
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 25 November 2024
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1481777
This article is part of the Research Topic The Molecular Mechanism in Anti-tumor Therapy Resistance View all 14 articles
Prostate cancer is a malignant tumor caused by the malignant proliferation of epithelial cells, which is highly heterogeneous and drug-resistant, and neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) is an essential cause of drug resistance in its late stage. Elucidating the evolution of NEPC and the resistance process of enzalutamide, a novel antiandrogen, will be of great help in improving the prognosis of patients. As a research hotspot in the field of molecular biology in recent years, the wide range of biological functions of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) has demonstrated their position in the therapeutic process of many diseases, and a large number of studies have revealed their critical roles in tumor progression and drug resistance. Therefore, elucidating the involvement of lncRNAs in the formation of NEPCs and their interrelationship with enzalutamide resistance may provide new ideas for a deeper understanding of the development of this disease and the occurrence of enzalutamide resistance and give a new direction for reversing the therapeutic dilemma of advanced prostate cancer. This article focuses on lncRNAs that regulate enzalutamide resistance and the neuroendocrine transition of prostate cancer through epigenetic, androgen receptor (AR) signaling, and non-AR pathways that act as “molecular sponges” interacting with miRNAs. Some insights into these mechanisms are used to provide some help for subsequent research in this area.
Prostate cancer progresses slowly but with a relatively high degree of malignancy, new cases with late clinical staging, high Gleason grade, and clinical presentation of prostate cancer with multiple metastases, which have lost the chance of surgery (1). Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is the clinically preferred treatment for prostate cancer and significantly inhibits prostate cancer progression, but almost all patients progress to the more aggressive castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) after 12-18 months of treatment (2). The emergence of a new generation of potent androgen receptor inhibitors, represented by enzalutamide, has revolutionized the concept of novel endocrine therapy for CRPC and has also primarily prolonged the survival time of CRPC-resistant patients. However, patients with effective initial therapy still experience drug resistance after a remission period of approximately 11.2 months (3). The transformation from adenocarcinoma to NEPC that occurs in patients with CRPC is now considered to be a significant cause of disease progression. Primary prostate neuroendocrine tumors are extremely rare, accounting for approximately 0.5%-2% of all prostate tumors, but the incidence of this tumor rises significantly after endocrine therapy, with 17%-30% of prostate cancer patients presenting with NEPC after endocrine therapy (4, 5). lncRNAs have essential biological functions in cells and can regulate relevant gene expression in epigenetic, pre-transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes, which are further involved in tumor development, metastasis, and drug resistance (6, 7). This article details how lncRNAs mediate CRPC treatment resistance to enzalutamide and its conversion to neuroendocrine.
