
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol. , 19 March 2025
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1539055
This article is part of the Research Topic Innovative Therapeutic Approaches for Complex Cancers: Exploring New Strategies in Glioblastoma, Urogenital, and Bladder Cancers View all 5 articles
 Wanqiong Chen1†
Wanqiong Chen1† Limian Hong2†
Limian Hong2† Shaomei Lin1†
Shaomei Lin1† Na Xian3,4
Na Xian3,4 Cailing Yan5
Cailing Yan5 Ningning Zhao6
Ningning Zhao6 Yonglei Xiao3
Yonglei Xiao3 Wanting Liao1
Wanting Liao1 Yuxiang Huang1
Yuxiang Huang1 Mingzhu Chen1*
Mingzhu Chen1*Despite the remarkable success of CAR-T cell therapy in hematologic malignancies, its progress in solid tumors has been slow. Overcoming challenges such as the recruitment and infiltration of CAR-T cells into the tumor site and the survival issues in the harsh tumor microenvironment are crucial for successful application in solid tumors. In this study, CAR-T cells were engineered to secrete both IL-15 and CCL19, and their efficacy was evaluated in a human glioblastoma orthotopic xenograft model. The results reveal that 15 × 19 CAR-T cells exhibit superior proliferation, chemotaxis, and phenotypic characteristics compared to conventional CAR-T cells in vitro. In vivo, 15 × 19 CAR-T cells exhibit superior control over tumors compared to conventional counterparts. Mechanistically, the improved efficacy can be attributed, in part, to IL-15 and CCL19 enhancing T-cell infiltration at the tumor site and fortifying resistance to exhaustion within the tumor microenvironment. In conclusion, the incorporation of IL-15 and CCL19 into CAR-T cells emerges as a promising strategy to elevate the anti-tumor efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy, positioning 15 × 19 CAR-T cells as a potential breakthrough for enhancing the application of CAR-T therapy in solid tumors.
Glioblastoma (GBM) remains the most prevalent and aggressive form of brain tumor, with an annual incidence rate of approximately 3 per 100,000 (1). Despite employing diverse treatment modalities such as surgical resection, chemotherapy (typically temozolomide), radiotherapy and tumor-treating fields (TTF), the 5-year survival rate for GBM remains below 10% (2). Given the aggressive growth within the central nervous system (CNS), conventional treatments are often ineffective. The high malignancy, rapid progression, and high recurrence rate of GBM (3) necessitate the exploration of novel effective treatment approaches.
Immunotherapy has become a promising avenue for tumor treatment, offering more targeted advantages compared to traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy has demonstrated efficacy in hematological malignancies (4, 5). CAR-T cells are genetically engineered to express a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) specifically targeting tumor-associated antigens on the surface of T cells, enabling the elimination of tumor cells independently of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) recognition (6, 7). However, the success of CAR-T cell therapy in hematologic malignancies has not been replicated in solid tumors, with several challenges hampering the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy in this context. Challenges include the limited T cell presence at the tumor site in certain solid tumors and the inefficiency of T cells to expand and maintain functionality in the hostile tumor microenvironment (TME) (8–10). While CAR-T cell studies for GBM treatment are underway, and some have progressed to clinical trials, the unique location, highly aggressive nature, and profoundly immunosuppressive TME of GBM present substantial challenges that clinical trials currently struggle to meet (11–14).
Previous studies have revealed the pivotal role of Interleukin-15 (IL-15), a growth factor, in inhibiting the apoptosis of T, B, and NK cells while fostering their survival (15).Its importance further encompasses the regulation of T cell development and homeostasis (16). Simultaneously, IL-15 actively engages in the genesis, maintenance, and reactivation of naive T cells, effector T cells, and memory T cells (17). In tandem, C-C motif chemokine ligand 19 (CCL19), a chemotactic factor, can recruit T cells and dendritic cells (DCs) to migrate and infiltrate tumor sites (18, 19). These studies have motivated our interest in engineering the class III variant of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII)-targeted CAR-T cells designed to secrete IL-15 and CCL19. This dual action aims to not only sustain the functionality of T cells but also to attract T cells and DCs to the tumor site, ultimately improving the therapeutic efficacy of CAR-T cells against GBM.
EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cell line overexpressing EGFRvIII officially donated from Ludwig Institute, University of California. EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells were transduced with lentiviral vector encoding the luciferase reporter gene (pLenti CMV puro Luc, Miaoling biology) to generate EGFRvIII+ U87 MG-Luc cell line. 293T cells were acquired from TaKara company. All cell lines were incubated in DMEM medium (CORNING) supplemented with 10%FBS (PAN). NCG mice were purchased from Jiangsu Gempharmatech Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Jiangsu, China). Animal studies were conducted in accordance with the Experiment Animal Care Commission of Quanzhou Medical College and raised in specific pathogen-free conditions at the Quanzhou Medical College Institute Experimental Animal Center (Quanzhou, China).
CAR vector construction followed a previously established methodology (20). In brief, the EGFRvIII specific CAR was constructed by linking the EGFRvIII specific scFv to a CD8α hinge, CD8α transmembrane domain, an intracellular domain of 4-1BB, and CD3ζ in a sequential manner. To incorporate human cytokines IL-15 and CCL19 into the CAR expression, two P2A peptides were employed to facilitate the individual expression of each cytokine. For the production of lentivirus, 293T cells were transfected using a vector expressing CAR along with two lentiviral packaging plasmids (psPAX2 and pMD2.G, maintained by Tcelltech Biological Science and Technology Inc.) employing a calcium phosphate cell transfection kit from Beyotime. The lentiviral supernatant was collected at 48 and 72 h, followed by concentration through ultracentrifugation. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) sourced from healthy volunteers underwent activation using T Cell TransAct (Miltenyi Biotech) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. After 24 h, the calculated amount of virus (multiplicity of infection = 10) was introduced. The T cells were subsequently washed once after a 16-h co-incubation period.
