
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 28 February 2025
Sec. Breast Cancer
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1540538
This article is part of the Research Topic Challenges and Strategies in the Management of ER/PgR Low-Expression Breast Cancer: Exploring Fundamentals, Clinical Insights, and Treatment Approaches View all articles
Background: Advanced triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) presents significant therapeutic challenges, particularly in Asian populations, which exhibit distinct biological and genetic characteristics. Immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy has emerged as a promising approach; however, its efficacy compared to chemotherapy alone remains under investigation. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the clinical outcomes of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy (PIC) versus chemotherapy alone in the treatment of advanced TNBC in Asian patients.
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed across six databases for phase 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Only studies comparing the outcomes of PIC versus chemotherapy alone in patients with advanced TNBC, including subgroup analyses of Asian populations, were included. Data were pooled to assess overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), responses, and safety profiles.
Results: A total of 1041 patients from five phase 3 RCTs were included in the final analysis. Compared to chemotherapy alone, PIC therapy significantly improved PFS (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.74 [0.62, 0.88], P = 0.0008). No significant difference was observed in OS (HR: 0.78 [0.55, 1.12], P = 0.18), although a slight trend favoring PIC therapy was noted. Among PD-L1-positive patients, both OS (HR: 0.62 [0.44, 0.86], P = 0.005) and PFS (HR: 0.66 [0.50, 0.86], P = 0.003) were significantly improved in the PIC group. The PIC group also exhibited a substantially higher OS rate at 12–36 months and a higher PFS rate at 6–30 months. However, the incidence of immune-related AEs (irAEs) (risk ratio [RR]: 1.69 [1.33, 2.15], P < 0.0001) and grade 3–5 irAEs (RR: 3.11 [1.59, 6.10], P = 0.001) was significantly higher in the PIC group. The most common irAEs in the PIC group were hypothyroidism (14.40%), dermatitis (10.00%), and infusion reactions (8.85%). Both treatment groups exhibited similar response rates and treatment-related AEs (TRAEs).
Conclusions: In Asian patients with advanced TNBC, PIC significantly improved survival compared to chemotherapy alone. Although the combination therapy was associated with a higher incidence of irAEs, its clinical benefits support its use as a viable treatment option for this population.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42024622428.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) accounts for approximately 15-20% of all breast cancer cases and is associated with a poorer prognosis (1, 2). Chemotherapy has long been the cornerstone of treatment for advanced TNBC, offering some degree of efficacy. However, the prognosis remains unsatisfactory, with limited treatment options available (3). In recent years, the advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, has revolutionized cancer therapy, showing promising results in various malignancies, including TNBC (4).
Several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have investigated the impact of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy (PIC) in TNBC patients (5–9). For instance, the IMpassion130 trial demonstrated that the addition of atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel resulted in a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for patients with PD-L1-positive metastatic TNBC (5). Similarly, the KEYNOTE-355 trial showed that pembrolizumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, combined with chemotherapy, led to significant improvements in both PFS and OS in PD-L1-positive metastatic TNBC patients (8). A comprehensive meta-analysis by Wang et al. evaluated the efficacy and safety of PIC for patients with unresectable TNBC. The study concluded that this combination therapy significantly improved PFS and OS compared to chemotherapy alone, particularly in PD-L1-positive populations (10). Despite these encouraging outcomes, the applicability of these findings to Asian populations remains uncertain. TNBC exhibits distinct biological and genetic characteristics across different ethnic groups, which can influence treatment responses (11). Moreover, the prevalence of TNBC subtypes and PD-L1 expression levels may vary among populations, potentially affecting the efficacy of immunotherapy. Notably, Asian patients have been underrepresented in major clinical trials, resulting in a paucity of evidence regarding the effectiveness of these therapies in this demographic (12).
Given these considerations, our meta-analysis seeks to compare the PIC versus chemotherapy alone focusing specifically on Asian patients with advanced TNBC. By synthesizing data from phase III RCTs, we aim to provide robust evidence to guide clinical decision-making and optimize treatment strategies for this population.
The search strategy employed the following keywords: “PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors”, “Breast Cancer”, and “Randomized”. A comprehensive search was conducted across six databases (PubMed, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, Scopus, EMBASE, and Web of Science) from their inception up to November 12, 2024 (Supplementary Table S1).
Inclusion criteria (PICOS) were as follows: (1) Participants: Asian patients with advanced TNBC; (2) Intervention and Control: PIC versus chemotherapy alone; (3) Outcomes: OS, PFS, responses, and adverse events (AEs); (4) Study design: Phase III RCTs. Animal studies, reviews, meta-analyses, and case reports were excluded.
Two researchers independently extracted information on study characteristics (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 type, period), patient characteristics (e.g., age, metastatic disease), survival metrics (e.g., OS, PFS), response rates (e.g., objective response rate [ORR]), and AEs (e.g., treatment-related AEs [TRAEs]). Missing data were requested from the corresponding authors, and any discrepancies were resolved through re-assessment.
The Cochrane Risk Assessment Tool and the Jadad scale, a 5-point system where scores of 3 to 5 indicate high quality, were used to evaluate the quality of the included studies (13, 14). The GRADE approach was employed to assess results, classifying them into four categories: high, medium, low, and very low (15).
