
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol., 24 February 2025
Sec. Genitourinary Oncology
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1490264
Background: Approximately 25% to 30% of clinical stage I (CSI) germ cell cancer (GCT) patients will experience disease relapse after an orchiectomy. Adding adjuvant treatment will decrease the relapse rate but could lead to over-treatment. Prognostic biomarkers such as lymphovascular invasion (LVI) and/or embryonal carcinoma (EC) in non-seminoma (NSGCT) and rete testis invasion (RTI) and/or primary tumor size (PTS) in seminoma (SGCT) add limited value in treatment decision- making. The aim of this study is to assess the systemic inflammatory index (SII) and lactate-dehydrogenase (LDH) with clinicopathological findings along with their prognostic impact.
Methods: This is a retrospective study that included 159 diagnosed CSI GCT patients, who underwent active surveillance (AS) from June 2004 to November 2023. Medical records and pathology reports were collected retrospectively. Drawn blood must have been done less than 3 months after the orchiectomy had been done. For the survival analysis, we used dichotomized values of the studied biomarkers from “low” to “high” based on the median values.
Results: The median follow-up time was 61 months (ranging from 1 to 230 months), with 2-year relapse- free survival (RFS) of 81.3% and 69.0% in SGCT and NSGCT, respectively. We confirm inferior RFS in the presence of LVI compared to an absence of LVI in NSGCT ([HR]= 2.59, 95%CI (0.74-9.07), p=0.04). A trend of inferior RFS in NSGCT patients with EC predominance (≥50%) was also observed ([HR]= 2.59, 95%CI (0.98-6.85), p=0.06). A prognostic impact of RTI and a PTS >4cm in SGCT was not observed with p=0.24 and p=0.51, respectively. The SII was assessed in the population, and a higher neutrophil- to- lymphocyte ratio (NLR) value was associated with LVI presence and with advanced tumor stage in NSGCT. In SGCT, a higher SII level was associated with LVI presence and advanced pathological stage. A PTS >4cm was associated with a higher LDH level among all the studied patients, without significance in SGCT or NSGCT. A higher LDH value in NSGCT was also associated with EC predominance (≥50%).
Conclusion: Our study, for the first time, revealed associations of post-orchiectomy systemic inflammatory indices and/or LDH in CSI GCT. These new associations deserve further evaluation in a larger cohort of patients with CSI GCT to elucidate whether its associations in certain histology subgroups will improve the stratification of the at-risk population.
A testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT) is the most common solid cancer among men < 34 years old (1). Clinical stage I (CSI) testicular germ cell tumors are characterized by a restriction of the tumor to the testicle without any signs of distant spread and postoperative levels of serum tumor markers within the normal range (2). Cure rates for TGCTs are >99% (3, 4). Overall survival (OS) of CSI TCGTs regardless of histological type is approaching 100% independent of the treatment modality; thus, the treatment choice is mostly driven by risks associated with treatment-related toxic effects and by the patients’ quality of life (5, 6). The results from several studies showed that 4% to 50% (7–12) of patients with a TGCT classified as CSI will relapse after an orchiectomy.
Current post-orchiectomy treatment approaches vary between chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and active surveillance (AS) in CSI SGCTs, whereas, CSI non-seminoma germ cell tumors (NSGCTs) lack radiosensitivity (13); thus, treatment approaches for these tumors include AS, adjuvant chemotherapy, and retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND), according to recommendations by international societies such as NCCN, ESMO, and EAU (14–16).
A current biomarker used in treatment decision- making in CSI NSGCT is the presence of lymphovascular invasion (LVI), however, the use of LVI as a biomarker is accompanied by various pitfalls such as over-treatment in approximately 50% of patients (9, 10). Due to this, many centers do not conduct treatment decision- making based on LVI, thus patients with the presence of LVI are mostly advised to choose active surveillance. In contrast, data regarding a primary tumor size (PTS) >4cm and rete testis invasion (RTI) as biomarkers in CSI SGCT are ambiguous and have led to conflicting results (17, 18), thus treatment decisions based on these biomarkers in CSI SGCT are not justifiable (12, 19). Due to this, there is an effort to investigate new biomarkers for more precise patient stratification. A recent review evaluated biomarkers investigated in stage I TGCT (20).
Blood- based parameters such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, platelets, neutrophil- to- lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet- to- lymphocyte ratio (PLR), systemic inflammatory index (SII), or lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and their association with relapse and clinical pathological characteristics were studied in various types of cancer such as colorectal, melanoma, gastric, and breast cancer (21–24). The role of NLR and SII was also evaluated in metastatic TGCTs (25–28), however, its association with clinicopathological features in patients with CSI TGCTs has not been studied yet. It is also known that LDH has a prognostic role and its level is associated with clinical and/or pathological features such as tumor stage, LVI, and node metastasis in solid tumors (29, 30). Moreover, LDH is one of three serum tumor markers that are generally used in assessing clinical staging in germ cell tumors, therefore, providing additional information in treatment decision- making (14–16). However, associations between post-orchiectomy levels with clinical and/or tumor characteristics have not been assessed in precisely selected CSI germ cell tumors yet.
The aim of this study was to assess the relationship between clinicopathological characteristics and systemic inflammatory indexes and/or LDH in patients with CSI TGCTs and to determine their impact on prognosis.
In our retrospective study, we initially included 183 patients (Figure 1). Eligible patients were aged ≥ 18 years old and had a histologically confirmed germ cell tumor that was staged as clinical stage I with drawn blood that must have been done ≤ 3 months after the orchiectomy. Patients for whom the place of orchiectomy was unknown were excluded. Of the initially included patients, 24 patients were excluded due to unknown pathology laboratories or no patient contact in order to find out pathological laboratory. After exclusion, this study included 159 patients with TGCTs, staged as clinical stage I according to ACJJC 8th edition (2) staging. The patients were treated with curative orchiectomy between June 2004 and November 2023 in regional urological departments in the Slovak Republic and most of them underwent active surveillance at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) afterward. Since 2014, the paradigm of treatment has changed towards active surveillance, therefore, most of the patients were included after 2014. Some patients were referred to the NCI due to a relapse being diagnosed. The patients’ blood test results were available in the hospital system. Data regarding tumor histology and other patient/tumor characteristics were collected and correlated with blood draw results and risk of relapse. The study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB project number: IZLO-1) of the National Cancer Institute of Slovakia. Each participant signed informed consent before the study was initiated.
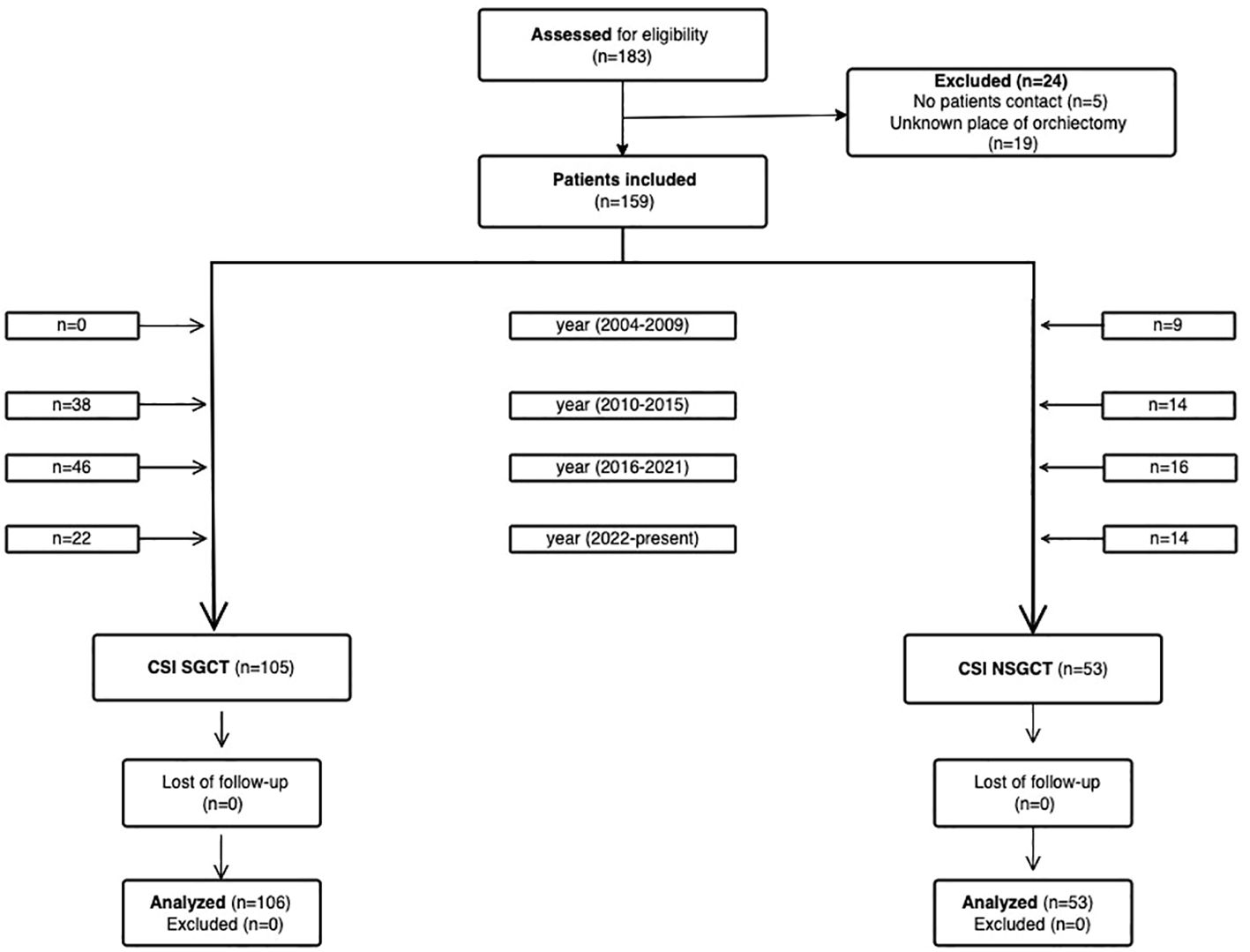
Figure 1. Flow diagram showing patient enrollment from identification to inclusion. No patient contact and data paucity led to patients being excluded. (Created with the Visual Paradigm app).
