- 1Department of General Surgery, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, Dongxiang District People’s Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 3Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Dongxiang District People’s Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 4Department of Molecular Diagnostics and Experimental Therapeutics, Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope, Biomedical Research Center, Comprehensive Cancer Center, Monrovia, CA, United States
- 5Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 6Institute (College) of Integrative Medicine, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
Objective: We aimed to compare the perioperative outcomes and postoperative complications of laparoscopic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (L-RAMPS) versus laparoscopic distal pancreatosplenectomy (L-DPS) for left-sided pancreatic cancer through a meta-analysis.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis, conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, were performed. Literature searches were conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Embase for studies published from their inception up to June 14th, 2024.
Results: A total of three retrospective studies involving 242 patients were included in this meta-analysis, with 116 patients in the L-RAMPS group and 126 in the L-DPS group. The meta-analysis results indicated that L-RAMPS was associated with the retrieval of more lymph nodes (MD: 3.06; 95% CI: 2.51 to 3.62, p < 0.00001) and longer operative time (MD: 20.05; 95% CI: 13.97 to 26.12, p < 0.00001) compared to L-DPS for left-sided pancreatic cancer patients. However, no significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of R0 resection margins, the incidence of pancreatic fistula (Grade B and C), postpancreatectomy hemorrhage, or postoperative complications (Clavien-Dindo Grades II and III).
Conclusions: In patients with left-sided pancreatic cancer, L-RAMPS resulted in the retrieval of more lymph nodes, a longer operative time, and a similar incidence of postoperative complications compared to L-DPS. Larger sample sizes, extended follow-up periods, and well-conducted randomized controlled trials are needed to further validate these findings
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=558977, identifier CRD42024558977.
1 Introduction
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly aggressive tumor with increasing global incidence, making its early diagnosis and management particularly challenging due to its rapid progression (1). Typically, it is diagnosed during an advanced stage of the disease when the tumor has spread beyond the margins of the pancreas to adjacent tissues or distant organs. (2)
Surgical resection remains the only potentially curative treatment for PDAC (3, 4). Specifically, laparoscopic distal pancreatosplenectomy (L-DPS) is recommended as the standard procedure for left-sided PDAC resection (5). A number of studies have demonstrated that L-DPS is a feasible, safe, and oncologically equivalent treatment for PDAC (6, 7). However, uncertainties remain regarding the extent of posterior resection and the effectiveness of achieving complete lymph node resection during L-DPS (7).
A radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (RAMPS) procedure was developed in 2003 by Strasberg in order to achieve a radical operation with the most extensive lymphadenectomy possible (8). In comparison with DPS, RAMPS attempts to achieve negative retroperitoneal margins and higher lymph node retrieval in order to improve survival outcomes (9–11), Despite this, comparisons between RAMPS and DPS have yielded mixed results, with recent meta-analyses suggesting minimal impact on prognosis from RAMPS for left-sided pancreatic cancer (11–15).
Given the importance of understanding the comparative effectiveness and safety of these surgical techniques, and the limited clinical analysis of laparoscopic RAMPS (L-RAMPS) versus L-DPS, this meta-analysis aims to evaluate the perioperative outcomes and postoperative complications associated with each approach in patients with left-sided pancreatic cancer.
2 Methods
This study adhered to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) reporting guidelines, and AMSTAR 2 guidelines (assessing the methodological quality of systematic reviews) (16–18). The current meta-analysis was registered on the PROSPERO website (registration number: CRD42024558977). As this research involved a secondary analysis of existing published data, ethical approval was not necessary.
2.1 Database search
Literature searching was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library and Embase for studies published rom their inception through June 14th, 2024. The search had no language or regional restrictions. Keywords and medical subject heading (MeSH) terms used included “laparoscopic”, “radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy”, “distal pancreatosplenectomy”, and “pancreatic cancer”. Additionally, we examined the bibliographies of relevant articles to identify further studies.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) clinical studies comparing L-RAMPS and L-DPS for patients with left-sided PDAC; (2) full-text articles reporting at least one outcome of interest, such as perioperative outcomes or postoperative complications; and (3) in the case of duplicate reports, the study with the most comprehensive, up-to-date, and largest dataset was included.
Exclusion criteria included: (1) duplicate publications; (2) studies lacking complete and valid outcome data for statistical analysis; and (3) case reports, reviews, animal studies, editorial comments, meeting abstracts, and other unrelated research.
