
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 11 March 2025
Sec. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Hepato Pancreatic Biliary Cancers
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1559343
This article is part of the Research Topic Liver Cancer Awareness Month 2024: Current Progress and Future Prospects on Advances in Primary Liver Cancer Investigation and Treatment View all 18 articles
Background: The comparative evaluation of laparoscopic and percutaneous techniques for liver radiofrequency ablation remains unexplored. This study aims to determine the most effective ablation technique and patient selection for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by analyzing the efficacy and safety of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation (LRFA) versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (PRFA).
Methods: Two investigators (Y-QW and PZ) independently performed a literature search in the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science and Embase databases. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale or Cochrane risk-of-bias tool. Meta-analysis was conducted with Review Manager 5.4, applying either fixed- or random-effects models depending on study heterogeneity. The chi-square test (χ²) and I² statistics were employed for heterogeneity analysis.
Results: Eight publications involving 1059 patients were included. Among them, 456 underwent LRFA and 603 underwent PRFA. LRFA showed a significantly better 3-year RFS than PRFA (OR: 1.89, 95% CI: 1.27-2.83, p = 0.002), the incidence rate of local recurrence was significantly fewer in the LRFA group (OR: 0.40, 95% CI: 0.23-0.69, p = 0.0010), but the postoperative hospital stay time was slightly shorter in the PFRA group (MD = 1.30; 95% CI 0.26 to 2.35; p=0. 01). Patients in the LRFA group had no significant difference in total postoperative complications, ablation success rates, overall survival (OS) and 1,5-year disease-free survival (DFS).
Conclusion: Both LRFA and PRFA are effective treatments for HCC. LRFA shows better oncologic outcomes, including lower local recurrence and improved mid-term DFS. PRFA is simpler, less invasive and shorter hospital stays. The choice should be tailored to individual patient needs, considering tumor characteristics, comorbidities, and available expertise. Future research should focus on large-scale, prospective trials to validate these findings.
Systematic review and registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42024601797.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a primary liver malignancy, accounting for more than 90% of all liver tumors (1). In China, HCC exhibits high incidence and mortality rates, ranking among the top malignant tumors nationwide (2). Globally, the incidence of HCC is increasing annually, with a rising trend observed in recent years (3). In terms of incidence and mortality rates, HCC ranks 6th and 4th, respectively, among all malignant tumors (4). According to estimates, approximately 840,000 new cases and 780,000 deaths occur annually (5).
Hepatocellular carcinoma has potential curative treatments in the form of liver transplantation, liver resection (LR) and local ablation therapies (6). Liver transplantation is considered the most effective treatment option for patients who fulfill the Milan criteria. However, the widespread use of this technique is significantly hampered by the critical shortage of donor organs (7). LR remains the first-line curative treatment for many HCC patients. However, only 5-15% of patients are suitable candidates for resection due to various contraindications such as multifocal tumors, unresectable locations, and insufficient hepatic reserve (8).
In recent years, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has gained widespread acceptance as a local thermal ablation method owing to its technical feasibility, safety, effective local tumor management, and minimally invasive characteristics (9). RFA can be performed via percutaneous or laparoscopic approaches. When considering treatment options for HCC, the debate between LRFA and PRFA continues. A multitude of studies have been undertaken, but some have been unable to definitively demonstrate the superiority of one treatment option (10, 11). Meta-analysis combines the results of multiple studies to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular research question (12). It is necessary to evaluate the efficacy and safety of RFA from the perspectives of percutaneous and laparoscopic approaches.
This systematic review followed the guidelines for the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses” (PRISMA) (13). We registered our protocol with PROSPERO (ID: CRD42024601797).
We included patients with HCC meeting the Milan criteria (a single tumor ≤5cm or up to 3 nodules ≤3cm) and preserved liver function. The inclusion criterion for tumor size was ≤5cm due to the poor efficacy of RFA in treating HCC larger than 5.0 cm, regardless of whether single-electrode conventional RFA or multi-electrode RFA was applied (14). We excluded patients with extrahepatic metastases, vascular invasion, or a history of previous or concurrent malignancy.
