- Department of Oncology, Bishan Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Background: Esophageal cancer (EC) is associated with a high morbidity and mortality rate. Immunotherapy has demonstrated effective antitumor activity in patients with EC, making it imperative to investigate easily accessible prognostic factors. Consequently, we conducted a meta-analysis to explore the prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in EC patients treated with immunotherapy.
Methods: The literature search was conducted across three databases: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. The primary deadline for literature retrieval was July 2024. Hazard ratio (HR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was utilized to assess the association between NLR or PLR and overall survival (OS) as well as progression-free survival (PFS). Statistical analysis was performed using Review Manager version 5.4 and STATA version 15.0.
Results: The meta-analysis included a total of 16 studies involving 1,481 patients. The results indicated a significant correlation between high pretreatment NLR and poor PFS (HR=1.76, 95%CI:1.38-2.25, p<0.001) as well as poor OS (HR=2.61,95%CI:1.86-3.67, p<0.001). Subgroup analyses based on tumor stage revealed that the association between elevated NLR and poor PFS was only observed in advanced EC patients. Regarding PLR, an increased PLR was found to be indicative of inferior PFS (HR=1.44, 95%CI: 1.20-1.72, p<0.001) and OS (HR=1.72,95%CI:1.08-2.74, p=0.020). However, the sensitivity analyses suggested that the observed increase in PLR lack robustness in terms of its impact on inferior OS.
Conclusion: Elevated NLR and PLR are associated with inferior PFS and OS in EC patients receiving immunotherapy. These findings suggest that NLR and PLR levels hold promise as prognostic biomarkers in clinical practice, offering valuable guidance for personalized immunotherapy strategies.
Systematic Review Registration: PROSPERO https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42024596737.
1 Introduction
The incidence of esophageal cancer (EC) ranks seventh, while its mortality rate ranks sixth in the world. Approximately 70% of cases occur in men. Eastern Asia exhibits the highest regional incidence rates, primarily due to the substantial burden in China (1). The predominant histopathological subtypes encompass esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), with ESCC accounting for approximately 90% of annual cases (2).
The current treatment options encompass multimodality therapy, which comprises the mainstays of surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The latest research findings demonstrated that immunotherapy has yielded substantial survival advantages for the patients diagnosed with EC (3–5), and ESCC was more sensitive to immunotherapy than EAC (6). Among EC patients who underwent resection after receiving neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, CheckMate577 demonstrated that those who received adjuvant therapy with nivolumab had a significantly longer disease-free survival (DFS) compared to those who received placebo (5). For patients with advanced EC, the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy offers a more significant survival advantage compared to chemotherapy alone. In the first-line treatment of advanced EC patients, the efficacy of immunotherapy and chemotherapy has been demonstrated in numerous phase III clinical trials. For example, KEYNOTE-590 found that pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy improved OS and PFS in patients with previously untreated, locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic EC (3). The CheckMate648 study found that the addition of nivolumab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment led to a significantly prolonged OS compared to chemotherapy alone (13.2 vs. 10.7 months; HR=0.74, 99.1% CI: 0.58 to 0.96; P = 0.002) in patients with advanced ESCC. Additionally, the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab as first-line treatment also resulted in a significantly longer OS than chemotherapy alone (median, 12.7 vs. 10.7 months; hazard ratio, 0.78; 98.2% CI, 0.62 to 0.98; P = 0.01) (7). The studies of JUPITER-06, ORIENT-15 and ESCORT-1st have also confirmed that the combination of toripalimab, sintilimab or camrelizumab with chemotherapy leads to significant benefits in OS and PFS (4, 8, 9). In the second-line treatment of advanced EC patients, KEYNOTE-181 revealed pembrolizumab prolonged OS compared to chemotherapy in patients with PD-L1 CPS ≥ 10, while also presenting a reduced incidence of treatment-related adverse events (10). The ESCORT trial and RATIONALE-302 trial demonstrated that second-line camrelizumab and tislelizumab improved OS in patients with advanced or metastatic ESCC compared to chemotherapy (11, 12). Furthermore, in patients with PD-L1 TAP ≥ 10%, tislelizumab demonstrated a statistically significant survival advantage over chemotherapy (12). Therefore, the utilization of immunotherapy is progressively increasing, necessitating the requirement for convenient and cost-effective indicators to assess the prognosis.
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), a systemic inflammatory marker, is determined by the ratio of circulating neutrophil counts to lymphocyte counts. The Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) is a quantitative measure of systemic inflammation, obtained by dividing the circulating platelet count by the lymphocyte count. Previous studies have demonstrated the prognostic role of NLR and PLR in many malignant tumors, such as lung cancer, breast cancer and prostate cancer (13–16). The results of a meta-analysis have demonstrated that raised NLR and PLR are associated with unfavorable OS and PFS in advanced gastric cancer and gastroesophageal junction cancer patients undergoing immunotherapy (17). However, the prognostic significance of NLR and PLR in EC patients treated with immunotherapy remains controversial.
Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the prognostic roles of NLR and PLR in EC patients receiving immunotherapy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
This systematic review and meta-analysis followed the PRISMA guidelines for the reporting of meta-analyses. The literature search was conducted across three databases: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. The primary deadline for literature retrieval was July 2024. The search strategy employed the following terms: (“Esophageal neoplasms” OR “Esophageal cancer” OR “Carcinoma, Esophagus”) AND (“NLR” OR “PLR” OR “neutrophil” OR “platelet”) AND (“immunotherapy” OR “PD” OR “checkpoint” OR “pembrolizumab” OR “nivolumab” OR “atezolizumab” OR “ipilimumab” OR “avelumab” OR “durvalumab” OR “camrelizumab” OR “tislelizumab” OR “Sintilimab”). The specific retrieval strategy is detailed in Supplementary Text S1.
This meta-analysis was registered in the PROSPERO network with the following ID: CRD42024596737.
2.2 Exclusion and inclusion criteria
The included studies met the following criteria: (a) patients with EC who received immunotherapy were included, regardless of treatment line; (b) investigation was conducted to determine the prognostic significance of baseline NLR or PLR in relation to OS or PFS; (c) the 95% confidence interval (CI) and hazard ratio (HR) could be obtained from the original studies; (d) publication in English literature was required.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (a) systematic reviews, case reports, abstracts, letters, and expert opinions; (b) populations of patients with other primary tumors; (c) studies lacking sufficient data to conclude on the HR and 95% CI; (d) literature with Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) scores below 6; (e) non-English publications.
2.3 Literature’s data extraction and quality validation
Two authors independently extracted the following information from all eligible studies: The first author’s name, the year of publication, period of study, median follow-up (months), study design, country, sample size, pathological category, cut-off values, survival data (PFS or OS), and hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The HRs from the multivariate analysis were initially extracted when both multivariate and univariate analyses were conducted. In this meta-analysis, we employed the median value of NLR or PLR cut-off from the studies included to determine subgroup analysis cut-off values.
We assessed the quality of the literature involved based on the scoring system of the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) (18). The NOS encompasses three key components: patient selection, comparability, and outcome assessment. The studies rated 6 or higher were deemed to possess high quality. Studies with lower scores were considered low quality and thus excluded from the analysis.
