- 1Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery & Retroperitoneal Tumor Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Women and Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 4Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Women and Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
In recent years, an increasing number of studies have utilized molecular biology techniques to reveal important molecular heterogeneity among different subtypes of liposarcoma. Each subtype exhibits distinct genetic patterns and molecular pathways, which may serve as important targets for molecular therapy. In the present review, we focus on the molecular characteristics, molecular diagnostics, driver genes, and molecular mechanisms of liposarcoma. We also discuss the clinical research progress of related targeted therapies, with an aim to provide a reference and crucial insights for colleagues in the field.
1 Introduction
Liposarcoma (LPS) is the most common soft tissue sarcoma (STS) in adults, accounting for 15%–20% of STS, and can also occur in adolescents and children. It is a malignant tumor derived from adipose cell differentiation (1). According to the fifth edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone, published in 2020 (2), the LPS subtypes comprise atypical lipomatous tumor (ATL)/well-differentiated LPS (WDLPS), dedifferentiated LPS (DDLPS), myxoid LPS (MLPS), pleomorphic LPS (PLPS), and myxoid pleomorphic LPS. The main treatment for all LPS subtypes is surgical resection; however, for patients with unresectable, advanced, or metastatic LPS, treatment options are currently limited and often ineffective, resulting in a generally poor prognosis. New drugs are therefore urgently needed to improve the current state of treatment. In recent years, the continuous development of molecular biology techniques has resulted in the stratification of genetic subgroups within LPS. Concurrently, an increasing number of clinical and research-oriented treatments have been tested based on an understanding of the specific molecular pathology of each subtype; these studies have yielded good progress and results. In the present review, we discuss the molecular characteristics, molecular diagnostics, driver genes, and molecular pathogenesis of LPS. We also explore the corresponding therapeutic targets and downstream pathways, and summarize progress toward targeted therapies for several subtypes of LPS.
2 Molecular characteristics of LPS
The LPS subtypes differ in their clinical behaviors, treatment sensitivities, and underlying biological characteristics. In the following sections, the detailed molecular characteristics of each subtype are described in terms of genomics, proteomics, and epigenetics.
2.1 Genomics
The different STS subtypes exhibit molecular heterogeneity. Nacev et al. identified specific somatic mutations and copy number alterations in some subtypes via the genetic sequencing of STS samples, and compared tumor mutational burden and microsatellite instability across the different subtypes (3). STS can be divided into two genomic categories. One category (80%) consists of tumors with complex karyotypes, such as leiomyosarcoma, undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, DDLPS, and anigosarcoma. These tumors are characterized by many gene rearrangements and chromosomal gains or losses that often include cell cycle–related genes such as TP53, MDM2, RB1, and CDK4 (4). The other category (20%) consists of tumors with specific genetic alterations, such as gene translocations and activating point mutations (5). Importantly, tumors with specific genetic alterations can also develop complex karyotypes as the tumor progresses. Taylor et al. reported that different subtypes of retroperitoneal liposarcoma (RPL) have distinct genomic landscapes, and discussed the genomic differences between RPL and extremity LPS (6).
WDLPS and DDLPS share several common genetic features. Research by Wagner and his team indicates that WDLPS and DDLPS evolve from common precursors into distinct patterns (7). The molecular signatures of both subtypes are characterized by amplifications in the 12q13-15 region on the long arm of chromosome 12 (8). Molecular testing indicates that approximately 90% of WDLPS/DDLPS cases have confirmable MDM2 and CDK4 gene amplifications, which are the primary driver genes (9). In recent years, an increasing number of whole-genome sequencing studies have identified that additional gene amplifications within the 12q13-15 region in WDLPS/DDLPS (such as the amplification of HMGA2, TSPAN31, FRS2, GLI1, YEATS4, YEATS2, NAV3, and CPM in WDLPS), new genes outside the 12q13-15 region (such as DDR2 and SDHC in WDLPS, and FGFR3 in DDLPS), and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-related signaling pathways are closely associated with the occurrence and progression of WDLPS/DDLPS (10–12).
Given the shared genetic characteristics between DDLPS and WDLPS, and the observation of both well-differentiated and poorly differentiated areas in many DDLPS samples, DDLPS is commonly believed to evolve from WDLPS. However, these two sarcomas differ substantially. During dedifferentiation, ongoing DNA damage leads to genomic instability and the further accumulation of complex genomic aberrations. In DDLPS, pathways related to cell proliferation and the DNA damage response are upregulated, whereas in WDLPS, pathways related to adipocyte differentiation and metabolism are upregulated (13). Studies have also reported that the loss of 11q23 and the amplification of 6q23 or 1q32 (or the co-amplification of 6q23 and 1q32) are DDLPS-specific genomic abnormalities. Additionally, intrachromosomal and interchromosomal gene rearrangements and gene fusions (such as C15orf7::CBX3, CTDSP1::DNM3OS, and CTDSP2::DNM30S) have been identified in DDLPS but not in WDLPS. DDIT3 is also amplified in DDLPS patients (14). Furthermore, a study that comprehensively analyzed the molecular characteristics of retroperitoneal sarcoma-WDLPS revealed that FOXD4L3 has periodic mutations that interact with the PAX pathway to promote tumorigenesis. Moreover, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, as well as genes associated with the transition from an adipose to a “tumor” phenotype, are all dysregulated (15). Pollock et al. reported that Aurora A kinase (AURKA) is significantly overexpressed in retroperitoneal sarcoma-DDLPS and is strongly associated with metastasis and recurrence (16). Combined, large-scale whole-exome and RNA sequencing in Japan has revealed that somatic copy number alterations are the most common genomic mutations in DDLPS (17). The frequency of mutations varies for each chromosome, ranging from 0.114 (chromosome 21) to 0.482 (chromosome 12). In this study, DDLPS was then divided into the following three groups based on the associations between somatic copy number alterations and clinical features: cluster 1, with only 12q15 high magnification; cluster 2, with 12q15 and 1p32.1 high magnification; and cluster 3, without 12q15 high magnification. A survival analysis conducted after the genomic clustering revealed that, compared with cluster 1 patients, cluster 2 DDLPS patients had better progression-free survival (PFS) rates. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that cluster 1 was a significant predictor of poor PFS, independent of the surgical margin and primary tumor site. Furthermore, a comparative analysis of WDLPS and DDLPS components revealed that the gene sets associated with cell cycle progression, including the G2/M checkpoint and E2F target genes, were significantly enriched in DDLPS. By contrast, a gene set associated with adipocyte differentiation or lipid metabolism, including adipogenesis and fatty acid metabolism, was significantly enriched in WDLPS.
Lago et al. reported that DNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) in the promoters of lipopolysaccharide-treated cells are associated with high transcription levels in open chromatin, indicating that promoter G4s and related transcription factors work in concert to form cell-specific transcriptional programs (18). Moreover, Richter et al. reported that mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) induces the formation of stable G-quadruplexes, which are specifically recognized by cellular helicases. The targeting of G-quadruplexes can reduce MDM2 expression and p53 degradation, thereby promoting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells (19).
MLPS is genetically characterized by the translocation of t(12;16)(q13;p11) in more than 95% of cases; this results in the FUS-DDIT3 fusion gene, which stimulates cell proliferation and disrupts adipogenic differentiation (20). The remaining 5% of MLPS cases are genetically characterized by the translocation of t(12;22)(q13;q12), which results in the EWSR1-DDIT3 fusion gene (20). These features are considered unique to MLPS. Additionally, high RET expression has been observed in MLPS, and approximately 25% of all cases have mutations that activate the PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway (21). Moreover, over 50% of MLPS cases carry mutations in the TERT promoter (22).
PLPS is characterized by marked chromosomal abnormalities, including chromosomal deletions and duplications (23). Although related molecular research is limited, studies have reported that mutations or inactivation of RB1 are associated with PLPS development (24). Furthermore, genetic testing of a metastatic lesion in a patient with uterine PLPS with liver metastasis revealed an IQGAP-NTRK3 gene fusion (25).
Myxoid pleomorphic LPS exhibits complex chromosomal changes; however, it lacks the FUS-DDIT3 gene fusion that is characteristic of MLPS and the MDM2/CDK4 gene amplification found in DDLPS (2). Molecular research in this area is also limited.
