
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol., 24 March 2025
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1511564
Background: Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) is a malignant disease associated with poor therapeutic responses and prognosis. Preliminary studies have shown that the dysregulation of long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) is linked to cancer development and prognosis. However, research on the role of LncRNAs in LUSC remains limited.
Methods: In this study, we aimed to develop a LncRNA signature for improved prognostic prediction in LUSC and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms. We utilized expression data of LncRNAs and clinical information from 471 LUSC patients in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), randomly dividing them into a training set (n=236) and a testing set (n=235).
Results: A prognostic signature model comprising seven LncRNAs was constructed using multivariate Cox regression analysis based on the training set. Using a risk score cutoff value of -0.12 (log2-transformed), patients were categorized into high-risk (n=101) and low-risk (n=370) groups. The high-risk group demonstrated significantly worse overall survival (OS) compared to the low-risk group (p<0.0001). The risk score showed strong prognostic predictive ability for LUSC patients, as evidenced by the area under the ROC curve (AUC: 0.66, 0.67, and 0.67) and nomogram analysis (C-index, calibration, and decision curve analysis) for 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival predictions. Independent prognostic factors for LUSC were identified, including risk group (HR=0.3, 95% CI: 0.22–0.4), stage (HR=1.78, 95% CI: 1.28–2.48), and age (HR=1.02, 95% CI: 1.00–1.04). KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that mRNAs influenced by the seven targeted LncRNAs, associated with immune evasion, were primarily linked to pathways such as chemical carcinogenesis, Th17 cell differentiation, NF-κB signaling, and proteoglycans in cancer. Expression levels of 14 target genes related to tumor immune tolerance were significantly suppressed, with eight confirmed via real-time PCR and western blot analysis. Additionally, CIBERSORT analysis of immune cell-related gene expression between normal and LUSC tissues indicated activation of the immune system in LUSC patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our findings highlight the clinical significance of the seven LncRNA signature in predicting survival outcomes for LUSC patients.
In recent years, the incidence of lung cancer has been steadily increasing, making it the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with a five-year survival rate of less than 15% (1, 2). Despite advances in treatment, the etiology of lung cancer remains largely unclear, and the primary treatment for patients is still surgery combined with adjuvant therapy. The majority of lung cancer cases are classified as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which primarily consists of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and LUSC. Patients with LUSC are often diagnosed at an advanced stage, limiting the effectiveness of available treatments, which may not be administered in a timely manner. Additionally, LUSC patients generally exhibit lower sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiation compared to patients with small-cell lung cancer. Currently, the tumor node metastasis (TNM) staging system is widely used in clinical settings to guide treatment decisions and predict the prognosis of cancer patients, including those with lung cancer (3, 4). However, the clinical application of TNM staging has certain limitations, such as its inability to accurately predict survival outcomes for many patients following surgical resection, and the presence of inconsistent results among patients within the same stage category (5, 6). Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify novel independent biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting the prognosis of LUSC.
Recent advancements in high-throughput technologies, such as microarrays, sequencing, and mass spectrometry, now allow for the simultaneous evaluation of thousands of molecular expression profiles (7). These breakthroughs, coupled with the growing body of research, have revealed that certain molecular markers are closely associated with tumor phenotype and clinical behavior, particularly LncRNAs. These findings hold significant promise for clinical practice in predicting the long-term outcomes of cancer patients (8–10). Aberrant expression of LncRNAs is frequently observed in various types of cancer and has been linked to tumorigenesis and progression. For example, several well-characterized LncRNAs, such as HOTAIR, MALAT1, and NEAT1, are upregulated in breast cancer, gastric cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma (11–13). Moreover, multiple differentially expressed LncRNAs have been identified in lung cancer studies, some of which have been implicated in clinical diagnosis and treatment (14). In this study, we identified a set of seven prognostic LncRNA biomarkers associated with overall survival (OS) in LUSC patients. Using these LncRNAs, we developed a 7-LncRNA risk score model that effectively predicts patient OS. These findings were subsequently validated in both the testing set and the entire dataset.
This study included six patients who underwent resection for LUSC at the Department of General Surgery, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province. All resected specimens were collected and preserved at the Bioresource Center of Taizhou Hospital. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Taizhou Hospital.
Reagents used in the study included: Trizol reagent (CW2602M, Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology), Reverse Transcription Kit (CW0744M, Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology), Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Kit (CW2602M, Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology), and primary antibodies including CFLAR, CSF2RA, ICAM1, IL18R1, CISH, CXCL3, IL17D, p-NF-κBα, NF-κBα, and β-Actin (YT0877, YT5262, YT2269, YT5472, YT5920, YT2075, YT6048, YP1372, YT2419, and YT0099 from ImmunoWay Biotechnology).
Raw RNA-Seq count data and corresponding clinical information for LUAC patients were obtained from the TCGA-LUAC database (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/). Patients lacking essential data, such as RNA expression profiles from lung cancer tissue, follow-up survival information, age, gender, and TNM stage, were excluded. Ultimately, 471 patients were included in the study and randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 236) and a testing cohort (n = 235) for model development and validation, respectively. Raw RNA-Seq data were annotated using GENCODE v33 and subsequently normalized using FPKM values.
The most significant survival-related LncRNAs were identified using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression model in the training group, based on common prognostic LncRNAs previously filtered by univariate Cox regression (P < 0.05). Stepwise multivariate Cox regression analysis was employed to construct the LncRNAs risk signature (LncRS), following collinearity testing based on the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC). The aim was to establish a prognostic signature with optimal predictive capability while using the fewest LncRNAs. The LncRS formula is as follows: LncRS = , where k and i represent the total number and the sequence number of the significant prognostic LncRNAs, Expi represents the normalized expression values of the corresponding LncRNA for each sample, and represents the regression coefficient of the corresponding LncRNA from multivariate Cox regression analysis.
Risk scores were calculated for each patient in the training cohort, and patients were divided into high- and low-risk groups using a predefined cutoff determined by the “survminer” R package. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank tests were performed to compare survival between high- and low-risk groups. A scatter plot was used to illustrate patient survival status and time based on ascending risk scores, with a heatmap showing the expression levels of LncRS-related LncRNAs. Time-dependent ROC analysis was performed at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 years to assess the diagnostic performance of LncRS.
To assess whether LncRS could serve as an independent prognostic index, univariate (P < 0.2) and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed, adjusting for clinical factors such as age, gender, tumor location, tumor stage, and pathologic TNM stage in the TCGA cohort (P < 0.05). We also examined the correlation between LncRS-related LncRNA expression levels and survival outcomes. Key findings from univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, including Hazard Ratios and P-values, were visualized in a forest plot.
A nomogram was constructed to visually represent the survival probabilities of LUAC patients at 1, 3, and 5 years based on their risk group and key clinical parameters. The concordance index (C-index) and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the prognostic accuracy of the nomogram.
Patients in the TCGA-LUAC cohort were stratified into subgroups based on critical clinical parameters, including age, gender, tumor location, tumor stage, and pathologic TNM stage. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and subgroup forest plots were generated to compare survival between high- and low-risk groups within these subgroups.