NEPC is a lethal subtype of prostate cancer that encompasses all phenotypes ranging from prostate adenocarcinoma with focal NEPC cells to pure small-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Prostate tissue mainly contains ductal cells, basal cells, and neuroendocrine cells (1%) located in the basal layer, which secrete proteins involved in the composition of male semen (8, 9). NEPC can be divided into primary and treatment-related neuroendocrine prostatic carcinoma (t-NEPC); the former refers to NEPC that is present at the time of tumor development and accounts for about 0.5%-2% of first-diagnosed prostate cancers, while the latter refers to prostate cancers that show partial or complete neuroendocrine differentiation after ADT, which accounts for about 10%-20% of CRPC (10, 11). Primary NEPC is relatively rare and is clinically characterized by susceptibility to visceral metastases, low prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, and mutations or deletions in the TP53 and RB1 genes (12). Histologically, t-NEPC may present as a neuroendocrine carcinoma or a mixture of neuroendocrine carcinoma and adenocarcinoma (13, 14). Compared with adenocarcinoma, NEPC has unique gene expression characteristics. NEPC cells have delicate chromatin in the nucleus, whereas adenocarcinoma cells have a more obvious nucleolus, which suggests that the distribution of heterochromatin in NEPC is quite different from that in adenocarcinoma. In addition, it was found that there are neurodevelopment-related transcription factors such as MYCN, FOXA2, BRN2, ASCL1, and NEUROD1 that activate and drive the development of NEPC (15–17). For the evolution of NEPC (Figure 1), many previous studies have focused on the neuroendocrine transformation of prostate adenocarcinoma cells under the pressure of endocrine therapy, with reduced or loss of AR expression and expression of neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin (SYP), chromogranin A (CgA), and neuron-specific enolase (NSE), thereby transdifferentiating into NEPC (18–20). However, recent studies have found that NEPC may also originate from neuroendocrine cells with a neuroendocrine phenotype already present in adenocarcinomas. A scRNA-seq-based research found that a subpopulation of CRPC-like cells and a subpopulation of neuroendocrine cells independent of the AR signaling pathway, which share the exact origin as prostate luminal and basal cells, were present in primary prostate cancer tissues without endocrine therapy. ADT resulted in the predominance of these more value-adding AR-positive neuroendocrine cells, leading to rapid resistance to endocrine therapy and the development of NEPC in prostate cancer (18, 21, 22). NEPC is highly aggressive and lethal, capable of extensive metastasis to organs and bones, and has limited treatment options, insensitivity to hormonal therapy, and short-lived effects of chemotherapy, with a median survival of about seven months from diagnosis. It represents the terminal stage of prostate cancer (23, 24). The relevant literature suggests that the availability of the more potent hormone enzalutamide may increase the incidence of NEPC (25). Diagnosing NEPC in clinical practice is also tricky. It usually relies on features such as the paradoxical decrease in PSA and tumor metastasis; therefore, exploring its diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets and determining its resistance mechanism are the primary needs of clinical diagnosis and treatment.
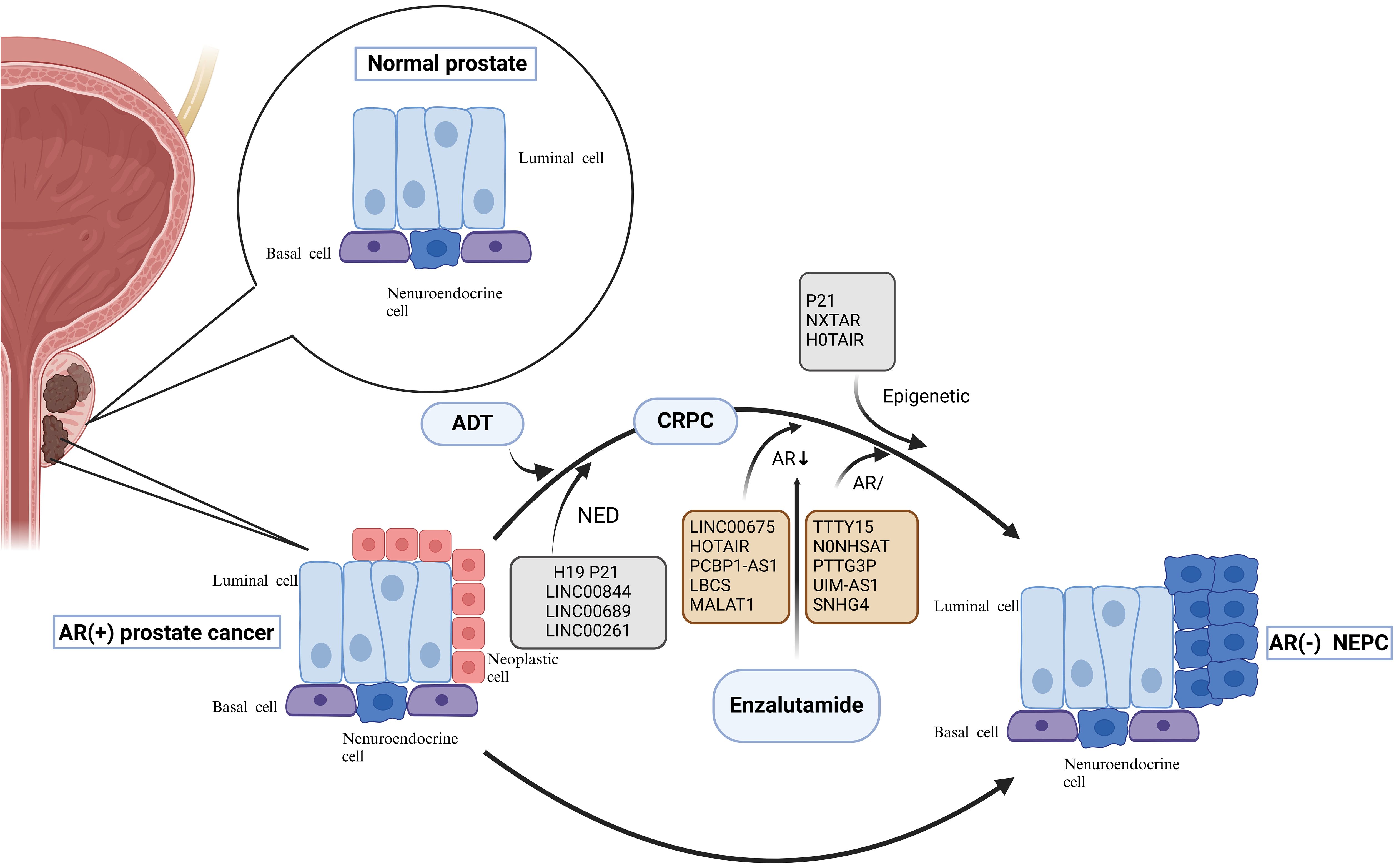