Complete blood count (CBC) and LDH results were collected retrospectively for each study participant from the hospital medical system. The blood draw must have been done less than or equal to 3 months after the orchiectomy had been done. In the case of patients who were referred to our center due to a relapse being diagnosed, laboratory results were requested from the local oncology and/or urology outpatient centers. SII was calculated based on platelet (P), neutrophil (Ne), and lymphocyte (L) counts using a formula described previously (27): SII=P × Ne/L (31). NLR was calculated by the formula: NLR= Ne/L (32) and PLR was calculated by the formula: PLR=P/L (33).
Primary TGCTs had been diagnosed in all the included patients. A TGCT was classified according to the current WHO classification (34). Orchiectomy specimens were histo-pathologically examined in pathology laboratories in the Slovak Republic. Pathology reports were requested and collected systematically afterward.
Tumor pathological and clinical data were tabulated. The patients’ characteristics and the CBC and biochemistry parameters were summarized using the mean or median (range) for continuous variables and frequency (percentage) for categorical variables. Statistical analyses were performed using non-parametric tests as the distribution of the neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocytes, platelet, SII, NLR, PLR, and LDH values had a non-normal distribution (Shapiro–Wilk test). The non-parametric Kruskal– Wallis test was used for the analysis of the association between hematological and biochemistry parameters and clinicopathological variables in the two groups of patients. The independence of the variables in the two groups with dichotomized values for each parameter (“low” vs “high” based on the median value) was compared using Fisher’s test. Relapse-free survival (RFS) was calculated from the date the orchiectomy was performed to the date of progression or the date of the last adequate follow-up. OS was calculated from the date the orchiectomy was performed to the date of death or last follow-up. The univariate Kaplan–Meier statistical approach was used to assess the outcome of survival data in certain populations in our studied groups. All p- values presented are two-sided, and associations were considered significant if the p- value was less than or equal to 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using NCSS 2022 statistical software.
From June 2004 to November 2023, this study encompassed 159 patients with diagnosed TGCTs with a median follow-up of 61 months (ranging from 1 to 230 months). Table 1 summarizes the patient and tumor characteristics. The majority of the patients were classified as seminoma and pathologically staged as pT1. Relapses were observed in 41 patients (25.8%), with a median time to relapse of 9 months and a median follow-up of 111 months. In CSI NSGCT, relapses occurred in 18 (33.96%) patients with a median time to relapse of 5.5 months and a median follow-up of 72 months, whereas in the CSI SGCT subgroup, relapses were observed in 23 (21.70)% patients with a median time to relapse of 11 months and a median follow-up of 56 months. RFS at 2 years was 81.25% and 69.04% for the CSI SGCT and NSGCT subgroups, respectively.
Late relapses (≥24 months) were detected in five patients (3.1%), of whom four4 patients were classified as CSI SGCT and one as CSI NSGCT. Their median time to late relapse was 38 months with a median follow-up of 89 months.
We investigated the prognostic association between tumor and/or patients’ characteristics and RFS in all patients and in subgroup analyses in seminoma and non-seminoma histologies separately.
In the seminoma subgroup analysis, we were not able to prove any prognostic association between tumor and/or clinical characteristics and RFS. Neither rete testis invasion [hazard ratio (HR) = 0.60, 95% CI (0.27-1.37), p=0.240] nor PTS >4cm [HR = 1.12, 95% CI (0.492.58), p=0.781] were associated with survival outcomes.
In the non-seminoma subgroup analysis, the prognostic significance of certain tumor characteristics was retained in patients with LVI presence [HR = 2.59, 95% CI (0.74-9.07), p=0.044 for RFS] (Figure 2). Similarly, we observed prognostic significance in tumors that were pathologically staged as pT2 [HR = 2.72, 95% CI (0.76-9.072, p=0.034 for RFS)] (Figure 3). EC predominance (50%) was not significantly associated with inferior RFS, however, a trend of inferior RFS in CSI NSGCT patients was observed, [HR= 2.59, 95% CI (0.98-6.85), p=0.062].
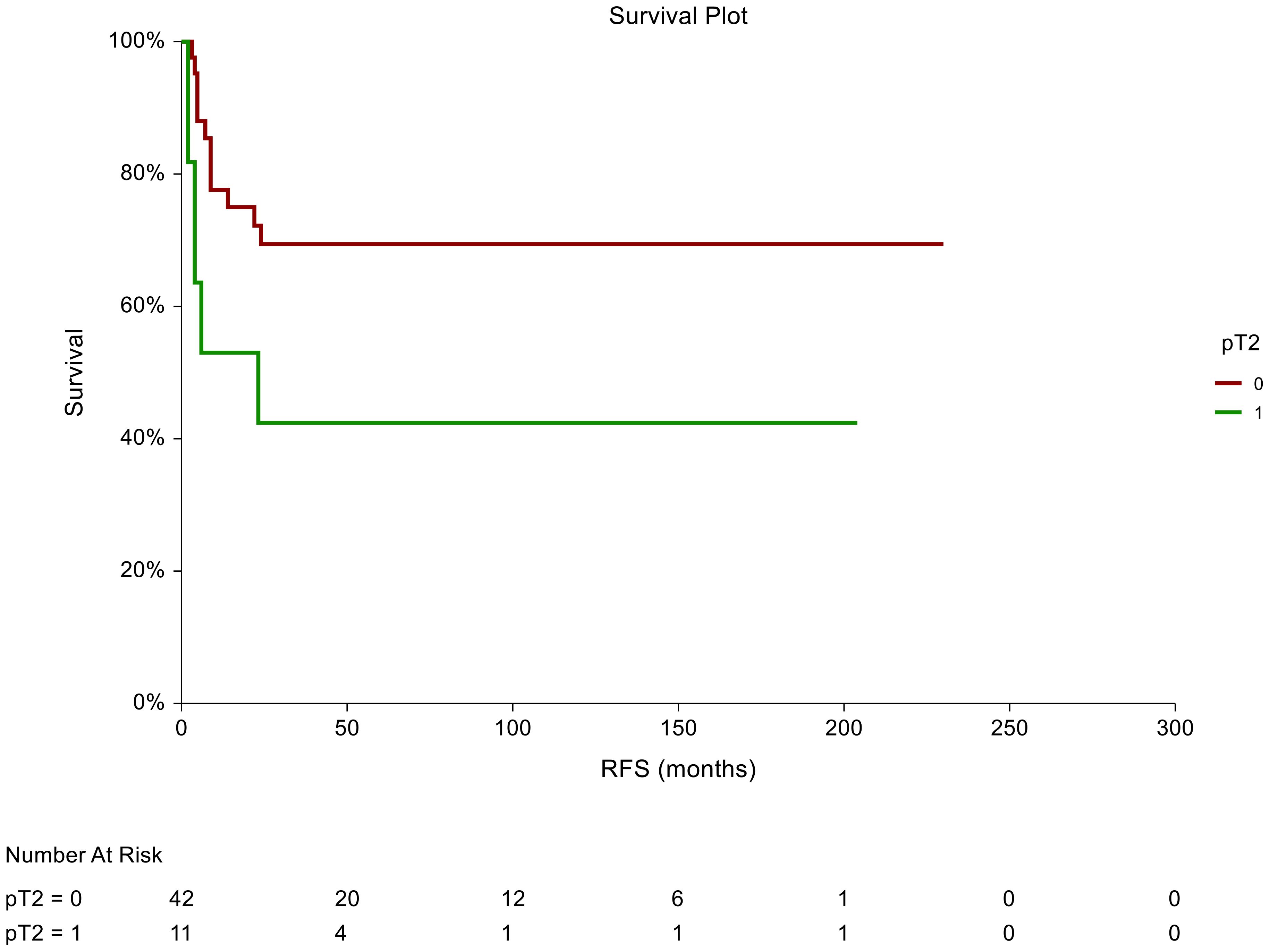
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier estimates of probabilities of relapse-free survival according to pT2 tumor characteristics in patients with TGCTs (N = 159). Patients with non-pT2 tumor histology had significantly better RFS compared to patients with pT2 [HR= 2.72, 95%CI (0.76-9.072, p=0.034)]; 0 = non- pT2 tumor stage in tumor specimen, 1 = pT2 tumor stage in tumor specimens. HR, hazard ratio; TCGT, testicular germ cell tumor; RFS, relapse- free survival.
