- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 2Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Wuhan, China
- 3Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 4Department of Radiology, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang, China
- 5Department of Pathology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Epithelioid angiomyolipoma (EAML) is a tumor with malignant potential, as evidenced by its pathological features. Further investigation into its additional characteristics, particularly in imaging, is of great significance for non-invasive detection methods to understand its malignant potential. In this context, we present a case study of a 47-year-old male patient with a right renal EAML. The patient underwent nephrectomy but subsequently developed liver metastasis. Next-generation sequencing confirmed mutations of tuberous sclerosis 2 (TSC2) in both the primary and metastatic lesions. Consequently, the patient received maintenance treatment with the mTOR inhibitor, everolimus. However, treatment was discontinued after six months due to disease progression. Subsequent 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging revealed a large heterogeneous hypermetabolic mass in the liver, along with two other hypermetabolic metastases near the liver capsule. The patient’s prognosis was poor, with indicators such as TSC2 mutation, tumor necrosis, high Ki-67 expression, and α-SMA-negative fibroblasts. Despite reoperation, the patient still succumbed to disease progression. The occurrence of malignant metastatic EAML detected using 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging is infrequent. We conducted a comprehensive review of the relevant literature on 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for EAML. Notably, this article emphasizes that elevated 18F-FDG uptake in EAML may serve as a novel indicator of malignant EAML.
Introduction
Angiomyolipoma (AML) is a well-characterized mesenchymal neoplasm classified within a unique category of perivascular epithelioid cell tumors. It predominantly occurs in the kidneys, with the liver being the second most prevalent site of occurrence. Epithelioid angiomyolipoma (EAML) constitutes less than 5% of all AML cases (1). EAML have the potential to exhibit malignant behavior, with documented rates of metastasis or recurrence ranging from 5% to 50% (2–4). Distinguishing EAML from hepatocellular carcinoma or renal cell carcinoma can be challenging during imaging assessments. