- 1Department of Hematology, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases, Zhoukou Central Hospital, Zhoukou, China
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Zhengzhou First People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) represented by Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTAC) is the frontier field in the research and development of antitumor therapy, in which oral drug HP518 Receives FDA Proceed Authorization for its IND Application for Prostate Cancer Treatment. Recently, molecular glue, functioning via degradation of the target protein is emerging as a promising modality for the development of therapeutic agents, while exhibits greater advantages over PROTAC, including improved efficiency, resistance-free properties, and the capacity to selectively target “undruggable” proteins. This marks a revolutionary advancement in the landscape of small molecule drugs. Given that molecular glue research is still in its early stage, we summarized the mechanisms of molecular glue, the promising drugs in clinical trials and diverse feasible design strategies for molecular glue therapeutics.
1 Introduction
Molecular glue emerges as a class of diminutive compounds orchestrating the proximity necessary for the meticulous regulation of specific biological phenomena, including signal transduction, transcription, chromatin modulation, as well as protein folding, localization, and degradation (1). Operating as chemical facilitators, molecular glue effectively promotes the dimerization or co-localization of two proteins by instigating ternary complexes, thereby engendering diverse biological and pharmacological functions (2–4). The story of molecular glue degraders begins with thalidomide. Thalidomide began as a drug to treat pregnancy sickness, but was shelved in the early 1960s due to horrific birth defects (5). It was approved for the treatment of leprosy in 1998 and for multiple myeloma in 2006 (6, 7), but its mechanism remains unclear. In 2010, Hiroshi Handa’s team discovered that thalidomide binds the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRBN(cereblon), while Handa first hypothesized that the drug inhibited ubiquitination (8, 9). In 2014, research group revealed that lenalidomide, a thalidomide derivative, is a glue that enables ubiquitination and degradation of two transcription factors (10, 11), which has made molecular glue drug be attractive in academic research. Presently, the predominant focus of investigational drugs lies in modifying the surfaces of E3 ubiquitin ligases, aiding the identification and subsequent degradation of target proteins. Owing to its pronounced cytotoxicity against tumor cells, molecular glue has attracted much attention in the field of anticancer drug development (12, 13). Remarkably, molecular glue possesses a modest molecular weight, showcases favorable drug-like properties, and is currently under scrutiny in numerous clinical studies. The ensuing sections will delve comprehensively into the mechanistic intricacies of molecular glue, ongoing strides in drug development, and innovative strategies for designing molecular glue drugs (Table 1) (14–16).
2 E3 ubiquitin ligase-related drug mechanisms
Molecular glues serve as mediators in coordinating protein-protein interactions, particularly when one of the proteins involved is an E3 ligase. In the presence of an E3 ligase, molecular glue instigates a unique interaction between the E3 ubiquitin ligase substrate receptor and the target protein, ultimately resulting in ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the target protein (17). When the target protein is a tumor pathogenic protein, this process, in turn, imparts a pronounced anticancer effect. Presently, drugs employed in clinical settings or undergoing clinical research predominantly target E3 ubiquitin ligases, including but not limited to CRL4 (Cullin-4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase), SIAH1, and SCF(β-TRCP).
2.1 E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4
Cullin-RING E3 ligases (CRLs), as important elements of the human ubiquitin-proteasome system, are the largest family of E3 ubiquitin ligases in mammalian cells, regulating substrate specific recognition, ubiquitination, and is a key regulator of the body’s normal function (18–20). The E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4 is a multifaceted assembly, consisting of the zinc finger domain protein ROC1 (also denoted as RBX1), the Cul4 scaffold protein, and DDB1-associated proteins (21–23), which are mainly involved in biological processes such as cellular DNA damage repair, DNA replication, chromatin remodeling, and maintenance of genome stability (19, 24, 25). It has been found that many molecular glue degraders achieve antitumor efficacy mainly by binding to the substrate receptor proteins, represented by CRBN and DCAF15 (CUL4-associated factor 15),of the CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, triggering unprecedented interactions that ubiquitinate and degrade target proteins essential for tumor cell survival (17).
2.1.1 IKZF1/IKZF3 degrader
IKZF1 (Ikaros) and IKZF3 (Aiolos) function as interferon (IFN)-stimulated transcriptional repressors (26, 27). The prompt degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 hinders the expression of IRF4 (interferon regulatory factor 4) and c-MYC, leading to the concurrent upregulation of IL-2 (interleukin-2) and IFN-γ (interferon-gamma) in NK (natural killer) cells (28). This orchestrated mechanism mediates potent transcriptional inhibitory effects, resulting in the suppression of tumor cell growth and the induction of apoptosis (29). Notably, studies affirm that the loss or malfunction of IKZF1 is closely linked to drug resistance, heightened relapse rates, and unfavorable prognosis in acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (30–32). A recurring mutation in IKZF3 is identified as a potential cancer driver in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (32, 33). Additionally, overexpression of IKZF1/3 is observed in multiple myeloma (MM), which stimulate malignant proliferation of plasma cells (34).
Thalidomide and its derivatives modulate the activity of immune cells, such as T cells and NK cells, by inducing the production of cytokines (IL-2, interferon-gamma, etc.) (35–37). Consequently, they are categorized as immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) (38–41). Currently, molecular glue compounds extensively employed in clinical applications predominantly belong to the IMiDs category.
Lenalidomide (Len), another immunomodulator with stronger inhibition of IKZF1 and IKZF3 gene expression, is widely used in the treatment of multiple myeloma (42–44).
The substrate receptor protein of the CRL4, CRBN, comprises an N-terminal Lon-like domain (LLD) reminiscent of the bacterial Lon protease and a C-terminal domain binding thalidomide (TBD). The adaptor protein for the CUL4 ligase, DDB1, provides the binding site for CRBN (Figure 1A). The DDB1-binding motif of CRBN encompasses a series of alpha-helices situated on residues 188-248 of LLD. DDB1 consists of three beta-helical domains (BPA, BPB, and BPC), with CRBN binding within a cavity between BPA and BPC (45, 46). The succinimide ring of Len inserts into a hydrophobic pocket composed of three tryptophan residues (W386, W380, W400) and one phenylalanine residue (F402) within TBD (Figure 1B) (45, 46). Upon binding, the exposed segment interacts with complementary substrates, thereby modulating ubiquitination and activating diverse downstream anti-tumor responses. In contrast to traditional drugs such as thalidomide and pomalidomide, the next generation of IMiDs shares common adjacent benzene diamine and glutarimide moieties but displays specific distinctions in the glutarimide ring (46–48).
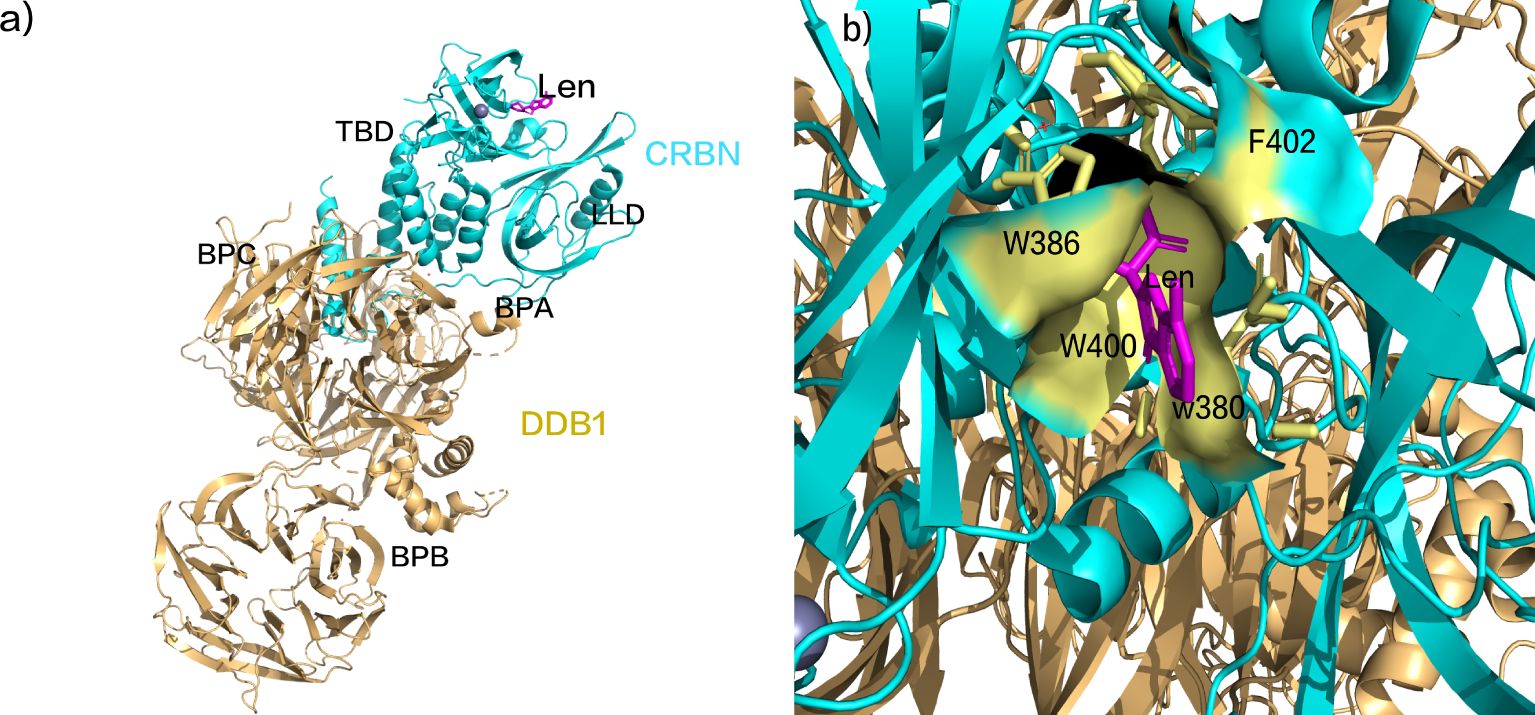
Figure 1. (A) Schematic representation of lenalidomide binding to CRBN. (B) Schematic representation of the succinimide ring insertion into the TBD hydrophobic pocket. (pdb ID: 4CI2).
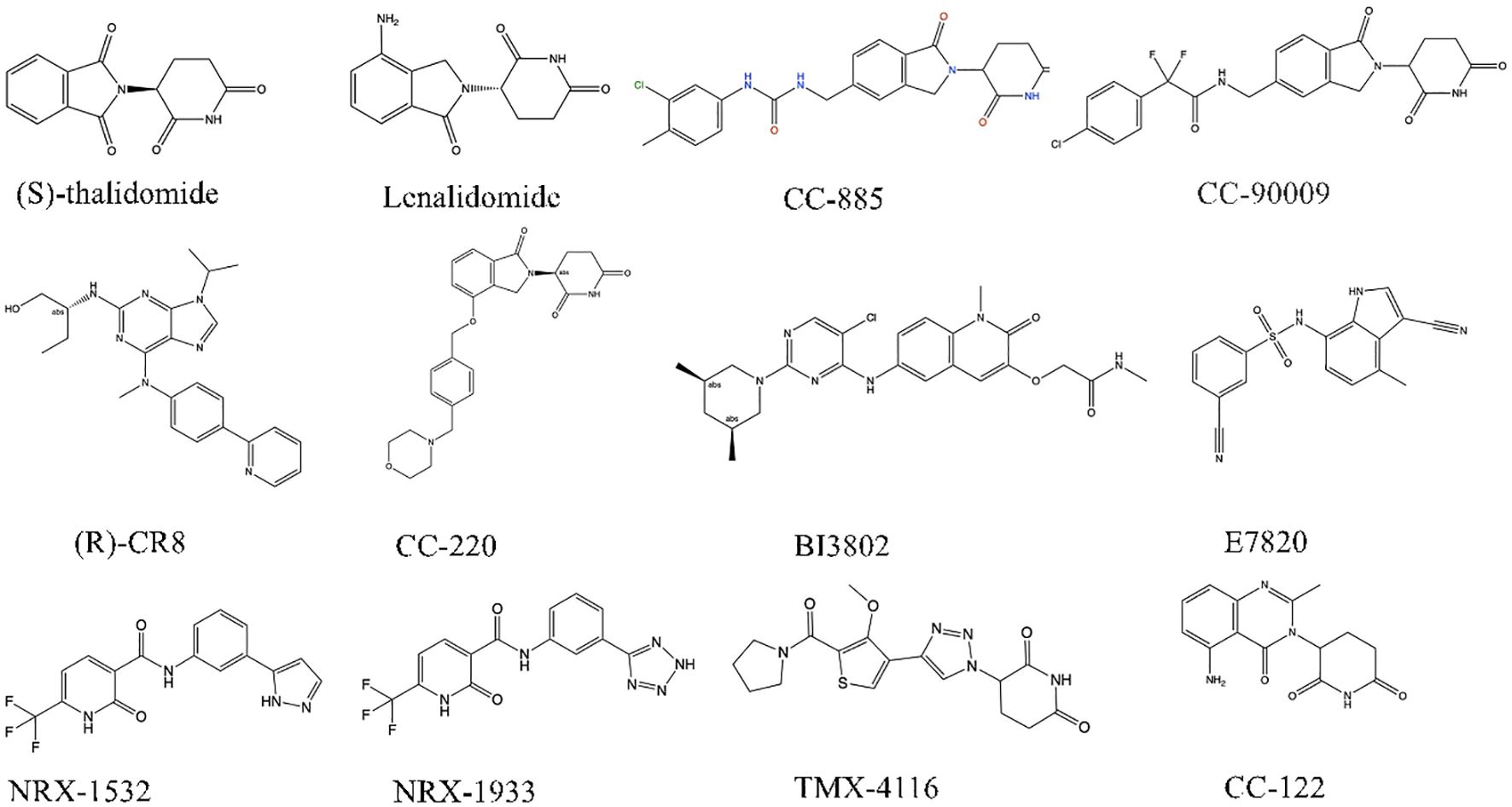
CELMoDs constitute an innovative category of thalidomide analogs, leveraging akin mechanisms for IKZF1/3 degradation. Structurally, both IMiDs and CELMoDs share the succinimide and isoindolinone ring motifs (Figure 1). Nevertheless, CELMoDs incorporate supplementary features, including a phenyl ring and a cyclohexyl group, fostering more intricate interactions with CRBN. This heightened interaction induces a significant alteration in CRBN’s protein conformation, augmenting substrate binding affinity and specificity.
