
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol., 30 January 2025
Sec. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Gastric and Esophageal Cancers
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1498213
Triptolide, the major component of Chinese herbal medicine Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, possesses potent anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects. IL-8, a proinflammatory cytokine, is associated with cancer cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Here, we found that Triptolide has an inhibitory effect on IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in human gastric cancer cells, via the suppression of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, AP-1, and NF-κB activation, which in turn affects human endothelial cell angiogenetic activity in tumor microenvironments. Human gastric AGS cells were treated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL) and Triptolide (0–20 nM), and the ROS generation, ERK, AP-1, and NF-κB signaling were all investigated. These results demonstrate that Triptolide inhibits the IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in gastric cancer cells by inhibiting ROS production and angiogenesis, via the dose-dependent attenuation of ERK, AP-1, and NF-κB activation. In this study, we showed that Triptolid inhibits ROS/ERK-mediated AP-1 and ROS-mediated NF-κB axes potentially leading to an improved treatment outcome for gastric cancer and its associated tumor microenvironment.
Gastric cancer is a global health issue and is ranked the fifth most common cancer and the third most lethal worldwide (1). Gastric cancer (GC), also known as gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma or stomach cancer, results from cancerous growth in the digestive tract (2). It is a geographically diverse disease (3), with the highest incidence rate in Asia/Pacific regions, where one million cases are diagnosed each year (4), and it has a global mortality rate of 783,000 deaths (5, 6). Therefore, it is essential to understand the mechanisms that cause and develop gastric cancer in order to refine its prevention and treatment. There is growing evidence that chemokines are linked to cancer and could be used as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis predictions (7). Recent research has confirmed that interleukin-1β (IL-1β) is associated with the facilitation of gastric cancer following Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection, and chronic inflammation plays a critical role in the growth and proliferation of GC. IL-1β induces gastric cancer by blocking the production of gastric acid, causing epigenetic changes, stimulating angiogenesis, attracting adhesive factors, and releasing other inflammatory factors, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8/CXCL8) (8–11). Although IL-1β increases IL-8 expression in various cells, including endothelial, epithelial, and smooth muscle cells, the molecular mechanism underlying IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in gastric cancer is unknown.
A growing body of evidence suggests that IL-8/CXCL8 has chemotactic, proangiogenic, and tumorigenic properties (12, 13). The primary regulators of IL-8 expression are transcription factors including nuclear factor-κB-mediated transcription factors (NF-κB) (14). When activated through CXCR1 and CXCR2 (cell-surface G protein-coupled receptors), IL-8 activates phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase or phospholipase C, which activates the Akt/PKB, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathways, which are mainly responsible for inflammation (15, 16). Evidence indicates that IL-8 derived from tumors significantly impacts the tumor microenvironment (17–19). Its role is critical in maintaining cancer cells in the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) trait (20), which confers proliferation and invasiveness, as well as promoting angiogenesis in various cancers (21, 22). However, there is only limited research available on the relationship between IL-1ß and IL-8, as well as the molecular mechanisms involved in gastric cancer progression. Therefore, it has been suggested that unraveling and targeting CXC-chemokine signaling may have significant implications in halting disease progression and assisting in sensitizing tumors to chemotherapeutic and biological agents, given the multiple effects of IL-8 signaling on gastric cells within the tumor microenvironment.
Nonetheless, therapeutic interventions for advanced/metastatic gastric cancer have evolved dramatically in recent years. Indeed novel drugs have emerged at an exponential rate, primarily focusing on inhibiting the oxidative stress-induced inflammatory response, which counteracts aberrant cancer signaling by inhibiting cancer growth and proliferation. This has provided oncologists with a wide range of advanced treatment options against late-stage GC. Triptolide is a primary bioactive compound derived from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, which belongs to the Celastraceae family and the Tripterygium genus, and has been found in Southern China. Its roots have been used in a myriad of practices to “relieve stasis and internal warmth,” among many other diseases diagnosed by Traditional Chinese medicine practitioners. Recent studies have shown that Triptolide inhibits tumor proliferation and metastasis, induces apoptosis, and enhances the impact of other therapeutic interventions in various types of cancers (23–26). Thus, considering all this, the objective of this study was to determine the effect of Triptolide on IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in gastric cancer by modulating ROS-mediated AP-1/NF-κB and ERK signaling.
Human gastric cancer AGS cell line and endothelial cell line EA.hy926 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells used in this study were cultured under the same conditions described in our previous study (27). Briefly, the effect of Triptolide on the IL-1β-stimulated expression of IL-8 was examined by harvesting the cells at different intervals and measuring the level of IL-8 mRNA by RT-PCR. To determine the effects of Triptolide in IL-1β (R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) induced ERK1/2 activation, cells were harvested at various intervals, and the phosphorylated and total protein levels were determined by Western blot.
Protein extraction and Western blot analysis were performed as previously described (27). Several primary antibodies were used (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA): anti-phospho-ERK1/2, anti-phospho-p65, anti-phospho-c-Fos, and anti-phospho-c-Jun. The secondary antibody was horseradish peroxidase-labeled anti-rabbit immunoglobulins from donkey (Amersham Corp., Arlington Heights, IL, USA), which was used at a dilution of 1:3000. Protein bands were visualized using a Western chemiluminescent HRPV substrate (Millipore Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA). The total protein levels were assayed by washing the blotted membrane with stripping solution [100 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate, and 62.5 mM Tris–HCl (pH 6.7)] for 30 min at 50°C, and then, the membrane was applied with anti-ERK1/2 and anti-p65 antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) diluted to 1:2000.
Intracellular H2O2 was measured using 5-(and 6)-carboxyl-2’,7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA, Grand Island, NY, USA), according to the same procedure in a previous study (28). To investigate the role of Triptolide in IL-1β-induced ROS production, cells were grown in serum-starved DMEM medium supplemented with 0.5% FBS for an additional 2 days. Then, the cells were stabilized in serum-free DMEM medium without phenol red for at least 30 min before exposure to IL-1β for 0–20 min. To assess the effect of Triptolide, the cells were pretreated with Triptolide for 30 min. Then, the cells were incubated with the H2O2-sensitive fluorophore DCFDA (10 μM) for 30 min and immediately observed under a laser-scanning confocal microscope. DCF fluorescence was excited at 458 nm using an argon laser, and the evoked emission was filtered with a 538 nm long pass filter.
The transcriptional regulation of IL-8 by IL-1β was examined following the transient transfection of an IL-8 promoter-luciferase reporter construct (pGL2-IL-8) (29). AGS cells (5 × 105) were seeded and grown to 60–70% confluence, and then, pRLTK (an internal control plasmid containing the herpes simplex thymidine kinase promoter linked to the constitutively active Renilla luciferase reporter gene) and pGL2-IL-8 were cotransfected into the cells using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). According to the manufacturer’s protocol, pRLTK and pGL2 were cotransfected as the negative control. Cells were incubated in the transfection medium for 20 h and pretreated with different doses of Triptolide for 1h prior to their incubation with IL-8 for 4 h. After incubation, the cells were harvested and lysed with passive lysis buffer (Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System; Promega, Madison, WI, USA), and luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer.
Conditioned medium (CM) derived from AGS cells was prepared as follows: Cells were grown to 95–100% confluence and incubated for 24 h in DMEM medium with 1% FBS and 10 ng/mL IL-1β or Triptolide pretreated for 1h. After incubation, supernatants [CM or CM(T)] were collected, centrifuged, and stored at -20°C. To determine the effect of CM on endothelial cell proliferation, EA.hy926 cells (5 × 103) were plated in 96-well plates (Falcon Laboratories, McLean, VA, USA) and incubated for 24 h with DMEM containing 10% FBS. The medium was replaced with CM, and the cells were incubated for a further 24 h. The neutralizing effect of the anti-IL-8 antibody on the proliferation activity of CM was determined by incubating the cells with CM and CM(T) after CM and CM(T) were treated for 1h with 1 μg/mL neutralizing antibody to IL-8 (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) Cell proliferation was determined using the MTT assay in which the MTT was converted to formazan granules in the presence of molecular oxygen. After incubation, 50 μL of 5 mg/mL MTT was added to each well of the 96-well plates and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The formazan granules obtained were dissolved in 100% DMSO, and the absorbance was detected at 562 nm using a 96-well ELISA reader (Biotek Inc., Winooski, VT, USA).