We compared LRFA with PRFA and LRFA as an intervention. LRFA is a surgical procedure that involves several steps. First, patients are administered general anesthesia, and tumor locations are determined through preoperative imaging studies such as CT or MRI. During the surgery, a laparoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity, and a pneumoperitoneum is established, typically using CO2 gas at a pressure of around 1.3 kPa. Intraoperative laparoscopic ultrasound (LOUS) is then used to locate the tumor, and any adhesions are separated to protect surrounding organs. An appropriate puncture site is selected, and a cooled radiofrequency needle is used to perform the ablation, with treatment time and power adjusted based on the tumor size and location. The temperature of the tumor is maintained above 60°C, and each treatment session lasts between 10 to 15 minutes. For tumors smaller than 3 cm, a single-point, single-session puncture is used, while for larger tumors, multiple points and overlapping punctures are employed. Intraoperative assessment is conducted using LOUS to ensure that the ablation zone adequately covers the tumor and an additional 0.5 to 1.0 cm of surrounding liver tissue. After the procedure, the needle track is heated and coagulated to prevent bleeding and track seeding. Postoperative assessment includes blood tests on the first day after surgery and a contrast-enhanced CT scan one month later to evaluate the ablation effect. Regular follow-ups are conducted to monitor patient survival and recurrence rates.
PRFA also involves a series of steps. Patients receive general or locate anesthesia, and tumor locations are confirmed through imaging studies. The procedure begins with the use of an external liver probe to determine the tumor’s position, often utilizing fusion imaging techniques that combine ultrasound with CT or MRI for precise localization. A puncture needle is inserted using a puncture frame, ensuring that the puncture site and angle are carefully selected to avoid direct tumor puncture. Similar to LRFA, a radiofrequency needle is used, and the tumor temperature is maintained above 60°C during treatment sessions. The approach for tumors smaller than 3 cm is the same as in LRFA, while larger tumors require multiple points and overlapping punctures. Intraoperative assessment is performed using ultrasound to confirm the ablation effect, ensuring that the zone covers the tumor and surrounding liver tissue adequately. The needle track is also managed to prevent complications. Postoperative assessments include blood tests and a contrast-enhanced CT scan one month after the procedure, followed by regular follow-ups to monitor patient outcomes.
The primary outcome we focused on were OS and DFS. Secondary outcomes were ablation success rates, Local recurrence rate, postoperative hospital stay time, and overall complications. OS was defined as the length of time from the start of ablation to the date of the death or the last follow-up. DFS was defined as the length of time that the patient survived without any signs of HCC after ablation. Ablation success was defined as the complete eradication of the tumor, confirmed by high-quality cross-sectional contrast-enhanced imaging. Local recurrence was defined as any new lesion within or adjacent to the ablated area. Postoperative complications were evaluated according to the Clavien-Dindo classification. Hospital stay was defined as duration of patient admission for treatment and recovery.
For our analysis, we considered randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomized trials (NRTs) that have been published in any language.
Lack of the required data in the Studies or statistical methods that are unreasonable.
Reviews, studies in animals, Case reports, letters, conference abstracts, and laboratory studies
We conducted a systematic search of the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases to identify RCTs and NRTs published up to March 1, 2024.A comprehensive search strategy (Supplemental Digital 1) was developed for this systematic review, utilizing a combination of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and text words for each database. In addition to database searching, as a supplementary step, we conducted a manual exploration of the references within the selected articles.
Two reviewers, Yaqiong Wang and Zha Peng, independently extracted and assessed the following data: author’s first name, year of publication, study design, patient characteristics, interventions, and outcomes. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion and consensus, with a third investigator, Zhenkun Tan, serving as an arbiter if necessary.
A modified Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (15) was employed to evaluate the methodological quality of the non-randomized studies. Studies receiving >7 stars were categorized as high quality, 4–6 stars as medium quality, and <4 stars as low quality. We used Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials version 2 for quality assessment of RCTs.
Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.4 (The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark). Dichotomous data was evaluated using odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), while standardized mean differences were used for continuous outcomes such as hospital stay, when data were presented as medians and ranges instead of means and standard deviations (SD) for continuous variables, we converted these values to means and SD using the formula described by Luo et al (16). Heterogeneity was assessed using the chi-squared (χ²) and I² statistics. Initially, a fixed-effects model was considered if heterogeneity was not statistically significant (I² ≤ 50%, P >.10). However, the final decision on the model was also based on the clinical and methodological characteristics of the included studies. If significant clinical or methodological heterogeneity was identified, a random-effects model was employed to provide a more conservative estimate of the effect size, even if the I² value was below the threshold. Sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess the influence of individual studies with high heterogeneity (I² ≥ 75%) on the pooled estimates. Statistical significance was defined as P <.05. Publication bias was not assessed because <10 studies were included in the meta-analysis.
Figure 1 shows the literature screening process. A total of 487 studies were retrieved from the initial literature search. After eliminating duplicate records and conducting a title and abstract screening, 10 studies were deemed eligible for full-text review. Subsequent full-text assessment resulted in the inclusion of 8 studies (10, 11, 17–22). A total of 1059 patients (PRFA 603, LRFA 456) were included in the meta-analysis. The characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1. All of studies exhibited a NOS score exceeding 7. (Table 2). Geographically, the studies were distributed across East Asia, with four conducted in China, three in Korea, and one in Japan. Comparative analysis revealed no statistically significant differences between the two groups with respect to age, gender, laboratory findings (specifically serum AFP and PIVKA-II levels), Child–Pugh classification, and tumor diameter.