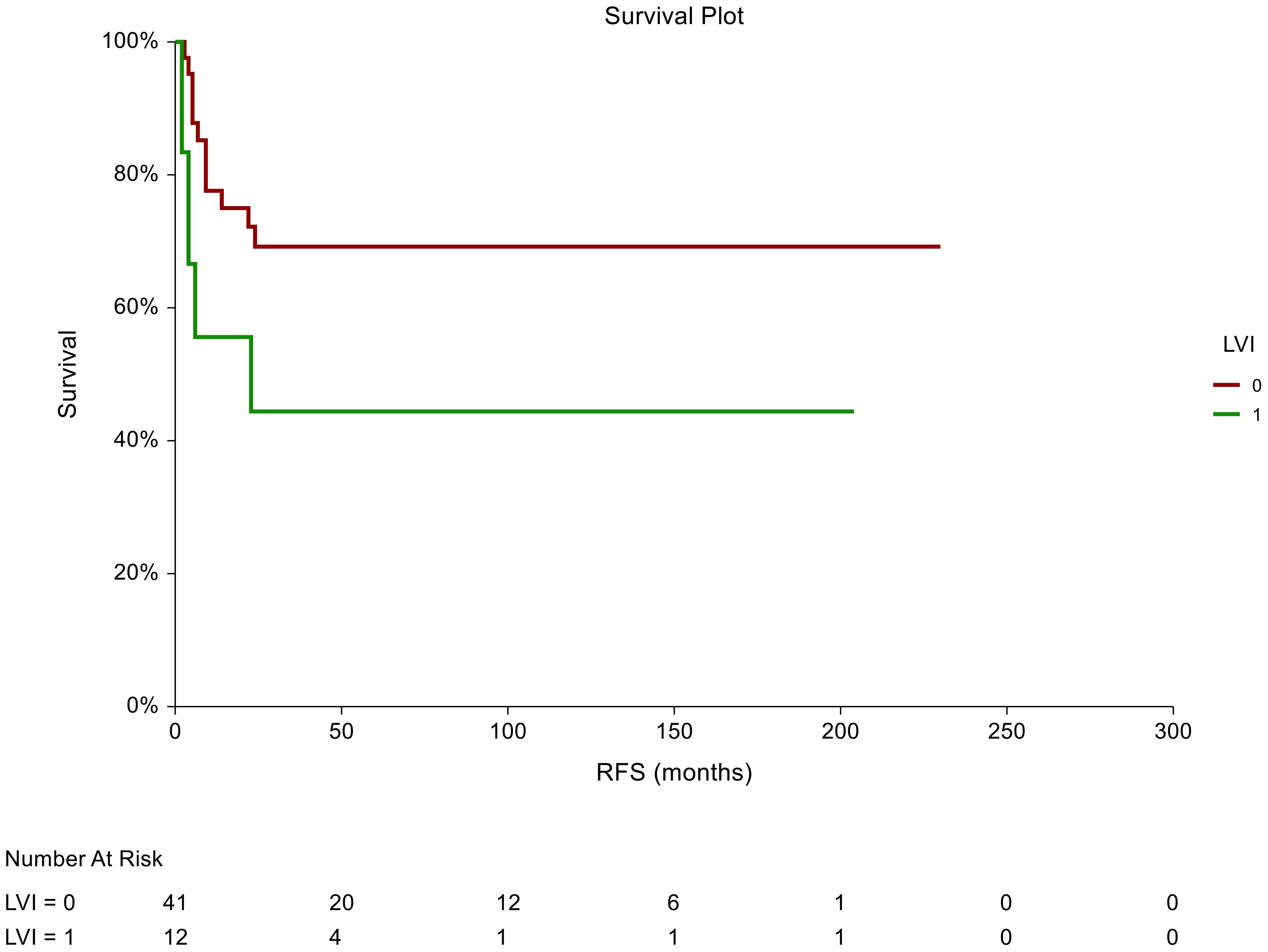
Figure 3. Kaplan–Meier estimates of probabilities of relapse-free survival according to LVI tumor characteristics in patients with TGCTs (N = 159). Patients with the absence of LVI had significantly better RFS compared to patients with LVI [HR= 2.59, 95%CI (0.74-9.07), p=0.044]; 0 = LVI absent, 1 = LVI presence in tumor histology specimens. HR, hazard ratio; TCGT, testicular germ cell tumor; RFS, relapse- free survival.
In all patients, there was a statistically significant prognostic association between RFS and tumors pathologically staged as pT2 [HR = 1.9, 95%CI (0.94-3.85), p=0.039]. Moreover, we observed an association between RFS and lymphovascular invasion as patients who were LVI+ in the pathological evaluation had a poorer RFS than those who were LVI- [HR = 1.87, 95%CI (0.92-3.76), p=0.046].
The mean value of post-orchiectomy neutrophils, platelets, lymphocytes, monocytes, SII, NLR, PLR, and LDH ± SEM were compared with the pathological variables of the tumor specimens and the clinical variables in all the patients (Table 2).
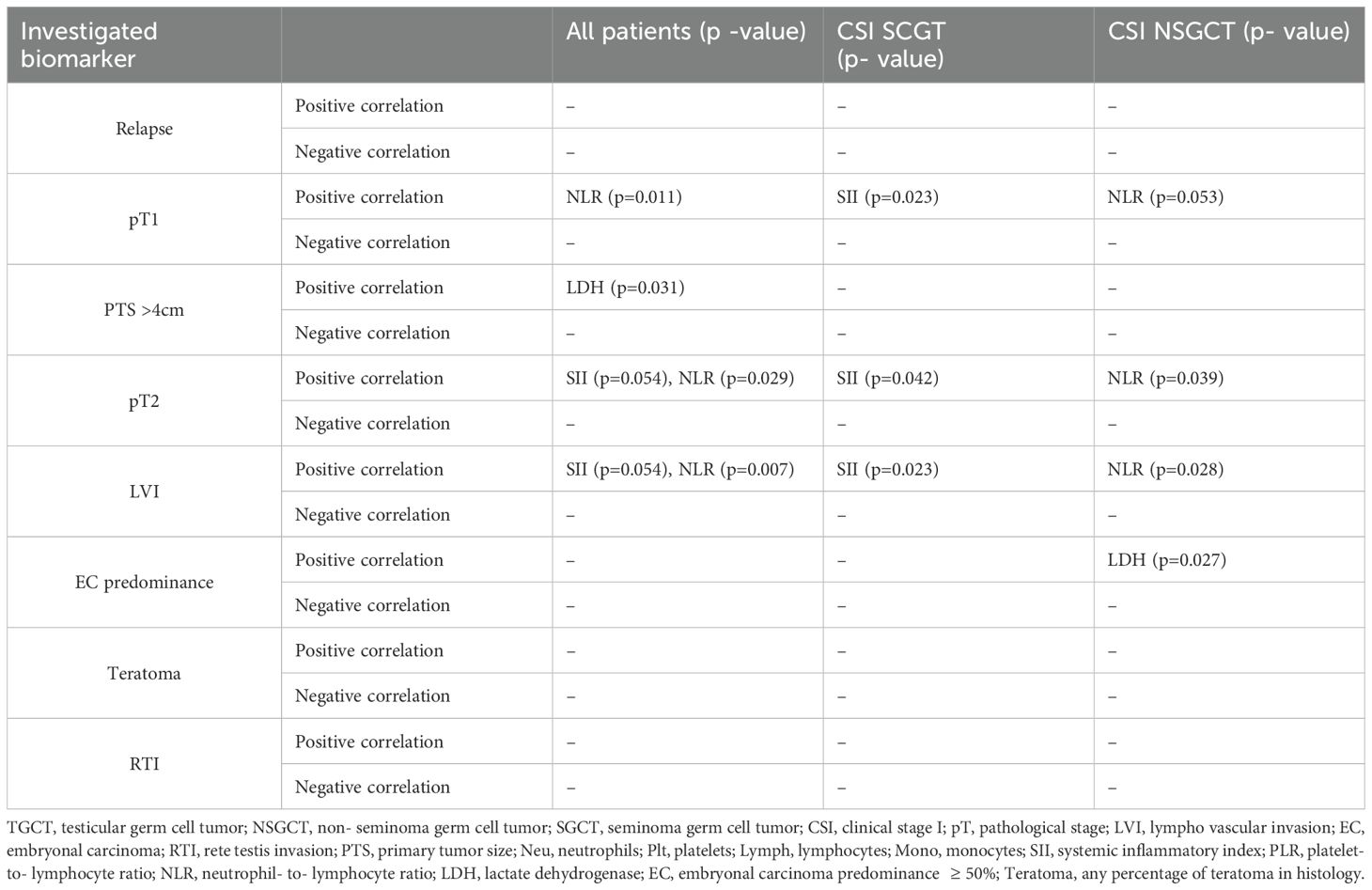
Table 2. Associations between investigated biomarkers (neutrophils, platelets, lymphocytes monocytes, SII, NLR, PLR, and LDH) and clinical and/or tumor characteristics.
