
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol., 04 December 2024
Sec. Thoracic Oncology
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1485849
This article is part of the Research TopicAdvancements in Immune Heterogeneity in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer: New Targets, Mechanisms, and StrategiesView all 11 articles
Background: There is a strong association between inflammation and the formation, progression, and metastasis of malignant tumors, according to earlier studies. Some composite inflammation-nutritional indicators, such as the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and the prognostic nutritional index (PNI), have a certain predictive effect on the prognosis of patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC). However, the relationship between these indicators and the efficacy of immunotherapy in SCLC patients is still not well understood. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to explore how the pre-treatment SII-PNI score can predict the tumor response and prognosis of extensive-stage SCLC patients treated with PD-L1 inhibitors and first-line chemotherapy.
Methods: This research conducted a retrospective review of 70 ES- SCLC patients from December 2019 to January 2023. According to the SII-PNI score, all patients were categorized into three groups. Overall survival (OS) was assessed by implementing the Kaplan Meier and Cox regression models. In addition, we devised a nomogram and scrutinized its accuracy in prediction through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and visualized it by calibration plots. Subsequently, a risk classification system was established.
Results: Patients with higher SII-PNI scores exhibited notably poorer survival outcomes compared to their counterpart with low SII-PNI score (p=0.008), as well as poorer short-term curative effects (p=0.004). The results of the multivariate analysis revealed that the SII-PNI score (p=0.036) had an independent association with a less favorable OS. The nomogram has been demonstrated to be a reliable prognostic tool for ES-SCLC patients. A notable difference was identified between the two different levels of risk.
Conclusion: The baseline SII-PNI score can serve as a reliable prognostic indicator for ES-SCLC patients receiving immunotherapy. Higher SII-PNI scores imply a worse prognosis.
Lung cancer stands as the most common reason for mortality from malignant tumors worldwide. It is typically classified into two main categories. SCLC constitutes approximately 15% of all lung cancers (1, 2). Compared with NSCLC, SCLC has the characteristics of higher malignancy, shorter tumor cell doubling time, and an earlier susceptibility to distant metastasis (3). A great deal of SCLC patients are already in the extensive stage when diagnosed, with extremely poor clinical prognosis (4). Over the past three decades, platinum combined with etoposide chemotherapy remains the typical treatment for SCLC (5). In the last several years, the use of PD-L1 inhibitors to treat SCLC patients has made tremendous progress. In the phase III clinical trial known as IMpower133, the combination of Atezolizumab with first-line chemotherapy resulted in an increased OS for patients compared to chemotherapy alone. In another clinical study CASPIAN, found that the median OS of patients receiving the combination of Durvalumab and chemotherapy was 2.7 months longer than the control group (6, 7). Durvalumab and Atezolizumab were approved as one of the first-line treatments for SCLC in February and March 2020, respectively.
However, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) can also lead to a range of immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including rash, pruritus, pneumonitis, diarrhea, and endocrine system problems (8). Only a portion of SCLC patients can benefit from immunotherapy, so it is crucial to search for biomarkers that can predict the prognosis and accurately identify subgroups of patients suitable for immunotherapy. At present, numerous studies have explored biomarkers for the efficacy of immunotherapy, proposing the predictive value of PD-L1 expression level, tumor mutation burden (TMB), tumor microenvironment, etc. (9). However, these biomarkers face difficulties in clinical application due to limitations in tissue sampling, inconsistent detection standards, and tumor expression heterogeneity. Their predictive value for the efficacy of SCLC immunotherapy is still unclear. Numerous investigations have revealed that the occurrence, development, invasion, metastasis, and anti-tumor response of tumors are strongly influenced by inflammation, immunity, and overall nutritional status (10). Research have found that some composite inflammatory indicators, such as the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and the prognostic nutritional index (PNI), can predict the prognosis of many malignant tumors, especially lung cancer (11–15). These hematological inflammatory biomarkers are inexpensive and readily accessible, but their predictive effectiveness in the efficacy of immunotherapy for ES-SCLC remains largely uncertain.
The SII-PNI is highly useful in predicting the curative effect and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (16) and gastric cancer (17) patients in earlier studies. The predictive ability of SII-PNI score for the efficacy and prognosis of ES-SCLC patients undergoing immunotherapy is the main focus of this study, providing guidance for screening the most suitable patients for immunotherapy.
We selected all 70 eligible ES-SCLC patients who received PD-L1 inhibitors combined with first-line chemotherapy when newly diagnosed from December 2019 to June 2022 at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. The next selection standards were adopted: (1) small cell lung cancer diagnosed through histological or cytological examination; (2) ES-SCLC evaluated according to the VALSG staging criteria; (3) normal organ functionality to withstand immunotherapy and chemotherapy; (4) ECOG activity status score ≤ 2; (5) no other coexisting malignant tumors; (6) expected survival > 3 months; (7) there was at least one measurable lesion that can be assessed using response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST). The exclusive standards are as follows: (1) previously received systemic anti-tumor therapy; (2) unable to make a clear pathological diagnosis or unclear primary lesion; (3) active autoimmune diseases still require hormone therapy; (4) combined with other primary tumors; (5) suffering from severe lung and heart diseases, etc.; (6) ECOG score > 2. The study was conducted following the guidelines of Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2024-KY-1197-001).
