
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 03 February 2025
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1517995
This article is part of the Research Topic The Role of Circular RNAs and MicroRNAs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential View all articles
Lung cancer (LC) is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer among both men and women, and it stands as the leading cause of cancer-related mortality, characterized by high rates of morbidity and mortality. Among its subtypes, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent and one of the most challenging malignant tumors to treat. To date, various therapeutic approaches, including surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, have been employed in the management of lung cancer; however, due to its aggressive nature, the survival rates remain low. Consequently, exploring novel treatment strategies is of paramount importance. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a large family of non-coding RNAs, play crucial roles in regulating several key biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, inflammation, and apoptosis. Among these, microRNA155(miR-155) is one of the most conserved and versatile miRNAs, predominantly overexpressed in various diseases, including malignant tumors. This review elucidates the biological functions and roles of miR-155 in NSCLC and discusses its potential significance as a therapeutic target for future research directions and clinical applications.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, characterized by high morbidity and mortality rates. In 2021, there were an estimated 2.3 million confirmed cases and 1.8 million deaths. Based on comprehensive staging, the current five-year relative survival rate is approximately 22%. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent histological type, and most cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage. Comprehensive treatment options, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, have been employed for lung cancer management; however, the therapeutic outcomes remain unsatisfactory. The emergence of drug resistance in current lung cancer treatments underscores the urgent need to explore new therapeutic avenues (1–5). Recent epigenetic advancements have opened new pathways for understanding the mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets associated with NSCLC progression and metastasis (6, 7). MiRNAs are a class of endogenous non-coding small RNAs, ranging from 18 to 24 nucleotides in length. Within the nucleus, Drosha, in conjunction with DGCR8 (also known as Pasha), first cleaves the primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) into a miRNA precursor (pre-miRNA) of approximately 70 nucleotides. This precursor is then transported to the cytoplasm via the nuclear export protein Exportin 5(Exportin 5). In the cytoplasm, the loop region of the miRNA precursor is removed by Dicer RNase III and the transactivation response element RNA-binding protein (TRBP), resulting in the formation of a miRNA duplex, from which one strand is discarded to produce a mature miRNA (8–10). Ultimately, by binding to the 3’ untranslated region (3’ UTR) of the target mRNA, miRNAs reduce the levels of proteins encoded by the target mRNA through mechanisms such as mRNA degradation and inhibition of mRNA translation. Consequently, miRNAs regulate gene expression via translation inhibition, mRNA cleavage, and rapid deadenylation of mRNA (11) (See Figure 1).
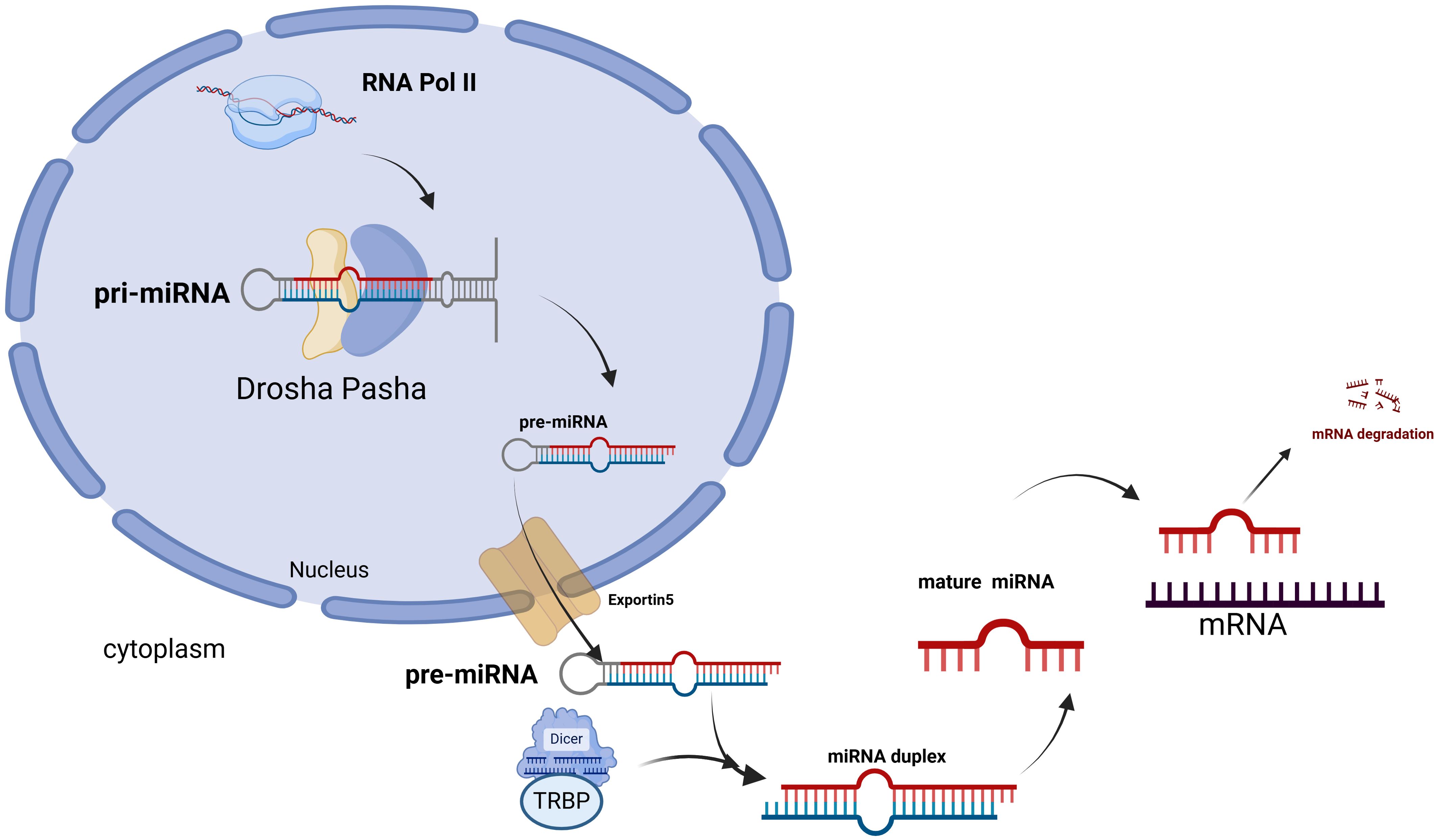
Figure 1. In the nucleus, primary miRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase II, and these molecules are subsequently cleaved by the RNase III enzyme Drosha, along with its cofactor DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCR8, also known as Pasha), to generate single-stranded RNA precursors. These precursors are then transported into the cytoplasm by the nuclear export protein Exportin 5. In the cytoplasm, the loop region of pre-miRNA is cleaved by the RNase III enzyme Dicer and the transactivation response element RNA-binding protein (TRBP), resulting in the formation of a miRNA duplex. Following the discarding of one strand, mature miRNA is produced. Finally, mature miRNA binds to the 3’ untranslated region (3’ UTR) of the target mRNA, which leads to mRNA degradation.
As a member of the microRNA family, miR-155 is processed from the exons of a non-coding RNA known as the B-cell Integration Cluster (BIC) and exhibits strong sequence homology across mammals, indicating that its function is evolutionarily conserved (12). Increasing evidence suggests that miR-155 possesses a distinct expression profile and is involved in various physiological and pathological processes, including cancer, inflammation, hematopoiesis, and immunity (13).
Several studies have indicated that, in addition to its abnormal expression in NSCLC, miR-155 is also implicated in the differential expression observed in various other cancers. This characteristic allows miR-155 to effectively differentiate tumor tissues from normal tissues based on expression levels. For instance, its expression is notably upregulated in a range of human malignancies, including breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and colon cancer, as well as in B-cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (14, 15). Conversely, its expression is downregulated in esophageal cancer (which is associated with a reduced immune response), gastric cancer (16) (where it inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis), and ovarian cancer (where it down-regulates Claudin-1), among others.
In summary, the dysregulation of miR-155 holds significant implications for cancer. Regulating miR-155 expression has emerged as a promising approach for cancer treatment, and investigating the role of miR-155 in the pathogenesis of NSCLC will enhance our understanding. Identifying and targeting key genes involved in NSCLC metastasis and treatment will be crucial for future therapeutic strategies. This study discusses the potential impact of these findings on the clinical management of NSCLC and their relevance to clinical treatment (17–19).
Lung cancer is primarily categorized into two types (See Figure 2): non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases, and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), comprising the remaining 15% (20). NSCLC is the most prevalent subtype of lung cancer and is recognized as one of the most challenging malignancies to treat. This subtype is further classified into three histological categories: adenocarcinoma (AC, LUAD), which represents around 40%; squamous cell carcinoma (SCC, LUSC), accounting for 30%; and large cell carcinoma (LCC), which constitutes about 10% (21). The pathogenesis of NSCLC is highly complex and involves the impaired activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways, including the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K),mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathways. Additionally, mutations in several genes, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic alpha (PIK3CA), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), and Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS), play a significant role in NSCLC development (22). Furthermore, research indicates that the progression of NSCLC is influenced by the tumor microenvironment (TME) (23), which encompasses the tumor itself, adjacent immune cells, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells, extracellular matrix components, and various cytokines. The TME significantly promotes tumor growth, suppresses immune responses, and facilitates tumor invasion and metastasis (24, 25). Despite ongoing advancements in lung cancer treatments and a decline in incidence rates, lung tumors remain a leading cause of death and morbidity worldwide due to late diagnosis and poor prognostic outcomes.