We did not observe any significant associations between neutrophils, platelets, lymphocytes, monocytes, SII, NLR, PLR, or LDH value and relapse in the histological subgroups for seminoma and non-seminoma separately or in all the patients. We were not able to prove any association between LDH value and relapse in the subgroups (seminoma and non-seminoma) or in all patients.
In the seminoma subgroup, there was a significant correlation between SII value and pT2 tumor stage, as patients with a higher SII level tended to be staged as pT2 (618.3 ± 73.21 vs 495.76 ± 51.40, p=0.042). In contrast, our results showed an association between pT1 tumor stage and SII index, where patients with a CSI SGCT with a lower SII level tended to have a tumor staged as pT1 (491.84 ± 72.08 vs 622.55 ± 72.08, p=0.023). An association between NLR and tumor stage in patients with CSI SGCTs was not noted in the pT1 or pT2 population with p=0.113 and p=0.201, respectively. In the non-seminoma subgroup of patients, we observed that pathological tumor staging correlated with NLR count, thus, a lower NLR count was associated with pT1 tumor stage (2.13 ± 0.17 vs 2.53 ± 0.30, p=0.053) and, in contrast, a higher NLR count was associated with pT2 pathological tumor staging (2.44 ± 0.33 vs 2.18 ± 0.17, p=0.039). However, an association between tumor stage and SII index in patients with CSI NSGCTs was not observed with p=0.68. The patients in the unselected cohort of patients with CSI TGCTs with lower NLR values were more prone to be pathologically staged as pT1 (2.22 ± 0.13 vs 2.60 ± 1.93, p= 0.011), which was confirmed by a further association between pT2 pathology staging and higher NLR count (2.53 ± 0.20 vs 2.25 ± 0.13, p= 0.029). Moreover, a borderline positive association between SII and tumor stage in all the patients was observed as patients staged as pT2 were associated with higher SII values (588.85 ± 56.4 vs 501.58 ± 36, p= 0.054).
Our study proved an association between tumor size (PTS >4cm) and LDH post-orchiectomy level in the unselected CSI TGCT population. A primary tumor size >4cm was positively associated with LDH value, thus, a higher LDH level was associated with larger tumors (PTS >4cm) (2.95 ± 0.09 vs 2.73 ± 0.06, p= 0.018). This statistical significance was not retained in the patients with CSI NSGCTs or CSI SGCTs with p=.258 and p=0.066, respectively. However, a trend towards statistical significance was observed in the patients with CSI SGCTs.
Additionally, our study found an association in the seminoma subgroup analysis, where we confirmed a significant association between SII and LVI presence (622.55 ± 72.09 vs 491.84 ± 51.70, p= 0.023). However, this was without statistical significance in the selected CSI NSGCT population with p=0.318 (Figure 4). This association was also retained in the unselected cohort of CSI TGCT. Thus, in the unselected cohort of patients with CSI TGCTs a higher SII value tended to be associated with being LVI + (601.72 ± 55.0 vs 494.44 ± 36.0, p=0.017). LVI presence in the patients with CSI NSGCTs was positively associated with NLR value (2.61 ± 0.31 vs 2.12 ± 0.16, p=0.039) but this significant association was not retained in the patients with CSI SGCT with p=0.113 (Figure 5).
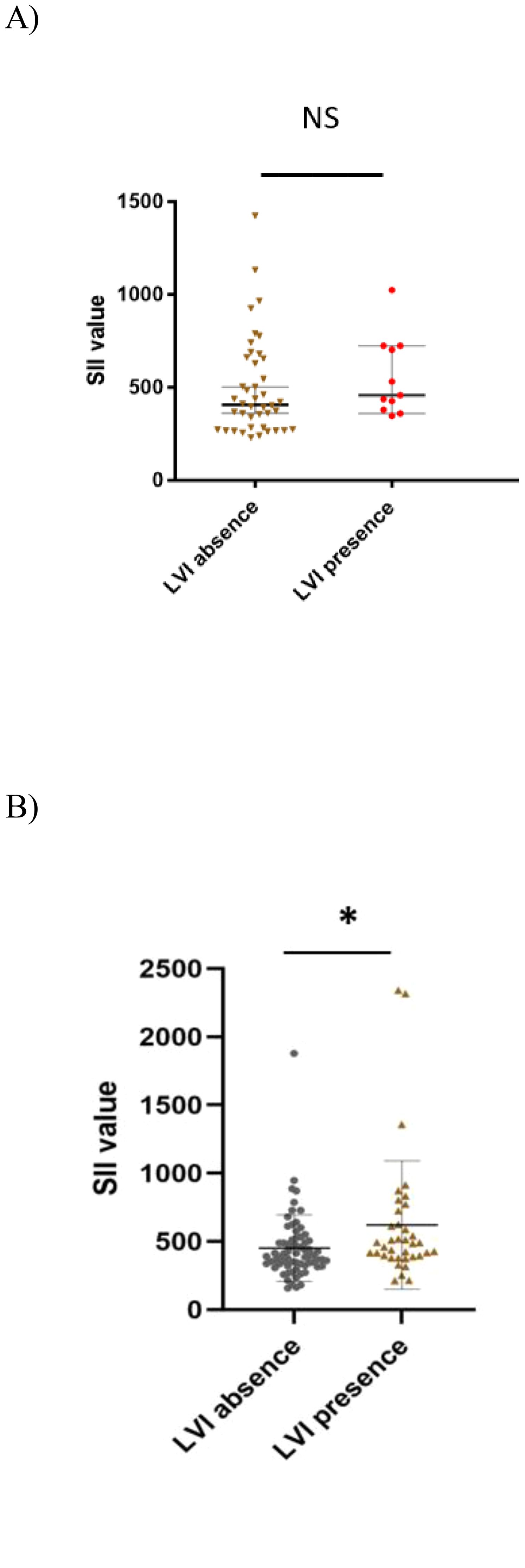
Figure 4. Association between systemic inflammatory index and lymphovascular invasion in CSI NSGCT and CSI SGCT. (A) CSI NSGCT. NS, non- significant p- value (> 0.05); SII, systemic inflammatory index; LVI, lympho vascular invasion. (B) CSI SGCT. *, p- value < 0.05; SII, systemic inflammatory index; LVI, lympho vascular invasion.

Figure 5. Association between neutrophil- to- lymphocyte ratio and lymphovascular invasion in CSI NSGCT and CSI SGCT. (A) CSI NSGCT. *, p value < 0.05; NLR, neutrophil- to- lymphocyte ratio; LVI, lympho vascular invasion. (B) CSI SGCT. NS, non-significant p- value (> 0.05); NLR, neutrophil- to- lymphocyte ratio; LVI, lympho vascular invasion.
This study also proved an association between EC predominance ( and CSI NSGCT histology (Figure 6). Patients with a higher LDH level tended to have EC predominance in their histology tumor specimens (3.13 ± 0.16 vs 2.71 ± 0.14, p=0.027).