2.2 Proteomics
Proteomic technologies and strategies are increasingly being applied to the study of STS. Huang et al. conducted proteomic analyses of different STS subtypes. By mining the proteomic data of cluster of differentiation 3 (CD3)+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) groups in patients with DDLPS, these authors revealed that the high CD3+ TIL group was enriched in aspects such as T-cell activation, T-cell receptor signaling, leukocyte proliferation, cell adhesion, and the interferon response. By contrast, the low-CD3+ TIL group was enriched in the complement cascade, with an active complement system. These findings support the future evaluation of combination therapy with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) checkpoint inhibitors and complement inhibitors to treat DDLPS patients in the low CD3+ TIL group (26, 27). Moreover, the data from this study suggest that, at the protein level, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) is expressed at a relatively high level in DDLPS. This finding is consistent with the amplification of CDK4 in many DDLPS, although no enriched ontology was observed in an overexpression analysis of DDLPS. It has also been reported that vesicular trafficking proteins are an independent prognostic factor for distant metastasis. In addition, through the joint analysis of proteomic and phosphorylation data, a team led by Ding demonstrated STS subtypes with different molecular characteristics and clinical outcomes, and identified the key driving molecules for STS metastasis and proliferation (28). Fat metabolism-related pathways, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR) pathways, and vitamin metabolism pathways are significantly upregulated in DDLPS and MLPS. Furthermore, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway was significantly upregulated in DDLPS. Numerous molecular markers associated with pathological subtypes were also validated, including CDK4 in DDLPS. Notably, this study conducted an integrated analysis of histopathological subtypes, a hierarchical clustering of pathological subtypes, a proteomic analysis of subtypes, and an analysis of immune subtypes. The findings revealed the relationships between STS subtypes under different classification criteria, as well as their respective molecular, pathway, and clinical characteristics. In this integrated analysis, a detailed division of STS was noted, and STS heterogeneity was explored in great detail.
Together, these findings indicate that LPS has extensive molecular heterogeneity. Further exploration and discoveries of molecular differences and unique molecular characteristics will provide a wide range of ideas and directions for the experimental design and treatment of LPS.
3 Driver genes and molecular mechanisms
The generation of different LPS subtypes is caused by their relatively unique driver genes and molecular mechanisms, which ultimately lead to large differences between subtypes. In the following sections, the main driver genes and molecular pathways of each LPS subtype are described.
3.1 Molecular mechanisms related to WDLPS/DDLPS
3.1.1 Molecular mechanisms associated with MDM2 amplification in WDLPS/DDLPS
The most important function of MDM2 is to control p53 activity, by acting as a negative regulator of p53 (29). MDM2 amplification is mutually exclusive with p53 gene mutation; when MDM2 is amplified, p53 is not mutated, and only wild-type p53 is present (30). The cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) pathway in cancer cells can be reactivated by inhibiting MDM2−TP53 interactions, thereby inducing apoptosis and inhibiting tumorigenesis.
MDM2 may also promote tumor growth through other mechanisms. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A, also known as P14ARF or p16INK4a) is a tumor suppressor protein encoded by CDKN2A, which is overexpressed in WDLPS/DDLPS. CDKN2A causes MDM2 to be localized in the nucleolus, thus preventing TP53 degradation (31). Furthermore, MDM2 regulates serine metabolism and redox homeostasis independently of TP53 to drive tumor growth, and targeting the function of MDM2 in serine metabolism can inhibit DDLPS growth (32). Chen et al. reported that panhistone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) is co-expressed with MDM2 in DDLPS, and that specific targeting of HDAC2 can reduce the expression of MDM2, which plays a role in antitumor activity (33).
3.1.2 Molecular mechanisms associated with CDK4 amplification in WDLPS/DDLPS
CDK4 plays a role in LPS progression by negatively regulating the retinoblastoma protein (Rb) signaling pathway. However, CDK4 can also promote tumor growth through mechanisms that are independent of the Rb pathway. For example, CDKN2A overexpression can inhibit the Rb pathway–dependent function of CDK4 (34).
3.1.3 Role of the fibroblast growth factor/FGF receptor signaling pathway in LPS
In LPS, studies have identified activating mutations, amplifications, and the overexpression of genes related to the FGFR pathway (35–37). FGFR1 and FGFR4 overexpression is observed in approximately 30% of DDLPS cases and is associated with a poor prognosis (38). In approximately 90% of DDLPS cases, FRS2 is coamplified with MDM2 and plays a role in tumor progression. Additionally, FGFR2 is overexpressed in MLS, where it regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration (39).
3.1.4 Possible molecular mechanisms of dedifferentiation
Although up to 10% of WDLPS can progress to DDLPS, molecular research on the progression from WDLPS to DDLPS remains limited. Amplification events, such as c-Jun amplification during dedifferentiation, play a role in the occurrence and development of LPS. In DDLPS, transcription factor Jun (JUN) and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)/mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 (MAP3K5) are coamplified; these are located in the regions of chromosomes 6q23 and 1p32. By contrast, these changes have never been reported in WDLPS. JUN amplification is strongly associated with DDLPS, although it is also observed in some cases of ATL and WDLPS. Approximately 91% of DDLPS cases express c-Jun, whereas its amplification or expression is rare in pure WDLPS. Both the JUN and ASK1/MAP3K5 products are involved in the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway. JUN encodes a protein that regulates the activity of transcription-related factors in adipocytes, and ASK1 encodes a kinase that activates the JNK pathway, leading to JUN activation. JUN or ASK1 amplification suggests that the dedifferentiation of WDLPS ultimately leads to changes in the tissue type and the development of DDLPS (10).
In a study of exome and transcriptome sequencing data from 17 patients diagnosed with both WDLPS and DDLPS, DDLPS samples generally had a slightly greater mutational burden than matched WDLPS samples; however, this apparent difference did not reach significance. When the overall differences in gene expression between WDLPS and DDLPS samples were compared, 357 genes were highly expressed in WDLPS tumors compared with DDLPS tumors; FABP4, ADIPOQ, LPL, LEP, and PTGER3 had the highest gene expression. The 395 genes that were less highly expressed in WDLPS tumors included the genes that were upregulated in DDLPS. In addition, among the known markers of adipocyte differentiation, PPPARG, CEBPB, CEBPD, FOXO1, FOXO3, FOS, JUN, MYC, and CDKN1A were also expressed at higher levels in WDLPS than in DDLPS.
In nine frozen pairs of WDLPS and DDLPS samples, 933 gene fusion transcripts were identified, with a median of 39 fusion transcripts per sample. Notably, the number of fusions in DDLPS samples was significantly greater than that in matched WDLPS samples. In DDLPS samples, only 17% of fusions were shared with homologous WDLPS samples, on average. This finding suggests that, after detachment from the clonal origin, new chromosomes in DDLPS tumors may experience more break-fusions than those in WDLPS tumors. HMGA2 and CPM fusions on Chr12q occurred more frequently and were more prevalent in DDLPS samples than in WDLPS samples. In addition, HMGA2 was significantly overexpressed in DDLPS samples. Shared somatic mutations indicated the clonal origin of matched WDLPS and DDLPS tumors, with early differentiation and genomic instability caused by the continued production and selection of new chromosomes. The random generation and expression of fusion transcripts of new chromosomes, such as HMGA2 and CPM, may influence subsequent tumor differentiation status (40).
The amplification of genes located at chromosome 12q13-15 differs significantly between WDLPS and DDLPS, and may be related to progression and dedifferentiation. Amplification of the following genes in the 12q region was confined primarily to DDLPS: MAP3K12, TBX5, CDK2, GLI1, and ALX1. Moreover, DDLPS had a significantly higher average amplification rate than WDLPS. A key component of dedifferentiation is the loss or downregulation of adipogenesis, which leads to the formation of nonadipogenic masses that are histologically indistinguishable. Various genes are involved in fat cell metabolism. Some of these genes, including PLIN, PLIN2, and LIPE, are uniquely absent in DDLPS, suggesting that these cells have lost their ability to function as fat.