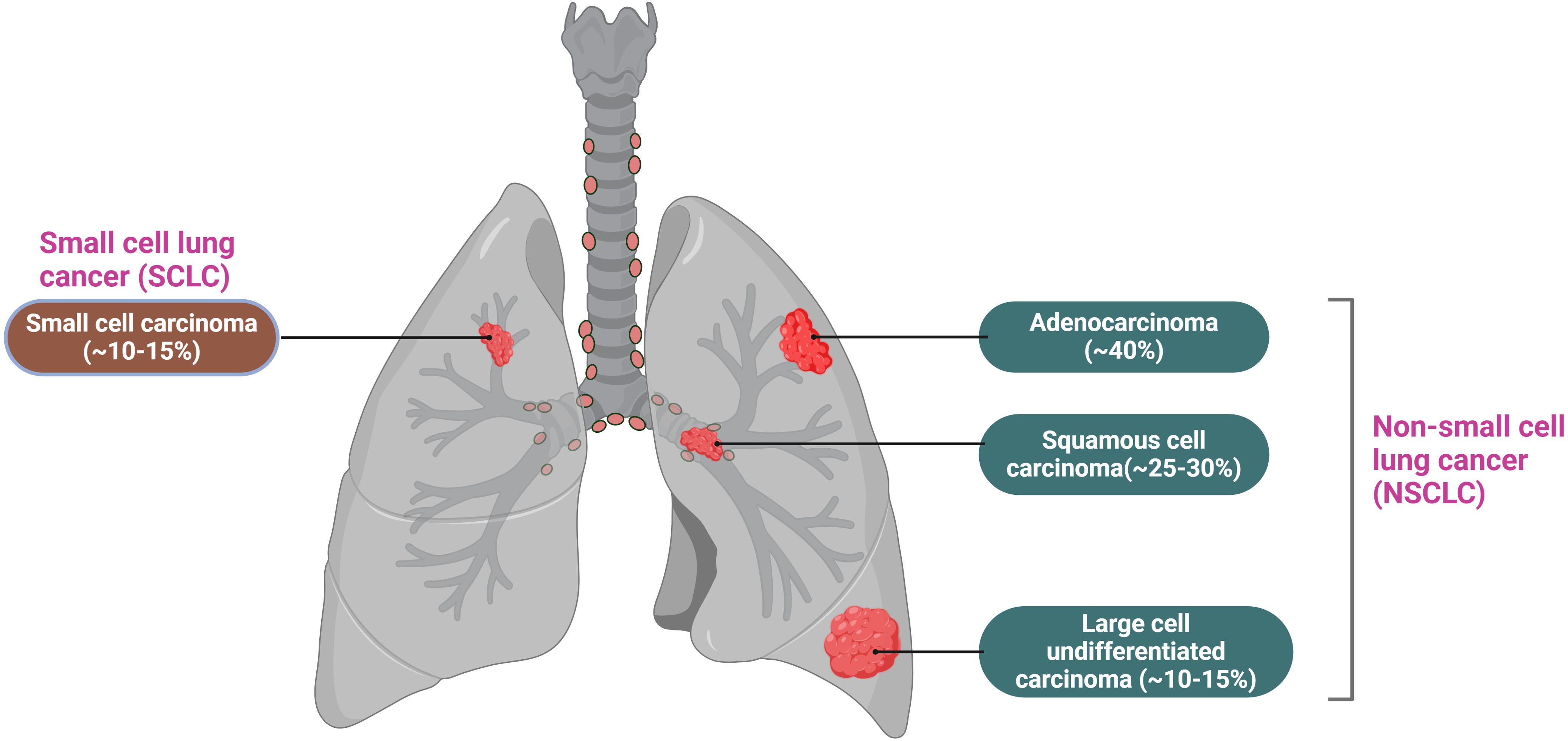
Figure 2. Lung cancer is mainly divided into two types: small cell lung cancer, which accounts for 15%, and non-small cell lung cancer, which accounts for 85%. Among non-small cell lung cancer, it is further classified into adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell undifferentiated carcinoma, accounting for 40%, 25-30%, and 10-15%, respectively.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) can act as either oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes, thus playing a crucial role in regulating tumor progression. A growing body of evidence indicates that miRNAs are significantly involved in various aspects of tumor biology, including proliferation, inhibition, diagnosis, prognosis, and metastasis (26, 27).
Research by Lu et al. (28) demonstrated that the expression patterns of a specific group of cellular miRNAs are altered in cancerous tissues compared to normal tissues. Furthermore, the expression profiles of these miRNAs are associated with both the tumor’s origin and, notably, its differentiation stage. Dysregulation of miRNA expression in cancer can occur through four primary mechanisms: chromosomal abnormalities, genomic mutations and polymorphisms, epigenetic alterations, and disruptions in miRNA biosynthesis (29). Based on their biological roles in cancer, miRNAs can be broadly classified into two categories: tumor suppressor miRNAs and oncogenic miRNAs (See Figure 3). Tumor suppressor miRNAs typically target cellular oncogenes and are often down-regulated in cancer. An example is the let-7 family in lung cancer (30), which inhibits various oncogenes such as Rat Sarcoma (RAS), Myelocytomatosis Viral Oncogene Homolog (MYC), and High Mobility Group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2), thereby reducing the expression of cell cycle proteins (31–35). Another tumor suppressor miRNA, miR-34a, targets oncogenes including MYC and Bcl-2-Associated X Protein(Bax) (36).In contrast, oncogenic miRNAs, such as miR-21, target tumor suppressor genes like Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) and Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4). Following this classification, therapeutic strategies based on miRNAs can be divided into two major subgroups: replacement of the loss of specific miRNAs using miRNA restoration agents such as miRNA mimics, and blocking aberrantly overexpressed miRNAs using inhibiting agents, such as antagomiRs (anti-miRs), miRNA sponges and target protectors (37, 38). In summary, miRNAs play a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes involved in cancer progression. Given their ability to target multiple oncogenic or tumor suppressor signaling pathways, miRNAs hold significant potential as therapeutic agents (39–42).
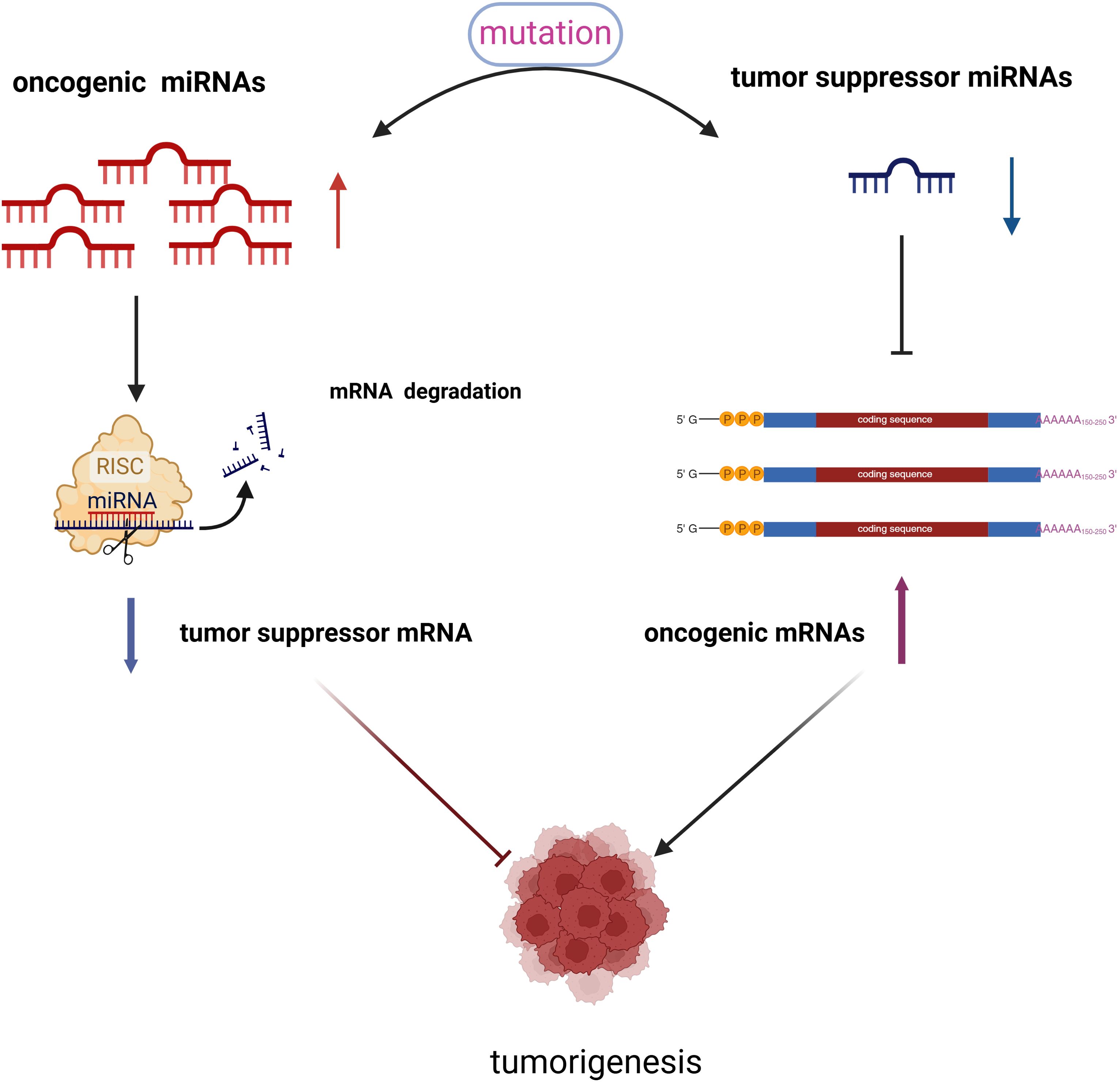
Figure 3. There exists a competitive relationship between oncogenic miRNAs and tumor suppressor miRNAs. When the expression levels of oncogenic miRNAs increase in cells, the expression of certain tumor suppressor genes is inhibited, which occurs through mechanisms such as mRNA degradation or hypermethylation. Consequently, the expression of tumor suppressor miRNAs decreases. Conversely, when the expression of tumor suppressor miRNAs is reduced, the expression of oncogenic miRNAs increases. It is through this interplay that oncogenic miRNAs and tumor suppressor miRNAs collaboratively contribute to the occurrence and progression of tumors.