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) plays a crucial role in diagnosis, with positive staining for melanocytic markers, such as HMB-45, and muscle markers, such as α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), being the most significant features (1).
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) is a widely utilized imaging modality for staging tumors, predicting malignancy, monitoring treatment response, and assessing prognosis (5, 6). Nonetheless, its application in EAML has rarely been reported, and the metabolic pathways of 18F-FDG in EAML have/ been infrequently explored. In this study, we report a case of hepatic-metastatic EAML that exhibited increased 18F-FDG uptake on PET/CT. Furthermore, we conducted a comprehensive literature review on EAML cases assessed with 18F-FDG PET/CT to evaluate its diagnostic value.
Case presentation
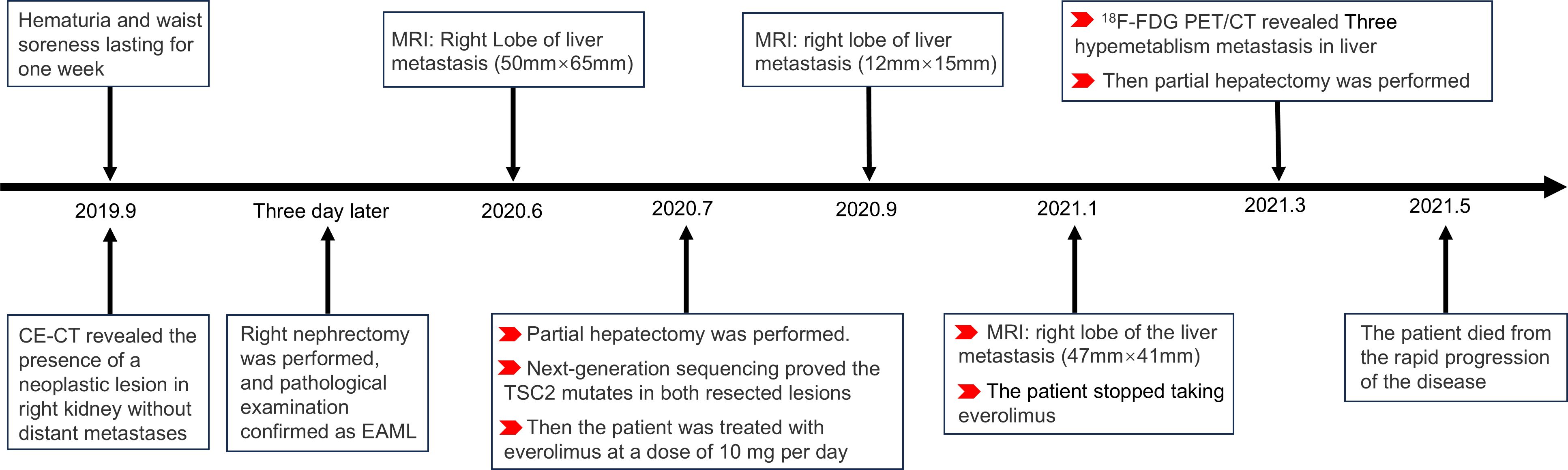
A 47-year-old male patient presented with one-week history of hematuria and lumbar discomfort. An abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CE-CT) scan identified a neoplastic lesion measuring 9.9 cm × 7.6 cm × 6.2 cm in the right kidney, without macroscopic lymphadenopathy or distant metastasis (Figure 1). The lesion demonstrated heterogeneous enhancement during the arterial phase and wash-out in the delayed phase, suggesting the possibility of renal carcinoma or angiomyolipoma with tumoral necrosis. Subsequently, a right nephrectomy was performed, and histopathological analysis confirmed the diagnosis of EAML with tumoral necrosis (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated positive expression of HMB45, Melan-A, TFE3, and P53, whereas α-SMA and S-100 were negative. The Ki-67 labeling index was 40%. Nine months later, the patient felt upper abdominal pain, and MRI indicated liver metastasis measuring 6.5 cm × 5.0 cm. Subsequently, one month later, a partial hepatectomy was performed due to liver metastasis, which displayed a high risk of recurrence and progression upon pathological examination. Histopathological analysis revealed epithelioid tumor cells with marked heteromorphism, pathological mitosis, and tumor necrosis. The Ki-67 labeling index was 60%. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) of EAML revealed mutations in TSC2, TP53, and ATRX in resected lesions. Subsequently, the patient was administered everolimus at a dose of 10 mg/day. After a two-month treatment period, the tumor recurred at the right margin of the liver and exhibited progressive growth. The patient had no obvious adverse reaction. After four months, treatment was discontinued owing to tumor progression. To assess potential metastasis in the whole body, 18F-FDG PET/CT and CE-CT were performed. The 18F-FDG PET/CT scan revealed a huge heterogeneous hypermetabolic mass measuring 11.3 cm × 10.5 cm at the right margin of the liver, with a maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of 10.7. Additionally, two lesions were detected at the anterior and posterior edges of the liver, measuring 3.2 cm × 2.9 cm and 0.9 cm × 0.8 cm, with SUVmax of 12.1 and 7.6, respectively. CE-CT revealed three prominent metastases in the arterial phase (Figure 2). Consequently, a surgical resection was performed. Regrettably, EAML recurred in the liver two months later, and the patient died soon after the rapid progression of the disease.
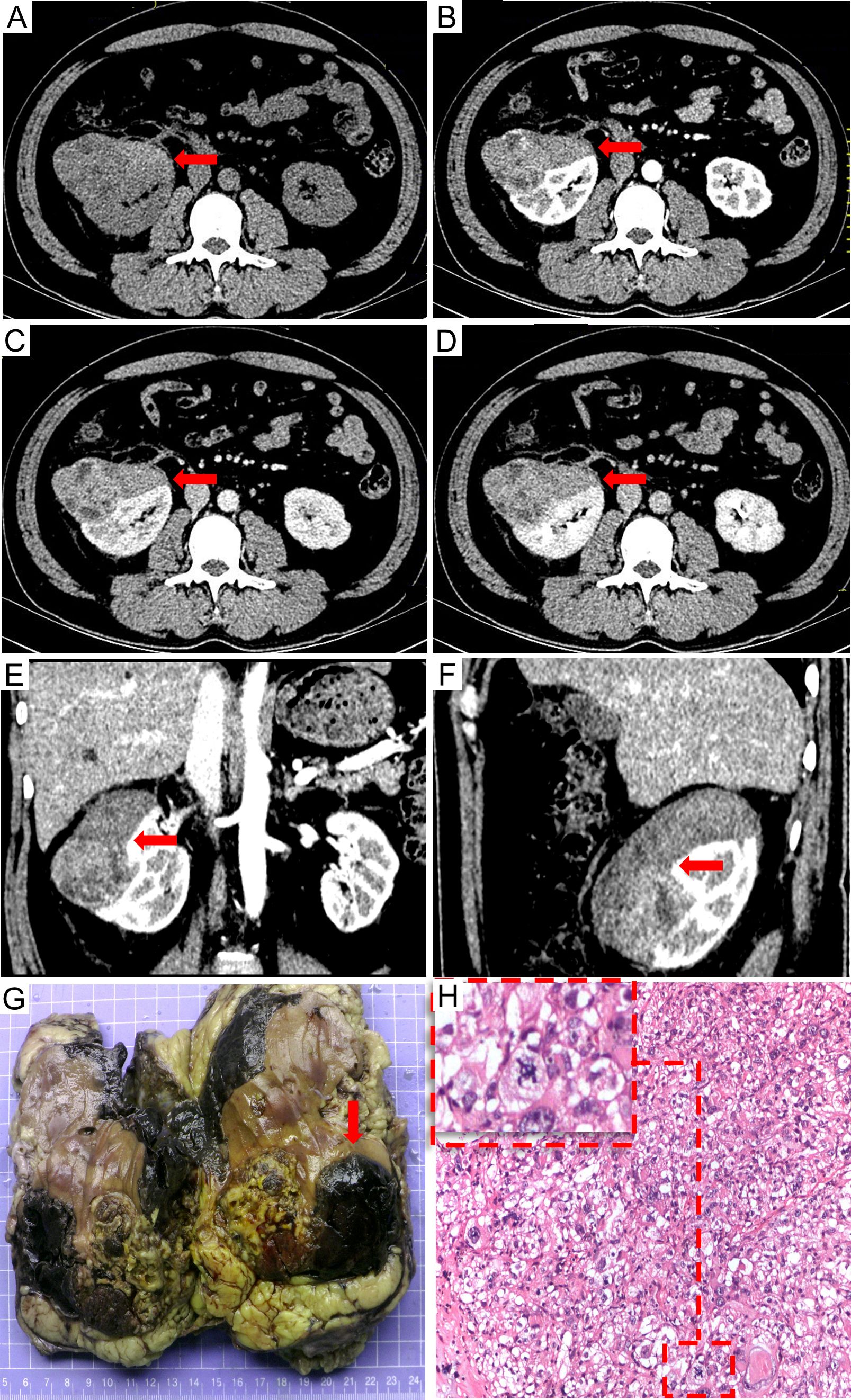
Figure 1. The preoperative contrast-enhanced CT scan: (A) non-contrast, (B) arterial phase, (C) venous phase, (D) delayed phase, (E) sagittal planes in arterial phase, and (F) coronal planes in arterial phase. Contrast-enhanced CT scan revealed a neoplastic lesion in the right kidney measuring 9.9 cm × 7.6 cm × 6.2 cm size neoplastic lesion in the right renal with heterogeneous enhancement in the arterial phase and wash out in the delayed phase. Multiple tumoral necrosis were suspected. The pathological diagnosis identified the tumor as epithelioid angiomyolipoma. The tumor exhibited an invasive growth pattern, enveloping and fusing with the right kidney. Macroscopic appearances revealed hemorrhage and necrosis [(G) the red arrow]; Additionally, significant pathological mitotic figures were observed within the tumor cells [(H) H&E stain, 100×, the red frame].