Pearson correlation analysis was used to assess co-expression relationships between LncRS-related LncRNAs and mRNAs in the entire TCGA dataset [correlation coefficient (r) > 0.25, P < 0.05]. Tumor immune-related genes were obtained from GeneCards using the search term “tumor immune” (https://www.genecards.org/). Overlapping genes from these sets were subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis. We identified 14 key regulatory genes associated with tumor immune function and pathways through GO and KEGG analysis [r > 0.25; abs (log2 Fold change) > 1.3].
Total RNA was extracted from LUSC tissue samples using Trizol reagent. The RNA was then reverse transcribed into cDNA using a reverse transcription kit. Quantitative PCR was performed using a fluorescent PCR kit to measure the mRNA expression levels of target genes. Data were expressed as 2- ΔΔCt, with β-actin serving as the internal control (n=6).
Tissue samples were lysed using RIPA buffer containing 1% protease inhibitors in an ice bath for 30 minutes to extract proteins. Protein concentrations were determined using a BCA protein quantification kit (P1511, Beijing Applygen Technologies). Protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE at 120V for 75 minutes and transferred to PVDF membranes at 250mA. Membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk for 2 hours, then incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies (1:1000 dilution). The next day, membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (1:10,000 dilution) for 2 hours at room temperature, and protein bands were visualized using an ECL kit (P1050, Beijing Applygen Technologies). β-actin served as an internal control.
Statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 4.1.1). Nomogram plots were generated using the “rms” R package. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted using the “survival” package, with P-values calculated by log-rank tests. Independent prognostic factors were identified through univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses using the “survival” package.
A total of 471 LUSC patients were randomly divided into a training dataset (n = 236) and a testing dataset (n = 235). Multivariate Cox regression was initially used to identify prognostic LncRNAs from the training set. This analysis revealed a significant association between the OS of LUSC patients and seven specific LncRNAs were RP11.279O17.1, DKFZP434A062, RP11.534L20.5, CTA.292E10.6, CDIPT.AS1, RP6.24A23.7, and LINC00628. A 7-LncRNA risk signature was constructed by linearly combining the expression levels of these seven LncRNAs, weighted by their respective Cox regression coefficients. The heatmap (Figure 1B) illustrates the relative expression levels of the seven prognostic LncRNAs, sorted according to their risk scores. Patients were then stratified into low- and high-risk groups based on an optimal cutoff for their risk scores, as shown in Figure 1B. Furthermore, the distribution of risk scores for each patient was visually represented, demonstrating that the mean survival time of high-risk patients was significantly shorter than that of low-risk patients, with a higher mortality rate observed in the high-risk group (Figure 1B). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that patients in the high-risk group had significantly poorer prognosis compared to those in the low-risk group (Figure 1E). Additionally, the AUCs for 1-, 3-, 5-, 7-, and 10-year OS in the training cohort were 0.65, 0.73, 0.69, 0.71, and 0.80, respectively (Figure 2H).
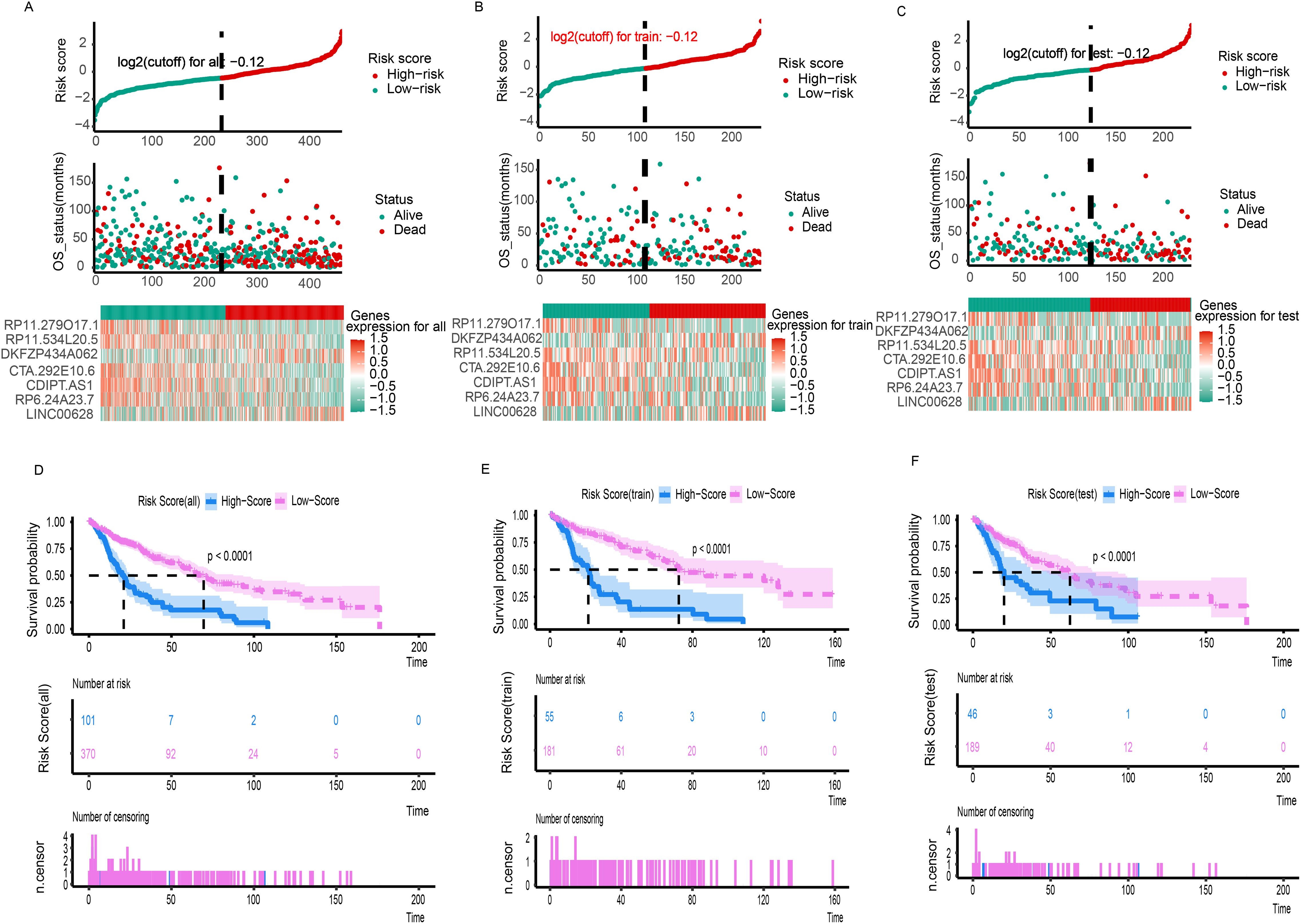
Figure 1. The risk score distribution, duration and survival statues of LC patients and heatmaps of the seven-gene signature relative expression in the total TCGA cohort (A), training TCGA cohort (B), and testing TCGA cohort (C). Kaplan-Meier analysis of the low‐ and high-risk group patients in the total TCGA cohort (D), training TCGA cohort (E), and testing TCGA cohort (F).