In recent decades, numerous studies have established that miRNAs function as either tumor suppressors or oncogenic factors, influencing processes from the initial uncontrolled growth of tumor cells to metastasis and angiogenesis. This regulatory role primarily occurs through the modulation of tumor-related signaling pathways (23). Dysregulation of miRNAs can lead to the development of various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, single-gene disorders, and autoimmune diseases, all of which have been linked to the disruption of miRNA function (34). MiRNA plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of NSCLC. These small non-coding RNA molecules are involved in the regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by binding to the 3’ untranslated region (3’ UTR) of target mRNA, which results in mRNA degradation or translational inhibition. In NSCLC, the dysregulation of miRNAs contributes to various stages of cancer development, including initiation, progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. Key miRNAs associated with NSCLC include miR-21 (43, 44), miR-126 (45, 46), miR-155 (47), miR-146a (20), miR-210 and miR-486 (48, 49), miR-182,miR-183 and miR-210 (50), miR-10b and miR-145 (51), miR-340 (52), miR-133b (53), miR-132 (24), miR-106a (25), miR-152 (26), miR- 195 (28), miR- 378 (29), miR- 6713p and miR- 646 (30, 31), miR-223 (54–57), miR-489-3p (58), miR-6884-5p (59), miR-522-3p (60)(See Table 1).
Many recent studies have demonstrated that miR-155 plays a significant role in the occurrence and progression of various solid tumors as well as hematological malignancies. For instance, In breast cancer tissues and plasma or serum, the expression of miR-155 is elevated and shows a negative correlation with the levels of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) (11). Peng et al. suggested that miR-155 promotes bladder cancer growth by inhibiting the tumor suppressor DMTF1 (68). Additionally, Al-Haidari et al. found that miR-155-5p positively regulates CCL17-induced colon cancer by targeting RhoA, thereby enhancing cell migration (69). Fu et al. posited that miR-155-5p inhibits PTEN through the AKT signaling pathway, promoting the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (70). Lei et al. indicated that miR-155 is involved in glioma progression by regulating the expression and function of the caudal-type homeobox 1(CDX1) (71). Furthermore, Charles H et al. observed that the expression levels of miR-155 and miR-21 in activated B cells were higher than those in biochemical center B cells (72). Li et al.indicated that miR-155-5p regulated the development of cervical cancer cells by regulating the expression of TP53INP1 (73). Several researchers have also discovered that by targeting the cytokine signaling inhibitor the suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1(SOCS1), they regulate STAT3-related signaling pathways, ultimately leading to the occurrence and development of cancer (74–76). In 2018, Seto et al. demonstrated that miR-155 simultaneously regulates multiple parallel survival pathways associated with the pathogenesis of mycosis fungoides, including the JAK/STAT, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways (77). Besides, miR-155 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through targeting the PTEN-PI3K/AKT pathway (78). In summary, miR-155 is implicated in the occurrence and progression of various cancers, which suggests its potential utility in exploring novel cancer treatments. While the abnormal expression of miR-155 can serve as a marker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis, as well as an important target for therapy, it is crucial to consider the differential mechanisms of miR-155 across different tumor types. Therefore, we propose that future studies should adopt a combined targeting strategy based on tumor-specific biomarkers, which may enhance the therapeutic effects of anti-miR-155 therapies in conjunction with immunotherapy (79).
MiR-155 is one of the most extensively studied microRNA (miRNA) molecules, with its abnormal expression implicated in a variety of pathological processes. Research indicates that its expression levels regulate pathways associated with fundamental cellular functions, including cell proliferation, invasion, migration, metastasis, drug resistance, and immune responses. Given its broad regulatory potential in key cellular mechanisms in NSCLC, miR-155 is particularly promising for both research and clinical applications (78, 80, 81).
MiR-155 is one of the most conserved and versatile microRNAs, primarily overexpressed in various diseases, including malignant tumors. The overexpression of miR-155 may enhance cell proliferation by downregulating the cell cycle regulator WEE1 and tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1). This downregulation can increase the mutation rate by targeting core components of the DNA mismatch repair mechanism, ultimately leading to the genesis of cancer. A study by Hou et al. demonstrated that the expression of miR-155 is elevated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. The increased levels of miR-155 significantly enhanced the proliferation of A549 cells, reduced the S phase cell population (the DNA replication phase), and increased the G2/M phase cell population (mitosis) (82). Conversely, downregulation of miR-155 expression significantly inhibited cell proliferation, increased the proportion of cells in the S phase, and decreased the proportion of cells in the G2/M phase. Additionally, miR-155 promotes NSCLC cell proliferation through FOXO1 and increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (83). Coincidentally, research by Liu et al. also revealed that miR-155 inhibits proliferation and invasion in NSCLC by directly targeting PDCD4. The expression of the 64-kDa protein PDCD4 is significantly downregulated in various cancers, including colorectal, lung, gastric, and breast cancers, and is thus generally regarded as an important tumor suppressor (84). A recent study has, for the first time, demonstrated the high expression of miR-155-5p and the low expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 9(FGF9) in lung squamous cell carcinoma tissues and cells, revealing a negative correlation between the two. Molecular mechanism experiments indicate that miR-155-5p promotes the proliferation and invasion of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting and negatively regulating FGF9 (85). Additionally, studies by Xue et al. have demonstrated that the Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS1) (86), Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 6 (SOCS6) (87), and Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) (88) are implicated in various human malignant tumors, including NSCLC. Identified as tumor suppressors, miR-21 and miR-155 promote the development of NSCLC by downregulating SOCS1, SOCS6, and PTEN.
MiR-155-5p refers to the mature strand of miR-155, specifically the 5’strand that is processed following the transcription of this gene. MicroRNAs typically exist as two strands: the 5’strand and the 3’ strand. miR-155-5p, being the mature form of the 5’chain, inhibits the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by targeting Smad2 (89).Furthermore, it is posited that the activation of Smad2/3 regulates the expression of target genes, including members of the zinc finger E‐box‐binding homeobox (ZEB) transcription factor family, by binding to Smad4 and translocating to the nucleus, thus contributing to lung cancer progression (90, 91).
The metastatic process is complex and involves interactions between cancer cells and surrounding tissues in the new microenvironment and cellular signaling within the cancer cells. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a biological process in which epithelial cells lose polarity and intercellular adhesion. It is a key step in initiating cancer metastasis (92).In the study conducted by Karina, network analysis of 92 proteins exhibiting differential expression between CL16 cell transplant tumors with high miR-155 expression and control CL16 cell transplant tumors revealed three potential roles for miR-155. The protein expression of target genes ALDH1A1, PIR, and PDCD4 was reduced, indicating that miR-155 inhibits the expression of these proteins, which are known to be involved in metastasis formation. Consequently, these proteins may serve as effectors of altered miR-155 in our model, demonstrating that high expression of miR-155 in cancer cells inhibits extravasation and/or colonization during the later stages of the metastasis process (93). Current research indicates that the RASSF protein plays a significant role in tumor suppression and is involved in various critical biological functions, including proliferation, cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and DNA repair (94). Notably, RASSF4 is widely expressed in normal tissues, whereas its expression is down-regulated in tumors, suggesting that RASSF4 functions as a tumor suppressor in a range of malignant tumors (95). In the study conducted by Li et al., it was found that exosomal miR-155 and miR-196a-5p secreted by M2-type tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in NSCLC metastasis promote NSCLC progression by regulating RASSF4 (92, 93).
In general, the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs is limited in the treatment of lung cancer, and the carcinoma cells may readily develop resistance to the drugs in clinical practice, significantly reducing the therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy. Cisplatin is a chemotherapeutic agent that is commonly used for the treatment of lung cancers, but resistance to cisplatin and its severe toxic side effects limit its clinical application. The apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) may be a target for miR-155. In the cytosol, Apaf-1 can bind with cytochrome c released from the mitochondrial inter-membrane and activate the initiator caspase-9, eventually resulting in cellular apoptosis. BCL2-associated X protein (Bax) is an important factor in destabilizing mitochondrial integrity, serving as an essential gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway (96). Zang et al. postulated that the deregulation of miR-155 expression could modulate the Apaf-1-related mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and enhance the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to cisplatin treatment (97). Doxorubicin targets DNA and topoisomerase II (Topo I I) to inhibit DNA synthesis and transcription, arrest tumor cell growth, and induce apoptosis. Clinical studies have found that doxorubicin, in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs, acts as a treatment for lung carcinoma. LV et al. found that miR-155 suppression inhibited the activation of AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (98). The transcriptional activity of nuclear factor-KB and activator protein-1 were also downregulated Arsenic trioxide (AS203, ATO) has been successfully used in the treatment of relapsed/refractory acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) since the 1970s. Subsequent research by Alice et al. indicated that ATO is cytotoxic to lung cancer cells, with its biological activity linked to oxidative damage, alterations in cell morphology, and apoptosis. In 2017, Gu et al. demonstrated that miR-155 mediates the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2(NRF2) signaling pathway by upregulating resistance to ATO in lung cancer cells; however, its downregulation can lead to increased cell apoptosis (99–101). Additionally, miR-155 is essential in resistance to targeted therapies, such as the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) gefitinib, used to treat lung cancers with activating EGFR mutations. It induces gefitinib resistance by targeting Forkhead Box O3A (FOXO3A) (102, 103). Current research indicates that miR-155 promotes resistance to chemotherapy drugs and can mitigate this resistance when treated with miR-155 inhibitors. This drug resistance is mediated by a novel TP53/miR-155 feedback loop, suggesting that miR-155-targeted therapies hold promise for overcoming the development of drug resistance (104). Notably, the overexpression of miR-155 in tumor cells has emerged as a significant contributor to chemotherapy resistance and is linked to increased invasiveness and poor prognosis in NSCLC. These findings underscore the pivotal role of miR-155 in promoting chemoresistance, highlighting the necessity for targeted strategies in cancer therapy to address this challenge. Furthermore, given that high levels of miR-155 are associated with resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, the therapeutic downregulation of miR-155 is warranted. The current study demonstrates that the overexpression of miR-155 significantly enhances glucose metabolism regulated by hexokinase 2(HK2). Significantly, the inhibition of miR-155 sensitizes lung cancer cells to radiation by disrupting glucose metabolism, thereby clarifying the role of miR-155 in regulating the radiosensitivity of NSCLC cells. In this context, miR-155 inhibitors may represent a promising therapeutic approach to enhance tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiotherapy (105, 106).