Bouzid et al. reported that HMGA2 amplification is significantly associated with ATL/WDLPS but not DDLPS (10). Furthermore, Wood et al. speculated that several potential parallel signaling pathways may be involved in the dedifferentiation process of WDLPS/DDLPS (41). The Wnt signaling pathway reportedly inhibits preadipocyte differentiation (42). Moreover, Wnt signaling plays an important role in LPS occurrence and development (11). The Wnt antagonist Frzb reduces c-Met expression and inhibits Met-mediated signaling, which may be a new therapeutic strategy for STS (43). MiR-193b targets the Hippo signaling effector YAP1 to indirectly inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling, resulting in the inhibition of LPS cells (44). Hedgehog signaling is also involved in the regulation of adipogenesis, with one study suggesting that the aberrant activation of Hedgehog signaling during adipose tissue development leads to myogenic cell–derived rhabdomyosarcoma (45). Gli is reported to be commonly coamplified with MDM2 and CDK4, and Gli-mediated upregulation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway is enriched in dedifferentiated adipose progenitor cells and DDLPS tumor cells, resulting in undesirable immune cell infiltration of the tumor (46). Notch signaling also plays a role in the adipocyte differentiation process. A recent study reported that Notch signaling activation is associated with DDLPS occurrence through the inhibition of lipid metabolism (47).
Notably, a synthetic PPAR-γ ligand reverses DDLPS dedifferentiation and blocks LPS formation. Moreover, activation of the autophagy and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways can inhibit Notch signaling, thereby promoting the adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (48). Activation of the Notch/platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRβ) signaling pathway can also inhibit the differentiation of brown adipose progenitor cells in mice (49). Furthermore, the synthesis of PPAR-γ ligands reverses DDLPS cell dedifferentiation and prevents LPS formation (47).
3.1.5 Changes in microRNA expression in WDLPS/DDLPS
The differential expression of multiple miRNAs has been identified in WDLPS/DDLPS and may have an important effect on WDLPS/DDLPS growth. In one study, more than 40 dysregulated miRNAs were identified in DDLPS, and restoring the expression of downregulated miR-143 inhibited DDLPS cell proliferation and induced apoptosis (50). In another study, compared with normal adipose tissue, miR-155 expression was upregulated in all LPS subtypes except WDLPS, and the knockdown of overexpressed miR-155 inhibited DDLPS proliferation and growth (51). A later study revealed 35 miRNAs (four with high expression and 31 with low expression) that were able to distinguish between WDLPS/DDLPS and normal fat (52). The targeting of these aberrantly expressed miRNAs may have therapeutic potential for patients with WDLPS/DDLPS; however, their exact roles and mechanisms of action in WDLPS/DDLPS remain to be clarified.
3.2 Preclinical research advances in determining the molecular mechanisms of MLS
3.2.1 Role of the Hippo/YAP1 pathway in MLS
Hartmann et al. reported that MLS occurrence and development depend on the Hippo/YAP1 pathway, and that the FUS-DDIT3-driven tyrosine-protein kinase receptor (IGF-IR)/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway promotes the stability and nuclear accumulation of YAP1 by “turning off” the Hippo signal. FUS-DDIT3 and YAP1/TEAD colocalize in mesenchymal stem cells and MLS cells to jointly regulate proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and adipogenic differentiation (53, 54). Moreover, an increasing body of research emphasizes the importance of dysregulated Hippo signaling in MLS (55).
3.2.2 Key functional interactants of FUS-DDIT3 in chromatin remodeling complexes in MLS
Nelson et al. reported that several members of chromatin remodeling complexes, including NuRD (Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylase) and SWI/SNF (SWItch/Sucrose NonFermenting), are present in the FUS-DDIT3 interactome and play key roles in regulating genomic structure and gene expression (56). Kadoch et al. confirmed that, in MLS, FUS-DDIT3 inhibits the targeting and activity of the BAF complex, thereby suppressing DNA accessibility and failing to activate the target gene CEBPB (an adipogenic transcription factor), which ultimately reduces adipogenesis (57). Additionally, FUS-DDIT3 activates the SRC/focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/RHOA/C GTPases (RHO)/Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinases (ROCK) signaling axis in MLS to increase the invasive capacity of MLS cells (58).
3.2.3 Others
The bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family is a group of epigenetic regulatory proteins that can modulate gene expression and are involved in tumor occurrence and development. Chen et al. reported that BET proteins promote core transcriptional regulatory programs in DDLPS (59). Furthermore, Xu et al. reported that the absence of MAPK-interacting serine/threonine protein kinases 1 and 2 (MNK1/2) inhibits STS occurrence (60).
3.3 Roles of long noncoding RNAs in LPS
Kirtonia et al. reported that many oncogenic long noncoding RNAs, including MALAT1, PVT1, SNHG15, LINC00152, and MIR210HG, are differentially expressed in LPS (61). Similarly, Yuhong et al. reported that LINC00423 expression is downregulated in retroperitoneal sarcoma; this is primarily caused by the disruption of NFATC3 stability, thus activating the MAPK signaling pathway (62).
3.4 Interaction of extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment of LPS
Cancer-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate intercellular communication and transport bioactive molecules within the tumor microenvironment to impact tumor occurrence, progression, and metastasis. In RPL-DDLPS, extracellular vesicles carrying “cargo” MDM2 are released into the microenvironment, and MDM2 DNA from RPLPS is transferred to target recipient cells—preadipocytes—in the tumor microenvironment. This transfer leads to impaired p53 activity and increased matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) production in preadipocytes, which is involved in tumor cell dissemination and recurrence (63, 64).
3.5 Cancer stem cells
3.5.1 Notch signaling in tumor-initiating LPS cells
Shihua et al. enriched tumor-initiating cells to obtain cells with sustained Notch activation (mLPS1) and cells with normal Notch activity (mLPS2). When transplanted into mice, only mLPS1 gave rise to LPS; these cells highly expressed tumor stem cell markers (CD133) and mesenchymal stem cell markers (CD73, CD90, CD105, and Delta-like homolog 1 [DLK1]). Moreover, the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-mediated destruction of Notch signaling inhibited mLPS1 tumorigenicity (65).
3.5.2 Role of the Janus kinase/Signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway in cancer stem cells in MLS
Steinberg et al. reported that a subpopulation of MLS cells with cancer stem cell characteristics possess an activated JAK/STAT signaling pathway, which controls and monitors the number of cells with cancer stem cell properties (66).
3.5.3 Role of the PIK3R3/Extracellular signal-regulated kinase/Nanog signaling pathway in sarcoma stem-like DDLPS cells
Yoon et al. reported that the PIK3R3/ERK/Nanog signaling pathway promotes the cancer stem cell phenotype in DDLPS, and identified PIK3R3 as a potential therapeutic target for DDLPS. In addition, Nanog knockdown and AKT inhibition can reduce the formation of spheroid cells and reverse drug resistance to doxorubicin and radiation (67, 68).
To date, progress in research into driver genes and molecular pathways has elucidated the mechanisms of LPS in a stepwise manner. These studies have also provided insights and guidance regarding the content and direction of clinical research.
4 Molecular targeted therapies
Genes and their expression products, related molecular pathways, and intermolecular interactions all play important roles in LPS occurrence and development. On the basis of these findings, the corresponding possible therapeutic targets have been explored in clinical practice.