Figure 1. Neuroendocrine Evolution and drug resistance mechanism of prostate cancer. Evolution of NEPC. On the one hand, under the pressure of endocrine therapy, adenocarcinoma cells with reduced or no AR expression undergo neuroendocrine transformation; on the other hand, neuroendocrine cells in the prostate gland that share a common origin with basal and official cells progress directly to NEPC. Among them, lncRNAs can participate in the transformation of prostate cancer to NEPC by regulating the NED process; lnc RNAs can also mediate the resistance process of enzalutamide through the epigenetic pathway, the AR pathway, and related non-AR pathways. AR, androgen receptor; ADT, androgen deprivation therapy; NED, neuroendocrine differentiation; CRPC, castration-resistant prostate cancer; NEPC, neuroendocrine prostate cancer; lncRNAs, Long noncoding RNAs.
lncRNA is a class of RNA molecules with more than 200 bp length. lncRNAs are expressed less than mRNAs and are involved in tumorigenesis, drug resistance, metastasis, and prognosis by interacting with DNA, RNA, and proteins in pre-transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes (26, 27). lncRNA alterations are essential drivers of tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis. They are involved in tumor progression through mechanisms such as chromatin remodeling, transcriptional co-activation or repression, regulation of protein activity, post-transcriptional regulation, or acting as a deceptive element (19, 28, 29). The development of molecular detection techniques has led to a significant increase in the detection of lncRNAs in related fields, such as the detection of the prostate cancer lncRNA-associated transcript prostate cancer associated transcript (PCAT), paved the way for many subsequent studies. Another pan-cancer study, MiTranscriptome, identified various tissue and tumor type-specific lncRNAs (30, 31). One study investigated the expression of LINC00467 in prostate cancer tissues and cells using Western blot analysis and reverse-transcriptase PCR (RT-qPCR), and they determined that the expression of LINC00467 was upregulated in prostate cancer tissues and cells. Western blot analysis showed that LINC00467 could regulate the STAT3 pathway, and bioinformatics analysis and salvage experiments indicated that LINC00467 promoted prostate cancer progression and mediated the transformation of prostate cancer to NEPC through the miR-494-3p/STAT3 axis (32). In addition, researchers have found that one of the most prominent mechanisms by which Linc00467 regulates the development of other human malignant tumors is the Linc00467/miRNA/mRNA signaling regulation axis (Table 1). Here, LncRNAs have the properties of ceRNAs and mediate tumorigenesis and development by interacting with miRNAs. Specifically, it was found in hepatocellular carcinoma cells that Linc00467 could exert its pro-tumorigenic effect by adsorbing and inhibiting the expression of miR-9-5P/miR-18a-5p and deregulating the inhibitory effect of miR-9-5p/miR-18a-5p on PPARA/NEDD9 (33). Linc00467 can target miR-4779 and miR-7978 in lung cancer to promote lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis, and it can also adsorb miR-20b-5p to relieve the inhibitory effect of miR-20b-5p on CCND1 to promote lung adenocarcinoma cell growth (34, 35). In the study of cervical cancer, Linc00467 exerted its pro-cancer effect by targeting miR-107 and promoting the expression of KIF23 (36). In fact, in colorectal cancer, neurological tumors, and head and neck phosphoribocytic carcinoma, Linc00467 can exert its pro-cancer effects by acting on miRNAs with the properties of ceRNAs (37–39). In prostate cancer, it has been shown that Linc00467 can promote the expression of STAT3 by acting on miR-494-3, which in turn promotes the malignant progression of prostate cancer and its transformation to NEPC (32). In recent years, some researchers have discovered differential expression of lncRNAs in tumor drug-resistant cells through relevant technologies. For example, Yang (40) used high-throughput lncRNA expression profiling microarrays to detect lung cancer cell lines and cisplatin-resistant cell