One of the most extensively studied microRNAs in tumors and the immune system is miR-155. Research indicates that it plays a complex and significant role in the immune response associated with lung cancer. miR-155 not only enhances the anti-tumor immune response but also regulates the tumor microenvironment by influencing immune escape mechanisms, thereby contributing to the initiation and progression of tumors (107). The anti-tumor immune response refers to the process by which the body’s immune system recognizes and eliminates tumor cells through a series of immune cells, molecules, and mechanisms. miR-155 can significantly influence immune cells by targeting key regulatory molecules and transcription factors that modulate the immune system, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity (108, 109). Among the various immune cell types, miR-155 primarily regulates innate and adaptive immunity mechanisms. Dendritic cells (DCs), as professional antigen-presenting cells, are a crucial link between innate and adaptive immunity due to their unique ability to activate naive T cells (110). In vitro studies have shown that DCs treated with miR-155-rich exosomes produce more IL-12 and IFN-γ, and these cytokines significantly contribute to the anti-tumor activity of DCs (111). In addition,miR-155 was reported to change a “cold tumor” into a “hot one” and thus sensitize the tumor for checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Consequently, miR-155 may facilitate communication between tumors and immune cells, thereby influencing the immune editing process of tumors (112). The potential of miR-155 as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapy efficacy has been reported (113). The mechanism underlying this process may involve the potential of miR-155 to alter the tumor microenvironment, specifically the immune cells present within it. An example of this alteration is illustrated by the repolarization of tumor-infiltrating macrophages (TAMs) (114, 115). Other studies have demonstrated that encapsulating miR-155 within nanomaterials such as sPEG/GLC can repolarize tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) into anti-tumor M1 macrophages. This finding supports the notion that the delivery mechanism of miR-155 represents a promising approach to cancer treatment (115). Immune evasion is an important hallmark of cancer, and a better understanding of this mechanism is essential for developing effective strategies against cancer. Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), also known as B7-H1 or CD274, is expressed in T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and mesenchymal stem cells (116). PD-L1 is also one of the key molecules in mediating tumor immune evasion. PD-L1 expressed in cancer cells could specifically bind to the receptor (PD-1) on the surface of activated T cells in the tumor microenvironment and transmit negative regulatory signals to inhibit T cell activation, proliferation, or cytokine secretion (117–119). Studies have shown that miR-155-5p inhibits PD-L1 gene expression by directly binding to relevant sites in response to cytokine stimulation. This suggests that the interaction between miR-155 and PD-L1 may reveal a novel mechanism for inflammation-related tumorigenesis and highlights the potential therapeutic applications of miR-155-5p and PD-L1 in LUAD (120).
In summary, the function of miR155 can be elucidated through its target genes (See Figure 4). Its expression is regulated by various proteins, primarily at the post-transcriptional level.
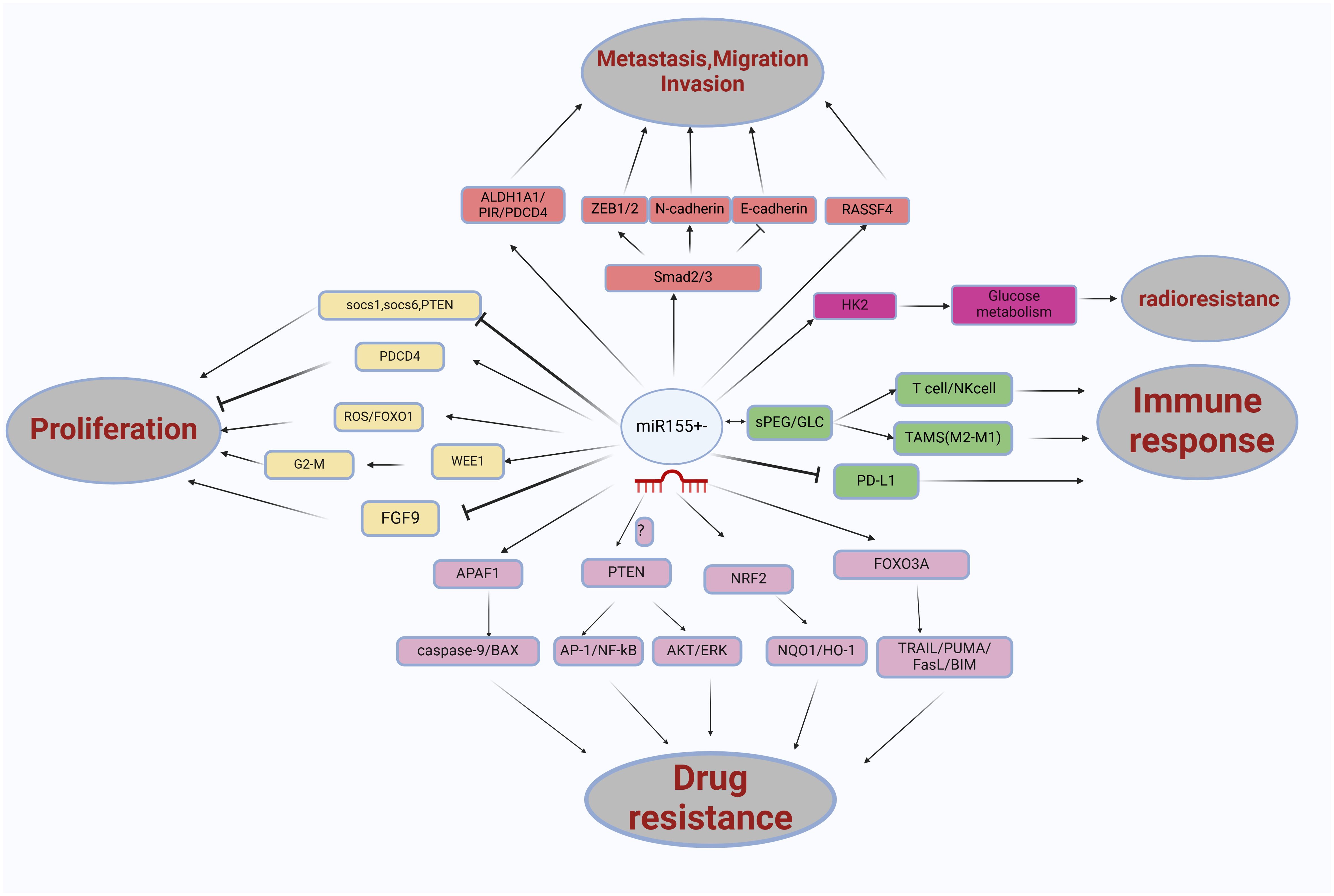
Figure 4. The role miRNA-155 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is multifaceted, involving various pathways and interactions. miRNA-155 influences several key factors, including FOXO1/ROS, WEE1/G2/M, SOCS1/SOCS6/PTEN, PDCD4, FGF9, ALDH1A1/PIR/PDCD4, SMAD2/3, RASSF4, APAF1, NRF2, FOXO3A, PTEN, and nano-encapsulated materials such as sPEG/GLC. These interactions significantly affect glucose metabolism processes, contributing to the proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis, drug resistance, and immune response in NSCLC.
Numerous articles in cancer research have demonstrated the oncogenicity of miR-155. Some studies indicate that miR-155 is essential for activating immune responses, suggesting that inhibiting miR-155 in tumor-associated immune cells may promote tumor immune evasion and enhance tumor growth rather than suppressing it. This notion is supported by evidence showing that the loss of miR-155 in cells within the tumor microenvironment facilitates tumor growth (121, 122). Conversely, many studies have established that cancer cells generate sufficient energy for proliferation through increased glycolysis and mitochondrial dysfunction, known as the Warburg effect. Elevated levels of glycolysis in cancer cells have been linked to resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy (123). Furthermore, radiation has been shown to induce aerobic glycolysis via reactive oxygen species (124). Relevant studies indicate that the inhibition of miR-155 reduces glycolysis, ultimately rendering NSCLC cells more sensitive to radiation. Consequently, miR-155 may be a promising therapeutic target for developing anti-cancer drugs (106, 125). Hou et al.’s study demonstrated that miR-155 promotes the proliferation of NSCLC cells by inhibiting FoxO1 and increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. This finding underscores the miR-155/FoxO1/ROS axis as a novel therapeutic target for inhibiting NSCLC growth. Compared to traditional small molecule drugs, miRNA and mRNA-targeting oligonucleotides offer several advantages, the most significant being their capacity for chemical modification to enhance pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles and their ability to target multiple genes (126) simultaneously. Immunotherapy represents a promising approach for utilizing miR-155 in tumor treatment. Among various strategies, active immunotherapy based on dendritic cells (DCs) is one of the most promising current treatments. Research conducted by Hodge et al. indicated that the overexpression of miR-155 in DCs enhances their capacity to stimulate CD8+ T cell anti-tumor responses (127). Additionally, a study demonstrated that delivering a miR-155 mimic to dendritic cells within the tumor microenvironment of orthotopic ovarian cancer xenografts activated anti-tumor immune responses, inhibited tumor growth, and improved mouse survival (128). Other studies suggest that miR-155 should be down-regulated during treatment, as elevated levels of miR-155 have been linked to cancer resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. In this context, miR-155 inhibitors may represent a novel therapeutic approach to enhance tumor sensitivity to these treatments while also reshaping the tumor’s immune microenvironment, increasing its susceptibility to the immune system and its resistance to immunotherapy (105). In November 2015, a phase I clinical trial was initiated to evaluate the LNA-modified anti-miR-155 antibody MRG-106, which further supports the potential effectiveness of miRNA inhibition in clinical applications and may inspire future developments of anti-miR-155 antibodies for cancer treatment (81). Importantly, given the favorable safety of cobomarsen, a miR-155 inhibitor, reported in phase 1 clinical trial (77). Considering the favorable safety profile reported in phase 1 clinical trials of the miR-155 inhibitor cobomarsen, a subsequent study conducted by researchers from the Department of Medicine at Houston Methodist Research Institute in the United States built upon previous findings published in Cancer. By establishing a multi-scale mechanistic model and calibrating it with in vivo data, the study extrapolated its results to humans, revealing that anti-miR-155 delivered via nanoparticles holds promise for treating non-small cell lung cancer. The findings are detailed: First, in monotherapy, anti-miR-155 administered at 2.5 mg/kg every three weeks demonstrated significant anti-cancer activity, with a median progression-free survival of 6.7 months. Second, in combination therapy, the two-drug regimen of anti-miR-155 and cisplatin resulted in a median progression-free survival of 11.3 months. Furthermore, the three-drug combination therapy comprising anti-miR-155, cisplatin, and pembrolizumab achieved a median progression-free survival of 13.1 months. Notably, the latter combination regimen is regarded as more practical due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness (47). These promising, though early, results with Cobomarsen highlight the value of miR-155 as a therapeutic target and support further research on miR-155 in other diseases and other miRNAs in cancer. Expanded anti-miR-155 therapies could focus on targeting miR-155 in stromal cells of tumors to reduce inflammation in different malignancies. Meanwhile, applying the optimized backbone chemistry from the anti-miR-155 molecule to other anti-miR molecules may accelerate the development of future therapeutics targeting miRNAs.