A total of four studies (11, 17, 19, 21) examined the 1-year OS data, and the meta-analysis demonstrated no significant difference between the two groups (OR: 1.17, 95% CI: 0.53-2.57, p = 0.69) (Figure 2A). The same studies (11, 17, 19, 21) also assessed 3-year OS rate, and the results indicated no significant difference (OR: 1.40, 95% CI: 0.85-2.29, p = 0.19) (Figure 2B). Additionally, three studies (17, 19, 21) evaluated 5-year OS data, and the meta-analysis showed no significant difference in the 5-year OS rate between the two groups (OR: 1.41, 95% CI: 0.81-2.47, p = 0.22) (Figure 2C). The heterogeneity analysis for the 1- and 3-year OS rates revealed no significant results (p = 0.78, I2 = 0%; p = 0.42, I2 = 0%, respectively), but moderate heterogeneity was observed in the 5-year OS rates (p = 0.15, I2 = 47%). The fixed effects model was used.
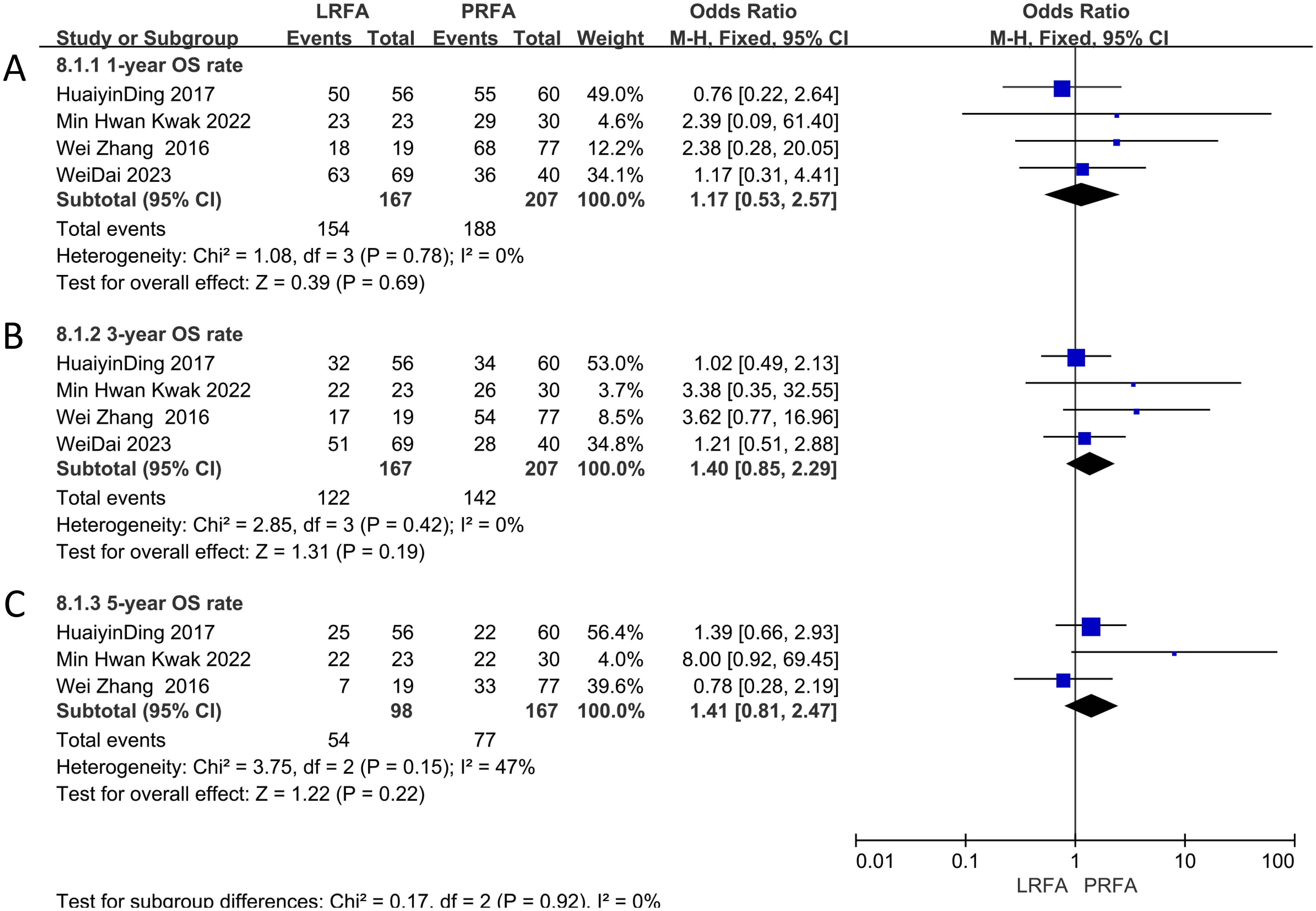
Figure 2. Forest plots of Overall survival (OS) between LRFA and PRFA on (A) 1-, (B) 3-, and (C) 5-y.
