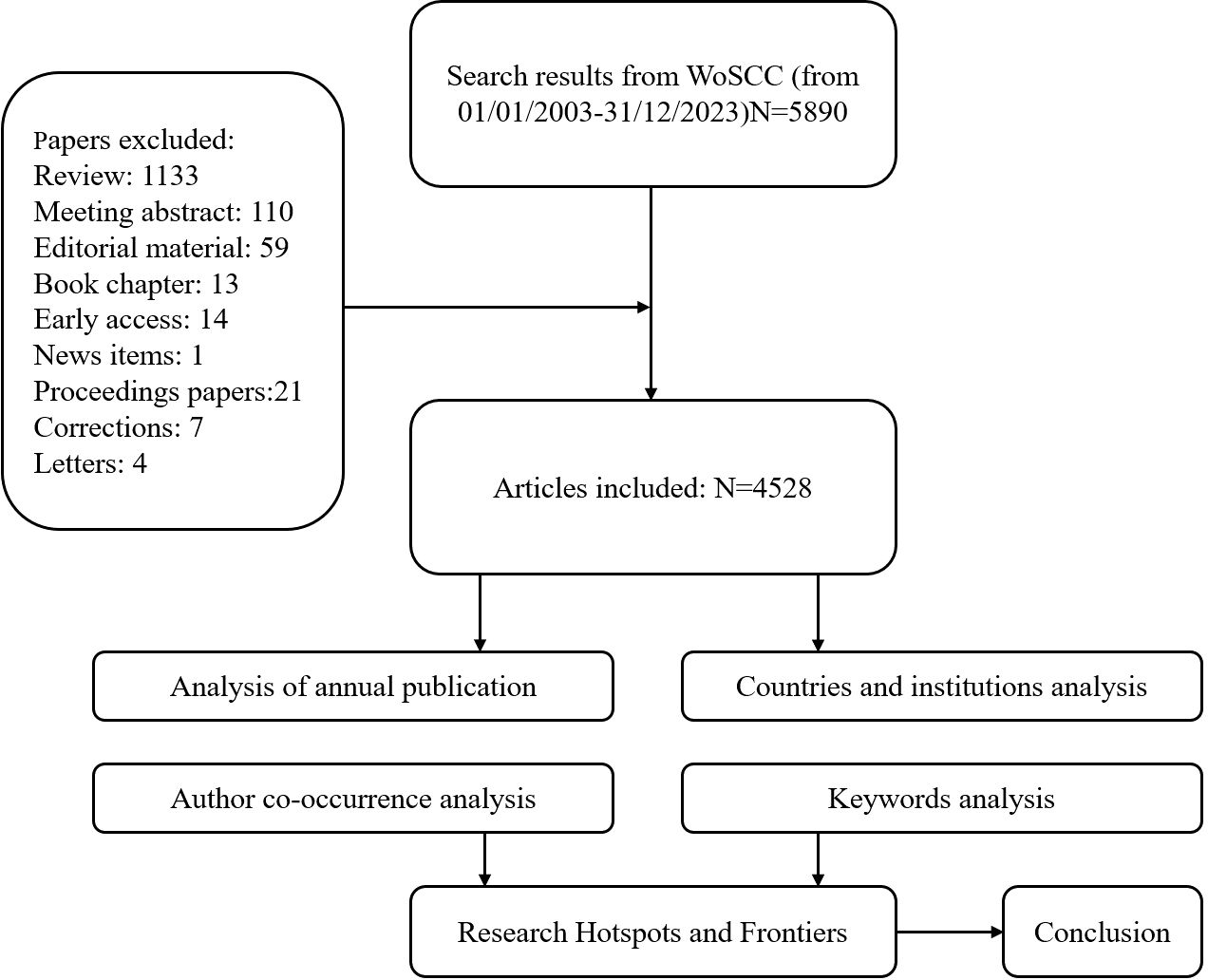
- 1The Editorial Department of the Journal of Southern Medical University, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2Clinical Research Center, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 3Nanfang hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Background: Glioma is the most aggressive primary malignant tumor of the central nervous system, characterized by high recurrence rates and resistance to chemoradiotherapy, making therapeutic resistance a major challenge in neuro-oncology. Recent research emphasizes the role of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and immune modulation in glioma progression and resistance. Despite these advances, a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of research trends in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance over the past two decades is lacking. This study aims to systematically evaluate the research landscape, identify emerging hotspots, and provide guidance for future investigations.
Methods: Articles on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance published between 2003 and 2023 were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection, resulting in 4,528 publications. Bibliometric tools, including VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and R packages such as bibliometrix and ggplot2, were used to analyze co-authorship networks, keyword evolution, and citation bursts to identify collaboration patterns, thematic developments, and influential contributions.
Results: Publication output increased significantly between 2013 and 2022, peaking at 650 articles in 2022. Over 1,000 institutions from 88 countries contributed to this research. The United States, Switzerland, and Germany showed the highest citation impact, while China led in publication volume but demonstrated relatively lower citation influence. The research focus has shifted from traditional topics such as the “MGMT gene” to emerging areas including the “tumor microenvironment,” “immune infiltration,” and “nanoparticles.” The androgen receptor was identified as a promising but underexplored therapeutic target.
Conclusions: Research on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance has seen substantial growth, with increasing emphasis on immune modulation, the tumor microenvironment, and novel therapeutic targets such as the androgen receptor. This study represents the first comprehensive bibliometric analysis of this field, providing a detailed overview of research trends and potential directions for future studies. The findings highlight the need for strengthened international collaboration and multidisciplinary approaches to address the challenges of therapeutic resistance in glioma.
Introduction
Gliomas are the most prevalent and aggressive malignant tumors of the central nervous system (CNS), accounting for over 70% of all CNS tumors (1). Despite significant advancements in treatment, the prognosis for glioma patients remains poor (2). The standard approach involves maximal surgical resection, followed by radiotherapy and chemotherapy, with temozolomide (TMZ) being the most commonly used agent (3). Chemoradiotherapy induces DNA damage leading to apoptosis in tumor cells (4, 5). However, high recurrence rates and resistance to therapies continue to pose significant challenges (6).
TMZ plays a crucial role in treatment, increasing median survival from 12.1 to 14.6 months and raising two-year survival rates from 10.4% to 26.5% (7). Nevertheless, resistance to TMZ, primarily mediated by O6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) repair mechanisms, remains a significant obstacle (8). Additional DNA repair pathways, such as base excision repair (BER) and mismatch repair (MMR), also contribute to therapeutic resistance (9–11). Furthermore, autophagy, apoptotic signaling pathways, and the tumor microenvironment (TME) are increasingly recognized as critical factors in TMZ resistance (8, 12).
The TME including tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), microglia, neutrophils, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and T cells interacts with glioma cells to promote tumor growth and therapeutic resistance (13). Current research is exploring MGMT inhibitors, DNA repair pathway inhibitors, and combination therapies to overcome resistance (14, 15).
Despite these advancements, comprehensive bibliometric analyses focusing on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance are limited. Bibliometric studies provide quantitative and qualitative assessments of scientific literature, offering valuable insights into research trends and collaborations (16, 17). In this study, we use bibliometric tools to systematically analyze the research landscape, pinpoint key focus areas, and outline potential future directions in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance.
Materials and methods
Data sources and search strategy
Bibliographic data were obtained from the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) within the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) (18). A systematic search strategy was developed to ensure a comprehensive literature review of glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance and its underlying mechanisms.
Search Query:
Keywords for Disease: (“Glioma” OR “Glioblastoma Multiforme” OR “GBM” OR “Glioblastoma”).
Keywords for Resistance: (“Chemoradiotherapy Resistance” OR “Radioresistance” OR “Chemoresistance” OR “Temozolomide Resistance” OR “Adaptive resistance” OR “Acquired resistance” OR “TMZ” OR “Temozolomide” OR “TMZ resistance”).
Keywords for Mechanisms: (“MGMT Promoter Methylation” OR “DNA Repair Mechanisms” OR “Cancer Stem Cells” OR “Tumor Microenvironment” OR “Epigenetic Alterations” OR “Signal Transduction Pathways” OR “PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway” OR “RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway” OR “Apoptosis and Autophagy” OR “Cell Cycle Dysregulation” OR “Immunotherapy” OR “Targeted Therapy” OR “Biomarkers of Resistance” OR “Molecular Profiling” OR “Precision Medicine” OR “Radiosensitizers” OR “MicroRNA” OR “Long Non-coding RNA” OR “Blood-Brain Barrier” OR “Tumor-associated macrophages” OR “Post-translational modification” OR “Methylation” OR “Acetylation” OR “Ubiquitination” OR “Clinical trial” OR “Cell cycle capture” OR “chemosensitivity”).
The search was restricted to articles and reviews published in English between 2003 and 2023. A total of 5,890 documents were retrieved. After excluding conference abstracts, book chapters, and non-article documents, 4,528 articles remained for bibliometric analysis and visualization. The flow of the search and exclusion process is illustrated in Figure 1. The search was finalized on April 2, 2024.
Data extraction and analysis
This study analyzed the bibliometric characteristics of publications related to chemoradiotherapy resistance in glioma, focusing on publication year, geographical distribution, institutional contributions, journals, core authors, keywords, and key references. Bibliometric analyses and network visualizations were conducted using VOSviewer (version 1.6.20, Leiden University), CiteSpace (version 6.2.6, Drexel University), and the bibliometrix package in R (version 4.2.0, R Foundation). Temporal trends in publication volume were analyzed by fitting curves using the model ƒ(x)= k/[1 + a * e^(− b * x)] to predict future literature accumulation (19). Scimago Graphica was used to map the distribution and connections of countries/regions.
Co-authorship and co-occurrence analyses were conducted using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Microsoft Excel 2019. The Bibliometrix package was utilized to create thematic maps and analyze the evolution of keyword themes. A thesaurus file in VOSviewer was employed to merge variant terms and standardize capitalization. In the visualizations, nodes represented entities such as countries and regions, institutions, or researchers, while links between them indicated relationships evaluated by total link strength. Specific thresholds for items included in the VOSviewer maps are provided in the Results section. CiteSpace parameters were set as follows: time slicing of one year, selection criteria of the top 50 cited or co-occurring items per slice (g-index: k = 15), and pruning using pathfinder and merged network pruning methods.
Results
Trends in publication and citation
Based on data from the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, 4,528 articles on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance were indexed between 2003 and 2023, accumulating a total of 205,658 citations. The average citations per article were 45.42, and the H-index was 167. The top 100 most-cited papers accounted for 33.68% of total citations, averaging 692.58 citations each. The top 50 papers contributed 27.05% of citations, averaging 1,112.46 citations per paper. Figure 2A shows the annual publication trends. From 2003 to 2007, publication and citation grew slowly. Since 2013, publications increased significantly, peaking at nearly 650 articles in 2022. Citation counts rose sharply after 2018, exceeding 30,000 in 2022. The decline in publications and citations in 2023 may be due to incomplete data collection. Although the WoS has indexed these publications since 1995, our analysis focuses on 2003 to 2023 for a comprehensive overview of recent trends. The logistic growth curve f(x) = 821.62/[1 + 187.42 * exp(-0.243 * (x - 1995))] models the global publication accumulation (Figure 2B), suggesting that the field will sustain a favorable development trend over an extended period, the growth trend is beginning to level off. The USA and China have maintained high levels of academic output over the past decade, with China showing a particularly notable increase in research productivity, surpassing other countries in publication volume (Figure 2C).