The administration regimen was as follows: (1) Atezolizumab 1200 mg, intravenous infusion on the first day (the first infusion should last for at least 60 minutes; if well tolerated, subsequent infusions should last for at least 30 minutes) or Durvalumab 1500 mg, intravenous infusion on the first day (infusion time 60 minutes). (2) etoposide injection 100mg/m², intravenous infusion for 1-3 days. (3) carboplatin injection AUC=5, intravenous infusion on the first day, or cisplatin injection 75mg/m², intravenous infusion on the first day. All included patients were treated with PD-L1 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy with a cycle of 3 weeks. After 4-6 cycles of treatment, PD-L1 inhibitor monotherapy was maintained until disease progression occurred. Whether or not to combine radiotherapy is based on the patient’s condition.
Collect clinical pathological data and pre-immunotherapy hematological examination results, especially age, gender, Body Mass Index (BMI), ECOG scores, smoking history, extrapulmonary metastases; hematological indicators before receiving PD-L1 inhibitor treatment, including blood routine, liver and kidney function, C-reactive protein (CRP), and tumor markers, etc. Collect fasting peripheral venous blood samples within one week before immunotherapy. Inflammatory indicators were determined using the following formulas: (1) SII = platelet count(/L) × neutrophil count(/L)/lymphocyte count(/L). (2) PNI = serum albumin(g/L)/+5 × lymphocyte count (/L).
All participants received consistent follow-up through a combination of telephone, inpatient medical records, and outpatient review, with a follow-up deadline of January 20, 2023. Imaging evaluations were as follows: electronic computed tomography (performed every 42 days), color Doppler flow imaging (performed every 42 days), cranial magnetic resonance imaging (performed every 3months), and whole-body bone scanning (performed every 6 months). Tumor response was evaluated every two cycles (42 days) through imaging examinations, tumor markers, symptoms, etc., using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1 by clinical doctors. The patients’ reactions to treatment were classified as complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD). The definition of Partial response (PR): The total diameter of all measurable target lesions is≥30% lower than baseline. All target lesions must be evaluated. For conflicting assessments, we focused on the overall tumor burden and determined treatment response based on the sum of the diameters of all target lesions. Main endpoint: OS was determined as the duration from the initiation of first-time immunotherapy until death from any cause or, alternatively, the last date of follow-up.
SPSS 25.0 and R software (3.6.1) were used to statistically analyze the clinical data, and GraphPad Prism 8.0 was used for graphing. We used X-tile software 3.6.1 to figure out the optimal cut-off values of SII, PNI, and total points obtained from the nomogram. We performed a Spearman correlation analysis to assess the connection between the PNI and the SII. The relationships between SII‐PNI score and the baseline characteristics were examined by chi‐square test for categorical variables. The study utilized the Kaplan-Meier model to conduct survival analysis. We carried out both univariate analysis and multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazards regression model. To assess the relative risks, we examined the hazard ratios (HR) along with their 95% confidence interval (CI). The significant independent risk factors identified in the multivariate analysis were incorporated into the construction of the nomogram. To assess the reliability and predictive accuracy of the nomogram, we performed the ROC curve, calibration plots, and DCA curve. P values<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Table 1 provides a summary of the demographic data of 70 newly treated ES-SCLC patients engaged in the study. 54 males (77.1%) and 16 females (22.9%) were included. The patients’ median age was 60 years, with a range of 34 to 92. 34 cases (48.6%) had a smoking history. 25 cases received chest radiation therapy (35.7%). 64 cases were treated with Durvalumab (91.4%), and 6 cases were treated with Atezolizumab (8.6%). After four cycles of treatment, the tumor response led to the division of 70 patients into the following categories: PR (48 cases) and non-PR (22 cases). The patients had a median OS of 17.4 months. The median values of the SII and PNI before PD-L1 inhibitors with first-line chemotherapy were 1003.4 (ranging from 131.7 to 7415.2) and 48.0 (ranging from 33.3 to 60.5), respectively. Meanwhile, a significant negative correlation was discovered between SII and PNI (r=-0.421, p<0.001; Figure 1).
According to X-tile 3.6.1 software, the optimal cut-off values of pre-treatment SII and PNI were 623.91 and 45.25, respectively. The 70 ES-SCLC patients were classified into two groups: low SII (SII ≤ 623.91) and high SII (SII>623.91), with 28 and 42 patients, respectively. Similarly,70 patients were sorted into two groups: low PNI (PNI ≤ 45.25) and high PNI (PNI>45.25), with 48 and 22 patients. In order to examine the relationship between the patient’s systemic inflammation/immune status and curative effect, we next assessed how the baseline SII and PNI correlate with the tumor response. The PR group’s baseline SII was notably lower compared to that observed in the non-PR group(p=0.036) (Figure 2A). Meanwhile, the PR group had a significantly higher pre-treatment PNI level than the non-PR group (p<0.001) (Figure 2B).