The 1-year DFS data were evaluated in five studies (11, 17, 19, 21, 22), and the results showed no significant difference between the LRFA and PRFA groups (OR: 1.71, 95% CI: 0.90-3.25, p = 0.10) (Figure 3A). However, the meta-analysis of 3-year DFS rates from 5 studies (11, 17, 19, 21, 22) revealed a significantly higher rate in the LRFA group (OR: 1.89, 95% CI: 1.27-2.83, p = 0.002) (Figure 3B). Additionally, the 5-year DFS rates from three studies (17, 19, 21) showed no significant difference between the two groups (OR: 1.50, 95% CI: 0.85-2.64, p = 0.16) (Figure 3C). The analysis of heterogeneity revealed no significant differences in the 1- and 3-year DFS rates (p = 0.83, I2 = 0%; p = 0.77, I2 = 0%, respectively), but moderate heterogeneity was observed in the 5-year DFS rates (p = 0.14, I2 = 50%). The fixed effects model was used for the analysis.
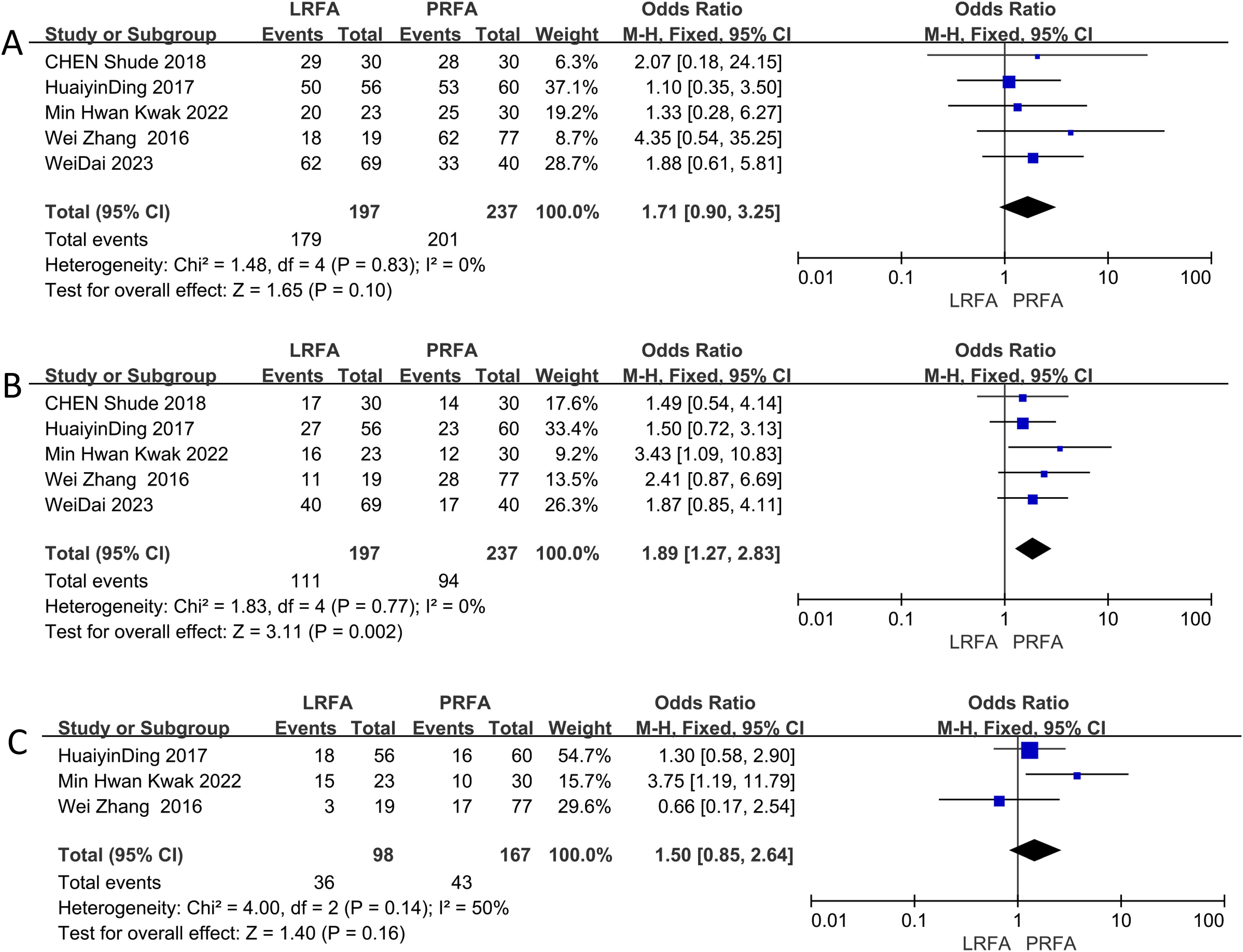
Figure 3. Forest plots of Disease Free Survival (DFS) between LRFA and PRFA on (A) 1-, (B) 3-, and (C) 5-y.