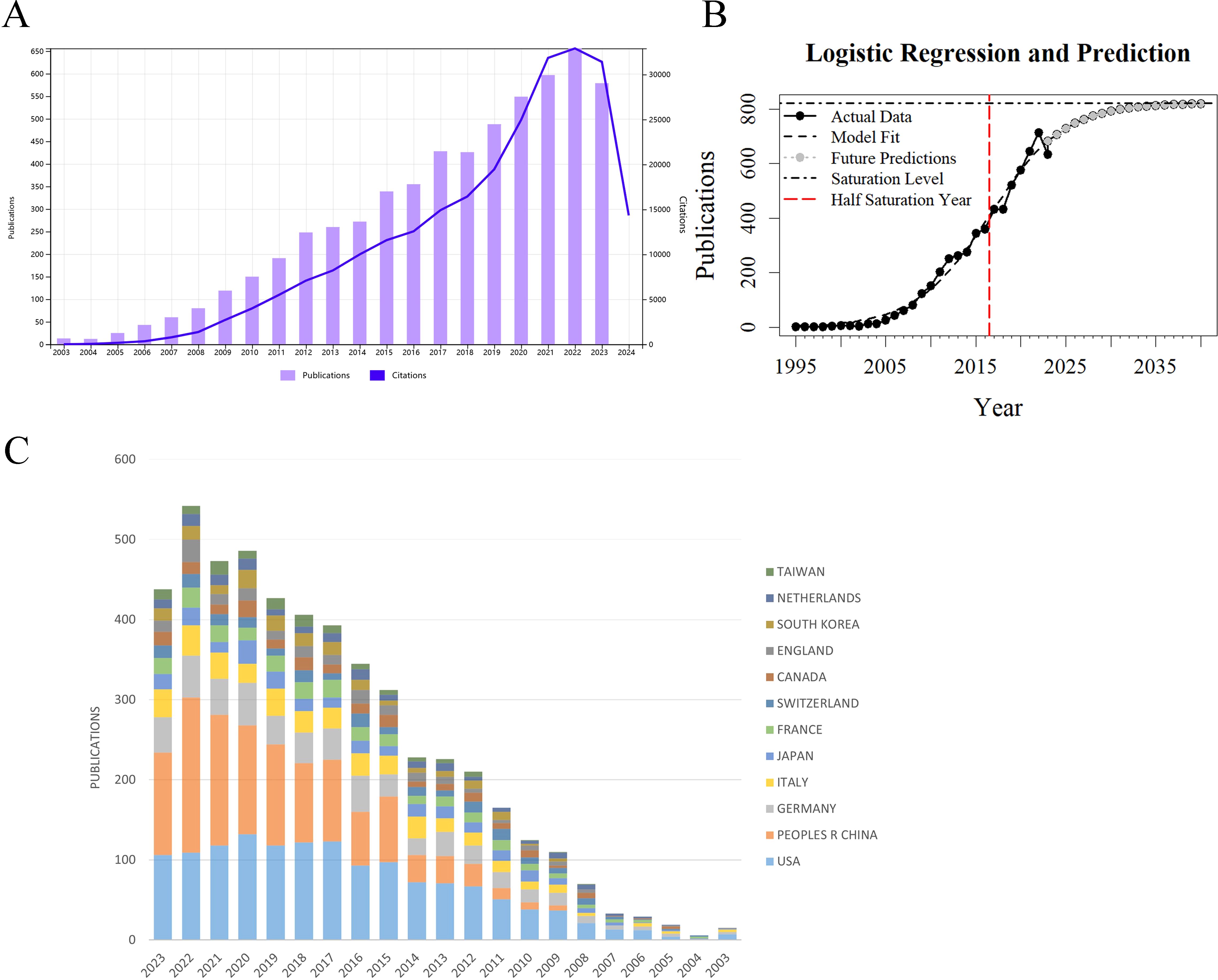
Figure 2. Trends in publication volume and citation count for research on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance from 2003 to 2023 (A) Annual publication and citation trends for glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance: The purple bar graph represents the annual publication volume, while the blue line graph represents the annual citation count. (B) Model-fitted curves of the cumulative number of publications (C) Annual publication volume by country: This graph shows the annual publication volume distribution across different countries or regions in the field.
Distribution of publication and citation metrics
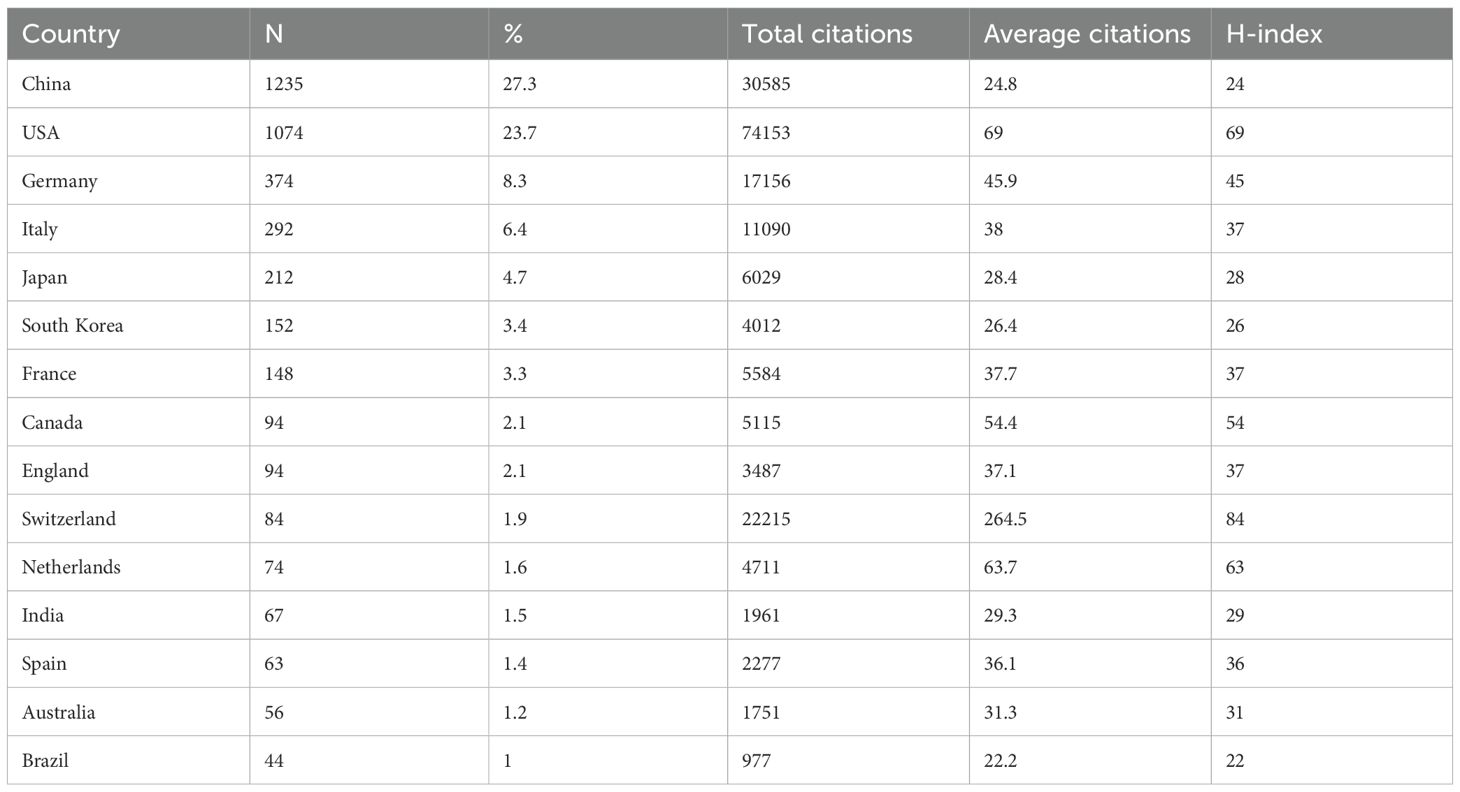
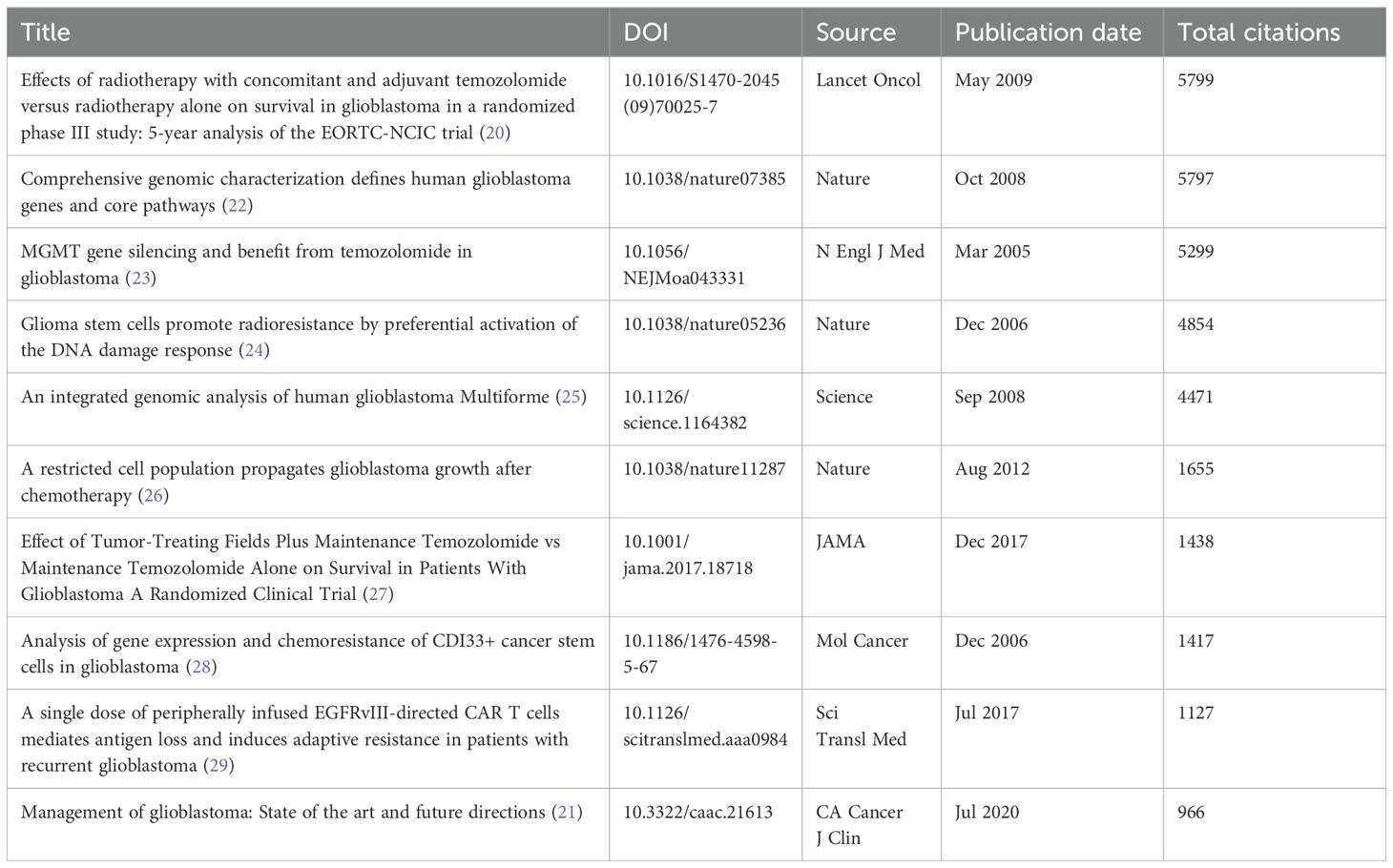
Key bibliometric indicators such as the H-index, which reflects both productivity and impact, and citation bursts, which highlight emerging research trends, are used to analyze the research landscape. Research on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance has been conducted in 88 countries and regions. The contributions from international collaborations are analyzed separately, and their spatial distribution is visualized in a heat map (Figure 3). Table 1 presents the top 15 countries with the highest publication counts. China leads with 1,235 publications (27.3%), followed by the United States with 1,074 publications (23.7%) and Germany with 374 publications (8.3%). Despite having the highest number of publications, China has relatively lower total citations, average citations per paper and H-index values compared to the United States and Switzerland. The United States ranks highest in critical metrics such as total citations, average citations per paper, and H-index, demonstrating its leading influence in the field. Switzerland also ranks prominently in citation metrics, boasting an H-index of 84. The top 10 most-cited articles account for a total of 32,823 citations, representing 15.56% of the total citations in the field. The most-cited article, authored by Stupp and Hegi (20), has garnered 5,799 citations, averaging 362.44 citations per year. The most-cited recent article, published by (21), has accumulated 966 citations (Table 2).