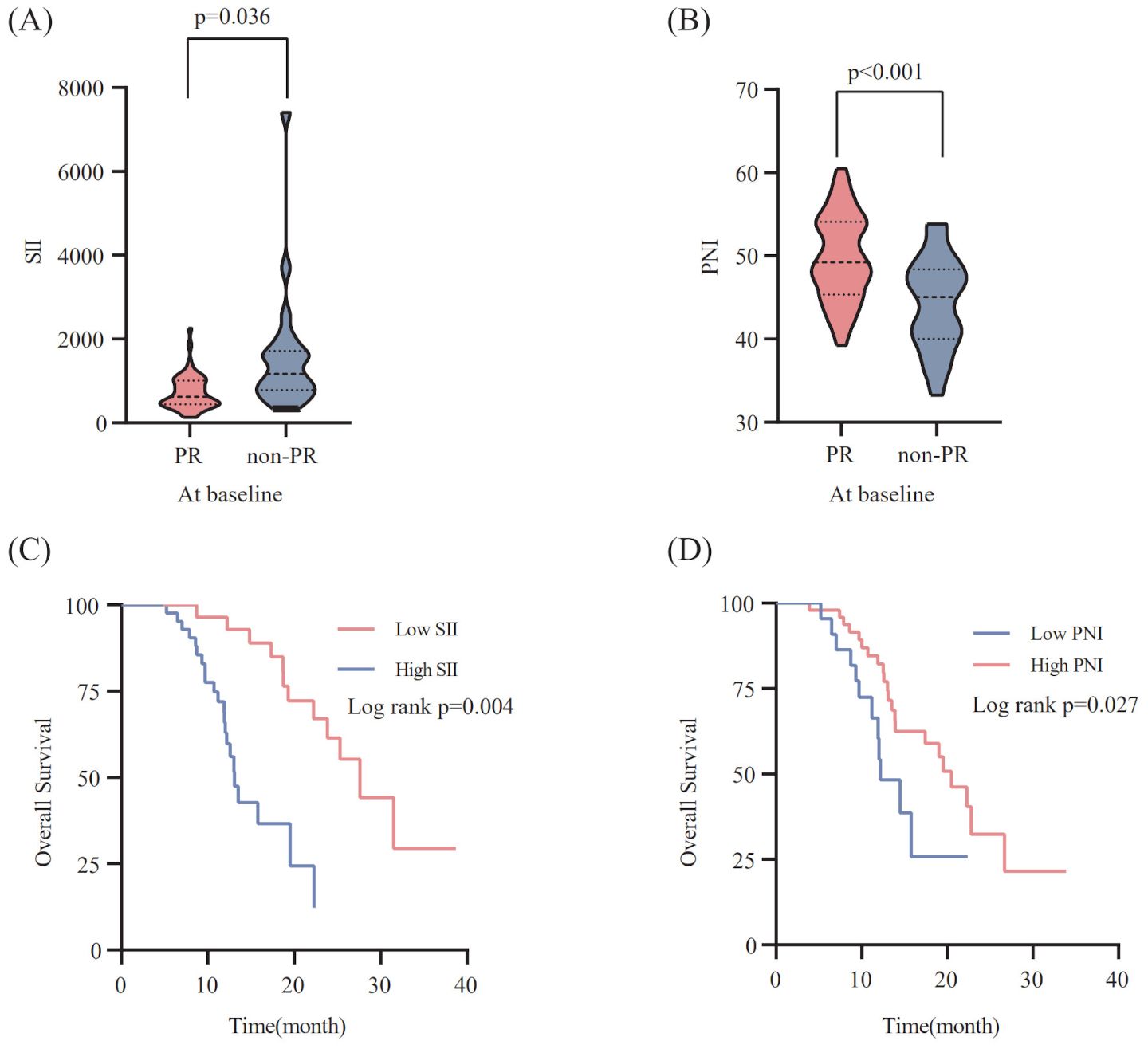
Figure 2. Relationship between the SII (A) / PNI (B) at baseline and the response to PD-L1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy. The Kaplan-Meier survival curves for overall survival according to pre-treatment SII (C) /PNI (D).
To explore the correlation between the baseline SII/PNI and OS, we analyzed the OS of patients from different levels. Patients with a high SII level (p=0.004; Figure 2C) had markedly poorer OS, whereas those with a high PNI level showed improved OS than patients in the low PNI group (p=0.027; Figure 2D).
The patients were classified into three groups on the basis of SII and PNI: 0, characterized by both a low SII score and high PNI score (n=25); 1, presented with either a high SII score or a low PNI score (n=26); 2, exhibited a high SII score and a low PNI score (n=19). No notable statistical differences were found in age, gender, smoking history, ECOG PS, BMI, PD-L1 category, and metastasis site (all p>0.05) among the three groups, according to the correlation analysis between SII-PNI score and the baseline clinicopathological characteristics (Table 2). There was also no notable association observed between the pre-treatment SII-PNI score and a history of receiving chest radiation therapy (p>0.05).
All patients received whole chest and abdominal enhanced CT scans after 4 cycles of PD-L1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy. A notable difference in the SII-PNI score was observed between the PR group and the non-PR group (Table 2). Patients who achieved a PR had a significantly lower SII-PNI score compared to those with non-PR.
The 2-year OS rate was 62.9%, with a median OS of 17.4 months (95% CI,11.4-23.4 months). Patients with SII-PNI scores of 0, 1, and 2 had median OS of 22.8, 14.5, and 12.0 months, respectively. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated that the best outcome was observed in the SII-PNI score of 0 group (median OS 22.8 months; 95% 16.5-29.0 months), whereas the worst outcome was observed in the SII-PNI score of 2 group (median OS 12.0 months; 95% 10.8-13.2 months; p=0.008, Figure 3). Cox regression analyses were conducted to evaluate OS (Table 3). The multivariate analysis indicated that liver metastasis (p=0.025), poorer tumor response (p=0.002), and SII-PNI score (p=0.036) had an independent association with a less favorable OS. We observed a nearly four-fold change in the HR of survival between the SII-PNI score of 2 and the SII-PNI of 0 groups. The hazard ratio (HR) of the SII-PNI score of 1 group was 1.8 times higher than that of the SII-PNI score of 0 group.