Three studies reported data regarding the length of hospitalization (17–19). PRFA was associated with a significant reduction in the length of hospital stay (MD = 1.30; 95% CI 0.26 to 2.35; p=0. 01) (Figure 4A). Heterogeneity was significant (I2 = 89%; p<0.0001), the random-effects model was used. After excluding the any single study, and heterogeneity still exists.
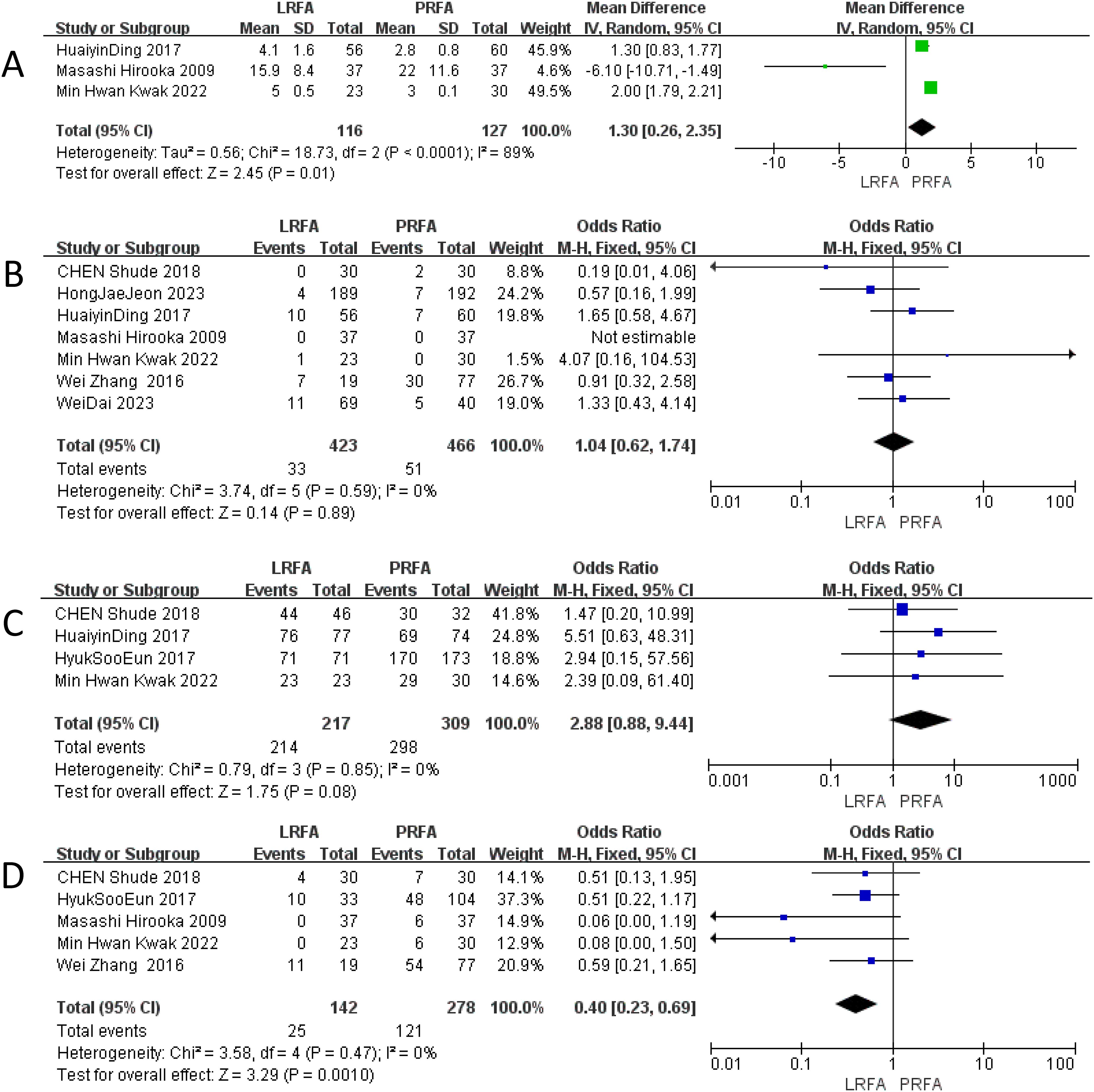
Figure 4. Forest plots of LRFA vs. PRFA on (A) length of hospital stay, (B) overall complication rates, (C) ablation success rates, (D) local recurrence rate.