4.1 Targeting MDM2: selective MDM2 inhibitors
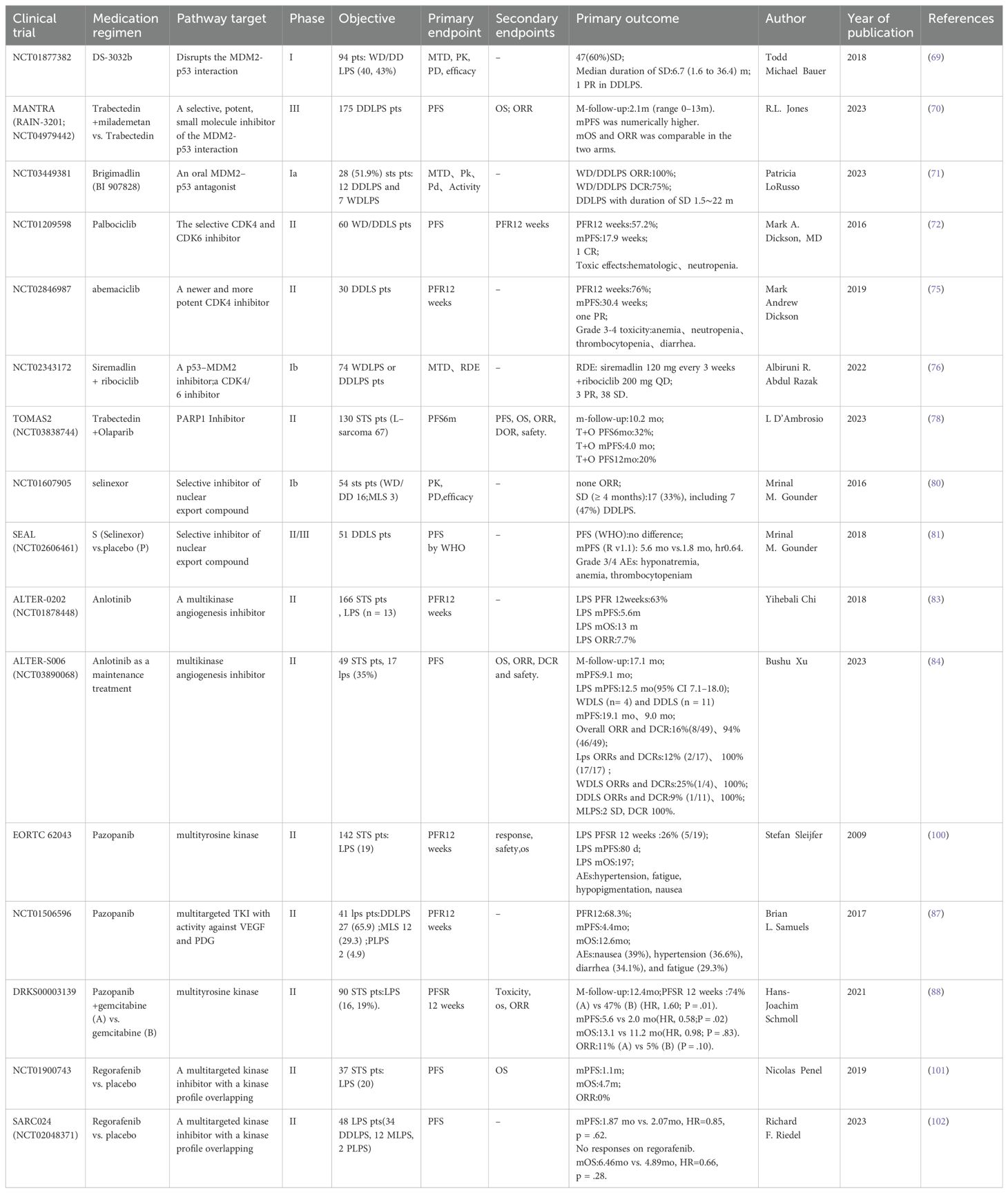
A phase I study of the MDM2 inhibitor milademetan included 48 patients with recurrent or refractory WDLPS/DDLPS, with a median PFS (mPFS) of 6.3 months; one DDLPS patient achieved a partial response (69). The MANTRA study compared the efficacy of milademetan with that of trabectedin in 178 patients with unresectable or metastatic DDLPS who had failed to respond to prior treatments. No significant differences in mPFS were observed (3.6 months vs. 2.2 months, respectively), the median overall survival was comparable (9.5 months vs. 10.2 months, respectively), and the objective response rate did not significantly differ (4.7% vs. 3.4%, respectively) between the two treatments. On the basis of these findings, the MDM2 inhibitor failed as a second-line treatment for DDLPS (70).
4.2 Brigimadlin, an MDM2-p53 antagonist
A phase Ia study evaluated the efficacy of the MDM2-p53 antagonist brigimadlin in the treatment of 54 patients with advanced/metastatic MDM2-amplified and TP53 wild-type solid tumors. The overall objective response rate was 11.1% (6 of 54), the disease control rate was 74.1% (40 of 51), and the mPFS was 8.1 months. These findings indicate that brigimadlin has potential antitumor activity in patients with DDLPS and WDLPS. In the phase Ib (dose expansion) study, the number of evaluable DDLPS patients increased to 76 cases, with a preliminary mPFS of 8.1 months (95% confidence interval: 5.7–13.6 months), an objective response rate of 19%, and a disease control rate of 85%. Moreover, in the five evaluable WDLPS patients, the disease control rate was 100% (71). A phase II/III global multicenter study comparing brigimadlin with doxorubicin as first-line treatments for advanced DDLPS patients is currently underway (Clinical Trial: NCT05218499).
4.3 Targeting CDK4: CDK4/6 inhibitors
A phase II clinical study of palbociclib in 59 patients with WD/DDLPS revealed an mPFS of 17.9 weeks, with one patient achieving a complete response that lasted over 2 years. Thirty-six percent of the patients experienced grade 3–4 neutropenia (72). In 61 patients with retroperitoneal WDLPS/DDLPS treated with the single agent palbociclib, the practical application and surgical outcomes were as follows. The mPFS for WDLPS and DDLPS patients were 9.2 and 2.6 months, respectively. In addition, 12 patients ultimately underwent surgical resection, with half of the patients achieving R0/R1 resection; however, surgery did not improve overall survival (73).
Higuchi et al. reported that a combination of palbociclib and recombinant methioninase enhanced the efficacy of palbociclib against DDLPS in a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft mouse model of LPS (74). Moreover, a phase II clinical study of patients with recurrent or metastatic DDLPS treated with abemaciclib reported an mPFS of 30.4 weeks, with two patients achieving a partial response (75).
4.4 Combination of MDM2 inhibitors and CDK4/6 inhibitors
A phase Ib study combined siremadlin (a p53-MDM2 inhibitor) with ribociclib (a CDK4/6 inhibitor) in 74 patients with advanced WDLPS and DDLPS. Three patients achieved a partial response and 38 patients had stable disease, thus demonstrating the good antitumor activity of this combination treatment (76).
4.5 Targeting PARP1: PARP1 inhibitors
PARP1 expression is heterogeneous across subtypes. High PARP1 expression is mostly found in leiomyosarcoma, is often found in Grade 3 CINSARC (Complexity INdex in SARComas) and high-risk tumors, and is associated with a shorter MFS. By contrast, low PARP1 expression is mostly found in LPS and MFS (77). A multicenter, randomized, controlled phase II clinical study (TOMAS2) explored the efficacy of trabectedin combined with the PARP inhibitor olaparib versus trabectedin alone in 130 adult patients with STS whose previous treatments had failed. Of these, 67 patients had an L-sarcoma (LPS/leiomyosarcoma) subtype. The subgroup analysis did not yield positive results for mPFS or overall survival (78).
4.6 Targeting the nuclear export protein exportin 1
Zaffaroni et al. reported that selinexor (a selective XPO1 inhibitor) has stronger antitumor activity than doxorubicin against retroperitoneal DDLPS patient-derived xenografts (79). A phase Ib study of selinexor in the treatment of advanced STS included 15 DDLPS patients. Six patients experienced a reduction in the target lesion size and seven patients achieved stable disease as the best response; this was maintained for at least 4 months (80). A subsequent study, SEAL, included 285 patients with advanced DDLPS who had previously received two to three lines of treatment, and reported an mPFS of 2.8 months. The most common grade 3–4 adverse events associated with selinexor use were nausea (80.7%), decreased appetite (60.4%), and fatigue (51.3%) (81). Another study demonstrated that selinexor treatment can help to control pain and improve quality of life in patients with advanced DDLPS (82).
4.7 Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor
In the ALTER-0202 study, 13 patients with recurrent/metastatic advanced LPS were treated with anlotinib. This treatment resulted in a 12-week progression-free rate of 63%, and mPFS and median overall survival times of 5.6 and 13 months, respectively (83). The ALTER-S006 study revealed that anlotinib maintenance treatment resulted in an mPFS of 9.1 months in 49 STS patients who achieved a partial response or stable disease after at least four cycles of first-line anthracycline-based chemotherapy; LPS patients had an mPFS of 12.5 months (84). In another retrospective study, 17 patients with metastatic/recurrent WDLPS/DDLPS who were treated with anlotinib had an mPFS of 27.9 weeks, a 24-week progression-free rate of 58.8%, and an overall survival of 56.6 weeks (85). The aforementioned studies indicate the good efficacy of anlotinib for LPS, and the use of anlotinib as a second-line treatment for patients with STS is included in the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines.