The cells were incubated with corresponding flow cytometry antibodies at 4 ° C for 40 min, followed by two washes in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) before being run on FACS Verse (BD Biosciences). To assess the expression of EGFRvIII specific CARs on T cells, phycoerythrin(PE)-labeled human EGFRvIII protein (Acrobiosystems) was utilized. For the measurement of CAR-T cell proliferation, CAR-T cells and mitomycin-C-treated target cells (5 µg/µL) were co-cultured on a 6-cell culture plate. The absolute number of CAR+ T cells was determined using precision count beads (Biolegend) on days 3 and 5. Additionally, for the evaluation the proportion of central memory T cells (TCM) cells, effector memory T cells (TEM), naive T cells (TN), or effector T cells (Teff) were stained with allophycocyanin (APC)-labeled anti-CCR7 (BD Bioscience), fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled anti-CD45RA (Biolegend) and peridinin chlorophyll protein complex/cyanine5.5 (PerCP/Cy5.5)-labeled anti-CD45RO (Biolegend) monoclonal antibodies. To assess apoptosis of CAR-T cells on day 15, FITC-labeled anti-annexin V (BD Bioscience) and 7-amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) antibodies (BD Bioscience) were employed. To detect the exhaustion of CAR-T cells, FITC-labeled anti-TIM-3 (Biolegend), PerCP/Cy5.5-labeled anti-PD1 (Biolegend) and APC-labeled anti-LAG-3 monoclonal antibodies (BD Bioscience) were used. Tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs) were analyzed using Fixable Viability Dye 506 (eBioscience), PE/Cy7-labeled anti-human CD3 (Biolegend).
Untransduced (here-after referred to as UTD) T cells and CAR-T cells were co-cultured with target tumor cells at an effector-to-target ratio of 1:1 for 24 h. The supernatant was harvested after centrifugation at 500 g for 10 min to test the release of cytokines. The concentrations of IL-15 and CCL19 were measured by ELISA kits (MultiSciences Biotech; NeobioSciences Biotech).
To study the cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells, EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells were labeled with 0.5 µM CFSE (Invitrogen) and co-cultured with CAR-T cells and UTD T cells at varying effector-to-target ratio of 8:1, 4:1, 2:1 and 1:1. A certain amount of UTD T cells were added to EGFRvIII CAR-T cells before co-cultured to make it consistent with CAR+ population of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells. The mixed effector and target cells were combined in capped FACS tubes with a total volume 200 µL and centrifuged at 200 g for 1 min after mixing. After 10 h of co-culture, 0.1 µg DAPI (Invitrogen) was added to each sample, and the cells were immediately analyzed by flow cytometry within 5 s. The % CAR-T cells and UTD T cells lysis were calculated as follows: [(CFSE+DAPI+ cells−spontaneous apoptosis)/total CFSE+ cells] ×100%.
The transwell migration assay followed the protocol described previously (21). Briefly, CAR-T cells and UTD T cells were stimulated with 5 µg/µL mitomycin-C-treated EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells for 24 h to generate the co-culture supernatant. The supernatant was then added to the lower chambers (600 µL), while the T cells (activated for 1 day) were placed in the upper chambers. After 6 and 12 h, the cells migrated from the upper chamber to the lower chamber and were counted using the cellometer auto T4 bright field cell counter (Nexcelom Bioscience). Furthermore, to evaluate the role of CCR7 in T cell migration, T cells were incubated with anti-CCR7 monoclonal antibodies (Biolegend) for 1 h at 37 ° C to block CCR7. The absolute number of migrated cells was then determined using the same methodology described above.
In the human GBM orthotopic xenograft model, 4 × 104 EGFRvIII+ U87 MG-Luc cells were injected intracranially into 5- or 6-week-old NCG mice using an animal brain stereotaxic apparatus, with four mice per group. Briefly, the procedure involved locating the target position, using the anterior fontanel as a starting point, 0.50 mm anterior to the fontanel and 1.5 mm to the left of the lateral sagittal suture, and drilling a hole. The target position was confirmed again, and the needle was slowly inserted at a depth of 4.5 mm. The day of tumor cell injection was recorded as day 0. Mice were subjected to imaging using the IVIS imaging system (IVIS Spectrum, PerkinElmer) on day 7. Based on the in vivo imaging results, tumor-bearing mice were ranked by tumor size and randomly divided into three groups, each containing four mice. Group assignment was based on ensuring no significant difference in tumor size among the groups. A certain amount of UTD T cells were added to EGFRvIII CAR-T cells to make it consistent with CAR+ population of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells. On day 8, 6 × 106 CAR+ T cells and the corresponding amount UTD T cells were intravenously injected, respectively. Tumor size in each group of mice was measured by in vivo imaging on days 11, 16, 23, 30, and 37. Mouse body weight was measured every 5 days. On day 63, mice were sacrificed, and blood, spleen, and bone specimens were collected to prepare single-cell suspensions for flow cytometry analysis. For the analysis of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs), separate experiments were performed with the same treatments (n = 3). Mice in each group were sacrificed five days after CAR-T cell injection to analyze the function and number of TILs.
Statistical evaluation was conducted using GraphPad Prism software version 6.0. Data are shown of a minimum of three biological replicates or independent experiments. All data are presented as the means ± SD unless otherwise specified. P values < 0.05 were considered to be significant. *P< 0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001****P<0.0001.
We constructed anti-human EGFRvIII CAR incorporating signaling motifs consisting of 4-1BB and CD3ζ sequences, coupled with IL-15 and CCL19 sequences through a P2A oligopeptide (designated as 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR) (Figure 1A). Additionally, we constructed a conventional anti-human EGFRvIII CAR, serving as a control (referred to as EGFRvIII CAR). Upon lentiviral vector transduction of human PBMCs with either EGFRvIII CAR or 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR, transduction efficiencies were approximately 45% and 28%, respectively (Figure 1B). Notably, significant secretion of IL-15 (25.17 ± 2.3 pg/mL) and CCL19 (412.6 ± 17.2 pg/mL) was observed in the supernatant of co-cultures involving EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells and 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells, contrasting with minimal secretion in co-cultures involving EGFRvIII CAR-T cells or untransduced (referred to as UTD) T cells (Figure 1C). P<0.0001, one-way ANOVA was performed to assess differences between groups.