Presently, IMiDs find application in treating multiple myeloma, del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and various hematologic malignancies (49–51). While in multiple studies utilizing transplanted tumor models, including DL-40(large cell lymphoma cells) (52), CELMoDs have demonstrated a markedly superior tumor inhibition effect in animals compared to IMiDs (53). Based on compounds such as CC-92480, CC-220, CC-99282, and CFT-7455, CELMoDs have emerged as a promising technology in cancer treatment (Figure 2).
2.1.2 GSPT1 degrader
GSPT1 (G1 to S phase transition 1) functions as a crucial release factor in translation termination (54), contributing to diverse cellular processes such as cell cycle progression (55), cytoskeletal organization (56), and apoptosis (57, 58). Its overexpression is noted across various tumors, including gastric, breast, liver cancers (59–61), and AML. The molecular glue drug CC-885 facilitates the interaction of CRBN with the novel substrate GSPT1, resulting in its degradation and imparting anti-proliferative effects in AML. Researchers have delineated the CC-885-mediated CRBN-GSPT1 interaction at the crystal structure level (Figure 3A) (62). Specifically, GSPT1 domain 3 docks at the CC-885 binding site, directly interacting with both CC-885 and CRBN surfaces. CC-885 binds within CRBN’s three Trp pockets, forming hydrogen bonds (the hydrogen bond lengths are 2.7 Å and 2.8 Å, respectively) with the succinimide ring engaging residues W380 and H378 (Figure 3B) (62). The isoindolinone ring of CC-885 interacts with both CRBN and GSPT1. CC-885’s expanded chemical structure enables further interaction with CRBN and GSPT1. Its urea portion forms hydrogen bonds with CRBN residues E377 and H353 (the three hydrogen bond lengths are 2.7 Å, 2.8 Å, and 2.9 Å, respectively), while its methyl chlorobenzene ring, positioned near the β-segment of GSPT1 domain 3, facilitates additional interactions, mediating GSPT1 degradation (Figure 3C) (62). Despite its capability to degrade CRBN substrates IKZF1, IKZF3, and CK1α, leading to off-target effects, the clinical development of CC-885 was terminated. Nevertheless, the identification of the novel substrate GSPT1 expands the clinical application potential of CELMoDs. The elucidation of the crystal structure of the CRBN-DDB1-GSPT1-CC-885 complex establishes a foundation for uncovering new CRBN substrates. Notably, CC-90009, designed as a selective GSPT1 degrader with a 2-fluoromethyl substitution for the nitrogen atom in CC-885’s benzamide, represents the first clinical-grade CELMoD (63). In comparison to CC-885, CC-90009 exhibits dose-dependent efficacy in degrading GSPT1 and IKZF1, demonstrating increased selectivity for GSPT1 and improved safety (64, 65). Currently, A phase Ib clinical trial of CC-90009 in combination with venetoclax and azacitidine for acute myeloid leukemia is ongoing (64, 65).
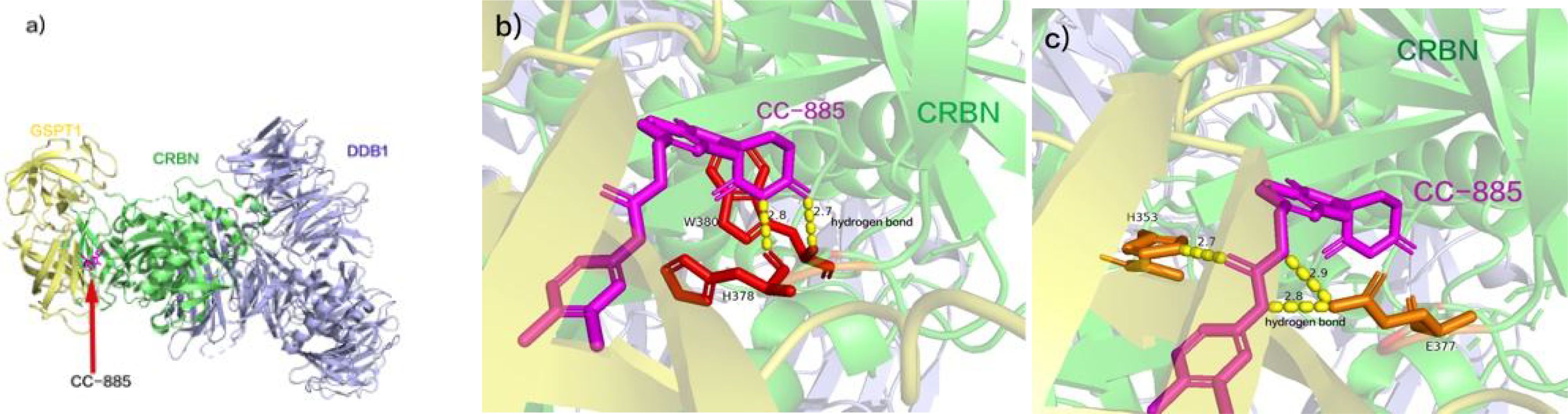
Figure 3. (A) CC-885 facilitates the interaction of CRBN with GSPT1. (B) CC-885 binds within CRBN’s three Trp pockets, forming three hydrogen bonds with the succinimide ring engaging residues W380 and H378. (C) The urea portion of CC-885 forms hydrogen bonds with CRBN residues E377 and H353, and the methyl chlorobenzene ring portion is located near the β-segment of GSPT1 structural domain 3. (pdb ID: 5HXB).
2.1.3 SALL4 degrader
Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4) acts as a transcription factor, contains the Cys2His2 zinc finger (C2H2-ZF) domain predominantly present in embryonic stem cells, playing a pivotal role in their self-renewal and differentiation. Throughout individual development, its expression gradually diminishes in most adult tissues, eventually reaching a silent state. Nevertheless, its reactivation in tumor cells significantly contributes to the initiation and progression of tumors (66–68). SALL4 exhibits notable overexpression in diverse cancers, such as colorectal, lung, breast cancer, and acute myeloid leukemia, establishing close associations with tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and drug resistance (69).
Thalidomide, a well-known drug, comprises two enantiomers, S(-) and R(+) (70, 71). (R)-thalidomide is recognized for alleviating morning sickness, vomiting, and inducing sedation (72), whereas (S)-thalidomide exhibits strong teratogenic effects (73). Intriguingly, the teratogenicity of (S)-thalidomide serves as a molecular glue degrader, targeting the degradation of SALL4 during the embryonic period (74).
A recent study has elucidated that enantiomeric (S)-thalidomide promotes the interaction between SALL4 and CRBN (Figure 4A). The thalidomide-binding domain (TBD) of SALL4 ZF2 emerges as an evolutionarily conserved positive selection site. SALL4 ZF2, featuring the typical C2H2 ZF domain, comprises β-hairpin structures (β1’ and β2’) and α-helical structures (α1’), connected by the Zn2+-binding conserved CXXC and HXXXH motifs (C412, C415, H428, and H432) (75). SALL4 ZF2 establishes contact with the open face of the twisted β-sheet of CRBN TBD, and in the 5HT-mediated complex structure, the β-hairpin ring aligns seamlessly with respect to the position of CRBN TBD. Notably, the side chains of W400 and H357 in CRBN TBD form direct hydrogen bonds (Figure 4B, the two hydrogen bond lengths are 2.8 Å, 2.9 Å, respectively) with the main chain carbonyls on the β-hairpin ring of SALL4 ZF2 (V414, C415, and G416) (75). Subsequently, binding to CRBN in the E3 ubiquitin ligase promotes ubiquitination of SALL4 on the C2H2-ZF domain, leading to its subsequent degradation (75). Presently, numerous molecular glue drugs in clinical trials are strategically designed based on the thalidomide structure (48, 76). The comprehensive elucidation of the mechanism and structural alterations of thalidomide not only enhances our understanding but also provides valuable insights for future drug development grounded in the thalidomide structure.
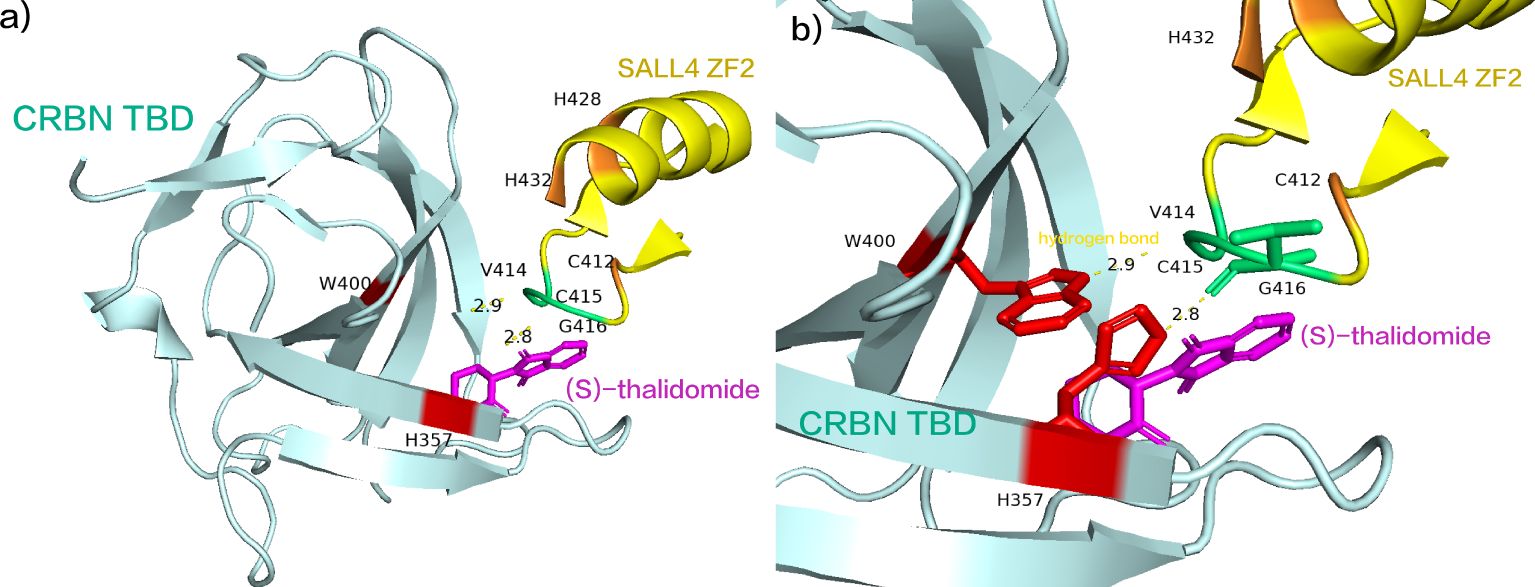
Figure 4. (A) (S)-thalidomide simultaneously binds SALL4 ZF2 and CRBN TBD. (B) the side chains of W400 and H357 in CRBN TBD form direct hydrogen bonds with the main chain carbonyls on the β-hairpin ring of SALL4 ZF2 (V414, C415, and G416). (pdb ID: 7BQU).
2.1.4 CDK degrader
Cell cycle cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) intricately regulate both the cell cycle and gene transcription. CDK12 assumes a critical role in transcriptional regulation by promoting the phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II, thereby influencing RNA splicing, DNA damage response, and maintaining genomic stability (77–79). It has been found that CDK12 is overexpressed in various tumors, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer, which could be a potential anti-tumor target (80–85).
The CDK12 molecular glue inhibitor, (R)-CR8, was identified through a comprehensive analysis correlating the cytotoxicity of over 4000 small molecules in diverse cancer cell lines with the expression levels of E3 ligases in a database (86, 87). Notably, CRL4 E3 ligase-related molecular glue exhibits two common modes: one reliant on CRBN and the other on DCAF15 (88–90). These modes share the DDB1-CUL4-RING-E2 complex, diverging at the receptor protein. Remarkably, (R)-CR8 exhibits the unique ability to recruit Cyclin K to form a ternary complex, cyclin K- CDK12-CR8, without necessitating a standard substrate receptor (bypassing CRBN or DCAF15) (91). This induces the ubiquitination of CDK, resulting in its degradation through the proteasome system and subsequent apoptosis in tumor cells.
Structurally, (R)-CR8 strategically occupies the ATP-binding pocket of CDK12, forming essential hydrogen bonds with the purine structure in the hinge region of CDK12(the three hydrogen bond lengths are 2.3 Å, 2.3 Å, and 2.7 Å, respectively) (91). Additionally, it establishes two π-cation interactions with the R928 in the BPC domain of DDB1 (Figure 5) (91). This interaction is facilitated by its solvent-domain oriented hydrophobic phenylpyridine ring, resulting in the formation of a CDK12-Cyclin K and CUL4 bridging protein DDB1 (RING BOX protein 1) complex (91). At present, (R)-CR8 is in the preclinical stage.