lines and found 1380 differentially expressed lncRNAs. Similarly, Jiang (41) used high-throughput lncRNA expression profiling microarrays to detect differentially expressed lncRNAs in breast cancer cell lines and adriamycin-resistant cell lines, and found that 1649 lncRNAs were up-regulated and 1267 lncRNAs were down-regulated. In addition, researchers have utilized lncRNA microarrays to detect differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and found that the expression of 3 lncRNAs and 46 mRNAs were significantly correlated (42). As a gene regulatory mechanism, ceRNAs can indirectly participate in the post-transcriptional regulation of mRNAs by competitively binding to the response elements of miRNAs. lncRNAs can play a regulatory role post-transcriptionally in the form of lncRNA-miRNAs. As mentioned above, lncRNAs act as miRNA “iRNAsned. spongese that influence the proteome by mediating complex formation. It was found that miRNAs interacting with the 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs can exert inhibitory effects on both RNAs and proteins. They also noted that the 3’ UTR of ceRNAs is shortened, which regulates RNA transcripts at the level of other RNA transcripts by competing for shared miRNAs and ultimately contributes to tumorigenesis. this concept of ceRNAs can also be applied to the interactions of lncRNAs and miRNAs depending on whether their genes play a promotional or inhibitory role in tumor development (43, 44). The specific signaling mechanisms by which lncRNAs interact with miRNAs to mediate neuroendocrine transformation in prostate cancer and enzalutamide resistance will also be developed later.
AR is a central signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Androgens bind to membrane-localized AR and activate AR, which binds to its homologous response elements, thereby recruiting co-regulatory factors to promote the expression of relevant genes and ultimately promote tumor cell proliferation, malignant metastasis, and resistance to relevant chemotherapeutic agents (45). Although therapeutic approaches to develop inhibitors against AR are widely used in the clinic, AR signaling can also be initiated in prostate cancer cells from the bypass via glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signaling, thus making prostate cancer cells resistant to AR inhibitors (46). Improving AR resistance is currently the most important part of prostate cancer research that needs to be addressed, and the development of lncRNA studies related to the AR signaling pathway may help to overcome AR resistance in prostate cancer. AR resistance is a great challenge to be faced during the current prostate cancer treatment, and there are multiple lncRNAs involved in the gradual development of AR resistance in prostate cancer, which can play the role of pro- or oncogenes. Long Noncoding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) is significantly overexpressed in NEPC patients. It was confirmed that H19 induced the differentiation of prostate cancer to NEPC and increased the resistance of tumor cells to ADT. It was shown that H19 acts as an epigenetic regulator in NEPC and regulates histone H3 lysine trimethylation at position 27 (H3K27me3) and histone H3 lysine trimethylation at position 4 (H3K4me3) by binding to the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) complex. This remodeled AR signaling (ARS) and NE genes in the vicinity of chromatin, which in turn regulated the expression of ARS and NE genes and activated the AR signaling pathway, ultimately promoting the transformation of prostate cancer to NEPC (23). Other studies have shown that lncRNAs can regulate enzalutamide resistance by promoting neuroendocrine in prostate cancer cells.