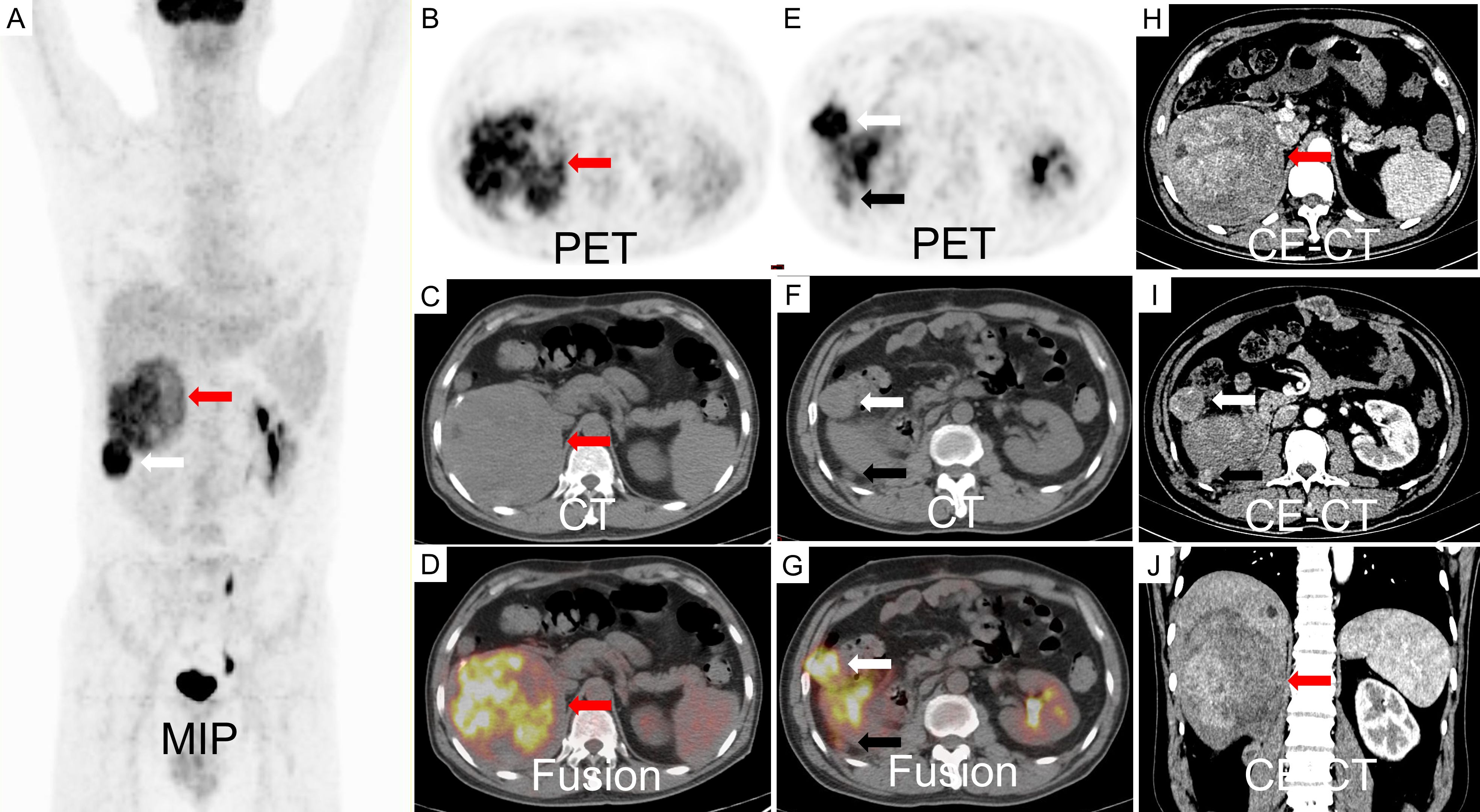
Figure 2. An 18F-FDG PET/CT scan revealed a large, inhomogeneous hypermetabolic mass in the liver, characterized by a SUVmax of 8.8, as indicated by the red arrow. Additionally, two hypermetabolic metastases were identified adjacent to the liver capsule, with SUVmax values of 12.1 (white arrow) and 3.1 (black arrow), respectively (A-G). The contrast-enhanced CT scan demonstrated inhomogeneous enhancement of the metastases during the arterial phase (H-J).
Discussion
EAML, a rare AML variant, is a potentially malignant neoplasm. The patient survived 32 months after the primary lesion was detected. The details of the diagnosis and treatment are shown in the flowchart (Figure 3). Relevant knowledge of this disease needs to be introduced before discussion. AML is a prevalent benign tumor with diverse cellular origins. Approximately 80% of AML cases are sporadic and frequently manifest as multiple or bilateral in individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) (4). AMLs < 4 cm are usually asymptomatic and are often detected during imaging examinations after an accident. Symptomatic AMLs such as abdominal pain and distension are more prone to hemorrhagic shock (7). AML can be classified into classic and epithelial types. Different from classic AML, epithelioid cells in epithelioid AML account for at least 80% of tumors (4). Furthermore, approximately 27% of patients with EAML have concomitant TSC, whereas it appears in 6.7% of patients with classic AML. The average reported patient age for EAML is approximately ten years earlier than that for AML, possibly due to the easier onset of symptoms such as abdominal symptoms, hemorrhagic shock, and TSC in EAML (2, 3, 8).