2.3 Data extraction
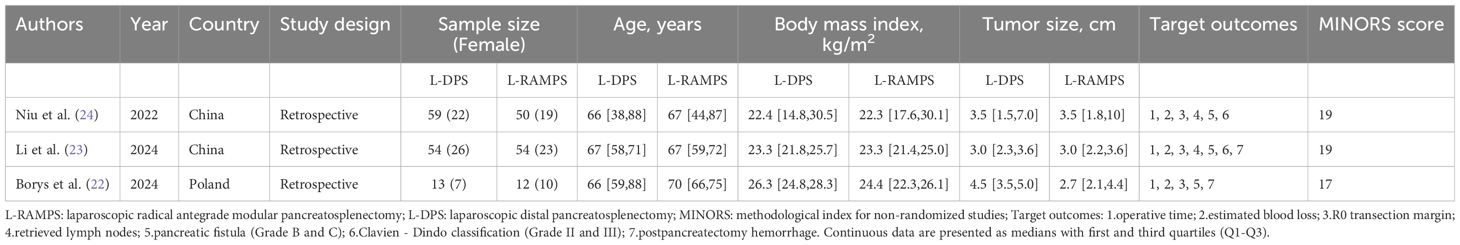
Two investigators independently screened and evaluated the studies based on the inclusion criteria and extracted relevant data from the included studies. In the case of disputes, a third investigator was consulted to resolve them. The following data were extracted: (1) baseline data: name of the first author, year of publication, country, study design, sample size, patients’ age, body mass index, and tumor size; (2) perioperative outcomes: operative time, estimated blood loss, R0 transection margin, and retrieved lymph nodes; and (3) postoperative complications such as pancreatic fistula (Grade B and C), Clavien - Dindo classification (Grade 2 and 3), postpancreatectomy hemorrhage, postoperative mortality, and long-term outcomes.
2.4 Quality assessment
The quality of the retrospective studies was assessed using the Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS), which includes 12 evaluation items. Each item was scored on a scale of 0 to 2 points: 0 points indicated the item was not reported, 1 point indicated the item was reported with insufficient information, and 2 points indicated the item was reported with sufficient information (19). The assessment was independently conducted by two authors, with any disagreements resolved through discussion with a third author.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Review Manager Version 5.4 (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK) was used for the statistical analysis. Continuous variables were expressed as weighted mean differences (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI), and binary variables were represented by odds ratios (OR) and 95% CI. When only median and extreme values were reported in the study, the mean and standard deviation (SD) were calculated from the median and range, as described by Hozo et al. (20) Heterogeneity among the studies was assessed using