Preclinical studies indicate that microRNAs (miRNAs) possess significant therapeutic potential in cancer management. However, the silencing of abnormally expressed miRNAs in vivo can be achieved through various nucleic acid analogs, including locked nucleic acids (LNA),2’-O-methyl oligonucleotides (such as antagomiRs), and peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) or nanoencapsulated PNAs. As with most RNA-based therapeutics, these strategies face challenges related to nonspecific organ biodistribution, reticuloendothelial (RES) clearance, and endolysosomal trafficking (129, 130). In a study, they introduce a novel antimiR delivery platform designed to target the acidic tumor microenvironment, evade systemic clearance by the liver, and facilitate cellular entry through non-endocytic pathways. Our findings indicate that linking peptide nucleic acid (PNA) antimiRs to a peptide featuring a low pH-induced transmembrane structure (PHLIP) results in a unique tumor-targetable construct under acidic conditions, such as those found in solid tumors (pH ~ 6). This approach enables antimiRs to effectively cross the plasma membrane and inhibit the miR-155 oncomiR in mouse models of lymphoma (131). Among them, a recent in vivo study showed that we used a 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3phosphocholine (DOPC) liposomal nanoparticle as a delivery vehicle for anti-miR-155 for the treatment of lung cancer, We showed that anti-miR-155-DOPC significantly reduces miR-155 expression in lung tumors and that it resensitizes chemoresistant tumors to chemotherapeutic agents, such as cisplatin. Even though DOPC is used for systemic delivery, we found that it did not induce the immune system or any toxicities in vivo in mice. DOPC nanoparticles containing siRNA against Ephrin A2 (EphA2) are currently being evaluated in a phase I clinical trial for the treatment of advanced, recurrent cancers and seem to have a favorable toxicity profile so far (ClinicalTrials.gov Identified NCT01591356) (104). Based on current research, we summarize the delivery methods of anti-miR-155. Specifically, there are two primary types: local delivery and systemic delivery. Local delivery may be a viable strategy for certain localized tumors, such as lung cancer and skin cancer, as it can reduce systemic toxicity and enhance drug concentration at the tumor site. This method includes the use of nanoparticles, liposomes, and local injections. Conversely, systemic delivery may be more appropriate for tumors that are difficult to locate or for cases involving multiple tumors. This approach encompasses drug-loaded nanoparticles, viral vectors, and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), among others.
Currently, despite an increased understanding of lung cancer and improvements in diagnosis and treatment methods, the disease continues to exhibit a high mortality rate and poor prognosis due to its aggressive nature. As researchers delve deeper into the study of miR-155, alterations in the miRNA sequence may emerge as critical factors in the pathogenesis of various tumors, including lung cancer(See Table 2). Furthermore, the production and expression of several miRNAs in cancer cells are significantly distinct from those in normal cells, indicating that these molecules may contribute to tumor growth, angiogenesis, and immune evasion (135). MiRNAs regulate numerous intracellular signaling pathways and elicit various effects, and they can be categorized based on their influence on tumor suppressor genes and oncogenic miRNAs (oncomirs) (10, 136). Notably, miR-200b-3p has been found to enhance the proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells (137). Additionally, miR-126 and miR-484 function as oncogenes that facilitate the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (138, 139). Conversely, the downregulation of miR-16-5p, which is a tumor suppressor, increases cancer signaling activity (140). In the context of cancer, the role of miRNAs as oncogenes or tumor suppressors is contingent upon the target genes they regulate. For instance, miR-21 is recognized as an oncogenic miRNA that targets tumor suppressor genes such as PTEN and PDCD4 (141), while miR-34a is another oncogenic miRNA that targets oncogenes such as MYC and BCL2 (142). Additionally, miRNAs can enhance cancer cell proliferation and survival by targeting cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and DNA damage response genes. For instance, the miR-17-92 gene cluster, frequently upregulated in various cancers, promotes cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the tumor suppressor gene PTEN (143). Furthermore, specific miRNAs have been demonstrated to regulate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by targeting genes involved in cell-cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization (144). Specifically, miR-200 family miRNAs inhibit EMT by targeting the transcription factors E box-binding zinc finger protein 1 (ZEB1) and ZEB2 (145). Similarly, miRNAs have been implicated in regulating angiogenesis by targeting genes that are part of angiogenic signaling pathways. For example, miR-126 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit 2 (PIK3R2) (146). Moreover, miRNAs can also influence immune responses by targeting genes involved in immune signaling pathways. For instance, miR-155 promotes inflammation by targeting the negative regulators of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) (147, 148). In addition to targeting gene regulation and immunotherapy, miRNA-targeted therapy encompasses various other aspects. For instance, Liu et al. investigated the application of miRNAs to reprogram tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Polarizing these macrophages into M1 macrophages, which possess anti-tumor properties, presents a viable approach for cancer treatment (115). Furthermore, Cubillos-Ruiz et al. intravenously administered miR-155 mimic RNA into tumor-associated dendritic cells (DCs) in vivo (128), demonstrating its ability to inhibit the progression of established ovarian cancer. They propose that enhancing miR-155 levels in TAMs may offer a potential strategy to repolarize these macrophages and mitigate immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment, thereby hindering tumor progression. Similarly, Wang et al. (149) found that the overexpression of miR-155 in breast cancer cells significantly delays tumor progression by increasing the recruitment of effector immune cells to TME. However, Price et al. (150) argue that several biological challenges must be addressed to achieve effective TAM-targeted miRNA therapy: ① specifically targeting TAMs within the tumor microenvironment; ② promoting the uptake and cytoplasmic release of miRNA; and ③ preventing miRNA capture by tumors or other cells. Recently, Hussen et al. highlighted the potential of miRNA-targeted cancer treatment utilizing the CRISPR/Cas (CRISPR-associated protein, Cas) system (151). In cancer research, the CRISPR/Cas system has enhanced our understanding of the non-coding genome, tumor heterogeneity, and previously unrecognized challenges in precision medicine, opening new avenues for exploration. CRISPR/Cas-based gene-editing technology now enables precise and permanent mutation targeting, offering opportunities to target small non-coding RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) (152, 153).
In the ongoing discussion regarding the significant controversies and unanswered questions in the field of miR-155 research, we summarize the discourse from several key perspectives. First, concerning the role of miR-155 in various diseases: Although miR-155 is believed to play a crucial role in immune response and tumorigenesis, its specific function in cancer remains contentious. For instance, in particular cancer types, miR-155 acts as an oncogene; in others, it may serve as a tumor suppressor gene. This is summarized in our article, as illustrated in Table 3. Secondly, we address the relationship between miR-155 and immune response, particularly regarding anti-tumor immunity and immune evasion. Finally, based on the interaction between miR-155-regulated NSCLC and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment, we propose investigating an immunomodulatory nanocarrier targeting miR-155 for treating NSCLC. This vector carries immunomodulatory factors, such as cytokines that promote immune activation or small molecules that inhibit immunosuppressive signaling pathways. On the one hand, these nanocarriers accurately deliver immune regulatory factors to tumor sites, altering the tumor microenvironment’s immunosuppressive state and enhancing immune cells’ cytotoxic activity against lung cancer cells. On the other hand, by inhibiting the expression or activity of miR-155, they can directly influence the malignant biological behavior of lung cancer cells while indirectly modulating immune cell function.
In recent years, the application of miR-155 in tumors and related diseases has emerged as a significant area of research. Dysregulation of gene expression is frequently observed across various types of cancer, significantly influencing cancer progression by modulating the expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), miR-155 interacts with multiple pathways and assumes diverse roles. Understanding the up or down-regulation of different miRNAs concerning disease stages may be crucial. Given that miR-155 plays a pivotal role in regulating the immune system and influencing anti-tumor responses through its effects on various immune cell populations, the role miR-155 in cancer therapy warrants reconsideration in light of emerging therapeutic strategies. The modulation of miR-155 should consider not only the disease’s severity, including tumor stage and grade, but also the immune signatures of both the tumor and the surrounding tissue induced by the disease or its treatment (154–156). Furthermore, the level of miR-155 could serve as a potential marker for assessing the prognosis of NSCLC and evaluating resistance to conventional therapies, thereby providing valuable insights for identifying new therapeutic targets. Given that miR-155 is a key regulator of immune responses in solid tumors, it impacts a variety of immune cells involved in anti-tumor responses, including T cells, natural killer cells, and myeloid cells such as dendritic cells (DCs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Consequently, applying miR-155 in conjunction with immunotherapy may prove advantageous for treating NSCLC. Future research on miRNA in NSCLC should further investigate its effects on tumor angiogenesis, glucose, lipid metabolism, and the maintenance of cancer stem cells. Although studies have incorporated miR-155 into the development of tumor biomarkers and inhibitors with significant potential, these efforts remain in the early stages and warrant ongoing attention. Although the role of miR-155 in NSCLC and other types of cancer is substantial, it remains controversial. Firstly, miR-155 acts as a double-edged sword in tumor development, possessing the ability to both suppress tumors and promote cancer. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in the immune response; however, the specific regulatory mechanisms by which it influences immune cells and the resultant effects are not yet fully understood. The intricate relationships among inflammation, immunity, and cancer involving miR-155 have yet to be verified. Furthermore, given the numerous potential targets of miR-155, there is ongoing debate regarding its primary functional targets. For instance, some studies indicate that miR-155 can target PTEN and regulate pathways such as AP-1/NF-kB and AKT/ERK, thereby influencing tumor immune response. Whether these processes are also implicated in NSCLC necessitates further investigation.
