
51. Chowdary J, Yogarajah P, Chaurasia P, Guruviah V. A multi-task learning framework for automated segmentation and classification of breast tumors from ultrasound images. Ultrasonic Imaging. (2022) 44:3–12. doi: 10.1177/01617346221075769
52. He Q, Yang Q, Su H, Wang Y. Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of breast tumors from ultrasound images. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 173:108319. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108319
53. Xu M, Huang K, Qi X. (2022). enMulti-task learning with context-oriented self-attention for breast ultrasound image classification and segmentation, in: 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2022), Kolkata, India. New York, USA: IEEE. doi: 10.1109/isbi52829.2022.9761685
54. Maji D, Sigedar P, Singh M. Attention res-unet with guided decoder for semantic segmentation of brain tumors. Biomed Signal Process Control. (2022) 71:103077. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103077
55. Yuan Y, Chen X, Wang J. (2020). Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation, in: Computer Vision -- ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK. pp. 173–90. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer International Publishing.
56. Al-Dhabyani W, Gomaa M, Khaled H, Fahmy A. Dataset of breast ultrasound images. Data Brief. (2020) 28:104863. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2019.104863
57. Yap MH, Pons G, Marti J, Ganau S, Sentis M, Zwiggelaar R, et al. Automated breast ultrasound lesions detection using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf. (2017) 22:1218–26. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2017.2731873
58. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. (2015). U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation, in: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention -- MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany. pp. 234–41. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer International Publishing.
59. Chen C, Bai W, Rueckert D. Multi-task learning for left atrial segmentation on ge-mri. Stat Atlases Comput Models Heart Atrial Segmentation LV Quantification Challenges. (2019), 292–301. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12029-0_32
Keywords: breast ultrasound images, segmentation, classification, deep learning, multi-task learning
Citation: Lu Y, Sun F, Wang J and Yu K (2025) Automatic joint segmentation and classification of breast ultrasound images via multi-task learning with object contextual attention. Front. Oncol. 15:1567577. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1567577
Received: 27 January 2025; Accepted: 28 February 2025;
Published: 08 April 2025.
Edited by:
Izidor Mlakar, University of Maribor, SloveniaReviewed by:
Alexandru Ciobotaru, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, RomaniaCopyright © 2025 Lu, Sun, Wang and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fengyuan Sun, ZnlzdW5AZ3VldC5lZHUuY24=; Kai Yu, eWtrbW9vbkAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.