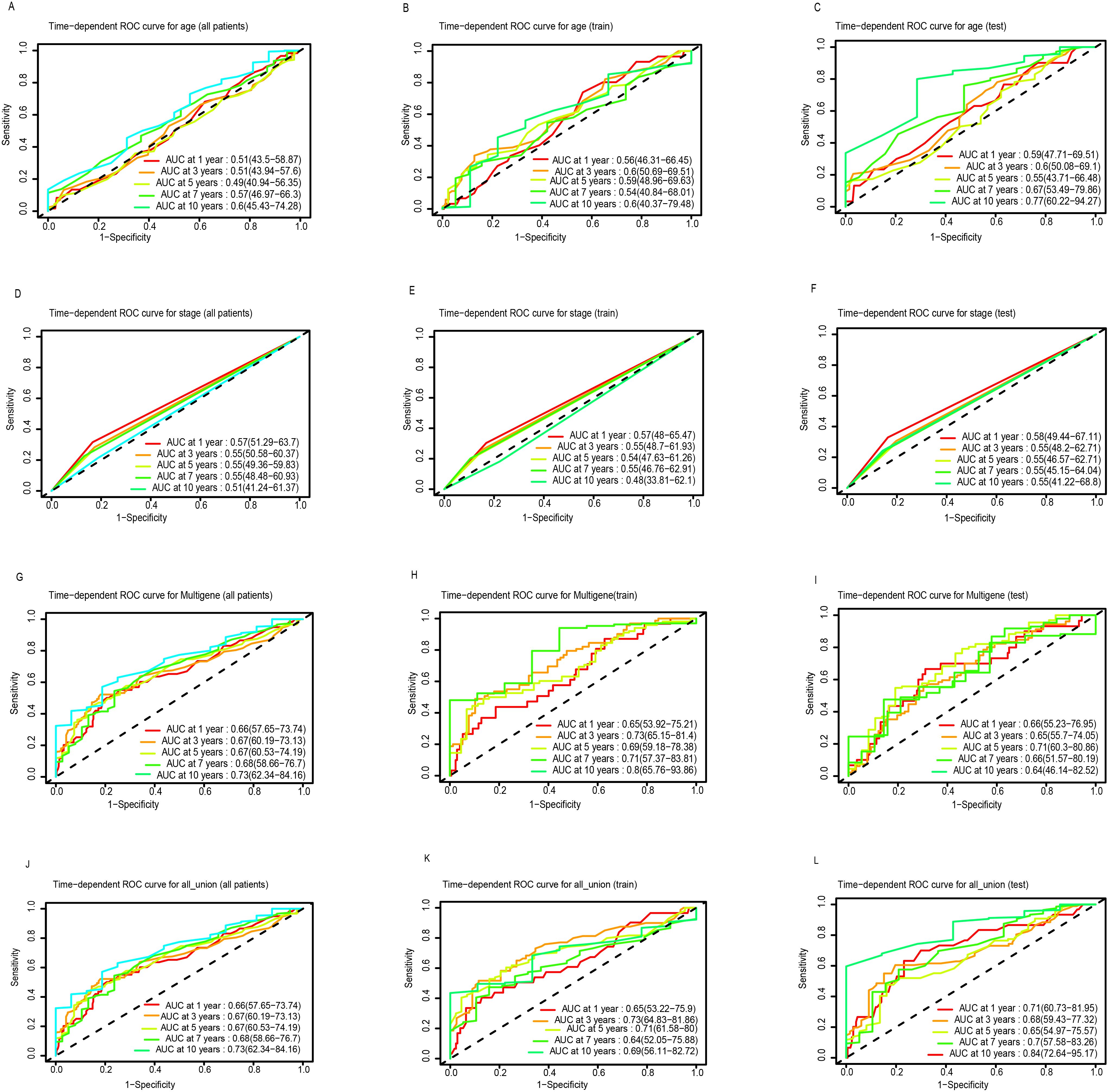
Figure 2. ROC curve analysis of age, stage, multigene and all union index according to the 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10-year survival of the area under the AUC value in the total TGCA cohort (A, D, G, J), training TGCA cohort (B, E, H, K), and testing TGCA (C, F, I, L).
The robustness of the 7-LncRNA signature was further validated in both the testing set and the entire cohort. As shown in Figure 1C, similar to the training cohort, the same risk score formula effectively stratified patients into high- and low-risk groups in the testing cohort using a cutoff of -0.12 (log2-transformed). A significant survival difference was observed between these two groups. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis confirmed that the high-risk group in the testing cohort had a significantly worse prognosis compared to the low-risk group (P < 0.001; Figure 1F). Consistent results were obtained when analyzing the entire TCGA dataset of 471 patients (Figures 1A, D). The AUCs for 1-, 3-, 5-, 7-, and 10-year OS in the testing cohort were 0.71, 0.68, 0.65, 0.70, and 0.84, respectively (Figure 2L). For the overall cohort, the AUCs for OS at these time points ranged from 0.66 to 0.73 (Figures 2J, K). Additionally, clinical factors such as age (Figures 2A, C), stage (Figures 2D, F), and multigene expression (Figures 2G, I) were also analyzed across risk groups. These findings are consistent with previous studies, supporting the 7-LncRNA signature as a robust prognostic indicator for LUSC patients.
To improve the accuracy of survival predictions for LUSC patients, a prognostic nomogram was developed based on clinical data from 471 LUSC patients, integrating the risk score derived from clinical factors such as age, multigene expression, and tumor stage (Figure 3A). Calibration plots demonstrated that the nomogram performed well in predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS for LUSC patients (Figures 3B–D). Decision curve analysis showed that the nomogram outperformed other models at various threshold probabilities (Figures 3E–G). These results suggest that the prognostic nomogram is highly effective in predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival outcomes for LUSC patients.