the I2 statistic (0-50%, low heterogeneity; 50-75%, moderate heterogeneity; and ≥75%, high heterogeneity) (21). For studies with obvious heterogeneity and an I2-value of more than 50%, the random-effects model was adopted. Sensitivity analyses were performed as appropriate. Publication bias was evaluated using Begg’s test and Egger’s test using the Stata software (Stata version 16.0, College Station, Texas, USA). For all tests, a P-value <0.05 (two-sided) was considered to indicate a significant difference.
3 Results
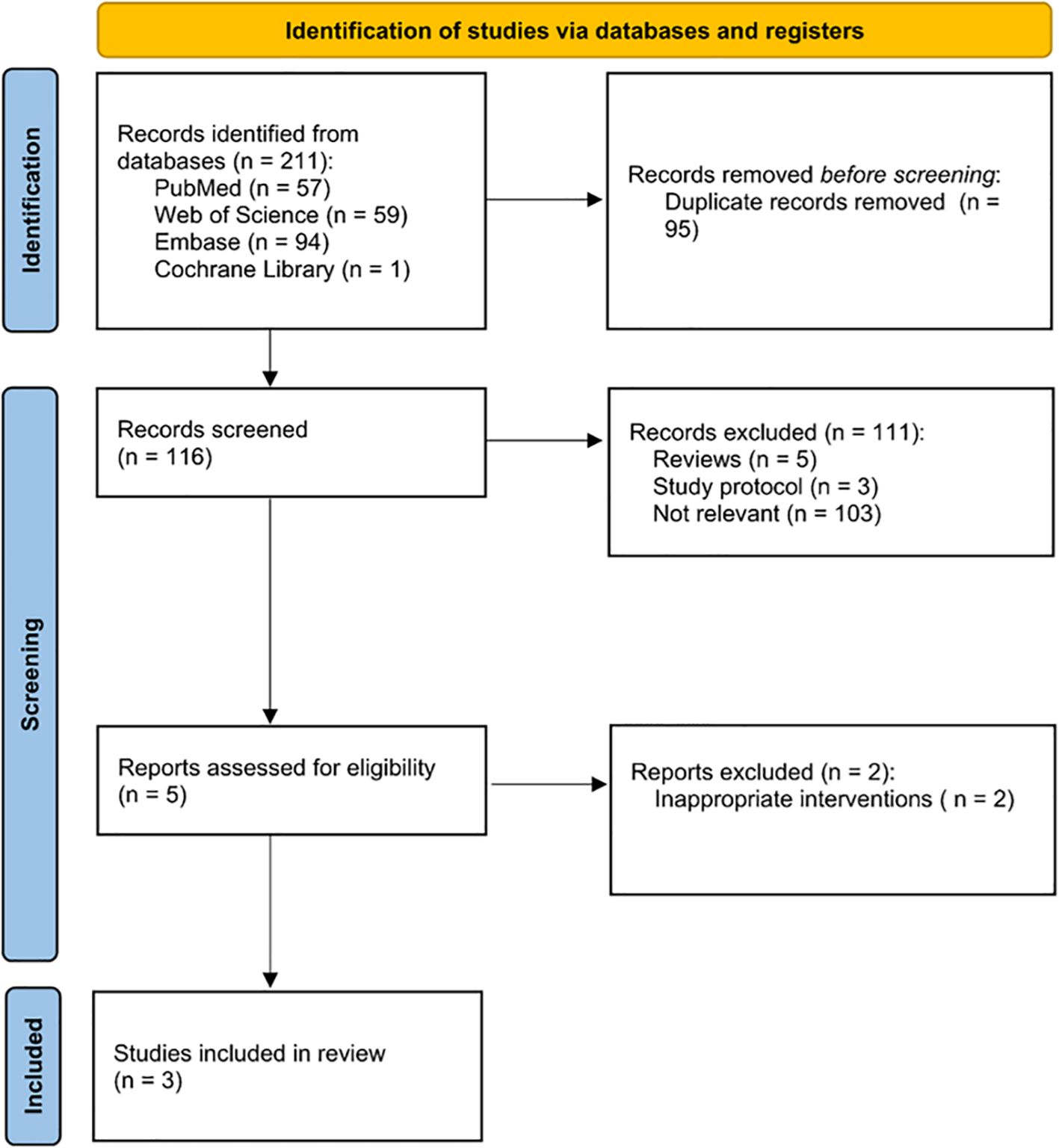
A flow diagram of the study selection process can be seen in Figure 1. No randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were available for analysis, however, three retrospective comparative studies were eligible (22–24). A total of three retrospective studies with 242 patients, of whom 116 patients were in the L-RAMPS group and 126 in the L-DPS group, were involved in this meta-analysis. The baseline characteristics of these studies, including author, country, study design, sample size, sex, patients’ age, body mass index, tumor size, target outcomes, and MINORS score, are provided in Table 1.
3.1 Perioperative outcomes
3.1.1 Operative time
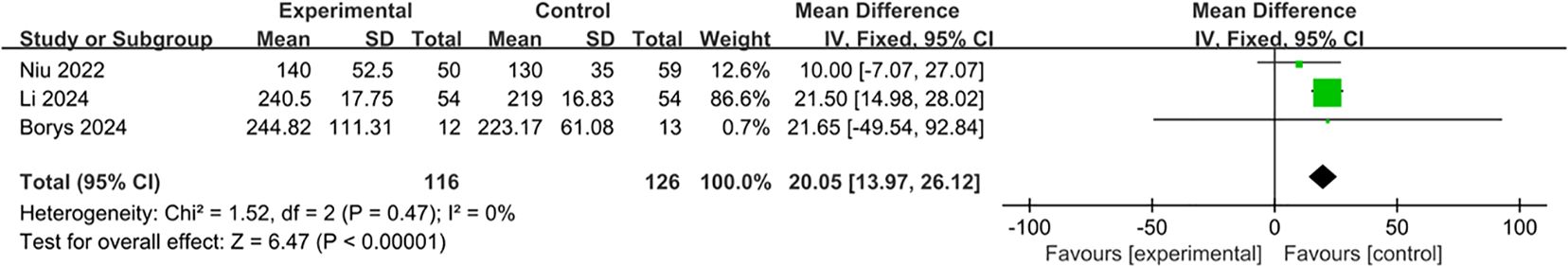
All of the three studies were included in the analysis of the operative time (22–24). The operative time was significantly shorter in the L-DPS group than that in the L-RAMPS group (MD: 20.05; 95% CI: 13.97 to 26.12, p < 0.00001). The between-study heterogeneity was low (I2 = 0%, p = 0.47) (Figure 2).
3.1.2 Estimated blood loss
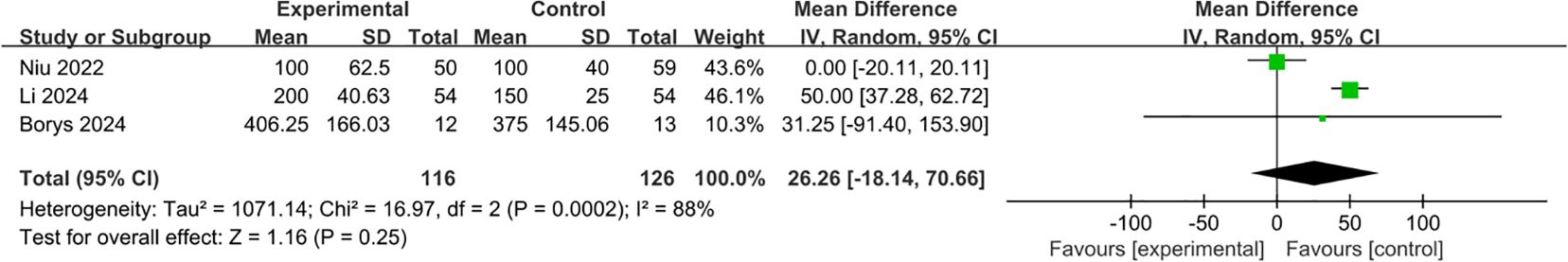
All three studies were included in the analysis of estimated blood loss (22–24). No significant difference in estimated blood loss was observed between the L-RAMPS group and the L-DPS group (MD: 26.26; 95% CI: -18.14 to 70.66, p = 0.25). The between-study heterogeneity was significant (I2 = 88%, p = 0.0002) (Figure 3).