Data analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.3 and STATA 12.0. Hazard ratios (HR) were used for survival outcomes, while risk ratios (RR) were employed for dichotomous variables. Survival rates for OS (OSR) and PFS (PFSR) were evaluated over periods ranging from 3 to 36 months. For low heterogeneity (I² < 50% or P > 0.1), a fixed-effects model was utilized, while a random-effects model was employed for greater heterogeneity. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. Publication bias was assessed visually through funnel plots. The study followed PRISMA guidelines and was registered with PROSPERO (ID: CRD42024622428).
From 2367 screened studies, 8 studies derived from 5 phase III RCTs (IMpassion130, IMpassion131, IMpassion132, KEYNOTE-355, and TORCHLIGHT), encompassing 1041 Asian patients with TNBC, were included (Figure 1) (5–9, 16–18). The baseline characteristics of these RCTs are detailed in Table 1. IMpassion130, IMpassion131, IMpassion132, and KEYNOTE-355 are international multicenter trials, whereas TORCHLIGHT is a multicenter trial conducted in China. In these four international multicenter studies, IMpassion130 and KEYNOTE-355 provide detailed data analysis of the Asian population, while IMpassion131 and IMpassion132 only include subgroup analyses of survival data for the Asian population. All studies were evaluated as high quality (Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S2). Using the GRADE approach, the quality of the results was classified as medium to high (Supplementary Table S3).
The OS (HR: 0.78 [0.55, 1.12], P = 0.18) tended to favor the PIC therapy, but no significant difference was observed (Figure 2). In the PD-L1-positive subgroup, the PIC group demonstrated better OS (HR: 0.62 [0.44, 0.86], P = 0.005) (Figure 3). OSR was significantly higher in the PIC group across 12-36 months (Figure 4, Supplementary Figure S2).
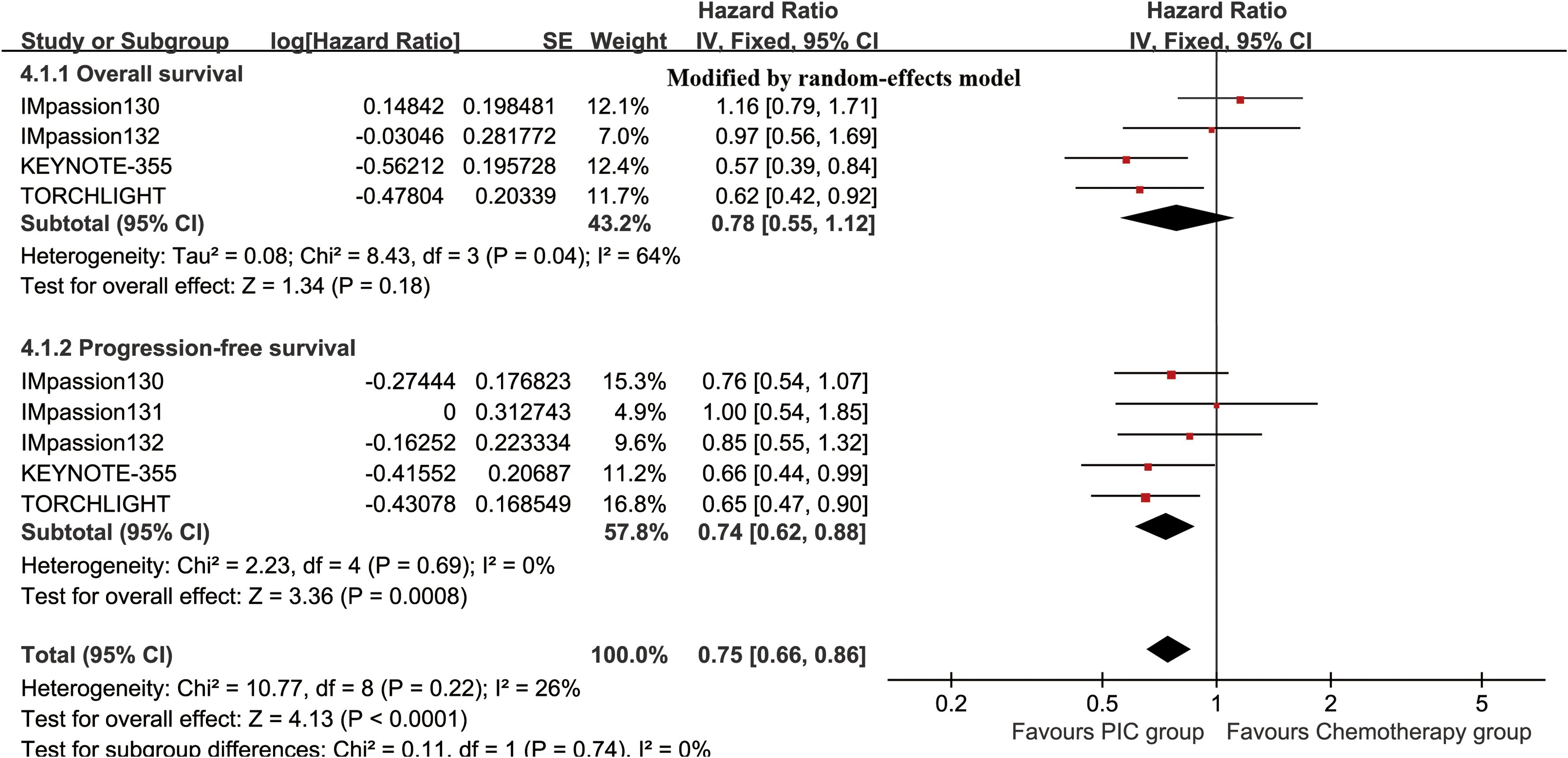
Figure 2. Forest plots of overall survival and progression-free survival associated with PIC versus chemotherapy.