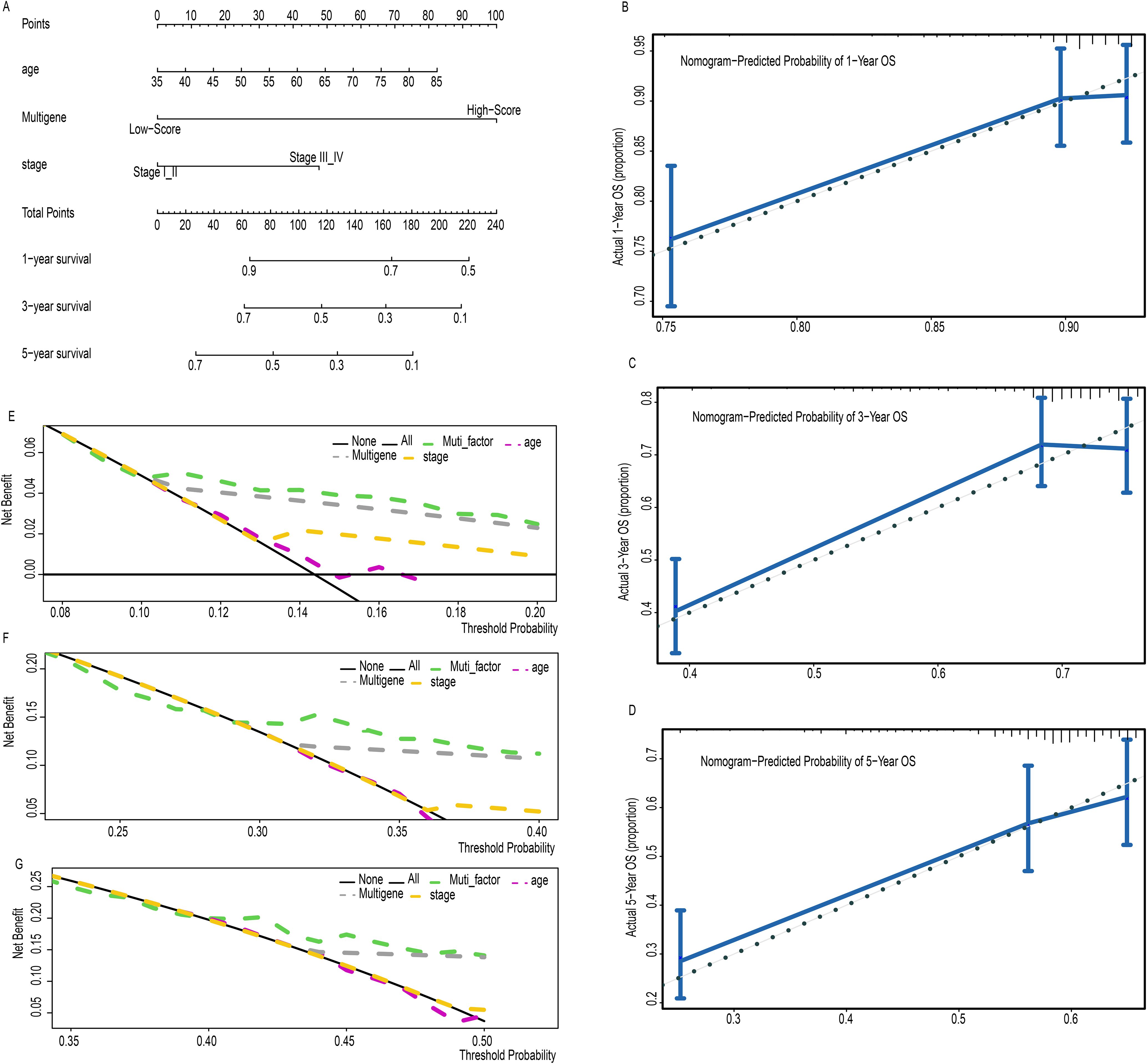
Figure 3. A prognostic nomogram predicting 1-, 3-, and 5- year OS of LC (A). Calibration plots of the nomogram for predicting the proportion of patients with 1-, 3-, or 5-year OS (B-D). Decision curve analysis of nomogram predicting 1-, 3-, and 5- year OS of LC comparing the age, stage and multigene (E-G).
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were conducted to evaluate whether the prognostic value of the 7-LncRNA signature was independent of other clinical factors. The results showed that both the risk group and the 7-LncRNA signature were independent prognostic indicators for LUSC patients in univariate analysis (Figures 4A, B). In multivariate analysis, after adjusting for clinical variables such as age and AJCC stage, the risk group and 7-LncRNA signature remained significant independent prognostic factors (Figures 4C, D). Furthermore, the prognostic efficacy of the 7-LncRNA signature was consistent across various subgroups in the entire cohort, stratified by age (Supplementary Figure S1A), gender (Supplementary Figure S1B), AJCC stage (Supplementary Figure S1C), and TNM grade (Supplementary Figure S1D–F).
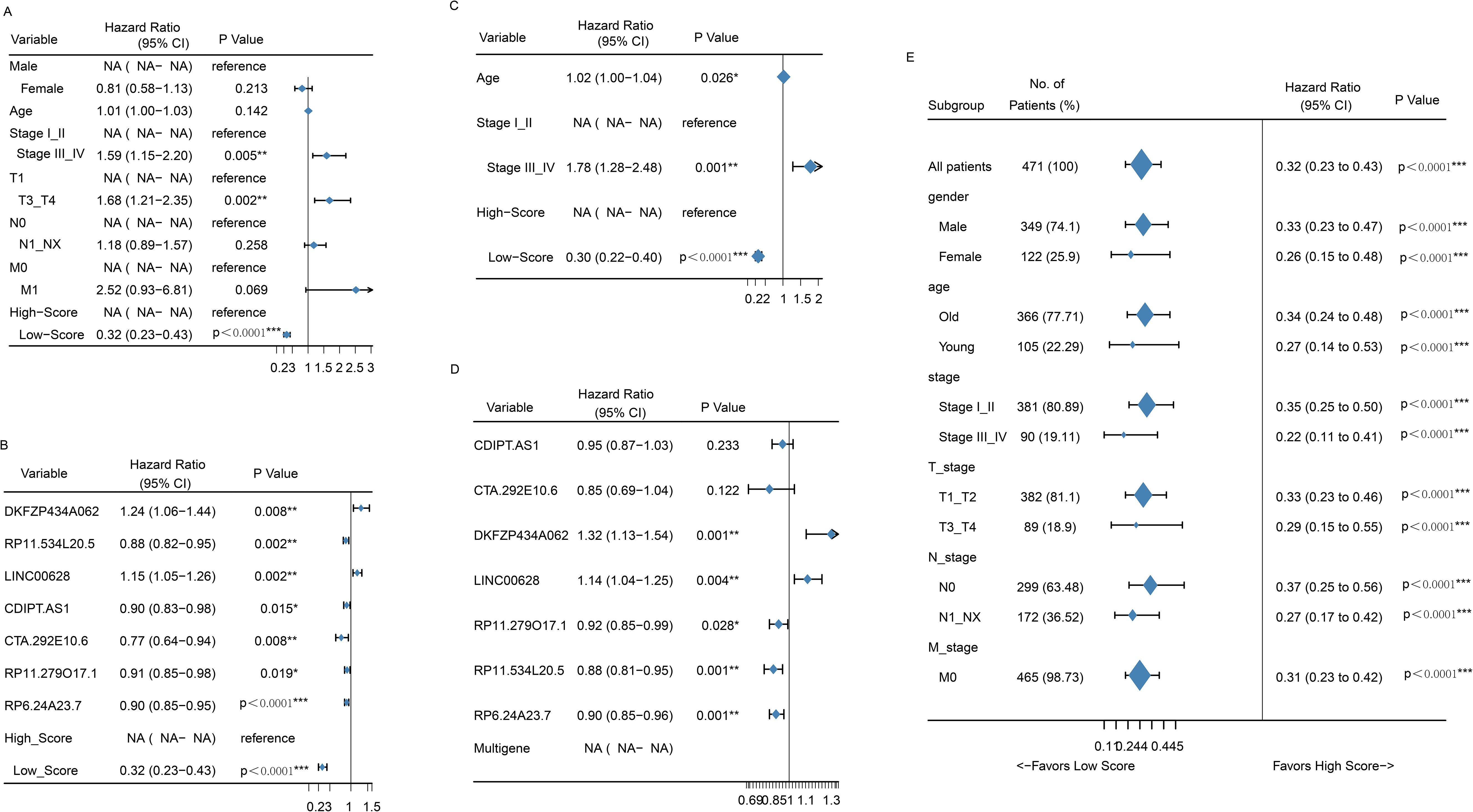
Figure 4. Forrest plot of the univariate Cox regression analysis OS of clinical factors (A) and seven-gene signatures (B). Forrest plot of the multivariate Cox regression analysis OS of clinical factors (C) and seven-gene signatures (D). Forrest plot of the univariate Cox regression analysis OS of risk score group in subgroup of clinical factors (E). *p<0.05; **<0.01; ***<0.0001.