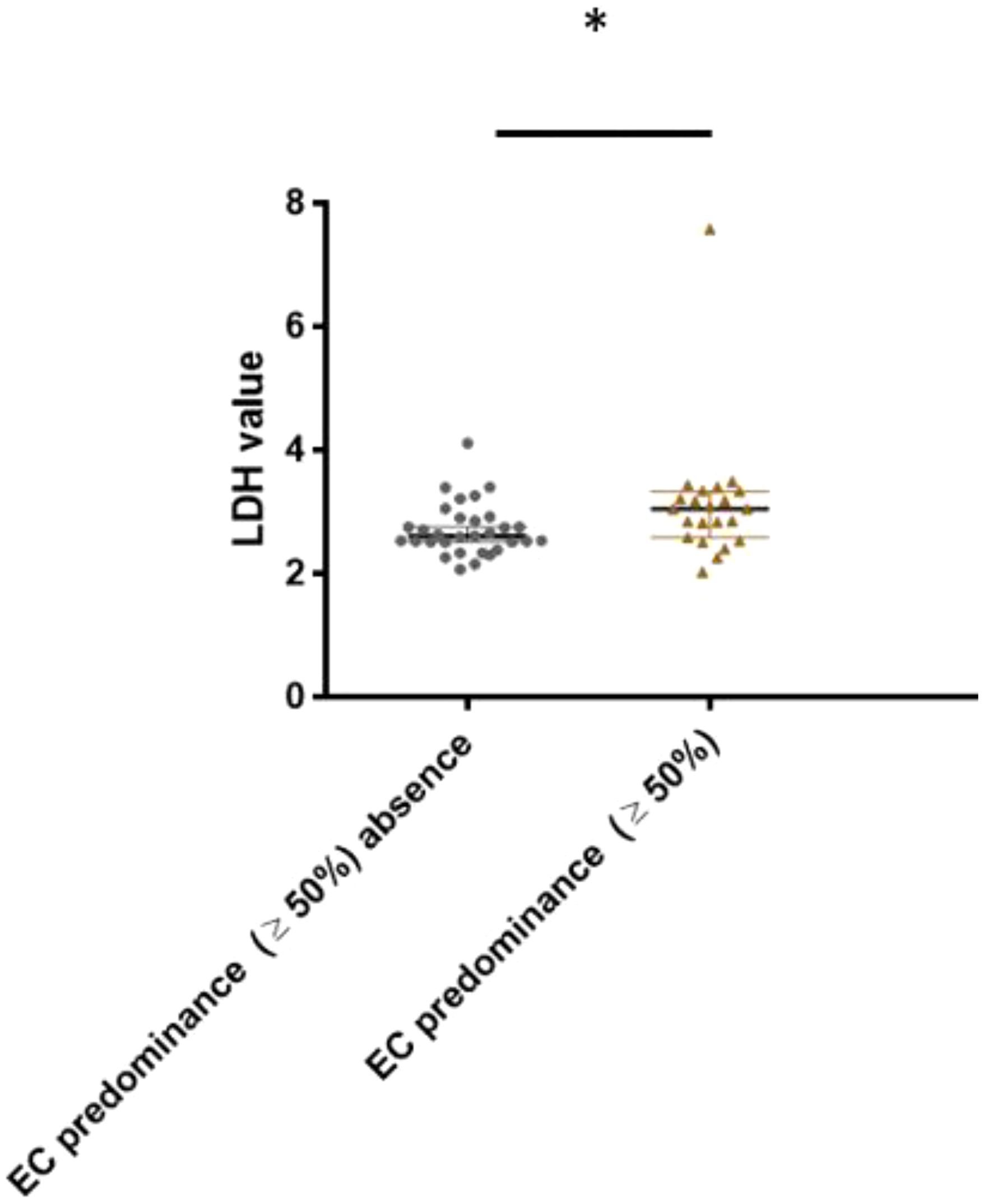
Figure 6. Association between lactate dehydrogenase level and embryonal carcinoma predominance (cut- off ≥ 50%) in CSI NSGCT. *, p value < 0.05; EC, embryonal carcinoma; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
In this retrospective study, we confirmed the prognostic role of LVI+ and pT2 in patients with CSI NSGCTs. The prognostic impact was significant in all the studied patients. However, these associations were not observed in the CSI SGCT subanalysis. The explanation is that the significance in all patients was derived from the inclusion of patients with CSI NSGCTs. In the CSI SGCT histology subgroup, we did not confirm the prognostic impact of a PTS of >4cm and RTI, therefore, our data added inconsistent results to the ambiguity (35–38) of prognostic biomarkers in CSI SGCT, thus the clinical utility of these biomarkers is not justifiable.
Several studies have proposed that LVI presence is associated with 2.2 to 3.2 times poorer relapse- free survival than the absence of LVI (39, 40). These data are consistent with our results, as almost 2.6 times poorer relapse- free survival compared to LVI- patients was observed. Our results also showed the prognostic impact of pT2 on RFS among all the studied patients, as patients with CSI NSGCTs staged as pT2 tended to have approximately 2.7 times poorer survival compared to the non-pT2 patients. The reason for our significant association might be explained by the high number of LVI + patients in pT2 pathologically staged patients, which was 100% of the patients. Studies evaluating tumor stage as a risk biomarker have shown conflicting results (41–43). Unfortunately, in our study, we were not able to prove any significant prognostic association between RFS in CSI NSGCT and EC predominance in tumor histology representation with p=0.062. Despite this association not being statistically significant, there was a trend of poorer relapse-free survival in patients who presented with EC ≥50%. A recent meta-analysis (44) found that EC predominance in histology was associated with a higher odds of experiencing occult metastasis (OR 2.62, 95% CI 1.93–3.56; p< 0.001) (44). Therefore, the statistical insignificance in this study could be caused by the small sample size with EC predominance.
To the best of our knowledge, NLR in patients with TGCTs has been studied in pre-treatment and post-treatment (25, 26, 45, 46),however, a study focused on relapse in patients with CSI TGCTs has not yet been conducted. Pre-orchiectomy NLR was studied in a cohort of 130 unselected patients with TGCTs who underwent radical orchiectomy. In this study, NLR >4 was associated with >pT1 tumor stage (45). Another study (25) assessed pre-orchiectomy NLR in 160 patients with TGCTs, of whom more than 60% were staged as CSI. Lymph node involvement was associated with pre-orchiectomy NLR ≥3.0 with an odds ratio (OR) of 2.91 (95% CI, 1.67–5.83; p=0.038) (25). Another study evaluated NLR post-orchiectomy (26). This study included 80 patients, of whom 40% were staged as CSI. In this study, NLR was independently associated with relapse in patients with CSI TGCTs with an HR of 1.85 (CI 95% 0,99—3,46), however, the p- value was not stated. The study also proposed that a post-orchiectomy NLR of >2.255 is a predictor for recurrence with an area under the curve of 78.7% (26). However, only 16 recurrences occurred in the studied cohort (including stage I and stage II), therefore, the results from this study are only hypothesis- generating. Our results addressed similar correlations between NLR and tumor histology staging, where pT1 was associated with lower NLR value than patients with ≥pT2 in all patients (p=0.011) and the NSGCT subgroup (p=0.053). LVI was also significantly associated with a higher NLR value compared with LVI- negative patients in the non-seminoma histology subgroup of patients. Given that, in previous studies, the NLR cut- off value for prediction of recurrence was > 2.255, our mean and median value was 2.61. Despite the higher NLR in our study, we were not able to prove concordance with a previous study (26). This could be due to the fact that our cohort of patients was more focused on CSI and our cohort consisted of >40 relapses.
PLR is another marker of systemic inflammationthat has been studied as a prognostic parameter in various cancers such as ovarian and gastric cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma (47). A study addressing the significance of PLR in TGCT proposed that there was a difference in PLR value observed between healthy donors and patients with GCT with p<0.05 (48). However, its prognostic role in TGCT has not been studied. Therefore, this is the first study that has assessed the association between post-orchiectomy PLR value and clinical and/or pathological TGCT characteristics. Nevertheless, we were not able to prove a prognostic impact of PLR on PFS nor were we able to prove any association with other investigated clinical and/or pathological characteristics.
It is known that SII reflects the local or systemic inflammatory response, which is known to have a prognostic association with PFS and/or OS and SII in cancers such as colorectal, pancreatic, and stomach cancer (28, 49, 50). The prognostic role of SII has already been investigated among patients with TGCTs treated with conventional and/or high- dose chemotherapy (27, 51), where it was shown that SII was inversely correlated with PFS and OS (27, 51). The authors in a study (27) proposed a cut- off value of SII≥1003 for shortened PFS and OS, however, this study only included 5% of patients with non-metastatic TGCTs. Another study (52) included approximately 60% of patients with CSI TGCTs and pre-orchiectomy SII was studied. There was no association found between pre-orchiectomy SII and LVI, pathology staging, or tumor size (52). A recent study evaluated SII in pre-orchiectomy manner, where approximately 50% of the patients in the study were staged as CSI. The study found that an SII <881.24 was associated with CSI compared to an SII ≥881.24 and an association with ≥CSII was noted (53). Therefore, extrapolating associations in patients with CSI remains unclear due to different study designs and different populations. In summary, SII in a precisely selected stage I TGCT population has not been recently studied. Surprisingly, in our study, we found an association between SII and pT2 tumor stage and LVI+ in all patients with p=0.054 and p=0.016, respectively. Moreover, tumor stage in patients with CSI SGCTs was also positively correlated with SII value. Regardless of these findings, we were not able to prove any prognostic association or additional association with other clinical/pathological features such as EC predominance, RTI, or teratoma presence. The reason why we did not observe any prognostic impact of SII could be explained by the highly selected population without systemic dissemination and with a minimum of patients who could have had occult disease at the time of their blood being drawn. Moreover, the mean SII value in the patients without relapse in our study regardless of histology subtype was <536, therefore, according to the cut- off values proposed by other studies (27, 28), this may explain why the prognostic impact was not pronounced. However, the predefined cut- off values were proposed for drawing blood pre-orchiectomy blood drawn. The difference in LVI + patients could be attributed to the fact that vascular invasion leads to more imminent attraction of inflammation cells into the tumor surroundings, thus, leading to a change in SII value, which could mirror tumor microenvironment changes. Our hypothesis that tumor microenvironment changes evaluated by SII was associated with relapse was not observed, however, an association with lymphovascular invasion was observed. The proposed associations may add an additional role for SII in more precise stratification of at-risk patients.