Conditioned medium (CM) derived from AGS cells was prepared as previously described (30). Briefly, AGS cells were grown to 95–100% confluency and incubated for 24 h in DMEM medium with 1% FBS and 10 ng/mL IL-1β or Triptolide pretreated for 1h. After incubation, the supernatants were collected, centrifuged, and stored at -80°C until use. Corning® Matrigel® Basement Membrane Matrix (9.1 mg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was loaded in a 96-well plate (60 μL/well) and incubated at 37°C for at least 30 min. EA.hy926 cells were plated (5 × 103) on the prepared thin Matrigel 96-well plate with 50 μL DMEM 10% FBS media for 4 h before the EA.hy926 cells were incubated for 6 h with the prepared CM. The IL-8 anti-body (1 μg/mL; R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and a non-specific IgG (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) were used. The synthesized IL-8 (1 ng/mL; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) along with the control CM was added to the EA.hy926 cells as the positive control to evaluate the IL-8 effect on the endothelial cell angiogenic activity. Quantification of the nodes, junctions, branches, and segments was conducted using an Angiogenesis Analyzer (software ImageJ; http://image.bio.methods.free.fr/ImageJ/?Angiogenesis-Analyzer-for-ImageJ&lang=en&artpage=3-6#outil_sommaire_3, accessed on 20, February 2023).
Each value represents three individual experiments and is presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). The results were analyzed using Graph Pad Prism software (Version 8.0). The differences between the two datasets were analyzed using a t-test. The statistically significant differences described in the text correspond to a p-value of < 0.05.
To determine the effect of Triptolide on IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in human gastric cancer AGS cells, the cells were pretreated with Triptolide (Figure 1A), and the levels of IL-8 mRNA were determined by RT-PCR and qPCR analyses. The RT-PCR and qPCR results showed that Triptolide decreased IL-1β-induced IL-8 mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner (Figures 1B, C). Additionally, Triptolide also decreased IL-8 promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1D). Similar results were observed in the ELISA evaluation (Figure 1E). Additionally, Triptolide inhibited IL-1β-induced AGS cell proliferation (Figure 1F). Collectively, these results demonstrated that Triptolide suppresses the IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in gastric cancer AGS cells and further inhibited the IL-1β-induced cancer cell proliferation.
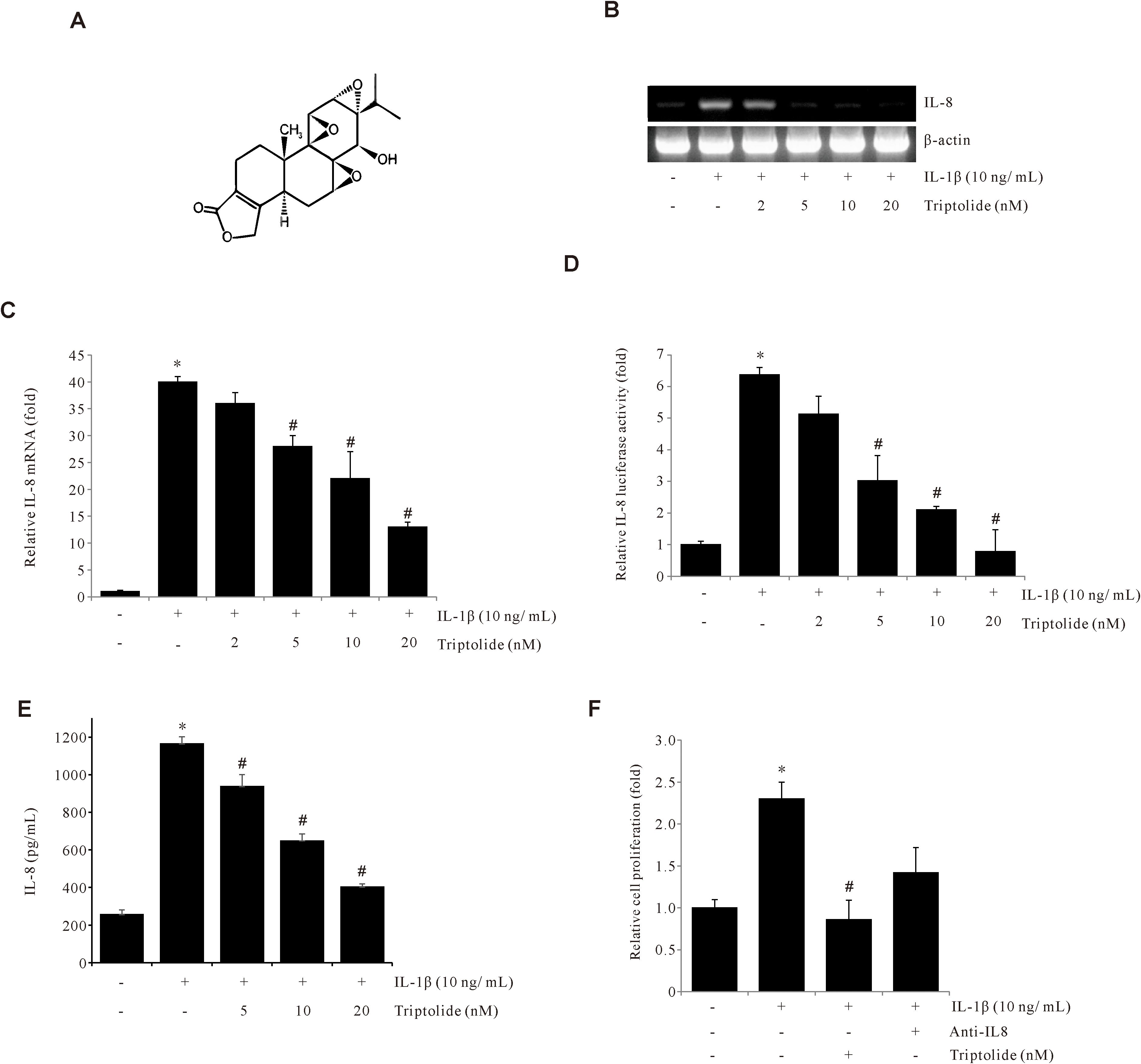
Figure 1. Triptolide inhibits IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in AGS cells. (A) The chemical structure of Triptolide. (B, C) AGS cells were pretreated with Triptolide (2, 5, 10, and 20 μM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and IL-8 mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR and qPCR. (D) AGS cells were transiently transfected with the pGL2-IL-8 promoter-luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with Triptolide (2, 5, 10, and 20 nM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. (E) AGS cells were pretreated with Triptolide (5, 10, and 20 nM) and incubated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 24 h, followed by ELISA to determine the amount of IL-8 secretion. (F) AGS cells were pretreated with Triptolide or IL-8 antibody and incubated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 24 h, and the cell viability was determined by MTT assay. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from triplicate measurements. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus treatment with IL-1β only.
To determine the effect of Triptolide on ROS production, the ROS production levels in AGS cells treated with IL-1β, in the presence or absence of Triptolide, were assessed using the H2DCFDA assay. As shown in Figures 2A, B, Triptolide suppressed the IL-1β-induced ROS production levels. We further observed that pretreatment of AGS cells with N-acetylcystein (NAC), a ROS scavenger, abrogated the IL-1β-induced IL-8 mRNA expression and the IL-1β-induced IL-8 promoter activity (Figures 2C, D). These results suggested that the suppression of IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression by Triptolide is mediated by inhibiting ROS production in human gastric cancer AGS cells.