Luo’s study showed that lncRNA-p21 increases neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer induced by enzalutamide treatment. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is the core unit of the epigenetic effector PRC2, and lncRNA-p21 binds to EZH2 while inhibiting the binding of EZH2 to another pair of lncRNAs that have stabilizing effects on PRC2, thereby decreasing interactions between the core subunits of PRC2, interfering with the PRC2 formation and enhance the methyltransferase activity of EZH2. LncRNA-p21 also promotes the interaction of EZH2 with ATK and ATAT3, exerts multiple functions in this pathway, enhances STAT3 methylation, and induces NED development and drug resistance (47, 48). lncRNAs not only act as oncogenes to promote prostate cancer progression but also suppress the malignant phenotype of this tumor by inhibiting the AR signaling pathway. Shreyas (49) showed that LINC00844 has an inhibitory effect on tumor progression and metastasis, and the expression level of LINC00844 in normal prostate tissues was much higher than that of metastatic prostate cancer in clinical specimens. LINC00844 has an inverse role in AR signaling and represses global transcription of androgen-regulated genes. In this process, LINC00844 promotes the expression of N-myc downstream regulatory gene 1 (NDRG1), and NDRG1 acts as an AR repressor to inhibit AR expression, and the metastasis and differentiation of prostate cancer cells are also inhibited after the AR signaling pathway is suppressed. However, many related literatures indicate that lncRNAs can affect the malignant phenotype of prostate cancer through the AR signaling pathway. However, the compensatory effect of the AR signaling pathway through bypass signaling leads to poor efficacy and a high recurrence rate of prostate cancer treatment relying on the AR pathway, which also indicates that AR signaling pathway-associated lncRNAs that can be used as efficient prostate cancer therapeutic targets have yet to be explored.
Wnt signaling is a class of evolutionarily conserved signal transduction cascade pathways that play a central role in embryogenesis, trauma repair, and malignancy (50, 51). Wnts can activate various intracellular pathways, including the classical Wnt/β-catenin and non-classical Wnt pathways. Classical Wnt/β-catenin signaling is evolutionarily highly conserved and is the most frequent Wnt pathway in prostate cancer (52, 53). Meng (54)found that the expression of LINC00689 was significantly elevated in advanced prostate cancer cells, and thus, knockdown of LINC00689 significantly inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and further differentiation of this tumor and ultimately induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Additional mechanistic studies showed that LINC00689 acted as a ceRNA for the calmodulin-associated protein CTNNB1 bound to miR-496 upstream of CTNNB1 and inhibited the expression of the miRNA. miR-496 inhibited the inhibitory effect on CTNNB1, and the expression of CTNNB1 was increased, activating the Wnt signaling pathway to promote proliferation, invasion, and differentiation. This Study illustrates that LINC00689 promotes prostate cancer progression through activation of the Wnt pathway via the miR-496/CTN-NB1 axis, and thus, studying LINC0068 may provide a new direction for further treatment of prostate cancer. Furthermore, In addition to the Wnt signaling pathway, it was shown that the LncRNA LINC00261, which is highly conserved, is also involved in regulating prostate cancer transformation to NEPC. LINC00261 is significantly upregulated in patients with NEPC and acts as a sponge for the miR-8485 molecule in the cytoplasm to increase the activity of chromobox homolog2 (CBX2), thereby promoting the transformation of NEPC (55). In summary, lncRNAs can mediate prostate conversion to NEPC through the AR signaling pathway, the Wnt signaling pathway, and interaction with mRNAs (Figure 2).