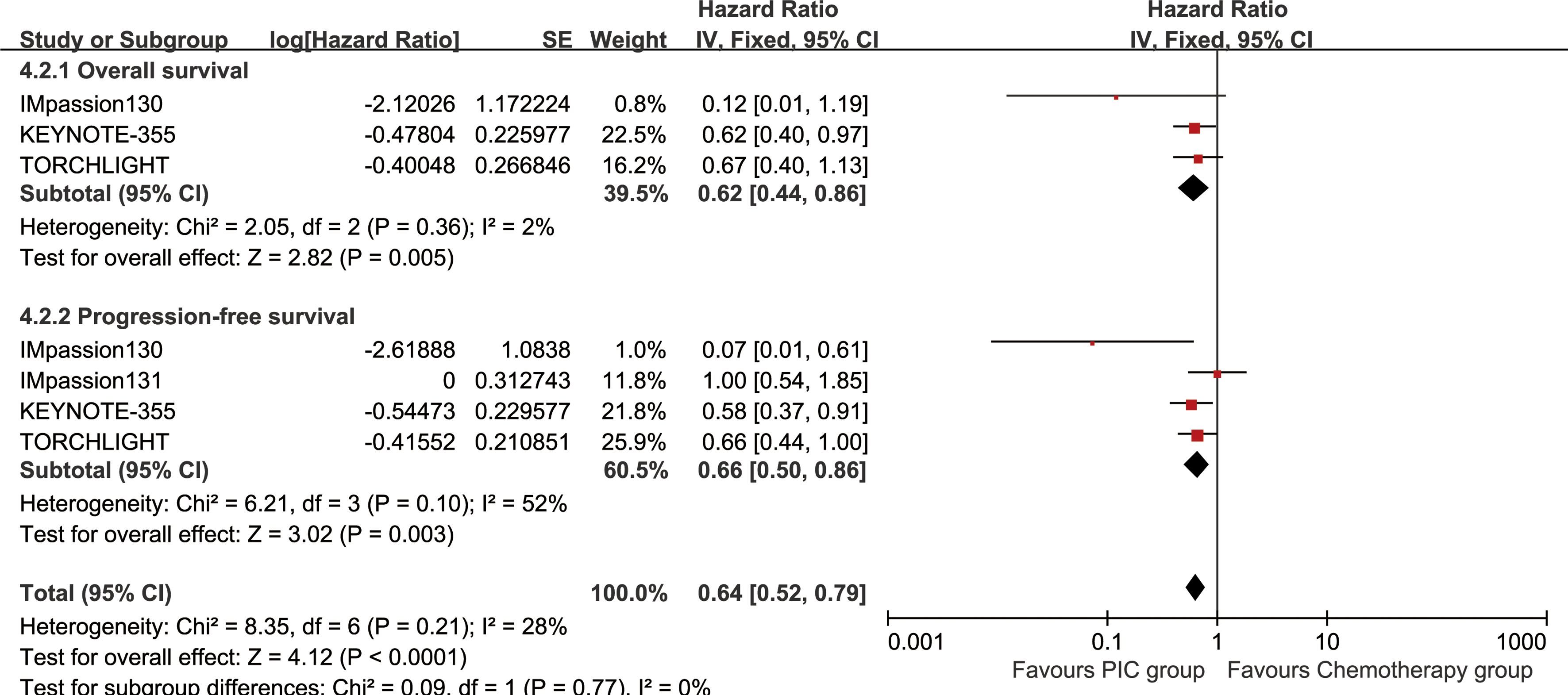
Figure 3. Forest plots of overall survival and progression-free survival associated with PIC versus chemotherapy in PD-L1-positive population.