4.8 Multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitors
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend pazopanib as a second-line treatment option for patients with STS (86). In a phase II study, pazopanib was used to treat 41 patients with LPS (27 with DDLPS). This treatment resulted in a 12-week progression-free rate of 68.3%, and for DDLPS patients, the mPFS was 6.24 months (87). A multicenter phase II randomized controlled trial in Germany compared the efficacy of combined pazopanib and gemcitabine with pazopanib alone in the treatment of 90 patients with refractory STS (19% with LPS). There was a 12-week PFS of 74% vs. 47%, an mPFS of 5.6 months vs. 2.0 months, and an overall survival of 13.1 months vs. 11.2 months, respectively. However, the objective response rate was generally low, at 11% vs. 5%, respectively (88). Similarly, a previous study revealed that preoperative pazopanib treatment for nonmetastatic, resectable, high-risk STS did not benefit patients (89). In addition, in the SARC024 study, regorafenib treatment did not yield positive results for mPFS or overall survival in 48 patients with advanced LPS (90).
In summary, many types of targeted drugs have been used in the exploration of clinical treatments, and have achieved different results. Nonetheless, through continuous in-depth research, more accurate targets are expected to be obtained. The ultimate goal is to develop new drugs and novel solutions to improve the quality of life and survival of patients.
5 Research progress in immunotherapy for LPS
Multiple studies have shown broad heterogeneity in the tumor immune microenvironment of LPS based on tumor subtype, grade, size, multifocality, and primary or recurrent status (91, 92). Regarding immune microenvironments, research has mainly focused on DDLPS and MLPS; WDLPS and PLPS are therefore less understood. DDLPS is characterized by a greater abundance of TIL and a higher expression of PD-L1, whereas MLPS displays the opposite characteristics, and WDLPS is likely positioned between the two (93, 94). In terms of treatment, immune checkpoint inhibitors, therapeutic antibodies, and tumor vaccines (95), immunomodulators (96), adoptive cell therapy, and T-cell receptor−genetically engineered T-cells may become new options for patients with advanced unresectable LPS. At present, the initial efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in LPS patients is poor (97). Nonetheless, the combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors with other strategies—such as chemotherapy (98), VEGF blockers (99), cytokines, immunomodulators, radiotherapy, and other regimens—is being actively explored, and is expected to improve the oncological prognosis of LPS.
6 Discussion
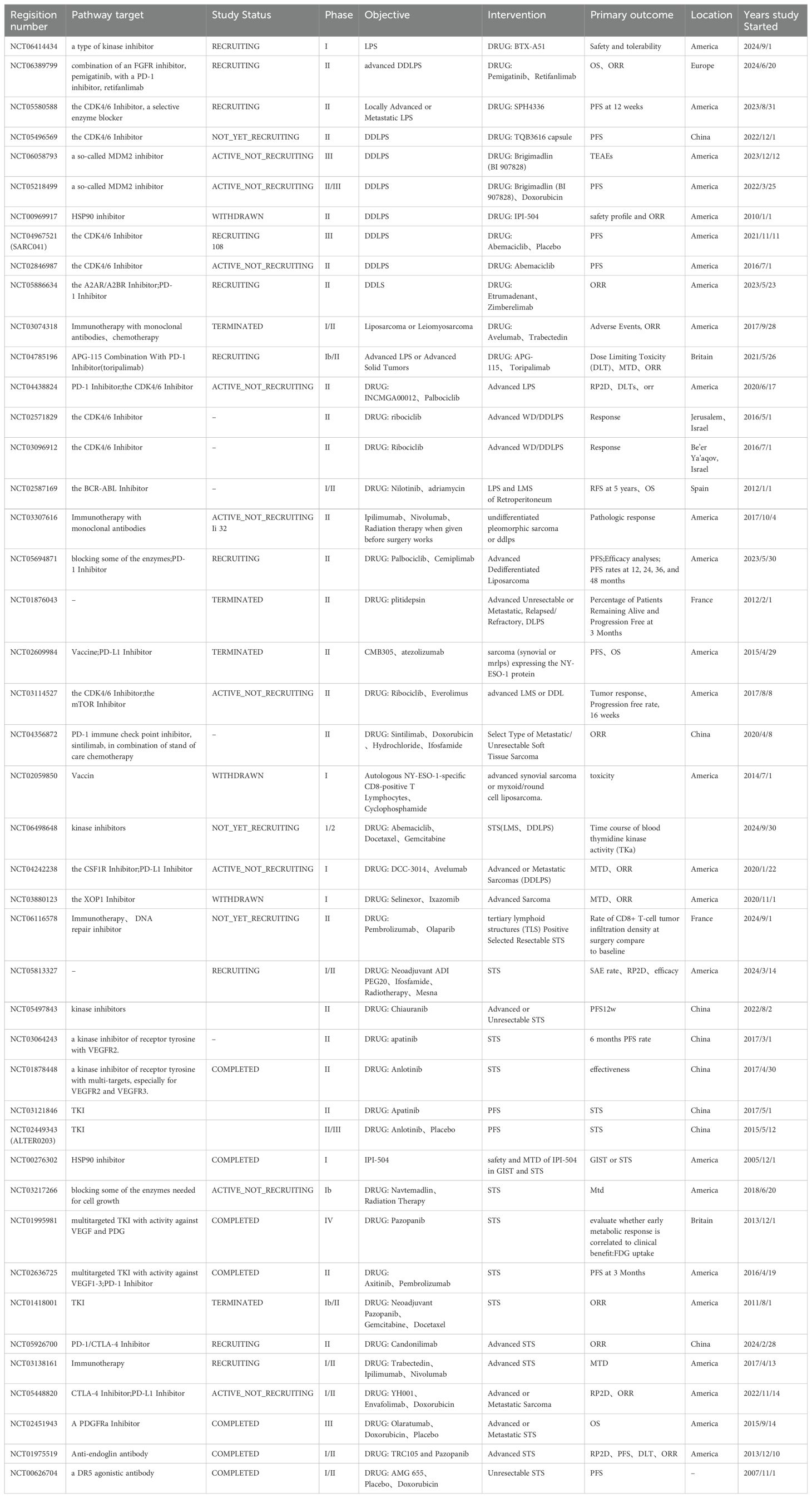
With the rapid development of medical science and technology and the continuous innovation of research methods, important progress has been made in the research and treatment of LPS. Clinical studies related to LPS targeted therapy have been collected by the authors and presented in table form. Information on clinical trials that have been completed can be found in Table 1. Information on ongoing clinical trials can be found in Table 2. In terms of LPS occurrence and the mechanisms of LPS development, extensive heterogeneity and unique characteristics exist at the molecular level. Notably, the rapid development of molecular diagnostic technology is opening the door to understanding these molecular mechanisms in a stepwise manner. Moreover, “targeted therapy” has been launched at the molecular level.
Ongoing research into LPS has led to important advancements in understanding its molecular biology. The identification of numerous genes, their RNA products, and associated downstream pathways has presented many potential targets for therapeutic intervention. In the future, the development of targeted treatment strategies based on these insights will be paramount.
Given the diversity of STS subtypes and their relatively low incidence compared with other malignancies, the research community faces the challenge of addressing a “rare” tumor with a dispersed pathology. The trajectory of future LPS research should therefore focus on two main avenues: identifying specific histological subtypes to reveal subtype-specific therapeutic opportunities, and discovering precise biomarkers to identify patient populations that are most likely to benefit from targeted therapies. Personalized medicine—crafted according to the intricate interplay of histological and molecular profiles—holds great promise for the treatment of LPS.
The progress made thus far lays a solid foundation for the next steps in LPS research. As we continue to unravel the complexities of this disease, the integration of molecular insights with clinical practice will be essential. Through this collaborative and targeted approach, we hope to improve the outcomes for patients with LPS.