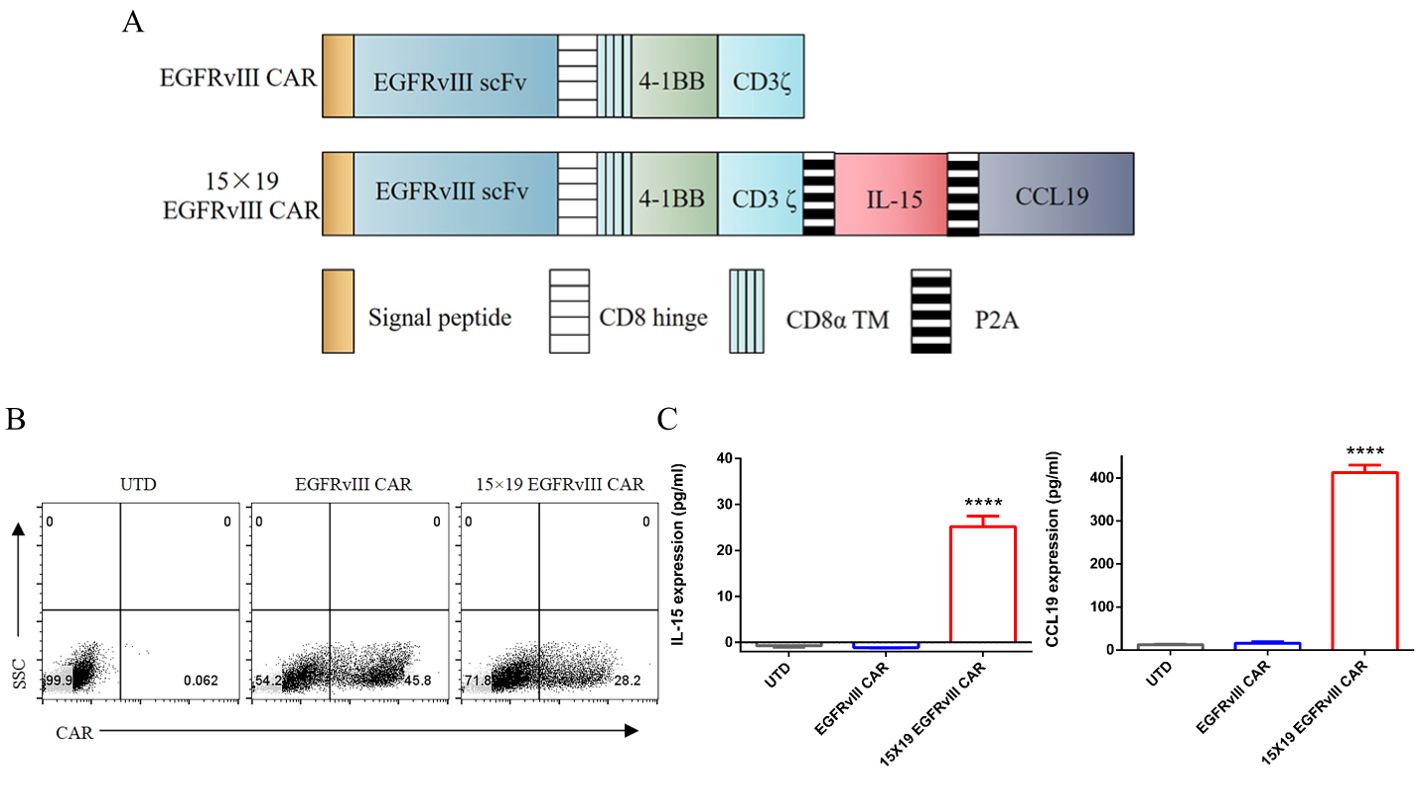
Figure 1. Generation of EGFRvIII specific CAR-T cells secreting IL-15 and CCL19. (A) Schematic representation of the lentiviral vector construction of EGFRvIII specific CAR secreting IL-15 and CCL19. (B) Flow cytometry analysis depicting the transduction efficiency of lentiviral vectors in transduced human T cells. The expression of EGFRvIII specific CAR was determined using the PE-labeled human EGFRvIII protein. (C) UTD T cells and CAR-T cells were co-cultured with target cells for 24 h. The supernatants from these co-cultures were collected for ELISA to measure the levels of IL-15 (left) and CCL19 (right). Each experiment was repeated independently 3 times, and representative data are shown. Data are the means ± SD of 3 independent experiments, ****P<0.0001.
To assess cytotoxic activity, we compared 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells and EGFRvIII CAR-T cells in co-culture with target cells at varying effector-to-target (E:T) ratios. Remarkably, no significant difference in cytotoxic activity was observed between the two groups (Figure 2A). To elucidate the effect of IL-15 on the proliferation of CAR-T cells, we co-cultured EGFRvIII CAR-T cells and 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells with U87 MG cells expressing EGFRvIII that were treated with mitomycin C for five days. Notably, on day 5, the number of CAR+ T cells in the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR group (5.89 ± 0.7 × 106 cells) was significantly higher than that in the EGFRvIII CAR group (4.03 ± 0.8 × 106 cells) (P < 0.05, two-tailed unpaired t-test) (Figure 2B). This represents a 46.2% increase in cell proliferation in the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR group compared to the EGFRvIII CAR group. Furthermore, to assess the chemotactic function of CCL19 secreted by 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells, transwell migration assays were performed. T cells (one day after activation) expressing high levels of CCR7 were in the upper chamber (Figure 2C). Results demonstrated a greater migration of T cells to the lower chamber in the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR group (20.25 ± 1.12 × 104 cells) compared to both the UTD (15.67 ± 0.78 × 104 cells) and EGFRvIII CAR groups (17.14 ± 1.49 × 104 cells) (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Turket’s multiple comparisons test) (Figure 2D, left). However, pre-incubation of T cells and CCR7 antibody for 1 h abolished these differences (Figure 2D, right). Given the role of IL-15 in preventing apoptosis and promoting T-cell survival, we evaluated apoptosis levels among different CAR-T cells. As expected, 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (10.94 ± 4.1%) exhibited lower levels of apoptosis compared to EGFRvIII CAR-T (18.80 ± 0.7%) (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (Figures 2E, F).