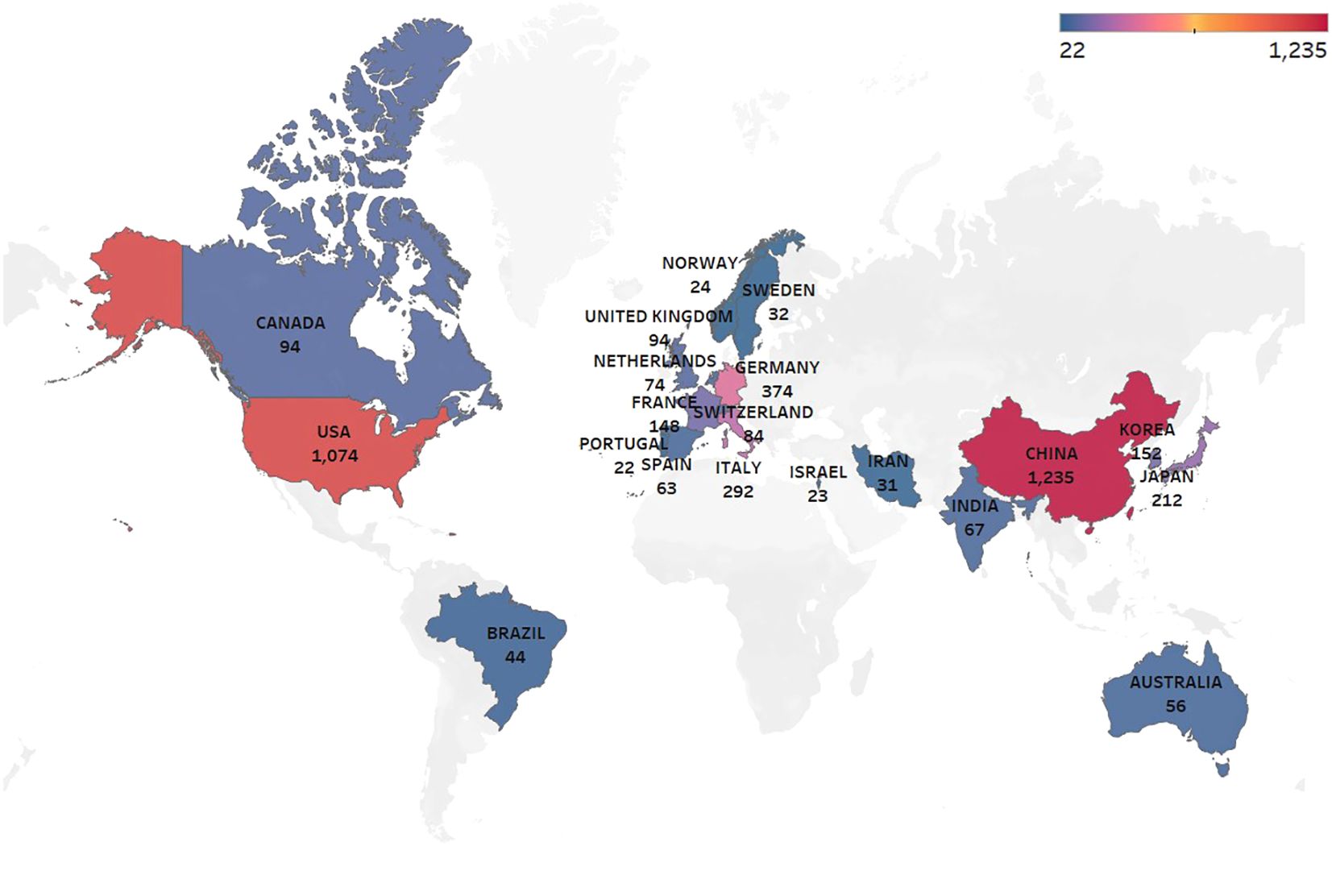
Figure 3. Geographic distribution of publications by country: The color intensity indicates the publication volume, with darker shades representing higher volumes.
Network analysis of country/region and institutional collaboration
Figure 4 illustrates the global collaboration network, with node size representing publication volume and line thickness indicating collaboration strength. The network comprises 87 nodes and 110 links, with a density of 0.0294 (Figure 4A). The United States plays a central role in collaborations, particularly with Germany, France, and Switzerland, and maintains strong ties with other European countries, including Italy and the UK (Figure 4B).
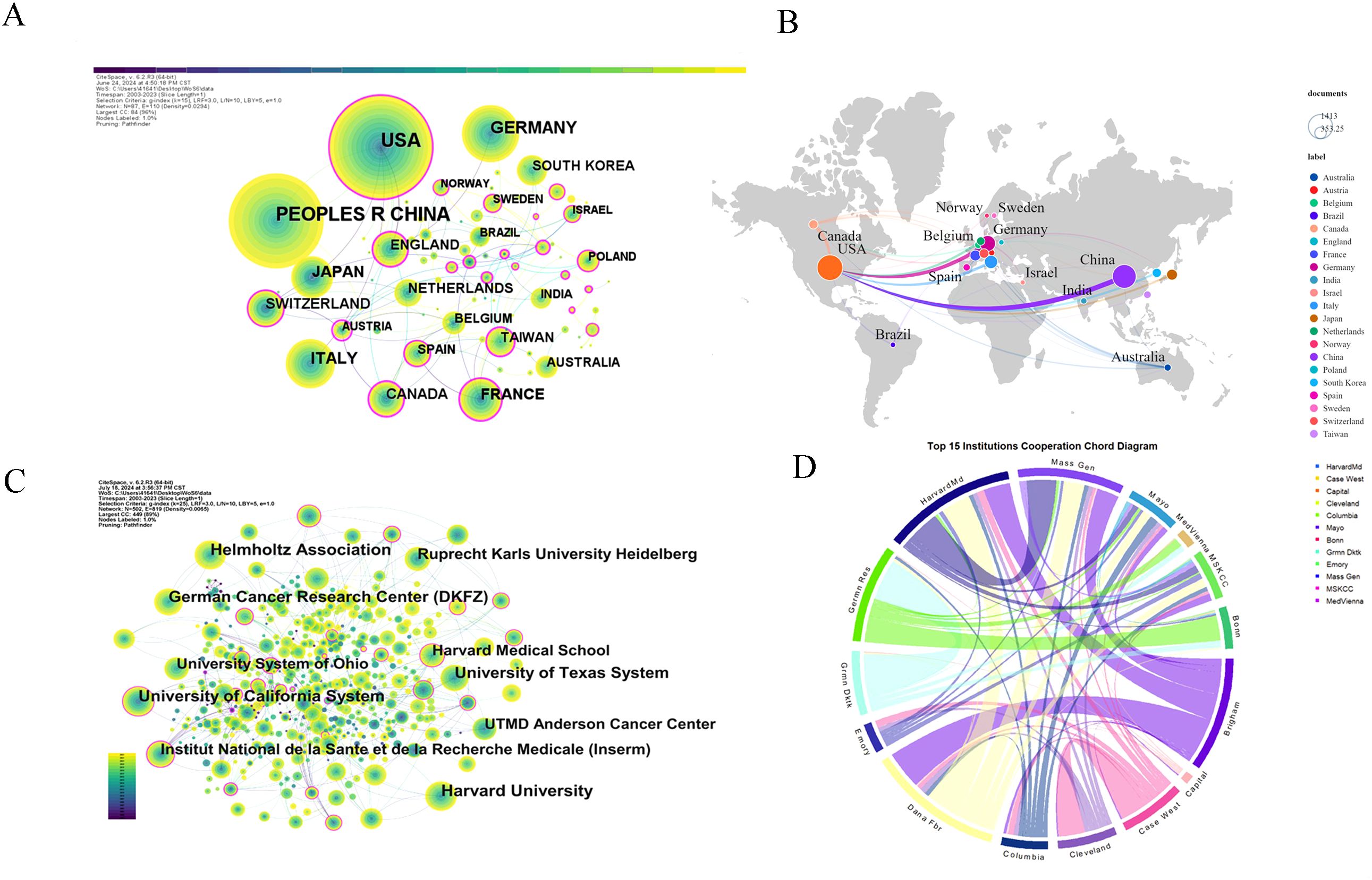
Figure 4. Co-occurrence relationships between countries and institutions. (A) Country cooperation network: Illustrates collaborative networks among countries researching glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance. (B) Country collaboration relationships: Displays specific collaborative relationships between countries within this research field. (C) Institutional collaboration network: Highlights collaborations between major research institutions focusing on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance. (D) Top 15 collaborative institutions: Lists the leading institutions with significant cooperative interactions in this research area.
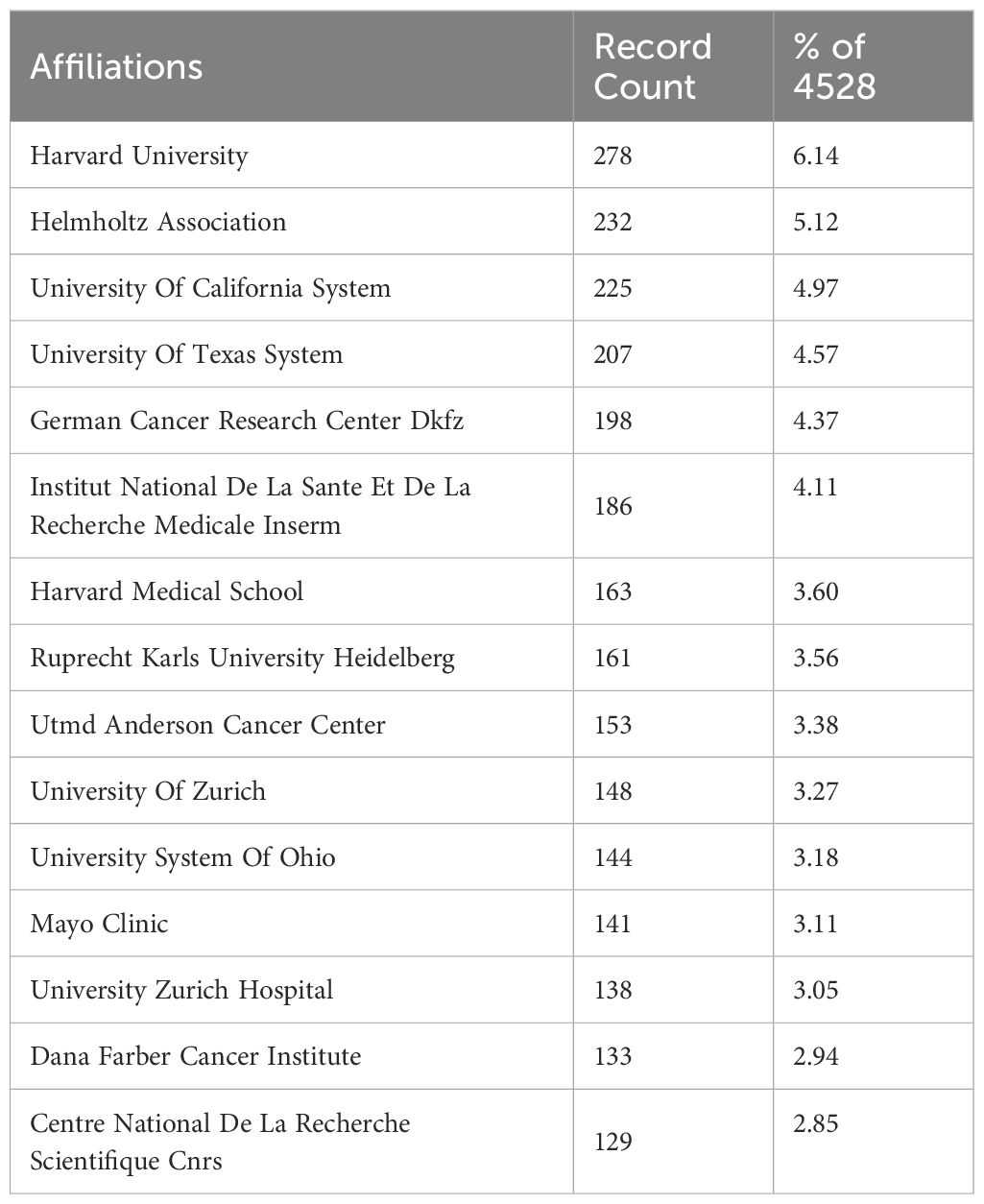
A total of 4,528 articles were published by 4,830 institutions and Table 3 lists the top 15 most productive institutions. Harvard University leads with 278 publications (6.14%), followed by the Helmholtz Association (Germany) with 232 publications (5.12%) and the University of California System with 225 publications (4.97%). Among the top 15 institutions, eight are from the United States, three from Germany, and two each from France and Switzerland, highlighting the geographical concentration of leading research hubs in these countries.