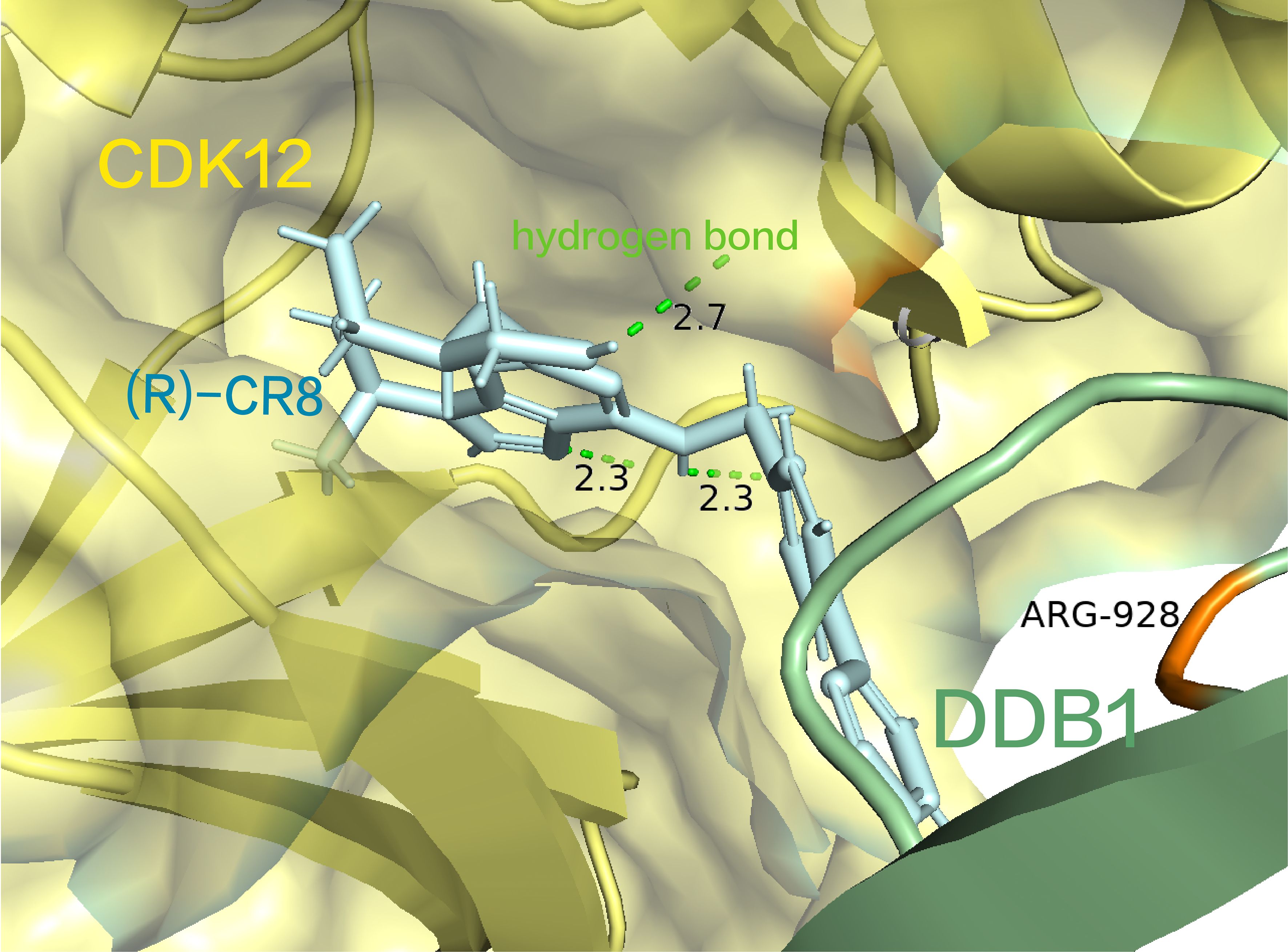
Figure 5. (R) -CR8 occupies the ATP-binding pocket of CDK12, forming critical hydrogen bonds with the purine structure and a cationic interaction with R928 in the BPC structural domain of DDB1. (pdb ID: 6TD3).
2.1.5 CK1α degrader
Casein kinase 1 alpha (CK1α), belonging to the CK1 protein family, plays a crucial role in regulating signaling pathways associated with autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancers (92–94). It was found that targeting CK1α disrupts CK1α/β-catenin signaling, could effectively controlling the growth and survival of organoid-like structures linked to developmental abnormalities in mice and humans (95, 96). These abnormalities indicate an increased risk of cancer (97). Moreover, infrequent CK1α mutations have been identified in various solid tumors and hematological malignancies, suggesting that CK1α may be an anti-cancer therapeutic target (94, 98).
The triazole compound FPFT-2216 induces the formation of a ternary compound involving the E3 ubiquitin ligase CUL4-DDB1-CRBN and CK1α, leading to CK1α ubiquitination and degradation (99). However, FPFT-2216 displays non-specific degradation activity, impacting not only known targets like IKZF1, IKZF3 and CK1α, but also PDE6D (100). This lack of drug selectivity has caused potential safety concerns. In contrast, TMX-4116, a molecular glue degrader derived from FPFT-2216, lacks a cyclic amide group (99). This structural distinction imparts selective degradation activity against CK1α. Cellular assays have validated that TMX-4116 significantly degrades CK1α in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells (MOLT4), human T lymphoblast cells (Jurkat), and MM cells (MM.1S), without affecting PDE6D, IKZF1, and IKZF3 (99). This enhanced degradation selectivity positions TMX-4116 in the preclinical research stage for multiple myeloma treatment.
2.1.6 RBM39 degrader
RNA-binding motif protein 39 (RBM39) is an RNA-binding protein involved in RNA splicing and transcriptional regulation (101, 102). Elevated RBM39 levels contribute to aberrant splicing events and differential gene expression (103). In liver cancer cells, increased arginine uptake is associated with RBM39, sustaining a higher oncogenic metabolism (101, 104). Additionally, in neuroblastoma, RBM39 acts as a crucial splicing factor stimulating malignancy (105). Degrading RBM39 disrupts abnormal splicing through splice dysregulation types, such as intron retention and exon skipping, resulting in anti-tumor activity (106).
Indisulam (E7070) relies on recruiting the splicing protein RBM39 to CUL4-DCAF15, acting as a molecular glue between E3 ubiquitin ligase CUL4-DDB1-DCAF15 and RBM39 to facilitate RBM39 degradation (106). Despite its relatively mild affinity for DCAF15, the cooperative binding of both Indisulam and RBM39 to DCAF15 allows the construction of a stable ternary complex (Figure 6A) (107). Indisulam binds to a shallow pocket on the surface of DCAF15, forming a modified interface that interacts with RBM39 through the α1 helix of the RRM2 domain (Figure 6B), ultimately leading to RBM39 ubiquitination and degradation (108). Studies have demonstrated significant regression of tumor tissue in a high-risk neuroblastoma xenograft mouse model with MYCN overexpression and ALK F1178L mutation upon Indisulam treatment (107). However, Indisulam exhibits inferior oral bioavailability and strong myelosuppression effects. In contrast, E7820, a novel aryl sulfonamide molecular glue, recruits DCAF15 to degrade RBM39 (90, 109). Unlike Indisulam, E7820 demonstrates favorable oral bioavailability and is currently in Phase II clinical trials (NCT05024994) for relapsed or refractory AML, MDS, or CMML (110).
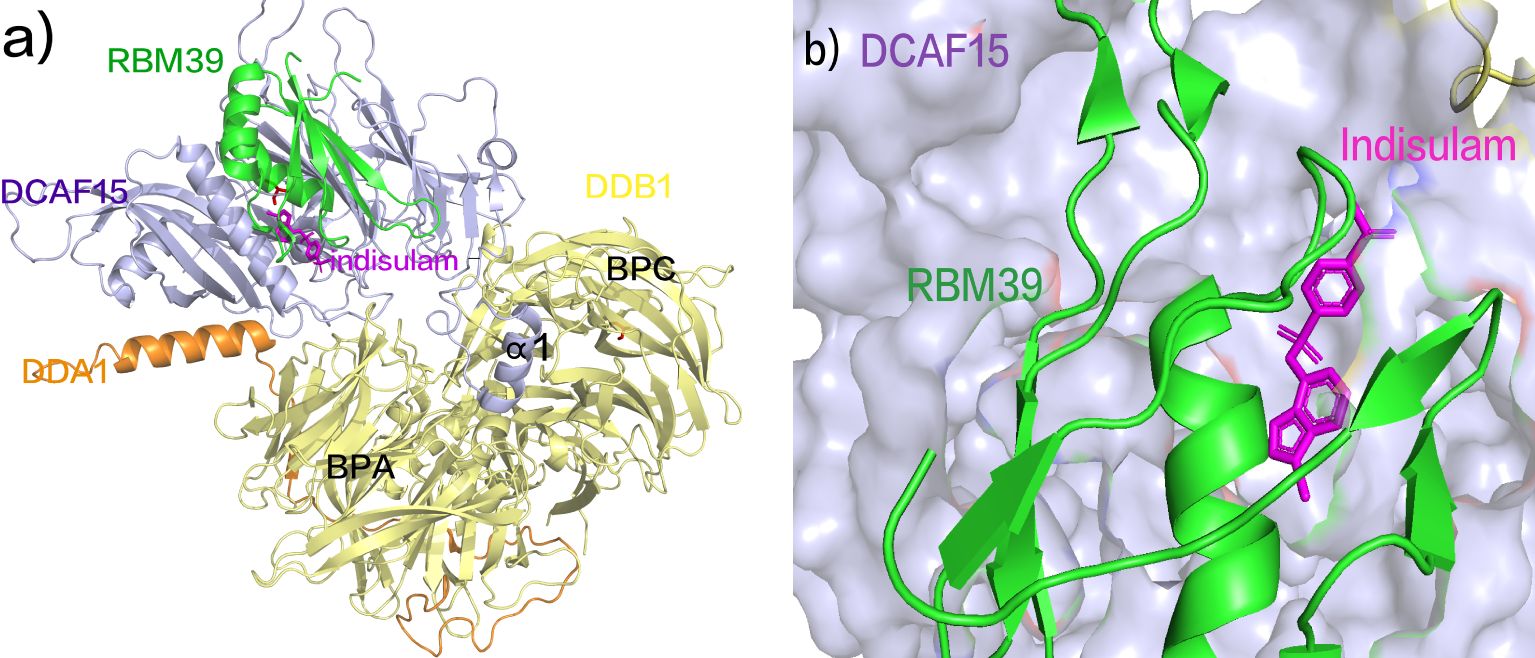
Figure 6. (A) Crystal Structure of DCAF15 DDB1 DDA1 indisulam RBM39 Composite. (B) Indisulam binds to a shallow pocket on the surface of DCAF15, forming a modified interface that interacts with RBM39 through the α1 helix of the RRM2 domain (pdb ID: 6SJ7).
2.2 E3 ubiquitin ligase SIAH1(BCL6 degrader)
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Siah1, a RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase, plays a pivotal role in protein ubiquitination, contributing to the degradation of key targets such as Tribbles 3 homolog (TRB3) and BCL6 (111). BCL6, functioning as a widely expressed transcriptional repressor, inhibits genes involved in cell cycle control, apoptosis, and differentiation, with selective growth suppression observed in BCL6-driven lymphoma cell lines (112, 113). Consequently, BCL6 emerges as a promising therapeutic target for anticancer treatment.
The molecular glue degrader BI-3802 leverages the E3 ubiquitin ligase SIAH1 to induce the degradation of BCL6 (114). This process focusses on the specific targeting of the Broad complex, Tramtrack, and Bric-à-brac (BTB) domain of BCL6 (115, 116). The 3,5-dimethylpiperidine component interacts with another molecule of the BTB domain homodimer, instigating BCL6 aggregation and the formation of higher-order BCL6 sinusoidal protein filaments (Figure 7A) (117). Specifically, BI-3802 establishes direct contact with Tyr58 of BTBα within the groove between BCL6 homodimers, engaging in a hydrophobic interaction with Cys84 of the adjacent BCL6 homodimer (BCL6γ/δ) (117). Furthermore, BI-3802’s binding to BCL6 homodimers facilitates the creation of a salt bridge between Arg28 of BTBβ and Glu41 of BTBγ, resulting in enhanced affinity for SIAH1 (Figure 7B) (117). The E3 ubiquitin ligase SIAH1 coordinates the degradation of aggregated proteins induced by BI-3802 through acting on the VxP motif of the BCL6 protein, located specifically at residues 249-251 of BCL6 (117). BI-3802 promotes the interaction between the BCL6 protein and SIAH1, thereby expediting the ubiquitination and degradation of BCL6 protein. This process culminates in a noteworthy inhibition of BCL6 target genes and imparts anti-proliferative effects in DLBCL cell lines (117). In comparison to traditional BCL6 inhibitors, BI-3802, as a small molecule, induces aggregation alongside highly specific protein degradation, showcasing superior pharmacological activity.