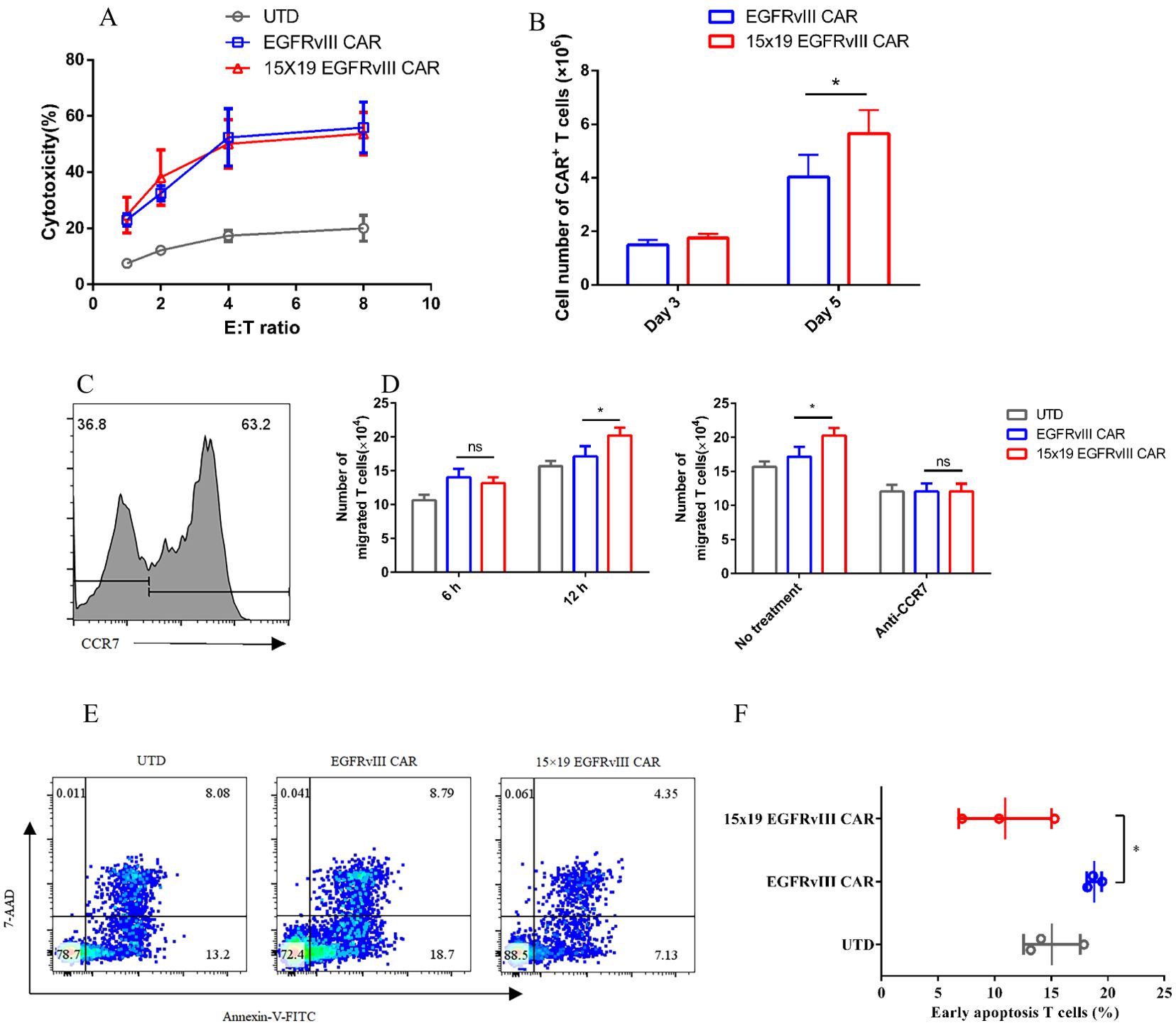
Figure 2. Enhancement of T cell T cells’ proliferation, migration, and anti-apoptosis by 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR T cells. (A) EGFRvIII CAR-T cells, 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells, or UTD T cells, were co-cultured with EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells for 10 h. Subsequently, the cytotoxicity against target cells by UTD T cells and CAR-T cells was analyzed. (B) Co-cultures of EGFRvIII CAR-T cells and 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells with mitomycin C-treated EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells were conducted. The absolute number of CAR+ T cells was measured using precision count beads via flow cytometry on days 3 and 5. (C) Human CCR7 expression on T cells was analyzed on day 1 post-activation using flow cytometry. (D) CAR-T cells were stimulated with mitomycin-C-treated EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cell for 24 h. The supernatant was then transferred to the lower chambers, while T cells were placed in the upper chambers. Migration of T cells to the lower chamber was quantified after 6 and 12 h (E, F). The percentage of apoptotic T cells was detected by flow cytometry on day 15. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate independent experiments, *P < 0.05.
Given the pivotal role of T cell differentiation status in their persistence and anti-tumor efficacy (22), we detected the differentiation phenotype of CAR-T cells upon antigen stimulation (co-cultured with mitomycin C-treated EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells). The findings revealed that a greater proportion of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells exhibited the CD45RO+CCR7+ central memory T cells (TCM) phenotype compared to EGFRvIII CAR-T cells. The findings revealed that the proportion of CD45RO+CCR7+ central memory T cells (TCM) in 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (8.03 ± 1.0%) was 4.7-fold higher than that in EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (1.70 ± 0.5%) (P < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired t-test) (Figure 3A). Additionally, we investigated the expression levels of inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1, TIM-3, and LAG-3, which are known to promote T-cell dysfunction and exhaustion upon activation (11). Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated that the expression of TIM-3 on 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (6.50 ± 2.4%) was significantly lower than that on EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (14.90 ± 4.4%), P < 0.05 (Figure 3B). Although the expression levels of PD-1 and LAG-3 did not significantly differ between the two CAR-T cell types, 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells displayed a trend toward lower expression. Specifically, the expression of PD-1 was 12.68 ± 3.3% in 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells compared to 16.47 ± 3.3% in EGFRvIII CAR-T cells, while the expression of LAG-3 was 3.49 ± 0.9% in 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells compared to 10.28 ± 3.2% in EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (Figures 3C, D).

Figure 3. Phenotypic features of 15 × 19 CAR-T cells. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of CAR-T cells’ differentiation phenotype upon antigen stimulation, delineating subsets including naive (CD45RO-CCR7+), TCM (CD45RO+CCR7+), and TEM (CD45RO+ CCR7-) T cells. The expression levels of TIM-3 (B), PD-1 (C), and LAG-3 (D) were determined by flow cytometry. Data are presented as means ± SD from three independent experiments, and one-way ANOVA is used for comparison of phenotypic features of CAR-T cells. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001; ns, not significant.