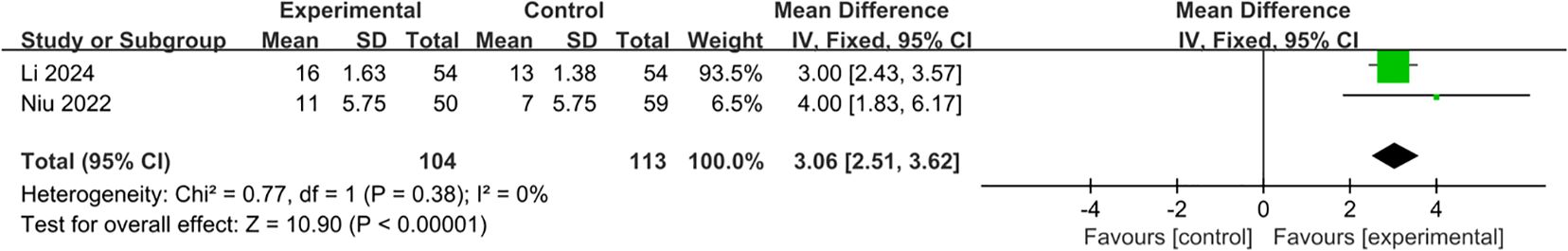
3.1.3 Retrieved lymph nodes
Two studies were included in the analysis of the number of retrieved lymph node (23, 24). Our analysis demonstrated that the number of retrieved lymph node was less in L-DPS group (MD: 3.06; 95% CI: 2.51 to 3.62, p < 0.00001). Between-study heterogeneity was low (I2 = 0%, p = 0.38) (Figure 4).
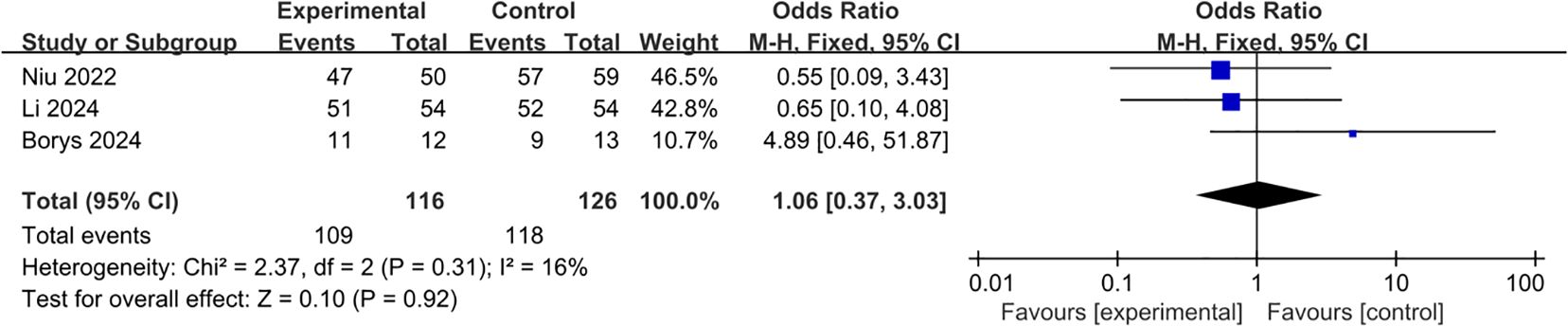
3.1.4 R0 transection margin
All of the three studies were included in the analysis of R0 transection margin (22–24). Pooling of the results indicated that the L-RAMPS procedure could not decrease the incidence of R0 transection margin compared with the L-DPS procedure (OR: 1.06; 95%CI: 0.37 to 3.03; p = 0.92), and low heterogeneity existed among the included studies (p = 0.31, I2 = 16%) (Figure 5).
3.2 Postoperative outcomes
3.2.1 Pancreatic fistula (Grade B and C)
All of the three studies were included in the analysis of pancreatic fistula. Pooling of the results indicated that the L-RAMPS procedure could not decrease the incidence of pancreatic fistula compared with the L-DPS procedure (OR: 0.67, 95%CI: 0.33 to 1.37, p = 0.27), and low heterogeneity existed among the included studies (p = 0.67, I2 = 0%) (Figure 6).