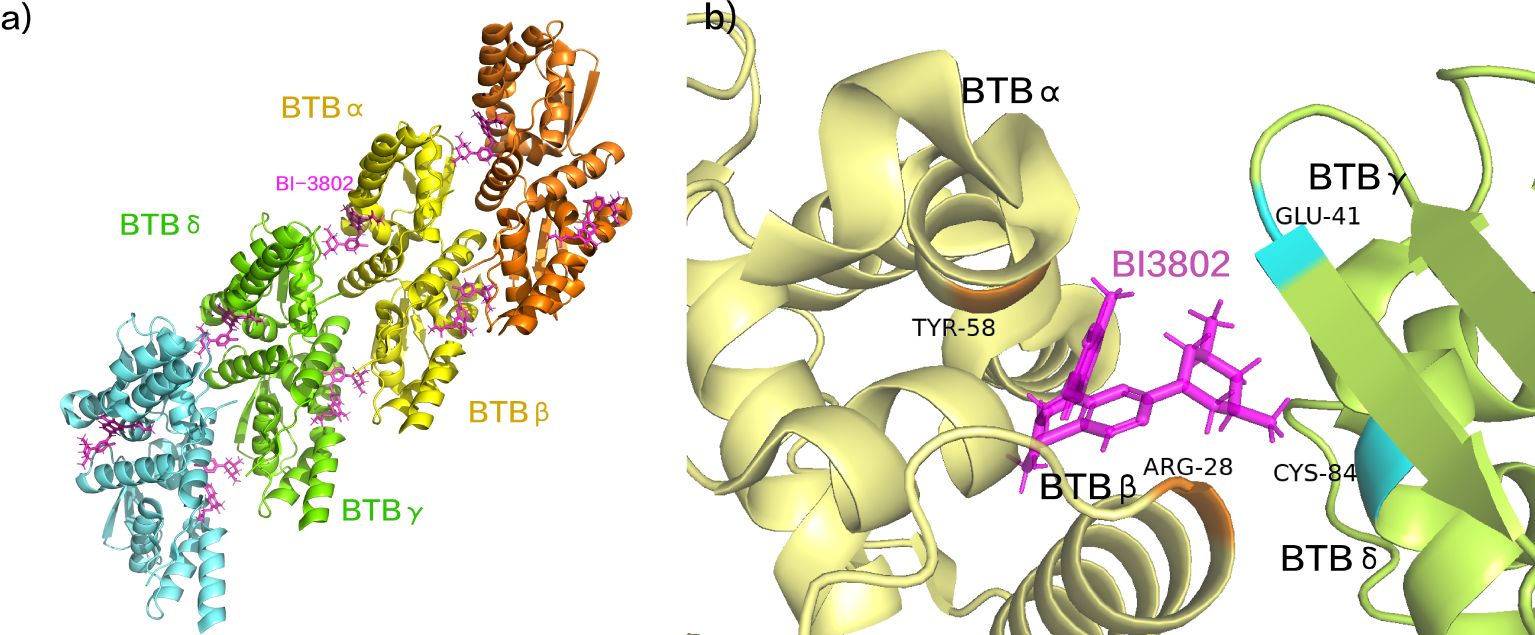
Figure 7. (A) BI-3802 induced BCL6 aggregation. (B) The interaction between BI-3802 and BTB structural domains. (pdb ID: 6XMX).
2.3 E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(β-TRCP)(β-catenin degrader)
The aberrant activation of the Wnt signaling pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis of diverse tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and breast cancer (52). Consequently, modulating Wnt signaling, either by downregulating or restoring its excessive activation, holds therapeutic promise for cancer treatment. In normal cells, β-catenin undergoes recognition by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCFβ-Trcp through phosphorylated Ser33 and Ser37, resulting in β-catenin degradation and maintaining it at lower levels. Conversely, colorectal cancer cells exhibit attenuated effective binding of β-catenin to β-TrCP, leading to its stabilization and augmentation of oncogenic transcription programs (118).
NRX-1933, identified as a molecular glue degrader, enhances the interaction between β-catenin and β-TrCP (Figure 8A). A study elucidated the structural mechanism by which NRX-1933, as a molecular glue-type drug, degrades β-catenin (118). Initially, NRX-1933 binds to the β-catenin:β-TrCP interface, where trifluoromethylpyridinone occupies a small pocket exposed due to the absence of phosphorylation at Ser37 (119). The trifluoromethyl substituent fills a hydrophobic pocket formed by Leu31 and Ile35 residues of the β-catenin peptide and Ala434 and Leu472 residues of β-TrCP, establishing crucial hydrophobic interactions with both β-catenin and β-TrCP (Figure 8B). Specifically, trifluoromethylpyridinone occupies the phosphorylation site of Ser37 on β-catenin, mimicking phosphorylation by forming a hydrogen bond with the main-chain N-H of Gly432 on β-TrCP. Finally, the phenyltetrazole tail group extends outward from the β-catenin: β-TrCP interface, with the phenyl ring overlapping with Arg431 of β-TrCP, and the anionic tetrazole adjacent to the cationic residues Arg410 and Arg431 of β-TrCP (Figure 8C) (118). This significantly enhances the binding affinity of the β-catenin: β-TrCP interface, ultimately leading to ubiquitination and degradation of β-catenin. Although NRX-1933 has not been developed into clinical trials, its reasonable molecular weight and physicochemical properties make it a promising starting point for structural design in the development of novel anti-cancer drugs.
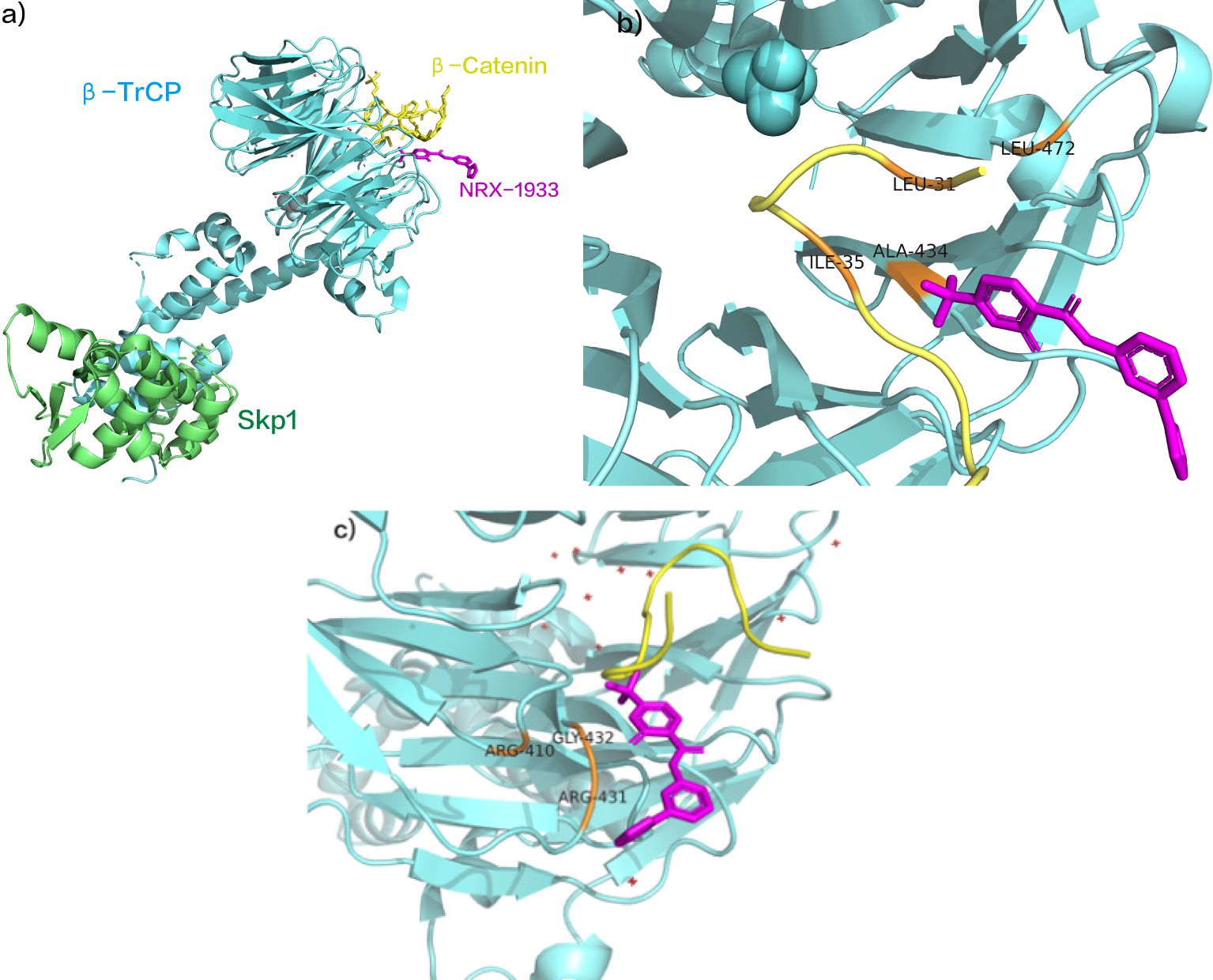
Figure 8. (A) NRX-1933 as SCF β- Trcp and β- Catenin intermolecular glue. (B) NRX-1933 combined with β- Catenin: β- TrCP interface. (C) NRX-1933 Enhancement β- Catenin: β- TrCP interaction. (pdb ID:6M93).
Simonetta et al. identified the molecular glue NRX-1532 through high-throughput screening, to restore the binding between non-phosphorylated β-catenin and CRL1β-TrCP. After structure optimization based on the binding interface, the drug activity of NRX-1532 is significantly improved. NRX-252114, a novel drug developed based on the compound NRX-1532, is intriguing as it restores the interaction between mutated β-catenin (typically unable to bind to β-TrCP) and β-TrCP, a natural E3 ubiquitin ligase. This interaction induces proteasomal degradation of mutated β-catenin, exerting anti-tumor effects. Both NRX-1532 and NRX-252114 are currently in the preclinical research stage.
3 Progress of clinical trials
Currently, numerous clinical trials are in progress to evaluate the tolerance, safety, pharmacokinetics, and various characteristics of molecular glue drugs in patients with solid tumors, hematologic malignancies, and immune system disorders (Table 2).
3.1 CC-220 (iberdomide)
CC-220 (Iberdomide), a novel drug developed by Celgene Corporation, represents a new generation of oral CELMoDs. It functions by inducing the degradation of the transcription factors IKZF1 and IKZF3 while inhibiting the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (120). According to published clinical research data, iberdomide has demonstrated promising therapeutic effects in the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) (121).
There are two ongoing clinical trials investigating the novel drug CC-220: the phase 1/2 CC-220-MM-001 (NCT02773030) and the phase 3 EXCALIBER-RRMM (NCT04975997) trials. In the initial phase of CC-220-MM-001, Iberdomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone were administered to transplant ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM), demonstrating favorable efficacy with sustained profound responses. The overall response rate (ORR) within the assessed population reached 100%, with 87.5% achieving ≥ very good partial response (VGPR) and 56.25% achieving ≥ complete response (CR). Among those achieving ≥ VGPR, 43% (6/14) attained minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, and 68.8% experienced responses within a 6-week timeframe (122). These findings provide support for the continued exploration of Iberdomide (IBER) in MM. When administered in combination with Dexamethasone (DEX), the recommended dose for the subsequent stage of IBER was 1.6 mg (123).
In the dose expansion phase of the CC-220-MM-001 trial, the IBER + DEX combination exhibited notable efficacy in heavily treated, triple-class-exposed, and refractory patients with RRMM, including those previously subjected to anti-BCMA therapies. The ORR was 26.2%, the clinical benefit rate (≥ minimal response) was 36.4%, and the disease control rate (≥ stable disease) was 79.4%. A significant proportion of patients (82.2%) reported grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE), predominantly hematologic TEAE, encompassing neutropenia (44.9%), anemia (28.0%), thrombocytopenia (21.5%), and leukopenia (20.6%) (123). The incidence of grade 3-4 non-hematologic TEAE was comparatively lower. In general, these patients exhibited a preserved health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The combination therapy of IBER and DEX for RRMM is slated for comparison with DRD in the phase 3 EXCALIBER-RRMM (NCT04975997) trial (123).
Based on preclinical research data, Iberdomide is presently undergoing phase 3 clinical trials for two indications: second-line (2L) treatment for MM and maintenance therapy for NDMM patients following autologous stem cell transplantation.
3.2 CC-122 (Avadomide)
CC-122 (Avadomide)also belongs to the CELMoD class of drugs, which can induce the degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 through the proteasome pathway (124), exhibiting anti-lymphoma, anti-angiogenesis, and immunomodulatory effects, making it a promising new-generation therapeutic agent for the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) (125–127).
The Phase I clinical trial of Avadomide (NCT01421524) focused on various solid tumors, NHL, and MM. In NHL patients, the objective response rate (ORR) reached 60%, with 50% of RRMM patients showing stable disease. The primary adverse reactions, fatigue, and neutropenia demonstrated acceptable safety and tolerability. These results provided the basis for the subsequent Phase Ib study, CC-122-NHL-001 (NCT02417285). This Phase Ib study assessed the safety and tolerability of Avadomide in combination with Obinutuzumab for treating patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma (R/R FL), along with the recommended Phase II dosage. In the dose expansion phase, the ORR for patients reached 71%, with 40% achieving a complete response (CR). The Recommended Phase 2 Dose (RP2D) was determined as 3 mg capsules in combination with 1000 mg Obinutuzumab. Overall, Avadomide exhibited manageable safety and durable responses (128, 129).
CELMoD class drugs, including CC-220 (iberdomide) and CC-122 (Avadomide), have been verified for acceptable safety and pharmacokinetics in patients with solid tumors, NHL, and MM.