Elevated levels of serum LDH are always observed in cancer due to tissue injury following the release of LDH into serum upon cell death (54). LDH is also one of three markers generally used in assessing clinical staging in TGCT, thus adding additional information for treatment decision- making (14–16). However, LDH seems to have minimal impact in assessing recurrence as a solitary marker on AS and its level is more prominent in the advanced stage of disease (55). In concordance with previous studies, (14–16, 55) the LDH level in our studied cohort was below the upper normal value (≤4.1ukat/L) and there was no association between relapse and post-orchiectomy LDH level with p=0.518. Surprisingly, in all the patients, we found that LDH was positively associated with a tumor >4cm with p=0.018. Moreover, in the CSI NSGCT subgroup, we found that EC predominance was associated with higher LDH levels with p=0.027. It has been found that the half-life of LDH is 24 hours (56), however, a study that evaluated the dynamics of LDH in stage I TGCT proposed that the decay of serum LDH after orchiectomy could take 1 to 3 weeks but depends on the initial LDH value (57). This could be an explanation for the positive association between LDH and tumor volume, even with the blood being drawn after the orchiectomy, due to higher values during its decay. Moreover, our study found an association with EC predominance, where EC predominance in the tumor histology specimen was positively associated with LDH value. This could be explained by more aggressive forms of TGCT with aggressive behavior and rapid cell turnover (58) that most probably caused elevated LDH levels, which could have been eliminated after the orchiectomy.
The reason why we observed significant correlations between NLR and the aforementioned biomarkers including LVI, pT2, and pT1 could be explained by the fact that neutrophils are a marker of systemic or local inflammation (59), which could have tumor- promoting and tumor- suppressing effects (60). Furthermore, lymphocytes are part of the adaptive immune system response and could be ameliorated by neutrophils (61). Therefore, neutrophilia with lymphocytopenia represents a significant decline in cell adaptive response (61). Neutrophils play a role in promoting cancer and metastasis, which is mostly associated with neutrophils in the tumor micro-environment called tumor- associated neutrophils (TAN). TAN can be polarized into the N1 population, which has an anti-tumor effect, and N2, which has a pro-tumorigenic effect (62). N2 neutrophils encompass granules with high levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and arginase 1 (ARG-1) (63). MMP-9 degrades the extracellular matrix and releases VEGF to promote angiogenesis along with cancer cell intravasation. (64, 65) Moreover, the release of AGR-1 has a significant effect, causing the inhibition of CD-3 mediated T cell activation and proliferation, thus promoting immunosuppression (66). Moreover, neutrophils secrete a spectrum of cytokines such as interleukin-1B, TNF-a, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL12 (61), which induce a chronic inflammatory process and are known to promote angiogenesis, and thus, tumor progression (67). Neutrophilia is always a sign of advanced cancers. It has been hypothesized that tumor production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) could be responsible for the increased value of neutrophils (68). Another study proposed the hypothesis that granulocyte- colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), IL-1, and IL-6 production by tumors may also contribute to higher neutrophil levels (69). Therefore, neutrophils may enhance tumor progression, thus causing an increase in neutrophil values.
SII is an inflammation parameter that consists of NLR multiplied by the level of platelets (31). The association between SII and LVI and/or pT2 tumor staging could be explained by a few hypotheses. Platelets play a role in cancer development from initiation to metastasis. The association with LVI could arise from the fact that platelets are one of many spectrum cells incorporated in the tumor microenvironment (70). Platelets are usually present in abundant tumor vessels where they secrete angiogenic factors such as stromal cell- derived factor, basic fibroblast factor, and VEGF, thus promoting angiogenesis (71). Moreover, the number of platelets changes during cancer development. Patients with active cancer have higher levels of G-CSF and IL-6 (72), which results in higher platelet counts (73). Therefore, platelets are part of the systemic inflammatory response, which may be elevated in cancer, however, their solitary role in GCT in our study was without any associations.
To the best of our knowledge, precise prognostic biomarkers in the assessment of relapse in CSI TCGT are still missing. Several biomarkers have been prognostically investigated in CSI TCGT, however, none of them have been clinically applied, except LVI, but it has drawbacks (20). The advantage of our studied biomarkers is that they are easy to implement and require cost-effective examinations that can be conducted in almost every out-patient and in-patient healthcare provider. On the other hand, the most promising biomarker in TGCT is miRNA 371a-3p. MiRNA 371a-3p is currently being investigated as a diagnostic tool to assess recurrence in stage I TCGT (74). It is known that post-orchiectomy miRNA value and/or percentage of decline between pre- and post-orchiectomy is not prognostic in CSI (75), however, using miRNA as a diagnostic biomarker in relapse could yield a diagnosis of relapse in CSI TGCT sooner (76). Despite this, several major drawbacks need to be resolved before the use of miRNA371a-3p in clinical practice, such as the standardization of technique, cut-off values for diagnosis, and the therapeutic approach in the case of elevated miRNA371a-3p levels post-orchiectomy (77). Moreover, stage I TCGT is a unique oncological entity, where the oncological therapeutic approach is mostly driven by toxicity due to similar OS regardless of the treatment approach (5, 6).Therefore, implementing miRNA 371a-3p in clinical practice would need to diminish false positive results despite its high sensitivity and specificity, and the impact of a biomarker- driven treatment approach needs to further validated (76).
This study has several limitations. One of them is the time of follow-up. It is known that > 95% of relapses occur in <2 years after an orchiectomy. However, 25% of the patients in our cohort consisted of patients who were observed less than 2 years after their orchiectomy. Therefore, potential relapses could be experienced in the future, which may contribute to data uncertainty. Another study limitation is that our cohort consisted mostly of patients with SGCTs, with 66%, compared to 34% of patients with NSGCTs. Moreover, discrepancies between pathology laboratories were present as well. Some pathology laboratories did not assess RTI or tumor size or provided unclear histological proportions in certain specimens. Therefore, central laboratory reassessment would add additional certainty to the pathology reports, which may enhance our data results and may provide more significant associations. In several cases, we needed to contact regional oncology outpatient clinics to find out post-orchiectomy blood drawing results. Thus, in some cases, blood samplings and laboratory methods and their standardization may vary. Furthermore, our study included 159 patients, in whom 41 relapses occurred, of which 18 were classified as non-seminoma and 23 as seminoma. Therefore, the size of the cohort in our study is appropriate for hypothesis- generating results. The advantage of our study is that it focused on stage I GCT, where we assessed the association between blood-based biomarkers and relapse and other clinical and/or tumor characteristics. To the best of our knowledge, these associations have not been studied in this highly selected population.
In conclusion, this is the first report that revealed associations between post-orchiectomy hematological parameters and/or LDH in CSI TGCT. These new associations deserve further evaluation on a larger cohort of CSI TGCT to elucidate whether the associations in certain histological subgroups will improve the stratification of the at-risk population.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics comitee National cancer institute. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
PL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Validation, Data curation. MM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, validation, Supervision.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education Grant (VEGA 1/0071/24) and a grant by Slovak Research and Development Agency (APVV-20-0158).