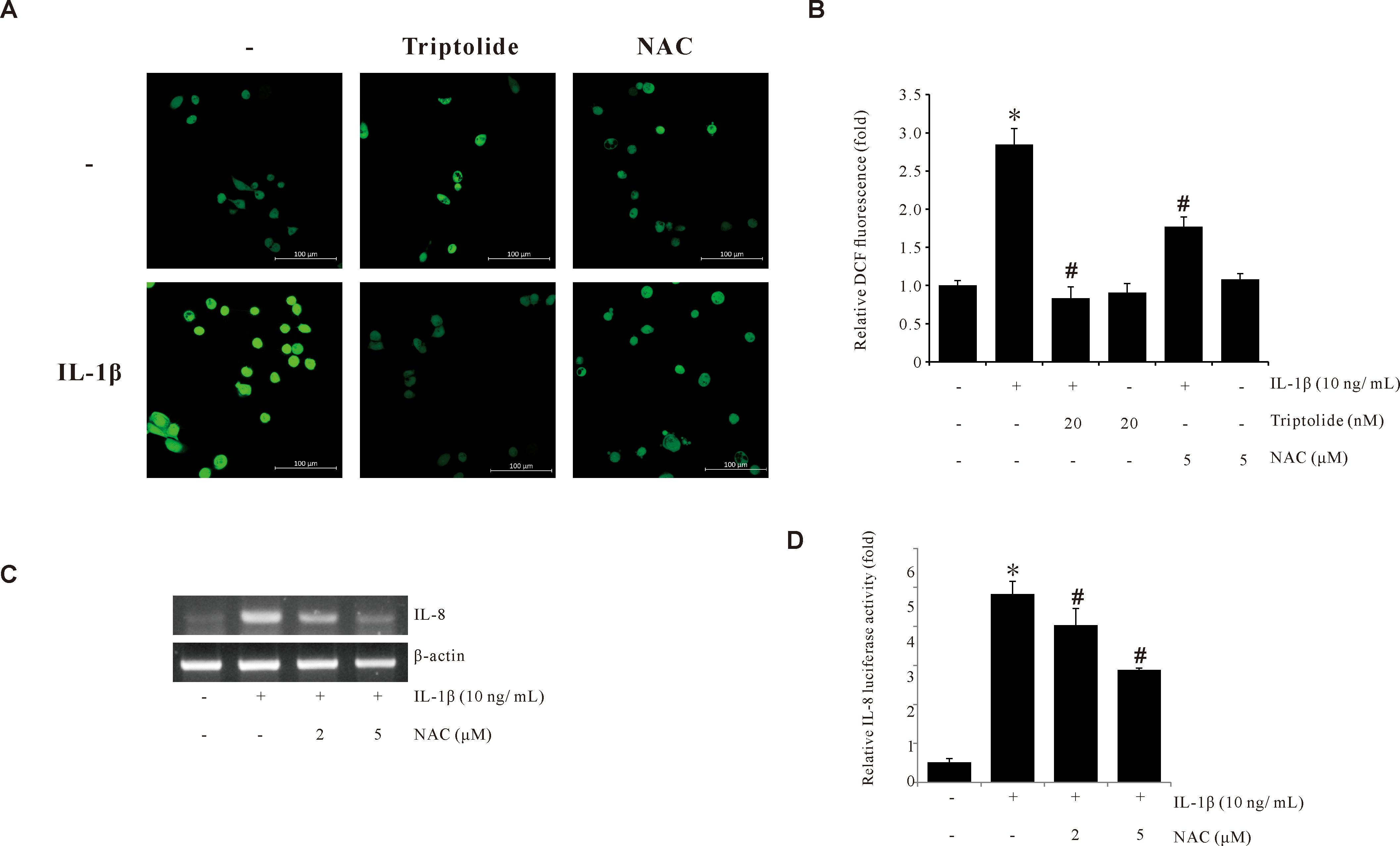
Figure 2. Triptolide inhibits IL-1β-induced ROS production in AGS cells. (A) Synchronized quiescent AGS cells pretreated with 20 nM Triptolide and 5 mM NAC for 1 h prior to IL-1β treatment for 30 min. Then, the cells were incubated in the dark for 10 min with 10 µM H2DCFDA. The H2DCFDA fluorescence was imaged using a confocal laser scanning fluorescence microscope. (B) ROS level quantifications detected by DCFDA fluorescence intensities. (C) AGS cells pretreated with 5 mM NAC for 1 h were incubated with IL-1β for 4 h. After incubation, IL-8 mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR. (D) AGS cells were transiently transfected with a pGL2-IL-8 promoter-luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with NAC (2 and 5 μM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from triplicate measurements. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus treatment with IL-1β only.
The molecules c-Fos and c-Jun are protein subunits of AP-1 and have been previously reported as playing an important role in gastric cancer development. Due to the crucial role that MAPK plays in AP-1 activation, we examined the effect of MAPK on IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression. We found that among the MAPK inhibitors we tested, only the ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059) was able to inhibit IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in AGS cells (Figure 3A). Further, Western blotting was used to confirm that Triptolide blocked the IL-1β-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in AGS cells (Figure 3B). These results indicate that the ERK1/2 pathway is crucial for IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression, which can be abrogated by Triptolide. Next, we examined if Triptolide can suppress AP-1 activity. As shown in Figures 3C, D, Triptolide inhibited transcriptional activity of AP-1 and suppressed c-Fos and c-Jun phosphorylation as well. Also, AP-1 inhibitor curcumin significantly reduced L-1β-induced IL-8 promoter activity (Figure 3E). Overall, these results demonstrate that Triptolide can inhibit IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression by suppressing AP-1 activation.
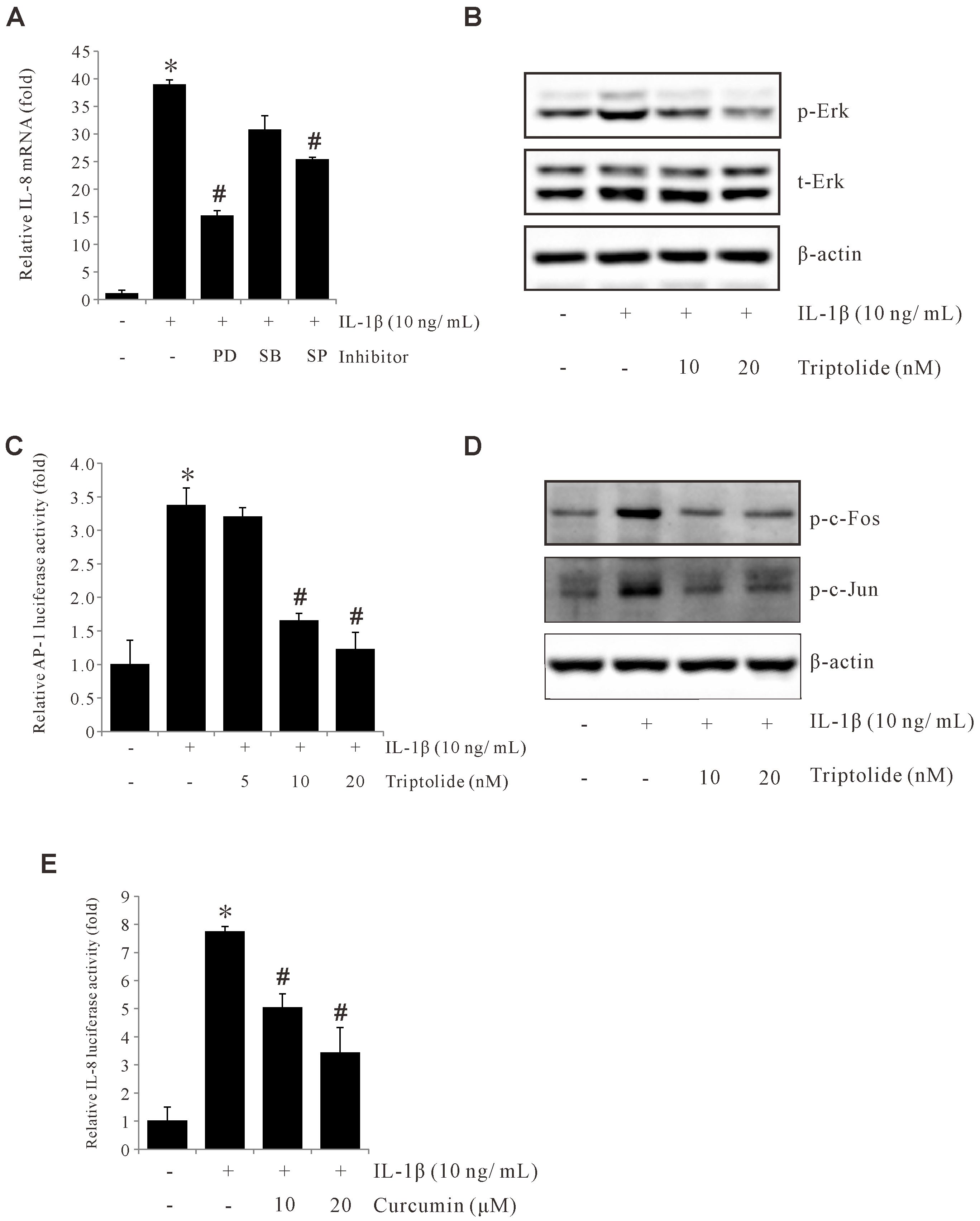
Figure 3. Triptolide inhibits IL-1β-induced IL-8 by suppressing ERK1/2, c-Fos, c-Jun, and AP-1 activation. (A) AGS cells were pretreated with 30 µM PD98059, 20 µM SB203580, and 30 μM SP600125 for 1 h and incubated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and IL-8 mRNA levels were determined by qPCR. (B) AGS cells were pretreated with Triptolide (10 and 20 nM) followed by 10 ng/mL IL-1β treatment for 30 min, and the extracted proteins were analyzed using Western blotting. (C) AGS cells were transiently transfected with AP-1 promoter-luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with Triptolide (5, 10, and 20 nM) for 1h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. (D) AGS cells were transiently transfected with a pGL2-IL-8 promoter-luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with curcumin (10 and 20 μM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. (E) AGS cells were transiently transfected with pGL2-IL-8 promoter luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with curcumin (10 and 20 μM) for 1h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. The above data represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from triplicate measurements. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus treatment with IL-1β only.