The fourth-generation drug, CC-99282, not only induces profound (>90%) and sustained degradation of Ikaros and Aiolos in immune cells but also shows a lower incidence of severe febrile neutropenia, ensuring good safety. The new-generation degrader, GLB-002, achieves highly selective degradation of IKZF1/3 proteins, demonstrating promising anti-proliferative activity in vitro in resistant cell lines of NHL and MM. This solves the challenges associated with non-specific degraders targeting IKZF1/3, such as poor selectivity, off-target toxicity, and resistance. GLB-002, a highly promising drug for hematologic malignancies as NHL and MM, was approved for clinical trials by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in July 2023(Acceptance number: CXHL2300799).
3.3 CC-99282(golcadomide)
The CELMoD drug CC-99282 (Golcadomide) triggers the proteasome pathway to degrade IKZF1 and IKZF3, thereby exhibiting antitumor effects (130). In vitro studies have demonstrated that CC-92480 potentiates anti-proliferative and tumoricidal activity in MM cell lines, even in those resistant to lenalidomide and pomalidomide, while also displaying robust immunostimulatory properties (131). Presently, a Phase 1 clinical trial is being conducted to evaluate its therapeutic potential in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
The CC-99282-NHL-001 study (NCT03930953) is a multicenter Phase I clinical trial designed for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (R/R NHL) patients who have received multiple prior treatments. This trial represents the inaugural human study, including a dosage escalation segment for individual therapy (Part A) and a dosage escalation phase with or without combination therapy with rituximab (Part B) (132). In Part A, individual therapy demonstrated notable efficacy among heavily treated R/R NHL patients, with an overall response rate of 43%, with a 17% complete response rate (132). For FL patients, the overall response rate reached 75%, with 38% achieving complete response. Golcadomide demonstrated reassuring safety, with 64% of patients experiencing neutropenia, within the expected range. In Part B, the golcadomide and rituximab combination demonstrated an overall response rate of 43%, the median duration of response (DOR) is 299 days for DLBCL patients and 448 days for FL patients (132). Presently, BeiGene’s Investigational New Drug application for CC-99282 capsules has received approval from NMPA, indicating its potential for advancing into clinical development.
3.4 E7070 (Indisulam)
The RBM39 protein plays a crucial role in maintaining AML by disrupting the alignment of the HOXA9 target gene (133). Furthermore, deleting RBM39 has been observed to modify the splicing of mRNA, which is essential for AML cell proliferation (134). Consequently, targeting RBM39 for degradation emerges as a potential therapeutic strategy for treating AML and other cancers. Notably, E7070(Indisulam) selectively induces the ubiquitination and degradation of the RBM39 protein, thereby exhibiting anti-AML effects. Presently, this compound is undergoing phase II clinical trials (135).
E7070 exhibited no solitary activity against leukemia, thus, in a Phase II trial (NCT01692197), it was combined with idarubicin and cytarabine for treating R/R AML and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients. In 40 patients, 17 (43%) had diploid cytogenetics, and 13 (33%) manifested -5/-7 abnormalities. Ultimately, 11 cases (35%) attained complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi) (135). Seven responders subsequently received stem cell transplantation (SCT). The most prevalent non-hematologic toxicities of Grade ≥ 3 were electrolyte abnormalities (50%) and febrile neutropenia (28%) (135). Overall, the combined therapy of E7070 with idarubicin and cytarabine proved advantageous for R/R AML and high-risk MDS patients, exhibiting good tolerability and promising efficacy in heavily treated AML/MDS patients.
3.5 E7820
Similar to Indisulam, E7820 also acts against AML by targeting RBM39 protein for ubiquitination degradation (109). The Phase II clinical trial of E7820 (NCT05024994) focuses on adults with relapsed/refractory myeloid malignancies, which have mutations like SF3B1, SRSF2, U2AF1 (136). Employing the optimal Simon 2-stage design, the trial reports ORRs of 10% and 30%, indicating less promising outcomes (136). E7820 demonstrates good tolerability with relatively low hematologic toxicity, and no treatment discontinuation due to drug-related adverse events was observed. Administered as a monotherapy at the maximum tolerated dose established in a previous trial (NCT01773421), E7820 exhibits acceptable safety profiles (110). Despite E7820’s limited efficacy, evidence targeting splicing factor-mutated diseases, particularly through RBM39 degradation, emphasizes its potential in managing human malignancies.
3.6 CC-90009
CC-90009 binds to CRL4CRBN, selectively targets GSPT1 ubiquitination and proteasome degradation, and promotes rapid apoptosis of AML cells by effectively eliminating GSPT1 (137). In primary leukemia xenotransplantation models, leukemia implantation and leukemia stem cell (LSC) counts were significantly reduced (64). These findings demonstrate that CC-90009 can be used in clinical or preclinical studies.
CC-90009 is presently under investigation in patients diagnosed with AML for its efficacy as a monotherapy (NCT02848001). CC-90009 treatment induces a rapid decrease in peripheral and bone marrow progenitor cells, indicating preliminary promise in patients with relapsed or refractory AML. Subsequently, the combined efficacy of CC-90009 with venetoclax (VEN)/azacitidine (AZA) is being evaluated in a Phase 1/2 trial involving AML patients (NCT04336982). The aim of this trial is to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and recommended Phase II dose (RP2D) of CC90009 in combination with anti-leukemic drugs for AML treatment, with an anticipated completion by 2025. Another potent, selective, and orally bioavailable GSPT1 degrader, MRT-2359, has entered Phase I/II clinical trials (NCT05546268) for treating myc-driven and other specified solid tumors, such as lung cancer and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. However, to date, no selective GSPT1 degraders have received clinical approval.
4 Design strategies for novel molecular glues
At present, the identification of pharmacologically active novel molecular glues is predominantly serendipitous. However, as researchers consistently to explore reasonable design methods for converting protein-targeting ligands into molecular glue degraders, a series of potential candidate molecules have attracted much attention.
4.1 Linking specific chemical handles
Coupling biologically active compounds to specific chemical handles for site-specific coupling to improve drug affinity is a commonly used approach for drug development (138, 139). Therefore, researchers have applied it to the development of new drugs as molecular glue degraders.
Research chose the CDK4/6 inhibitor Ribociclib as the foundational molecule, introducing various derivatives of “chemical handles” into the solvent-accessible region of Ribociclib, resulting in the creation of nine Ribociclib analogs (140, 141). Initially, the investigation pinpointed the small molecule EST1027, derived from trifluoromethylphenyl cinnamoyl amide, for its notable capability to degrade CDK4 (140). Subsequent inquiries disclosed that the degradative potential of both EST1027 and its analogue, EST1060, necessitates the existence of a covalent bond. Employing probes to identify proteins covalently bound to EST1027, the researchers figured out one E3 ligase, RNF126, intricately connected to the ubiquitin proteasome system (140). Consequently, commencing from the structures of EST1027 and EST1060, the authors incrementally expanded the functional groups on EST1027, conclusively establishing that the p-methoxyphenylpyrimidinyl fumarate structure constitutes the minimal unit proficient in covalently binding with RNF126 (140). Upon identifying JP-2-196 as the minimal covalent binding unit for the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF126, the researchers fused this minimal covalent structure with diverse target protein ligands, yielding molecular glue degraders efficacious against various targets, including CDK4, BCR-ABL, c-ABL, PDE5, BRD4, AR, AR-V7, BTK, SMARCA2, LRRK2, and others (140). In conclusion, the strategic transformation of protein ligands into protein degraders through the linkage of specific chemical handles has proved to be an innovative approach in molecular glue design.
4.2 Harnessing natural products
Both PROTACs and molecular glue degraders induce E3 ubiquitin ligases to approach the target protein, leading to ubiquitination of the protein and degradation of the target protein in a proteasome-dependent manner. PROTACs are relatively modular in design, consisting of the target protein-targeting ligand attached to the E3 ubiquitin ligase ligand by a “linker” (142, 143). The design of PROTAC is relatively modular, consisting of a target protein ligand attached to an E3 ubiquitin ligase ligand via a “linker”. The discovery of novel molecular glue degraders, on the other hand, has mostly come about by serendipity from phenotypic screening or through specific, well-characterized E3 ligase-targeting ligands (e.g., Cereblon). The researchers sought to identify a “chemical handle” that modularly attaches to different targeting ligands and converts these ligands into molecular glue degraders for the target proteins. The authors identified a minimal covalent chemical group that can be attached to multiple protein-targeting ligands to induce proteasome-mediated degradation of the target protein. This in turn enables the target-based modular design of molecular glue degraders.
KRAS G12C inhibitors are employed in treating solid cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer caused by KRAS mutations (144–146). Most of these inhibitors target the inactive form of KRAS G12C, bound to guanosine diphosphate (GDP), which exhibits slow onset and rapid resistance (147, 148).Researchers shifted their focus to the active state of KRAS G12C bound to guanosine triphosphate (GTP). Taking inspiration from the mechanism of action of molecular glues (such as cyclosporine A, rapamycin, and FK506, among other natural products) that alter protein conformation by binding to receptors (such as the affinity protein FKBP12) and forming ternary complexes with target proteins (such as calcineurin), the CYPA:compound-1:KRAS G12C ternary complex was synthesized (149). Various structural optimizations were applied to this ligand, including indole substitutions and removal of the phenol hydroxyl group, compound RMC-4998 was produced (149). Individually, neither RMC-4998 nor CYPA could bind to KRAS G12C. However, RMC-4998 could alter its conformation by initially binding to CYPA, forming a CYPA: RMC-4998 dimer, and then covalently binding to the active state of KRAS G12C (KRAS G12C - GTP) to create a stable ternary complex (149). This ternary complex is inherently stable and exhibits excellent selectivity, binding neither to the inactive state of KRAS G12C (KRAS G12C - GDP) nor affecting wild-type KRAS, NRAS, or HRAS. The formation of the CYPA: RMC-4998:KRAS G12C ternary complex can inhibit ERK downstream signaling in KRAS G12C mutant cancer cell models, attenuate signaling in the AKT-MTOR and RAL pathways, and induce tumor cell apoptosis, demonstrating significant tumor inhibitory effects (149). It is currently in the clinical trial phase (NCT05379985), changing the situation where KRAS is an undruggable target, and specifically target the active status of KRAS G12C to achieve faster and more precise anti-tumor effects.
4.3 Deuteration
Deuterated drugs are a class of drugs in which the hydrogen atoms at specific positions in the molecular structure of the original drug are replaced by isotope deuterium atoms (150), and the main purpose of such drug reconfiguration is to optimize the pharmacokinetic (PK) characteristics and/or metabolic profiles of the original drug while keeping the original drug’s activity unchanged (151–153). The introduction of deuteration technology into glue design can stabilize its active conformation, enhance its activity, reduce side effects, and improve pharmacokinetic properties.
Avadomide monotherapy demonstrated acceptable safety and favorable pharmacokinetics in patients with solid tumors, NHL, and multiple myeloma (154). Researchers employed deuteration reactions to control the molecular chirality, yielding the biologically more active S-configuration of avadomide, known as DRX-164 (155, 156). Both DRX-164 and CRBN exhibit superior binding properties compared to the parent compound CC-122 (Kd 110 nM vs. 330 nM). Preclinical data illustrate that DRX-164 could induce apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines (151). In animal models, DRX-164 demonstrates enhanced therapeutic efficacy compared to lenalidomide and pomalidomide (151).
4.4 Template-assisted covalent modification
Based on the idea that covalent strategies could, in principle, facilitate molecular glue discovery by stabilizing new protein interfaces, Professor Nathanael S. Gray introduced an innovative strategy in the development of molecular glue degraders: Template-assisted covalent modification. In this approach, they engineered small molecules with modified charge groups to interact with BRD4 (157). Through the interaction between BRD4 and the DCAF16 protein, these charge-modified molecules prompted a reaction between their charge groups and a cysteine residue on the E3 ligase DCAF16 (157–159). This interaction induced the ubiquitination of BRD4, leading to its subsequent degradation.
BRD4, a vital epigenetic regulatory protein, modulates fundamental physiological processes like the cell cycle, proliferation, and apoptosis (160–162). Its pivotal role extends to tumor cell infiltration, metastasis, and tumorigenesis in hematologic malignancies such as AML, MM, and solid tumors like breast cancer, glioblastoma, and renal cell carcinoma (163–166). Leveraging “template-assisted covalent modification” to alter electrophilic covalent groups and directly modify the E3 ligase presents a promising strategy specifically for BRD4 degradation, offering potential as an anti-cancer therapeutic method.
5 Conclusions and perspectives
Remarkable strides have been made in the domain of targeted protein degradation, particularly in the development of molecular glue degraders, which have evolved from serendipitous discoveries to a more methodical and tailored approach in drug design (15, 140, 167, 168). Key innovations highlighted include the creation of chemical handles to enhance degrader activity, the fusion of natural molecular glues with drug ligands to impart pharmaceutical properties, and the use of isotopic labeling to optimize pharmacokinetics (140, 169–171). These advancements have been pivotal in the discovery of new therapeutic agents, opening fresh possibilities for targeting disease proteins that were once considered “undruggable”. Nevertheless, challenges remain in refining the PK and PD properties of molecular glue degraders. The incomplete understanding of PK/PD profiles for many preclinical candidates continues to hinder their clinical translation (172, 173). Future research must focus on identifying precise binding sites on target proteins, developing more specific linkers to enhance binding affinity, and improving the degradation efficiency of pathogenic proteins. These issues are particularly pressing in the context of cancer therapeutics. Looking ahead, exploring PPI and designing functional ternary complexes will be pivotal for advancing high-throughput degrader design (3, 174). We anticipate that more efficient screening methods—potentially based on substrate structure—will enable the identification and rational design of molecular glue degraders capable of targeting a broader spectrum of “undruggable” disease proteins. While substantial progress has been made in understanding the mechanisms underlying molecular glue action, significant gaps remain. In particular, a deeper understanding of the precise molecular processes involved, along with the development of more potent and selective inhibitors, is crucial for minimizing off-target effects. Furthermore, long-term safety and efficacy must be carefully evaluated, especially as these therapies advance into clinical applications. Overcoming these challenges will be essential to unlocking the full therapeutic potential of molecular glue degraders, and addressing these unresolved issues will provide critical guidance for their future research and development.