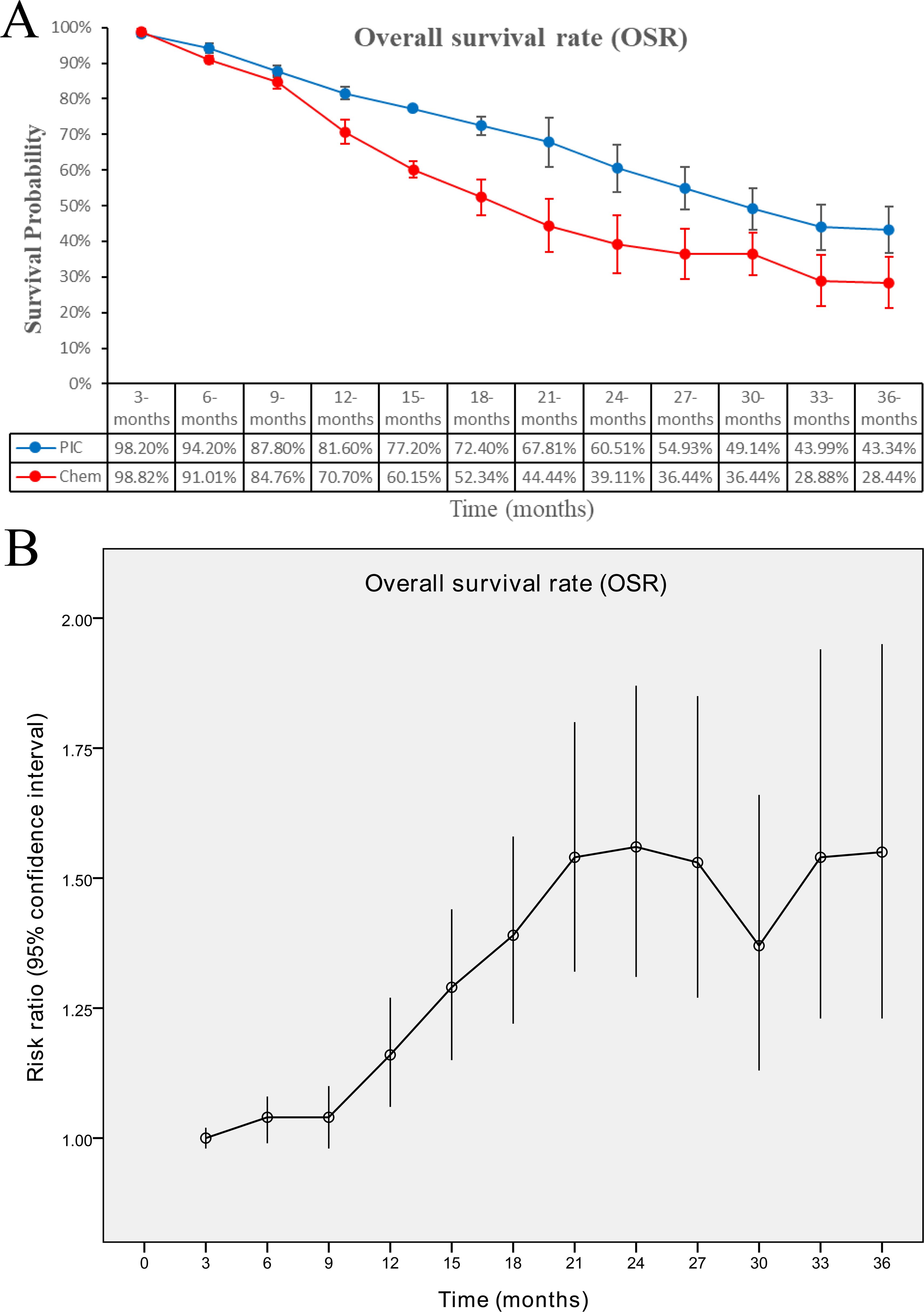
Figure 4. Comparisons of overall survival rate associated with PIC versus chemotherapy. (A) OSR at 3-36 months between the two groups; (B) trend of risk ratios in OSR.
The PIC group demonstrated improved progression-free survival (PFS) (HR: 0.74 [0.62, 0.88], P = 0.0008), with a more pronounced effect in the PD-L1-positive subgroup (HR: 0.66 [0.50, 0.86], P = 0.003) (Figure 2, 3). PFSR was significantly higher in the PIC group across 6-30 months (Figure 5, Supplementary Figure S3).
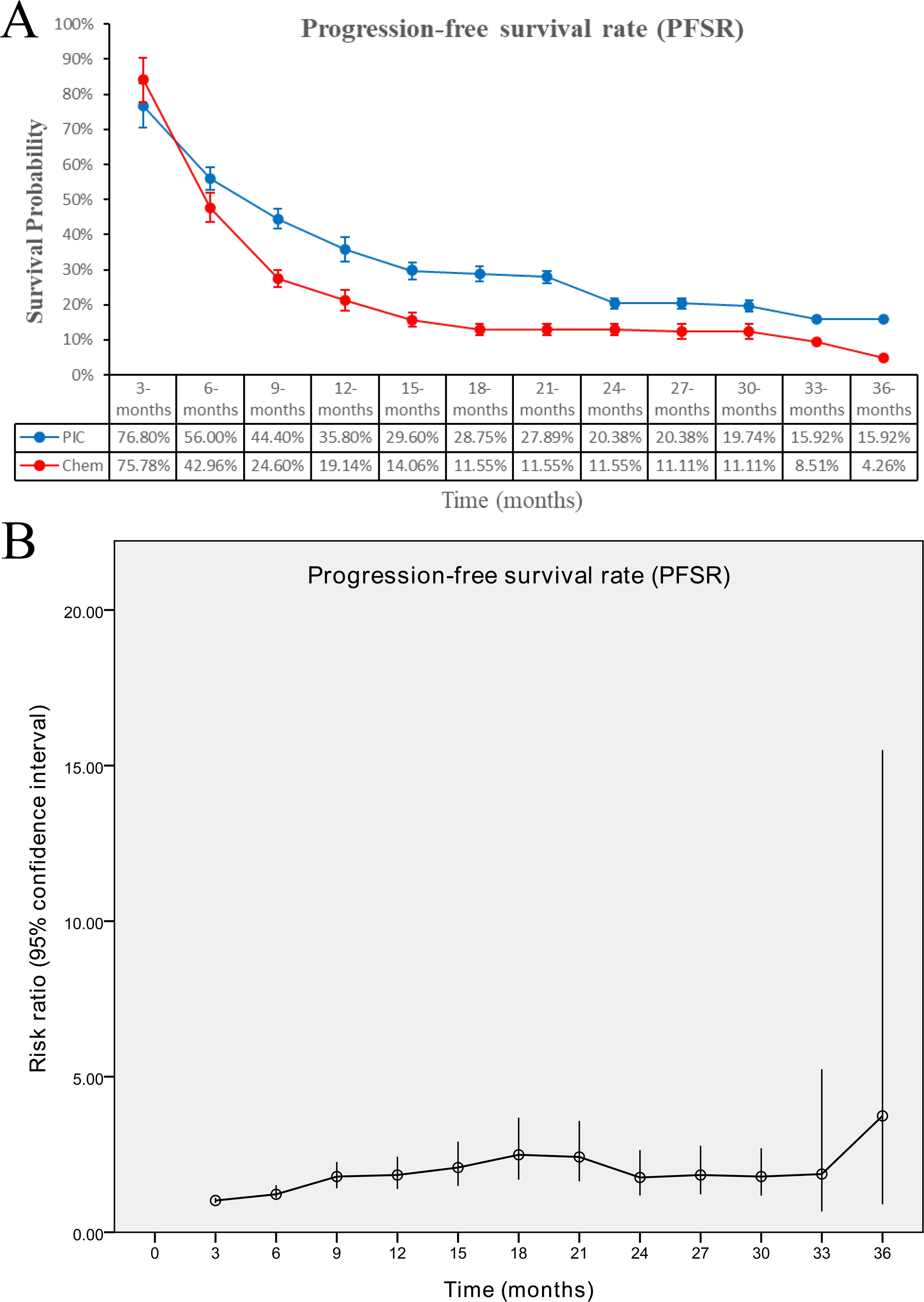
Figure 5. Comparisons of progression-free survival rate associated with PIC versus chemotherapy. (A) PFSR at 3-36 months between the two groups; (B) trend of risk ratios in PFSR.
The ORR (RR: 1.05 [0.93, 1.18], P = 0.47), DCR (RR: 1.03 [0.96, 1.10], P = 0.38), complete response (CR) (RR: 1.50 [0.90, 2.51], P = 0.12), partial response (PR) (RR: 0.98 [0.85, 1.14], P = 0.83), and stable disease (SD) (RR: 0.87 [0.60, 1.25], P = 0.45) were comparable between the two groups (Figure 6).
In summary, the PIC group experienced higher rates of immune-related AEs (irAEs) (RR: 1.69 [1.33, 2.15], P < 0.0001), grade 3-5 irAEs (RR: 3.11 [1.59, 6.10], P = 0.001), TRAEs-related deaths (RR: 1.57 [1.13, 2.19], P = 0.007), TRAEs leading to discontinuation (RR: 2.43 [1.32, 4.45], P = 0.004), and TRAEs leading to interruption (RR: 1.44 [1.19, 1.75], P = 0.0002). Total TRAEs and grade 3-5 TRAEs were comparable between the groups (Table 2, Supplementary Figure S4).
In the analysis of TRAEs, the PIC group experienced higher rates of any grade nasopharyngitis, nausea, asthenia, stomatitis, hypoesthesia, vomiting, hypothyroidism, and grade 3-5 AST increased (Tables 3, 4, S4, S5).
In the analysis of irAEs, the PIC group experienced higher rates of any grade hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism. All grade 3-5 irAEs were similar between the two groups (Supplementary Table S6, S7).
The funnel plot symmetry for survival (PD-L1-positive subgroup), PFSR, responses, and AEs summary indicated a low risk of publication bias (Figure 7).