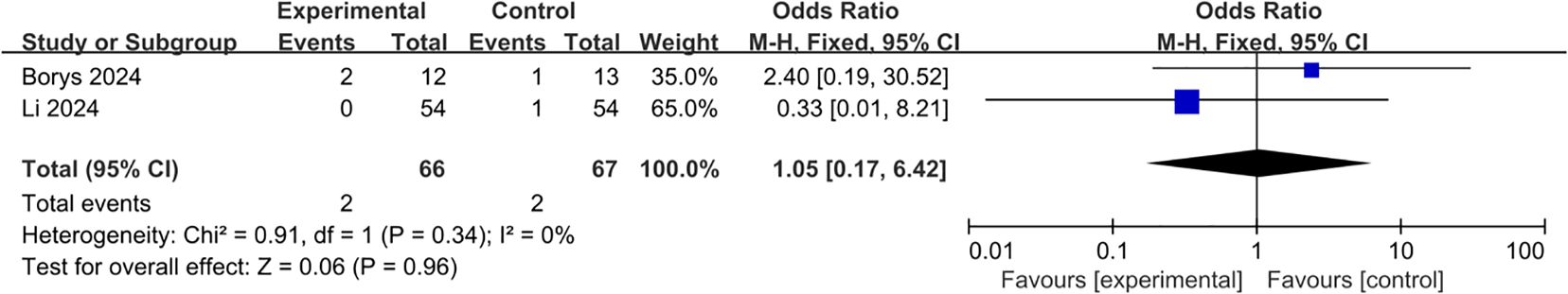
3.2.2 Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage
Two studies were included in the analysis of postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (22, 23). Pooling of the results indicated that the L-RAMPS procedure could not decrease the incidence of postpancreatectomy hemorrhage compared with the L-DPS procedure (OR: 1.05, 95%CI: 0.17 to 6.42, p = 0.96), and low heterogeneity existed among the included studies (p = 0.34, I2 = 0%) (Figure 7).
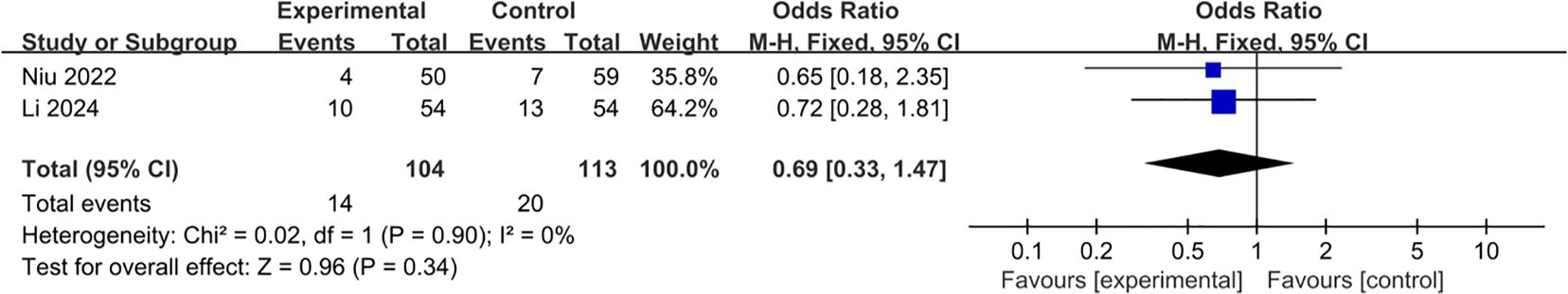
3.2.3 Postoperative complications (Clavien-Dindo Grade II and III)
Two studies were included in the analysis of postoperative complications (23, 24). Pooling of the results indicated that the L-RAMPS procedure could not decrease the incidence of postoperative complications (OR: 0.69, 95%CI: 0.33 to 1.47, p = 0.34), and low heterogeneity existed among the included studies (p = 0.90, I2 = 0%) (Figure 8).
3.2.4 Postoperative mortality
Postoperative mortality related indicators, such as 30-day mortality and 90-day mortality, were only reported in one study (22). L-DPS group has lower 30-day mortality (0 vs. 8.3%, p = N/A) and 90-day mortality (7.7% vs. 16.7%, p = 0.49) than L-RAMPS group, however the difference between the two groups was not statistically significant.
3.3 Long−term prognosis
Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was reported in one of the included studies (23). There was no significant difference in RFS observed between these two groups. The 6-month, 1-year, and 2-year RFS rates were 88.9%, 75.1%, and 41.6% for the L-RAMPS group, and 94.4%, 73.7%, and 48.6% for the LDP group, respectively (p = 0.715). Another study compared the disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) of two groups (24). According to the univariate analysis, L-RAMPS is not associated with an improvement in either DFS (p = 0.544) or OS (p = 0.336) over L-DPS.
For postoperative recurrence and metastasis, only one included study reported related data (23). The rates of early recurrence were 61.9% in the L-RAMPS group and 66.7% in the L-DPS group (p = 0.757). In the L-RAMPS group, the proportions of local recurrence, liver metastasis, and other distant metastasis were 23.8%, 52.4%, and 23.8%, respectively. In the L-DPS group, the corresponding proportions were 38.9%, 27.8%, and 33.3% (p = 0.293).