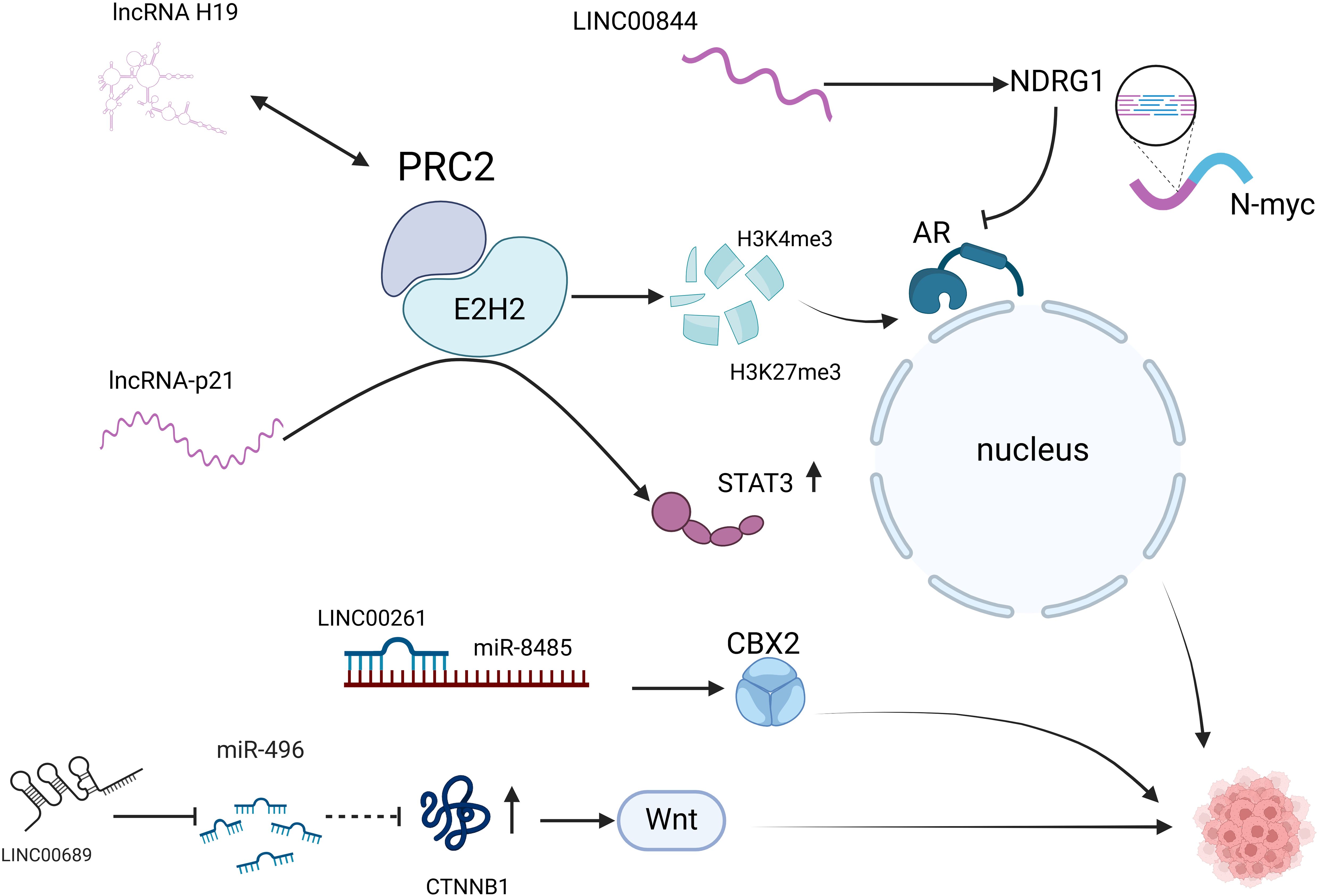
Figure 2. LncRNAs are involved in the neuroendocrine secretion of prostate cancer. AR pathway: lncRNA H19 activates AR signaling by binding to the PRC2 complex and regulating H3K27me3 and H3K4me3; lncRNA-p21 binds to EZH2 while inhibiting the binding of EZH2 to HOTAIR, interfering with PRC2 formation, and enhances methylation of STAT3; LINC00844: promotes NDRG1 expression and inhibits AR expression. Non-AR pathway: LINC00689 promotes CTNNB1 expression and activates the Wnt signaling pathway; LINC00261 acts as a miR-8485 molecular sponge and enhances CBX2 activity. AR, androgen receptor; PRC2, polycomb repressive complex 2; H3K27me3, Trimethylation modification of lysine at position 27 of histone H3; H3K4me3, The fourth lysine of histone H3 undergoes trimethylation catalyzed by methyltransferase (HMT); EZH2, enhancer of zeste homolog 2; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, STAT3; NDRG1, N-myc downstream regulatory gene 1; CTNNB1, Catenin Beta 1 is a Protein Coding gene; CBX2, chromobox homolog2.
Epigenetic modifications are closely related to tumorigenesis and development, mainly through DNA methylation, histone demethylation, and other ways to regulate gene function and expression levels. Abnormal DNA methylation is one of the critical epigenetic modifications that drive the occurrence and development of cancer. GHILDIYAL (56) reported for the first time that lncRNA-NXTAR (LOC105373241) is located on chromosome Xq12 and is repressed for expression in prostate tumors. NXTAR enhances cellular resistance to enzalutamide by interacting with AR at the epigenetic level. It was noted that NXTAR, by binding upstream of the AR promoter, promotes H3K27 methylation at the epigenetic level by mediating (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) EZH2 recruitment, resulting in a significant reduction or loss of AR and AR-V7 expression.