2.4 Statistical analysis
HRs and their corresponding 95% CIs were pooled employing the generic inverse variance and random effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins I2 model. Significant heterogeneity was indicated when the values of I2≥50% and p<0.05, in which case a random-effects model was employed. Conversely, studies that did not exhibit significant heterogeneity were evaluated using a fixed-effects model. Subgroup analyses were also conducted to investigate potential factors influencing the prognostic significance of NLR and PLR. Subsequent sensitivity analyses were conducted to identify the sources of heterogeneity and evaluate the stability of the results. Egger’s test and funnel plots were conducted to assess potential publication bias, where a value of p<0.05 was considered a statistically significant difference. The statistical analysis was conducted using Review Manager version 5.4 and STATA version 15.0.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search and study characteristics
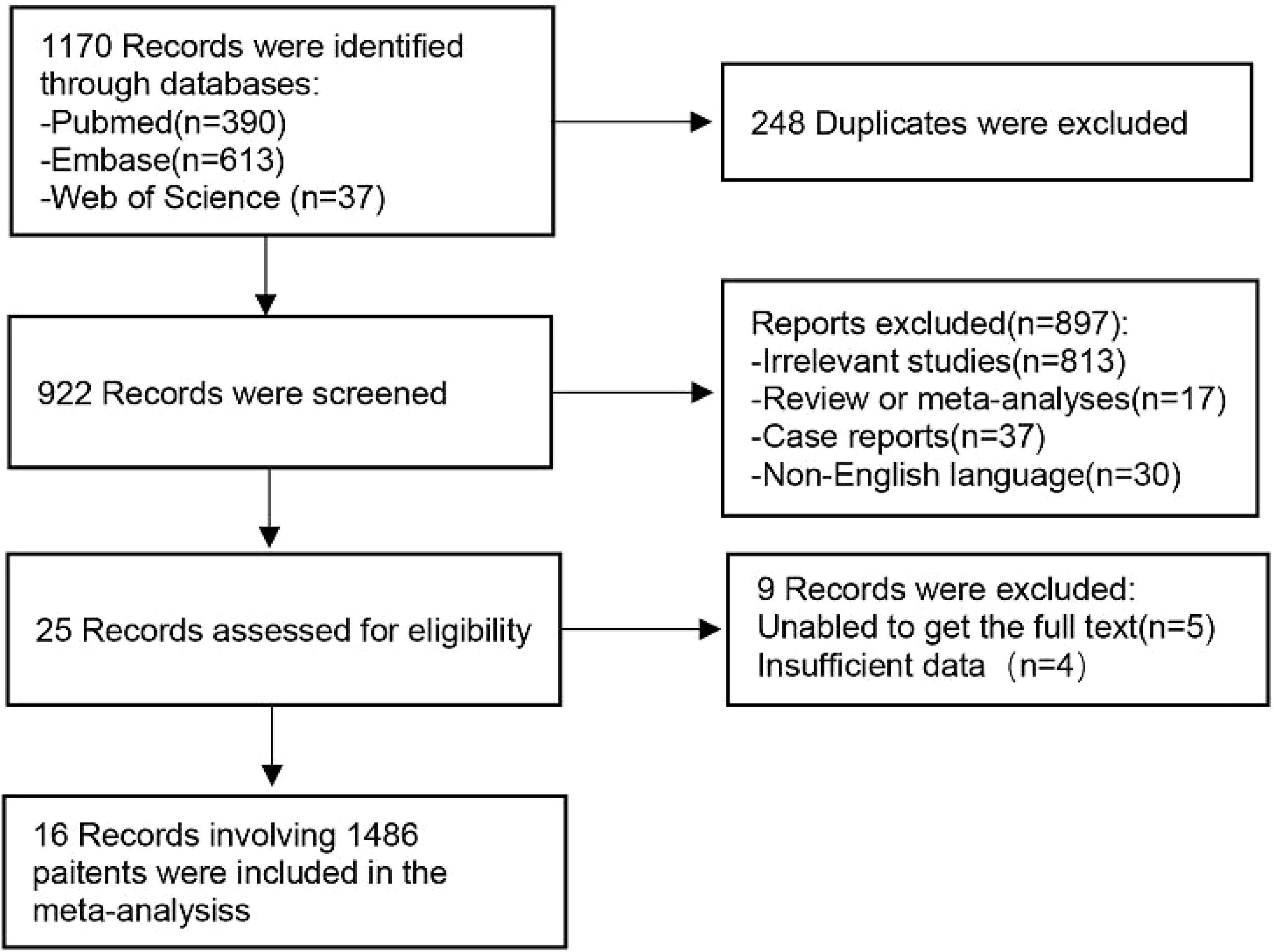
A total of 1170 articles were retrieved from the three databases. After removing duplicate entries, a preliminary screening based on titles and abstracts was conducted for 922 articles, out of which 897 were deemed irrelevant to the subject matter under review. Subsequently, a thorough examination of the full texts of the remaining 25 studies was performed, resulting in the exclusion of 9 studies according to our predefined exclusion criteria. Ultimately, this systematic review comprised 16 selected studies (19–34). The selection process is summarized in Figure 1.
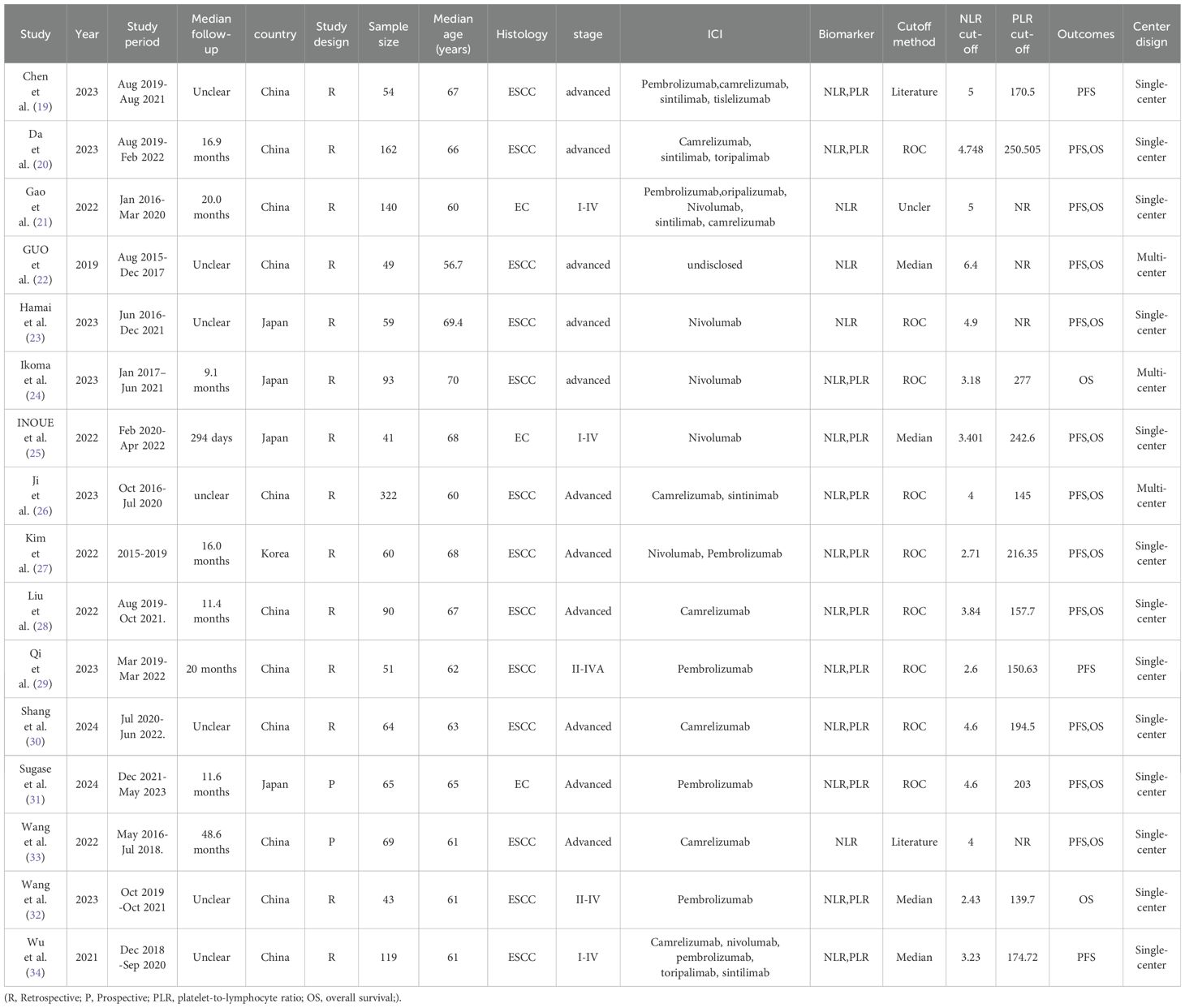