Figures 4C, D depict the institutional collaboration network in glioma research, emphasizing key institutions and their relationships. Strong partnerships between the United States and Germany highlight robust transatlantic collaboration. The collaboration chord diagram (Figure 4D) identifies central nodes such as Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, Mayo Clinic, the German Cancer Research Center, Columbia University, MD Anderson Cancer Center, and Seoul National University, all with high connectivity.
Analysis of high-contribution journals, leading researchers, and co-cited journals
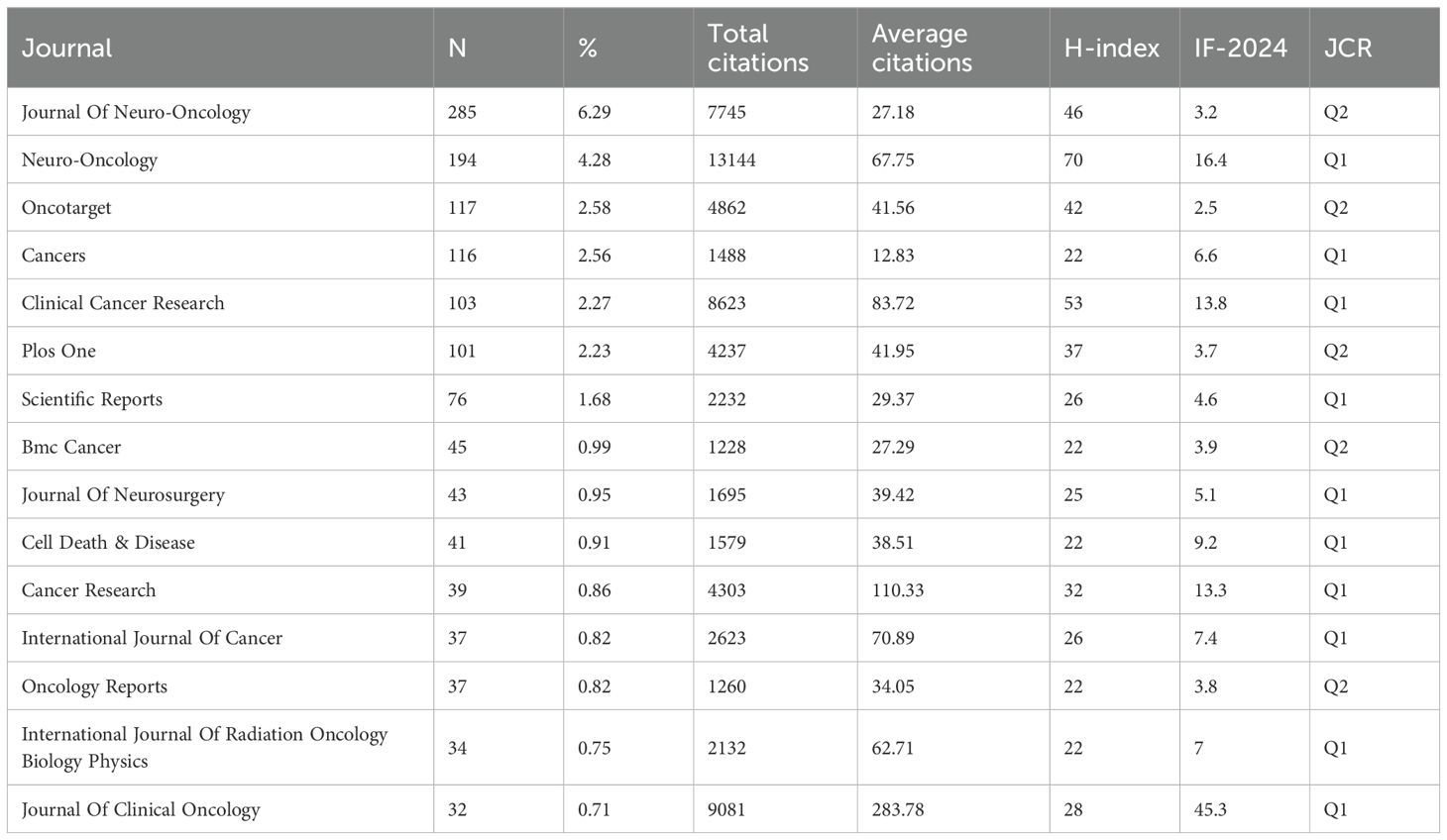
The top 15 journals published 1,300 papers on glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance, representing 28.71% of total publications (Table 4). Journal of Neuro-Oncology leads in publication count (285 papers), while Neuro-Oncology has the most citations (13,144) and the highest H-index (70). According to Bradford’s Law, core journals like Journal of Neuro-Oncology and Oncotarget play a significant role in this field (Figure 5A), while their local impact within glioma research is further evaluated in Figure 5B. Neuro-Oncology appears to be the most influential journal in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance research.
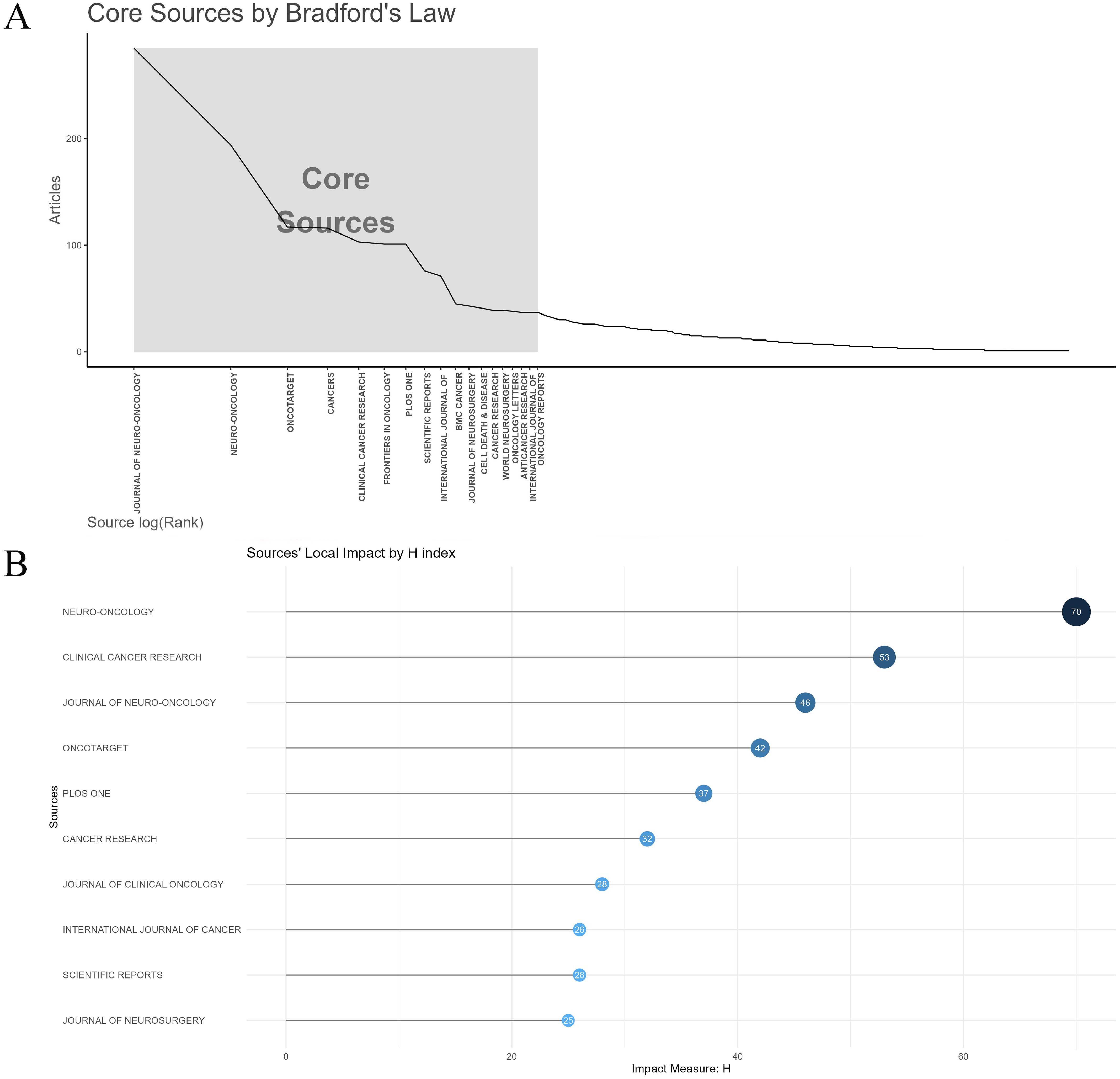
Figure 5. Analysis of core journals and impact metrics in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance research. (A) Core sources by Bradford’s law; (B) Sources’ Local Impact by H-index.