A total of seven studies (11, 17–22) with 889 patients (423 in the LRFA group and 466 in the PRFA group) provided data on overall complications. The results of the meta-analysis showed no significant difference in the overall complication rate between the two groups (OR: 1.04, 95% CI: 0.62 to 1.74, p = 0.89). The analysis revealed no significant heterogeneity among the studies, the fixed effects model was used (Figure 4B).
Four studies (17, 19, 20, 22) provided data on the ablation success rate. The reported ablation success rate was higher for the laparoscopic ablation (LRFA) group compared to the percutaneous ablation (PRFA) group in these 4 studies. The meta-analysis showed that the odds of a successful ablation were higher for the laparoscopic procedures compared to the percutaneous procedures, although this difference did not reach statistical significance (OR 2.88, 95% CI 0.88–9.44, p = 0.08). No significant heterogeneity was observed in this analysis, the fixed effects model was used. (Figure 4C).
The local recurrence rate was evaluated in five studies (10, 18, 19, 21, 22), and the results indicated a significantly lower rate in the LRFA group compared to the PRFA group (OR: 0.40, 95% CI: 0.23-0.69, p = 0.0010). No significant heterogeneity was observed among the included studies, suggesting consistent findings across the studies, the fixed effects model was used (Figure 4D).
Ablation techniques, particularly radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA), have emerged as widely used minimally invasive approaches. Over the past decade, several meta-analyses have been conducted in the field of ablation therapies to determine the most effective and safe treatment options for HCC. In comparison to the previous meta-analyses conducted by Joslin R. Musick in 2023 (23), Qian Yu in 2021 (24), Moustafa Abdalla in 2023 (25), and Tan in 2019 (26), our study focuses specifically on comparing LRFA and PRFA for HCC, excluding the influence of different ablation methods on the outcomes.
In our meta-analysis, LRFA showed significantly higher 3-year DFS rates and a lower local recurrence rate. Additionally, PRFA was associated with slightly shorter postoperative hospital stays compared to LRFA. However, no significant differences were observed between LRFA and PRFA in terms of OS rates at 1, 3, and 5 years, overall complication rates, ablation success rates, and 1- and 5-year DFS rates, indicating that both techniques are safe and effective for treating HCC.
Several factors may contribute to the superior 3-year DFS rates and lower local recurrence rate observed with LRFA compared to PRFA. Firstly, LRFA provides a direct visual inspection of the liver under laparoscopic guidance, allowing for a more comprehensive surgical view. Second, LOUS can help identify satellite lesions or additional tumors that may not have been detected on pre-procedure imaging (27). Santambrogio et al. (28) further underscore LOUS during LRFA identified 25% of HCC lesions missed by preoperative imaging. By detecting these tumors during the procedure, the physician can adjust the treatment plan to ensure that all tumor tissue is adequately treated, which can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence. Third, LRFA enables the Pringle maneuver, reducing hepatic blood flow and expanding the injury area through thermal coagulation. This allows for the ablation of tumors near major blood vessels with minimal hemorrhage risk (29). During the procedure, CO2 infusion increases intraabdominal pressure, significantly decreasing intrahepatic blood flow due to vascular collapse, which enhances ablation effectiveness (30). Fourth, LRFA can reduce the impact of rib obstruction on puncture angles, allowing for the selection of more optimal puncture angles to effectively cover liver cancer lesions, especially for tumors located in special positions (31).
Although LRFA demonstrated better 3-year DFS rates, no significant differences in OS rates and 1-year and 5-year DFS rates were observed between LRFA and PRFA. Specifically, in the analysis of 5-year DFS rates, significant heterogeneity was observed among the included studies. Given the limited number of studies (only three) in this analysis, subgroup analyses could not be conducted. However, sensitivity analysis identified the study by Min Hwan Kwak (19) as the primary source of heterogeneity. The extended follow-up period in this study may have provided a more accurate assessment of DFS but could also have introduced temporal bias. This highlights the importance of considering the duration of follow-up when interpreting DFS outcomes.