KEGG pathway analysis was performed on the protein-coding genes that were significantly associated with the model LncRNAs in TCGA-LUSC, using the entire human genome as the background. The results revealed that the prognostic LncRNAs were primarily enriched in pathways related to immune function, including Th17 cell differentiation, TNF signaling, NF-κB signaling, JAK-STAT signaling, Toll-like receptor signaling, and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction (Figure 5B, P < 0.05). Moreover, the expression levels of the enriched genes were notably suppressed in LUSC patients. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis indicated that co-expressed genes were significantly downregulated and enriched in immune-related GO terms, such as mast cell activation involved in immune response, negative regulation of TNF production, regulation of leukocyte degranulation, and negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production (Figure 5A, P < 0.05). These findings were further supported by cnetplot analyses for KEGG and GO (Figures 5C, D), and emapplot analysis revealed network interactions among key KEGG pathways and GO terms (Figures 5E, F). The expression levels of 14 target genes (BMP2, CCL4, CFLAR, CISH, CSF1, CSF2RA, CSF3, CXCL3, ICAM1, IL17D, IL18R1, NFKBIA, PYGM, TNFSF14) associated with tumor immune tolerance were significantly suppressed (Figure 5D). PCR and western blot analyses confirmed the downregulation of eight of these genes, yielding consistent results (Figure 6).
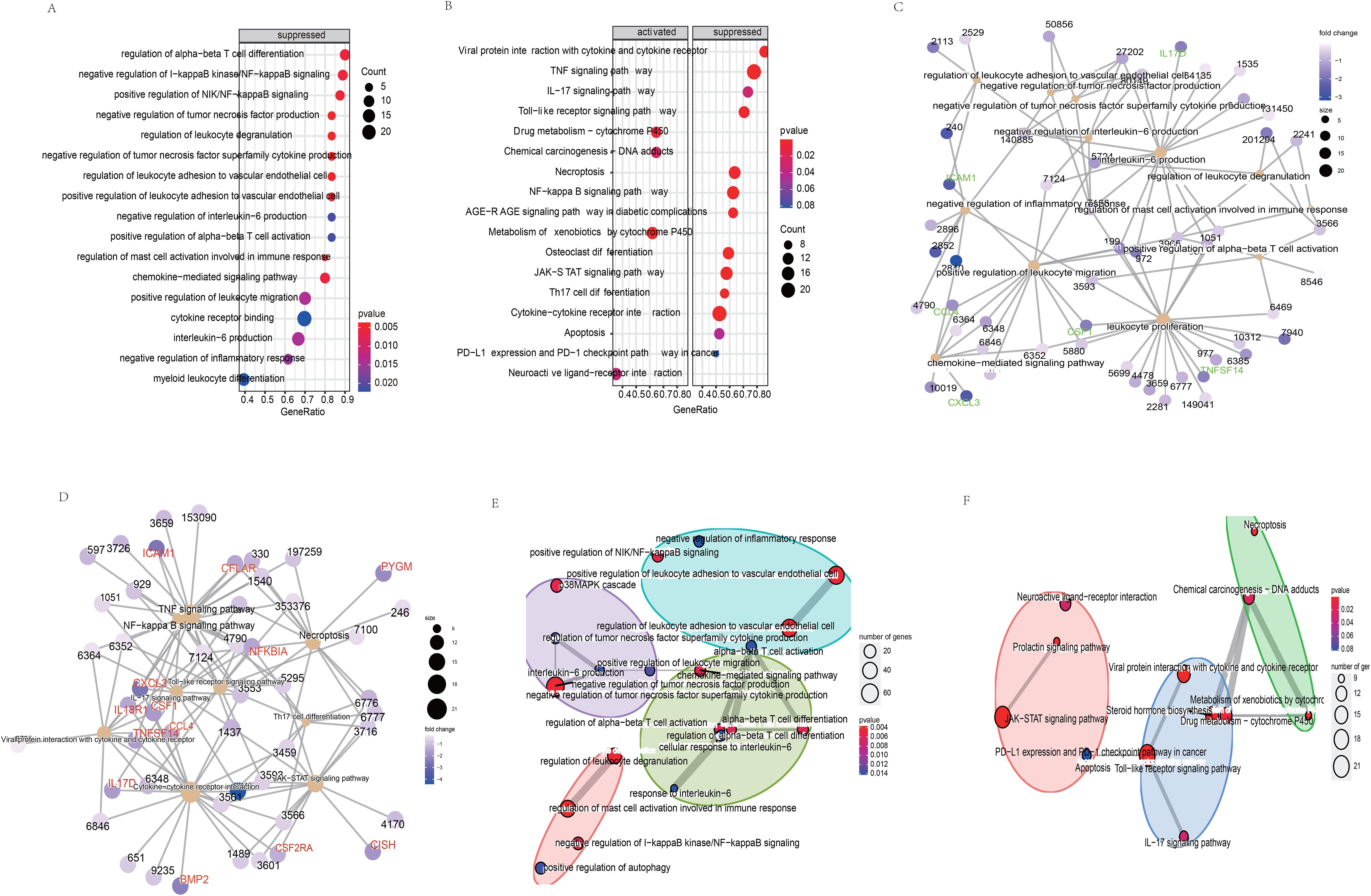
Figure 5. Biological functions (A) and the signaling pathways (B) of co-expressed genes related the model LncRNAs. The network regulation relationship between the co-expressed genes and biological functions (C)/the signaling pathways (D). The network regulation relationship among the biological functions (E)/the signaling pathways (F).