Author contributions
HL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – original draft. BY: Writing – review & editing. FQ: Writing – review & editing. BZ: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Bronwen Gardner, PhD, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn/) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Gronchi A, Miah AB, Dei Tos AP, Abecassis N, Bajpai J, Bauer S, et al. Soft tissue and visceral sarcomas: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(☆). Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:1348–65. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.07.006
2. Schaefer IM, Gronchi A. WHO pathology: highlights of the 2020 sarcoma update. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. (2022) 31:321–40. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2022.03.001
3. Nacev BA, Sanchez-Vega F, Smith SA, Antonescu CR, Rosenbaum E, Shi H, et al. Clinical sequencing of soft tissue and bone sarcomas delineates diverse genomic landscapes and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:3405. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30453-x
4. Gibault L, Pérot G, Chibon F, Bonnin S, Lagarde P, Terrier P, et al. New insights in sarcoma oncogenesis: a comprehensive analysis of a large series of 160 soft tissue sarcomas with complex genomics. J Pathol. (2011) 223:64–71. doi: 10.1002/path.v223:1
5. Antonescu CR. The role of genetic testing in soft tissue sarcoma. Histopathology. (2006) 48:13–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02285.x
6. Tyler R, Wanigasooriya K, Taniere P, Almond M, Ford S, Desai A, et al. A review of retroperitoneal liposarcoma genomics. Cancer Treat Rev. (2020) 86:102013. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102013
7. Amin-Mansour A, George S, Sioletic S, Carter SL, Rosenberg M, Taylor-Weiner A, et al. Genomic evolutionary patterns of leiomyosarcoma and liposarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:5135–42. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0271
8. Matthews A, Tang M, Cooper K. Cytogenetic aberrations in soft tissue tumors harvested from fresh tissue submitted for surgical pathology: a single institutional experience. Int J Surg Pathol. (2010) 18:260–7. doi: 10.1177/1066896909346270
9. Aleixo PB, Hartmann AA, Menezes IC, Meurer RT, Oliveira AM. Can MDM2 and CDK4 make the diagnosis of well differentiated/dedifferentiated liposarcoma? An immunohistochemical study on 129 soft tissue tumours. J Clin Pathol. (2009) 62:1127–35. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2009.070201
10. Saâda-Bouzid E, Burel-Vandenbos F, Ranchère-Vince D, Birtwisle-Peyrottes I, Chetaille B, Bouvier C, et al. Prognostic value of HMGA2, CDK4, and JUN amplification in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas. Mod Pathol. (2015) 28:1404–14. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2015.96
11. Kanojia D, Nagata Y, Garg M, Lee DH, Sato A, Yoshida K, et al. Genomic landscape of liposarcoma. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:42429–44. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i40
12. Barretina J, Taylor BS, Banerji S, Ramos AH, Lagos-Quintana M, Decarolis PL, et al. Subtype-specific genomic alterations define new targets for soft-tissue sarcoma therapy. Nat Genet. (2010) 42:715–21. doi: 10.1038/ng.619
13. Haddox CL, Riedel RF. Recent advances in the understanding and management of liposarcoma. Fac Rev. (2021) 10:1. doi: 10.12703/r/10-1
14. Mantilla JG, Ricciotti RW, Chen EY, Liu YJ, Hoch BL. Amplification of DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3) is associated with myxoid liposarcoma-like morphology and homologous lipoblastic differentiation in dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Mod Pathol. (2019) 32:585–92. doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0171-y
15. Tyler R, Dilworth MP, James J, Blakeway D, Stockton JD, Morton DG, et al. The molecular landscape of well differentiated retroperitoneal liposarcoma. J Pathol. (2021) 255:132–40. doi: 10.1002/path.v255.2
16. Casadei L, de Faria FCC, Lopez-Aguiar A, Pollock RE, Grignol V. Targetable pathways in the treatment of retroperitoneal liposarcoma. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061362
17. Hirata M, Asano N, Katayama K, Yoshida A, Tsuda Y, Sekimizu M, et al. Integrated exome and RNA sequencing of dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:5683. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13286-z
18. Lago S, Nadai M, Cernilogar FM, Kazerani M, Domíniguez Moreno H, Schotta G, et al. Promoter G-quadruplexes and transcription factors cooperate to shape the cell type-specific transcriptome. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3885. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24198-2
19. Lago S, Nadai M, Ruggiero E, Tassinari M, Marušič M, Tosoni B, et al. The MDM2 inducible promoter folds into four-tetrad antiparallel G-quadruplexes targetable to fight Malignant liposarcoma. Nucleic Acids Res. (2021) 49:847–63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1273
20. Powers MP, Wang WL, Hernandez VS, Patel KS, Lev DC, Lazar AJ, et al. Detection of myxoid liposarcoma-associated FUS-DDIT3 rearrangement variants including a newly identified breakpoint using an optimized RT-PCR assay. Mod Pathol. (2010) 23:1307–15. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2010.118
21. Trautmann M, Cyra M, Isfort I, Jeiler B, Krüger A, Grünewald I, et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling is functionally essential in myxoid liposarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2019) 18:834–44. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0763
22. Koelsche C, Renner M, Hartmann W, Brandt R, Lehner B, Waldburger N, et al. TERT promoter hotspot mutations are recurrent in myxoid liposarcomas but rare in other soft tissue sarcoma entities. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 33:33. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-33
23. Conyers R, Young S, Thomas DM. Liposarcoma: molecular genetics and therapeutics. Sarcoma. (2011) 2011:483154. doi: 10.1155/2011/483154
24. Libbrecht S, Van Dorpe J, Creytens D. The rapidly expanding group of RB1-deleted soft tissue tumors: an updated review. Diagnostics (Basel). (2021) 11. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030430
25. Valenciaga A, Iwenofu OH, Tinoco G. Larotrectinib in a patient with advanced pleomorphic liposarcoma of the uterus. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2021) 19:775–9. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.7039
26. Burns J, Wilding CP, Jones RL, Huang PH. Proteomic research in sarcomas - current status and future opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 61:56–70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.11.003
27. Burns J, Wilding CP, Krasny L, Zhu X, Chadha M, Tam YB, et al. The proteomic landscape of soft tissue sarcomas. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:3834. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39486-2
28. Tang S, Wang Y, Luo R, Fang R, Liu Y, Xiang H, et al. Proteomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of soft tissue sarcoma. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:1381. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45306-y
29. Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. (1992) 69:1237–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-R
30. Sciot R. MDM2 amplified sarcomas: A literature review. Diagnostics (Basel). (2021) 11. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030496
31. Ozenne P, Eymin B, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S. The ARF tumor suppressor: structure, functions and status in cancer. Int J Cancer. (2010) 127:2239–47. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v127:10
32. Cissé MY, Pyrdziak S, Firmin N, Gayte L, Heuillet M, Bellvert F, et al. Targeting MDM2-dependent serine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for liposarcoma. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay2163
33. Seligson ND, Stets CW, Demoret BW, Awasthi A, Grosenbacher N, Shakya R, et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 reduces MDM2 expression and reduces tumor growth in dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Oncotarget. (2019) 10:5671–9. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v10i55
34. Li J, Poi MJ, Tsai MD. Regulatory mechanisms of tumor suppressor P16(INK4A) and their relevance to cancer. Biochemistry. (2011) 50:5566–82. doi: 10.1021/bi200642e
35. Wang X, Asmann YW, Erickson-Johnson MR, Oliveira JL, Zhang H, Moura RD, et al. High-resolution genomic mapping reveals consistent amplification of the fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 gene in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. (2011) 50:849–58. doi: 10.1002/gcc.v50.11
36. Zhang K, Chu K, Wu X, Gao H, Wang J, Yuan YC, et al. Amplification of FRS2 and activation of FGFR/FRS2 signaling pathway in high-grade liposarcoma. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:1298–307. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2086
37. Jing W, Lan T, Chen H, Zhang Z, Chen M, Peng R, et al. Amplification of FRS2 in atypical lipomatous tumour/well-differentiated liposarcoma and de-differentiated liposarcoma: a clinicopathological and genetic study of 146 cases. Histopathology. (2018) 72:1145–55. doi: 10.1111/his.2018.72.issue-7
38. Dadone-Montaudié B, Laroche-Clary A, Mongis A, Chamorey E, Mauro ID, Chaire V, et al. Novel therapeutic insights in dedifferentiated liposarcoma: A role for FGFR and MDM2 dual targeting. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12. doi: 10.3390/cancers12103058