We would like to acknowledge Pekova Z for providing administrative support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin (2021) 71(1):7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654
3. Kamran SC, Markt SC, Miller R, O'Donnell E, Bernard BD, Curreri SA, et al. A review of clinical stage 1 testicular cancer mortality in a high-volume center. J Clin Oncol (2015) 33(7_suppl):390. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.33.7_suppl.390
4. Dong W, Gang W, Liu M, Zhang H. Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma. Oncol Lett (2016) 11(2):1361–6. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.4065
5. Mazzone E, Mistretta FA, Knipper S, Tian Z, Palumbo C, Gandaglia G, et al. Contemporary assessment of long-term survival rates in patients with stage I nonseminoma germ-cell tumor of the testis: Population-based comparison between surveillance and active treatment after initial orchiectomy. Clin Genitourin Cancer (2019) 17(6):e1153–e62. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.08.009
6. Petrelli F, Coinu A, Cabiddu M, Ghilardi M, Borgonovo K, Lonati V, et al. Surveillance or adjuvant treatment with chemotherapy or radiotherapy in stage I seminoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 13 studies. Clin Genitourin Cancer (2015) 13(5):428–34. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2015.04.005
7. Cummins S, Yau T, Huddart R, Dearnaley D, Horwich A. Surveillance in stage I seminoma patients: A long-term assessment. Eur Urol (2010) 57(4):673–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.06.006
8. Sogani PC, Perrotti M, Herr HW, Fair WR, Thaler HT, Bosl G. Clinical stage I testis cancer: Long-term outcome of patients on surveillance. J Urol (1998) 159(3):855–8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)63753-4
9. Kollmannsberger C, Moore C, Chi KN, Murray N, Daneshmand S, Gleave M, et al. Non-Risk-Adapted surveillance for patients with stage I nonseminomatous testicular germ-cell tumors: Diminishing treatment-related morbidity while maintaining efficacy. Ann Oncol (2010) 21(6):1296–301. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp473
10. Kollmannsberger C, Tandstad T, Bedard PL, Cohn-Cedermark G, Chung PW, Jewett MA, et al. Patterns of relapse in patients with clinical stage I testicular cancer managed with active surveillance. J Clin Oncol (2015) 33(1):51–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.2116
11. Sturgeon JF, Moore MJ, Kakiashvili DM, Duran I, Anson-Cartwright LC, Berthold DR, et al. Non-Risk-Adapted surveillance in clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ cell tumors: The princess margaret hospital's experience. Eur Urol (2011) 59(4):556–62. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.12.010
12. Tandstad T, Stahl O, Dahl O, Haugnes HS, Hakansson U, Karlsdottir A, et al. Treatment of stage I seminoma, with one course of adjuvant carboplatin or surveillance, risk-adapted recommendations implementing patient autonomy: A report from the swedish and norwegian testicular cancer group (Swenoteca). Ann Oncol (2016) 27(7):1299–304. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw164
13. Kersh CR, Constable WC, Hahn SS, Spaulding CA, Eisert DR, Jenrette JM, et al. Primary malignant extragonadal germ cell tumors. an analysis of the effect of the effect of radiotherapy. Cancer (1990) 65(12):2681–5. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900615)65:12<2681::aid-cncr2820651214>3.0.co;2-v
14. Gilligan T, Lin DW, Aggarwal R, Chism D, Cost N, Derweesh IH, et al. Testicular cancer, version 2.2020, nccn clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw (2019) 17(12):1529–54. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0058
15. Oldenburg J, Fossa SD, Nuver J, Heidenreich A, Schmoll HJ, Bokemeyer C, et al. Testicular seminoma and non-seminoma: Esmo clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol (2013) 24(Suppl 6):vi125–32. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt304
16. M.P. Laguna (Chair) PA, Algaba F, Bokemeyer C, Boormans JL, Fischer S, Fizazi K, et al. Eau guidelines. edn. presented at the eau annual congress milan. (2021).
17. Warde P, Specht L, Horwich A, Oliver T, Panzarella T, Gospodarowicz M, et al. Prognostic factors for relapse in stage I seminoma managed by surveillance: A pooled analysis. J Clin Oncol (2002) 20(22):4448–52. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.01.038
18. Zengerling F, Kunath F, Jensen K, Ruf C, Schmidt S, Spek A. Prognostic factors for tumor recurrence in patients with clinical stage I seminoma undergoing surveillance-a systematic review. Urol Oncol (2018) 36(10):448–58. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.06.047
19. Aparicio J, Sanchez-Munoz A, Guma J, Domenech M, Meana JA, Garcia-Sanchez J, et al. A risk-adapted approach to patients with stage I seminoma according to the status of rete testis: The fourth spanish germ cell cancer group study. Oncology (2018) 95(1):8–12. doi: 10.1159/000487438
20. Lesko P, Chovanec M, Mego M. Biomarkers of disease recurrence in stage I testicular germ cell tumours. Nat Rev Urol (2022) 19(11):637–58. doi: 10.1038/s41585-022-00624-y
21. Jia W, Yuan L, Ni H, Xu B, Zhao P. Prognostic value of platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte-to-White blood cell ratio in colorectal cancer patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat (2021) 20:15330338211034291. doi: 10.1177/15330338211034291
22. Wade RG, Robinson AV, Lo MCI, Keeble C, Marples M, Dewar DJ, et al. Baseline neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratios as biomarkers of survival in cutaneous melanoma: A multicenter cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol (2018) 25(11):3341–9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6660-x
23. Qiu Y, Zhang Z, Chen Y. Prognostic value of pretreatment systemic immune-inflammation index in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Front Oncol (2021) 11:537140. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.537140
24. Zhang Y, Sun Y, Zhang Q. Prognostic value of the systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int (2020) 20:224. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01308-6
25. Tan YG, Sia J, Huang HH, Lau WKO. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio independently predicts advanced pathological staging and poorer survival outcomes in testicular cancer. Investig Clin Urol (2019) 60(3):176–83. doi: 10.4111/icu.2019.60.3.176
26. Bauzá Quetglas JL, Tienza Fernández A, Bertolo R, Sabaté Arroyo XA, Guimerà García J, Tubau Vidaña V, et al, et al. The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with testicular cancer. Progrès en Urologie. (2020) 30:273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2020.02.002
27. Chovanec M, Cierna Z, Miskovska V, Machalekova K, Kalavska K, Rejlekova K, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index in germ-cell tumours. Br J Cancer (2018) 118(6):831–8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.460
28. Wang Q, Zhu D. The prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients after radical operation for carcinoma of stomach in gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol (2019) 10(5):965–78. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2019.05.03
29. Gu S, Yang C. Serum lactate dehydrogenase level predicts the prognosis in bladder cancer patients. BMC Urol (2023) 23(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01239-0
30. Zhang J, Yao YH, Li BG, Yang Q, Zhang PY, Wang HT. Prognostic value of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase level in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep (2015) 5:9800. doi: 10.1038/srep09800
31. Hu B, Yang XR, Xu Y, Sun YF, Sun C, Guo W, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res (2014) 20(23):6212–22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442
32. Stojkovic Lalosevic M, Pavlovic Markovic A, Stankovic S, Stojkovic M, Dimitrijevic I, Radoman Vujacic I, et al. Combined diagnostic efficacy of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and mean platelet volume (MPV) as biomarkers of systemic inflammation in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Dis Markers (2019) 2019:6036979. doi: 10.1155/2019/6036979
33. Song D, Li X, Zhang X. Expression and prognostic value of ratios of platelet lymphocyte, neutrophil lymphocyte and lymphocyte monocyte in breast cancer patients. Am J Transl Res (2022) 14(5):3233–9.