The classic AML contains blood vessels, smooth muscle, and mature adipose tissue, whereas EAML often lacks mature adipose tissue. EAML cells are epithelioid and may be misdiagnosed as leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, and even carcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining revealed the expression of the muscle marker α-SMA and melanocytic markers HMB-45 and Melan-A (2), but was negative for markers of epithelial or neural cells. Treatment with everolimus has been found to be more effective in AML patients with TSC than in those without TSC (8). The potential malignant behaviors of renal EAML are associated with TSC or concurrent AML, necrosis, extrarenal extension and/or renal vein involvement, tumor size >7 cm, and carcinoma-like growth pattern (3). Brimo et al. (9) summarized four pathological malignant characteristics of renal EAML: 1. atypical epithelioid cells ≥ 70%, 2. ≥2 mitotic figures per 10 HPF, 3. atypical mitotic figures, and 4. tumor necrosis. The presence of three or more features was highly suggestive of malignant behavior.
Generally, EAML are detected using CT and MRI. Most EAMLs have a “fast-in and slow-out” pattern on CE-CT, which usually shows hyperdensity with or without an adipose component (11). On MRI, EAMLs are mainly isointense on T1WI, hypointense on T2WI, restricted diffusion on DWI, round tumor-kidney interface, and reticular (12). Classic AML generally has dysmorphic blood vessels and adipose tissues. Tumor adipose tissue, hemorrhage, and cystic degeneration are all sensitive to detection using CT and MRI (12, 13). Radiologically, EAML resembles hepatocellular carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma due to the scarcity of adipose tissue. Consequently, the uncertainty of imaging diagnosis and lack of consensus on diagnostic characteristics restrict the comprehension of EAML.
18F-FDG PET/CT is an examination to identify systemic lesions and assess the malignant degree of tumors by the “Warburg effect”. Reports on 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging of EAML are scarce. Several studies have characterized classic AMLs as non-hypermetabolic tumors. Lin et al. (14) reviewed 21 patients with renal AML who underwent PET and PET/CT imaging. The result demonstrated None of the 21 classic AMLs showed an SUVmax greater than 1.98. The result was also proved by Jiang et al. (15) for eight AMLs, in which none of the eight AMLs demonstrated SUVmax higher than 2.3. In the present case, 18F-FDG PET/CT was performed to detect metastatic lesions in patients with EAML. Three metastatic lesions in the liver were found to have increased 18F-FDG uptake, which has rarely been reported. Consequently, this finding prompted further investigation of the relationship between glucose metabolism and EAML.