The significant reduction in hospital stay for PRFA is an important clinical advantage. This finding can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, PRFA is a less invasive procedure that does not require general anesthesia, which reduces the need for postoperative monitoring and recovery time. Secondly, the absence of surgical incisions and the lower risk of intra-abdominal complications associated with PRFA contribute to shorter hospital stays. This not only reduces the burden on healthcare resources but also decreases the economic burden on patients and their families. Additionally, shorter hospital stays can improve patient satisfaction and quality of life, particularly for elderly patients or those with multiple comorbidities. we observed heterogeneity in the analysis of hospital stay duration. Even after excluding any single study, the heterogeneity persisted, indicating that multiple factors may be contributing to this variability. Given the limited number of studies, subgroup analysis was not feasible. The differences in hospital stay duration may be related to the treatment modality, postoperative management, and the criteria for discharge used by different medical institutions.
The quality of the studies included in meta-analysis is a critical factor that may contribute to heterogeneity. Despite similarities in baseline patient characteristics across the studies, uncontrolled variables may influence the outcomes. Additionally, differences in specific interventions and measurement methods used in each study could lead to variability in the results. Therefore, we urge caution in interpreting these findings.
LRFA offers distinct technical advantages. Recent advancements in LOUS have further enhanced the accuracy of intraoperative tumor detection. The combined use of LRFA with laparoscopic liver resection for patients with multiple lesions, where larger lesions are resected and smaller lesions are ablated, represents a promising integrated approach increasingly recognized in the management of HCC. PRFA also offers several advantages. Firstly, its lower invasiveness results from the absence of incisions or laparoscopic access, leading to minimal trauma. This is particularly beneficial for patients who cannot tolerate surgery or are at risk of intra-abdominal adhesions. Secondly, PRFA is associated with a significantly shorter hospital stay, which not only reduces the utilization of medical resources but also provides economic benefits for patients. Additionally, PRFA can typically be performed under local anesthesia or sedation, thereby minimizing the risks associated with general anesthesia, such as cardiopulmonary complications. This is especially advantageous for elderly patients with multiple comorbidities. Lastly, while direct cost comparisons are lacking in current studies, PRFA’s shorter hospital stay and less complex procedural requirements suggest potential cost-effectiveness.
Our study has several limitations. First, the small sample size may indeed limit the statistical power. Additionally, not all studies reported critical outcomes. This reflects the inherent limitations of the original studies, where retrospective designs often prioritize specific outcomes based on clinical focus or data availability. The variability in reported outcomes stems from differences in study designs and objectives. Furthermore, heterogeneity across outcomes was evident, and there were indications of publication bias in multiple studies. It is crucial to undertake larger, long-term comparative studies and prioritize well-designed randomized controlled trials to validate the current findings. This will provide more robust evidence for clinical decision-making.
In summary, both LRFA and PRFA are viable treatment options for HCC, each with its own set of advantages. LRFA appears to be more effective in terms of oncologic outcomes, particularly in reducing local recurrence and improving mid-term DFS. The advantages of PRFA, including its lower invasiveness, shorter hospital stay, avoidance of general anesthesia, and potential cost-effectiveness. The choice between LRFA and PRFA should be individualized based on tumor characteristics, patient comorbidities, and the availability of technical expertise. Future research should focus on large-scale, prospective, multicenter trials to further validate these findings and explore the optimal integration of these techniques within a comprehensive liver cancer management strategy.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Y-QW: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Z-KT: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. ZP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. HH: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82060478).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1559343/full#supplementary-material
1. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:681–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
2. Lee MW, Lee JM, Koh YH, Chung JW. 2022 korean liver cancer association-national cancer center korea practice guidelines for local ablation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: what’s new? Korean J Radiol. (2023) 24:10–4. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2022.0555
3. Lazarus JV, Picchio CA, Colombo M. Hepatocellular carcinoma prevention in the era of hepatitis C elimination. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:14404. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814404
4. Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet Lond Engl. (2022) 400:1345–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4
5. Gnyawali B, Pusateri A, Nickerson A, Jalil S, Mumtaz K. Epidemiologic and socioeconomic factors impacting hepatitis B virus and related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. (2022) 28:3793–802. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3793
6. Ivanics T, Rajendran L, Abreu PA, Claasen MPAW, Shwaartz C, Patel MS, et al. Long-term outcomes of ablation, liver resection, and liver transplant as first-line treatment for solitary HCC of 3 cm or less using an intention-to-treat analysis: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Med Surg. (2022) 77:103645. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103645