We investigated the anti-tumor effects of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells in an orthotopic model of human GBM. Immunodeficient NCG mice received intracranial injections of EGFRvIII+ U87 MG-Luc cells on day 0. Subsequently, CAR-T cells or UTD cells were administered via the tail vein on day 8. Tumor growth was monitored using in vivo imaging with the IVIS system (Figure 4A). Treatment with both EGFRvIII CAR-T and 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells effectively inhibited the growth of the intracranial tumors. Notably, the tumor regression efficacy of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells significantly outperformed that of EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (tumor growth data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA) (Figures 4B, C). Specifically, treatment with 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells resulted in complete tumor regression in 100% of the mice on day 16 (8 days post-CAR-T cells), the mean bioluminescence signal was 3.38×105 ± 25216 p/s, exhibiting rapid tumor eradication, while the mean bioluminescence signal of EGFRvIII CAR-T cells was 1.93 ± 1.4×109 p/s (P< 0.05, two-tailed unpaired t-test) (Figure 4D). In contrast, among EGFRvIII CAR-treated mice, one out of four (25%) succumbed to the disease by day 20, and the remaining mice (3 of 4, 75%) did not achieve tumor regression until day 30, which was 14 days slower than observed with 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells. Notably, no significant reduction in mouse body weight was observed in the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cell-treated group (Supplementary Figure S1). Survival times were recorded for each group of mice (Figure 4E). Thus, our results underscored the promising therapeutic potential of 15× 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells in the orthotopic model of human GBM.

Figure 4. Anti-tumor effects of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells in human GBM orthotopic xenograft models. (A) Schematic representation of the in vivo anti-tumor experiment. NCG mice were intracranially injected with EGFRvIII+ U87 MG-Luc cells and subsequently treated with intravenous injections (i.v) of CAR-T cells or UTD T cells (n = 4). (B) Assessment of tumor growth using the IVIS system at different time points. (C) Calculations of total flux (p/s) using Living Image software at different time points. (D) Calculation of total flux (p/s) in the CAR-T cells group on day 16. Error bars denote SEM, *P<0.05. (E) The percentage survival per group was determined and is represented in a Kaplan–Meier survival curve.
To explore the mechanisms underlying the accelerated tumor regression observed with 15 × 19 CAR−T cells, we conducted analyses on the number and phenotypes of TILs five days after the injection of CAR-T cells. Remarkably, the number of TILs retrieved from the mice treated with 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (61.61 ± 15.7 cells/mg) was approximately four times higher than those from the mice treated with EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (14.76 ± 5.3 cells/mg) (Figure 5A). These findings indicate that 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells promote infiltration of T cells by secreting both IL-15 and CCL19. Furthermore, we observed a significant downregulation of TIM-3 expression in TILs from the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR group, consistent with the in vitro findings (Figure 5B). Notably, there was a higher proportion of effector memory T cells (TEM) in the TILs of mice treated with 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (77.37 ± 2.0%) compared to those treated with EGFRvIII CAR-T cells (64.4 ± 2.1%) (Figures 5C, D). Additionally, single-cell suspensions of spleen, bone marrow, and peripheral blood were prepared to evaluate the persistence of CAR-T cells on day 63, the end of the experiments. We observed that, compared with the EGFRvIII CAR group (419.2 ± 136.5 cells), the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR group (17464 ± 6103 cells) exhibited significantly higher number of CD3+CAR+ T cells in the spleen, with a trend towards greater numbers in peripheral blood and bone marrow (Figure 5E). Hence, based on the current findings, we propose a schematic representation to depict the potential mechanisms through which IL-15 and CCL19 augment the functionality of CAR-T cells within the tumor microenvironment (Figure 5F). These results indicated that 15 × 19 CAR-T cells not only demonstrated superior anti-tumor activity but also exhibited enhanced persistence, both in terms of quantity and quality.
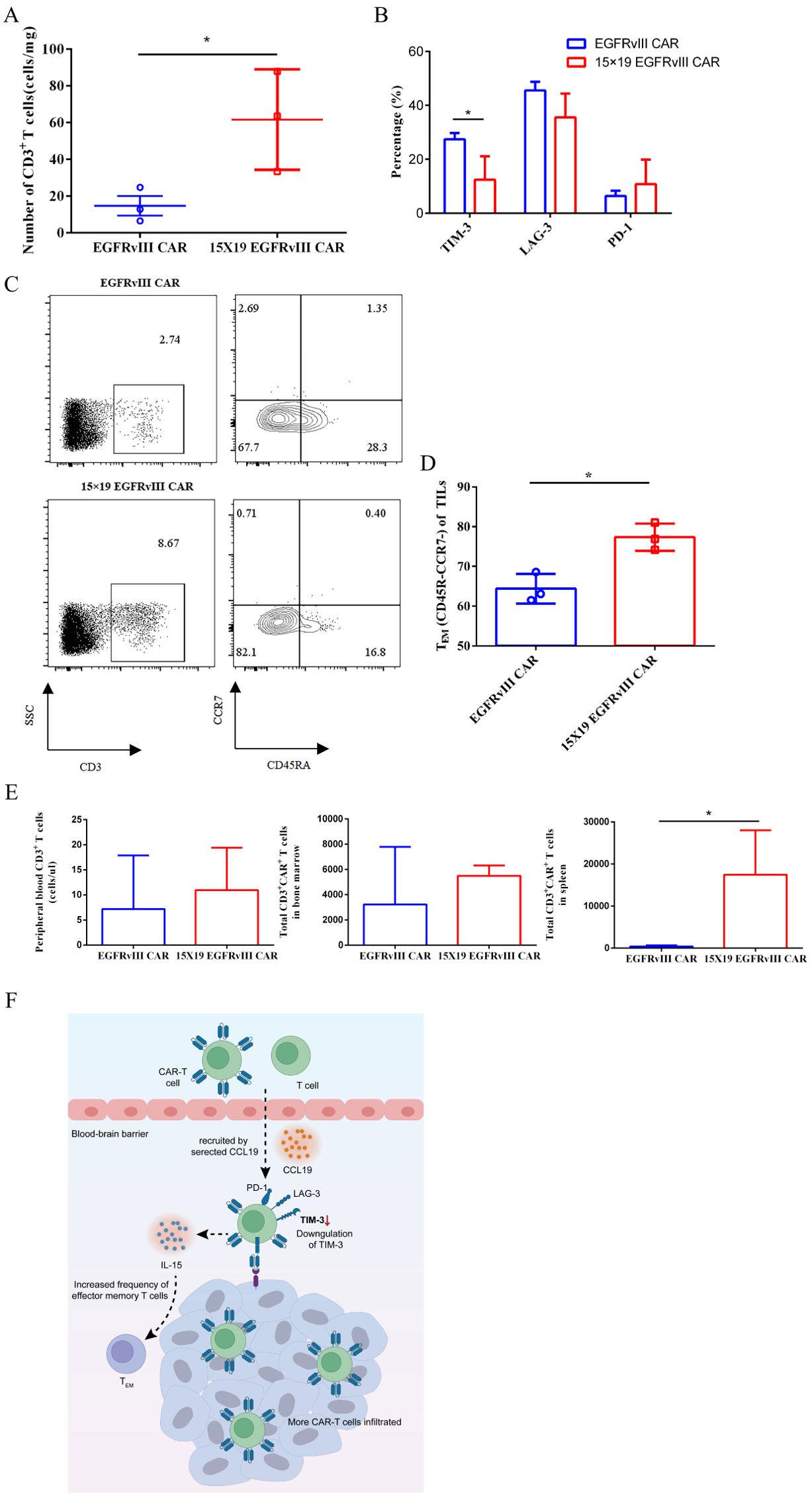