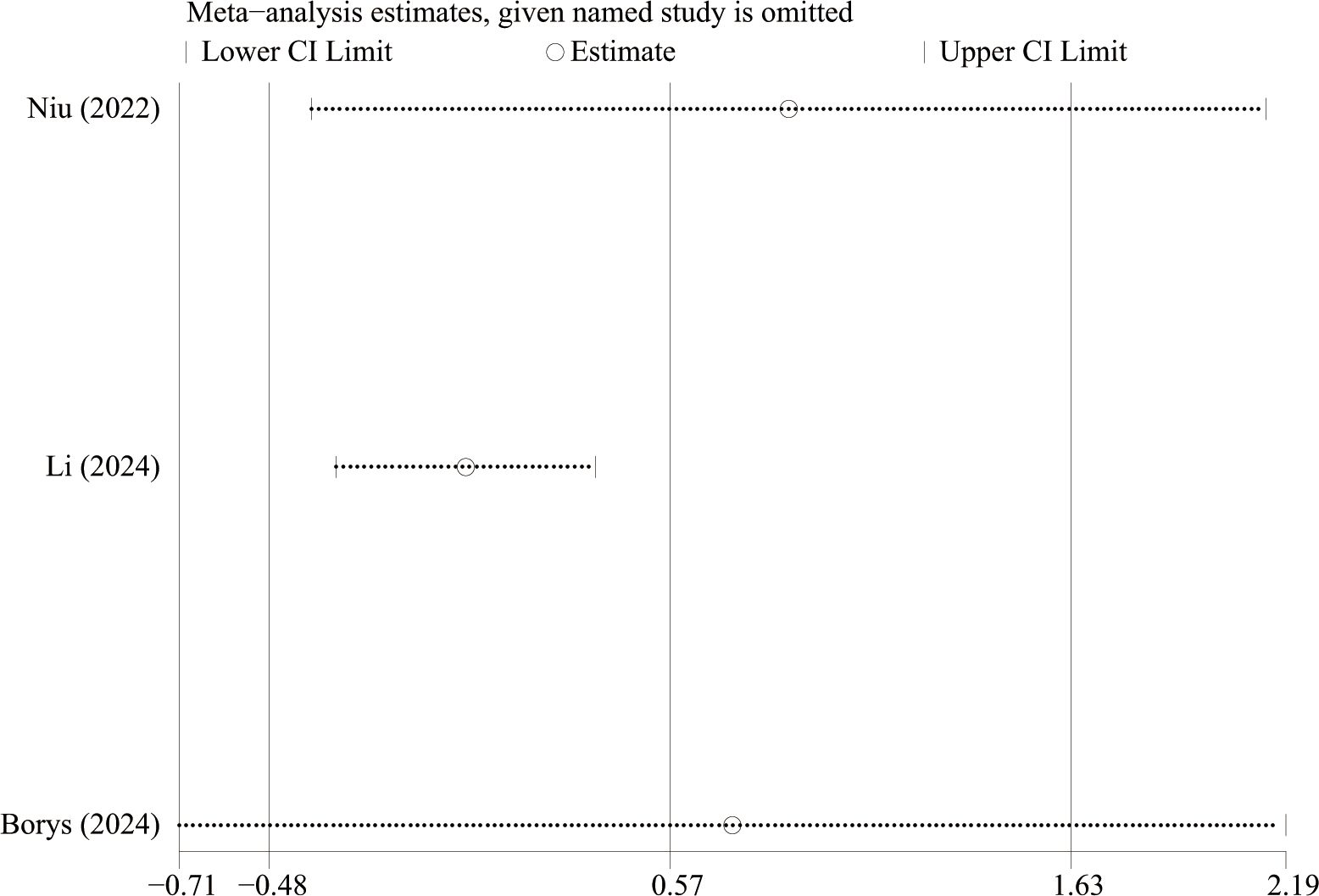
3.4 Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
We performed sensitivity analysis (Figure 9) to estimate the stability of the results via sequentially excluding the results of each individual study. Sensitivity analyses showed that no single article had a strong influence on the results of estimated blood loss. The Egger’s test result was p = 0.055 and the Begg’s test result was p = 0.296 suggesting that there was less possibility of publication bias in this study.
4 Discussion
In general, radical surgery plays a crucial role in the treatment of left-sided pancreatic cancer. RAMPS is an advanced surgical procedure designed to achieve complete dissection of D1 lymph nodes and increase the R0 resection rate, both of which are key prognostic factors for patients with left-sided PDAC (9, 25–27).
However, L-RAMPS is infrequently performed due to its technical complexity and the absence of clear superiority over other methods (28). Meta-analyses comparing open RAMPS with open DPS show that while RAMPS may improve disease-free survival (DFS), it has minimal impact on overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS). Although open RAMPS can retrieve more lymph nodes, it does not necessarily enhance R0 resection rates (13). Furthermore, another meta-analysis indicates that L-RAMPS yields similar outcomes to open RAMPS, with the added benefits of minimal invasiveness, such as less blood loss and shorter time to oral feeding. However, L-RAMPS harvested significantly fewer lymph nodes, which may potentially negatively influence the long-term survival of patients with left-sided pancreatic cancer (29).