The primary characteristics of the studies included in the meta-analysis are presented in Table 1. In summary, the sample sizes of the cases ranged from 41 to 322 across these studies, which were all published between 2019 and 2024. 13 studies focused on patients diagnosed with ESCC, whereas the remaining 3 studies encompassed patients with various histological subtypes. The study conducted by Gao et al. analyzed data from 140 patients, with 130 (92.86%) diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, 4 (2.86%) with adenocarcinoma, and 6 (4.29%) with an unspecified histological subtype. Inoue et al.’s study included 41 patients, of whom 38 (92.68%) were diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma. Sugase et al. examined data from 65 patients, comprising 62 cases (95.38%) of squamous cell carcinoma and 3 cases (4.62%) of adenocarcinoma. Among the included studies, 4 focused solely on NLR, while 12 evaluated both NLR and PLR. The meta-analysis comprised sixteen NLR studies with a total of 1481 cases and twelve PLR studies with a total of 1164 cases. All the studies were conducted in Asia, including 11 studies in China, 4 studies in Japan, and 1 study in Korea. The quality assessment using NOS scores revealed that the involved literature demonstrated high quality, with scores ranging from 7 to 9 among the sixteen studies. Detailed information regarding the quality assessment can be found in Supplementary Table S1.
3.2 Influence of NLR on PFS
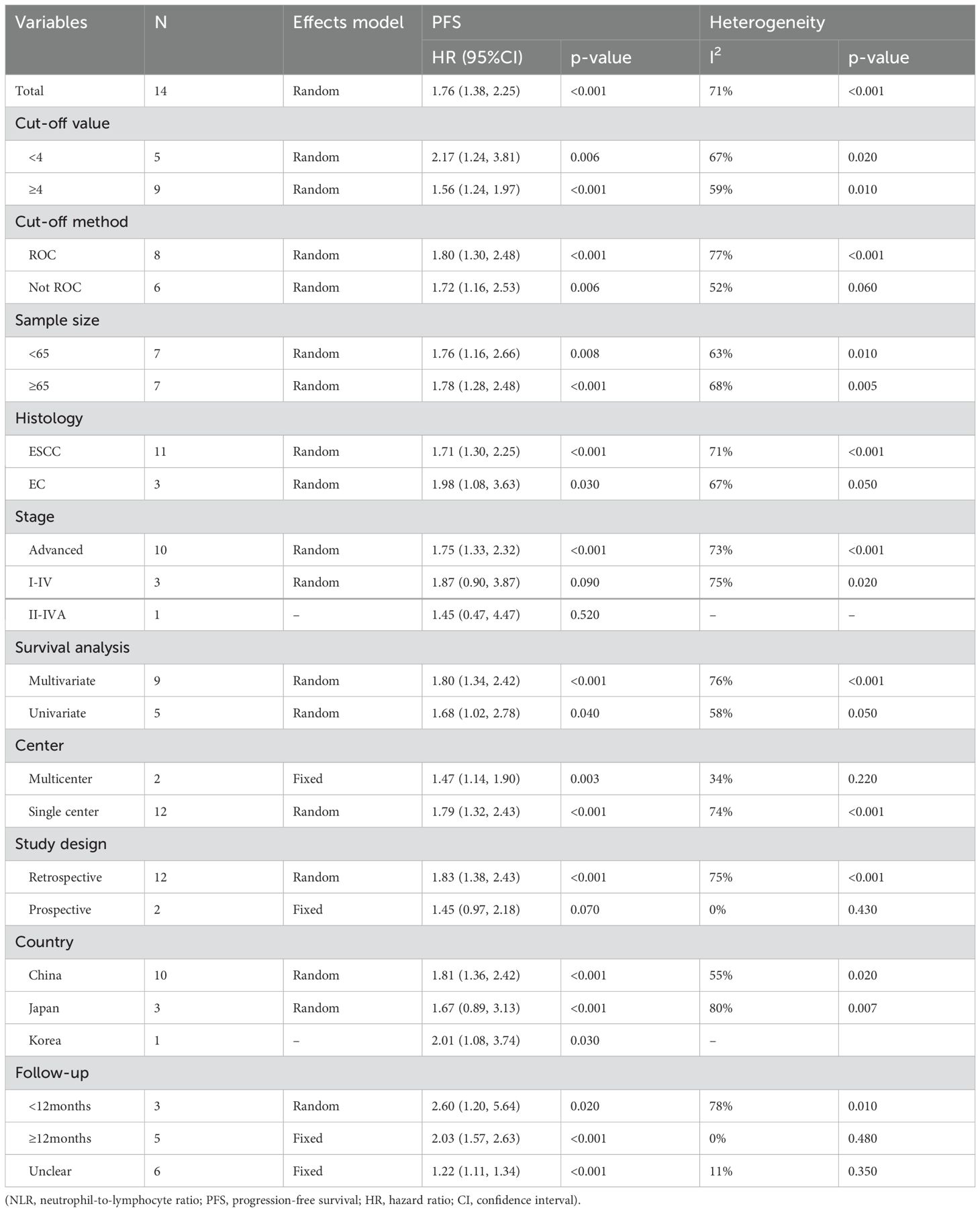
14 studies reported the correlation between NLR and PFS (Figure 2A). The results indicated that elevated NLR was significantly associated with poor PFS outcomes (HR=1.76, 95%CI:1.38-2.25, p<0.001). Due to substantial heterogeneity observed among the included studies (I2 = 71%, p<0.001), a random-effects model was employed for meta-analysis. In the subgroup analyses of tumor stage, a significant association between elevated NLR and poor PFS was observed only in advanced EC. The subgroup analyses, as presented in Table 2, demonstrated no association between elevated PLR and unfavorable PFS within subgroups characterized by prospective study, and geographical origin from Japan.