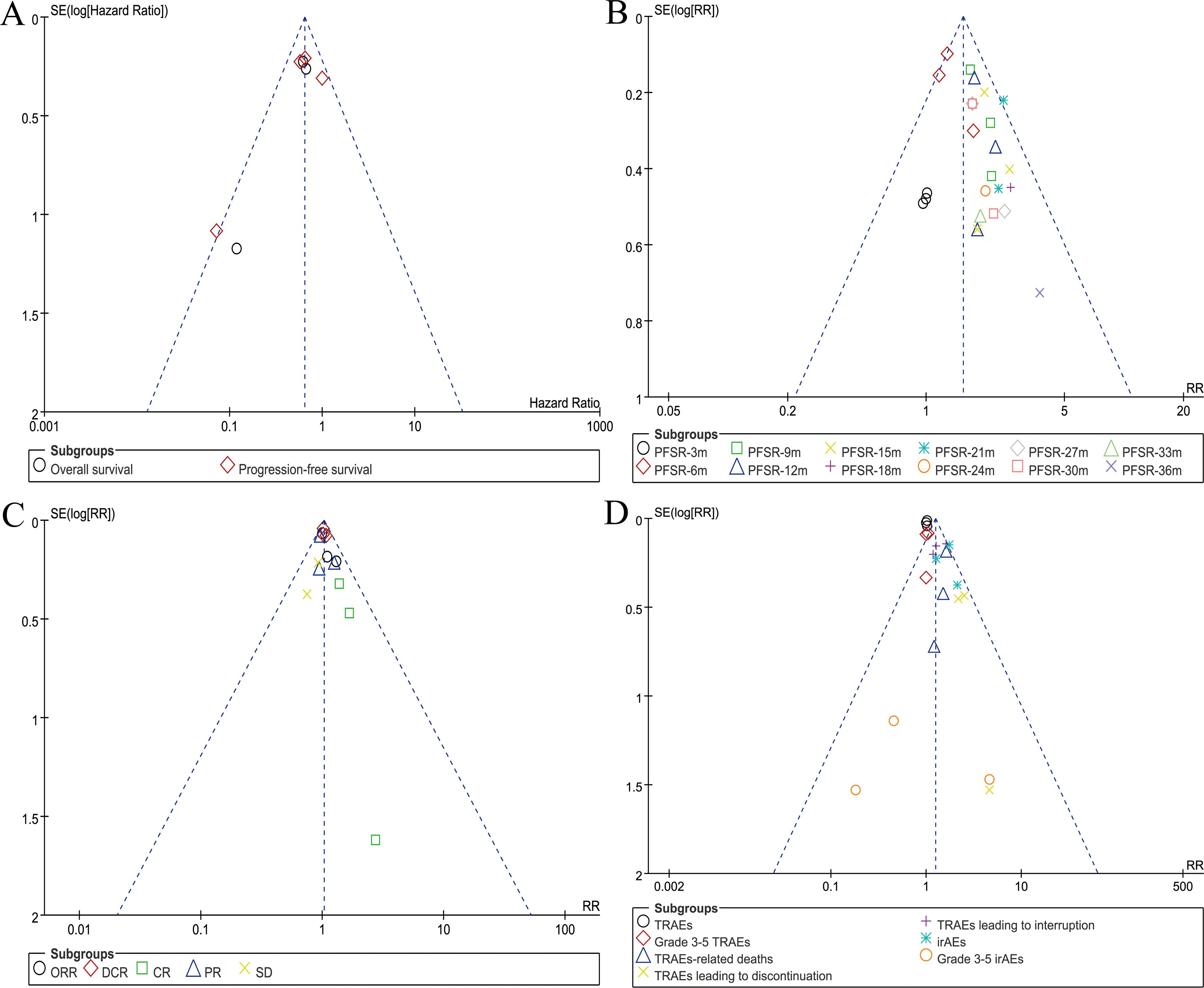
Figure 7. Funnel plots of survival (PD-L1-positive subgroup) (A), PFSR (B), responses (C), and AEs summary (D).
Compared to other breast cancer subtypes, TNBC is associated with a higher likelihood of recurrence and metastasis, leading to a worse prognosis (2). Traditional treatment options for advanced TNBC have been limited, primarily relying on chemotherapy, which often yields suboptimal outcomes (3). In recent years, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been introduced as an important complement to chemotherapy and have shown promise in enhancing antitumor efficacy. However, the specific benefits and risks of this combination in Asian populations remain underexplored (9, 16). Our study is the first meta-analysis that aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of PIC versus chemotherapy alone in Asian patients with advanced TNBC. The results showed that PIC therapy significantly improved survival, particularly in PD-L1-positive subgroup. However, the incidence of irAEs was increased in the PIC group. Both groups showed comparable response rates and TRAEs.
Our findings indicated a significant improvement in PFS in the PIC group. This result is consistent with the findings from pivotal studies such as IMpassion130, which demonstrated a significant improvement in PFS for patients with metastatic TNBC when treated with atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel (5). Likewise, the KEYNOTE-355 study showed similar results with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, particularly in PD-L1-positive subgroup (8). Interestingly, while we observed a trend toward improved OS in the PIC therapy group, statistical significance was not reached in the overall cohort. This observation mirrors the results from several other clinical trials, where improvements in OS have been difficult to demonstrate in early-phase trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors in TNBC (6, 7, 9). Several factors could account for this. First, the heterogeneous nature of TNBC means that patients respond differently to treatment, and the subgroup of patients benefiting from PIC therapy may be too small to show a significant OS benefit in the overall population (16). Second, the potential for crossover therapies-where patients in the chemotherapy group may receive subsequent immunotherapy upon progression-could dilute the observed OS differences (19). Furthermore, the duration of follow-up in many studies is often insufficient to fully capture the long-term survival effects of immunotherapy (7, 9). Immune checkpoint inhibitors tend to have a delayed onset of action, with benefits accruing over a longer period, which may be more apparent in studies with extended follow-up periods (20). Specifically, in the PD-L1-positive subgroup, PIC therapy significantly enhanced both PFS and OS. These findings align with the results from the IMpassion130 and KEYNOTE-355 studies, highlighting PD-L1 expression as an important biomarker for predicting the efficacy of PIC therapy in advanced TNBC (5, 8).