XW: Writing – original draft. WZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XX: Writing – original draft. ZC: Writing – original draft. BC: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. CZ: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Universities in Jiangsu Province (XZSYSKF2023018) and the Scientific Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (Grant No H2023005). The researchers had no relationships with the funder.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Majernikova SM. Risk and safety profile in checkpoint inhibitors on non-small-cel lung cancer: A systematic review. Hum Vaccines Immunotherapeutics. (2024) 20:2365771. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2365771
2. Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, Kwiatkowski DJ, Iafrate AJ, Wistuba II. Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA. (2014) 311:1998–2006. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3741
3. Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Wang Y, Cheng L, Bai Y, et al. Paclitaxel–carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non–small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. (2006) 355:2542–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa061884
4. Altıntop MD, Ertorun İ, Akalın Çiftçi G, Luo C, Zou X, Zou J, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a new series of imidazothiazole-hydrazone hybrids as dual EGFR and Akt inhibitors for NSCLC therapy. Eur J Medicinal Chem. (2024) 276:116698. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116698
5. Wang F, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Cheng L, Bai Y, et al. The value of microRNA-155 as a prognostic factor for survival in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0136889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136889
6. Zhou X, Chai K, Zhu H, Luo C, Zou X, Zou J, et al. The role of the methyltransferase METTL3 in prostate cancer: a potential therapeutic target. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:8. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11741-1
7. Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E. Epigenetic alteration and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Front Genet. (2013) 4:258. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00258
8. O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol. (2018) 9:402. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00402
9. Ipsaro JJ, Joshua-Tor L. From guide to target: molecular insights into eukaryotic RNAi machinery. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2015) 22:20–8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2931
10. Kiełbowski K, Ptaszyński K, Wójcik J. The role of selected non-coding RNAs in the biology of non-small cell lung cancer. Adv Med Sci. (2023) 68:121–37. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2023.02.004
11. Teoh SL, Das S. The role of microRNAs in diagnosis, prognosis, metastasis and resistant cases in breast cancer. Curr Pharm Design. (2017) 23:1845–59. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161027120043
12. Tam W. Identification and characterization of human BIC, a gene on chromosome 21 that encodes a noncoding RNA. Gene. (2001) 274:157–67. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00612-6
13. Faraoni I, Antonetti FR, Cardone J. miR-155 gene: A typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. (2009) 1792:497–505. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.02.013
14. Tili E, Croce CM, Michaille JJ. miR-155 : on the crosstalk between inflammation and cancer. Int Rev Immunol. (2009) 28:264–84. doi: 10.1080/08830180903093796
15. Kong W, He L, Richards E, Challa S, Xu C-X, Permuth-Wey J, et al. Upregulation of miRNA-155 promotes tumour angiogenesis by targeting VHL and is associated with poor prognosis and triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. (2014) 33:679–89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.636
16. Qu Y, Zhang H, Sun W, Han Y, Li S, Qu Y, et al. MicroRNA-155 promotes gastric cancer growth and invasion by negatively regulating transforming growth factor-β receptor 2. Cancer Sci. (2018) 109:618–28. doi: 10.1111/cas.2018.109.issue-3
17. Zhang CM, Zhao J, Deng HY. MiR-155 promotes proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through targeting tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. J Biomed Sci. (2013) 20:79. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-79
18. Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. (2006) 9:189–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.025
19. Takahashi R u, Prieto-Vila M, Hironaka A. The role of extracellular vesicle microRNAs in cancer biology. Clin Chem Lab Med (CCLM). (2017) 55. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0708
20. Dezfuli NK, Alipoor SD, Dalil Roofchayee N, Seyfi B, Salimi B, Adcock I M, et al. Evaluation Expression of miR-146a and miR-155 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:715677. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.715677
21. Tirpe A, Gulei D, Tirpe GR, Nutu A, Irimie A, Campomenosi P, et al. Beyond conventional: the new horizon of anti-angiogenic microRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8002. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218002
22. Nucera F, Ruggeri P, Spagnolo CC, Santarpia MC, Ieni A, Monaco F, et al. MiRNAs and microbiota in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): implications in pathogenesis and potential role in predicting response to ICI treatment. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6685. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126685
23. Berindan-Neagoe I, Braicu C, Gulei D. Noncoding RNAs in lung cancer angiogenesis. IntechOpen. (2017).
24. Akhurst T. Staging of non–small-cell lung cancer. PET Clinics. (2018) 13:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2017.09.004
25. Ren J, Zhao S, Lai J. Role and mechanism of COL3A1 in regulating the growth, metastasis, and drug sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. (2024) 25:2328382. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2328382
26. Xie X, Liu HT, Mei J, Ding F-B, Xiao H-B, Hu F-Q, et al. miR-106a promotes growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting PTEN. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2015) 8:3827–34.
27. Castro D, Moreira M, Gouveia AM. MicroRNAs in lung cancer. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:81679–85. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20955
28. Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. (2005) 435:834–8. doi: 10.1038/nature03702
29. Dong H, Lei J, Ding L, Wen Y, Ju H, Zhang X. MicroRNA: function, detection, and bioanalysis. Chem Rev. (2013) 113:6207–33. doi: 10.1021/cr300362f
30. Lamichhane SR, Thachil T, De Ieso P, Gee H, Moss SA, Milic N. Prognostic role of microRNAs in human non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis Markers. (2018) 2018:8309015. doi: 10.1155/2018/8309015
31. Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G, Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, et al. The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:7713–22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1083
32. Lee YS, Dutta A. The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev. (2007) 21:1025–30. doi: 10.1101/gad.1540407
33. Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, et al. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell. (2005) 120:635–47. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.014
34. Han Y, Li H. miRNAs as biomarkers and for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Thorac Dis. (2018) 10:3119–31. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.05.32
35. Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, Yang Q, Aris V, Soteropoulos P, et al. MicroRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:9762–70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2462
36. Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L. The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol. (2014) 6:214–30. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mju003
37. Choi WY, Giraldez AJ, Schier AF. Target protectors reveal dampening and balancing of nodal agonist and antagonist by miR-430. Science. (2007) 318:271–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1147535
38. Ebert MS, Sharp PA. MicroRNA sponges: Progress and possibilities. RNA. (2010) 16:2043–50. doi: 10.1261/rna.2414110
39. Tong AW, Nemunaitis J. Modulation of miRNA activity in human cancer: a new paradigm for cancer gene therapy? Cancer Gene Ther. (2008) 15:341–55. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2008.8
40. Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. (2006) 6:857–66. doi: 10.1038/nrc1997
41. Petrocca F, Lieberman J. Micromanipulating cancer: microRNA-based therapeutics? RNA Biol. (2009) 6:335–40. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.3.9013
42. Florczuk M, Szpechcinski A, Chorostowska-Wynimko J. miRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in non-small cell lung cancer: current perspectives. Targeted Oncol. (2017) 12:179–200. doi: 10.1007/s11523-017-0478-5
43. Alexandre D, Teixeira B, Rico A, Valente S, Craveiro A, Baptista PV, et al. Molecular beacon for detection miRNA-21 as a biomarker of lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3330. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063330
44. Zhang Jg, Wang Jj, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K, Yang G-h, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clinica Chimica Acta. (2010) 411:846–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2010.02.074
45. Sun L, Zhou H, Yang Y, Chen J, Wang Y, She M, et al. Meta-analysis of diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-126 in non-small cell lung cancer. Bioscience Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20200349. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200349
46. Zheng W, Zhou Y, Lu J, Xu H, Lei L, Chen C, et al. The prognostic value of miR-126 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. (2017) 17:71. doi: 10.1186/s12935-017-0440-8
47. Dogra P, Shinglot V, Ruiz-Ramírez J, Cave J, Butner JD, Schiavone C, et al. Translational modeling-based evidence for enhanced efficacy of standard-of-care drugs in combination with anti-microRNA-155 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:156. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02060-5
48. Wang X, Zhi X, Zhang Y. Role of plasma MicroRNAs in the early diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancers: a case-control study. J Thorac Dis. (2016) 8:1645–52. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.06.21
49. Hu X. Identification of miR-210 and combination biomarkers as useful agents in early screening non-small cell lung cancer. In Gene: An International Journal Focusing on Gene Cloning and Gene Structure and Function. (2020).
50. Zhu W, Zhou K, Zha Y, Chen DD, He JY, Ma HJ, et al. Diagnostic Value of Serum miR-182, miR-183, miR-210, and miR-126 Levels in Patients with Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0153046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153046
51. Li Y, Li Y, Liu J, Fana Y, Lia X, Dong M, et al. Expression levels of microRNA-145 and microRNA-10b are associated with metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. (2016) 17:272–9. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139242
52. Qin Y, Zhou X, Huang C, Li L, Liu H, Liang N, et al. Lower miR-340 expression predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell proliferation by targeting CDK4. Gene. (2018) 675:278–84. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.062
53. Li B, Ding CM, Li YX, Peng J-C, Geng N, Qin W-W, et al. Over-regulation of microRNA-133b inhibits cell proliferation of cisplatin-induced non-small cell lung cancer cells through PI3K/Akt and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting EGFR. Oncol Rep. (2018). doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6215
54. Barbagallo D, Ponti D, Bassani B, Bruno A, Pulze L, Akkihal SA, et al. MiR-223-3p in cancer development and cancer drug resistance: same coin, different faces. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8191. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158191
55. D’Antona P, Cattoni M, Dominioni L, Poli A, Moretti F, Cinquetti R, et al. Serum miR-223: A validated biomarker for detection of early-stage non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prev. (2019) 28:1926–33. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0626
56. Bagheri A, Khorram Khorshid HR, Mowla SJ, Mohebbi HA, Mohammadian A, Yaseri M, et al. Altered miR-223 expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. (2017) 9:189–95.