39. Künstlinger H, Fassunke J, Schildhaus HU, Brors B, Heydt C, Ihle MA, et al. FGFR2 is overexpressed in myxoid liposarcoma and inhibition of FGFR signaling impairs tumor growth in vitro. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:20215–30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i24
40. Beird HC, Wu CC, Ingram DR, Wang WL, Alimohamed A, Gumbs C, et al. Genomic profiling of dedifferentiated liposarcoma compared to matched well-differentiated liposarcoma reveals higher genomic complexity and a common origin. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. (2018) 4. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a002386
41. Lu J, Wood D, Ingley E, Koks S, Wong D. Update on genomic and molecular landscapes of well-differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Mol Biol Rep. (2021) 48:3637–47. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06362-5
42. Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL, et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science. (2000) 289:950–3. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5481.950
43. Guo Y, Xie J, Rubin E, Tang YX, Lin F, Zi X, et al. Frzb, a secreted Wnt antagonist, decreases growth and invasiveness of fibrosarcoma cells associated with inhibition of Met signaling. Cancer Res. (2008) 68:3350–60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3220
44. Mazzu YZ, Hu Y, Shen Y, Tuschl T, Singer S. miR-193b regulates tumorigenesis in liposarcoma cells via PDGFR, TGFβ, and Wnt signaling. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:3197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39560-0
45. Drummond CJ, Hanna JA, Garcia MR, Devine DJ, Heyrana AJ, Finkelstein D, et al. Hedgehog pathway drives fusion-negative rhabdomyosarcoma initiated from non-myogenic endothelial progenitors. Cancer Cell. (2018) 33:108–124.e105. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.12.001
46. Beadle EP, Bennett NE, Rhoades JA. Bioinformatics screen reveals Gli-mediated hedgehog signaling as an associated pathway to poor immune infiltration of dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133360
47. Bi P, Yue F, Karki A, Castro B, Wirbisky SE, Wang C, et al. Notch activation drives adipocyte dedifferentiation and tumorigenic transformation in mice. J Exp Med. (2016) 213:2019–37. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160157
48. Song BQ, Chi Y, Li X, Du WJ, Han ZB, Tian JJ, et al. Inhibition of notch signaling promotes the adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through autophagy activation and PTEN-PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 36:1991–2002. doi: 10.1159/000430167
49. Shi Z, Xiong S, Hu R, Wang Z, Park J, Qian Y, et al. The Notch-PDGFRβ axis suppresses brown adipocyte progenitor differentiation in early post-natal mice. Dev Cell. (2024) 59:1233–1251.e1235. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.03.012
50. Ugras S, Brill E, Jacobsen A, Hafner M, Socci ND, Decarolis PL, et al. Small RNA sequencing and functional characterization reveals MicroRNA-143 tumor suppressor activity in liposarcoma. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:5659–69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0890
51. Vincenzi B, Iuliani M, Zoccoli A, Pantano F, Fioramonti M, De Lisi D, et al. Deregulation of dicer and mir-155 expression in liposarcoma. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:10586–91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i12
52. Zhang P, Bill K, Liu J, Young E, Peng T, Bolshakov S, et al. MiR-155 is a liposarcoma oncogene that targets casein kinase-1α and enhances β-catenin signaling. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:1751–62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3027
53. Trautmann M, Cheng YY, Jensen P, Azoitei N, Brunner I, Hüllein J, et al. Requirement for YAP1 signaling in myxoid liposarcoma. EMBO Mol Med. (2019) 11. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809889
54. Berthold R, Isfort I, Erkut C, Heinst L, Grünewald I, Wardelmann E, et al. Fusion protein-driven IGF-IR/PI3K/AKT signals deregulate Hippo pathway promoting oncogenic cooperation of YAP1 and FUS-DDIT3 in myxoid liposarcoma. Oncogenesis. (2022) 11:20. doi: 10.1038/s41389-022-00394-7
55. Regina C, Hettmer S. Myxoid liposarcoma: it's a hippo's world. EMBO Mol Med. (2019) 11. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201910470
56. Yu JSE, Colborne S, Hughes CS, Morin GB, Nielsen TO. The FUS-DDIT3 interactome in myxoid liposarcoma. Neoplasia. (2019) 21:740–51. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2019.05.004
57. Zullow HJ, Sankar A, Ingram DR, Samé Guerra DD, D'Avino AR, Collings CK, et al. The FUS::DDIT3 fusion oncoprotein inhibits BAF complex targeting and activity in myxoid liposarcoma. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:1737–1750.e1738. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.019
58. Tornin J, Hermida-Prado F, Padda RS, Gonzalez MV, Alvarez-Fernandez C, Rey V, et al. FUS-CHOP promotes invasion in myxoid liposarcoma through a SRC/FAK/RHO/ROCK-dependent pathway. Neoplasia. (2018) 20:44–56. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.11.004
59. Chen Y, Xu L, Mayakonda A, Huang ML, Kanojia D, Tan TZ, et al. Bromodomain and extraterminal proteins foster the core transcriptional regulatory programs and confer vulnerability in liposarcoma. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:1353. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09257-z
60. Ke XY, Chen Y, Tham VY, Lin RY, Dakle P, Nacro K, et al. MNK1 and MNK2 enforce expression of E2F1, FOXM1, and WEE1 to drive soft tissue sarcoma. Oncogene. (2021) 40:1851–67. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01661-4
61. Kanojia D, Kirtonia A, Srujana NSV, Jeevanandan SP, Shyamsunder P, Sampath SS, et al. Transcriptome analysis identifies TODL as a novel lncRNA associated with proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenesis in liposarcoma through FOXM1. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 185:106462. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106462
62. Zhang Y, Tong H, He J, Shao Y, Guo X, Zhuang R, et al. Linc00423 as a tumor suppressor in retroperitoneal liposarcoma via activing MAPK signaling pathway through destabilizing of NFATC3. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:430. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1658-2
63. Casadei L, Calore F, Braggio DA, Zewdu A, Deshmukh AA, Fadda P, et al. MDM2 derived from dedifferentiated liposarcoma extracellular vesicles induces MMP2 production from preadipocytes. Cancer Res. (2019) 79:4911–22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0203
64. Poltavets V, Kochetkova M, Pitson SM, Samuel MS. The role of the extracellular matrix and its molecular and cellular regulators in cancer cell plasticity. Front Oncol. (2018) 8:431. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00431
65. Tien PC, Quan M, Kuang S. Sustained activation of notch signaling maintains tumor-initiating cells in a murine model of liposarcoma. Cancer Lett. (2020) 494:27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.029
66. Dolatabadi S, Jonasson E, Lindén M, Fereydouni B, Bäcksten K, Nilsson M, et al. JAK-STAT signalling controls cancer stem cell properties including chemotherapy resistance in myxoid liposarcoma. Int J Cancer. (2019) 145:435–49. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v145.2
67. Yoon C, Lu J, Ryeom SW, Simon MC, Yoon SS. PIK3R3, part of the regulatory domain of PI3K, is upregulated in sarcoma stem-like cells and promotes invasion, migration, and chemotherapy resistance. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:749. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04036-5
68. Yoon C, Lu J, Yi BC, Chang KK, Simon MC, Ryeom S, et al. PI3K/Akt pathway and Nanog maintain cancer stem cells in sarcomas. Oncogenesis. (2021) 10:12. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00300-z
69. Bauer TM, Gounder MM, Weise AM, Schwartz GK, Carvajal RD, Kumar P, et al. A phase 1 study of MDM2 inhibitor DS-3032b in patients with well/de-differentiated liposarcoma (WD/DD LPS), solid tumors (ST) and lymphomas (L). Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2018). doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.11514
70. Jones R, Sanfilippo R, Schuetze S, Sebio A, Alvarez R, Bui N, et al. LBA89 Efficacy and safety findings from MANTRA: A global, randomized, multicenter, phase III study of the MDM2 inhibitor milademetan vs trabectedin in patients with dedifferentiated liposarcomas. Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:S1331. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.091
71. LoRusso P, Yamamoto N, Patel MR, Laurie SA, Bauer TM, Geng J, et al. The MDM2-p53 antagonist brigimadlin (BI 907828) in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors: results of a phase Ia, first-in-Human, dose-Escalation study. Cancer Discovery. (2023) 13:1802–13. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0153
72. Dickson MA, Schwartz GK, Keohan ML, D'Angelo SP, Gounder MM, Chi P, et al. Progression-Free survival among patients with well-Differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma treated with CDK4 inhibitor palbociclib: A phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2016) 2:937–40. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0264
73. Nassif EF, Cope B, Traweek R, Witt RG, Erstad DJ, Scally CP, et al. Real-world use of palbociclib monotherapy in retroperitoneal liposarcomas at a large volume sarcoma center. Int J Cancer. (2022) 150:2012–24. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v150.12