34. Moch H, Amin MB, Berney DM, Comperat EM, Gill AJ, Hartmann A, et al. The 2022 world health organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part a: Renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol (2022) 82(5):458–68. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.06.016
35. Aparicio J, Maroto P, Garcia Del Muro X, Sanchez-Munoz A, Guma J, Margeli M, et al. Prognostic factors for relapse in stage I seminoma: A new nomogram derived from three consecutive, risk-adapted studies from the spanish germ cell cancer group (Sgccg). Ann Oncol (2014) 25(11):2173–8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu437
36. Chung P, Daugaard G, Tyldesley S, Atenafu EG, Panzarella T, Kollmannsberger C, et al. Evaluation of a prognostic model for risk of relapse in stage I seminoma surveillance. Cancer Med (2015) 4(1):155–60. doi: 10.1002/cam4.324
37. Mortensen MS, Lauritsen J, Gundgaard MG, Agerbaek M, Holm NV, Christensen IJ, et al. A nationwide cohort study of stage I seminoma patients followed on a surveillance program. Eur Urol (2014) 66(6):1172–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.07.001
38. Tandstad T, Smaaland R, Solberg A, Bremnes RM, Langberg CW, Laurell A, et al. Management of seminomatous testicular cancer: A binational prospective population-based study from the swedish norwegian testicular cancer study group. J Clin Oncol (2011) 29(6):719–25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1044
39. Daugaard G, Gundgaard MG, Mortensen MS, Agerbaek M, Holm NV, Rorth M, et al. Surveillance for stage I nonseminoma testicular cancer: Outcomes and long-term follow-up in a population-based cohort. J Clin Oncol (2014) 32(34):3817–23. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.53.5831
40. Lobo J, Stoop H, Gillis AJM, Looijenga LHJ, Oosterhuis W. Interobserver agreement in vascular invasion scoring and the added value of immunohistochemistry for vascular markers to predict disease relapse in stage I testicular nonseminomas. Am J Surg Pathol (2019) 43(12):1711–9. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001352
41. Li X, Guo S, Wu Z, Dong P, Li Y, Zhang Z, et al. Surveillance for patients with clinical stage I nonseminomatous testicular germ cell tumors. World J Urol (2015) 33(9):1351–7. doi: 10.1007/s00345-014-1454-7
42. Shinoda Y, Matsui Y, Fujimoto H. Cancer registration committee of the japanese urological a. outcomes of active surveillance of clinical stage I non-seminomatous germ cell tumors: Sub-analysis of the multi-institutional nationwide case series of the japanese urological association. Jpn J Clin Oncol (2018) 48(6):565–9. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyy051
43. Nicolai N, Miceli R, Necchi A, Biasoni D, Catanzaro M, Milani A, et al. Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection with no adjuvant chemotherapy in clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ cell tumours: Long-term outcome and analysis of risk factors of recurrence. Eur Urol (2010) 58(6):912–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.08.032
44. Blok JM, Pluim I, Daugaard G, Wagner T, Jozwiak K, Wilthagen EA, et al. Lymphovascular invasion and presence of embryonal carcinoma as risk factors for occult metastatic disease in clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ cell tumour: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJU Int (2020) 125(3):355–68. doi: 10.1111/bju.14967
45. Jankovich M, Jankovichova T, Ondrus D, Breza J. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of preoperative tumor staging in testicular germ cell tumors. Bratislavske Lekarske Listy (2017) 118(9):510–2. doi: 10.4149/bll_2017_098
46. Bolat D, Aydogdu O, Polat S, Yarimoglu S, Bozkurt IH, Yonguc T, et al. Predictive value of preoperative neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio on the prognosis of germ cell testicular tumors. Turk J Urol (2017) 43(1):55–61. doi: 10.5152/tud.2016.38924
47. Zhou X, Du Y, Huang Z, Xu J, Qiu T, Wang J, et al. Prognostic value of PLR in various cancers: A meta-analysis. PloS One (2014) 9(6):e101119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101119
48. Gokcen K, Dundar G, Gulbahar H, Gokce G, Gultekin EY. Can routine peripheral blood counts like neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio be beneficial in prediagnosis of testicular cancer and its stages? J Res Med Sci (2018) 23:64. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_1009_16
49. Dong M, Shi Y, Yang J, Zhou Q, Lian Y, Wang D, et al. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Ther Adv Med Oncol (2020) 12:1758835920937425. doi: 10.1177/1758835920937425
50. Shui Y, Li M, Su J, Chen M, Gu X, Guo W. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of 2,365 patients. Aging (Albany NY) (2021) 13(16):20585–97. doi: 10.18632/aging.203449
51. Cursano MC, Kopf B, Scarpi E, Menna C, Casadei C, Schepisi G, et al. Prognostic role of systemic inflammatory indexes in germ cell tumors treated with high-dose chemotherapy. Front Oncol (2020) 10:1325. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01325
52. Göger Y, Özkent M, Karaağaç M, Uçmak H, Artac M. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with testicular cancer: A retrospective case-control study. Bull Urooncology (2021) 20:252–7. doi: 10.4274/uob.galenos.2021.2021.3.2
53. Wang S, Yang X, Yu Z, Du P, Cao Y, Ji Y, et al. The values of systemic immune-inflammation index and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in predicting testicular germ cell tumors: A retrospective clinical study. Front Oncol (2022) 12:893877. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.893877
54. Kumar P, Nagarajan A, Uchil PD. Analysis of cell viability by the lactate dehydrogenase assay. Cold Spring Harb Protoc (2018) 2018(6):465–8. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot095497
55. Ackers C, Rustin GJ. Lactate dehydrogenase is not a useful marker for relapse in patients on surveillance for stage I germ cell tumours. Br J Cancer (2006) 94(9):1231–2. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603087
56. Weissbach L, Bussar-Maatz R, Mann K. The value of tumor markers in testicular seminomas. results of a prospective multicenter study. Eur Urol (1997) 32(1):16–22.
57. von Eyben FE, Blaabjerg O, Petersen PH, Horder M, Nielsen HV, Kruse-Andersen S, et al. Serum lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme 1 as a marker of testicular germ cell tumor. J Urol (1988) 140(5):986–90. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)41906-9
58. Janda J, Pecha V, Petrik F, Cizek F, Berkova M, Sterba J, et al. Retroperitoneal embryonal Carcinoma/Yolk sac tumor. a case report and a review of the histogenesis. Arch Geschwulstforsch (1988) 58(5):333–40.
59. Brostjan C, Oehler R. The role of neutrophil death in chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell Death Discovery (2020) 6:26. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0255-6
60. Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V, Cheng G, Ling L, et al. Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil phenotype by TGF-beta: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell (2009) 16(3):183–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.06.017
61. Uribe-Querol E, Rosales C. Neutrophils in cancer: Two sides of the same coin. J Immunol Res (2015) 2015:983698. doi: 10.1155/2015/983698
62. Yang P, Li Y, Xie Y, Liu Y. Different faces for different places: Heterogeneity of neutrophil phenotype and function. J Immunol Res (2019) 2019:8016254. doi: 10.1155/2019/8016254
63. Christoffersson G, Vagesjo E, Vandooren J, Liden M, Massena S, Reinert RB, et al. VEGF-A recruits a proangiogenic MMP-9-delivering neutrophil subset that induces angiogenesis in transplanted hypoxic tissue. Blood (2012) 120(23):4653–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-421040
64. Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol (2000) 2(10):737–44. doi: 10.1038/35036374
65. Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev (2006) 25(1):9–34. doi: 10.1007/s10555-006-7886-9
66. Rotondo R, Barisione G, Mastracci L, Grossi F, Orengo AM, Costa R, et al. IL-8 induces exocytosis of arginase 1 by neutrophil polymorphonuclears in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer (2009) 125(4):887–93. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24448
67. Gopinathan G, Milagre C, Pearce OM, Reynolds LE, Hodivala-Dilke K, Leinster DA, et al. Interleukin-6 stimulates defective angiogenesis. Cancer Res (2015) 75(15):3098–107. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1227
68. McGary CT, Miele ME, Welch DR. Highly metastatic 13762NF rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell clones stimulate bone marrow by secretion of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating Factor/Interleukin-3 activity. Am J Pathol (1995) 147(6):1668–81.
69. Lechner MG, Liebertz DJ, Epstein AL. Characterization of cytokine-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells from normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol (2010) 185(4):2273–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000901
70. Anderson NM, Simon MC. The tumor microenvironment. Curr Biol (2020) 30(16):R921–R5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.06.081
71. Yan M, Lesyk G, Radziwon-Balicka A, Jurasz P. Pharmacological regulation of platelet factors that influence tumor angiogenesis. Semin Oncol (2014) 41(3):370–7. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.04.007
72. Suzuki A, Takahashi T, Nakamura K, Tsuyuoka R, Okuno Y, Enomoto T, et al. Thrombocytosis in patients with tumors producing colony-stimulating factor. Blood (1992) 80(8):2052–9.
73. Kasuga I, Makino S, Kiyokawa H, Katoh H, Ebihara Y, Ohyashiki K. Tumor-related leukocytosis is linked with poor prognosis in patients with lung carcinoma. Cancer (2001) 92(9):2399–405. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20011101)92:9<2399::aid-cncr1588>3.0.co;2-w
74. Dieckmann KP, Radtke A, Spiekermann M, Balks T, Matthies C, Becker P, et al. Serum levels of microRNA miR-371a-3p: A sensitive and specific new biomarker for germ cell tumours. Eur Urol (2017) 71(2):213–20. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.07.029
75. Lobo J, Leao R, Gillis AJM, van den Berg A, Anson-Cartwright L, Atenafu EG, et al. Utility of serum miR-371a-3p in predicting relapse on surveillance in patients with clinical stage I testicular germ cell cancer. Eur Urol Oncol (2021) 4(3):483–91. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.11.004
76. Belge G, Dumlupinar C, Nestler T, Klemke M, Torzsok P, Trenti E, et al. Detection of recurrence through microRNA-371a-3p serum levels in a follow-up of stage I testicular germ cell tumors in the DRKS-00019223 study. Clin Cancer Res (2024) 30(2):404–12. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-0730
Keywords: inflammatory, relapse, testicle, stage I, biomarker
Citation: Lesko P and Mego M (2025) The post-orchiectomy systemic inflammatory index is associated with tumor characteristics in clinical stage I germ cell tumors. Front. Oncol. 15:1490264. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1490264
Received: 02 September 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 24 February 2025.
Edited by:
Francesco Esposito, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyReviewed by:
Daniel Adrian Landero Huerta, National Institute of Pediatrics, MexicoCopyright © 2025 Lesko and Mego. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Michal Mego, bWlzb21lZ29AZ21haWwuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.