57. Ma HP, Kong WX, Li XY, Li W, Zhang Y, Wu Y, et al. miRNA-223 is an anticancer gene in human non-small cell lung cancer through the PI3K/AKT pathway by targeting EGFR. Oncol Rep. (2019) 41:1549–59. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.6983
58. Cheng D, Liu Z, Sun R, Jiang Y, Zeng Z, Zhao R, et al. Overexpression of mir-489–3p inhibits proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing the HER2/PI3K/AKT/Snail signaling pathway. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e35832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35832
59. Zhang L, Chi W, Wang X, Li a J, Li a F, Ma Y, et al. miR-6884-5p inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e38428. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38428
60. Liu Q, Bao H, Zhang S, Li CL, Sun G, Sun X, et al. MicroRNA-522-3p promotes brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting Tensin 1 and modulating blood-brain barrier permeability. Exp Cell Res. (2024) 442:114199. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114199
61. Peng LP. Regarding: microRNA-126 targeting PIK3R2 inhibits NSCLC A549 cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Clin Lung Cancer. (2021) 22:e446–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.06.009
62. You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R, et al. MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e91827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091827
63. Cheng Z, Ma R, Tan W. MiR-152 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells by inhibiting FGF2. Exp Mol Med. (2014) 46:e112. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.51
64. Guo H, Li W, Zheng T. miR-195 Targets HDGF to inhibit proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells. Tumor Biol. (2014) 35:8861–6. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2153-0
65. Skrzypek K, Tertil M, Golda S, Ciesla M, Weglarczyk K, Collet G, et al. Interplay between heme oxygenase-1 and miR-378 affects non-small cell lung carcinoma growth, vascularization, and metastasis. Antioxidants Redox Signaling. (2013) 19:644–60. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5184
66. Wang J, Shu H, Guo S. MiR-646 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by repressing FGF2 and CCND2. Cancer Med. (2020) 9:4360–70. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v9.12
67. Yao Y, Zhou Y, Fu X. miR−671−3p is downregulated in non−small cell lung cancer and inhibits cancer progression by directly targeting CCND2. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:2407–12. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9858
68. Peng Y, Dong W, Lin Tx, Zhong G-Z, Liao B, Wang B, et al. MicroRNA-155 promotes bladder cancer growth by repressing the tumor suppressor DMTF1. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:16043–58. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i18
69. Al-Haidari AA, Syk I, Thorlacius H. MiR-155-5p positively regulates CCL17-induced colon cancer cell migration by targeting RhoA. Oncotarget. (2017) 8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14841
70. Fu X, Wen H, Jing L, Yang Y, Wang W, Liang X, et al. MicroRNA-155-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing PTEN through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Sci. (2017) 108:620–31. doi: 10.1111/cas.2017.108.issue-4
71. Yang L. MiRNA-155 promotes proliferation by targeting caudal-type homeobox 1 (CDX1) in glioma cells. (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.088
72. Lawrie CH, Soneji S, Marafioti T, Cooper CDO, Palazzo S, Paterson JC, et al. Microrna expression distinguishes between germinal center B cell-like and activated B cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int J Cancer. (2007) 121:1156–61. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22800
73. Li N, Cui T, Guo W. MiR-155-5p accelerates the metastasis of cervical cancer cell via targeting TP53INP1. OncoTargets Ther. (2019) 12:3181–96. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S193097
74. Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He X-H, Li Y, Gu H, et al. MicroRNA-155 functions as an oncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:3119–27. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4250
75. Wei H, Li Y, Ning Q. Regulation of miR-155 affects the invasion and migration of gastric carcinoma cells by modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. (2018) 16:4137–42. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9152
76. Huang C, Li H, Wu W. Regulation of miR-155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness and migration by modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway through SOCS1. Oncol Rep. (2013) 30:1223–30. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2576
77. Seto AG, Beatty X, Lynch JM, Hermreck M, Tetzlaff MT, Duvic M, et al. Cobomarsen, an oligonucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, co-ordinately regulates multiple survival pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and survival in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematology. (2018) 183:428–44. doi: 10.1111/bjh.2018.183.issue-3
78. MiR-155 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through targeting PTEN-PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:7935–42. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_19009
79. Czyzyk-Krzeska M, Zhang X. MiR-155 at the heart of oncogenic pathways. Oncogene. (2014) 33:677–8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.26
80. Witten L, Slack FJ. miR-155 as a novel clinical target for hematological Malignancies. Carcinogenesis. (2020) 41:2–7. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz183
81. Catela Ivkovic T, Voss G, Cornella H. microRNAs as cancer therapeutics: A step closer to clinical application. Cancer Lett. (2017) 407:113–22. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.007
82. Hou L, Chen J, Zheng Y. Critical role of miR-155/FoxO1/ROS axis in the regulation of non-small cell lung carcinomas. Tumor Biol. (2016) 37:5185–92. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4335-9
83. Kim W, Youn H, Kang C. Inflammation-induced radioresistance is mediated by ROS-dependent inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Apoptosis. (2015) 20:1242–52. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1141-1
84. Liu F, Song D, Wu Y, Liu X, Zhu J, Tang Y, et al. MiR-155 inhibits proliferation and invasion by directly targeting PDCD 4 in non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. (2017) 8:613–9. doi: 10.1111/tca.2017.8.issue-6
85. Liu F, Mao Q, Zhu S. MicroRNA-155-5p promotes cell proliferation and invasion in lung squamous cell carcinoma through negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor 9 expression. J Thorac Dis. (2021) 13:3669–79. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-882
86. Wan J, Ma J, Mei J. The effects of HIF-1alpha on gene expression profiles of NCI-H446 human small cell lung cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Research : CR. (2009) 28:150. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-150
87. Kabir NN, Sun J, Rönnstrand L. SOCS6 is a selective suppressor of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Tumor Biol. (2014) 35:10581–9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2542-4
88. Yu T, Liu L, Li J, Yan M, Lin H, Liu Y, et al. MiRNA-10a is upregulated in NSCLC and may promote cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:30239–50. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i30
89. Lin J, Chen Y, Liu L. MicroRNA-155-5p suppresses the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by targeting Smad2. Oncol Lett. (2018) 16:2444–52. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8889
90. Lv Xq, Qiao Xr, Su L. Honokiol inhibits EMT-mediated motility and migration of human non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro by targeting c-FLIP. Acta Pharmacologica Sin. (2016) 37:1574–86. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.81
91. Nagaraj NS, Datta PK. Targeting the transforming growth factor-β Signaling pathway in human cancer. Expert Opin investigational Drugs. (2010) 19:77–91. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0747
92. Kong W, Yang H, He L, Zhao JJ, Coppola D, Dalton WS, et al. MicroRNA-155 is regulated by the transforming growth factor β/smad pathway and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting rhoA. Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 28:6773–84. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00941-08
93. Thomsen KG, Terp MG, Lund RR, Søkilde R, Elias D, Bak M, et al. miR-155, identified as anti-metastatic by global miRNA profiling of a metastasis model, inhibits cancer cell extravasation and colonization in vivo and causes significant signaling alterations. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:29224–39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i30
94. Iwasa H, Hossain S, Hata Y. Tumor suppressor C-RASSF proteins. Cell Mol Life Sciences: CMLS. (2018) 75:1773–87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2756-5
95. Zhang M, Wang D, Zhu T, et al. RASSF4 overexpression inhibits the proliferation, invasion, EMT, and wnt signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Res. (2017) 25:83–91. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14719078133447
96. Chen SH, Chang JY. New insights into mechanisms of cisplatin resistance: from tumor cell to microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:4136. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174136
97. Zang YS, Zhong YF, Fang Z. MiR-155 inhibits the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to cisplatin via negative regulation of Apaf-1 expression. Cancer Gene Ther. (2012) 19:773–8. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.60
98. Lv L, An X, Li H. Effect of miR-155 knockdown on the reversal of doxorubicin resistance in human lung cancer A549/dox cells. Oncol Lett. (2016) 11:1161–6. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3995
99. Liu JX, Zhou GB, Chen SJ. Arsenic compounds: revived ancient remedies in the fight against human Malignancies. Curr Opin Chem Biol. (2012) 16:92–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.01.015
100. Walker AM, Stevens JJ, Ndebele K. Evaluation of arsenic trioxide potential for lung cancer treatment: assessment of apoptotic mechanisms and oxidative damage. J Cancer Sci Ther. (2016) 8:1–9. doi: 10.4172/1948-5956.1000379
101. Gu S, Lai Y, Chen H. miR-155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:12155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06061-x
102. Chiu CF, Chang YW, Kuo KT, Shend Y-S, Liue,f C-Y, Yug Y-H, et al. NF-κB–driven suppression of FOXO3a contributes to EGFR mutation-independent gefitinib resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2016) 113:E2526–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522612113
103. Narita M, Shimura E, Nagasawa A, Aiuchi T, Suda Y, Hamada Y, et al. Chronic treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer cells with gefitinib leads to an epigenetic loss of epithelial properties associated with reductions in microRNA-155 and -200c. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0172115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172115
104. Van Roosbroeck K, Fanini F, Setoyama T, Ivan C, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Vannini I, et al. A miR-155/TP53 regulatory feedback loop involved in resistance to therapy in lung cancer and leukemia. Clin Cancer research. (2017) 23:2891–904.