To find out the important DNA element for the IL-1β-induced activation of IL-8 promoter, IL-8 promoter activities were analyzed with deletion assays. Notably, a remarkable reduction was observed following the deletion of the upstream region at nucleotide positions –98 bp and –50 bp, after IL-1β treatment (Figure 4A), indicating that the –98 to –50 position is critical for the IL-1β-induced IL-8 promoter activity. This critical region for IL-1β-induced activity lies within a known NF-κB binding element on IL-8 promoter, spanning from -80 to -70. To examine if this reduced promoter activity is through NF-κB binding, BAY (AY11-7082, an NF-κB inhibitor) was used with the IL-8 promoter assay. As shown in Figure 4B, BAY significantly suppressed IL-1β-induced IL-8 promoter activity. Consistently, Triptolide inhibited IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation and p65 phosphorylation (Figures 4C, D). Collectively, these data suggest that IL-1β induces IL-8 expression by activating NF-κB and that Triptolide inhibited IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression by suppressing NF-κB activation.
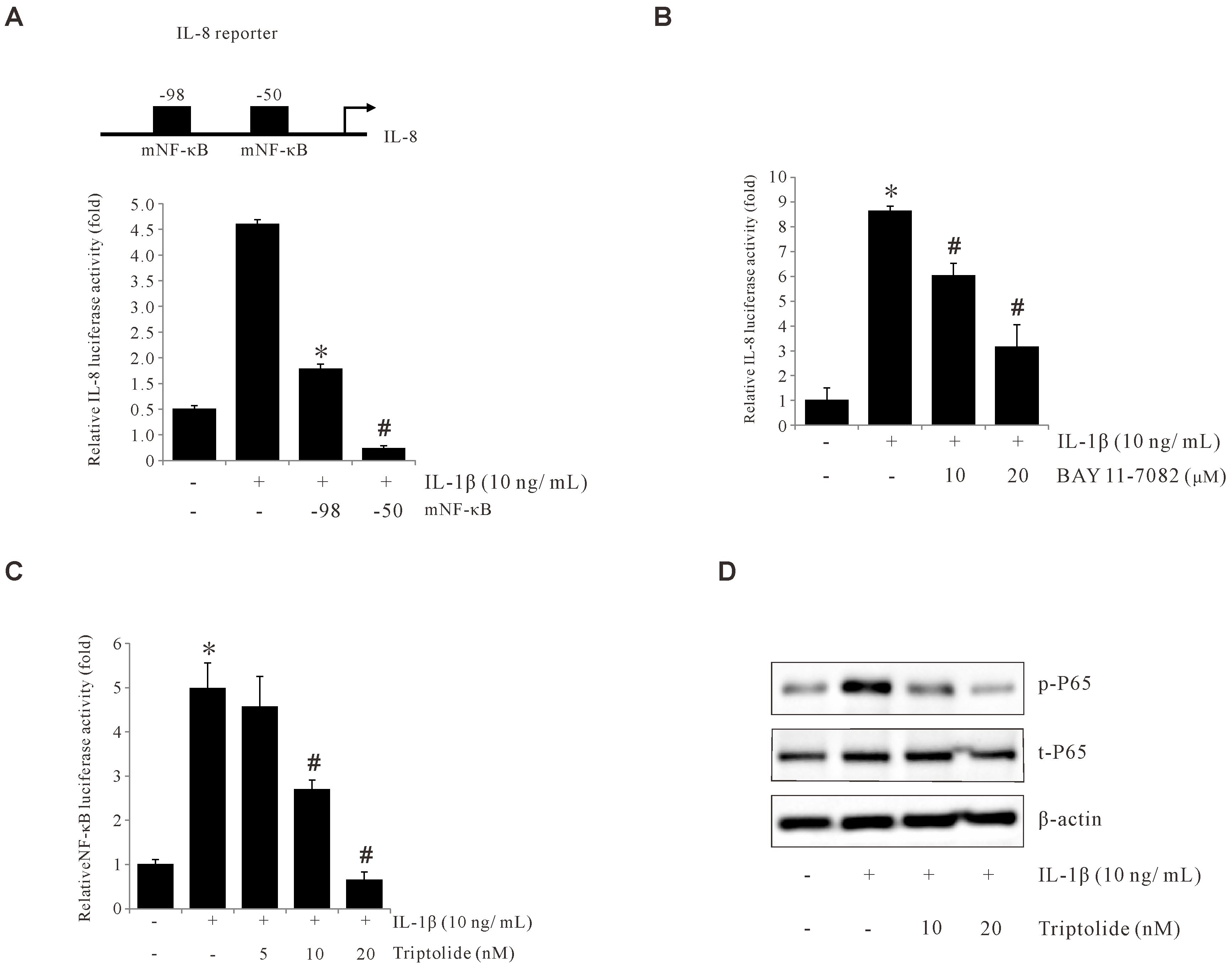
Figure 4. Triptolide inhibits IL-1β-induced IL-8 by suppressing p65 and NF-κB activation. (A) The IL-8 promoter was sequentially deleted in the 5′-flanking region, and the promoter-luciferase construct was transiently transfected into AGS cells. The transfected cells were incubated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three experimental trials. *p < 0.05 versus IL-1β only; # p < 0.05 versus –98. (B) AGS cells were transiently transfected with a pGL2-IL-8 promoter-luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with BAY11-7082 (10 and 20 μM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. (C) AGS cells were transiently transfected with an AP-1 promoter-luciferase construct. The transfected cells were pretreated with Triptolide (5, 10, and 20 nM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 4 h, and the luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer. (D) AGS cells were pretreated with Triptolide (10 and 20 nM) followed by 10 ng/mL IL-1β treatment for 30 min, and extracted proteins were analyzed using Western blotting. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from triplicate measurements. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus treatment with IL-1β only.
Angiogenesis is a vital process in the tumor microenvironment that plays a pivotal role in cancer progression. In the current study, we used the endothelial EA.hy926 cell line to determine the effect of Triptolide on IL-1β-induced angiogenesis in vitro. As shown in Figures 5A, B, the angiogenic activity assessed by tube formation was significantly promoted after treatment with IL-8, or IL-1β-treated conditioned medium (CM) compared to control-CM. Furthermore, this IL-1β-induced angiogenic activity of EA.hy926 cells is decreased after either IL-8 antibody or Triptolide treatment. And we utilized EA.hy926 endothelial cells to investigate whether modulation of IL-8 expression in AGS cells could influence endothelial cell proliferation. Our result revealed that conditioned medium (CM) from IL-1β-treated AGS cells significantly enhanced EA.hy926 cell proliferation, an effect that was effectively suppressed by triptolide (Figure 5C). These findings suggest that Triptolide could inhibit IL-1β-induced endothelial angiogenesis by suppressing IL-8 expression in gastric cancer AGS cells, thus having a potential impact on the tumor microenvironment.