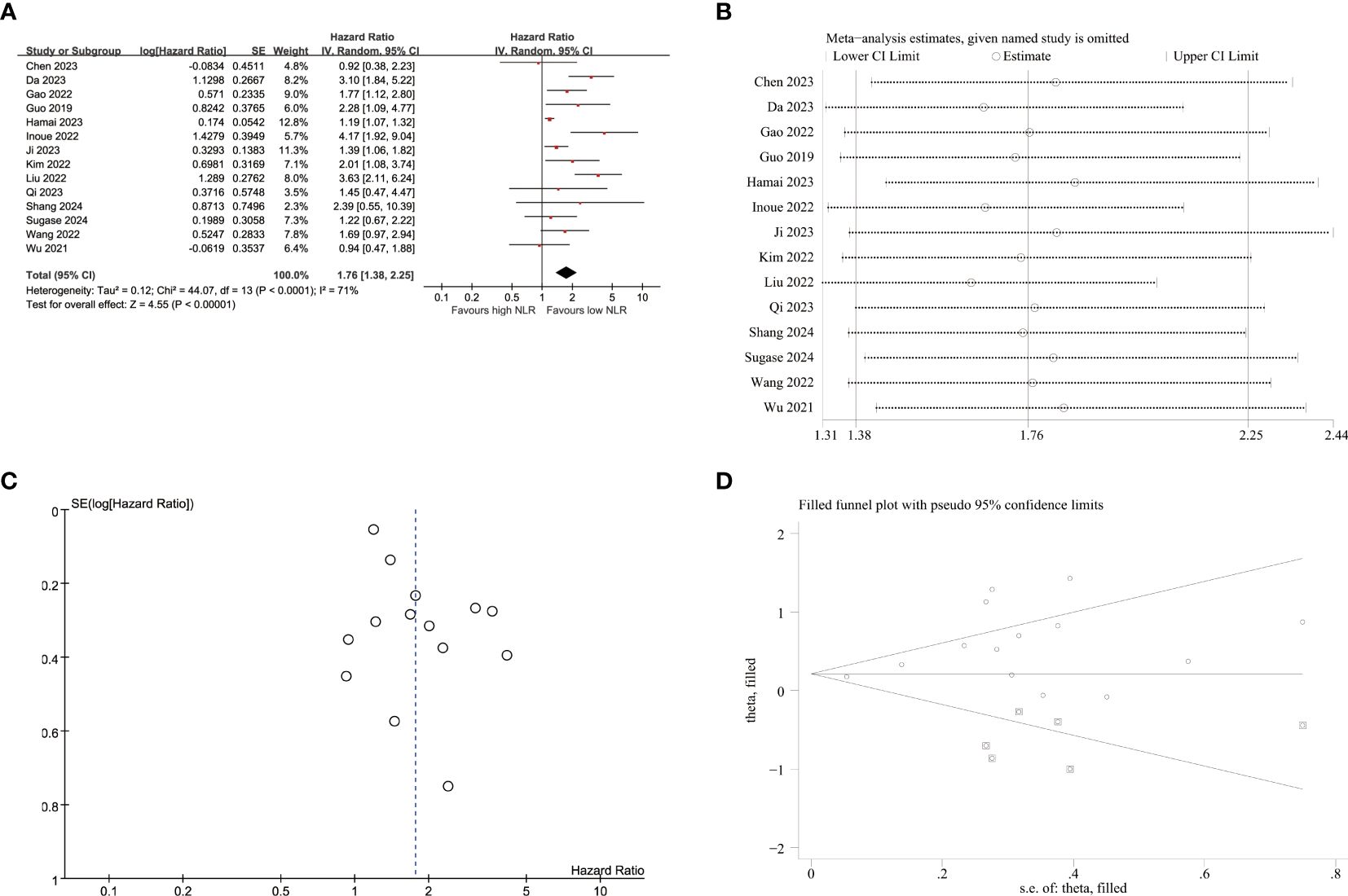
Figure 2. Pooled analyses of the association between pro-treatment NLR and PFS in EC patients. (A) Forest plot of the correlation between NLR and PFS. (B) Sensitivity analysis for PFS after excluding each study. (C) Funnel plot of publication bias regarding PFS. (D) Funnel plot adjusted by the trim and fill method regarding PFS.
Sensitivity analyses were conducted to assess the impact of individual studies on the relationship between NLR and PFS (Figure 2B; Supplementary Table S2). These analyses revealed that exclusion of any single study did not result in statistically significant changes regarding the influence of NLR on PFS outcomes. However, upon excluding Hamai et al.’s study, a notable decrease in heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 55%, p=0.009), yielding a pooled HR estimate of 1.86(95%CI:1.45-2.40, p<0.001).
3.3 NLR’s impact on OS
A total of 13 studies were included in the analysis to investigate the impact of NLR on OS, revealing high heterogeneity (I2 = 83%, p<0.001). Therefore, a random-effects model was employed, yielding a pooled hazard ratio (HR) of 2.61 (95% CI:1.86–3.67, p<0.001). These findings demonstrated that elevated NLR was significantly associated with worse OS in patients with EC (Figure 3A). Furthermore, apart from tumor stage II-IV, robust associations were confirmed between increased NLR and poor OS across all the subgroups, thus ensuring the reliability of our findings as presented in Table 3.
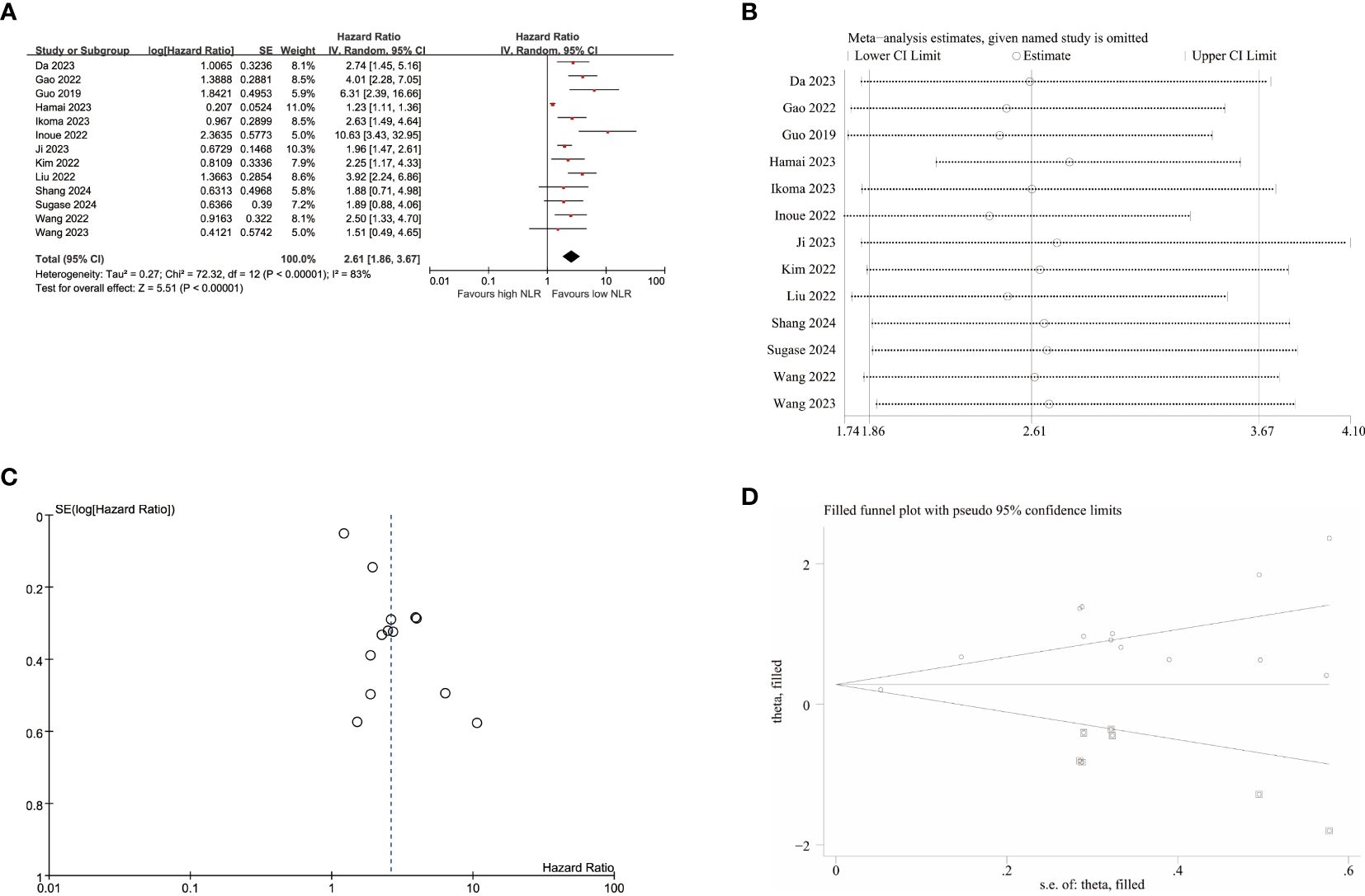
Figure 3. Pooled analyses of the association between pro-treatment NLR and OS in EC patients. (A) Forest plot of the correlation between NLR and OS. (B) Sensitivity analysis for OS after excluding each study. (C) Funnel plot of publication bias regarding OS. (D) Funnel plot adjusted by the trim and fill method regarding OS.