Although PFS was significantly improved with PIC therapy, our analysis found no significant difference in the ORR and DCR between the PIC and chemotherapy-alone groups. This finding, though unexpected, can be attributed to several factors that may influence how response rates are evaluated in immunotherapy-based treatments. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors primarily work by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and attack tumor cells, a process that can be slower and less apparent than the direct cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy (21). In contrast to traditional chemotherapy, which results in rapid tumor shrinkage, the effects of immunotherapy may take longer to manifest and can sometimes be delayed or not immediately reflected in conventional tumor response assessments, such as the standard RECIST criteria (22). For example, the phenomenon of “immune pseudoprogression”, where tumors temporarily increase in size due to immune cell infiltration, might lead to misleading conclusions regarding the effectiveness of treatment, as tumor growth during early treatment phases could be misinterpreted as a lack of response (23). In some cases, the tumor may stabilize or shrink later as the immune system mounts a sustained response, which cannot be captured through initial measurements of ORR. Furthermore, patients receiving PIC therapy may experience what is known as an “immune response flare”, where the immune system initially triggers inflammation in the tumor site, followed by subsequent tumor reduction (24). This complex immune response does not always translate into an immediate shrinkage of the tumor, further contributing to a lack of significant change in ORR. As observed in several clinical trials, this can explain why improvements in PFS, as seen in our study, might not be paralleled by increases in ORR and DCR, despite the potential for better long-term outcomes in terms of disease control (5–9). A more comprehensive understanding of how immune responses evolve over time, and how these dynamics differ from the cytotoxic response to chemotherapy, is critical in refining the criteria used to measure the effectiveness of combination therapies. Although our meta-analysis found no significant difference between the two groups in response rates, this does not necessarily diminish the potential of combining chemotherapy with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. The complex and evolving nature of the immune response, coupled with the biological heterogeneity of TNBC, suggests that longer follow-up periods and more refined methods of assessing treatment response are needed.
In the safety assessment, we observed a higher incidence of irAEs in the PIC therapy group. The most frequently reported irAEs in this group included thyroid disorders (particularly hypothyroidism), dermatitis, infusion-related reactions, and gastrointestinal toxicities, such as diarrhea and colitis. Hypothyroidism is one of the most common irAEs associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, resulting from autoimmune damage to the thyroid gland (25). Similarly, skin-related toxicities, including rash and pruritus, are also frequently observed. These side effects, while generally manageable, can significantly impact patients’ quality of life and may require dose adjustments, temporary treatment interruptions, or the use of corticosteroids (26). Our analysis also indicated an increased risk of grade 3-5 irAEs in the PIC therapy group, although the overall rate was still relatively low. The risk of severe irAEs is a well-known challenge with immunotherapy, particularly with agents that target the PD-1/PD-L1 axis (27). These toxicities can range from mild to life-threatening, and their occurrence often necessitates close monitoring and early intervention. In some cases, severe irAEs may lead to permanent discontinuation of the immune checkpoint inhibitor, although many of these AEs can be reversed with appropriate medical management, including the use of immune-suppressive agents like corticosteroids (28). In our study, the majority of AEs were reversible with prompt treatment, and the overall rate of treatment discontinuation due to toxicity was relatively low. However, the potential for these toxicities remains a significant concern when considering PIC therapy for advanced TNBC patients. Future studies should focus on optimizing treatment regimens to minimize toxicity, as well as identifying biomarkers that could predict which patients are most likely to experience severe irAEs.
This meta-analysis has several limitations. First, the included studies primarily enrolled patients from Western populations, with Asian patients constituting a smaller subset. This underrepresentation may limit the generalizability of our findings to the broader Asian TNBC population. Second, variations in PD-L1 assessment methods and cutoff values across studies could affect the comparability of results and the accurate identification of patients who would benefit from PIC therapy. Third, the relatively short follow-up durations in some trials may not adequately capture long-term survival benefits or late-onset AEs. Finally, potential publication bias and the exclusion of non-English studies may have influenced the comprehensiveness of our analysis.
PIC significantly improves survival (OS and PFS) compared to chemotherapy alone in Asian patients with advanced TNBC, particularly in the PD-L1-positive subgroup. However, the increased incidence of irAEs necessitates careful patient selection and vigilant management. These findings support the incorporation of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors into treatment paradigms for this population, emphasizing the need for further research to optimize outcomes and minimize risks.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
HR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. LH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. WZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. QO: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. LY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors appreciate all the public health workers who participated in the databases (PubMed, ScienceDirect, the Cochrane Library, Scopus, EMBASE, and Web of Science).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1540538/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Cochrane Risk Assessment.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Forest plots of OSR at 3-36 months associated with PIC versus chemotherapy.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Forest plots of PFSR at 3-36 months associated with PIC versus chemotherapy.
Supplementary Figure 4 | Forest plots of AEs summary associated with PIC versus chemotherapy.
AE, Adverse event; ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; AST, Aspartate aminotransferase; CR, Complete response; DCR, Disease control rate; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; GRADE, Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; HR, Hazard ratio; ICIs, Immune checkpoint inhibitors; irAE, Immune-related adverse event; ORR, Objective response rate; OS, Overall survival; OSR, Overall survival rate; PD-1, Programmed death-1; PD-L1, Programmed death-ligand 1; PFS, Progression-free survival; PFSR, Progression-free survival rate; PIC, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy; PR, Partial response; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; PROSPERO, International prospective register of systematic reviews; RCT, Randomized controlled trial; RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors; RR, Risk ratio; SD, Stable disease; TMB, Tumor mutational burden; TNBC, Triple-negative breast cancer; TRAE, Treatment-related adverse event.