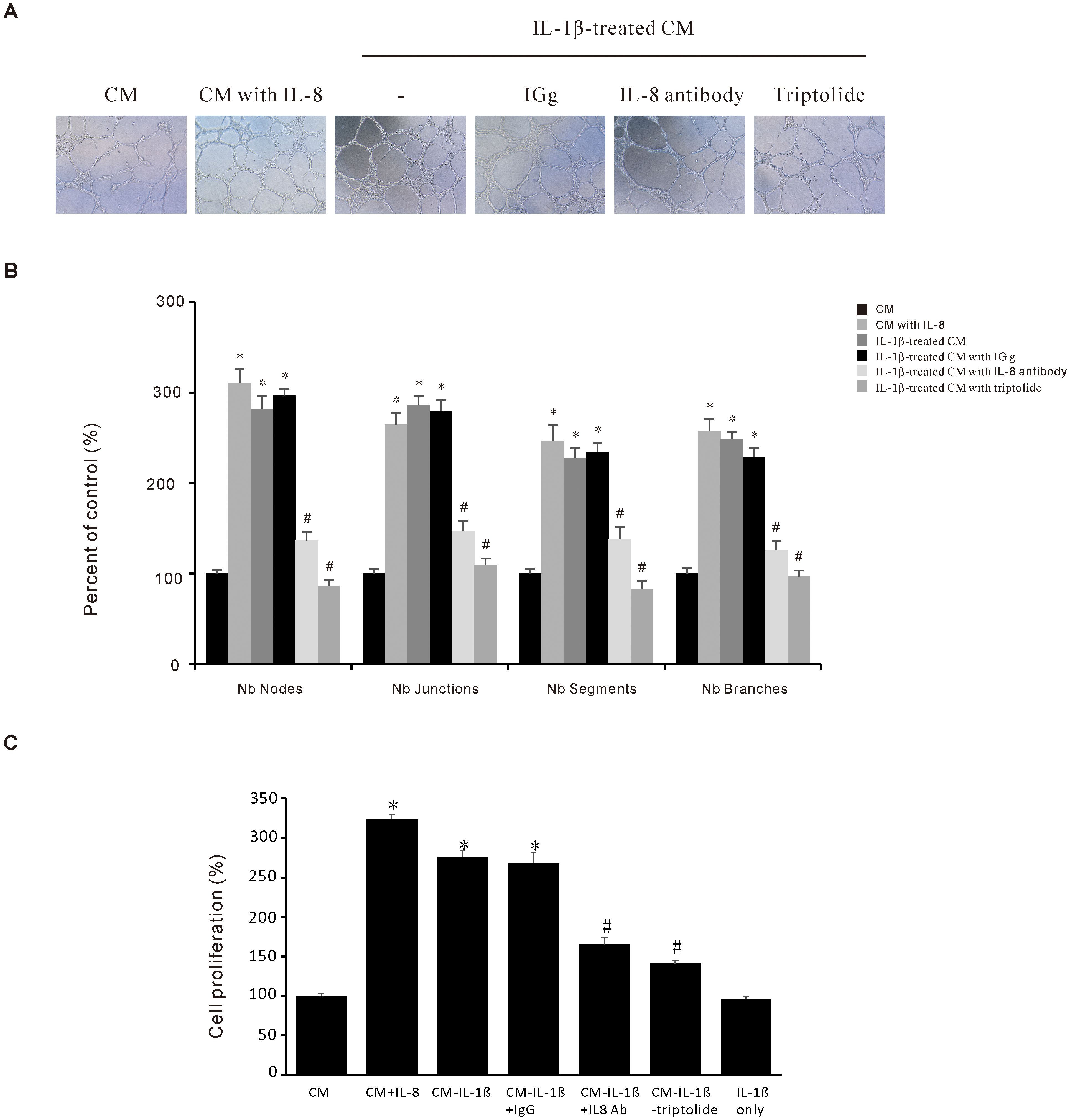
Figure 5. Triptolide suppresses the IL-1β-induced angiogenesis activity in gastric cancer AGS cells. (A) Representative images (10 ×) of endothelial EA. hy926 cells tube formations. The EA. hy926 cells were grown in a Matrigel-coated plate for 24 h and incubated with CM obtained from Triptolide-pretreated and IL-1β-stimulated AGS cells. After 6 h, the cells were observed and counted using a Nokia microscope (B) Quantitative data of the EA. hy926 tube formation. (C) EA.hy926 cells were incubated with 1000 pg/mL IL-8, 10 ng/mL IL-1β, or conditioned medium (CM) for 24 h, in the presence or absence of 1 mg/mL anti-IL-8 antibody, then cell proliferation was assessed. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from triplicate measurements. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus treatment with IL-8 only.
Herbal compounds, particularly those based on traditional medicines, have demonstrated their potential to serve as effective treatments. The pharmacologically active ingredients in herbal medicines have been extensively studied, leading to their widespread use in contemporary medical therapies. Research has shown that these herbal compounds can play crucial role in improving health outcomes and providing relief from a variety of ailments (31). Triptolide (diterpene triepoxide) (Figure 1A) is derived from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, a traditional Chinese perennial herb whose extracts have been used for centuries in antioxidative (32), anti-inflammatory (33), anticancer (34, 35), and immunosuppressive therapies (36, 37). Triptolide and its analogs exhibit potent bioactivities against various cancers, including breast (38, 39), lung (40–42), gastric (43, 44), and colon cancers (45–47).
The chemokine IL-8 is widely acknowledged to play an essential role in tumor sustenance, invasion, and angiogenesis, as well as immune suppression via various signaling pathways. Therefore, targeting IL-8 is the ideal therapeutic approach to prevent cancer progression. In this study, we found that IL-1β increased IL-8 expression, while Triptolide reduced this IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression in AGS gastric cancer cells (Figure 1). We further investigated the molecular mechanism of anticancer effect of Triptolide on gastric cancer.
The main etiological factor for gastric cancer is chronic Helicobactor pylori (HP) infection. IL-1β, a pluripotent proinflammatory cytokine, plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of HP-induced mucosal inflammation and gastric carcinogenesis (48, 49). Our findings demonstrated that IL-1β increased IL-8 expression by upregulating reactive oxygen species (ROS), ERK, AP-1, and NF-κB signaling pathways in gastric cancer cells, and that all these signaling pathways can be inhibited by Triptolide treatment.
A variety of intracellular signals have been proposed to mitigate the impacts of IL-1β, including the activation of MAPK, the secretion of arachidonic acid, the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin, and the formation of ROS (49, 50). The IL-1β signal is initiated by the binding of IL-1β to their receptor (IL-1R1) and coreceptors (IL-1RAP), resulting in the formation of a trimeric complex and activation of TRAF6 signaling. TRAF6 signaling can occur via two main pathways: IKK–IB–NF-κB and/or MKK–MAPK/JNK/ERK. Phosphorylated TAK1 activates the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta (IKKβ) and activated IKK phosphorylates the nuclear factor kappa-B inhibitor (IkB), which is degraded, allowing NF-κB to be released and migrate to the nucleus. TAK1 also activates MAPK p38, JNK, and ERK (51, 52). The IL-8 gene promoter contains the binding sites for AP-1, NF-κB, and CERB (49, 53). Our results also confirmed that IL-1β induced NF-κB activation to promote IL-8 promoter activity (Figures 4A, B), while Triptolide inhibited NF-κB activation. Alternatively, several studies have suggested that ROS can activate the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases (54) and NF-κB pathways (55). Our findings also demonstrated that IL-1β induced ROS production in AGS cells, whereas Triptolide treatment suppressed IL-1β-induced ROS generation (Figure 2).