105. Bayraktar R. miR-155 in cancer drug resistance and as target for miRNA-based therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2018) 37:33–44. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9724-7
106. Lv X, Yao L, Zhang J. Inhibition of microRNA-155 sensitizes lung cancer cells to irradiation via suppression of HK2-modulated glucose metabolism. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:1332–8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5394
107. Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N, et al. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. (2008) 455:58–63. doi: 10.1038/nature07228
108. Haasch D, Chen YW, Reilly RM, Chiou XG, Koterski S, Smith ML, et al. T cell activation induces a noncoding RNA transcript sensitive to inhibition by immunosuppressant drugs and encoded by the proto-oncogene, BIC. Cell Immunol. (2002) 217:78–86. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8749(02)00506-3
109. O’Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng G, Baltimore D. MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2007) 104:1604–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610731104
110. Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. The instructive role of dendritic cells on T-cell responses. Arthritis Res. (2002) 4:S127–32. doi: 10.1186/ar567
111. Hiramoto JS, Tsung K, Bedolli M. Antitumor immunity induced by dendritic cell-based vaccination is dependent on interferon-γ and interleukin-12. J Surg Res. (2004) 116:64–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2003.09.006
112. Kalkusova K, Taborska P, Stakheev D. The role of miR-155 in antitumor immunity. Cancers. (2022) 14:5414. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215414
113. Nguyen MHT, Luo YH, Li AL, Tsai J-C, Wu K-L, Chung P-J, et al. miRNA as a modulator of immunotherapy and immune response in melanoma. Biomolecules. (2021) 11:1648. doi: 10.3390/biom11111648
114. Sharma N, Atolagbe OT, Ge Z. LILRB4 suppresses immunity in solid tumors and is a potential target for immunotherapy. J Exp Med. (2021) 218:e20201811. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201811
115. Liu L, Yi H, He H, Pan H, Cai L, Ma Y, et al. Tumor associated macrophage-targeted microRNA delivery with dual-responsive polypeptide nanovectors for anti-cancer therapy. Biomaterials. (2017) 134:166–79. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.043
116. Francisco LM, Sage PT, Sharpe AH. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. (2010) 236:219–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00923.x
117. Rozali EN, Hato SV, Robinson BW, et al. Programmed death ligand 2 in cancer-induced immune suppression. Clin Dev Immunol. (2012) 2012:656340. doi: 10.1155/2012/656340
118. Sanmamed MF, Chen L. Inducible expression of B7-H1 (PD-L1) and its selective role in tumor site immune modulation. Cancer J (Sudbury Mass.). (2014) 20:256–61. doi: 10.1097/PPO.000000000000000061
119. Chen L, Tang W, Liu J, Zhu M, Mu W, Tang X, et al. On-demand reprogramming of immunosuppressive microenvironment in tumor tissue via multi-regulation of carcinogenic microRNAs and RNAs dependent photothermal-immunotherapy using engineered gold nanoparticles for Malignant tumor treatment. Biomaterials. (2025) 315:122956. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122956
120. Huang J, Weng Q, Shi Y, Mao W, Zhao Z, Wu R, et al. MicroRNA-155-5p suppresses PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma. FEBS Open Bio. (2020) 10:1065–71. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12853
121. Yu F, Jia X, Du F, Wang J, Wang Y, Ai W, et al. microRNA-155 deficiency in bone marrow results in enhanced tumor metastasis. Mol Cancer research : MCR. (2013) 11:923–36. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0686
122. Wang J, Yu F, Jia X, et al. microRNA-155 deficiency enhances the recruitment and functions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor microenvironment and promotes solid tumor growth. Int J cancer. J Int du Cancer. (2015) 136:E602–13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v136.6
123. Zhao Y, Butler EB, Tan M. Targeting cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis. (2013) 4:e532. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.60
124. Zhong J, Rajaram N, Brizel DM, Freesb AE, Ramanujam N, Batinic-Haberle I, et al. Radiation induces aerobic glycolysis through reactive oxygen species. Radiotherapy Oncology. (2013) 106:390–6. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.02.013
125. Suh DH, Kim MA, Kim H, Kim MK, Kim HS, Chung HH, et al. Association of overexpression of hexokinase II with chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Exp Med. (2014) 14:345–53. doi: 10.1007/s10238-013-0250-9
126. Li Z, Rana TM. Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs: current status and future challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2014) 13:622–38. doi: 10.1038/nrd4359
127. Hodge J, Wang F, Wang J, Liu Q, Saaoud F, Wang Y, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-155 enhances the efficacy of dendritic cell vaccine against breast cancer. OncoImmunology. (2020) 9:1724761. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1724761
128. Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Baird JR, Tesone AJ, Rutkowski MR, Scarlett UK, Camposeco-Jacobs AL, et al. Reprogramming tumor-associated dendritic cells in vivo using microrna mimetics triggers protective immunity against ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:1683–93. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3160
129. Babar IA, Cheng CJ, Booth CJ, Lianga X, Weidhaase JB, Saltzman WM, et al. Nanoparticle-based therapy in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155)-dependent mouse model of lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2012) 109:E1695–704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201516109
130. Elmén J, Lindow M, Schütz S. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature. (2008) 452:896–9. doi: 10.1038/nature06783
131. Cheng CJ, Bahal R, Babar IA, Pincus Z, Barrera F, Liu C, et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumor microenvironment. Nature. (2015) 518:107–10. doi: 10.1038/nature13905
132. Jiang S, Zhang LF, Zhang HW, Hu S, Lu M-H, Liang S, et al. A novel miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. (2012) 31:1985–98. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.45
133. Xue X, Liu Y, Wang Y, Meng M, Wang K, Zang X, et al. MiR-21 and MiR-155 promote non-small cell lung cancer progression by downregulating SOCS1, SOCS6, and PTEN. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:84508–19. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13022
134. Li X, Chen Z, Ni Y, Bian C, Huang J, Chen L, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages secret exosomal miR-155 and miR-196a-5p to promote metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Trans Lung Cancer Res. (2021) 10:1338–54. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1255
135. Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP, et al. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature. (2008) 455:64–71. doi: 10.1038/nature07242
136. Sadeghi MS, Lotfi M, Soltani N, Farmani E, Fernandez Ortiz JH, Akhlaghitehrani S, et al. Recent advances on high-efficiency of microRNAs in different types of lung cancer: a comprehensive review. Cancer Cell Int. (2023) 23:284. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03133-z
137. Chen S, Tu Y, Yuan H, Shi Z, Guo Y, Gong W, et al. Regulatory functions of miR-200b-3p in tumor development. Oncol Rep. (2022) 47:96. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8307
138. Grenda A, Kuźnar-Kamińska B, Kalinka E, Krawczyk P, Sawicki M, Filip A, et al. MicroRNA-126 selected with broad-spectrum analysis of microRNAs – a new predictive factor for the effectiveness of immunotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy in advanced NSCLC patients? Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1344858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1344858
139. Li T, Ding ZL, Zheng YL. MiR-484 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression through inhibiting Apaf-1 associated with the suppression of apoptosis. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2017) 96:153–64. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.102
140. Ghafouri-Fard S, Khoshbakht T, Hussen BM, Abdullah ST, Taheri M, Samadian M, et al. A review on the role of mir-16-5p in the carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:342. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02754-0
141. Rhim J, Baek W, Seo Y. From molecular mechanisms to therapeutics: understanding microRNA-21 in cancer. Cells. (2022) 11:2791. doi: 10.3390/cells11182791
142. Misso G, Di Martino MT, De Rosa G, Farooqi Ammad Ahmad, Lombardi A, Campani V, et al. Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2014) 3:e195. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2014.47
143. Fuziwara CS, Kimura ET. Insights into Regulation of the miR-17-92 Cluster of miRNAs in Cancer. Front Med. (2015) 2:64. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00064
144. Kishta MS, Khamis A, Am H. Exploring the tumor-suppressive role of miRNA-200c in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Potential and mechanisms of exosome-mediated delivery for therapeutic applications. Trans Oncol. (2025) 51:102216. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102216
145. Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. (2008) 22:894–907. doi: 10.1101/gad.1640608
146. Song L, Li D, Gu Y. MicroRNA-126 targeting PIK3R2 inhibits NSCLC A549 cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Clin Lung Cancer. (2016) 17:e65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2016.03.012
147. Ye J, Guo R, Shi Y, Qi F, Guo C, Yang L, et al. miR-155 regulated inflammation response by the SOCS1-STAT3-PDCD4 axis in atherogenesis. Mediators Inflammation. (2016) 2016:8060182. doi: 10.1155/2016/8060182
148. Alexandrov PN, Zhao Y, Li W. Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated, NF-kB-, miRNA-146a- and miRNA-155-mediated molecular-genetic communication between the human gastrointestinal tract microbiome and the brain. Folia Neuropathologica. (2019) 57:211–9. doi: 10.5114/fn.2019.88449
149. Wang J, Wang Q, Guan Y, Sun Y, Wang X, Lively K, et al. Breast cancer cell–derived microRNA-155 suppresses tumor progression via enhancing immune cell recruitment and antitumor function. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:e157248. doi: 10.1172/JCI157248
150. Price C, Chen J. MicroRNAs in cancer biology and therapy: Current status and perspectives. Genes Dis. (2014) 1:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.06.004
151. Hussen BM, Rasul MF, Abdullah SR, Hidayat HJ, Faraj GSH, Ali FA, et al. Targeting miRNA by CRISPR/Cas in cancer: advantages and challenges. Military Med Res. (2023) 10:32. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00468-6
152. Rasul MF, Hussen BM, Salihi A, Ismael BS, Jalal PJ, Zanichelli A, et al. Strategies to overcome the main challenges of the use of CRISPR/Cas9 as a replacement for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:64. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01487-4
153. Martinez-Lage M, Puig-Serra P, Menendez P. CRISPR/cas9 for cancer therapy: hopes and challenges. Biomedicines. (2018) 6:105. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040105
154. Strizova Z, Bartunkova J, Smrz D. The challenges of adoptive cell transfer in the treatment of human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy : CII. (2019) 68:1831–8. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02359-z
155. Strizova Z, Snajdauf M, Stakheev D, Taborska P, Vachtenheim JV, Biskup J, et al. The paratumoral immune cell signature reveals the potential for the implementation of immunotherapy in esophageal carcinoma patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2020) 146:1979–92. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03258-y
156. Strizova Z, Taborska P, Stakheev D, Partlova S, Havlova K, Vesely S, et al. NK and T cells with a cytotoxic/migratory phenotype accumulate in peritumoral tissue of patients with clear cell renal carcinoma. Urologic Oncology: Semin Original Investigations. (2019) 37:503–9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2019.03.014
Keywords: microRNA, microRNA155, non-small cell lung cancer, immune response, oncogenic
Citation: Wei X, Xiong X, Chen Z, Chen B, Zhang C and Zhang W (2025) MicroRNA155 in non-small cell lung cancer: a potential therapeutic target. Front. Oncol. 15:1517995. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1517995
Received: 27 October 2024; Accepted: 09 January 2025;
Published: 03 February 2025.
Edited by:
Paola Campomenosi, University of Insubria, ItalyReviewed by:
Anand Singh, National Cancer Institute (NIH), United StatesCopyright © 2025 Wei, Xiong, Chen, Chen, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenhui Zhang, eHp6eXoyMDAwQDEyNi5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.