Figure 5. Mechanistic analyses of accelerated tumor regression of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR−T cells in human GBM orthotopic xenograft model. NCG mice were intracranially implanted with EGFRvIII+ U87 MG-Luc cells on day 0, followed by i.v. injections of EGFRvIII CAR−T or 15 × 19 CAR-T cells on day 8. On day 13 (5 days post-CAR-T cell injection), mice were euthanized, and tumor masses were extracted to obtain single-cell suspensions for flow cytometric analysis. Expression levels of human CD3, EGFRvIII specific CAR, TIM-3, PD-1, and LAG-3 were examined. (A) The number of T cells at the tumor site following treatment with both types of CAR-T cells were shown. (B) The expression levels of TIM-3, PD-1, and LAG-3 of TILs were assessed. (C) Representative flow cytometric images depicting the percentage of T cells in tumor mass and the percentage of effector memory T cells (TEM, CD45RA-CCR7-) among T cells. (D) Histogram illustrating the percentage of TEM cells within TILs. (E) On day 63 (at the end of experiments), mice were euthanized, and single-cell suspensions were prepared from blood, spleen, and bone specimens for flow cytometry analysis to determine the number of CAR-T cells in vivo. (F) The schematic provides a depiction of the proposed mechanisms through which 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR−T cells augment their anti-tumor efficacy within the TME. * P<0.05.
Numerous studies have focused on augmenting CAR-T cells with IL-15, which has been shown to enhance CAR-T cells expansion and maintain a phenotype believed to potentiate their in vivo anti-tumor activity. This modification has also been associated with reduced expression levels of exhaustion-associated molecules by CAR-T cells within the tumor microenvironment (23–28). Additionally, the unique challenges posed by the blood-brain barrier in GBM necessitate innovative approaches for CAR-T cell delivery to tumor sites. Recognizing these challenges, we adopted a strategy of co-loading CAR-T cells with IL-15 and CCL19, expecting that this approach would facilitate the migration and infiltration of CAR-T cells into the tumor site while also supporting their sustained expansion and anti-tumor functionality within the TME. In this study, we engineered CAR-T cells directed against EGFRvIII to secret human IL-15 and CCL19 and assessed their anti-tumor efficacy against GBM in an orthotopic mouse model. The results demonstrated a significant enhancement in the anti-tumor efficacy of CAR-T cells armed with IL-15 and CCL19, characterized by more robust and rapid tumor control. Analysis of TILs indicated that the enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells was partly attributable to their enhanced ability to infiltrate and/or proliferate within the tumor site. These cells exhibited a greater proportion of TEM cells and demonstrated resistance to exhaustion within the TME.
The unfavorable immunosuppressive TME imposed constraints on T cell expansion, leading to dysfunction or anergy, a phenomenon also observed in CAR-T cells (29, 30). Previous studies have demonstrated that IL-15 can inhibit the apoptosis of T cells and improve T cell survival (15). Consistent with these findings, the results indicated that IL-15 promoted the proliferation of CAR-T cells and prevented the apoptosis of CAR-T cells in vitro. Additionally, we observed a greater presence of T cells in tumor tissue in the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells group. IL-15 has also been shown to reduce the expression level of exhaustion-associated molecules, especially TIM-3 (23, 26). Our results corroborated these findings, revealing lower expression levels of exhaustion-associated molecules in 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells compared to EGFRvIII CAR-T cells, both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, we hypothesized that the enhanced tumor control demonstrated by 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells may be due in part to the enhanced proliferation capacity and their resistance to exhaustion within the TME.
Furthermore, IL-15 plays an important role in the generation, maintenance, and reactivation of naive T cells, effector, and memory T cells (17). Therefore, we assessed the phenotype of CAR-T cells secreting IL-15 and CCL19 in response to antigen stimulation in vitro. Our results revealed that, following antigen stimulation, 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells displayed a greater proportion of TCM cell subsets. The phenotype of CAR-T cells has been shown to be a critical determinant of clinical efficacy (22, 31, 32). Evidence suggests that infusion of less differentiated CAR-T cells leads to increased in vivo expansion, prolonged persistence, and enhanced anti-tumor efficacy (33–35). TCM, characterized by increased proliferative potential (36) and greater retention in vivo, are considered ideal candidates for CAR-T cell therapy (37). Therefore, we propose that the enhanced tumor control observed with 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells in the orthotopic xenograft model may be partly attributed to the introduction of IL-l5, resulting in a less differentiated and more functionally viable phenotype of CAR-T cells cultured in vitro. However, the absence of a rechallenge model restricts the capacity to establish conclusive evidence regarding this issue.