Haifeng Zhang et al. mentioned that Triptolide inhibited the IL-1β expression in an ulcerative colitis mouse model (56). Their findings suggest that Triptolide might inhibit IL-1β expression directly, which in turn inhibits IL-8 expression in AGS gastric cancer cells. Our previous study demonstrated that Triptolide inhibits uPAR-induced ERK, NF-κB, AP-1, and ROS production in AGS cell lines (34). Furthermore, another study supported these findings, whereby Triptolide pretreatment inhibited ROS production by suppressing the Nrf2 and NF-κB transactivation in a caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis animal model and an in vitro cell model (57). All these reports support our findings that Triptolide reduces IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression by inhibiting ROS production, and activation of ERK1/2, AP-1 and NF-κB.
Triptolide inhibits the NF-κB signaling in various ways. NF-κB is a heterogeneous dimer, consisting of p50 and p65, which promotes cell proliferation, prevents apoptosis, and is involved in tumor development (58). Triptolide inhibits NF-κB via caspase activation by blocking the transactivation impact of the NF-κB p65 subunit (59). Triptolide also influences NF-κB indirectly via the AKT/GSK3/mTOR pathway and downstream of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (60). TPL also inhibits complex I in the mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC), which inhibits the production of ROS as well as the activation of NF-κB (61). Tao et al. reported that Triptolide decreased the IL-1β-induced NF-κB DNA binding capacity and cytosolic amount of p-IκBα in subepithelial myofibroblasts (62). Furthermore, Triptolide inhibited matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and invasion by inhibiting NF-κB and AP-1 expression in breast cancer cells (63). Similarly, Weiwei Yuan et al. reported that pretreatment with Triptolide increased apoptosis in TNF-α-induced gastric cancer cells by disrupting the H19/miR-204-5p/NF-κB/FLIP axis (64).
One of the most promising novel cancer treatment strategies is targeting angiogenic pathway. In vivo and in vitro studies on GC are ongoing, and the results of these studies are highly anticipated. Angiogenesis has been identified as a cancer hallmark required for tumor survival and tumor spread to a new location (65). IL-8 produced by tumor-infiltrating macrophages is reported as a proangiogenic factor that promotes angiogenesis in various cancers (21, 66, 67). However, whether IL-8 promotes angiogenesis in gastric cancer is unknown. Our results showed that IL-1β-induced IL-8 production induced angiogenesis and Triptolide treatment inhibited this angiogenesis in the EA.hy926 cell line. Liu et al. reported that Triptolide inhibits angiogenesis via the ERK1/2-HIF1-α-VEGFA axis (68). Similarly, Xiangying Kong et al. reported that Triptolide significantly decreased the expression of angiogenic activators, including IL-17, TNF-α, VEGF, VEGFR, Tie2, Ang-1, and Ang-2. Moreover, Triptolide suppressed the IL-1β-induced phosphorylation of ERK, p38, and JNK at the protein level in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) DA rat model (69). To summarize, Triptolide treatment inhibited the IL-1β-induced IL-8 expression by suppressing the ERK/AP-1/NF-κB signaling, which decreased ROS generation and tumor proliferation and angiogenesis of human gastric cancer AGS cells (Figure 6).
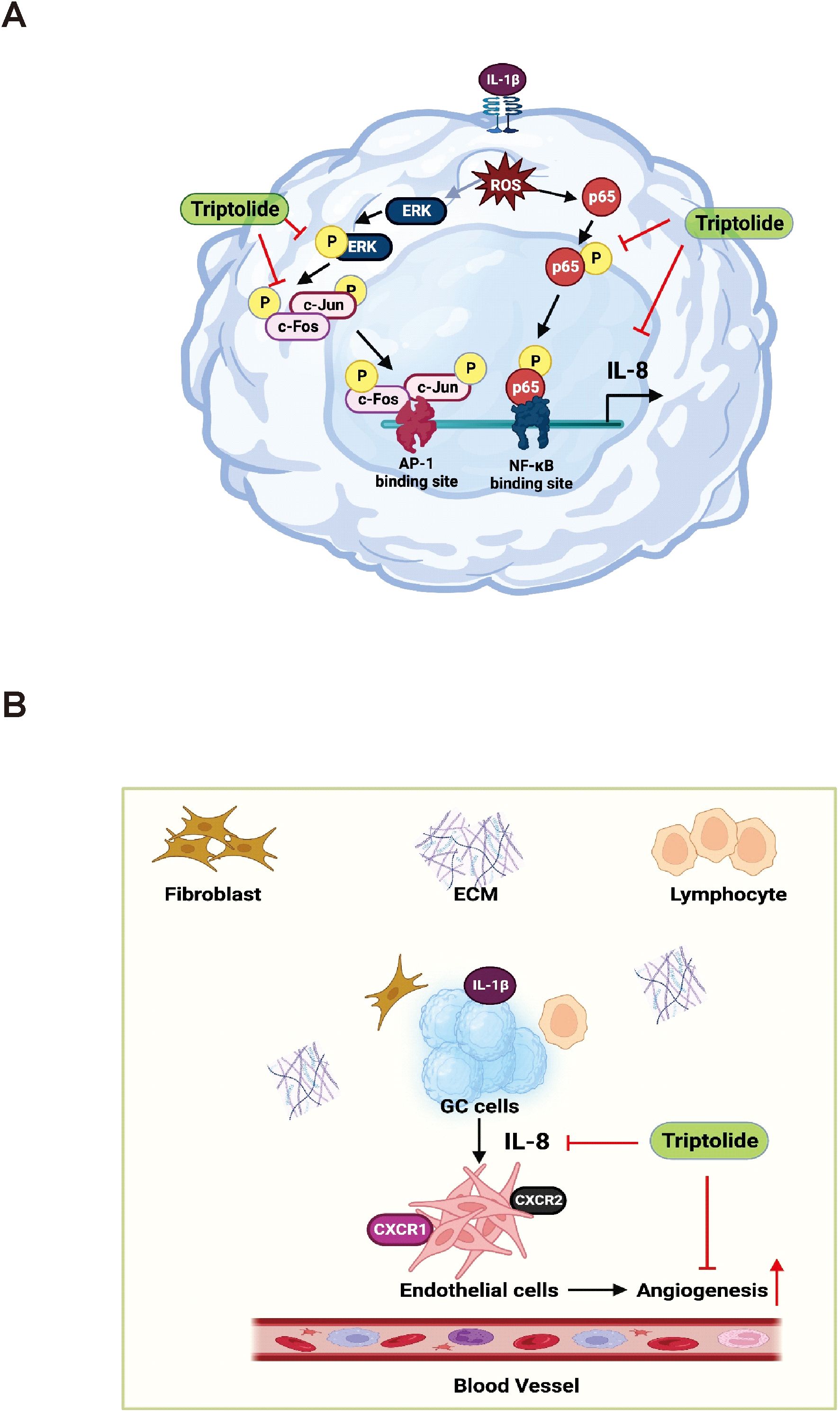
Figure 6. This schematic diagram illustrates the mechanisms through which Triptolide inhibits the expression of IL-8 in AGS cells, as well as the effect of AGS-derived angiogenesis on the tumor microenvironment. (A) Triptolide suppresses IL-8 expression in response to the activation of IL-1β by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of AP-1 and NF-KB, which mediate ROS-driven ERK1/2 signaling. (B) In the tumor microenvironment, AGS-derived IL-8 affects the angiogenic activity of endothelial cells.
Based on the data presented throughout this study, we can conclude that Triptolide has a potent chemopreventive effect and could be used as a novel therapeutic strategic approach for gastric cancer.
As a result of the significant health burden associated with gastric cancer, it is essential to identify effective biomarkers for predicting prognosis and determining the optimal therapeutic strategy. Triptolide, a naturally occurring compound, is critical in preventing gastric cancer development. It achieves this by inhibiting oxidative stress, downregulating the ERK, AP-1, and NF-KB signaling pathways, and inhibiting angiogenesis activity. Therefore, Triptolide’s anticancer properties and its potential as a chemopreventive agent warrant additional clinical research.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
SL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. DS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. AA: Software, Writing – review & editing. MA: Software, Writing – review & editing. BL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Basic Science Research Program grant through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (No. 2021R1C1C1013710), the Shanxi Medical University Provincial Doctoral Fund Project of Shanxi Province (No. SD2346), and the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (No. 202403021212283).