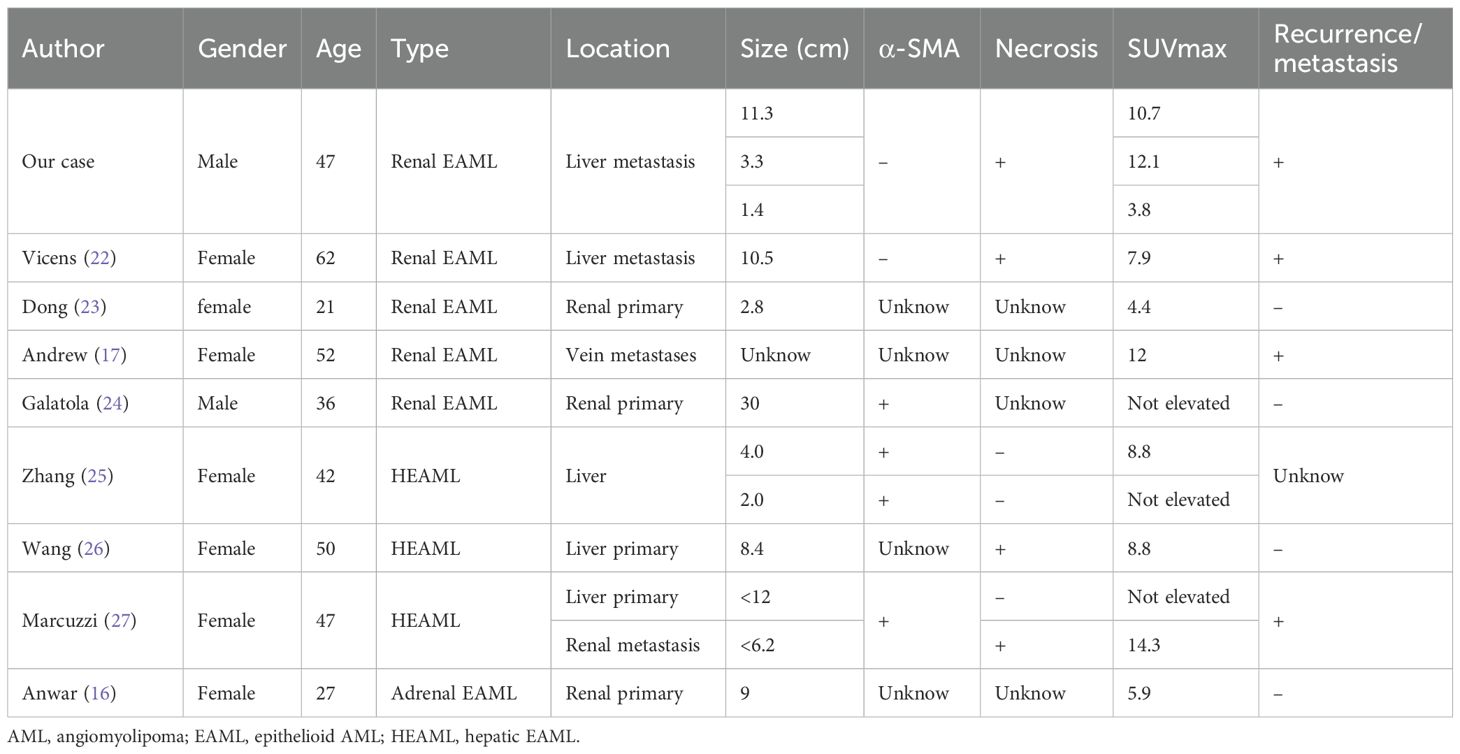
Based on the published reports, the metabolism and clinicopathological features of EAML are summarized in Table 1. The results of our research showed that the rate of high 18F-FDG uptake in metastatic EMALs was 100% (6/6), while it was 60% (3/5) in primary EAMLs. All EAMLs exhibiting necrosis (4/4) showed hypermetabolic lesions. Among the eight patients with hypermetabolic lesions, four (50%) were proven to have metastasized in follow-up studies. Consequently, SUVmax may serve as a potential marker for predicting the malignant potential of EAML, particularly in metastatic lesions. Two patients presented with both hypermetabolic and non-hypermetabolic lesions. The discrepancy between the primary lesions and metastatic lesions of 18F-FDG metabolism probably showed heterogeneity between the primary lesion and metastases. Consequently, more attention should be paid to distinguishing EAML metastases from other tumors. In addition to the above summary, the study also indicated that 18F-FDG PET/CT could monitor everolimus response assessment (16) and distinguish vascular invasion from thrombus in AML after nephrectomy from the uptake of 18F-FDG by the tumor (17).
The uptake of 18F-FDG is mainly determined by glucose transport, tumor blood flow, and glycolytic rate. AML is regarded as a benign hypervascular tumor with the potential for spontaneous hemorrhage. Consequently, blood flow cannot explain the low uptake of 18F-FDG in AML (14). Glucose transporter-1 (GLUT1) is one of the main factors that affect glucose transport. However, Zhang et al. (18) tested the expression of GLUT1 in seven cases of EAML and found that none of the EAML lesions expressed GLUT1. Therefore, glucose transport may not be the primary factor responsible for the uptake of 18F-FDG in EAML patients. The higher frequency of reports in hypermetabolic EAML proves that alternative mechanisms facilitate glucose uptake in EAML. TSC mutations occur more frequently in EAML than AML. The loss of 1/2 function in TSC leads to constitutive mTORC1 activation, which promotes cellular metabolism, including glycolytic rate (16, 19), and is associated with elevated 18F-FDG uptake in PET/CT scans.