Utilizing the findings from both univariate and multivariate analyses, liver metastasis, tumor response, and SII-PNI score were incorporated to develop a nomogram for predicting OS in ES-SCLC patients (Figure 4). The AUC values of 1 and 2 year were 0.808 and 0.833, respectively (Figure 5A). Besides, the calibration curves (Figure 5B/5C) demonstrated the exceptional prognostic capability of the nomogram. The calibration curves indicate that the model has a good fit between the standard and correction curves. The DCA curve (Figure 5D) demonstrated that the nomogram model’s net income peaks when risk thresholds range from 0.1 to 0.75. X-tile software 3.6.1 identified the optimal cut-off value of the total points as 98. Kaplan-Meier analysis was conducted to illustrate the stratification ability of the nomogram. Survival analysis identified significant differences between the groups classified as low-risk and high-risk (Figure 5E).
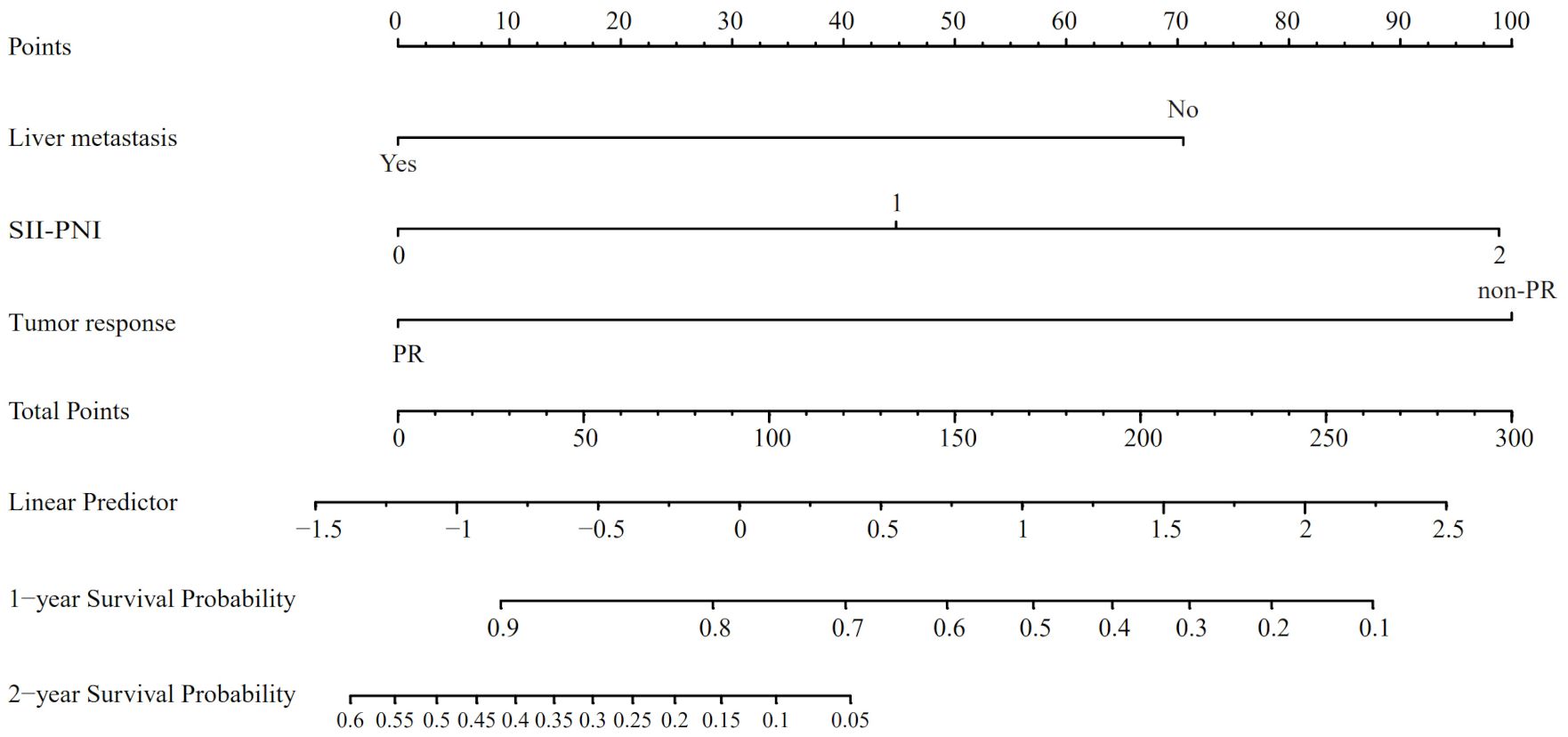
Figure 4. The nomogram model based on liver metastasis, tumor response, and SII-PNI score to predict the probabilities of 1- and 2-year OS.