There remains significant controversy regarding the efficacy and safety of RAMPS and DPS in the treatment of left-sided pancreatic cancer. This meta-analysis offers a comprehensive review of L-DPS and L-RAMPS outcomes in these patients. It represents the first analysis comparing the perioperative and postoperative results of L-RAMPS with L-DPS. Our findings highlight L-RAMPS’s advantage in retrieving more lymph nodes, consistent with previous meta-analyses comparing open-RAMPS and DPS, despite the increased operative time associated with L-RAMPS (13).
Both L-RAMPS and L-DPS demonstrated similar rates of estimated blood loss, R0 resection margins, and postoperative complications. RAMPS employs a no-touch isolation approach to control major blood vessels by separating the pancreatic neck early, which theoretically reduces blood loss (30). Despite this, our meta-analysis found no significant difference in blood loss between the two techniques. Similarly, R0 resection rates were comparable for both methods, though achieving R0 resection is crucial for improving survival in pancreatic cancer (31, 32). The postoperative mortality, including both 30-day and 90-day mortality rates, appears to be similar between the L-RAMPS and L-DPS groups, indicating that L-RAMPS is a safe surgical approach for patients with left-sided pancreatic cancer. Moreover, long−term prognosis, including recurrence-free survival (RFS), disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS), does not appear to be significantly affected by these two surgical strategies. Although L-RAMPS is technically more complex and raises concerns about postoperative complications, this analysis found no significant differences in rates of pancreatic fistula, postpancreatectomy hemorrhage, post-operative mortality, or other complications between L-RAMPS and L-DPS. The lack of substantial differences suggests that both techniques offer similar efficacy and safety in the treatment of left-sided pancreatic cancer. Therefore, the choice of treatment modality should depend on the surgeon’s expertise, the availability of equipment, and the patient’s expectations, understanding, and cooperation.
This meta-analysis has several limitations. Firstly, it is based on retrospective studies with small sample sizes and a limited number of included studies, which could be influenced by publication bias. Secondly, only retrospective studies included in this meta-analysis, high-quality, large-scale randomized controlled trials are needed to draw definitive conclusions about various outcomes. Thirdly, while the analysis focused on short-term perioperative and postoperative outcomes, long-term survival benefits of L-RAMPS versus L-DPS remain unclear due to limited data. Therefore, further research is needed to explore long-term outcomes, and clinicians should interpret these findings with caution.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, this meta-analysis is the first to demonstrate that L-RAMPS results in a higher number of lymph nodes retrieved and a longer operative time compared to L-DPS for left-sided pancreatic cancer. However, both approaches yield similar outcomes in terms of R0 resection margins and postoperative complications. To further validate these findings, larger sample sizes, extended follow-up periods, and well-conducted randomized controlled trials are necessary.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XJ: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. JL: Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WL: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CX: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cronin KA, Scott S, Firth AU, Sung H, Henley J, Sherman RL, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, part 1: National cancer statistics. Cancer. (2022) 128:4251–84. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34479
2. Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, La Vecchia C, Johnson CD, Biankin AV, et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:16022. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.22
3. GBD 2017 Pancreatic Cancer Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 4:934–47. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30347-4
4. Leonhardt CS, Gustorff C, Klaiber U, Le Blanc S, Stamm TA, Verbeke CS, et al. Prognostic factors for early recurrence after resection of pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. (2024) 167:977–92. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.05.028
5. de Rooij T, Van Hilst J, Van Santvoort H, Boerma D, Van Den Boezem P, Daams F, et al. Minimally invasive versus open distal pancreatectomy (LEOPARD): a multicenter patient-blinded randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. (2019) 269:2–9. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002979
6. Korrel M, Jones LR, Van Hilst J, Balzano G, Bjornsson B, Boggi U, et al. Minimally invasive versus open distal pancreatectomy for resectable pancreatic cancer (DIPLOMA): an international randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet Reg Health Eur. (2023) 31:100673. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100673
7. van Hilst J, De Rooij T, Klompmaker S, Rawashdeh M, Aleotti F, Al-Sarireh B, et al. Minimally invasive versus open distal pancreatectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma (DIPLOMA): A pan-european propensity score matched study. Ann Surg. (2019) 269:10–7. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002561
8. Strasberg SM, Drebin JA, Linehan D. Radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy. Surgery. (2003) 133:521–7. doi: 10.1067/msy.2003.146
9. Chun YS. Role of radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (RAMPS) and pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. (2018) 25:46–50. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5675-4
10. Dai M, Zhang H, Li Y, Xing C, Ding C, Liao Q, et al. Radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (RAMPS) versus conventional distal pancreatosplenectomy (CDPS) for left-sided pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Surg Today. (2021) 51:1126–34. doi: 10.1007/s00595-020-02203-3