Subsequently, sensitivity analyses were conducted to explore potential sources of heterogeneity for OS (Figure 3B; Supplementary Table S3), indicating that exclusion of any single study did not have a statistically significant impact for NLR’s influence on OS in this meta-analysis. After excluding the studies of Hamai et al, heterogeneity decreased to some extent (I2 = 43%, p=0.05), resulting in a merged HR of 2.79(95% CI:2.17-3.59, p<0.001).
3.4 Effect of PLR on PFS
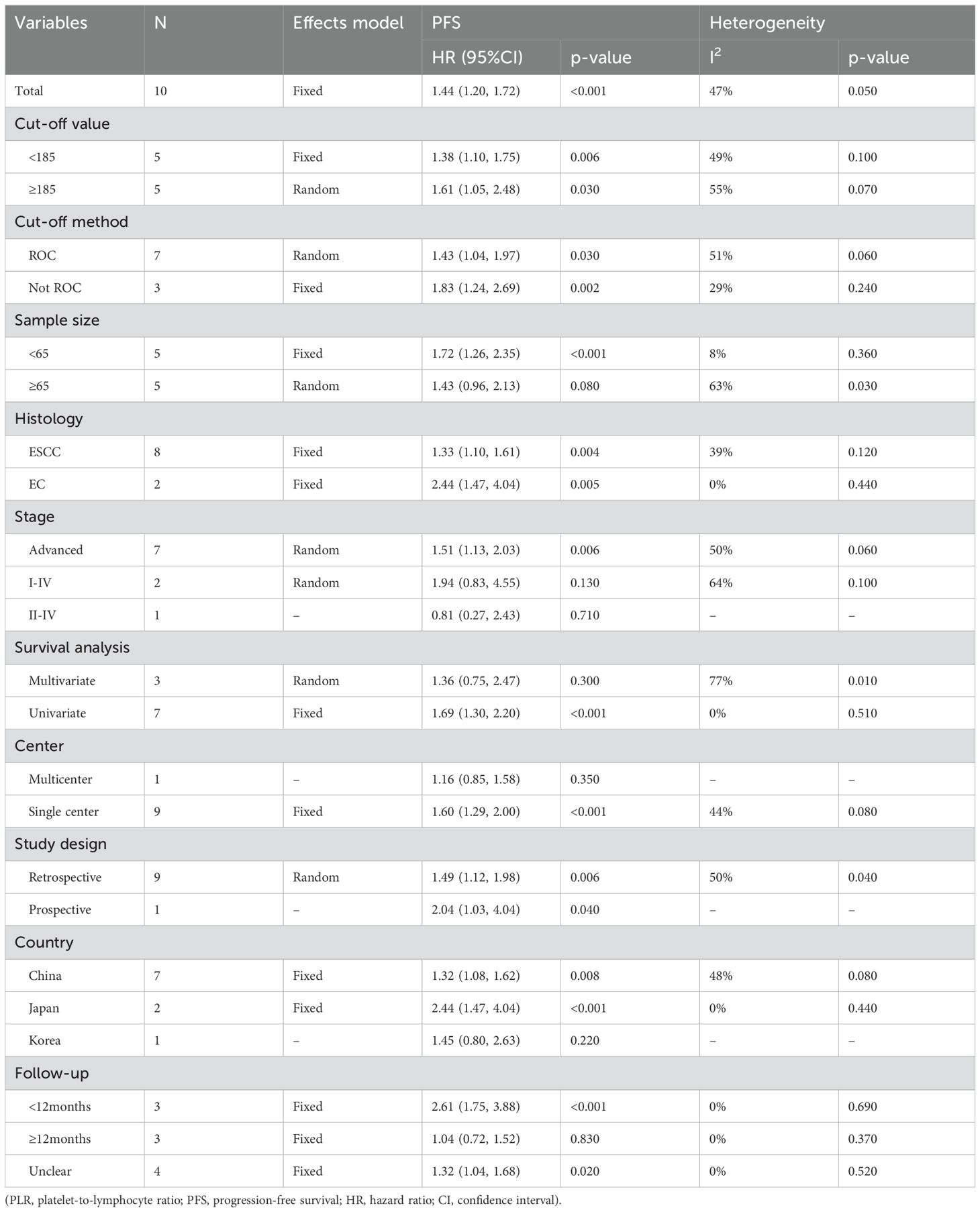
10 studies were included in the analysis of the correlation between PFS and PLR (Figure 4A), employing a fixed-effects model due to low heterogeneity (I2 = 47%, p=0.050). The pooled results demonstrated a significant association between elevated PLR and poorer PFS (HR=1.44, 95% CI:1.20–1.72, p<0.001). As listed in Table 4, the subgroup analyses didn’t reveal the significant association between elevated PLR and poor PFS in subgroups with sample size≥65, tumor stage of I-IV and II-IV, multivariate survival analysis, multicenter studies, study conducted in Korea and follow-up duration≥12 months.