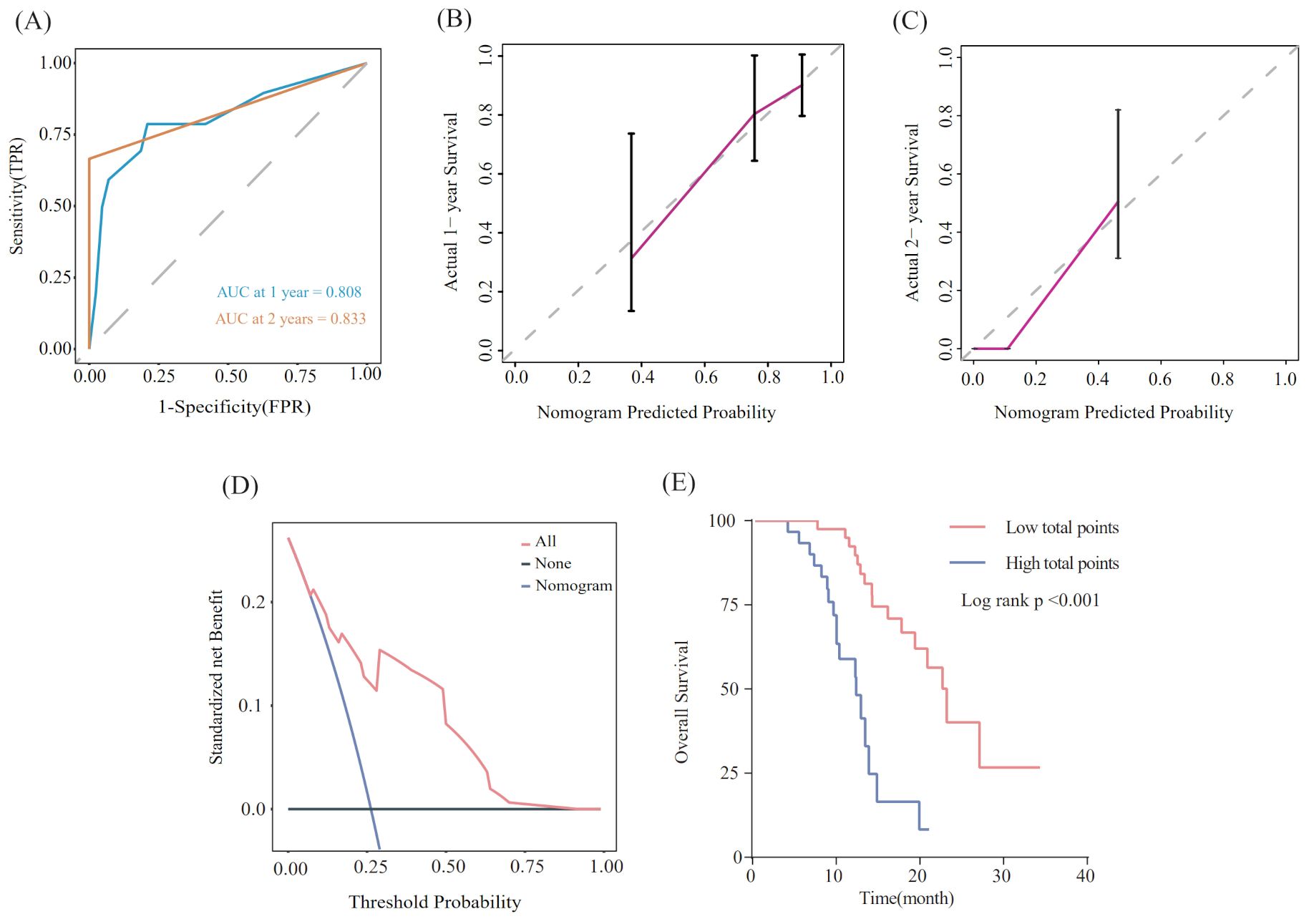
Figure 5. Evaluation of the nomogram model. (A) ROC curve that predicts 1- and 2-year survival. (B, C) Calibration curves of prediction models for predicting 1- and 2-year survival. (D) Decision Curve Analysis. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with high and low-risk groups.
For patients with extensive-stage SCLC, the median survival time typically ranges from 9 to 10 months, and the first-line standard chemotherapy is the main treatment option. The emergence of ICIs has changed the treatment approach of SCLC. ICIs prevent tumor cells from completing immune evasion through immune checkpoints, promoting the immune system to fully exert its anti-tumor activity (18, 19). Chemotherapy can induce immunogenic cell death of tumor cells, improve the ability of immune system to recognize the tumor cells (20), upregulate the expression of PD-L1, and enhance the efficacy of ICIs (21). Therefore, it is believed that chemotherapy and immunotherapy have a synergistic effect. The current research results show that the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy can benefit patients, but the factors affecting its efficacy and prognosis are still unclear. Immunotherapy can also bring serious adverse reactions, and only a portion of patients can benefit from it. Therefore, before PD-L1 inhibitor combined with first-line chemotherapy is utilized to those suffering from ES-SCLC, it would be advantageous to have a simple indicator that can reliably predict the efficacy and prognosis. This would significantly assist in formulating and selecting individualized treatment regimens.