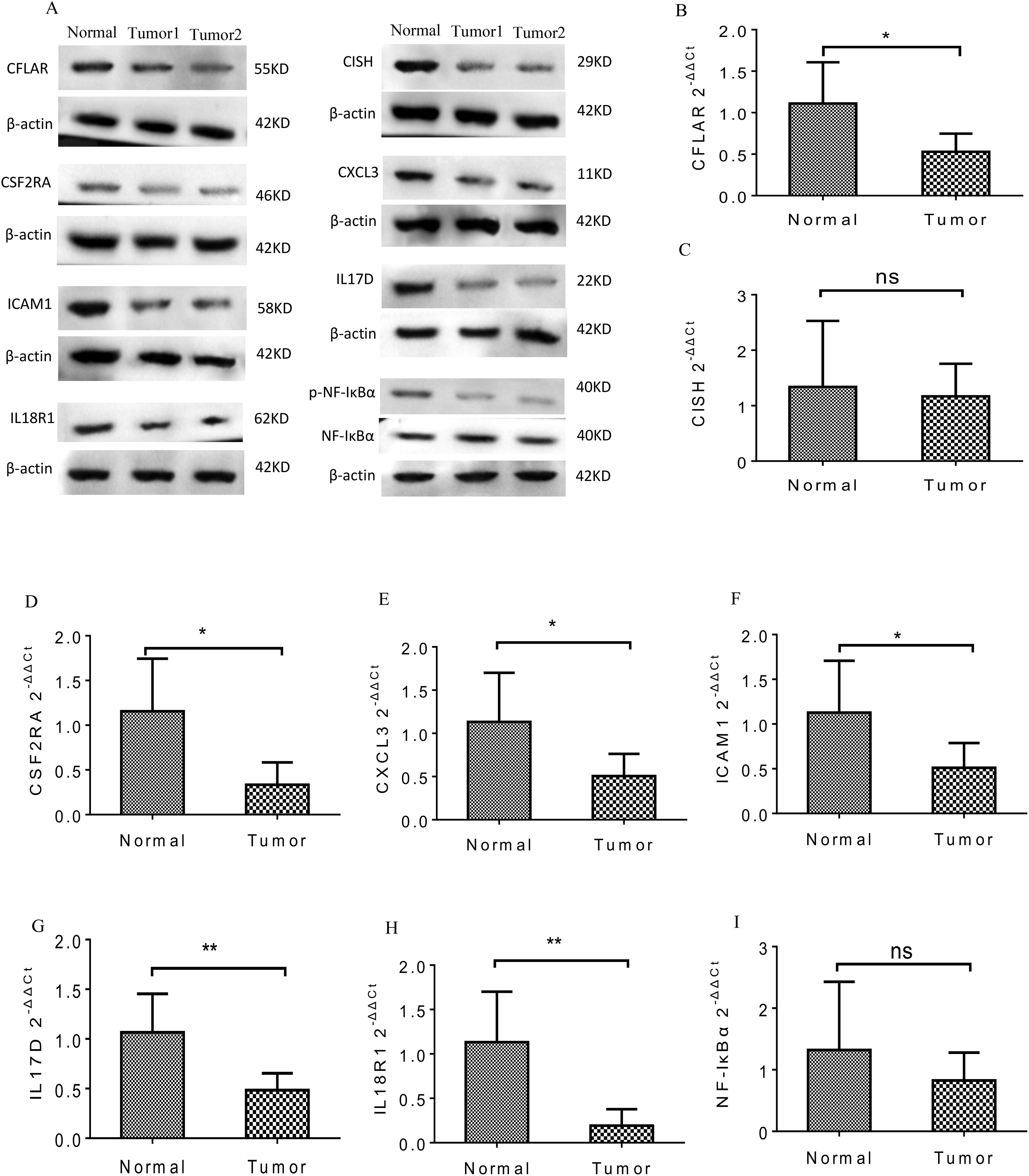
Figure 6. The PCR and WB analysis results of the eight genes in tumor tissues. (A) Protein expression of the eight genes was significantly decreased in the tumor groups. (B-I) mRNA expression of the eight genes was significantly inhibited in the tumor groups. *p<0.05; **<0.01; NS>0.05.
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, yet treatment options continue to be limited. The clinical efficacy of available treatments is hindered by delayed diagnosis, limited therapeutic approaches, and the emergence of relapse and resistance (15). LUSC, a subtype of NSCLC, accounts for nearly 40% of all lung cancer cases. Early detection and timely intervention in LUSC can significantly improve patient prognosis, alleviating both the financial burden on patients and enhancing their overall quality of life (16). For decades, cancer research focused predominantly on protein-coding genes (17). However, recent studies have shifted toward exploring the role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in cancer, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). These studies have highlighted the crucial regulatory roles of ncRNAs in cancer development and progression, broadening our understanding beyond protein-coding genes (18, 19). Chen et al. and Zhou et al. established a distinct panel of LncRNAs with significant diagnostic value for predicting the prognosis of LUAD (20, 21). Zhang et al. developed a prognostic model for LUSC patients based on nine specific LncRNAs (AC013457.1, AC124067.2, AP001189.1, AP002360.1, BANCR, LINC00519, LINC01807, MIR3945HG, FAM83A−AS1, and POU6F2−AS2) (22). However, research on prognostic biomarkers for LUSC patients remains limited.
In the present study, we further investigated the role of LncRNAs in LUSC and identified seven previously unstudied LncRNAs significantly associated with the OS of LUSC patients. A significant survival difference was observed between the low-risk and high-risk groups, stratified by the risk score derived from our model in the training set. In addition, mean survival time, mortality rates, and overall prognosis varied significantly between these groups (Figure 1). These findings were validated in the testing dataset and across the entire cohort, yielding consistent results that have not been previously reported (22). We assessed the prognostic ability of our model using ROC curve analysis. Although the prognostic value of the AUC is modest, there is currently no better alternative for prediction. Relevant studies have also used AUC values to predict overall survival (OS), demonstrating its strong predictive ability (23, 24). In our study, the AUCs for 1-, 3-, 5-, 7-, and 10-year OS in the training group were 0.65, 0.73, 0.69, 0.71, and 0.80, respectively (Figure 2H). Notably, the AUCs for 1- and 5-year OS were consistent with those reported in previous studies, further confirming the reliability of our results (23, 24). Moreover, our study offers more detailed information and greater accuracy than the single AUC value of 0.65 for 3-year survival reported by Zhang et al. (22). Notably, our prognostic model outperformed other clinical variables, including TNM stage (AUCs of 0.57, 0.55, 0.54, 0.55, and 0.40) and age (AUCs of 0.56, 0.60, 0.59, 0.54, and 0.60), across all time points in predicting the prognosis of LUSC patients. A prognostic nomogram was constructed, demonstrating excellent accuracy in predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS, an achievement not previously reported in the literature (Figure 3). Multivariate Cox regression analysis confirmed that the 7-LncRNA signature remained an independent predictor of OS in LUSC patients (Figure 4). Furthermore, subgroup analysis confirmed the strong predictive ability of the risk score for OS across various LUSC subpopulations, stratified by age, gender, tumor stage, and other clinical features (Supplementary Figure S1). These results suggest that the 7-LncRNA signature is a robust prognostic marker for LUSC that remains independent of other clinical variables.
To explore the underlying biological mechanisms of tumor immune inhibition in LUSC, we performed GO and KEGG enrichment analyses based on the 7-LncRNA model. Th17 cells, along with their associated cytokines, are implicated in immune responses across various tumors (25). IFN-γ and IL-17 stimulate Th17 cell differentiation, leading to the production of CXCL9 and CXCL10, which recruit Th1 and NK cells to the tumor microenvironment, enhancing antitumor immune responses (26). Interestingly, our results indicated that the expression of protein-coding genes involved in Th17 cell differentiation (Figure 5B) was significantly suppressed in LUSC patients (Figure 5D). NF-κB plays a key role in immune cell function, promoting inflammation by inducing the expression of cytokines and chemokines, which inhibit tumor growth (27). It has also been implicated in tumorigenesis (28). The activation of TNF-α and IL-1, which stimulate NF-κB through their receptors, enhances innate immune responses and promotes tumor cell apoptosis (29, 30). TNF-α exhibits antineoplastic properties (31), and its receptors are significantly downregulated in high-stage NSCLC. Additionally, STAT3 and STAT5, members of the STAT family, are implicated in tumor initiation and progression (32). It has been shown that STAT3 inactivation reduces TNF-α expression, leading to a loss of its ability to bind the TNF-α promoter (33, 34). Our findings (Figures 5, 6) demonstrated significant downregulation of genes associated with the TNF pathway (NFKBIA, CSF1, ICAM1, CXCL3), the NF-κB pathway (CCL4, CFLAR, NFKBIA, TNFSF14, ICAM1, CXCL3), JAK-STAT signaling (CSF2RA, CISH, CSF3), Toll-like receptor signaling (CCL4, NFKBIA), and Th17 cell differentiation (NFKBIA), further supporting the involvement of these pathways in LUSC (35–37).