Tumor metabolism is associated with various pathological indicators. Ki-67 labeling indicates that the cell proliferation rate, with high expression in Ki-67 labeling, is correlated with poorer prognosis and higher 18F-FDG uptake (10, 20), which is consistent with our report. Furthermore, α-SMA is the main indicator of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs). High expression of α-SMA in fibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinomas has been shown to be associated with a poorer prognosis. Conversely, Anwaier et al. showed that α-SMA-negative fibroblasts were significantly correlated with higher recurrence and metastasis rates in immunohistochemical indexes of fifty-seven patients with renal EAML (21). This finding suggests that the metastatic mechanism of EAML may differ from that of other tumors. In the present case, the patient underwent a right nephrectomy, followed by recurrent liver metastasis and progression. Rapid progression of the disease may have been influenced by the presence of α-SMA-negative fibroblasts, elevated Ki-67 labeling, increased 18F-FDG uptake, and necrosis.
Conclusion
We identified a rare case of renal EAML with liver metastasis that demonstrated high 18F-FDG uptake on PET/CT. Then, We comprehensively reviewed case reports on hypermetabolic EAML, analyzing the causes of 18F-FDG uptake and its association with malignancy, The reason for 18F-FDG uptake in EAML may be associated with TSC mutation and high Ki-67 expression. This study demonstrated the high sensitivity of PET/CT in detecting metastatic lesions of EAML. The uptake of 18F-FDG by EAML may be related to an increased glycolytic rate resulting from TSC mutations. Furthermore, the malignant potential of EAML is influenced by the expression of α-SMA and Ki-67, and the presence of necrosis within the tumor.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
LZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YD: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. PA: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JF: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DJ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. XL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WC: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0113302), the Open Foundation of Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging (2021fzyx0013).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. He W, Cheville JC, Sadow PM, Gopalan A, Fine SW, Al-Ahmadie HA, et al. Epithelioid angiomyolipoma of the kidney: pathological features and clinical outcome in a series of consecutively resected tumors. Mod Pathol. (2013) 26:1355–64. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.72
2. Mete O, van der Kwast TH. Epithelioid angiomyolipoma: a morphologically distinct variant that mimics a variety of intra-abdominal neoplasms. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2011) 135:665–70. doi: 10.5858/2009-0637-RSR.1
3. Nese N, Martignoni G, Fletcher CD, Gupta R, Pan CC, Kim H, et al. Pure epithelioid PEComas (so-called epithelioid angiomyolipoma) of the kidney: A clinicopathologic study of 41 cases: detailed assessment of morphology and risk stratification. Am J Surg Pathol. (2011) 35:161–76. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318206f2a9
4. McCarthy MR, Nichols PE, Sharma V, Stanton ML, Reynolds JP, Pitel BA, et al. Molecular and immunophenotypic correlates of metastatic epithelioid angiomyolipoma include alterations of TP53, RB1, and ATRX. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2023) 147:817–25. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0127-OA
5. Li H, Shao G, Zhang Y, Chen X, Du C, Wang K, et al. Nomograms based on SUVmax of (18)F-FDG PET/CT and clinical parameters for predicting progression-free and overall survival in patients with newly diagnosed extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Imaging. (2021) 21:9. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00379-y
6. Zhang L, Liu Y, Ding Y, Deng Y, Chen H, Hu F, et al. Predictive value of intratumoral-metabolic heterogeneity derived from (18)F-FDG PET/CT in distinguishing microsatellite instability status of colorectal carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1065744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1065744
7. Lienert AR, Nicol D. Renal angiomyolipoma. BJU Int. (2012) 110:25–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11618.x
8. Guo G, Gu L, Zhang X. Everolimus in invasive Malignant renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma. Front Oncol. (2021) 10:610858. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.610858
9. Brimo F, Robinson B, Guo C, Zhou M, Latour M, Epstein JI. Renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma with atypia: a series of 40 cases with emphasis on clinicopathologic prognostic indicators of Malignancy. Am J Surg Pathol. (2010) 34:715–22. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181d90370
10. Anwaier A, Xu WH, Tian X, Ding T, Su JQ, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of clinicopathological profiles and development of a risk model in renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma patients: a large-scale retrospective cohort study. BMC Urol. (2022) 22:148. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01101-9