11. Huo Z, Zhai S, Wang Y, Qian H, Tang X, Shi Y, et al. Comparison of radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy with standard retrograde pancreatosplenectomy for left-sided pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis and experience of a single center. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:4590–601. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914540
12. Cao F, Li J, Li A, Li F. Radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy versus standard procedure in the treatment of left-sided pancreatic cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis. BMC Surg. (2017) 17:67. doi: 10.1186/s12893-017-0259-1
13. Watanabe J, Rifu K, Sasanuma H, Kotani K, Sata N. The efficacy of radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. (2022) 29:1156–65. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.1120
14. Zhou Q, Fengwei G, Gong J, Xie Q, Liu Y, Wang Q, et al. Assessement of postoperative long-term survival quality and complications associated with radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy and distal pancreatectomy: a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Surg. (2019) 19:12. doi: 10.1186/s12893-019-0476-x
15. Zhou Y, Shi B, Wu L, Si X. A systematic review of radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy for adenocarcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas. HPB (Oxford). (2017) 19:10–5. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2016.07.014
16. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:ED000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
17. Page MJ, Mckenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
18. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. (2017) 358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008
19. Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. (2003) 73(9):712–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
20. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2005) 5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
21. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
22. Borys M, Wysocki M, Galazka K, Stanek M, Budzynski A. Laparoscopic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (RAMPS) for adenocarcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas - technical considerations with analysis of surgical outcomes. Langenbecks Arch Surg. (2024) 409:74. doi: 10.1007/s00423-024-03265-4
23. Li Z, Xu W, Wang T, Li B, Chen C, Shi Y, et al. Evaluating the efficacy of laparoscopic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy in selected early-stage left-sided pancreatic cancer: a propensity score matching study. Surg Endosc. (2024) 38:3578–89. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-10868-x
24. Niu N, He Y, Mou Y, Meng S, Xu P, Zhou Y, et al. Clinical outcome comparison of laparoscopic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy vs. laparoscopic distal pancreatosplenectomy for left-sided pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma surgical resection. Front Surg. (2022) 9:981591. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.981591
25. Strasberg SM, Fields R. Left-sided pancreatic cancer: distal pancreatectomy and its variants: radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy and distal pancreatectomy with celiac axis resection. Cancer J. (2012) 18:562–70. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e31827596c5
26. Rho SY, Hwang HK, Chong JU, Yoon DS, Lee WJ, Kang CM. Association of preoperative total lymphocyte count with prognosis in resected left-sided pancreatic cancer. ANZ J Surg. (2019) 89:503–8. doi: 10.1111/ans.15030
27. Sugawara T, Ban D, Nishino J, Watanabe S, Maekawa A, Ishikawa Y, et al. Prediction of early recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma after resection. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0249885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249885
28. Larkins K, Rowcroft A, Pandanaboyana S, Loveday BPT. A systematic scoping review of the initial experience with laparoscopic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy for pancreatic Malignancy. Surg Endosc. (2021) 35:4930–44. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08528-5
29. Tang W, Zhang YF, Zhao YF, Wei XF, Xiao H, Wu Q, et al. Comparison of laparoscopic versus open radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy for pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. (2022) 103:106676. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106676
30. Kuroki T, Eguchi S. No-touch isolation techniques for pancreatic cancer. Surg Today. (2017) 47:8–13. doi: 10.1007/s00595-016-1317-5
31. Lai CC, Wang SY, Liao CH, Hsu JT, Chiang KC, Yeh TS, et al. Surgical margin status of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma undergoing surgery with radical intent: risk factors for the survival impact of positive margins. In Vivo. (2018) 32:1591–7. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11419
32. Nagakawa Y, Nakagawa N, Takishita C, Uyama I, Kozono S, Osakabe H, et al. Reconsideration of the appropriate dissection range based on Japanese anatomical classification for resectable pancreatic head cancer in the era of multimodal treatment. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143605
Keywords: laparoscopic, radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy, pancreatic cancer, distal pancreatosplenectomy, meta-analysis
Citation: Jiang X, Zhu Y, Li J, Li W, Zheng W, Xu C and Zhang G (2025) Laparoscopic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy vesus laparoscopic distal pancreatosplenectomy for left-sided pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1510342. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1510342
Received: 12 October 2024; Accepted: 24 January 2025;
Published: 14 February 2025.
Edited by:
Tudor Mocan, Babeș-Bolyai University, RomaniaReviewed by:
Baltasar Pérez Saborido, Hospital Universitario Río Hortega, SpainYuancong Jiang, Zhejiang University, China
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Zhu, Li, Li, Zheng, Xu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guixin Zhang, emd4MDEwOUB5ZWFoLm5ldA==
 Xutao Jiang
Xutao Jiang Yu Zhu2
Yu Zhu2 Caiming Xu
Caiming Xu