Immune escape is a critical mechanism in tumorigenesis, and recent studies have shown that LncRNAs like SNHG12 facilitate immune evasion in NSCLC by interacting with HuR to increase PD-L1 and USP8 levels (38). Our study revealed that 14 target genes associated with immune tolerance were significantly suppressed in LUSC and were linked to the 7-LncRNAs of our risk model (Figures 5, 6). Despite this, immune infiltration, including T cells, B cells, NK cells, and monocytes, was prominently activated in LUSC patients (Figure 7). While numerous studies have reported immune infiltration in tumors such as breast cancer and glioblastoma multiforme (39, 40), not all immune infiltrates exert antitumor effects (41, 42). The mechanisms by which the seven prognostic LncRNAs contribute to immune escape in LUSC remain unclear and warrant further investigation.
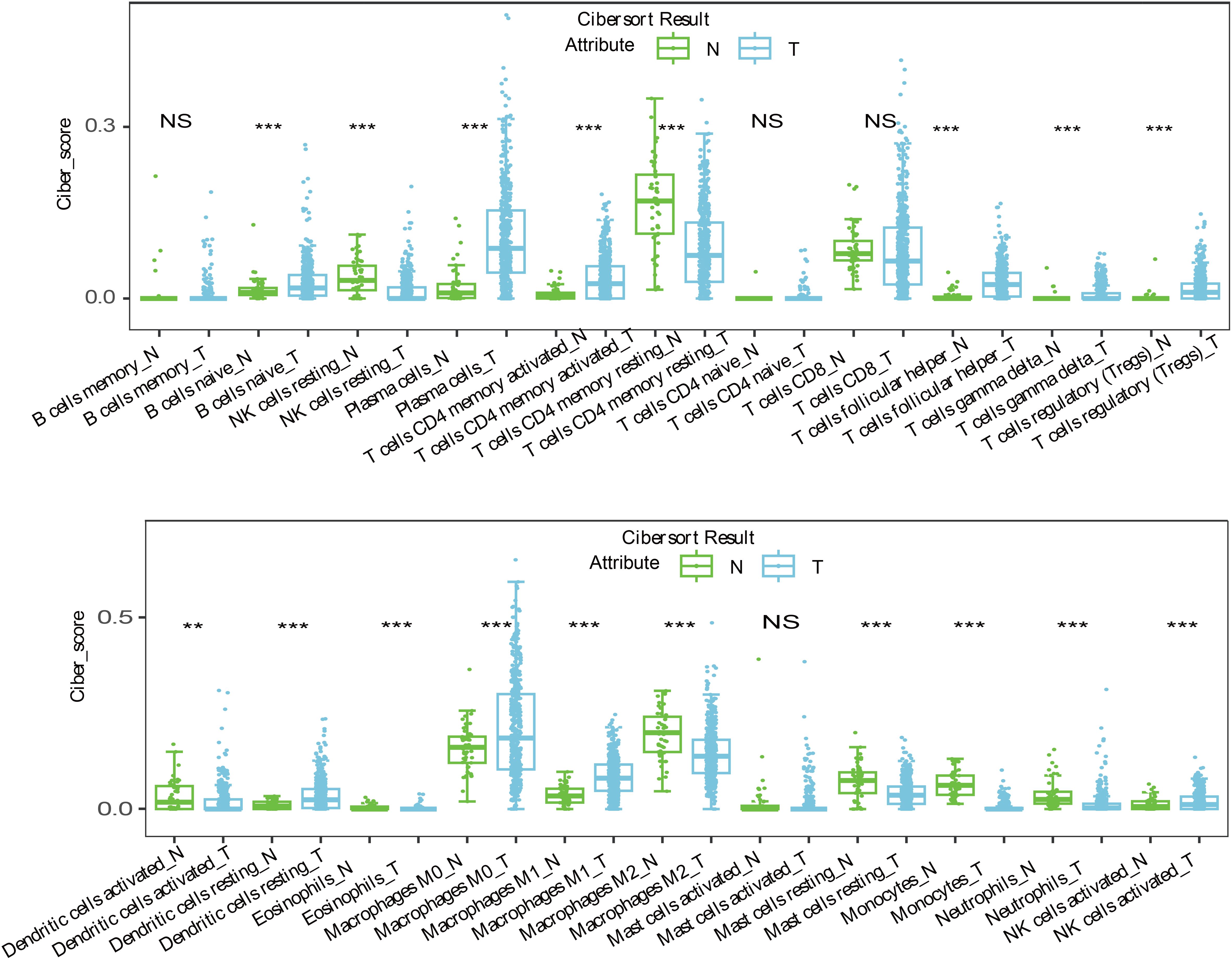
Figure 7. The immune infiltration reaction including T cells, B cells, NK cells and monocytes were prominent active in LUSC patients. **<0.01; ***<0.0001; NS>0.05.
There are several limitations to this study. First, the 7-LncRNA signature was derived from a relatively small cohort of 236 patients. Second, while bioinformatics analyses provided insights into the potential functions of the LncRNAs, the exact molecular mechanisms remain unclear and require further validation through experimental studies. Third, due to insufficient data, we were unable to assess the impact of treatment strategies or medications on patient outcomes in LUSC. In conclusion, we have identified seven LncRNA biomarkers that can effectively predict OS in LUSC patients, providing valuable insights for prognostic prediction in this patient population.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Review Committee of Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province with the approval number L2024-06-39-01. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from gifted from another research group. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
QG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. XW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Software, Writing – original draft. YH: Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Research Foundation of Taizhou (20ywa12) and Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Health Department (2025KY1823).
Thank you for the support from the platform of Taizhou Key Laboratory of Pharmaceuticals Therapy and Translation Research.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1511564/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of risk score group in subgroup of clinical factors. (A) age; (B) gender; (C) TNM stage; (D) N stage; (E) M stage; (F) T stage.
1. Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Branicki W, Taheri M. Non-coding RNA profile in lung cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. (2020) 114:104411. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104411
2. Ishola AA, La’ah AS, Le HD, Nguyen VQ, Yang YP, Chou SJ, et al. Non-coding RNA and lung cancer progression. J Chin Med Assoc. (2020) 83:8–14. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000225
3. Carter BW, Lichtenberger JP, Benveniste MK, Groot PM, Wu CC, Erasmus JJ, et al. Revisions to the TNM staging ofLung cancer: rationale, significance, and clinical application. Radiographics. (2018) 38:374–91. doi: 10.1148/rg.2018170081
4. Woodard GA, Jones KD, Jablons DM. Lung cancer staging and prognosis. Cancer Treat Res. (2016) 170:47–75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-40389-2_3
5. Zinicola R, Pedrazzi G, Haboubi N, Nicholls RJ. The degree of extramural spread of T3 rectalcancer: a plea to the UICC and AJCC. Colorectal Dis. (2017) 19:310. doi: 10.1111/codi.13456
6. Chen KN. Small cell lung cancer and TNM staging. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. (2016) 19:409–12. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.06.22
7. Goodwin S, McPherson JD, McCombie WR. Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat Rev Genet. (2016) 17:333–51. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.49
8. Ma X, Yang X, Bao W, Li S, Liang S, Sun Y, et al. Circular RNA circMAN2B2 facilitates lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion via miR-1275/FOXK1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 498:1009–15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.105
9. Zong L, Sun Q, Zhang H, Chen Z, Deng Y, Li D, et al. Increased expression of circRNA_102231 in lung cancer and its clinical significance. BioMed Pharmacother. (2018) 102:639–44. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.084
10. Lai XN, Li J, Tang LB, Chen WT, Zhang L, Xiong LX. MiRNAs and lncRNAs: dual roles in TGF-beta signaling-regulated metastasis in lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) . 21:1193. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041193
11. Avazpour N, Hajjari M, Tahmasebi Birgani M. HOTAIR: A promising long non-coding RNA with potential role in breast invasive carcinoma. Front Genet. (2017) 8:170. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00170
12. Lee NK, Lee JH, Ivan C, Ling H, Zhang X, Park CH, et al. MALAT1 promoted invasiveness of gastric adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:46. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2988-4
13. Yu X, Li Z, Zheng H, Chan MT, Wu WK. NEAT1: A novel cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Cell Prolif. (2017) 50:e12329. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12329
14. Chen Z, Lei T, Chen X, Gu J, Huang J, Lu B, et al. Long non-coding RNA in lung cancer. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 504:190–200. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.11.031
15. Iqbal MA, Arora S, Prakasam G, Calin GA, Syed MA. MicroRNA in lung cancer: role, mechanisms, pathways and therapeutic relevance. Mol Aspects Med. (2019) 70:3–20. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.07.003
16. Wang C, Tan S, Li J, Liu WR, Peng Y, Li W. CircRNAs in lung cancer - Biogenesis, function and clinical implication. Cancer Lett. (2020) 492:106–15. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.013
17. Slack FJ, Chinnaiyan AM. The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell. (2019) 179:1033–55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.017
18. Yan H, Bu P. Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. (2021) 65:625–39. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200032
19. Li Y, Li G, Guo X, Yao H, Wang G, Li C. Non-coding RNA in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. (2020) 485:38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.04.023
20. Jiawei Z, Min M, Yingru X, Xin Z, Danting L, Yafeng L, et al. Identification of key genes in lung adenocarcinoma and establishment of prognostic mode. Front Mol Biosci. (2020) 7:561456. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.561456
21. Chen X, Guo J, Zhou F, Ren W, Pu J, Mutti L, et al. Over-expression of long non-coding RNA-AC099850.3Correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:895708. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.895708
22. Zhang X, Su Y, Fu X, Xiao J, Qin G, Yu M, et al. Evaluation of the prognostic value of long noncoding RNAs in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J Oncol. (2022) 2022:9273628. doi: 10.1155/2022/9273628
23. Wang Y, Yang F, Zhuang Y. Identification of a progression-associated long non-coding RNA. signature for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 15:1185–92. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5571
24. Zhu J, Wang M, Hu D. Development of an autophagy-related gene prognostic signature in lung. adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. PeerJ. (2020) 8:e8288. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8288
25. Atarashi K, Nishimura J, Shima T, Umesaki Y, Yamamoto M, Onoue M, et al. ATP drives lamina propria T(H)17 cell differentiation. Nature. (2008) 455:808–12. doi: 10.1038/nature07240
26. Kryczek I, Banerjee M, Cheng P, Vatan L, Szeliga W, Wei S, et al. Phenotype, distribution, generation, and functional and clinical relevance of Th17 cells in the human tumor environments. Blood. (2009) 114:1141–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-208249
27. Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. (2004) 25:280–8. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.03.008
28. Perkins ND, Gilmore TD. Good cop, bad cop: the different faces of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ. (2006) 13:759–72. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401838
29. Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP. Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol. (1999) 17:331–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.331
30. O’Neill LA, Dinarello CA. The IL-1 receptor/toll-like receptor superfamily: crucial receptors for inflammation and host defense. Immunol Today. (2000) 21:206–9. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(00)01611-x
31. Jeon YJ, Middleton J, Kim T, Lagana A, Piovan C, Secchiero P, et al. A set of NF-kappaB-regulated microRNAs induces acquired TRAIL resistance in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:E3355–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504630112
32. Thomas SJ, Snowden JA, Zeidler MP, Danson SJ. The role of JAK/STAT signalling in the pathogenesis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumours. Br J Cancer. (2015) 113:365–71. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.233
33. Li T, Wu S, Zhang H, Wang Y, Luo H, Zuo X, et al. Activation of nicotinic receptors inhibits TNF-alpha-induced production of pro-inflammatory mediators through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathwayin fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation. (2015) 38:1424–33. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0117-1
34. Yu LJ, Wang B, Parobchak N, Roche N, Rosen T. STAT3 cooperates with the non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling to regulate pro-labor genes in the human placenta. Placenta. (2015) 36:581–6. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.02.013
35. Xia R, Geng G, Yu X, Xu Z, Guo J, Liu H, et al. LINC01140 promotes the progression and tumor immune escape in lung cancer by sponging multiple microRNAs. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002746. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002746
36. Li C, Pan B, Wang X, Liu X, Qin J, Gao T, et al. Upregulated LINC01088 facilitates Malignant phenotypes and immune escape of colorectal cancer by regulating microRNAs/G3BP1/PD-L1 axis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2022) 148:1965–82. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-03981-8
37. Ma F, Ding MG, Lei YY, Luo LH, Jiang S, Feng YH, et al. SKIL facilitates tumorigenesis and immune escape of NSCLC via upregulating TAZ/autophagy axis. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:1028. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03200-7
38. Huang Y, Xia L, Tan X, Zhang J, Zeng W, Tan B, et al. Molecular mechanism of LncRNA SNHG12 in immune escape of non-small cell lung cancer through the HuR/PD-L1/USP8 axis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2022) 27:43. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00343-7
39. Dieci MV, Miglietta F, Guarneri V. Immune infiltrates in breast cancer: recent updates and clinical implications. Cells. (2021) 10:223. doi: 10.3390/cells10020223
40. Sokratous G, Polyzoidis S, Ashkan K. Immune infiltration of tumor microenvironment following immunotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2017) 13:2575–82. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1303582
41. Picard E, Verschoor CP, Ma GW, Pawelec G. Relationships between immune landscapes, genetic subtypes and responses to immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:369. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00369
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, prognosis, lung squamous cell carcinoma, immune escape, seven LncRNA signature
Citation: Ge Q, Lin Z, Wang X, Jiang Z and Hu Y (2025) A seven-LncRNA signature for prognosis prediction of patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma through tumor immune escape. Front. Oncol. 15:1511564. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1511564
Received: 15 October 2024; Accepted: 05 March 2025;
Published: 24 March 2025.
Edited by:
Ahmed Lasfar, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, United StatesReviewed by:
Denggang Fu, Indiana University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Ge, Lin, Wang, Jiang and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Hu, aHV5YW4wNzI5MTRAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Zhengli Jiang, MTM3MzY1MjA5MTdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.