
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 10 January 2025
Sec. Gynecological Oncology
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1545180
This article is a correction to:
DYNLT3 overexpression induces apoptosis and inhibits cell growth and migration via inhibition of the Wnt pathway and EMT in cervical cancer
A Corrigendum on
DYNLT3 overexpression induces apoptosis and inhibits cell growth and migration via inhibition of the Wnt pathway and EMT in cervical cancer
By Zhang J, Shen Q, Xia L, Zhu X and Zhu X (2022) Front. Oncol. 12:889238. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889238
In the published article, a minor error was identified in Figure 5C. Due to carelessness during the preparation of the figures, the panels labeled “Invasion, SiHa, sh2-Dynlt3” and “Migration, CaSki, sh1-Dynlt3” were incorrectly pasted. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
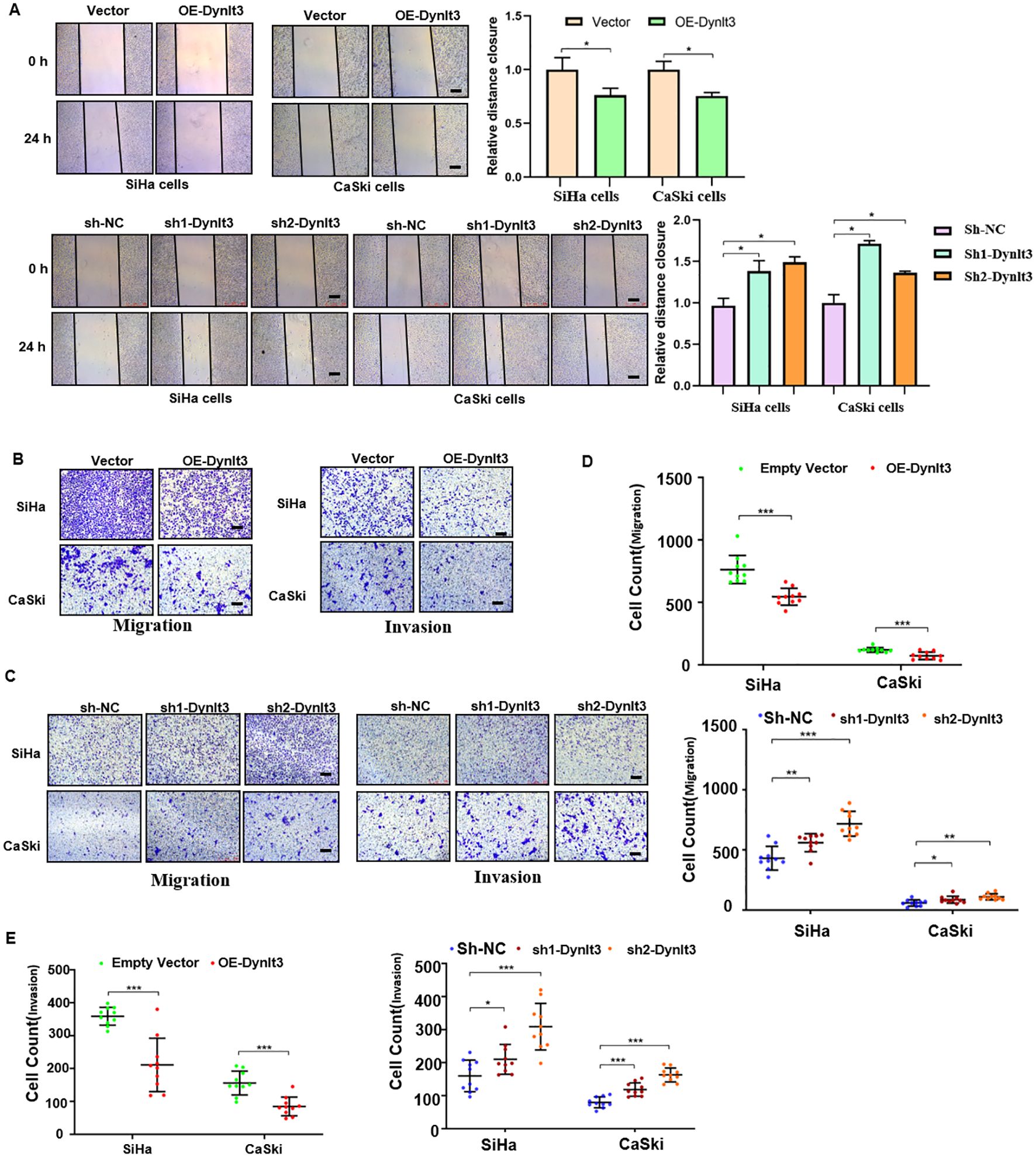
Figure 5. Effects of DYNLT3 on the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells. (A) Left panel: The effects of DYNLT3 on the migration of cervical cancer cells were detected by wound healing assay. Right panel: The quantification of wound closure is shown. (B) The effects of DYNLT3 overexpression on the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells were measured by Transwell assay. (C) The effects of DYNLT3 knockdown on the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells were detected by Transwell assay. Scale bar: 250 μM. (D) The quantification of cell migration is illustrated. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (E) The quantification of cell invasion is presented. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: DYNLT3, cervical cancer, proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration
Citation: Zhang J, Shen Q, Xia L, Zhu X and Zhu X (2025) Corrigendum: DYNLT3 overexpression induces apoptosis and inhibits cell growth and migration via inhibition of the Wnt pathway and EMT in cervical cancer. Front. Oncol. 14:1545180. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1545180
Received: 14 December 2024; Accepted: 17 December 2024;
Published: 10 January 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Joon-Yong Chung, National Cancer Institute (NIH), United StatesCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Shen, Xia, Zhu and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xueqiong Zhu, d3p6eHFAd3poZWFsdGguY29t; Xuejie Zhu, emh1eHVlamllQHd6aG9zcGl0YWwuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.