GBM is identified as “intracranial neoplasms,” presents a formidable challenge for systemically administered CAR-T cells. These cells must navigate through the blood circulation, traverse the blood-brain barrier, and penetrate the stiffen tumor-associated extracellular matrix (ECM) before encountering tumor cells (38). Previous studies have highlighted the role of CCL19 in promoting immune cell migration and infiltration to tumor sites (39, 40). Consistent with these findings, our observations demonstrated that CCL19 promoted T cell migration in vitro, and we observed an increased presence of TILs in the 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cell-treated group in animal experiments. However, elucidating whether the observed increase in TILs was attributable to the migratory properties of CCL19 or the expansion-inducing effects of IL-15 warrants further investigation, possibly through real-time observation of CAR-T cell distribution experiments (41).
While a previous study introduced IL-15 and CCL19 into CAR-T cells and evaluated the anti-tumor effects using a zebrafish xenotransplantation model (42), mouse xenograft models remain the gold standard for preclinical evaluation of CAR-T cell therapy. Thus, to our knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of IL-15 and CCL19-producing CAR-T cells using a mouse orthotopic xenotransplantation model. Our findings reveal the promising potency of 15 × 19 CAR-T cells for clinical application.
In summary, the study represents the first demonstration that CAR-T cells expressing human IL-15 and CCL19 can promote therapeutic efficacy against GBM using a human GBM orthotopic mouse xenograft model. While further exploration is needed to elucidate the detailed mechanisms underlying the enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of 15 × 19 CAR-T cells and to ensure their safety, our current results are encouraging and provide evidence for the clinical development of 15 × 19 EGFRvIII CAR-T cells for GBM and cancers positive for EGFRvIII expression.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Quanzhou Medical College. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
WC: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LH: Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation. SL: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Software, Writing – review & editing. NX: Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Resources. CY: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software. NZ: Writing – review & editing, Project administration. YX: Writing – review & editing, Project administration. WL: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. YH: Writing – review & editing. MC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Quanzhou City (2023NS089), Startup Fund for scientific research of Fujian Medical University (2019QH1014) and Tcelltech Biological Science and Technology Inc. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
We thank Dr. Cavenee from University of California for providing EGFRvIII+ U87 MG cells and WT U87 MG. We thank Professor Xu and Dr. Huang for helpful discussions. We also thank Dr. Wu for his technical support in animal experiments.
Author NX was employed by the company Tcelltech Biological Science and Technology Inc.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1539055/full#supplementary-material
1. Yuan B, Wang G, Tang X, Tong A, Zhou L. Immunotherapy of glioblastoma: Recent advances and future prospects. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2022) 18:2055417. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2055417
2. Majd NK, Dasgupta PR, de Groot JF. Immunotherapy for neuro-oncology. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2021) 1342:233–58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-79308-1_7
3. Ou A, Yung WKA, Majd N. Molecular mechanisms of treatment resistance in glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 22:351. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010351
4. Labanieh L, Majzner RG, Mackall CL. Programming CAR-T cells to kill cancer. Nat BioMed Eng. (2018) 2:377–91. doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0235-9
5. Oved JH, Barrett DM, Teachey DT. Cellular therapy: Immune-related complications. Immunol Rev. (2019) 290:114–26. doi: 10.1111/imr.12768
6. Chmielewski M, Hombach AA, Abken H. Antigen-specific T-cell activation independently of the MHC: chimeric antigen receptor-redirected T cells. Front Immunol. (2013) 4:371. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00371
7. Gross G, Waks T, Eshhar Z. Expression of immunoglobulin-T-cell receptor chimeric molecules as functional receptors with antibody-type specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1989) 86:10024–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10024
8. Jansen JA, Omuro A, Lucca LE. T cell dysfunction in glioblastoma: a barrier and an opportunity for the development of successful immunotherapies. Curr Opin Neurol. (2021) 34:827–33. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000988
9. Mikucki ME, Fisher DT, Matsuzaki J, Skitzki JJ, Gaulin NB, Muhitch JB, et al. Non-redundant requirement for CXCR3 signalling during tumoricidal T-cell trafficking across tumour vascular checkpoints. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:7458. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8458
10. Munn DH, Bronte V. Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Immunol. (2016) 39:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.10.009
11. O’Rourke DM, Nasrallah MP, Desai A, Melenhorst JJ, Mansfield K, Morrissette JJD, et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. (2017) 9:eaaa0984. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa0984
12. Goff SL, Morgan RA, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Robbins PF, Restifo NP, et al. Pilot trial of adoptive transfer of chimeric antigen receptor-transduced T cells targeting EGFRvIII in patients with glioblastoma. J Immunother. (2019) 42:126–35. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000260
13. DeCordova S, Shastri A, Tsolaki AG, Yasmin H, Klein L, Singh SK, et al. Molecular heterogeneity and immunosuppressive microenvironment in glioblastoma. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1402. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01402
14. Guo L, Chen Y, Hu S, Gao L, Tang N, Liu R, et al. GDF15 expression in glioma is associated with Malignant progression, immune microenvironment, and serves as a prognostic factor. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2022) 28:158–71. doi: 10.1111/cns.13749
15. Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA. Interleukin 15: biology and relevance to human disease. Blood. (2001) 97:14–32. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.1.14
16. Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y. The multifaceted regulation of interleukin-15 expression and the role of this cytokine in NK cell differentiation and host response to intracellular pathogens. Annu Rev Immunol. (1999) 17:19–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.19
17. Kokaji AI, Hockley DL, Kane KP. IL-15 transpresentation augments CD8+ T cell activation and is required for optimal recall responses by central memory CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. (2008) 180:4391–401. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.7.4391