High expression of PD-L1 is associated with greater immune benefits in NSCLC and some malignant tumors (22–24). However, unlike NSCLC, biopsy samples of SCLC often contain necrotic tissue, so it is usually not possible to provide sufficient samples for PD-L1 detection. In addition, among detectable specimens, compared with NSCLC, the expression frequency of PD-L1 in SCLC is significantly lower (25, 26), with only about 25% of SCLC patients showing positive PD-L1 expression in tumor cells (27). Moreover, due to the strong heterogeneity of SCLC, there are significant differences in PD-L1 detection results, which limits the application of PD-L1 in predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy in SCLC populations (28). TMB has been approved by the FDA as a predictive indicator for the efficacy of pan-tumor immunotherapy (29). However, issues such as insufficient sample size for testing and inconsistent cut-off values also prevent TMB from accurately predicting the efficacy of SCLC immunotherapy. Increasing numbers of investigations have discovered the predictive role of hematological indicators in the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Finding effective biomarkers from economically available test items such as blood routine and liver and kidney function is currently one of the most active areas of cancer treatment research.
The occurrence and development of malignancies are heavily influenced by systemic nutrition and inflammation status. An increasing number of studies have demonstrated the correlation between chronic inflammation and an elevated risk of getting cancer (10). A high SII level has shown a strong correlation with poorer prognosis in malignant solid tumors (30–32). Many studies have also identified that the SII correlates with the prognosis of SCLC patients. In addition, the nutritional status also matters greatly in disease progression and prognosis of cancers (8). PNI is a widely used nutritional index that was originally introduced to evaluate patients’ nutritional status before surgery and to predict the risk of complications after surgery (33, 34). More and more studies have found that PNI has prognostic value for many types of cancers, including lung (35), gastric (36), colorectal (37), and hepatocellular carcinoma (38). Previous studies have indicated that the SII-PNI score is a significant prognostic tool in NSCLC (16), gastric cancer (17, 39), and urothelial carcinoma (40). As far as we know, we are pioneering in integrating the SII and PNI of ES-SCLC patients to define the SII-PNI score as a novel indicator for predicting efficacy and prognosis.
Tumor response plays a crucial role in predicting the survival outcome of ES-SCLC patients treated with PD-L1 inhibitors. It is challenging to anticipate how tumors will respond based solely on clinical pathological data before immunotherapy. We pay attention to SII and PNI to address the difficulties in predicting tumor response. The results of this study indicated a significant correlation between the baseline SII-PNI score and the tumor response to immunotherapy. Patients with lower SII-PNI scores were found to have a higher possibility of responding well to PD-L1 inhibitors. These findings indicated that the SII-PNI score may function as a potential biomarker for predicting short-term efficacy in ES-SCLC patients taking immunotherapy with chemotherapy.
The prognostic analysis revealed that a higher SII-PNI score has a strong association with a poorer prognosis. The following elements could potentially contribute to the SII-PNI score’s predictive capability: (1) An elevated SII-PNI score suggests that the count of neutrophils or platelets has increased proportionally compared to the lymphocyte count present within the blood sample. Elevated neutrophil count has been seen having as an unwelcome role in tumor development, invasion, metastasis, and resistance to treatment (41). Previous studies have shown that neutrophils can suppress anti-tumor cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro and produce cytokines that promote angiogenesis (42). Platelets can activate a large number of bioactive factors, increase tumor vascular permeability, and serve as a shield for tumor cells against the infiltration of cytotoxic lymphocytes and natural killer cells, as well as promote the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (43). (2) An elevated SII-PNI score also reflects a relative reduction in lymphocyte levels. As immune cells in the body, lymphocytes can inhibit cancer cell division and metastasis by inducing cell apoptosis, playing a role in immune monitoring and tumor defense (44, 45). The decrease in lymphocyte count can also reduce the efficacy of ICIs, which primarily release inhibitory signaling properties of T lymphocytes. Research has shown that increased infiltration of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is associated with better efficacy and prognosis of immunotherapy in patients with solid tumors (46). (3) Malnutrition and inflammatory status of the body can both affect the synthesis of serum albumin. Low levels of albumin often suggest malnutrition and weakened immune function in patients. It can also reflect the body’s inflammatory status and anti-tumor immune response. Cachexia can also lead to disease progression (47).
We found liver metastasis, tumor response, and SII-PNI score were independently associated with OS. Following this, we developed a nomogram using the above-mentioned factors. To ensure our results were reliable and accurate, we conducted additional analyses using ROC curves and calibration curves. These statistical tools confirmed that our model had excellent predictive accuracy, with its prediction closely aligning with actual observations. In addition, we implemented a system stratifying mortality risk that categorizes patients into high- and low-risk subgroups. This system facilitates the effective management of risk stratification and the provision of individual treatment. A significant difference in OS was identified between the two different levels of risk.
Nevertheless, this study had certain limitations. Because PD-L1 inhibitors are prohibitively expensive, only a small population of patients have access to them. This study was constrained by a limited sample size. Additionally, there was a lack of an external validation cohort to further validate the effectiveness and predictive power of the nomogram for patients with ES-SCLC. Due to the small sample size of the study and the overfitting issues in the model, the SII-PNI score system has a certain risk of bias. Thirdly, systemic inflammation and nutritional status can be affected by various factors unrelated to cancer. However, this study did not address the potential confounding factors that may affect SII-PNI scores, such as concurrent infections or drug use (such as antibiotics or proton pump receptor inhibitors). Lastly, due to the fact that most patients have not undergone PD-L1 expression level and TMB testing, the correlation between these indicators and efficacy has not been explored. In the future, we may consider the possibility of combining the SII-PNI score with biomarkers such as PD-L1 expression level and TMB to improve the prognostic accuracy. In order to explore predictive biomarkers for ES-SCLC immunotherapy and identify the most suitable population for immunotherapy, more large-scale, prospective, and multi-center studies are still needed.