In conclusion, molecular glue degraders are emerging as a powerful and versatile class of therapeutics in tumor therapy. Their ability to target previously “undruggable” proteins, bypass resistance mechanisms, and selectively degrade oncogenic proteins presents a novel and promising strategy in cancer treatment. As research progresses, these agents hold significant potential to transform the landscape of cancer therapy, offering new avenues for treating both solid and hematological tumors.
Author contributions
YH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization. YY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft. JW: Software, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JH: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Zhongyuan Young Top Talent Project (ZYCYU202012163). This funding agency provided financial support for the experimental design, data collection, and analysis of results. The agency played no role in the interpretation of data or the preparation of the manuscript. This study was also funded by the Henan Medical Science and Technology Tackling Program Key Project (SBGJ202302026); funded by QL. This grant supported the computational analysis and modeling portion of the research, including the development of software tools used in the study. The agency had no involvement in the manuscript writing or decision-making processes.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Stanton BZ, Chory EJ, Crabtree GR. Chemically induced proximity in biology and medicine. Science. (2018) 359(6380):eaao5902. doi: 10.1126/science.aao5902
2. Dewey JA, Delalande C, Azizi SA, Lu V, Antonopoulos D, Babnigg G. Molecular glue discovery: current and future approaches. J Med Chem. (2023) 66:9278–96. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00449
3. Rui H, Ashton KS, Min J, Wang C, Potts PR. Protein-protein interfaces in molecular glue-induced ternary complexes: classification, characterization, and prediction. RSC Chem Biol. (2023) 4:192–215. doi: 10.1039/D2CB00207H
5. Kim JH, Scialli AR. Thalidomide: the tragedy of birth defects and the effective treatment of disease. Toxicol Sci. (2011) 122:1–6. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr088
6. Schwab C, Jagannath S. The role of thalidomide in multiple myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myelom. (2006) 7:26–9. doi: 10.3816/CLM.2006.n.035
8. Ito T, Ando H, Suzuki T, Ogura T, Hotta K, Imamura Y, et al. Identification of a primary target of thalidomide teratogenicity. Science. (2010) 327:1345–50. doi: 10.1126/science.1177319
9. Ito T, Ando H, Handa H. Teratogenic effects of thalidomide: molecular mechanisms. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2011) 68:1569–79. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0619-9
10. Krönke J, Udeshi ND, Narla A, Grauman P, Hurst SN, McConkey M, et al. Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells. Science. (2014) 343:301–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1244851
11. Lu G, Middleton RE, Sun H, Naniong M, Ott CJ, Mitsiades CS, et al. The myeloma drug lenalidomide promotes the cereblon-dependent destruction of Ikaros proteins. Science. (2014) 343:305–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1244917
12. Vaden SL. Cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Semin Vet Med Surg Small Anim. (1997) 12:161–6. doi: 10.1016/S1096-2867(97)80028-X
13. Baraldo M, Furlanut M. Chronopharmacokinetics of ciclosporin and tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2006) 45:775–88. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200645080-00002
14. Kozicka Z, Thomä NH. Haven’t got a glue: Protein surface variation for the design of molecular glue degraders. Cell Chem Biol. (2021) 28:1032–47. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.04.009
15. Mayor-Ruiz C, Bauer S, Brand M, Kozicka Z, Siklos M, Imrichova H, et al. Rational discovery of molecular glue degraders via scalable chemical profiling. Nat Chem Biol. (2020) 16:1199–207. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0594-x
16. Sasso JM, Tenchov R, Wang D, Johnson LS, Wang X, Zhou QA. Molecular glues: the adhesive connecting targeted protein degradation to the clinic. Biochemistry. (2023) 62:601–23. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00245
17. Angers S, Li T, Yi X, MacCoss MJ, Moon RT, Zheng N. Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature. (2006) 443:590–3. doi: 10.1038/nature05175
18. Samant RS, Clarke PA, Workman P. E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin-5 modulates multiple molecular and cellular responses to heat shock protein 90 inhibition in human cancer cells. P Natl Acad Sci USA. (2014) 111:6834–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322412111
19. Thirunavukarasou A, Singh P, Govindarajalu G, Bandi V, Baluchamy S. E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin4B mediated polyubiquitination of p53 for its degradation. Mol Cell Biochem. (2014) 390:93–100. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-1960-3
20. Uchida S. Regulation of blood pressure and renal electrolyte balance by Cullin-RING ligases. Curr Opin Nephrol Hy. (2014) 23:487–93. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000049
21. He YJ, McCall CM, Hu J, Zeng Y, Xiong Y. DDB1 functions as a linker to recruit receptor WD40 proteins to CUL4-ROC1 ubiquitin ligases. Genes Dev. (2006) 20:2949–54. doi: 10.1101/gad.1483206
22. Jin J, Arias EE, Chen J, Harper JW, Walter JC. A family of diverse Cul4-Ddb1-interacting proteins includes Cdt2, which is required for S phase destruction of the replication factor Cdt1. Mol Cell. (2006) 23:709–21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.08.010
23. Higa LA, Wu M, Ye T, Kobayashi R, Sun H, Zhang H. CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase interacts with multiple WD40-repeat proteins and regulates histone methylation. Nat Cell Biol. (2006) 8:1277–83. doi: 10.1038/ncb1490
24. Shibata E, Dar A, Dutta A. CRL4Cdt2 E3 ubiquitin ligase and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) cooperate to degrade thymine DNA glycosylase in S phase. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:23056–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.574210
25. Zhu G, Fan Z, Ding M, Mu L, Liang J, Ding Y, et al. DNA damage induces the accumulation of Tiam1 by blocking β-TrCP-dependent degradation. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:15482–94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553388
26. Rebollo A, Schmitt C. Ikaros, Aiolos and Helios: transcription regulators and lymphoid Malignancies. Immunol Cell Biol. (2003) 81:171–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2003.01159.x
27. Schmitt C, Tonnelle C, Dalloul A, Chabannon C, Debré P, Rebollo A. Aiolos and Ikaros: regulators of lymphocyte development, homeostasis and lymphoproliferation. Apoptosis. (2002) 7:277–84. doi: 10.1023/A:1015372322419
28. Mazzurana L, Forkel M, Rao A, Van Acker A, Kokkinou E, Ichiya T, et al. Suppression of Aiolos and Ikaros expression by lenalidomide reduces human ILC3-ILC1/NK cell transdifferentiation. Eur J Immunol. (2019) 49:1344–55. doi: 10.1002/eji.201848075
29. Yamamoto J, Ito T, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H. Discovery of CRBN as a target of thalidomide: a breakthrough for progress in the development of protein degraders. Chem Soc Rev. (2022) 51:6234–50. doi: 10.1039/D2CS00116K
30. Matulić M, Paradzik M, Puskarić BJ, Stipić J, Antica M. Analysis of Ikaros family splicing variants in human hematopoietic lineages. Coll Antropol. (2010) 34:59–62.
31. Mitchell JL, Yankee TM. Variations in mRNA and protein levels of Ikaros family members in pediatric T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Transl Med. (2016) 4:363. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.09.29
32. Orozco CA, Acevedo A, Cortina L, Cuellar GE, Duarte M, Martín L, et al. The combined expression patterns of Ikaros isoforms characterize different hematological tumor subtypes. PloS One. (2013) 8:e82411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082411
33. Duhamel M, Arrouss I, Merle-Béral H, Rebollo A. The Aiolos transcription factor is up-regulated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. (2008) 111:3225–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-113191
34. Li S, Fu J, Yang J, Ma H, Bhutani D, Mapara MY, et al. Targeting the GCK pathway: a novel and selective therapeutic strategy against RAS-mutated multiple myeloma. Blood. (2021) 137:1754–64. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006334
35. Davies FE, Raje N, Hideshima T, Lentzsch S, Young G, Tai YT, et al. Thalidomide and immunomodulatory derivatives augment natural killer cell cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Blood. (2001) 98:210–6. doi: 10.1182/blood.V98.1.210
36. De Raeve H, Vanderkerken K. Immunomodulatory drugs as a therapy for multiple myeloma. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. (2006) 7:415–21. doi: 10.2174/138920106779116847
37. Quach H, Ritchie D, Stewart AK, Neeson P, Harrison S, Smyth MJ, et al. Mechanism of action of immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDS) in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. (2010) 24:22–32. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.236
38. Raje N, Anderson KC. Thalidomide and immunomodulatory drugs as cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. (2002) 14:635–40. doi: 10.1097/00001622-200211000-00008
39. Bamias A, Dimopoulos MA. Thalidomide and immunomodulatory drugs in the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2005) 14:45–55. doi: 10.1517/13543784.14.1.45
40. Raza S, Safyan RA, Lentzsch S. Immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) in multiple myeloma. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2017) 17:846–57. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666170214104426
41. Galustian C, Labarthe MC, Bartlett JB, Dalgleish AG. Thalidomide-derived immunomodulatory drugs as therapeutic agents. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2004) 4:1963–70. doi: 10.1517/14712598.4.12.1963
42. Awwad MHS, Kriegsmann K, Plaumann J, Benn M, Hillengass J, Raab MS, et al. The prognostic and predictive value of IKZF1 and IKZF3 expression in T-cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Oncoimmunology. (2018) 7:e1486356. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1486356
43. Pourabdollah M, Bahmanyar M, Atenafu EG, Reece D, Hou J, Chang H. High IKZF1/3 protein expression is a favorable prognostic factor for survival of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients treated with lenalidomide. J Hematol Oncol. (2016) 9:123. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0354-2
44. Hideshima T, Cottini F, Ohguchi H, Jakubikova J, Gorgun G, Mimura N, et al. Rational combination treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. (2015) 5:e312. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2015.38
45. Fischer ES, Böhm K, Lydeard JR, Yang H, Stadler MB, Cavadini S, et al. Structure of the DDB1-CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase in complex with thalidomide. Nature. (2014) 512:49–53. doi: 10.1038/nature13527
46. Chamberlain PP, Lopez-Girona A, Miller K, Carmel G, Pagarigan B, Chie-Leon B, et al. Structure of the human Cereblon-DDB1-lenalidomide complex reveals basis for responsiveness to thalidomide analogs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2014) 21:803–9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2874
47. Saini N, Mahindra A. Novel immunomodulatory compounds in multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2013) 22:207–15. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.749235
48. Sievers QL, Petzold G, Bunker RD, Renneville A, Słabicki M, Liddicoat BJ, et al. Defining the human C2H2 zinc finger degrome targeted by thalidomide analogs through CRBN. Science. (2018) 362(6414):eaat0572. doi: 10.1126/science.aat0572
49. Shah JJ, Stadtmauer EA, Abonour R, Cohen AD, Bensinger WI, Gasparetto C, et al. Carfilzomib, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory myeloma. Blood. (2015) 126:2284–90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-05-643320
51. Lindner S, Krönke J. The molecular mechanism of thalidomide analogs in hematologic Malignancies. J Mol Med (Berl). (2016) 94:1327–34. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1450-z
52. Henderson J, Kirby R, Perino S, Agafonov R, Chaturvedi P, Class B, et al. Abstract LB007: CFT7455: A novel, IKZF1/3 degrader that demonstrates potent tumor regression in IMiD-resistant multiple myeloma (MM) xenograft models. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:Lb007–lb. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2021-LB007
53. Thakurta A, Pierceall WE, Amatangelo MD, Flynt E, Agarwal A. Developing next generation immunomodulatory drugs and their combinations in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. (2021) 12:1555–63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v12i15
54. Hoshino S, Imai M, Mizutani M, Kikuchi Y, Hanaoka F, Ui M, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel member of the eukaryotic polypeptide chain-releasing factors (eRF). Its identification as eRF3 interacting with eRF1. J Biol Chem. (1998) 273:22254–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.35.22254
55. Chauvin C, Salhi S, Jean-Jean O. Human eukaryotic release factor 3a depletion causes cell cycle arrest at G1 phase through inhibition of the mTOR pathway. Mol Cell Biol. (2007) 27:5619–29. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00035-07
56. Valouev IA, Kushnirov VV, Ter-Avanesyan MD. Yeast polypeptide chain release factors eRF1 and eRF3 are involved in cytoskeleton organization and cell cycle regulation. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. (2002) 52:161–73. doi: 10.1002/cm.10040
57. Hegde R, Srinivasula SM, Datta P, Madesh M, Wassell R, Zhang Z, et al. The polypeptide chain-releasing factor GSPT1/eRF3 is proteolytically processed into an IAP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:38699–706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303179200
58. Lee JA, Park JE, Lee DH, Park SG, Myung PK, Park BC, et al. G1 to S phase transition protein 1 induces apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 activation by dissociating 14-3-3 from ASK1. Oncogene. (2008) 27:1297–305. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210740
59. Malta-Vacas J, Aires C, Costa P, Conde AR, Ramos S, Martins AP, et al. Differential expression of the eukaryotic release factor 3 (eRF3/GSPT1) according to gastric cancer histological types. J Clin Pathol. (2005) 58:621–5. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.021774
60. Malta-Vacas J, Chauvin C, Gonçalves L, Nazaré A, Carvalho C, Monteiro C, et al. eRF3a/GSPT1 12-GGC allele increases the susceptibility for breast cancer development. Oncol Rep. (2009) 21:1551–8.