18. Marsland BJ, Bättig P, Bauer M, Ruedl C, Lässing U, Beerli RR, et al. CCL19 and CCL21 induce a potent proinflammatory differentiation program in licensed dendritic cells. Immunity. (2005) 22:493–505. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.02.010
19. Cheng HW, Onder L, Cupovic J, Boesch M, Novkovic M, Pikor N, et al. CCL19-producing fibroblastic stromal cells restrain lung carcinoma growth by promoting local antitumor T-cell responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 142:1257–1271.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.12.998
20. Huang B, Luo L, Wang J, He B, Feng R, Xian N, et al. B7-H3 specific T cells with chimeric antigen receptor and decoy PD-1 receptors eradicate established solid human tumors in mouse models. Oncoimmunology. (2020) 9:1684127. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1684127
21. Luo H, Su J, Sun R, Sun Y, Wang Y, Dong Y, et al. Coexpression of IL7 and CCL21 increases efficacy of CAR-T cells in solid tumors without requiring preconditioned lymphodepletion. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:5494–505. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-0777
22. Hinrichs CS, Borman ZA, Cassard L, Gattinoni L, Spolski R, Yu Z, et al. Adoptively transferred effector cells derived from naive rather than central memory CD8+ T cells mediate superior antitumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106:17469–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907448106
23. Chen Y, Sun C, Landoni E, Metelitsa L, Dotti G, Savoldo B. Eradication of neuroblastoma by T cells redirected with an optimized GD2-specific chimeric antigen receptor and interleukin-15. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:2915–24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1811
24. Krenciute G, Prinzing BL, Yi Z, Wu MF, Liu H, Dotti G, et al. Transgenic expression of IL15 improves antiglioma activity of IL13Rα2-CAR T cells but results in antigen loss variants. Cancer Immunol Res. (2017) 5:571–81. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0376
25. Hoyos V, Savoldo B, Quintarelli C, Mahendravada A, Zhang M, Vera J, et al. Engineering CD19-specific T lymphocytes with interleukin-15 and a suicide gene to enhance their anti-lymphoma/leukemia effects and safety. Leukemia. (2010) 24:1160–70. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.75
26. Batra SA, Rathi P, Guo L, Courtney AN, Fleurence J, Balzeau J, et al. Glypican-3-specific CAR T cells coexpressing IL15 and IL21 have superior expansion and antitumor activity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. (2020) 8:309–20. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0293
27. Ataca Atilla P, McKenna MK, Tashiro H, Srinivasan M, Mo F, Watanabe N, et al. Modulating TNFα activity allows transgenic IL15-Expressing CLL-1 CAR T cells to safely eliminate acute myeloid leukemia. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e001229. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001229
28. Shi H, Li A, Dai Z, Xue J, Zhao Q, Tian J, et al. IL-15 armoring enhances the antitumor efficacy of claudin 18.2-targeting CAR-T cells in syngeneic mouse tumor models. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1165404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165404
29. Melero I, Rouzaut A, Motz GT, Coukos G. T-cell and NK-cell infiltration into solid tumors: a key limiting factor for efficacious cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Discovery. (2014) 4:522–6. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0985
30. Kankeu Fonkoua LA, Sirpilla O, Sakemura R, Siegler EL, Kenderian SS. CAR T cell therapy and the tumor microenvironment: Current challenges and opportunities. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2022) 25:69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.03.009
31. Singh N, Perazzelli J, Grupp SA, Barrett DM. Early memory phenotypes drive T cell proliferation in patients with pediatric Malignancies. Sci Transl Med. (2016) 8:320ra3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad5222
32. Sabatino M, Hu J, Sommariva M, Gautam S, Fellowes V, Hocker JD, et al. Generation of clinical-grade CD19-specific CAR-modified CD8+ memory stem cells for the treatment of human B-cell Malignancies. Blood. (2016) 128:519–28. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-683847
33. Blaeschke F, Stenger D, Kaeuferle T, Willier S, Lotfi R, Kaiser AD, et al. Induction of a central memory and stem cell memory phenotype in functionally active CD4+ and CD8+ CAR T cells produced in an automated good manufacturing practice system for the treatment of CD19+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2018) 67:1053–66. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2155-7
34. Gattinoni L, Zhong XS, Palmer DC, Ji Y, Hinrichs CS, Yu Z, et al. Wnt signaling arrests effector T cell differentiation and generates CD8+ memory stem cells. Nat Med. (2009) 15:808–13. doi: 10.1038/nm.1982
35. Sommermeyer D, Hudecek M, Kosasih PL, Gogishvili T, Maloney DG, Turtle CJ, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells derived from defined CD8+ and CD4+ subsets confer superior antitumor reactivity. vivo Leukemia. (2016) 30:492–500. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.247
36. Huster KM, Koffler M, Stemberger C, Schiemann M, Wagner H, Busch DH. Unidirectional development of CD8+ central memory T cells into protective Listeria-specific effector memory T cells. Eur J Immunol. (2006) 36:1453–64. doi: 10.1002/eji.200635874
37. Wang X, Popplewell LL, Wagner JR, Naranjo A, Blanchard MS, Mott MR, et al. Phase 1 studies of central memory-derived CD19 CAR T-cell therapy following autologous HSCT in patients with B-cell NHL. Blood. (2016) 127:2980–90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-12-686725
38. Wang C, Sinha S, Jiang X, Murphy L, Fitch S, Wilson C, et al. Matrix stiffness modulates patient-derived glioblastoma cell fates in three-dimensional hydrogels. Tissue Eng Part A. (2021) 27:390–401. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2020.0110
39. Adachi K, Kano Y, Nagai T, Okuyama N, Sakoda Y, Tamada K. IL-7 and CCL19 expression in CAR-T cells improves immune cell infiltration and CAR-T cell survival in the tumor. Nat Biotechnol. (2018) 36:346–51. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4086
40. Goto S, Sakoda Y, Adachi K, Sekido Y, Yano S, Eto M, et al. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of IL-7/CCL19-producing human CAR-T cells in orthotopic and patient-derived xenograft tumor models. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2021) 70:2503–15. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02853-3
41. Espie D, Donnadieu E. CAR T-cell behavior and function revealed by real-time imaging. Semin Immunopathol. (2023) 45:229–39. doi: 10.1007/s00281-023-00983-7
Keywords: CAR-T cells, glioblastoma, IL-15, CCL19, cancer immunotherapy, EGFRv III
Citation: Chen W, Hong L, Lin S, Xian N, Yan C, Zhao N, Xiao Y, Liao W, Huang Y and Chen M (2025) Enhanced anti−tumor efficacy of “IL−15 and CCL19” −secreting CAR−T cells in human glioblastoma orthotopic xenograft model. Front. Oncol. 15:1539055. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1539055
Received: 03 December 2024; Accepted: 28 February 2025;
Published: 19 March 2025.
Edited by:
Kavita Arora, Jawaharlal Nehru University, IndiaReviewed by:
Mengyao Wang, Sichuan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Chen, Hong, Lin, Xian, Yan, Zhao, Xiao, Liao, Huang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mingzhu Chen, MjAwODAyNUBxem1jLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.