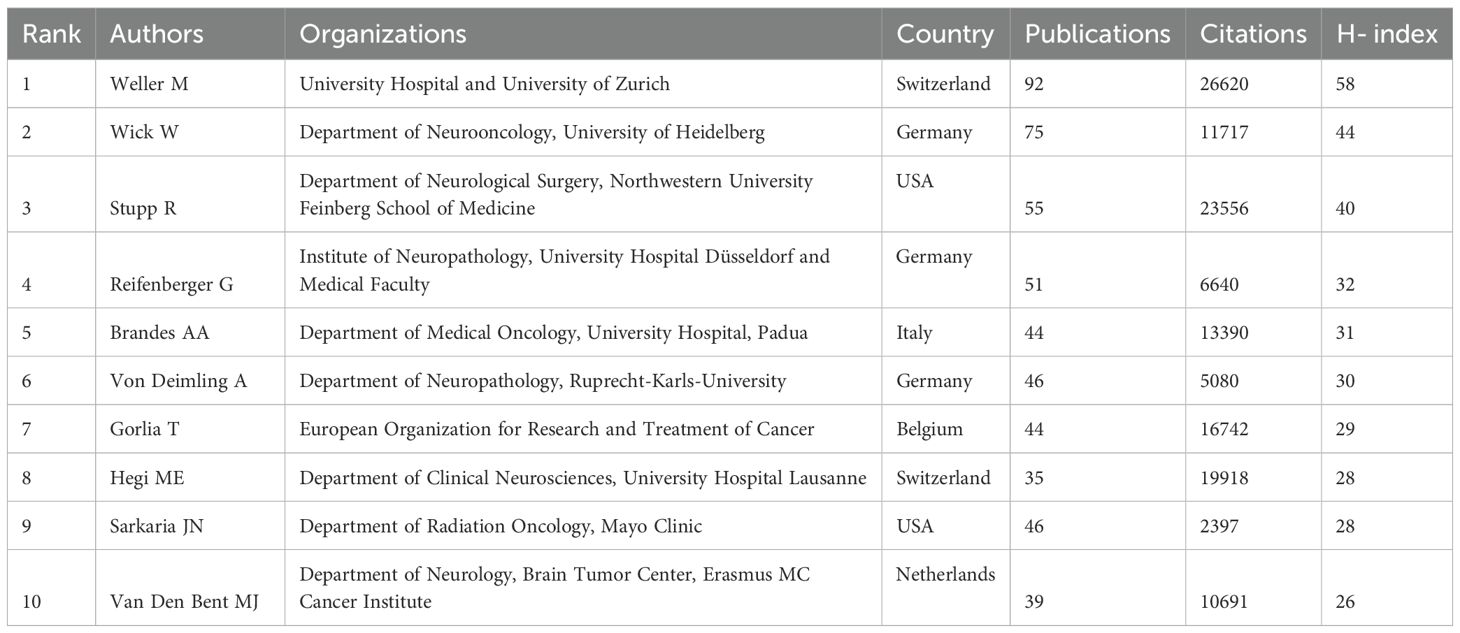
In terms of leading researchers, the top 10 authors were ranked based on publication count, citations, and H-index (Table 5). Michael Weller from the University of Zurich leads with 92 publications, 26,620 citations, and an H-index of 58, followed by Wolfgang Wick and Roger Stupp. These authors represent Switzerland, the USA, and Germany, contributing 11.64% of total publications but 66.49% of total citations, demonstrating their substantial impact on the field.
A co-authorship map generated by VOSviewer shows collaboration networks of 27,310 authors, with Michael Weller, Guido Reifenberger, and Roger Stupp as key figures in glioma research (Figure 6A). Chinese researchers, including Jiang Tao, have become more active since 2016, though China’s rate of multinational collaboration remains relatively low (Figure 6B).
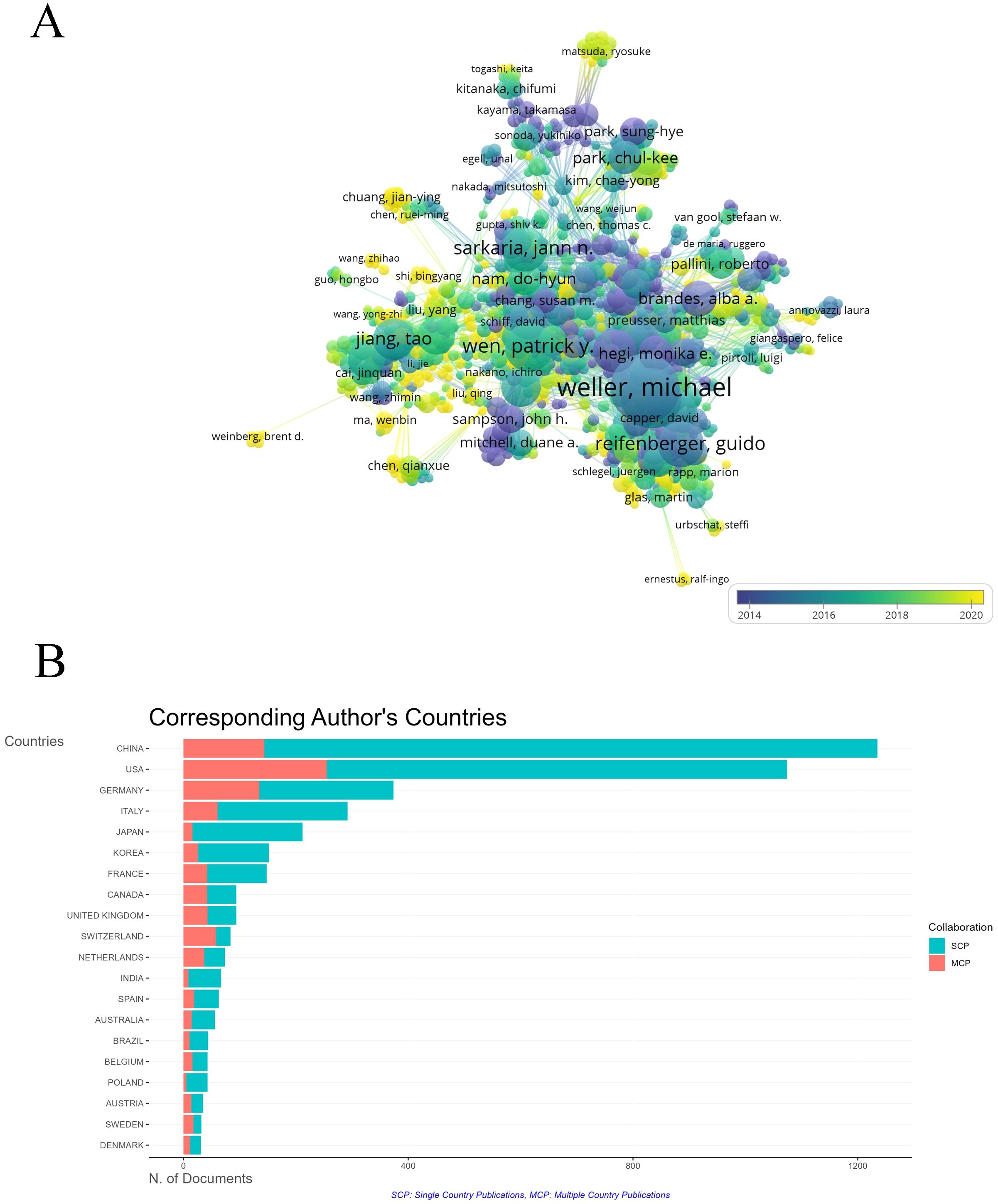
Figure 6. The co-occurrence of authors. (A) Overlay visualization of co-authorship relationships between authors. The analysis method was Linlog/modularity. The weight was citations. Scores are the average year of publication. The thickness of the lines indicates the strength of the relationships. The colors of the circles represent the average year of publication. (B) Co-responding author’s countries based on their publication volume in the field. The green bars represent Single Country Publications (SCP), The red bars represent Multiple Country Publications (MCP).
Figure 7 presents the dual-map overlay, illustrating the citation relationships in glioma-related research. Journals on the left represent the citing map, while those on the right show the cited map, with curved lines indicating citation flows. Publications in Molecular Biology and Immunology are mainly influenced by journals in Molecular Biology and Genetics (z = 7.17, f = 1,478,330), following the orange trajectory. Similarly, articles in Medicine, Medical, and Clinical fields are influenced by journals in Molecular Biology and Genetics (z = 2.53, f = 557,970), shown by the green trajectory. This highlights the strong influence of molecular biology and genetics in glioma research, reflecting its interdisciplinary nature and its integration into clinical studies.
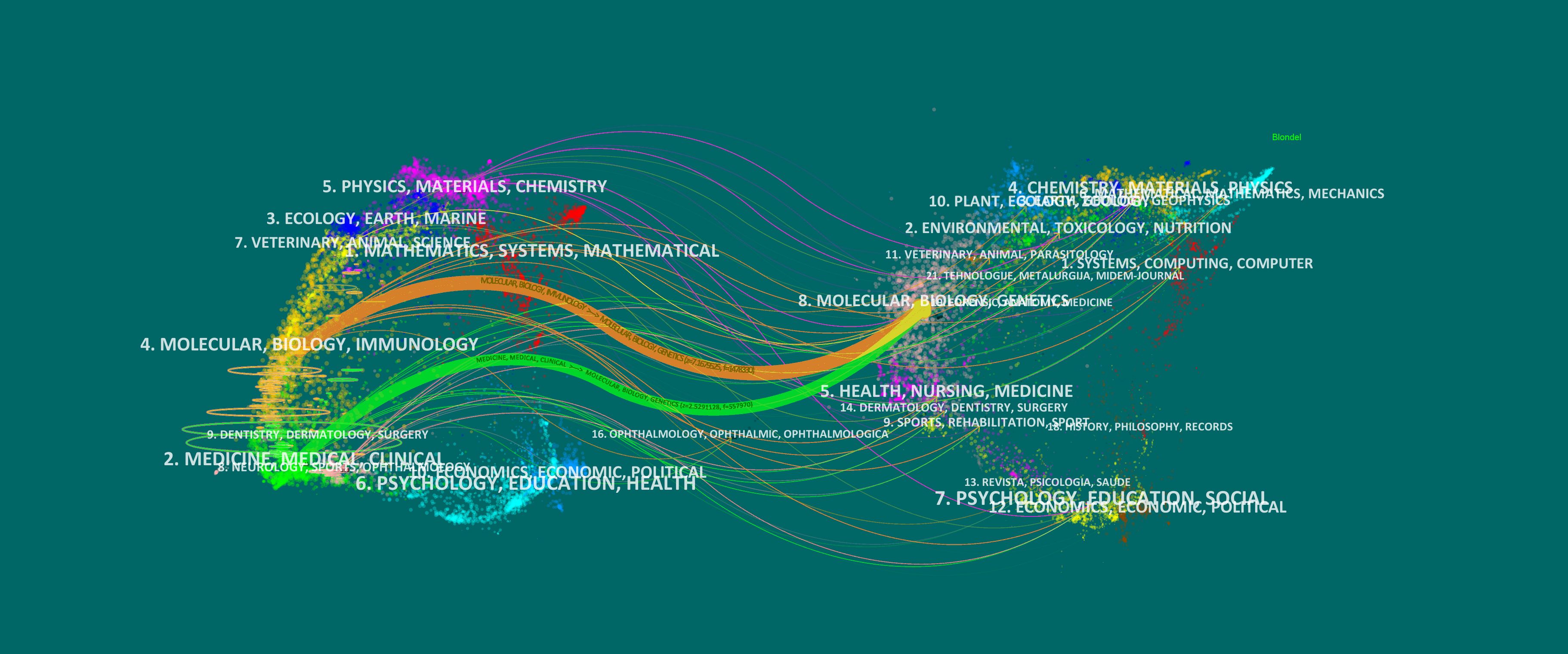
Figure 7. Dual-map overlay of the journals on research (2003–2023). Each point on the map represents a journal. The left side of the map shows the citing journals, and the right part presents the cited journals. Colored paths represent reference relationships, with thicker lines represent the main paths.
Keywords and co-citation analysis
We performed keyword co-occurrence and co-citation analyses to uncover key research trends and foundational studies in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance. The keyword co-occurrence network (507 nodes, 1213 links, Q = 0.7558, S = 0.8868) highlighted prominent terms such as “temozolomide,” “radiotherapy,” “resistance,” and “apoptosis” (Figure 8A, Table 5). Ten major clusters were identified, with the largest focusing on topics like #0 glioblastoma, #1 treatment resistance, #3 MGMT, and #4 immunotherapy, reflecting critical challenges in glioma therapy.