61. Xi YQ, Gao JB, Li XF, Xu LH, Li Z, Yang LJ, et al. GSPT1 functions as a tumor promoter in human liver cancer. Curr Med Sci. (2023) 43:104–14. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2665-6
62. Matyskiela ME, Lu G, Ito T, Pagarigan B, Lu CC, Miller K, et al. A novel cereblon modulator recruits GSPT1 to the CRL4(CRBN) ubiquitin ligase. Nature. (2016) 535:252–7. doi: 10.1038/nature18611
63. Fuchs O. Treatment of lymphoid and myeloid Malignancies by immunomodulatory drugs. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. (2019) 19:51–78. doi: 10.2174/1871529X18666180522073855
64. Surka C, Jin L, Mbong N, Lu CC, Jang IS, Rychak E, et al. CC-90009, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator, targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells. Blood. (2021) 137:661–77. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008676
65. Hansen JD, Correa M, Alexander M, Nagy M, Huang D, Sapienza J, et al. CC-90009: A cereblon E3 ligase modulating drug that promotes selective degradation of GSPT1 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. J Med Chem. (2021) 64:1835–43. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01489
66. Nicolè L, Sanavia T, Veronese N, Cappellesso R, Luchini C, Dabrilli P, et al. Oncofetal gene SALL4 and prognosis in cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:22968–79. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14952
67. Yang J. SALL4 as a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator in normal and leukemic hematopoiesis. biomark Res. (2018) 6:1. doi: 10.1186/s40364-017-0115-6
68. Zhang X, Yuan X, Zhu W, Qian H, Xu W. SALL4: an emerging cancer biomarker and target. Cancer Lett. (2015) 357:55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.037
69. Vienot A, Monnien F, Truntzer C, Mougey V, Bouard A, Pallandre JR, et al. SALL4-related gene signature defines a specific stromal subset of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with poor prognostic features. Mol Oncol. (2023) 17:1356–78. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13370
70. Tokunaga E, Yamamoto T, Ito E, Shibata N. Understanding the thalidomide chirality in biological processes by the self-disproportionation of enantiomers. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:17131. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35457-6
71. Eriksson T, Björkman S, Roth B, Höglund P. Intravenous formulations of the enantiomers of thalidomide: pharmacokinetic and initial pharmacodynamic characterization in man. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2000) 52:807–17. doi: 10.1211/0022357001774660
72. Meyring M, Mühlbacher J, Messer K, Kastner-Pustet N, Bringmann G, Mannschreck A, et al. In vitro biotransformation of (R)- and (S)-thalidomide: application of circular dichroism spectroscopy to the stereochemical characterization of the hydroxylated metabolites. Anal Chem. (2002) 74:3726–35. doi: 10.1021/ac0203138
73. Liu WM, Strauss SJ, Chaplin T, Shahin S, Propper DJ, Young BD, et al. s-thalidomide has a greater effect on apoptosis than angiogenesis in a multiple myeloma cell line. Hematol J. (2004) 5:247–54. doi: 10.1038/sj.thj.6200351
74. Watson ER, Novick S, Matyskiela ME, Chamberlain PP, HdlP A, Zhu J, et al. Molecular glue CELMoD compounds are regulators of cereblon conformation. Science. (2022) 378:549–53. doi: 10.1126/science.add7574
75. Furihata H, Yamanaka S, Honda T, Miyauchi Y, Asano A, Shibata N, et al. Structural bases of IMiD selectivity that emerges by 5-hydroxythalidomide. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:4578. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18488-4
76. Ichikawa S, Flaxman HA, Xu W, Vallavoju N, Lloyd HC, Wang B, et al. The E3 ligase adapter cereblon targets the C-terminal cyclic imide degron. Nature. (2022) 610:775–82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05333-5
77. Dzimková M, Procházková J, Klát J, Kohoutek J. Th e role of CDK12 in tumor bio logy. Klin Onkol. (2020) 33:260–7. doi: 10.14735/amko2020260
78. Lui GYL, Grandori C, Kemp CJ. CDK12: an emerging therapeutic target for cancer. J Clin Pathol. (2018) 71:957–62. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2018-205356
79. Magnuson B, Bedi K, Narayanan IV, Bartkowiak B, Blinkiewicz H, Paulsen MT, et al. CDK12 regulates co-transcriptional splicing and RNA turnover in human cells. iScience. (2022) 25:105030. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105030
80. Paculová H, Kohoutek J. The emerging roles of CDK12 in tumorigenesis. Cell Div. (2017) 12:7. doi: 10.1186/s13008-017-0033-x
81. Quereda V, Bayle S, Vena F, Frydman SM, Monastyrskyi A, Roush WR, et al. Therapeutic targeting of CDK12/CDK13 in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell. (2019) 36:545–58.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.09.004
82. Eeckhoutte A, Saint-Ghislain M, Reverdy M, Raynal V, Baulande S, Bataillon G, et al. Lack of evidence for CDK12 as an ovarian cancer predisposing gene. Fam Cancer. (2020) 19:203–9. doi: 10.1007/s10689-020-00169-2
83. Chilà R, Chiappa M, Guffanti F, Panini N, Conconi D, Rinaldi A, et al. Stable CDK12 knock-out ovarian cancer cells do not show increased sensitivity to cisplatin and PARP inhibitor treatment. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:903536. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903536
84. Marciscano AE, Barbieri CE. CDK12 gene alterations in prostate cancer: present, but clinically actionable? Eur Urol. (2020) 78:680–1. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.04.007
85. Wu YM, Cieślik M, Lonigro RJ, Vats P, Reimers MA, Cao X, et al. Inactivation of CDK12 delineates a distinct immunogenic class of advanced prostate cancer. Cell. (2018) 173:1770–82.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.034
86. Yu C, Mannan AM, Yvone GM, Ross KN, Zhang YL, Marton MA, et al. High-throughput identification of genotype-specific cancer vulnerabilities in mixtures of barcoded tumor cell lines. Nat Biotechnol. (2016) 34:419–23. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3460
87. Corsello SM, Nagari RT, Spangler RD, Rossen J, Kocak M, Bryan JG, et al. Discovering the anti-cancer potential of non-oncology drugs by systematic viability profiling. Nat Cancer. (2020) 1:235–48. doi: 10.1038/s43018-019-0018-6
88. Han T, Goralski M, Gaskill N, Capota E, Kim J, Ting TC, et al. Anticancer sulfonamides target splicing by inducing RBM39 degradation via recruitment to DCAF15. Science. (2017) 356(4):419–23. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3755
89. Uehara T, Minoshima Y, Sagane K, Sugi NH, Mitsuhashi KO, Yamamoto N, et al. Selective degradation of splicing factor CAPERα by anticancer sulfonamides. Nat Chem Biol. (2017) 13:675–80. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2363
90. Faust TB, Yoon H, Nowak RP, Donovan KA, Li Z, Cai Q, et al. Structural complementarity facilitates E7820-mediated degradation of RBM39 by DCAF15. Nat Chem Biol. (2020) 16:7–14. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0378-3
91. Słabicki M, Kozicka Z, Petzold G, Li YD, Manojkumar M, Bunker RD, et al. The CDK inhibitor CR8 acts as a molecular glue degrader that depletes cyclin K. Nature. (2020) 585:293–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2374-x
92. Janovská P, Normant E, Miskin H, Bryja V. Targeting casein kinase 1 (CK1) in hematological cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(23):9026. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239026
93. Park SM, Miyamoto DK, Han GYQ, Chan M, Curnutt NM, Tran NL, et al. Dual IKZF2 and CK1α degrader targets acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:726–39.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.02.010
94. Spinello Z, Fregnani A, Quotti Tubi L, Trentin L, Piazza F, Manni S. Targeting protein kinases in blood cancer: focusing on CK1α and CK2. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(7):3716. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073716
95. Yu N, Kakunda M, Pham V, Lill JR, Du P, Wongchenko M, et al. HSP105 recruits protein phosphatase 2A to dephosphorylate β-catenin. Mol Cell Biol. (2015) 35:1390–400. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01307-14
96. Huang Q, Chen L, Schonbrunn E, Chen J. MDMX inhibits casein kinase 1α activity and stimulates Wnt signaling. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e104410. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104410
97. Aristizabal-Pachon AF, Carvalho TI, Carrara HH, Andrade J, Takahashi CS. AXIN2 polymorphisms, the β-catenin destruction complex expression profile and breast cancer susceptibility. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2015) 16:7277–84. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.16.7277
98. Yamanaka S, Furihata H, Yanagihara Y, Taya A, Nagasaka T, Usui M, et al. Lenalidomide derivatives and proteolysis-targeting chimeras for controlling neosubstrate degradation. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4683. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40385-9
99. Teng M, Lu W, Donovan KA, Sun J, Krupnick NM, Nowak RP, et al. Development of PDE6D and CK1α Degraders through chemical derivatization of FPFT-2216. J Med Chem. (2022) 65:747–56. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01832
100. Gemechu Y, Millrine D, Hashimoto S, Prakash J, Sanchenkova K, Metwally H, et al. Humanized cereblon mice revealed two distinct therapeutic pathways of immunomodulatory drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2018) 115:11802–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1814446115
101. Coomar S, Mota P, Penson A, Schwaller J, Abdel-Wahab O, Gillingham D. Overlaid transcriptome and proteome analyses identify mitotic kinesins as important targets of arylsulfonamide-mediated RBM39 degradation. Mol Cancer Res. (2023) 21(8):768–78. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.c.6672895.v2
102. Song Y, Guo Y, Li X, Sun R, Zhu M, Shi J, et al. RBM39 alters phosphorylation of c-jun and binds to viral RNA to promote PRRSV proliferation. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:664417. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.664417
103. Cheng X, Wang X, Nie K, Cheng L, Zhang Z, Hu Y, et al. Systematic pan-cancer analysis identifies TREM2 as an immunological and prognostic biomarker. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:646523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.646523
104. Mossmann D, Müller C, Park S, Ryback B, Colombi M, Ritter N, et al. Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39. Cell. (2023) 186:5068–83.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.011
105. Singh S, Quarni W, Goralski M, Wan S, Jin H, Van de Velde LA, et al. Targeting the spliceosome through RBM39 degradation results in exceptional responses in high-risk neuroblastoma models. Sci Adv. (2021) 7:eabj5405. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abj5405
106. Xu Y, Spear S, Ma Y, Lorentzen MP, Gruet M, McKinney F, et al. Pharmacological depletion of RNA splicing factor RBM39 by indisulam synergizes with PARP inhibitors in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:113307. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113307
107. Nijhuis A, Sikka A, Yogev O, Herendi L, Balcells C, Ma Y, et al. Indisulam targets RNA splicing and metabolism to serve as a therapeutic strategy for high-risk neuroblastoma. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:1380. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28907-3
108. Bussiere DE, Xie L, Srinivas H, Shu W, Burke A, Be C, et al. Structural basis of indisulam-mediated RBM39 recruitment to DCAF15 E3 ligase complex. Nat Chem Biol. (2020) 16:15–23. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0411-6
109. Du X, Volkov OA, Czerwinski RM, Tan H, Huerta C, Morton ER, et al. Structural basis and kinetic pathway of RBM39 recruitment to DCAF15 by a sulfonamide molecular glue E7820. Structure. (2019) 27:1625–33.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.10.005
110. Bewersdorf JP, Stahl M, Taylor J, Mi X, Chandhok NS, Watts J, et al. E7820, an anti-cancer sulfonamide, degrades RBM39 in patients with splicing factor mutant myeloid Malignancies: a phase II clinical trial. Leukemia. (2023) 37:2512–6. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-02050-4
111. Ko HR, Jin EJ, Lee SB, Kim CK, Yun T, Cho SW, et al. SIAH1 ubiquitin ligase mediates ubiquitination and degradation of Akt3 in neural development. J Biol Chem. (2019) 294:15435–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009618
112. Leeman-Neill RJ, Bhagat G. BCL6 as a therapeutic target for lymphoma. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2018) 22:143–52. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1420782
113. Wagner SD, Ahearne M, Ko Ferrigno P. The role of BCL6 in lymphomas and routes to therapy. Br J Haematol. (2011) 152:3–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08420.x
114. Zeng X, Zhao F, Jia J, Ma X, Jiang Q, Zhang R, et al. Targeting BCL6 in gastrointestinal stromal tumor promotes p53-mediated apoptosis to enhance the antitumor activity of imatinib. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:3624–35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0082
115. Nitsch L, Jensen P, Yoon H, Koeppel J, Burman SSR, Fischer ES, et al. BTB(BCL6) dimers as building blocks for reversible drug-induced protein oligomerization. Cell Rep Methods. (2022) 2:100193. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100193
116. Zacharchenko T, Wright S. Functionalization of the BCL6 BTB domain into a noncovalent crystallization chaperone. IUCrJ. (2021) 8:154–60. doi: 10.1107/S2052252520015754
117. Słabicki M, Yoon H, Koeppel J, Nitsch L, Roy Burman SS, Di Genua C, et al. Small-molecule-induced polymerization triggers degradation of BCL6. Nature. (2020) 588:164–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2925-1
118. Simonetta KR, Taygerly J, Boyle K, Basham SE, Padovani C, Lou Y, et al. Prospective discovery of small molecule enhancers of an E3 ligase-substrate interaction. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:1402. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09358-9
119. Park WJ, Kim MJ. A new wave of targeting ‘Undruggable’ Wnt signaling for cancer therapy: challenges and opportunities. Cells. (2023) 12(8):1110. doi: 10.3390/cells12081110
120. Matyskiela ME, Zhang W, Man HW, Muller G, Khambatta G, Baculi F, et al. A cereblon modulator (CC-220) with improved degradation of ikaros and aiolos. J Med Chem. (2018) 61:535–42. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01921
121. Bjorklund C, Kang J, Lu L, Amatangelo M, Chiu H, Gandhi A, et al. CC-220 is a potent cereblon modulating agent that displays anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and immunomodulatory activity on sensitive and resistant multiple myeloma cell lines. Blood. (2016) 128:1591. doi: 10.1182/blood.V128.22.1591.1591
122. Niels W.C.J. MP, Rakesh P, Jeremy L, Monique CM, Sundar J, Jeffrey Z, et al. First results of iberdomide (IBER; CC-220) in combination with dexamethasone (DEX) and daratumumab (DARA) or bortezomib (BORT) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood. (2020) 136:16–7.