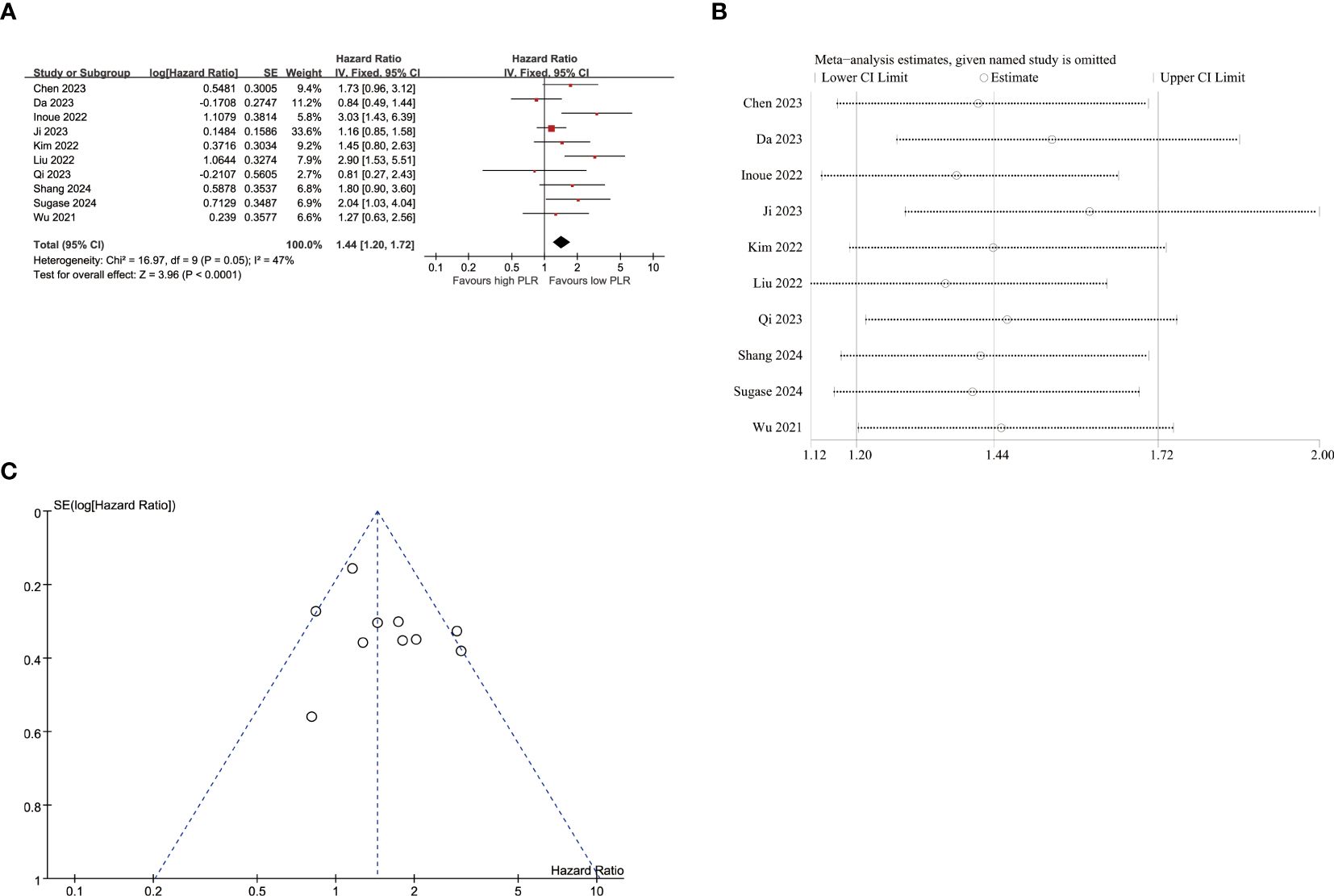
Figure 4. Pooled analyses of the association between pro-treatment PLR and PFS in EC patients. (A) Forest plot of the correlation between PLR and PFS. (B) Sensitivity analysis for PFS after excluding each study. (C) Funnel plot of publication bias regarding PFS.
Sensitivity analyses were performed to evaluate the impact of individual studies on the association between PLR and PFS (Figure 4B; Supplementary Table S4). These analyses demonstrated that exclusion of any single study did not lead to statistically significant changes in terms of the influence of NLR on PFS outcomes.
3.5 PLR’s influence on OS
The data from 9 studies (Figure 5A) provided evidence on the impact of PLR on OS. A high degree of heterogeneity was observed among these studies (I2 = 73.00%, p<0.001). Consequently, a meta-analysis was conducted using the random-effect model, revealing a significant association between raised PLR and worse OS outcomes (HR=1.72,95%CI:1.08-2.74, p=0.020). The subgroup analyses, as presented in Table 5, demonstrated a significant correlation between elevated PLR and poor OS exclusively within subgroups characterized by cut-off method of not using receiver operating characteristic (ROC), sample size<65, histology of EC, tumor stage of I-IV, single-center study design, retrospective study, study conducted in China and duration of follow-up less than 12 months.

Figure 5. Pooled analyses of the association between pro-treatment PLR and OS in EC patients. (A) Forest plot of the correlation between PLR and OS. (B) Sensitivity analysis for OS after excluding each study. (C) Funnel plot of publication bias regarding OS. (D) Funnel plot adjusted by the trim and fill method regarding OS.
Regarding the sensitivity analyses of OS (Figure 5B; Supplementary Table S5), exclusion of the study conducted by Liu et al. resulted in a partial decrease in heterogeneity (I2 = 59%, p=0.020). However, the combined hazard ratio (HR) didn’t maintain statistical significance upon exclusion of the study conducted by Liu et al. (HR=1.45, 95%CI:0.96-2.18, p=0.020) or Inoue et al. (HR=1.50, 95%CI: 0.97-2.33, p=0.070), suggesting that the observed increase in PLR may lack robustness in terms of its impact on inferior OS.
3.6 Publication bias
The funnel plots exhibited visual asymmetry in terms of the influence of NLR on PFS (Figure 2C) and OS (Figure 3C), suggesting a significant presence of publication bias. This observation was further substantiated by the results obtained from Egger’s test for PFS (p = 0.019) and OS (p < 0.001). Subsequently, trim and fill methods were employed to investigate the impact of publication bias on effect estimates. No statistically significant alterations were observed in the findings (Figures 2D, 3D).
Regarding the influence of PLR on PFS (Figure 4C), the p-values of Egger’s test (p=0.255) did not indicate publication bias, as supported by symmetrical funnel plots upon visual inspection. The absence of publication bias detected by Egger’s test led us to refrain from employing additional trim and fill methods. In terms of the impact of PLR on OS (Figure 5C), the p-values of Egger’s test (p=0.022) revealed significant publication bias, which was evident from asymmetrical funnel plots upon visual examination. Furthermore, employing trim and fill methods once again demonstrated no statistically significant alterations in the results (Figures 5D).
4 Discussion
Esophageal cancer is a prevalent malignancy, and its management has been improved through continuous exploration of the disease and advancements in science and technology. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have demonstrated effective antitumor activity in patients with EC.
The utilization of immunotherapy in esophageal cancer is progressively expanding. However, the efficacy of immunotherapy may not be enhanced in all patients diagnosed with EC. Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) have emerged as biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy (35, 36). But their assessment requires complex and expensive laboratory techniques. Therefore, we need cost-effective, convenient, and rapid predictive biomarkers. Peripheral blood specimens, which exhibit high patient acceptance rates, are easier to obtain in clinical practice. Previous literatures have demonstrated that cancer-related inflammatory indicators, such as NLR and PLR, exhibit prognostic significance in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing immunotherapy (21, 22, 31).
The NLR, determined by the ratio of circulating neutrophil counts to lymphocyte counts, serves as a prognostic indicator for cancer patients (37, 38). Several studies have confirmed that neutrophils contribute to the processes of angiogenesis and immunosuppression (39–41). Coussens et al. revealed that the MMP-9 produced by neutrophils contributes to the carcinogenesis of squamous carcinogenesis (42). Christoffersson et al. demonstrated that the extracellular matrix is degraded by MMP-9 released from neutrophils, leading to the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and promotion of angiogenesis (43). Moreover, the release of Arg-1 from neutrophils leads to the downregulation of CD3ζ chain translation in T cells, thereby contributing to the inhibition of T cell proliferation. This mechanism establishes an immunosuppressive microenvironment that also facilitates cancer growth (44). Neutrophils also contribute to cancer progression by releasing cytokines and growth factors, such as IL-6, TNF, epidermal growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and platelet-derived growth factor (41, 45). The high PLR indicates an elevated platelet count or a reduced lymphocyte count, which may be indicative of tumor recurrence and metastasis. Platelets provides a procoagulant surface that enhances the amplification of cancer-related coagulation, and can be recruited to envelop tumor cells, thereby shielding them from immune responses and promoting cancer growth and dissemination (46). Tao et al. proposed that platelets have been implicated in inducing epigenetic modifications, such as upregulation of oncoproteins within circulating tumor cells, and secretion of potent growth factors may contribute to the promotion of mitogenesis, angiogenesis, and metastatic outgrowth (47). Additionally, numerous clinical and experimental studies have established the crucial role of lymphocytes in the immune response against tumors (48), and lymphopenia is correlated with an unfavorable prognosis in patients with recurrent metastatic EC patients who undergo immunotherapy (49).