In summary, our study showed that the SII-PNI score can effectively predict the efficacy and prognosis of extensive-stage SCLC patients treated with PD-L1 inhibitors combined with first-line chemotherapy. Baseline hematological inflammation indicators can be obtained through blood routine, which has the advantages of simplicity, economy, and minimal trauma. Clinicians should take into account this innovative biomarker when making clinical decisions, managing risk stratification, and selecting the best patients for PD-L1 inhibitors.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (approval number: 2024-KY-1197-001). We retrospectively used information about the participants’ previous clinical visits without direct contact with them and protected their privacy. The Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University approved the requirement for the waiver of informed consent for this study.
YG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YS: Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. LW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors are grateful to the patients and their families and the investigators, nurses, and staff members who participated in this study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Kalemkerian GP, Loo BW, Akerley W, Attia A, Bassetti M, Boumber Y, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: small cell lung cancer, version 2.2018. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2018) 16:1171–82. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0079
3. Oronsky B, Reid TR, Oronsky A, Carter CA. What’s new in SCLC? A review. Neoplasia. (2017) 19:842–7. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.07.007
4. Farago AF, Keane FK. Current standards for clinical management of small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2018) 7:69–79. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2018.01.16
5. Rossi A, Di Maio M, Chiodini P, Rudd RM, Okamoto H, Skarlos DV, et al. Carboplatin- or cisplatin-based chemotherapy in first-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: the COCIS meta-analysis of individual patient data. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:1692–8. doi: 10.1200/jco.2011.40.4905
6. Liu SV, Reck M, Mansfield AS, Mok T, Scherpereel A, Reinmuth N, et al. Updated overall survival and PD-L1 subgroup analysis of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide (IMpower133). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:619–30. doi: 10.1200/jco.20.01055
7. Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomized, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2019) 394:1929–39. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32222-6
8. Mayne ST, Playdon MC, Rock CL. Diet, nutrition, and cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2016) 13:504–15. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.24
9. Longo V, Catino A, Montrone M, Pizzutilo P, Annese T, Pesola F, et al. What are the biomarkers for immunotherapy in SCLC? Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(20). doi: 10.3390/ijms222011123
10. Zitvogel L, Pietrocola F, Kroemer G. Nutrition, inflammation and cancer. Nat Immunol. (2017) 18:843–50. doi: 10.1038/ni.3754
11. Chrom P, Zolnierek J, Bodnar L, Stec R, Szczylik C. External validation of the systemic immune-inflammation index as a prognostic factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and its implementation within the international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium model. Int J Clin Oncol. (2019) 24:526–32. doi: 10.1007/s10147-018-01390-x
12. Hong YM, Yoon KT, Cho M. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:569. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08124-9
13. Mirili C, Yılmaz A, Demirkan S, Bilici M, Basol Tekin S. Clinical significance of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in Malignant melanoma. Int J Clin Oncol. (2019) 24:1301–10. doi: 10.1007/s10147-019-01461-7
14. Guller M, Herberg M, Amin N, Alkhatib H, Maroun C, Wu E, et al. Nutritional status as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapy outcomes in advanced head and neck cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13(22). doi: 10.3390/cancers13225772
15. Xu S, Cao S, Geng J, Wang C, Meng Q, Yu Y. High prognostic nutritional index (PNI) as a positive prognostic indicator for non-small cell lung cancer patients with bone metastasis. Clin Respir J. (2021) 15:225–31. doi: 10.1111/crj.13288
16. Fan R, Chen Y, Xu G, Pan W, Lv Y, Zhang Z. Combined systemic immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index predict outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving platinum-doublet chemotherapy. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:996312. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.996312
17. Ding P, Guo H, Sun C, Yang P, Kim NH, Tian Y, et al. Combined systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts chemotherapy response and prognosis in locally advanced gastric cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy with PD-1 antibody sintilimab and XELOX: a prospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:121. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02199-9
18. Iams WT, Porter J, Horn L. Immunotherapeutic approaches for small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2020) 17:300–12. doi: 10.1038/s41571-019-0316-z
19. Pavan A, Attili I, Pasello G, Guarneri V, Conte PF, Bonanno L. Immunotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: from molecular promises to clinical challenges. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:205. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0690-1
20. Jackaman C, Majewski D, Fox SA, Nowak AK, Nelson DJ. Chemotherapy broadens the range of tumor antigens seen by cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells in vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2012) 61:2343–56. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1307-4
21. Leduc C, Adam J, Louvet E, Sourisseau T, Dorvault N, Bernard M, et al. TPF induction chemotherapy increases PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and immune cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. ESMO Open. (2018) 3:e000257. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000257
22. Horn L, Spigel DR, Vokes EE, Holgado E, Ready N, Steins M, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: two-year outcomes from two randomized, open-label, phase III trials (CheckMate 017 and checkMate 057). J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:3924–33. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.74.3062
23. Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M, Kowanetz M, Vansteenkiste J, Mazieres J, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicenter, open-label, phase 2 randomized controlled trial. Lancet. (2016) 387:1837–46. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)00587-0
24. Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. (2016) 387:1540–50. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(15)01281-7
25. Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicenter, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17:883–95. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(16)30098-5
26. Yu H, Batenchuk C, Badzio A, Boyle TA, Czapiewski P, Chan DC, et al. PD-L1 expression by two complementary diagnostic assays and mRNA in situ hybridization in small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:110–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.09.002
27. Acheampong E, Abed A, Morici M, Bowyer S, Amanuel B, Lin W, et al. Tumor PD-L1 expression in small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cells. (2020) 9(11). doi: 10.3390/cells9112393
28. Navarro A, Felip E. Pembrolizumab in advanced pretreated small cell lung cancer patients with PD-L1 expression: data from the KEYNOTE-028 trial: a reason for hope? Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2017) 6:S78–s83. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.10.04
29. Subbiah V, Solit DB, Chan TA, Kurzrock R. The FDA approval of pembrolizumab for adult and pediatric patients with tumor mutational burden (TMB) ≥10: a decision centered on empowering patients and their physicians. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1115–8. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.002
30. Chen L, Yan Y, Zhu L, Cong X, Li S, Song S, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index as a useful prognostic indicator predicts survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Manag Res. (2017) 9:849–67. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S151026
31. Nøst TH, Alcala K, Urbarova I, Byrne KS, Guida F, Sandanger TM, et al. Systemic inflammation markers and cancer incidence in the UK Biobank. Eur J Epidemiol. (2021) 36:841–8. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00752-6
32. Tong YS, Tan J, Zhou XL, Song YQ, Song YJ. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicting chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. (2017) 15:221. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1326-1
33. Li D, Yuan X, Liu J, Li C, Li W. Prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index in lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. (2018) 10:5298–307. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.08.51
34. Buzby GP, Mullen JL, Matthews DC, Hobbs CL, Rosato EF. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery. Am J Surg. (1980) 139:160–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90246-9
35. Sheng J, Yang YP, Ma YX, Qin T, Hu ZH, Hong SD, et al. Low prognostic nutritional index correlates with worse survival in patients with advanced NSCLC following EGFR-TKIs. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0147226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147226
36. Yang Y, Gao P, Song Y, Sun J, Chen X, Zhao J, et al. The prognostic nutritional index is a predictive indicator of prognosis and postoperative complications in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2016) 42:1176–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.05.029
37. Ikeya T, Shibutani M, Maeda K, Sugano K, Nagahara H, Ohtani H, et al. Maintenance of the nutritional prognostic index predicts survival in patients with unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2015) 141:307–13. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1799-8
38. Tada T, Kumada T, Hiraoka A, Kariyama K, Tani J, Hirooka M, et al. Nutritional status is associated with prognosis in patients with advanced unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. Oncology. (2023) 101:270–82. doi: 10.1159/000527676
39. Ding P, Yang P, Sun C, Tian Y, Guo H, Liu Y, et al. Predictive effect of systemic immune-inflammation index combined with prognostic nutrition index score on efficacy and prognosis of neoadjuvant intraperitoneal and systemic paclitaxel combined with apatinib conversion therapy in gastric cancer patients with positive peritoneal lavage cytology: A prospective study. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:791912. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.791912
40. Zheng Y, Yu D, Yu Z, Zhao D, Chen Y, Chen W, et al. Association of preoperative systemic Immune-inflammation Index and Prognostic Nutritional Index with survival in patients with Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. J Cancer. (2020) 11:5665–77. doi: 10.7150/jca.44915
41. Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. (2014) 15:e493–503. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(14)70263-3
42. Coffelt SB, Wellenstein MD, de Visser KE. Neutrophils in cancer: neutral no more. Nat Rev Cancer. (2016) 16:431–46. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.52
43. Schmied L, Höglund P, Meinke S. Platelet-mediated protection of cancer cells from immune surveillance - possible implications for cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:640578. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640578
44. Whiteside TL. Immune modulation of T-cell and NK (natural killer) cell activities by TEXs (tumor-derived exosomes). Biochem Soc Trans. (2013) 41:245–51. doi: 10.1042/bst20120265
45. Feng XY, Wen XZ, Tan XJ, Hou JH, Ding Y, Wang KF, et al. Ectopic expression of B and T lymphocyte attenuator in gastric cancer: a potential independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 11:658–64. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2699
46. Gooden MJ, de Bock GH, Leffers N, Daemen T, Nijman HW. The prognostic influence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. (2011) 105:93–103. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.189
Keywords: small cell lung cancer, PD-L1 inhibitors, systemic immune-inflammation index, prognostic nutritional index, survival
Citation: Ge Y, Liu X, Xu Y, Su Y, Li Y and Wang L (2024) Combined systemic immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index predicts the efficacy and prognosis of ES-SCLC patients receiving PD-L1 inhibitors combined with first-line chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 14:1485849. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1485849
Received: 25 August 2024; Accepted: 12 November 2024;
Published: 04 December 2024.
Edited by:
Vinay Kumar, The Pennsylvania State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Sabyasachi Mohanty, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Ge, Liu, Xu, Su, Li and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liping Wang, d2xwQHp6dS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.