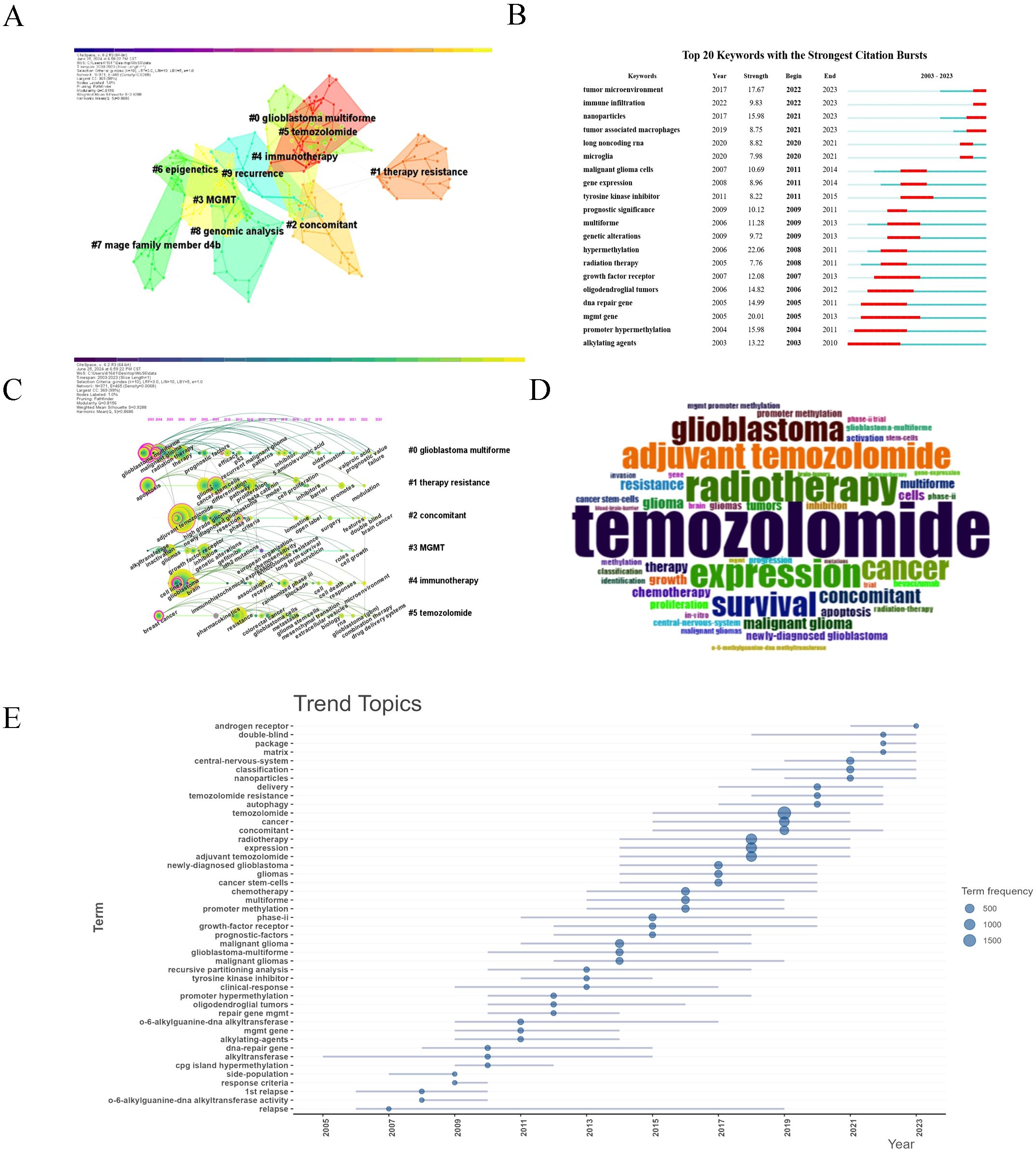
Figure 8. Keyword co-occurrence analysis. (A) The top 10 clusters of keywords. Each color region represents a cluster, and each node denotes a keyword. Areas with the same color represent a cluster with the same topic. Silhouette S = 0.9288. Modularity Q = 0.8156. (B) Top 20 keywords with the strongest citation bursts from 2003 to 2023. The “Strength” represents the strength of citation bursts. The red segment represents the begin and end year of the burst duration. (C) Timeline view of the keywords. Each circle represents a keyword, and circles on the same line represent a cluster with the same topic. The position of each circle represents the time it first appeared. The size of the circle is proportional to the frequency of keyword occurrences. (D) Word cloud generated by R, word size representing frequency. (E) Trend topics from 2003~2023, blue dots of different sizes represent word frequency.
Keyword frequency analysis (Table 6) confirmed “temozolomide” as the most frequent term, highlighting its critical role in glioma treatment. The timeline analysis (Figures 8B, C) showed a shift from early research on glioblastoma and chemotherapy to recent interest in temozolomide resistance, MGMT gene methylation, and immunotherapy. From 2018-2023, topics like immune infiltration, nanoparticles, and tumor-associated macrophages gained prominence, reflecting the rise of precision therapies. The word cloud (Figure 8D) confirmed these themes, while trend analysis (Figure 8E) highlighted increased focus on “cancer stem cells” and “precision medicine.”
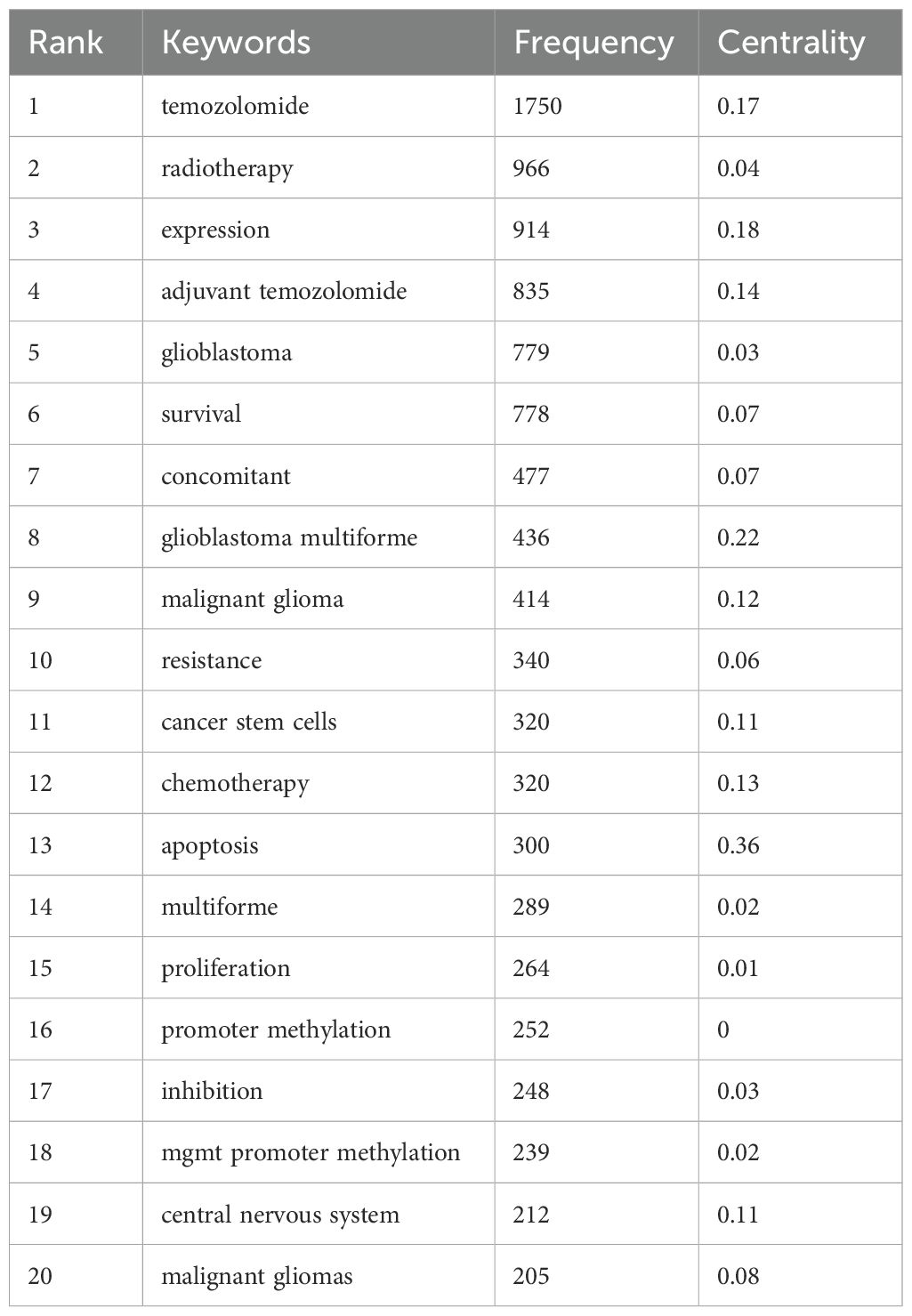
Table 6. Top20 keywords in the publications on the “mechanisms of glioma drug resistance” according to frequency.
Co-citation analysis (662 nodes, 815 links, Q = 0.6394, S = 0.8542) revealed 16 key clusters (Figure 9A), with the largest—#0 “tumor microenvironment” and #1 “immunotherapy”—providing insights into resistance mechanisms. Several influential studies, such as Stupp et al. (20, 30) and Louis et al. (31), showed strong citation bursts, highlighting their foundational role. Emerging fields, like immunotherapy and PD-1 inhibitors, were identified with ongoing citation bursts (Figures 9B, C). A three-field plot (Figure 9D) mapped relationships between frequently cited references, key researchers (Weller M, Wick W, Stupp R), and terms like “glioblastoma” and “MGMT,” illustrating collaborative networks driving innovation in this domain.