In this present study, we conducted a meta-analysis by merging 16 studies on NLR involving 1481 EC cases and 12 studies on PLR involving 1164 EC cases to investigate the prognostic impact of NLR and PLR in patients treated with immunotherapy. The results of our meta-analysis revealed a significant association between elevated NLR and adverse PFS and OS outcomes. Additionally, the study by Wang et al. also corroborated that elevated pretreatment NLR is correlated with poorer outcomes in cancer immunotherapy (50). The prognostic effect of NLR with PFS remained robust in subgroup analyses considering various factors such as cut-off value, cut-off method, sample size, histology, survival analysis, research center and follow-up duration. Despite observing high heterogeneity, the association between increased NLR and poor OS was further supported by all subgroup analyses. These findings further support the reliability of our meta-analysis. Additionally, our combined findings regarding PLR demonstrated that increased PLR was also associated with unfavorable PFS and OS outcomes. This observation aligns with the study by Zhou et al., which demonstrated that lung cancer patients with lower PLR had superior OS and PFS when undergoing immunotherapy (51).The subgroup analyses didn’t reveal the significant association between elevated PLR and poor PFS in subgroups with sample size≥65, tumor stage of I-IV and II-IV, multivariate survival analysis, multicenter studies, study conducted in Korea and follow-up duration ≥12 months. Additionally, the subgroup analyses demonstrated a significant correlation between elevated PLR and poor OS exclusively within subgroups characterized by cut-off method of not using receiver operating characteristic (ROC), sample size<65, histology of EC, tumor stage of I-IV, single-center study design, retrospective study, study conducted in China and duration of follow-up less than 12 months. The combined hazard ratio (HR) didn’t remain significant upon exclusion of the study conducted by Liu et al. or Inoue et al. These findings suggest that the combined outcomes of PLR and OS may lack robustness, potentially due to the limited number of studies included in the meta-analysis. In the subgroup analyses of advanced EC patients undergoing immunotherapy, a significant association was observed between increased NLR and poor PFS as well as OS, while an elevated PLR was found to be linked with inferior PFS. Consistent with these findings, Matsas et al. reported that elevated NLR and PLR were also linked to unfavorable OS and PFS outcomes in patients with advanced gastric cancer (GC) and gastroesophageal junction cancer (GEJC) treated with immunotherapy (17).
As a literature-dependent meta-analysis, several limitations of this study should be acknowledged. Firstly, the majority of included studies were retrospective with small sample sizes, potentially introducing selection bias and influencing the findings. Therefore, it is imperative to conduct more large-scale prospective studies to validate our results. Secondly, only English-language publications were considered in this analysis, excluding non-English studies and unpublished data which may have limited the available evidence for analysis. Thirdly, variations in characteristics such as cut-off value, sample size, tumor stage, survival analysis, and follow-up duration across different studies could contribute to substantial heterogeneity observed in the meta-analysis. Fourthly, we can’t disregard the possibility that non-tumor-related factors might impact patients’ blood markers. Lastly but importantly, there was a lack of standardized cut-off values for NLR or PLR among included studies in this meta-analysis. The range of NLR cut-off values varied from 2.43 to 6.40 while PLR cut-off values ranged from 139.7 to 277 across different studies involved herein, thus limiting clinical applicability and necessitating standardization efforts for NLR and PLR thresholds.
5 Conclusion
Despite its limitations, our meta-analysis found the association between elevated peripheral blood NLR or PLR and inferior PFS and OS in EC patients receiving immunotherapy. These findings suggest that NLR and PLR levels hold promise as prognostic biomarkers in clinical practice, offering valuable guidance for personalized immunotherapy strategies. Future investigations should focus on prospective, multi-center, large-scale studies to validate the results of this meta-analysis and facilitate its integration with other prognostic indicators.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. DQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. JZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Project administration. LS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1536920/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ. Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology. (2018) 154:360–73. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.023
3. Sun JM, Shen L, Shah MA, Enzinger P, Adenis A, Doi T, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet. (2021) 398:759–71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01234-4
4. Lu Z, Wang J, Shu Y, Liu L, Kong L, Yang L, et al. Sintilimab versus placebo in combination with chemotherapy as first line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ORIENT-15): multicentre, randomised, double blind, phase 3 trial. BMJ. (2022) 377:e068714. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-068714
5. Kelly RJ, Ajani JA, Kuzdzal J, Zander T, Van Cutsem E, Piessen G, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab in resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1191–203. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032125
6. Kelly RJ. Emerging multimodality approaches to treat localized esophageal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2019) 17:1009–14. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.7337
7. Doki Y, Ajani JA, Kato K, Xu J, Wyrwicz L, Motoyama S, et al. Nivolumab combination therapy in advanced esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:449–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2111380
8. Wang ZX, Cui C, Yao J, Zhang Y, Li M, Feng J, et al. Toripalimab plus chemotherapy in treatment-naive, advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (JUPITER-06): A multi-center phase 3 trial. Cancer Cell. (2022) 40:277–288.e273. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.02.007
9. Luo H, Lu J, Bai Y, Mao T, Wang J, Fan Q, et al. Effect of camrelizumab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the ESCORT-1st randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2021) 326:916–25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.12836
10. Kojima T, Shah MA, Muro K, Francois E, Adenis A, Hsu CH, et al. Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-181 study of pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in advanced esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:4138–48. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01888
11. Huang J, Xu J, Chen Y, Zhuang W, Zhang Y, Chen Z, et al. Camrelizumab versus investigator’s choice of chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCORT): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:832–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30110-8
12. Shen L, Kato K, Kim SB, Ajani JA, Zhao K, He Z, et al. Tislelizumab versus chemotherapy as second-line treatment for advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (RATIONALE-302): A randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:3065–76. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01926
13. Deng M, Ma X, Liang X, Zhu C, Wang M. Are pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio useful in predicting the outcomes of patients with small-cell lung cancer? Oncotarget. (2017) 8:37200–7. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16553
14. Cao W, Yu H, Zhu S, Lei X, Li T, Ren F, et al. Clinical significance of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in the prognosis of resected early-stage patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Med. (2022) 12:7065–76. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5505
15. Kim JY, Jung EJ, Kim JM, Lee HS, Kwag SJ, Park JH, et al. Dynamic changes of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts breast cancer prognosis. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:1206. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07700-9
16. Huszno J, Kolosza Z, Mrochem-Kwarciak J, Telka E, Jochymek B, Miszczyk L. Role of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte-monocyte ratio and platelets in prognosis of patients with prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. (2022) 24:305. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13425
17. Matsas S, Aguiar PN Jr., Del Giglio A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as biomarkers to prognosticate survival in advanced gastric cancer patients in the era of immunotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastrointestinal Oncol. (2024) 15:33–51. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-808
18. Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The newcastle-ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available online at: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (Accessed 25 April 2022).