74. Higuchi T, Igarashi K, Yamamoto N, Hayashi K, Kimura H, Miwa S, et al. Review: Precise sarcoma patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse models enable identification of novel effective combination therapies with the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor palbociclib: A strategy for clinical application. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:957844. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.957844
75. Dickson MA, Koff A, D'Angelo SP, Gounder MM, Keohan ML, Kelly CM, et al. Phase 2 study of the CDK4 inhibitor abemaciclib in dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2019). doi: 10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.11004
76. Abdul Razak AR, Bauer S, Suarez C, Lin CC, Quek R, Hütter-Krönke ML, et al. Co-Targeting of MDM2 and CDK4/6 with siremadlin and ribociclib for the treatment of patients with well-Differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma: results from a proof-of-Concept, phase Ib study. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28:1087–97. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1291
77. Bertucci F, Finetti P, Monneur A, Perrot D, Chevreau C, Le Cesne A, et al. PARP1 expression in soft tissue sarcomas is a poor-prognosis factor and a new potential therapeutic target. Mol Oncol. (2019) 13:1577–88. doi: 10.1002/mol2.2019.13.issue-7
78. D'Ambrosio L, Merlini A, Brunello A, Ferraresi V, Paioli A, Vincenzi B, et al. LBA91 TOMAS2: a randomized phase II study from the Italian Sarcoma Group (ISG) of trabectedin plus olaparib (T+ O) or trabectedin (T) in advanced, metastatic, or unresectable soft tissue sarcomas (STS) after failure of standard treatments. Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:S1332. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.093
79. Thirasastr P, Somaiah N. Overview of systemic therapy options in liposarcoma, with a focus on the activity of selinexor, a selective inhibitor of nuclear export in dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2022) 14:17588359221081073. doi: 10.1177/17588359221081073
80. Gounder MM, Zer A, Tap WD, Salah S, Dickson MA, Gupta AA, et al. Baker S et al: Phase IB Study of Selinexor, a First-in-Class Inhibitor of Nuclear Export, in Patients With Advanced Refractory Bone or Soft Tissue Sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:3166–74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.6346
81. Gounder MM, Somaiah N, Attia S, Chawla SP, Villalobos VM, Chmielowski B, et al. Phase 2 results of selinexor in advanced de-differentiated (DDLS) liposarcoma (SEAL) study: A phase 2/3, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled cross-over study. Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2018). doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.11512
82. Gounder M, Abdul Razak AR, Gilligan AM, Leong H, Ma X, Somaiah N, et al. Health-related quality of life and pain with selinexor in patients with advanced dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Future Oncol. (2021) 17:2923–39. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0284
83. Chi Y, Fang Z, Hong X, Yao Y, Sun P, Wang G, et al. Safety and efficacy of anlotinib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with refractory metastatic soft-Tissue sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 24:5233–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3766
84. Xu B, Pan Q, Pan H, Li H, Li X, Chen J, et al. Anlotinib as a maintenance treatment for advanced soft tissue sarcoma after first-line chemotherapy (ALTER-S006): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. EClinicalMedicine. (2023) 64:102240. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102240
85. Li ZK, Liu J, Deng YT, Jiang Y. Efficacy and safety of anlotinib in patients with unresectable or metastatic well-differentiated/dedifferentiated liposarcoma: a single-center retrospective study. Anticancer Drugs. (2021) 32:210–4. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001023
86. Cassinelli G, Pasquali S, Lanzi C. Beyond targeting amplified MDM2 and CDK4 in well differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas: From promise and clinical applications towards identification of progression drivers. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:965261. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.965261
87. Samuels BL, Chawla SP, Somaiah N, Staddon AP, Skubitz KM, Milhem MM, et al. Results of a prospective phase 2 study of pazopanib in patients with advanced intermediate-grade or high-grade liposarcoma. Cancer. (2017) 123:4640–7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v123.23
88. Schmoll HJ, Lindner LH, Reichardt P, Heißner K, Kopp HG, Kessler T, et al. Efficacy of pazopanib with or without gemcitabine in patients with anthracycline- and/or ifosfamide-Refractory soft tissue sarcoma: final results of the PAPAGEMO phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2021) 7:255–62. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6564
89. Ronellenfitsch U, Karampinis I, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Sachpekidis C, Jakob J, Kasper B, et al. Preoperative pazopanib in high-Risk soft tissue sarcoma: phase II window-of opportunity study of the German interdisciplinary sarcoma group (NOPASS/GISG-04). Ann Surg Oncol. (2019) 26:1332–9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07183-4
90. Riedel RF, Ballman KV, Lu Y, Attia S, Loggers ET, Ganjoo KN, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II study of regorafenib versus placebo in advanced/metastatic, treatment-refractory liposarcoma: results from the SARC024 study. Oncologist. (2020) 25:e1655–62. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2020-0679
91. Yan L, Wang Z, Cui C, Guan X, Dong B, Zhao M, et al. Comprehensive immune characterization and T-cell receptor repertoire heterogeneity of retroperitoneal liposarcoma. Cancer Sci. (2019) 110:3038–48. doi: 10.1111/cas.v110.10
92. Tseng WW, Malu S, Zhang M, Chen J, Sim GC, Wei W, et al. Analysis of the intratumoral adaptive immune response in well differentiated and dedifferentiated retroperitoneal liposarcoma. Sarcoma. (2015) 2015:547460. doi: 10.1155/2015/547460
93. Klaver Y, Rijnders M, Oostvogels A, Wijers R, Smid M, Grünhagen D, et al. Differential quantities of immune checkpoint-expressing CD8 T cells in soft tissue sarcoma subtypes. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000271
94. Dancsok AR, Gao D, Lee AF, Steigen SE, Blay JY, Thomas DM, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages and macrophage-related immune checkpoint expression in sarcomas. Oncoimmunology. (2020) 9:1747340. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1747340
95. Chawla SP, Van Tine BA, Pollack SM, Ganjoo KN, Elias AD, Riedel RF, et al. Phase II randomized study of CMB305 and atezolizumab compared with atezolizumab alone in soft-Tissue sarcomas expressing NY-ESO-1. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:1291–300. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03452
96. Zhang S, Kohli K, Black RG, Yao L, Spadinger SM, He Q, et al. Systemic interferon-γ Increases MHC class I expression and T-cell infiltration in cold tumors: results of a phase 0 clinical trial. Cancer Immunol Res. (2019) 7:1237–43. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0940
97. Tawbi HA, Burgess M, Bolejack V, Van Tine BA, Schuetze SM, Hu J, et al. Pembrolizumab in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma (SARC028): a multicentre, two-cohort, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:1493–501. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30624-1
98. Livingston MB, Jagosky MH, Robinson MM, Ahrens WA, Benbow JH, Farhangfar CJ, et al. Phase II study of pembrolizumab in combination with doxorubicin in metastatic and unresectable soft-Tissue sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:6424–31. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-2001
99. Nowsheen S, Wieland CN, Camilleri MJ, Gibson LE, Lehman JS. Peristomal pemphigoid: A single-center retrospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2022) 86:204–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.066
100. Sleijfer S, Ray-Coquard I, Papai Z, Le Cesne A, Scurr M, Schöffski P, et al. Pazopanib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with relapsed or refractory advanced soft tissue sarcoma: a phase II study from the European organisation for research and treatment of cancer-soft tissue and bone sarcoma group (EORTC study 62043). J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:3126–32. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.3223
101. Penel N, Mir O, Wallet J, Ray-Coquard I, Le Cesne A, Italiano A, et al. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized phase II trial assessing the activity and safety of regorafenib in non-adipocytic sarcoma patients previously treated with both chemotherapy and pazopanib. Eur J Cancer. (2020) 126:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.12.001
Keywords: liposarcoma, driver genes, molecular pathogenesis, targeted therapy, outlook
Citation: Liu H, Wang X, Liu L, Yan B, Qiu F and Zhou B (2024) Targeting liposarcoma: unveiling molecular pathways and therapeutic opportunities. Front. Oncol. 14:1484027. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1484027
Received: 21 August 2024; Accepted: 25 November 2024;
Published: 11 December 2024.
Edited by:
Hanxing Tong, Fudan University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Liu, Wang, Liu, Yan, Qiu and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Zhou, YmluYWxpbkAxNjMuY29t; Fabo Qiu, cWl1ZmFib0BzaW5hLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hongliang Liu
Hongliang Liu Xi Wang
Xi Wang Lingyan Liu3†
Lingyan Liu3† Bin Zhou
Bin Zhou