11. Wang D, Gong G, Fu Y, Zhu L, Yin H, Liu L, et al. CT imaging findings of renal epithelioid lipid-poor angiomyolipoma. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:4919–30. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08528-y
12. Cong X, Zhang J, Xu X, Zhang M, Chen Y. Renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma: magnetic resonance imaging characteristics. Abdom Radiol (NY). (2018) 43:2756–63. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1548-6
13. Luo C, Liu Z, Gao M, Hu Q, He X, Xi Y, et al. Renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma: computed tomography manifestation and radiologic-pathologic correlation depending on different epithelioid component percentages. Abdom Radiol (NY). (2022) 47:310–9. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03313-3
14. Lin CY, Chen HY, Ding HJ, Yen KY, Kao CH. FDG PET or PET/CT in evaluation of renal angiomyolipoma. Korean J Radiol. (2013) 14:337–42. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.337
15. Jiang X, Kenerson H, Aicher L, Miyaoka R, Eary J, Bissler J, et al. The tuberous sclerosis complex regulates trafficking of glucose transporters and glucose uptake. Am J Pathol. (2008) 172:1748–56. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070958
16. Anwar H, Sachpekidis C, Schwarzbach M, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A. Fluorine-18-FDG PET/CT in a patient with angiomyolipoma: Response to mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor therapy. Hell J Nucl Med. (2017) 20:169–71. doi: 10.1967/s002449910559
17. Griffin A. 18F-FDG PET/CT of Malignant angiomyolipoma With Tumor Thrombus. Clin Nucl Med. (2017) 42:628–9. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000001710
18. Zhang W, Wang K, Yu W, Liu Y, Chu J, Jiang Y, et al. Diagnostic utility of S100A1, GLUT-1 and Caveolin-1 in renal tumors with oncocytic features: a comparative study. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. (2015) 44:767–71. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2015.11.002
19. Reinfeld BI, Madden MZ, Wolf MM, Chytil A, Bader JE, Patterson AR, et al. Cell-programmed nutrient partitioning in the tumour microenvironment. Nature. (2021) 593:282–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03442-1
20. Libé R, Pais A, Violon F, Guignat L, Bonnet F, Huillard O, et al. Positive correlation between 18 F-FDG uptake and tumor-proliferating antigen Ki-67 expression in adrenocortical carcinomas. Clin Nucl Med. (2023) 48:381–6. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000004593
21. Dourado MR, Guerra ENS, Salo T, Lambert DW, Coletta RD. Prognostic value of the immunohistochemical detection of cancer-associated fibroblasts in oral cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Pathol Med. (2018) 47:443–53. doi: 10.1111/jop.12623
22. Vicens RA, Jensen CT, Korivi BR, Bhosale PR. Malignant renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma with liver metastasis after resection: a case report with multimodality imaging and review of the literature. J Comput Assist Tomogr. (2014) 38:574–7. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000101
23. Dong A, Wang Y, Zuo C. Synchronous pure epithelioid angiomyolipoma of the kidney and retroperitoneal schwannoma in the same patient on 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging. Clin Nucl Med. (2013) 38:98–100. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e31825b2218
24. Galatola R, Stanzione A, Sirignano C, Mainolfi C, Guadagno E, Carlomagno N, et al. Giant epithelioid angiomyolipoma: An imaging-related differential diagnosis among fat-containing renal masses. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2020) 18:5–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.10.028
25. Zhang Y, Li B, Hou J, Yu H, Shi H. Hepatic epithelioid angiomyolipoma and 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. (2018) 43:422–4. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000002048
26. Wang S, Xia H, Liu X, Liu Y, Lou C. Hepatic epithelioid angiomyolipoma mimicking hepatocellular carcinoma on MR and 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging: A case report and literature review. Hell J Nucl Med. (2022) 25:205–9. doi: 10.1967/s002449912480
Keywords: epithelioid angiomyolipoma, 18 F-FDG PET/CT, tumor metabolism, cancer metabolism, tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)
Citation: Zhang L, Chen L, Deng Y, Chen H, Wu Y, An P, Fan J, Jiang D, Lan X and Cao W (2025) Elevated 18F-FDG accumulation in a malignant epithelioid angiomyolipoma: a case report and review of literature. Front. Oncol. 15:1555092. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1555092
Received: 03 January 2025; Accepted: 24 March 2025;
Published: 16 April 2025.
Edited by:
Giulia Maria Stella, University of Pavia, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, Deng, Chen, Wu, An, Fan, Jiang, Lan and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Cao, Y2Fvd2VpQGh1c3QuZWR1LmNu
 Li Zhang
Li Zhang Leqing Chen
Leqing Chen Yinqian Deng1,2
Yinqian Deng1,2 Jun Fan
Jun Fan Dawei Jiang
Dawei Jiang Xiaoli Lan
Xiaoli Lan