123. Sagar L MA, Rakesh P, Monique CM, Jeffrey AZ, Jeremy L, Albert OR, et al. Translational and clinical evidence of a differentiated profile for the novel CELMoD, iberdomide (CC-220). Blood. (2019) 134:3119. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-124298
124. Renneville A, Gasser JA, Grinshpun DE, Jean Beltran PM, Udeshi ND, Matyskiela ME, et al. Avadomide induces degradation of ZMYM2 fusion oncoproteins in hematologic Malignancies. Blood Cancer Discovery. (2021) 2:250–65. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-20-0105
125. Nastoupil LJ, Kuruvilla J, Chavez JC, Bijou F, Witzig TE, Santoro A, et al. Phase Ib study of avadomide (CC-122) in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. EJHaem. (2022) 3:394–405. doi: 10.1002/jha2.v3.2
126. Nastoupil L, Bijou F, Ribrag V, Chavez J, Witzig T, Andorsky D, et al. Avadomide (CC-122), a novel cereblon modulating agent, plus rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma. Blood. (2018) 132:1602. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-99-114409
127. Ioannou N, Hagner P, Towfic F, Gandhi A, Stamatopoulos K, Patten P, et al. Eliciting anti-tumor T cell immunity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with PD-L1/PD-1 blockade is enhanced by avadomide immunotherapy through the triggering of immunogenic interferon signaling. Blood. (2018) 132:237. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-99-111605
128. Michot JM, Bouabdallah R, Doorduijn JK, Boccomini C, Kersten MJ, Chiappella A, et al. Long-term results from a phase 1b study of avadomide in combination with obinutuzumab in patients with relapsed and/or refractory B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. (2020) 136:41–2.
129. Rasco DW, Gandhi AK, James A, Li S, O'Mara E, Chopra R, et al. A first in human dose escalation study of CC-122, A first-in-class pleiotropic pathway modulator™ (PPM) compound in subjects with relapsed or refractory solid tumors, multiple myeloma and non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood. (2013) 122:2905.
130. Carrancio S, Fontanillo C, Galasso R, Colombo M, Wood S, Guarinos C, et al. Abstract 3932: Pathway interaction and mechanistic synergy of CC-99282, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator (CELMoD) agent, with enhancer of zeste homolog 2 inhibitors (EZH2is). Cancer Res. (2022) 82:3932. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2022-3932
131. Carrancio S, Groocock L, Janardhanan P, Jankeel D, Galasso R, Guarinos C, et al. CC-99282 is a novel cereblon (CRBN) E3 ligase modulator (CELMoD) agent with enhanced tumoricidal activity in preclinical models of lymphoma. Blood. (2021) 138:1200. doi: 10.1182/blood-2021-148068
132. Julio CC LJ, Franck M, Guillaume C, Judit MJ, Emmanuel B, Pierre B, et al. Efficacy and safety of golcadomide, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator (CELMoD) agent, combined with rituximab in a phase 1/2 open-label study of patients with relapsed/refractory non-hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. (2023) 142:4496. doi: 10.1182/blood-2023-188771
133. Wang E, Lu SX, Pastore A, Chen X, Imig J, Chun-Wei Lee S, et al. Targeting an RNA-binding protein network in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. (2019) 35:369–84.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.010
134. Jin P, Tan Y, Zhang W, Li J, Wang K. Prognostic alternative mRNA splicing signatures and associated splicing factors in acute myeloid leukemia. Neoplasia. (2020) 22:447–57. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2020.06.004
135. Assi R, Kantarjian HM, Kadia TM, Pemmaraju N, Jabbour E, Jain N, et al. Final results of a phase 2, open-label study of indisulam, idarubicin, and cytarabine in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. (2018) 124:2758–65. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v124.13
136. Jan PB, Namrata SC, Justin MW, Andriy D, Omar AW, Eytan MS, et al. E7820, an anti-cancer sulfonamide, in combination with venetoclax in patients with splicing factor mutant myeloid Malignancies: A phase II clinical trial. Blood. (2023) 142:1547. doi: 10.1182/blood-2023-182369
137. Pierce D, Yao T, Pace E, Wang H, Flandin-Blety P, Benitez A, et al. Synergistic combination activity of the novel GSPT1 degrader CC-90009 in acute myeloid leukemia models. Blood. (2021) 138:3330. doi: 10.1182/blood-2021-147160
138. Doytchinova I. Drug design-past, present, future. Molecules. (2022) 27(5):1496. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051496
139. Yu W, MacKerell AD. Computer-aided drug design methods. Methods Mol Biol. (2017) 1520:85–106. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6634-9_5
140. Toriki ES, Papatzimas JW, Nishikawa K, Dovala D, Frank AO, Hesse MJ, et al. Rational chemical design of molecular glue degraders. ACS Cent Sci. (2023) 9:915–26. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c01317
141. Poratti M, Marzaro G. Third-generation CDK inhibitors: A review on the synthesis and binding modes of Palbociclib, Ribociclib and Abemaciclib. Eur J Med Chem. (2019) 172:143–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.064
142. Koroleva OA, Dutikova YV, Trubnikov AV, Zenov FA, Manasova EV, Shtil AA, et al. PROTAC: targeted drug strategy. Principles and limitations. Russ Chem Bull. (2022) 71:2310–34. doi: 10.1007/s11172-022-3659-z
143. Li X, Song Y. Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) for targeted protein degradation and cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:50. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00885-3
144. Yang H, Liang SQ, Schmid RA, Peng RW. New horizons in KRAS-mutant lung cancer: dawn after darkness. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:953. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00953
145. Simanshu DK, Nissley DV, McCormick F. RAS proteins and their regulators in human disease. Cell. (2017) 170:17–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.009
146. Zhu K, Li C, Wu KY, Mohr C, Li X, Lanman B. Modeling receptor flexibility in the structure-based design of KRAS(G12C) inhibitors. J Comput Aided Mol Des. (2022) 36:591–604. doi: 10.1007/s10822-022-00467-0
147. Janes MR, Zhang J, Li LS, Hansen R, Peters U, Guo X, et al. Targeting KRAS mutant cancers with a covalent G12C-specific inhibitor. Cell. (2018) 172:578–89.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.006
148. Yun SD, Scott E, Moghadamchargari Z, Laganowsky A. 2’-deoxy guanosine nucleotides alter the biochemical properties of ras. Biochemistry. (2023) 62:2450–60. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00258
149. Schulze CJ, Seamon KJ, Zhao Y, Yang YC, Cregg J, Kim D, et al. Chemical remodeling of a cellular chaperone to target the active state of mutant KRAS. Science. (2023) 381:794–9. doi: 10.1126/science.adg9652
150. Timmins GS. Deuterated drugs: where are we now? Expert Opin Ther Pat. (2014) 24:1067–75. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.943184
151. Di Martino RMC, Maxwell BD, Pirali T. Deuterium in drug discovery: progress, opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2023) 22:562–84. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00703-8
152. Howland RH. Deuterated drugs. J Psychosoc Nurs Men. (2015) 53:13–6. doi: 10.3928/02793695-20150821-55
153. Timmins GS. Deuterated drugs; updates and obviousness analysis. Expert Opin Ther Pat. (2017) 27:1353–61. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2017.1378350
154. Rasco DW, Papadopoulos KP, Pourdehnad M, Gandhi AK, Hagner PR, Li Y, et al. A first-in-human study of novel cereblon modulator avadomide (CC-122) in advanced Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:90–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1203
155. Jacques V, Czarnik AW, Judge TM, van der Ploeg LH, DeWitt SH. Differentiation of antiinflammatory and antitumorigenic properties of stabilized enantiomers of thalidomide analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:E1471–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417832112
156. DeWitt S, Czarnik AW, Jacques V. Deuterium-enabled chiral switching (DECS) yields chirally pure drugs from chemically interconverting racemates. ACS Med Chem Lett. (2020) 11:1789–92. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00052
157. Li YD, Ma MW, Hassan MM, Hunkeler M, Teng M, Puvar K, et al. Template-assisted covalent modification of DCAF16 underlies activity of BRD4 molecular glue degraders. bioRxiv. (2023) 2023.02.14.528208. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.14.528208
158. Zhang X, Crowley VM, Wucherpfennig TG, Dix MM, Cravatt BF. Electrophilic PROTACs that degrade nuclear proteins by engaging DCAF16. Nat Chem Biol. (2019) 15:737–46. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0279-5
159. Hassan MM, Li YD, Ma MW, Teng M, Byun WS, Puvar K, et al. Exploration of the tunability of BRD4 degradation by DCAF16 trans-labelling covalent glues. bioRxiv. (2023) 279:116904. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.07.561308
160. Hu J, Pan D, Li G, Chen K, Hu X. Regulation of programmed cell death by Brd4. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:1059. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05505-1
161. Liang Y, Tian J, Wu T. BRD4 in physiology and pathology: ‘‘BET’’ on its partners. Bioessays. (2021) 43:e2100180. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100180
162. Bao Y, Wu X, Chen J, Hu X, Zeng F, Cheng J, et al. Brd4 modulates the innate immune response through Mnk2-eIF4E pathway-dependent translational control of IκBα. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:E3993–e4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700109114
163. Donati B, Lorenzini E, Ciarrocchi A. BRD4 and Cancer: going beyond transcriptional regulation. Mol Cancer. (2018) 17:164. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0915-9
164. Wu SY, Lee CF, Lai HT, Yu CT, Lee JE, Zuo H, et al. Opposing functions of BRD4 isoforms in breast cancer. Mol Cell. (2020) 78:1114–32.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.034
165. Baragaño Raneros A, Rodriguez RM, Bernardo Flórez A, Palomo P, Colado E, Minguela A, et al. Bromodomain protein BRD4 is an epigenetic activator of B7-H6 expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncoimmunology. (2021) 10:1897294. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1897294
166. Chen C, Xu L, Gao R, Wang S, Zhang Y, Wang C, et al. Transcriptome-based co-expression of BRD4 and PD-1/PD-L1 predicts poor overall survival in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:582955. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.582955
167. Chen D, Lin S, Zeng Z, An J, Yan W, Gu Z, et al. Serendipitous discovery of Class I HDAC inhibitors from rational design of molecular glue degraders targeting HDAC. Eur J Med Chem. (2024) 263:115926. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115926
168. Guo M, Li Z, Gu M, Gu J, You Q, Wang L. Targeting phosphatases: From molecule design to clinical trials. Eur J Med Chem. (2024) 264:116031. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.116031
169. Chen C, Feng Y, Zhou C, Liu Z, Tang Z, Zhang Y, et al. Development of natural product-based targeted protein degraders as anticancer agents. Bioorg Chem. (2024) 153:107772. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107772
170. Lim M, Cong TD, Orr LM, Toriki ES, Kile AC, Papatzimas JW, et al. DCAF16-based covalent handle for the rational design of monovalent degraders. ACS Cent Sci. (2024) 10:1318–31. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00286
171. Liu TT, Yang H, Zhuo FF, Yang Z, Zhao MM, Guo Q, et al. Atypical E3 ligase ZFP91 promotes small-molecule-induced E2F2 transcription factor degradation for cancer therapy. EBioMedicine. (2022) 86:104353. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104353
172. Keramatnia F, Chang Y, Nishiguchi G, Min J, Mullighan C, Fischer M, et al. Abstract LBA002: Targeting GSPT1 by a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator for the treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther. (2021) 20:Lba002–lba. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.TARG-21-LBA002
173. Lin C, Li Z, Medley K, Bearss D, Vankayalapati H. Abstract LB161: Discovery of an oral, potent, and selective CDK9 molecular glue degrader SLX-3065 active in aggressive variant prostate cancers (AVPC). Cancer Res. (2024) 84:Lb161–lb. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2024-LB161
Keywords: molecular glue degrader, tumor, design strategies, mechanism, clinical trials
Citation: Hu Y, Yan Y, Wang J, Hou J and Lin Q (2024) Molecular glue degrader for tumor treatment. Front. Oncol. 14:1512666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1512666
Received: 17 October 2024; Accepted: 19 November 2024;
Published: 12 December 2024.
Edited by:
Hasem Habelhah, The University of Iowa, United StatesReviewed by:
Jyoti Bala Kaushal, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United StatesMohammad Abid, Jamia Millia Islamia, India
Copyright © 2024 Hu, Yan, Wang, Hou and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Quande Lin, emx5eWxpbnF1YW5kZTE1NzdAenp1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Yuhan Hu
Yuhan Hu Yan Yan
Yan Yan Jiehao Wang
Jiehao Wang Jiangxue Hou
Jiangxue Hou Quande Lin
Quande Lin