19. Chen W, Li D, Bian X, Wu Y, Xu M, Wu M, et al. Peripheral blood markers predictive of progression-free survival in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy as first-line therapy. Nutr Cancer. (2023) 75:207–18. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2022.2123533
20. Da L, Qu Z, Zhang C, Shen Y, Huang W, Zhang Y, et al. Prognostic value of inflammatory markers and clinical features for survival in advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients receiving anti-programmed death 1 treatment. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1144875. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1144875
21. Gao Y, Zhang Z, Li Y, Chen S, Lu J, Wu L, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker in unresectable or metastatic esophageal cancer patients with anti-PD-1 therapy. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:834564. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.834564
22. Guo JC, Lin CC, Lin CY, Hsieh MS, Kuo HY, Lien MY, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and use of antibiotics associated with prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39:5675–82. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13765
23. Hamai Y, Emi M, Ibuki Y, Kurokawa T, Yoshikawa T, Ohsawa M, et al. Ability of blood cell parameters to predict clinical outcomes of nivolumab monotherapy in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. (2023) 16:263–73. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S404926
24. Ikoma T, Shimokawa M, Matsumoto T, Boku S, Yasuda T, Shibata N, et al. Inflammatory prognostic factors in advanced or recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab. Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy. (2023) 72:427–35. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03265-7
25. Inoue H, Shiozaki A, Fujiwara H, Konishi H, Kiuchi J, Ohashi T, et al. Absolute lymphocyte count and C−reactive protein−albumin ratio can predict prognosis and adverse events in patients with recurrent esophageal cancer treated with nivolumab therapy. Oncol Lett. (2022) 24:257–66. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13377
26. Ji S, Zhao C, Liu R, Wang Y, Yang Q, Yang H, et al. A combined immune prognostic index in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 therapy. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:1–12. doi: 10.1177/17588359231174869
27. Kim JH, Ahn B, Hong S-M, Jung H-Y, Kim DH, Choi KD, et al. Real-world efficacy data and predictive clinical parameters for treatment outcomes in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 54:505–16. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.1198
28. Liu J, Gao D, Li J, Hu G, Liu J, Liu D. The predictive value of systemic inflammatory factors in advanced, metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with camrelizumab. OncoTargets Ther. (2022) 15:1161–70. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S382967
29. Qi WX, Wang X, Li C, Li S, Li H, Xu F, et al. Pretreatment absolute lymphocyte count is an independent predictor for survival outcomes for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and pembrolizumab: An analysis from a prospective cohort. Thorac Cancer. (2023) 14:1556–66. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14898
30. Shang H, Chen Y, Wang Q, Yang Y, Zhang J. A correlation evaluation between the peripheral blood index and the prognosis of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with camrelizumab. J Inflammation Res. (2024) 17:2009–21. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S450669
31. Sugase T, Kanemura T, Takeoka T, Matsuura N, Masuike Y, Shinno N, et al. Survival impact of inflammation-based prognostic scores in metastatic or unresectable esophageal cancer treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. J Immunotherapy. (2024) 47:249–57. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000529
32. Wang H-C, Huang X, Chen J, Li Y, Cong Y, Qu B-L, et al. Long-term efficacy and predictors of pembrolizumab-based regimens in patients with advanced esophageal cancer in the real world. World J Gastroenterol. (2023) 29:5641–56. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i41.5641
33. Wang L, Zhu Y, Zhang B, Wang X, Mo H, Jiao Y, et al. Prognostic and predictive impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and HLA-I genotyping in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy. Thorac Cancer. (2022) 13:1631–41. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14431
34. Wu X, Han R, Zhong Y, Weng N, Zhang A. Post treatment NLR is a predictor of response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (vol 21, 356, 2021). Cancer Cell Int. (2021) 21:356–66. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02401-0
35. Doroshow DB, Bhalla S, Beasley MB, Sholl LM, Kerr KM, Gnjatic S, et al. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:345–62. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00473-5
36. Banchereau R, Leng N, Zill O, Sokol E, Liu G, Pavlick D, et al. Molecular determinants of response to PD-L1 blockade across tumor types. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3969. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24112-w
37. Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Seruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocana A, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2014) 106:dju124. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju124
38. Li S, Qian Y, Xie W, Li X, Wei J, Wang L, et al. Identification and validation of neutrophils-related subtypes and prognosis model in triple negative breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:149. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05651-3
39. Jaillon S, Ponzetta A, Di Mitri D, Santoni A, Bonecchi R, Mantovani A. Neutrophil diversity and plasticity in tumour progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 20:485–503. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0281-y
40. Mackey JBG, Coffelt SB, Carlin LM. Neutrophil maturity in cancer. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1912. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01912
41. Xiong S, Dong L, Cheng L. Neutrophils in cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:173. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01187-y
42. Coussens LM, Tinkle CL, Hanahan D, Werb Z. MMP-9 supplied by bone marrow-derived cells contributes to skin carcinogenesis. Cell. (2000) 103:481–90. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00139-2
43. Christoffersson G, Vagesjo E, Vandooren J, Liden M, Massena S, Reinert RB, et al. VEGF-A recruits a proangiogenic MMP-9-delivering neutrophil subset that induces angiogenesis in transplanted hypoxic tissue. Blood. (2012) 120:4653–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-421040
44. Romano A, Parrinello NL, Vetro C, Tibullo D, Giallongo C, La Cava P, et al. The prognostic value of the myeloid-mediated immunosuppression marker Arginase-1 in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:67333–46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12024
45. Jablonska E, Kiluk M, Markiewicz W, Piotrowski L, Grabowska Z, Jablonski J. TNF-alpha, IL-6 and their soluble receptor serum levels and secretion by neutrophils in cancer patients. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). (2001) 49:63–9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11266093.
46. Bambace NM, Holmes CE. The platelet contribution to cancer progression. J Thromb Haemost. (2011) 9:237–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04131.x
47. Tao DL, Tassi Yunga S, Williams CD, McCarty OJT. Aspirin and antiplatelet treatments in cancer. Blood. (2021) 137:3201–11. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003977
48. Nagai S, Abouljoud MS, Kazimi M, Brown KA, Moonka D, Yoshida A. Peritransplant lymphopenia is a novel prognostic factor in recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Transplantation. (2014) 97:694–701. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000437426.15890.1d
49. Zhao Q, Bi Y, Xue J, Liu Y, Zhu J, Qin S. Prognostic value of absolute lymphocyte count in patients with advanced esophageal cancer treated with immunotherapy: a retrospective analysis. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:744. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2669
50. Wang H, Yang R, Liu D, Li W. Association of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with clinical outcomes in cancer immunotherapy: An evidence synthesis from 30 meta-analyses. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 132:111936. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111936
51. Zhou K, Cao J, Lin H, Liang L, Shen Z, Wang L, et al. Prognostic role of the platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in the clinical outcomes of patients with advanced lung cancer receiving immunotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:962173. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.962173
Keywords: esophageal cancer (EC), immunotherapy, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), prognosis, meta-analysis
Citation: Deng M, Qing Y, Qiu D, Sheng Y, Zhou J and Sun L (2025) The prognostic value of pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing immunotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1536920. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1536920
Received: 29 November 2024; Accepted: 22 January 2025;
Published: 14 February 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Mangogna, University of Udine, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Deng, Qing, Qiu, Sheng, Zhou and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lan Sun, c3VubGFuNjIwM0AxNjMuY29t
 Min Deng
Min Deng Yun Qing
Yun Qing Lan Sun
Lan Sun