7. Drefs M, Schoenberg MB, Börner N, Koliogiannis D, Koch DT, Schirren MJ, et al. Changes of long-term survival of resection and liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma throughout the years: A meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2024) 50:107952. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2024.107952
8. Singal AG, Llovet JM, Yarchoan M, Mehta N, Heimbach JK, Dawson LA, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2023) 78:1922–65. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000466
9. Deng M, Li S-H, Guo R-P. Recent advances in local thermal ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am Surg. (2023) 89:1966–73. doi: 10.1177/00031348211054532
10. Eun HS, Lee BS, Kwon IS, Yun GY, Lee ES, Joo JS, et al. Advantages of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation over percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. (2017) 62:2586–600. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4688-6
11. Dai W, Fang S, Mo C, Liu Y, Shen T, Li M, et al. Comparison of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma involving specific sites: A retrospective cohort study. Asian J Surg. (2024) 47:100–6. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2023.04.073
12. Malički M, Jerončić A, Aalbersberg IJ, Bouter L, ter Riet G. Systematic review and meta-analyses of studies analysing instructions to authors from 1987 to 2017. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:5840. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26027-y
13. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. (2021) 134:178–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.03.001
14. Chen L, Sun J, Yang X. Radiofrequency ablation-combined multimodel therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status. Cancer Lett. (2016) 370:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.09.020
15. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
16. Luo D, Wan X, Liu J, Tong T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res. (2018) 27:1785–805. doi: 10.1177/0962280216669183
17. Ding H, Su M, Zhu C, Wang L, Zheng Q, Wan Y. CT-guided versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma against the diaphragmatic dome. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:44583. doi: 10.1038/srep44583
18. Hirooka M, Kisaka Y, Uehara T, Ishida K, Kumagi T, Watanabe Y, et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma compared to percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with artificial ascites. Dig Endosc. (2009) 21:82–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2009.00836.x
19. Kwak MH, Lee MW, Ko SE, Rhim H, Kang TW, Song KD, et al. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for subphrenic hepatocellular carcinoma. Ultrasonography. (2022) 41:543–52. doi: 10.14366/usg.21241
20. Jeon HJ, Eun HS, Kwon IS, Lee BS, Lee ES, Rou WS, et al. Outcomes of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Endosc. (2023) 37:5176–89. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-09956-1
21. Zhang W, Jiang L, Yan L, Yang J, Li B, Wen T, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for HCC patients with multifocal tumours meeting the Milan criteria: A single-centre experience. Dig Liver Dis. (2016) 48:1485–91. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.07.018
22. Chen S, Wang H, Zhang W, Chen J, Lu P. Clinical application of laparoscopy-assisted and percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. (2018) 38:1147–50. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.09.21
23. Musick JR, Gaskins JT, Martin RCG. A meta-analysis and systematic review of the comparison of laparoscopic ablation to percutaneous ablation for hepatic Malignancies. Int J Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:565–75. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02304-2
24. Yu Q, Liu C, Navuluri R, Ahmed O. Percutaneous microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Abdom Radiol. (2021) 46:4467–75. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03080-1
25. Abdalla M, Collings AT, Dirks R, Onkendi E, Nelson D, Ozair A, et al. Surgical approach to microwave and radiofrequency liver ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal liver metastases less than 5 cm: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. (2023) 37:3340–53. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09815-5
26. Tan H-Y, Gong J-F, Yu F, Tang W-H, Yang K. Long-term efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in early hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech. (2019) 29:770–9. doi: 10.1089/lap.2018.0642
27. Bartoş A, Bartos D, Spârchez Z, Iancu I, Ciobanu L, Iancu C, et al. Laparoscopic contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for real time monitoring of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an observational pilot study. J Gastrointest Liver Dis JGLD. (2019) 28:457–62. doi: 10.15403/jgld-263
28. Santambrogio R, Costa M, Barabino M, Opocher E. Laparoscopic radiofrequency of hepatocellular carcinoma using ultrasound-guided selective intrahepatic vascular occlusion. Surg Endosc. (2008) 22(9):2051–5. doi: 10.1007/s00464-008-9751-0
29. Wong J, Lee K-F, Yu SC-H, Lee PS-F, Cheung Y-S, Chong C-N, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus surgical radiofrequency ablation for Malignant liver tumours: the long-term results. HPB. (2013) 15:595–601. doi: 10.1111/hpb.12014
30. Lee SD, Han H-S, Cho JY, Yoon Y-S, Hwang DW, Jung K, et al. Safety and efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatic Malignancies. J Korean Surg Soc. (2012) 83:36–42. doi: 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.1.36
Keywords: meta-analysis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation, percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (PRFA), radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
Citation: Wang Y-Q, Tan Z-K, Peng Z and Huang H (2025) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the comparison of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation to percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 15:1559343. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1559343
Received: 12 January 2025; Accepted: 24 February 2025;
Published: 11 March 2025.
Edited by:
Francisco Tustumi, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
Tiago Siqueira, Albert Einstein Israelite Hospital, BrazilCopyright © 2025 Wang, Tan, Peng and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hai Huang, SHVhbmdoYWlfZG9jdG9yQDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.