The authors acknowledge Biorender.com for creating the figures.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1498213/full#supplementary-material
1. Cuzzuol BR, Vieira ES, Araújo GRL, Apolonio JS, de Carvalho LS, da Silva Junior RT, et al. Gastric cancer: A brief review, from risk factors to treatment. Arch Gastroenterol Res. (2020) 1:34–9. doi: 10.33696/Gastroenterology.1.008
2. Chen Z-d, Zhang P-F, Xi H-Q, Wei B, Chen L, Tang Y. Recent advances in the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and prognosis of advanced gastric cancer: A literature review. Front Med. (2021) 8:1962. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.744839
3. Joshi SS, Badgwell BD. Current treatment and recent progress in gastric cancer. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:264–79. doi: 10.3322/caac.21657
4. Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 18:534–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045
5. Rawla P, Barsouk A. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: global trends, risk factors and prevention. Gastroenterol Review/Przegląd Gastroenterologiczny. (2019) 14:26–38. doi: 10.5114/pg.2018.80001
6. Zhang Z, Liu Z, Chen Z. Comparison of treatment efficacy and survival outcomes between asian and western patients with unresectable gastric or gastro-esophageal adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2022) 852. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.831207
7. Poon RT-P, Fan S-T, Wong J. Clinical significance of angiogenesis in gastrointestinal cancers: A target for novel prognostic and therapeutic approaches. Ann Surg. (2003) 238:9. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000075047.47175.35
8. Apte RN, Dotan S, Elkabets M, White MR, Reich E, Carmi Y, et al. The involvement of il-1 in tumorigenesis, tumor invasiveness, metastasis and tumor-host interactions. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2006) 25:387–408. doi: 10.1007/s10555-006-9004-4
9. Kim G-Y, Lee J-W, Ryu H-C, Wei J-D, Seong C-M, Kim J-H. Proinflammatory cytokine il-1β Stimulates il-8 synthesis in mast cells via a leukotriene B4 receptor 2-linked pathway, contributing to angiogenesis. J Immunol. (2010) 184:3946–54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901735
10. Suswam EA, Nabors LB, Huang Y, Yang X, King PH. Il-1β Induces stabilization of il-8 mrna in Malignant breast cancer cells via the 3′ Untranslated region: involvement of divergent rna-binding factors hur, ksrp and tiar. Int J Cancer. (2005) 113:911–9. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0215
11. Yin S, Lan C, Pei H, Zhu Z. Expression of interleukin 1β in gastric cancer tissue and its effects on gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. (2015) 9:31–5. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S94277
12. Bakouny Z, Choueiri TK. Il-8 and cancer prognosis on immunotherapy. Nat Med. (2020) 26:650–1. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0873-9
13. Brat DJ, Bellail AC, Van Meir EG. The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro-oncology. (2005) 7:122–33. doi: 10.1215/S1152851704001061
14. Gonzalez-Aparicio M, Alfaro C. Retracted article: significance of the il-8 pathway for immunotherapy. Hum Vaccines immunotherapeutics. (2020) 16:2312–7. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1696075
15. Stillie R, Farooq SM, Gordon JR, Stadnyk AW. The functional significance behind expressing two il–8 receptor types on pmn. J leukocyte Biol. (2009) 86:529–43. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0208125
16. Xiong X, Liao X, Qiu S, Xu H, Zhang S, Wang S, et al. Cxcl8 in tumor biology and its implications for clinical translation. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.723846
17. Callaway CS, Delitto AE, D’Lugos AC, Patel R, Nosacka RL, Delitto D, et al. Il-8 released from human pancreatic cancer and tumor-associated stromal cells signals through a cxcr2-erk1/2 axis to induce muscle atrophy. Cancers. (2019) 11:1863. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121863
18. Wang Z, Hou Y, Yao Z, Zhan Y, Chen W, Liu Y. Expressivity of interleukin-8 and gastric cancer prognosis susceptibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dose-Response. (2021) 19:15593258211037127. doi: 10.1177/15593258211037127
19. Xiong H, Ye J, Xie K, Hu W, Xu N, Yang H. Exosomal il-8 derived from lung cancer and colon cancer cells induced adipocyte atrophy via nf-Kb signaling pathway. Lipids Health Dis. (2022) 21:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01755-2
20. Zhang J, Shao N, Yang X, Xie C, Shi Y, Lin Y. Interleukin-8 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via downregulation of mir-200 family in breast cancer cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2020) 19:1533033820979672. doi: 10.1177/1533033820979672
21. Ning Y, Manegold PC, Hong YK, Zhang W, Pohl A, Lurje G, et al. Interleukin-8 is associated with proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and chemosensitivity in vitro and in vivo in colon cancer cell line models. Int J Cancer. (2011) 128:2038–49. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v128.9
22. Shi J, Wei PK. Interleukin-8: A potent promoter of angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. (2016) 11:1043–50. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.4035
23. Liu Q, Wang W, Li F, Yu D, Xu C, Hu H. Triptolide inhibits breast cancer cell metastasis through inducing the expression of mir-146a, a negative regulator of rho gtpase. Oncol Res. (2019) 27:1043. doi: 10.3727/096504019X15560124931900
24. Noel P, Hussein S, Ng S, Antal CE, Lin W, Rodela E, et al. Triptolide targets super-enhancer networks in pancreatic cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogenesis. (2020) 9:100. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00285-9
25. Oliveira AR, Beyer G, Chugh R, Skube SJ, Majumder K, Banerjee S, et al. Triptolide abrogates growth of colon cancer and induces cell cycle arrest by inhibiting transcriptional activation of E2f. Lab Invest. (2015) 95:648–59. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.46
26. Yang Y, Zhang L-J, Bai X-G, Xu H-J, Jin Z-L, Ding M. Synergistic antitumour effects of triptolide plus gemcitabine in bladder cancer. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2018) 106:1307–16. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.083
27. Li S, Nguyen TT, Ung TT, Sah DK, Park SY, Lakshmanan VK, et al. Piperine attenuates lithocholic acid-stimulated interleukin-8 by suppressing src/egfr and reactive oxygen species in human colorectal cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:530(1–19). doi: 10.3390/antiox11030530
28. Li S, Ung TT, Nguyen TT, Sah DK, Park SY, Jung YD. Cholic acid stimulates mmp-9 in human colon cancer cells via activation of mapk, ap-1, and nf-kappab activity. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3420(1–16). doi: 10.3390/ijms21103420
29. Lian S, Li S, Zhu J, Xia Y, Do Jung Y. Nicotine stimulates il-8 expression via ros/nf-kappab and ros/mapk/ap-1 axis in human gastric cancer cells. Toxicology. (2022) 466:153062. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.153062
30. Nguyen TT, Ung TT, Li S, Lian S, Xia Y, Park SY, et al. Metformin inhibits lithocholic acid-induced interleukin 8 upregulation in colorectal cancer cells by suppressing ros production and nf-kb activity. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:2003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38778-2
31. Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J Natural products. (2020) 83:770–803. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
32. Yu G-M, Zhou L-F, Zeng B-X, Huang J-J, She X-j. The antioxidant effect of triptolide contributes to the therapy in a collagen-induced arthritis rat model. Redox Rep. (2021) 26:197–202. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2021.2004047
33. Tang B, Zhu J, Zhang B, Wu F, Wang Y, Weng Q, et al. Therapeutic potential of triptolide as an anti-inflammatory agent in dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:592084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.592084
34. Chang HJ, Kim MH, Baek MK, Park JS, Chung IJ, Shin BA, et al. Triptolide inhibits tumor promoter-induced upar expression via blocking nf-Kb signaling in human gastric ags cells. Anticancer Res. (2007) 27:3411–7.