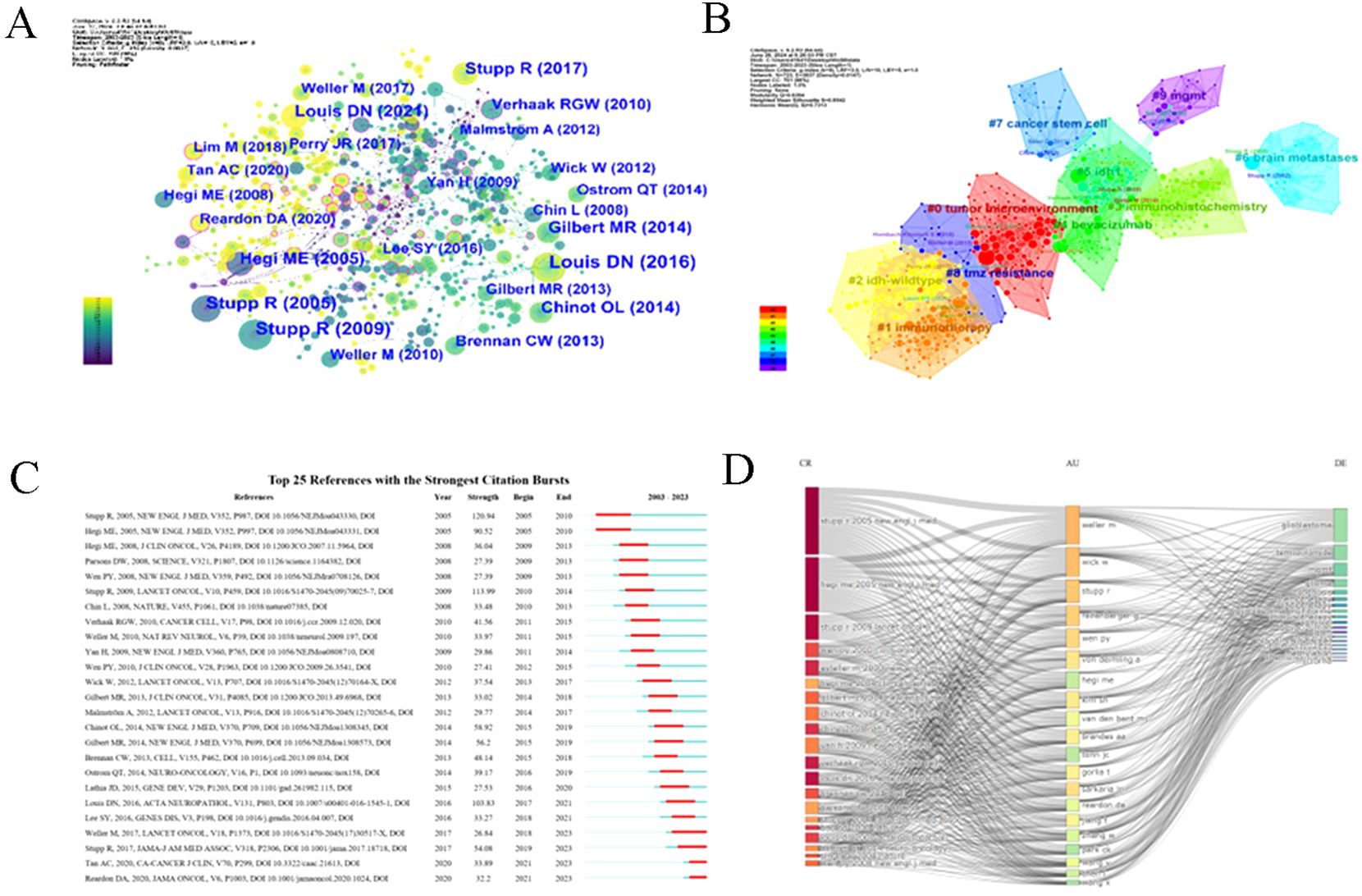
Figure 9. Co-cited references and burst references. (A) The network map of co-cited references. Nodes in the visualized network represent co-cited references. Lines between nodes represent co-cited links. (B) The network map of co-cited clusters. 10 clusters with diversified research themes were formed and illustrated in different colors. Areas with the same color represent a cluster with the same topic. Silhouette S = 0.8542. Modularity Q = 0.6394. (C) Top 25 references with the strongest citation burst from 2003-2023. The “Strength” represents the strength of citation bursts. The red segment represents the begin and end year of the burst duration. (D) A three-field plot illustrates the relationships between frequently cited references, key researchers, and pivotal terms.
Discussion
Global research trends in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance mechanisms
The increasing number of publications reflects heightened global attention to glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance mechanisms. Since Friedman’s seminal 1998 study on temozolomide efficacy and tumor DNA mismatch repair activity (32), research in this field has expanded significantly. Our bibliometric analysis reveals a notable rise in publications and citations, with annual publications exceeding 400 since 2017 and peaking at 650 in 2022. This surge indicates not only the maturation of theoretical frameworks but also a growing recognition of the clinical challenges posed by glioma resistance.
Countries with higher glioma incidence, primarily developed nations, have historically dominated publication output, possibly due to regional differences in tumor incidence (33). A 2012 European Journal of Cancer study highlighted global variations in malignant CNS tumor rates, with the highest in Europe, North America, and Australia/New Zealand (34). Studies in Neuro-Oncology also revealed significant incidence differences, with the highest rates in Europe and lower rates in Asia (35). This likely contributed to the United States’ increased research focus on glioma resistance mechanisms (36).
In Asia, South Korea’s 2002 nationwide CNS tumor survey highlighted differences in CNS tumor incidence compared to Western populations (37). Factors like HDI, GDP, and occupational carcinogen exposure correlate with glioma incidence, driving increased research in countries like China since 2009 (38, 39). However, global collaboration remains limited, underscoring the need for interdisciplinary research to advance glioma resistance studies and develop effective treatments.
Hot topics in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance mechanisms: temozolomide resistance and tumor microenvironment
Keywords highlight research hotspots, with temozolomide (TMZ) resistance and the tumor microenvironment (TME) emerging as core topics in glioma research (40, 41). TMZ, the standard chemotherapeutic for glioblastoma (GBM), often faces efficacy challenges due to resistance mechanisms (9, 19, 42–45). Despite its effectiveness, glioma cells develop resistance through various mechanisms, such as MGMT repair of TMZ-induced DNA damage, overexpression of EGFR, and mutations in Mdm2, p53, and PTEN. Strategies to overcome these include MGMT inhibitors and EGFR inhibitors, which require further clinical validation (23, 27, 46).
MGMT promoter methylation is a critical biomarker for predicting TMZ response, and developing MGMT inhibitors remains a significant research focus (24, 47). Additionally, researchers are exploring other DNA repair pathways, such as APNG, for potential therapeutic targets (48–50).
Recent research has increasingly focused on the TME, which plays a key role in glioma progression and treatment resistance (5). Immune infiltration, nanoparticle drug delivery, and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are major areas of interest. TAMs in the TME contribute to tumor growth and resistance by secreting cytokines and growth factors, while the blood-brain barrier limits TMZ penetration (51). Modulating the TME to enhance immune responses is a growing field of study (52). New technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 and single-cell RNA sequencing are being used to identify and target resistant cell populations, offering new therapeutic strategies (53).
Future research trends
Our bibliometric analysis reveals the evolving research focus in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance. Prior to 2010, studies primarily centered on foundational mechanisms such as “promoter hypermethylation,” “DNA repair genes,” and “alkylating agents.” Between 2011 and 2015, the focus shifted toward treatment strategies, including the “MGMT gene,” “growth factor receptors,” and “tyrosine kinase inhibitors.” Since 2016, interdisciplinary research has become increasingly prominent, with key topics such as the “tumor microenvironment,” “immune infiltration,” and “nanoparticles” reflecting significant advances in immunology and nanotechnology.
The keyword timeline shows “tumor microenvironment,” “combination therapy,” and “drug delivery” as the most frequent terms in 2023, expected to remain key in future research. The androgen receptor (AR) also emerges as a potential target, with studies linking AR expression to poor prognosis and increased resistance to temozolomide (TMZ) (54–60). A study (61) highlights a dual-targeted delivery system for temozolomide using a multi-responsive nanoplatform that modulates the tumor microenvironment to overcome drug resistance in glioblastoma. This innovative approach addresses key challenges such as low delivery efficiency and chemotherapy resistance, offering a promising new avenue for improving GBM treatment outcomes.
While sex hormones like estrogen and androgen are well-studied in other cancers (62, 63), their role in GBM remains unclear. Targeting AR with antiandrogen drugs presents a promising therapeutic strategy to combat treatment resistance (57, 64). Brain-penetrant antiandrogens offer potential in biomarker-guided treatments, and ongoing studies aim to refine these therapies by exploring biological sex and the immune microenvironment (65). Emerging clinical trials highlight the potential of androgen receptor (AR)-targeted therapies in glioblastoma. Researchers have initiated a trial to evaluate the safety and tolerability of enzalutamide combined with radiotherapy (RT) and TMZ (66). The study also uses Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria to assess clinical responses and examines the pharmacokinetics of enzalutamide with TMZ. These efforts mark a key step toward integrating AR-targeted therapies into standard glioblastoma treatment, offering new possibilities for overcoming resistance and improving outcomes.
Limitations of our bibliometric analysis
This bibliometric analysis provides valuable insights into the research landscape of glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance, but some limitations must be acknowledged. First, the data were sourced exclusively from the Web of Science database, potentially introducing bias by excluding publications indexed in other databases like Scopus or PubMed. Additionally, the search strategy excluded non-English articles, possibly leading to language bias and omission of relevant studies. Another limitation lies in the reliance on metadata and citation data rather than full-text content, meaning the analysis cannot capture detailed discussions, such as authors’ interpretations or insights into future directions. As a result, certain nuances of the field may be overlooked. Finally, citation-based metrics like the H-index and citation bursts reflect research impact but not necessarily the quality or clinical relevance of studies, which may affect result interpretation. Acknowledging these limitations provides context for our findings and highlights the need for complementary approaches, such as systematic reviews or meta-analyses, to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance.
Conclusion
This study represents the first bibliometric analysis of glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance using visualization software, illustrating the current research landscape over the past 21 years. The number of published papers has shown a significant upward trend, particularly in the past decade, indicating substantial global interest in the field of glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance. Currently, the main research hotspots focus on temozolomide resistance, tumor microenvironment, and nanoparticle drug delivery systems, aiming to explore resistance mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches. Overall, this bibliometric analysis provides valuable references for researchers, helping them to comprehensively understand the key contributors to glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance mechanisms and discover further research ideas and inspiration from the identified hotspots and frontier studies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
SY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JW: Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. PL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WC: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. WL: Data curation, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YL: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Project No. 2024B1212110007), and the Chinese Association for Science and Technology Society Service Center (Grant No. Excellence Phase II-B1-035) under the Phase II of China Excellence Action Plan for Scientific Journals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The author(s) verify and take full responsibility for the use of generative AI in the preparation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used to assist with language translation only. All scientific content, analysis, and conclusions were produced and reviewed by the authors to ensure accuracy and integrity.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Pellerino A, Caccese M, Padovan M, Cerretti G, Lombardi G. Epidemiology, risk factors, and prognostic factors of gliomas. Clin Trans imaging: Rev Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2022) 10:467–75. doi: 10.1007/s40336-022-00489-6
2. Zhao J, Xu L, Sun J, Song M, Wang L, Yuan S, et al. Global trends in incidence, death, burden and risk factors of early-onset cancer from 1990 to 2019. BMJ Oncol. (2023) 2:e000049. doi: 10.1136/bmjonc-2023-000049
3. Yalamarty S, Filipczak N, Li X, Subhan MA, Parveen F, Ataide JA, et al. Mechanisms of resistance and current treatment options for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:(7). doi: 10.3390/cancers15072116
4. Ishiai M. Regulation of the fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway by phosphorylation and monoubiquitination. Genes. (2021) 12:1763. doi: 10.3390/genes12111763
5. Jurkovicova D, Neophytou CM, Gašparović AČ, Gonçalves AC. DNA damage response in cancer therapy and resistance: challenges and opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:14672. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314672
6. Messaoudi K, Clavreul A, Lagarce F. Toward an effective strategy in glioblastoma treatment. Part I: resistance mechanisms and strategies to overcome resistance of glioblastoma to temozolomide. Drug Discovery Today. (2015) 20:899–905. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.02.011
7. Darefsky AS, King JT, Dubrow R. Adult glioblastoma multiforme survival in the temozolomide era: A population-based analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries. Cancer. (2012) 118:2163–72. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v118.8
8. Noch EK, Ramakrishna R, Magge R. Challenges in the treatment of glioblastoma: multisystem mechanisms of therapeutic resistance. World Neurosurg. (2018) 116:505–17. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.022
9. Stupp R, Hegi ME, Gilbert MR, Chakravarti A. Chemoradiotherapy in Malignant glioma: standard of care and future directions. J Clin Oncol. (2007) 25:4127–36. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.8554
10. Woo P, Li Y, Chan A, Ng S, Loong H, Chan D, et al. A multifaceted review of temozolomide resistance mechanisms in glioblastoma beyond O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. Glioma. (2019) 2:68–82. doi: 10.4103/glioma.glioma_3_19
11. Li J, Song C, Gu J, Li C, Zang W, Shi L, et al. RBBP4 regulates the expression of the Mre11-Rad50-NBS1 (MRN) complex and promotes DNA double-strand break repair to mediate glioblastoma chemoradiotherapy resistance. Cancer Lett. (2023) 557:216078. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216078
12. Agosti E, Panciani PP, Zeppieri M, De Maria L, Pasqualetti F, Tel A, et al. Tumor microenvironment and glioblastoma cell interplay as promoters of therapeutic resistance. Biol (Basel). (2023) 12(5):736. doi: 10.3390/biology12050736
13. Nakamura K, Smyth MJ. Myeloid immunosuppression and immune checkpoints in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0306-1
14. Higgins GS, O'Cathail SM, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG. Drug radiotherapy combinations: review of previous failures and reasons for future optimism. Cancer Treat Rev. (2015) 41:105–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.12.012
15. Chargari C, Levy A, Paoletti X, Soria JC, Massard C, Weichselbaum RR, et al. Methodological development of combination drug and radiotherapy in basic and clinical research. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:4723–36. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-4155
16. Cooper ID. Bibliometrics basics. J Med Libr Assoc. (2015) 103:217–8. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.103.4.013
17. Bibliometrics, U. O. W. W. White paper: Using bibliometrics in evaluating research. Research Department, Thomson Reuters, Philadelphia, PA, USA: University of Waterloo (2016).