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
2. Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Newman LA, Freedman RA, Smith RA, Star J, et al. Breast cancer statistics 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:477–95. doi: 10.3322/caac.21863
3. Yadav SK, Leon-Ferre RA. Current treatment paradigms for triple-negative breast cancer. Minerva Med. (2024) 115:589–98. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4806.24.09458-8
4. Jin M, Fang J, Peng J, Wang X, Xing P, Jia K, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade in breast cancer: research insights and sensitization strategies. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:266. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02176-8
5. Emens LA, Adams S, Barrios CH, Diéras V, Iwata H, Loi S, et al. First-line atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel for unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: IMpassion130 final overall survival analysis. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:983–93. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.355
6. Miles D, Gligorov J, André F, Cameron D, Schneeweiss A, Barrios C, et al. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:994–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801
7. Dent R, André F, Gonçalves A, Martin M, Schmid P, Schütz F, et al. IMpassion132 double-blind randomised phase III trial of chemotherapy with or without atezolizumab for early relapsing unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:630–42. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.04.001
8. Im SA, Cortes J, Cescon DW, Yusof MM, Iwata H, Masuda N, et al. Results from the randomized KEYNOTE-355 study of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for Asian patients with advanced TNBC. NPJ Breast Cancer. (2024) 10:79. doi: 10.1038/s41523-024-00679-7
9. Jiang Z, Ouyang Q, Sun T, Zhang Q, Teng Y, Cui J, et al. Toripalimab plus nab-paclitaxel in metastatic or recurrent triple-negative breast cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:249–56. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02677-x
10. Wang Z, You P, Yang Z, Xiao H, Tang X, Pan Y, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis on their efficacy and safety. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:1339. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13105-9
11. Li Y, Ma J, Ma X, Chen C, Ruan M, Yang W, et al. PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: Correlations and prognostic values in Chinese triple-negative breast cancer patients with different molecular subtyping. Pathol Res Pract. (2024) 262:155556. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155556
12. Bahrin NWS, Matusin SNI, Mustapa A, Huat LZ, Perera S, Hamid MRWHAv. Exploring the effectiveness of molecular subtypes, biomarkers, and genetic variations as first-line treatment predictors in Asian breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. (2024) 13:100. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02520-5
13. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. (1996) 17:1–12.
14. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
15. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Knottnerus A. GRADE guidelines: a new series of articles in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. J Clin Epidemiol. (2011) 64:380–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.09.011
16. Iwata H, Inoue K, Kaneko K, Ito Y, Tsugawa K, Hasegawa A, et al. Subgroup analysis of Japanese patients in a Phase 3 study of atezolizumab in advanced triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130). Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2019) 49:1083–91. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyz135
17. Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A, Barrios CH, Iwata H, et al. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:2108–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809615
18. Hattori M, Masuda N, Takano T, Tsugawa K, Inoue K, Matsumoto K, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in Japanese patients with triple-negative breast cancer: Results from KEYNOTE-355. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:10280–93. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v12.9
19. Geurts V, Kok M. Immunotherapy for metastatic triple negative breast cancer: current paradigm and future approaches. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2023) 24:628–43. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01069-0
20. Emens LA, Cruz C, Eder JP, Braiteh F, Chung C, Tolaney SM, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes and biomarker analyses of atezolizumab therapy for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: A phase 1 study. JAMA Oncol. (2019) 5:74–82. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4224
21. Bullock KK, Richmond A. Beyond anti-PD-1/PD-L1: improving immune checkpoint inhibitor responses in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16:2189. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122189
22. Feinberg BA, Zettler ME, Klink AJ, Lee CH, Gajra A, Kish JK. Comparison of solid tumor treatment response observed in clinical practice with response reported in clinical trials. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e2036741. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36741
23. Li Y, Wang P, Xu J, Shi X, Yin T, Teng F. Noninvasive radiomic biomarkers for predicting pseudoprogression and hyperprogression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibition. Oncoimmunology. (2024) 13:2312628. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2024.2312628
24. Sparks JA. Pre-existing autoimmune diseases and immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer treatment: considerations about initiation, flares, immune-related adverse events, and cancer progression. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. (2024) 50:147–59. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2024.01.001
25. Zhao C. Correlation between thyroid dysfunction and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced solid tumors. Discovery Oncol. (2024) 15:663. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01546-4
26. Bai R, Chen N, Chen X, Li L, Song W, Li W, et al. Analysis of characteristics and predictive factors of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related adverse events. Cancer Biol Med. (2021) 18:1118–33. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2021.0052
27. Naidoo J, Johnson DB, Doran C, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Le TK, et al. Management of severe immune-related adverse events and outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Oncologist. (2024), oyae318. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae318
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, chemotherapy, triple-negative breast cancer, randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis
Citation: Ruan H, Zou Y, Huang L, Zha W, Ouyang Q and Yang L (2025) PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for Asian patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer: a phase III RCTs based meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1540538. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1540538
Received: 06 December 2024; Accepted: 13 February 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
San-Gang Wu, First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yuan Tian, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Ruan, Zou, Huang, Zha, Ouyang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ling Yang, eHl5bDE5NzYwNzE5QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.