35. Meng C, Zhu H, Song H, Wang Z, Huang G, Li D, et al. Targets and molecular mechanisms of triptolide in cancer therapy. Chin J Cancer Res. (2014) 26:622. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2014.09.01
36. Qiu D, Kao PN. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of triptolide, the principal active diterpenoid from the chinese medicinal herb tripterygium wilfordii hook. F. Drugs R D. (2003) 4:1–18. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304010-00001
37. Tong L, Zhao Q, Datan E, Lin G-Q, Minn I, Pomper MG, et al. Triptolide: reflections on two decades of research and prospects for the future. Natural product Rep. (2021) 38:843–60. doi: 10.1039/D0NP00054J
38. He J, Peng T, Peng Y, Ai L, Deng Z, Wang X-Q, et al. Molecularly engineering triptolide with aptamers for high specificity and cytotoxicity for triple-negative breast cancer. J Am Chem Soc. (2020) 142:2699–703. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b10510
39. Xiong J, Su T, Qu Z, Yang Q, Wang Y, Li J, et al. Triptolide has anticancer and chemosensitization effects by down-regulating akt activation through the mdm2/rest pathway in human breast cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:23933. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i17
40. Deng Q-d, Lei X-p, Zhong Y-h, Chen M-s, Ke Y-y, Li Z, et al. Triptolide suppresses the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting B-catenin-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Acta Pharmacologica Sin. (2021) 42:1486–97. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00657-w
41. Huang Y, Chen Z, Wang Y, Ba X, Huang Y, Shen P, et al. Triptolide exerts an anti-tumor effect on non−Small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting activation of the il−6/stat3 axis. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 44:291–300. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4197
42. Philips BJ, Kumar A, Burki S, Ryan JP, Noda K, D’Cunha J. Triptolide-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer via a novel mir204-5p/caveolin-1/akt-mediated pathway. Oncotarget. (2020) 11:2793. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v11i28
43. Wang B-Y, Cao J, Chen J-W, Liu Q-Y. Triptolide induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via inhibiting the overexpression of mdm2. Med Oncol. (2014) 31:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0270-7
44. Wang S, Jiang H, Wang J, Wu H, Wu T, Ni M, et al. Superior in vitro anticancer effect of biomimetic paclitaxel and triptolide co-delivery system in gastric cancer. J Biomed Res. (2021) 35:327. doi: 10.7555/JBR.35.20210102
45. Jiang X, Cao G, Gao G, Wang W, Zhao J, Gao C. Triptolide decreases tumor-associated macrophages infiltration and M2 polarization to remodel colon cancer immune microenvironment via inhibiting tumor-derived cxcl12. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:193–204. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v236.1
46. Liang X, Xie R, Su J, Ye B, Wei S, Liang Z, et al. Inhibition of rna polymerase iii transcription by triptolide attenuates colorectal tumorigenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1232-x
47. Song X, He H, Zhang Y, Fan J, Wang L. Mechanisms of action of triptolide against colorectal cancer: insights from proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses. Aging (Albany NY). (2022) 14:3084. doi: 10.18632/aging.203992
48. Huang FY, Chan AOO, Rashid A, Wong DKH, Seto WK, Cho CH, et al. Interleukin−1β Increases the risk of gastric cancer through induction of aberrant DNA methylation in a mouse model. Oncol Lett. (2016) 11:2919–24. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4296
49. Hwang YS, Jeong M, Park JS, Kim MH, Lee DB, Shin BA, et al. Interleukin-1β Stimulates il-8 expression through map kinase and ros signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncogene. (2004) 23:6603–11. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207867
50. Sah DK, Khoi PN, Li S, Arjunan A, Jeong J-U, Jung YD. (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents il-1β-induced upar expression and invasiveness via the suppression of nf-Kb and ap-1 in human bladder cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:14008. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214008
51. Acuner Ozbabacan SE, Gursoy A, Nussinov R, Keskin O. The structural pathway of interleukin 1 (Il-1) initiated signaling reveals mechanisms of oncogenic mutations and snps in inflammation and cancer. PloS Comput Biol. (2014) 10:e1003470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003470
52. Weber A, Wasiliew P, Kracht M. Interleukin-1 (Il-1) pathway. Sci Signaling. (2010) 3:cm1–cm. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3105cm1
53. Elliott C, Allport V, Loudon J, Wu G, Bennett P. Nuclear factor-kappa B is essential for up-regulation of interleukin-8 expression in human amnion and cervical epithelial cells. MHR: Basic Sci Reprod Med. (2001) 7:787–90. doi: 10.1093/molehr/7.8.787
54. Lo YY, Wong JM, Cruz TF. Reactive oxygen species mediate cytokine activation of C-jun nh2-terminal kinases. J Biol Chem. (1996) 271:15703–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.26.15703
55. van de Veerdonk FL, Smeekens SP, Joosten LA, Kullberg BJ, Dinarello CA, van der Meer JW, et al. Reactive oxygen species–independent activation of the il-1β Inflammasome in cells from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2010) 107:3030–3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914795107
56. Zhang H, Gong C, Qu L, Ding X, Cao W, Chen H, et al. Therapeutic effects of triptolide via the inhibition of il-1β Expression in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. Exp Ther Med. (2016) 12:1279–86. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3490
57. Yang J, Tang X, Ke X, Dai Y, Shi J. Triptolide suppresses nf-Kb-mediated inflammatory responses and activates expression of nrf2-mediated antioxidant genes to alleviate caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1252. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031252
58. Xia L, Tan S, Zhou Y, Lin J, Wang H, Oyang L, et al. Role of the nfκb-signaling pathway in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. (2018) 11:2063–73. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S161109
59. Park S-W, Kim YI. Triptolide induces apoptosis of pma-treated thp-1 cells through activation of caspases, inhibition of nf-Kb and activation of mapks. Int J Oncol. (2013) 43:1169–75. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2033
60. Tang Y, Liu Q, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Wen C, et al. Tripterygium ingredients for pathogenicity cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:583171. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.583171
61. Zhong YY, Chen HP, Tan BZ, Yu HH, Huang XS. Triptolide avoids cisplatin resistance and induces apoptosis via the reactive oxygen species/nuclear factor−Kb pathway in skov3pt platinum−Resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Lett. (2013) 6:1084–92. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1524
62. Tao Qs, Ren Ja, Li Js. Triptolide suppresses il-1β-induced chemokine and stromelysin-1 gene expression in human colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts 1. Acta pharmacologica Sin. (2007) 28:81–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00482.x
63. Hong O-Y, Jang H-Y, Park K-H, Jeong Y-J, Kim J-S, Chae HS. Triptolide inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and invasion of breast cancer cells through the inhibition of nf-Kb and ap-1 signaling pathways. Oncol Lett. (2021) 22:1–9. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12823
64. Yuan W, Huang J, Hou S, Li H, Bie L, Chen B, et al. The antigastric cancer effect of triptolide is associated with H19/nf-Kb/flip axis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:918588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918588
65. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
66. Al-Khalaf HH, Al-Harbi B, Al-Sayed A, Arafah M, Tulbah A, Jarman A, et al. Interleukin-8 activates breast cancer-associated adipocytes and promotes their angiogenesis-and tumorigenesis-promoting effects. Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 39:e00332–18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00332-18
67. Yang F, Liu XQ, He JZ, Xian SP, Yang PF, Mai ZY, et al. Occludin facilitates tumour angiogenesis in bladder cancer by regulating il8/stat3 through stat4. J Cell Mol Med. (2022) 26:2363–76. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17257
68. Liu H, Tang L, Li X, Li H. Triptolide inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor−Mediated angiogenesis in human breast cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 16:830–6. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6200
Keywords: angiogenesis, ERK1/2, gastric cancer, Interleukin-1ß, reactive oxygen species, triptolide, Interleukin-8
Citation: Li S, Sah DK, Arjunan A, Ameer MY, Lee B and Jung Y-D (2025) Triptolide suppresses IL-1β-induced expression of interleukin-8 by inhibiting ROS-Mediated ERK, AP-1, and NF-κB molecules in human gastric cancer AGS cells. Front. Oncol. 14:1498213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1498213
Received: 18 September 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Etsuro Ito, Waseda University, JapanReviewed by:
Reza Valadan, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, IranCopyright © 2025 Li, Sah, Arjunan, Ameer, Lee and Jung. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bora Lee, YmxlZTAzQGpudS5hYy5rcg==; Young-Do Jung, eWRqdW5nQGNob25uYW0uYWMua3I=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.