18. McClave S, Taylor B. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: society of critical care medicine (SCCM) and american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2016). doi: 10.1177/0148607115621863
19. Bagley SC, White H, Golomb BA. Logistic regression in the medical literature: standards for use and reporting, with particular attention to one medical domain. J Clin Epidemiol. (2001) 54:979–85. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(01)00372-9
20. Stupp R, Hegi ME. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomized phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. (2009). doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7
21. Tan AC, Ashley DM, Lopez GY, Malinzak M, Friedman HS, Khasraw M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. (2020) 70:299–312. doi: 10.3322/caac.21613
22. Chin L. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature. (2008) 455:1061–8. doi: 10.1038/nature07385
23. Hegi M, Diserens A, Gorlia T. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. New Engl J Med. (2005). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043331
24. Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. (2006) 444:756–60. doi: 10.1038/nature05236
25. Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P, et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science. (2008) 321:1807–12. doi: 10.1126/science.1164382
26. Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK, Kernie SG, et al. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. (2012) 488:522–6. doi: 10.1038/nature11287
27. Stupp R, Taillibert S, Kanner A, Read W, Steinberg DM, Lhermitte B, et al. Effect of tumor-treating fields plus maintenance temozolomide vs maintenance temozolomide alone on survival in patients with glioblastoma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA: J Am Med Assoc. (2017) 318:2306–16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.18718
28. Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H, Abdulkadir IR, et al. Analysis of gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. (2006) 5:67. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-67
29. O'Rourke DM, Nasrallah MP, Desai A, Melenhorst JJ, Mansfield K, Morrissette JJD, et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci Trans Med. (2017) 9:(399). doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa0984
30. Stupp R, van den Bent MJ, Hegi ME. Optimal role of temozolomide in the treatment of malignant gliomas. Curr Neurol Neurosci (2005) 5(3):198–206. doi: 10.1007/s11910-005-0047-7
31. Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol (2016) 131(6):803–20. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1
32. Friedman HS, Kokkinakis DM, Pluda J, Friedman AH, Cokgor I, Haglund MM, et al. Phase I trial of O6-benzylguanine for patients undergoing surgery for Malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. (1998) 16:3570. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1998.16.11.3570
33. Miranda-Filho A, Piñeros M, Soerjomataram. I. Cancers of the brain and CNS: global patterns and trends in incidence. Neuro-Oncology. (2017) 19:270–80.
34. Crocetti E, Trama A, Stiller C, Caldarella A, Soffietti R, Jaal J, et al. Epidemiology of glial and non-glial brain tumors in Europe. Eur J Cancer. (2012) 48:1532–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.013
35. Wanner M, Rohrmann S, Stiller C, Caldarella A, Soffietti R, Jaal J. Geographical variation in Malignant and benign/borderline brain and CNS tumor incidence: a comparison between a high-income and a middle-income country. J neuro-oncology. (2020) 149:273–82. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03595-5
36. Gittleman HR, Ostrom QT, Rouse CD, Dowling JA, de Blank PM, Kruchko CA, et al. Trends in central nervous system tumor incidence relative to other common cancers in adults, adolescents, and children in the United States 2000 to 2010. Cancer. (2015) 121:102–12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v121.1
37. Suh YL, Koo H, Kim TS, Chi JG, Park SH, Khang SK, et al. Tumors of the central nervous system in Korea: a multicenter study of 3221 cases. J Neurooncol. (2002) 56:251–9. doi: 10.1023/A:1015092501279
38. Huang J, Chan SC, Lok V, Zhang L, Lin X, Lucero-Prisno DE, et al. Disease burden, risk factors, and trends of primary central nervous system (CNS) cancer: A global study of registries data. Neuro Oncol. (2023) 25:995–1005. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac213
39. Khanmohammadi S, Mobarakabadi M, Mohebi F. The economic burden of Malignant brain tumors. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2023) 1394:209–21. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14732-6_13
40. Li F, Li M, Guan P, Ma S, Cui L. Mapping publication trends and identifying hot spots of research on Internet health information seeking behavior: a quantitative and co-word biclustering analysis. J Med Internet Res. (2015) 17:e81. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3326
41. Singh N, Miner A, Hennis L. Mechanisms of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma - a comprehensive review. Cancer Drug Resist. (2021). doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.79
42. Lindau D, Gielen P, Kroesen M, Wesseling P, Adema GJ. The immunosuppressive tumor network: myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T cells and natural killer T cells. Immunology. (2013) 138:105–15. doi: 10.1111/imm.2013.138.issue-2
43. Wu L, Chai R, Zhao Z, Wang Q, Jiang T. Role of the tumor microenvironment in shaping IDH-wildtype glioma plasticity, and potential therapeutic strategies. Cancer Biol Med. (2022) 19:1423–7. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2022.0363
44. Wu Y, Mao M, Wang L. Integrated clustering signature of genomic heterogeneity, stemness and tumor microenvironment predicts glioma prognosis and immunotherapy response. Aging (Albany NY.). (2023) 15(17):9086–104. doi: 10.18632/aging.205018
45. Yang Q, Guo N, Zhou Y, Chen J, Wei Q, Han M. The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumor progression and relevant advance in targeted therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2020) 10:2156–70. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.04.004
46. Arora A, Somasundaram K. Glioblastoma vs temozolomide: can the red queen race be won? Cancer Biol Ther. (2019) 20:1083–90. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1599662
47. Mathur R, Zhang Y, Grimmer MR, Hong C, Zhang M, Bollam S, et al. MGMT promoter methylation level in newly diagnosed low-grade glioma is a predictor of hypermutation at recurrence. Neuro-oncology (Charlottesville Va.). (2020) 22(11):1580–90. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa059
48. Sousa JF, Serafim RB, Freitas LM, Fontana CR, Valente V. DNA repair genes in astrocytoma tumorigenesis, progression and therapy resistance. Genet Mol Biol. (2019) 43:e20190066. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0066
49. Berdis JA. Examining the role of specialized DNA polymerases in the development of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Obm Neurobiol. (2021). doi: 10.21926/obm.neurobiol.2102096
50. Jimenez-Alcazar M, Curiel-Garcia A, Nogales P, Perales-Paton J, Schuhmacher AJ, Galan-Ganga M, et al. Dianhydrogalactitol overcomes multiple temozolomide resistance mechanisms in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2021) 20:1029–38. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0319
51. Kizilbash SH, Gupta SK, Chang K, Kawashima R, Parrish KE, Carlson BL, et al. Restricted delivery of talazoparib across the blood-brain barrier limits the sensitizing effects of PARP inhibition on temozolomide therapy in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2017) 16:2735–46. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0365
52. Haist M, Stege H, Grabbe S, Bros M. The functional crosstalk between myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells within the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Cancers. (2021) 13:210. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020210
53. Kang X, Wang Y, Liu P, Huang B, Zhou B, Lu S, et al. Progresses, challenges, and prospects of CRISPR/cas9 gene-editing in glioma studies. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:(2). doi: 10.3390/cancers15020396
54. Artene SA, Folcuti C, Dricu A. beta-arrestin 1 overexpression increases temozolomide resistance in human Malignant glioma cells. Curr Health Sci J. (2017) 43:112–9. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.43.02.02
55. Qi X, Jha SK, Jha NK, Dewanjee S, Dey A, Deka R, et al. Antioxidants in brain tumors: current therapeutic significance and future prospects. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:204. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01668-9
56. Obrador E, Moreno-Murciano P, Oriol-Caballo M, López-Blanch R, Pineda B, Gutiérrez-Arroyo JL, et al. Glioblastoma therapy: past, present and future. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:2529. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052529
57. Anbarasu S, Anbarasu A. Cancer-biomarkers associated with sex hormone receptors and recent therapeutic advancements: a comprehensive review. Med Oncol. (2023) 40:171. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02044-3
58. Barthel L, Hadamitzky M, Dammann P. Glioma: molecular signature and crossroads with tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2022). doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-09997-9
59. Ferraris C, Cavalli R, Panciani PP, Battaglia L. Overcoming the blood-brain barrier: successes and challenges in developing nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery systems for the treatment of brain tumors. Int J Nanomedicine. (2020) 15:2999–3022. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S231479
60. Gallego-Ortega D, Law. AMK. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as a therapeutic target for cancer. Cells. (2020). doi: 10.3390/cells9030561
61. Chen X, Zheng Y, Zhang Q, Chen Q, Chen Z, Wu D. Dual-targeted delivery of temozolomide by multi-responsive nanoplatform via tumor microenvironment modulation for overcoming drug resistance to treat glioblastoma. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:264. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02531-3
62. Ozdemir BC, Dotto GP. Sex hormones and anticancer immunity. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:4603–10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0137
63. Velho PI, Bastos DA. New approaches to targeting the androgen receptor pathway in prostate cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. (2021) 19:228–40.
64. Kim TJ, Lee YH, Koo KC. Current status and future perspectives of androgen receptor inhibition therapy for prostate cancer: A comprehensive review. Biomolecules. (2021) 11(4). doi: 10.3390/biom11040492
65. Conforti F, Pala L, Pagan E, Bagnardi V, De Pas T, Queirolo P, et al. Sex-based dimorphism of anticancer immune response and molecular mechanisms of immune evasion. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:4311–24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0136
Keywords: glioma, chemoradiotherapy resistance, tumor microenvironment, bibliometric analysis, immune infiltration, androgen receptor
Citation: Yu S, Wu J, Jing Y, Lin P, Lang L, Xiong Y, Chen W, Liu W, Sun C and Lu Y (2025) Research trends in glioma chemoradiotherapy resistance: a bibliometric analysis (2003–2023). Front. Oncol. 15:1539937. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1539937
Received: 05 December 2024; Accepted: 16 January 2025;
Published: 07 February 2025.
Edited by:
Yuanbo Pan, Zhejiang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Wang Bin Bin, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaLiuxi Chu, Wenzhou Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Wu, Jing, Lin, Lang, Xiong, Chen, Liu, Sun and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuntao Lu, bGxsdTIwMDB5dW5AZ21haWwuY29t; Changpeng Sun, ZXZhbjIwMTMxN0AxNjMuY29t
 Shishi Yu
Shishi Yu Jinya Wu1
Jinya Wu1 Wenhua Liu
Wenhua Liu