Conversely, AR can bind to the NXTAR promoter and inhibit AR expression using a small molecule inhibitor of ACK1/TNK2, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of enzalutamide-resistant cells and reducing enzalutamide resistance during tumor therapy. It suggests that this pharmacological restoration approach’s up-regulation of NXTAR expression can provide new ideas for treating patients who develop resistance to new-generation AR antagonists.
AR is a central signaling pathway in prostate cancer. lncRNAs can also affect enzalutamide resistance by regulating AR signaling axis transduction through different mechanisms (Figure 3). LINC00675 promotes depot resistance by blocking the binding region between AR and MDM2 and protects against ubiquitination-mediated degradation. Meanwhile, antisense oligonucleotides (ASO)-LINC00675 significantly inhibited enzalutamide resistance in CRPC cells (57). lncRNA-HOTAIR from the HOXC genome is significantly increased in prostate cancer cell lines, and HOTAIR binds to AR proteins to block their interaction with the E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2, thereby preventing AR ubiquitination and protein degradation. Knockdown of HOTAIR inhibits the proliferation of enzalutamide-resistant tumor cells and is a potential therapeutic target for reversing enzalutamide resistance (26, 58). CHANG’s (59) study concluded that HOTAIR is involved in NEPC development and drug resistance through multiple mechanisms. HOTAIR is a downstream target RNA of the neuronal restriction silencing element REST, which plays a central role in NEPC. In vitro experiments confirmed that HOTAIR was significantly upregulated in CRPC cell lines with neuroendocrine (NE) phenotype and synchronized with the increased expression of trans-neuroendocrine markers. Knockdown of the HOTAIR gene resulted in the suppression of cytokine 6 (IL-6)-induced NED, which led to the hypothesis that HOTAIR is involved in regulating IL-6-induced NED process. In addition, a gene ontology analysis of dysregulated genes in CRPC cell lines overexpressing HOTAIR identified the autophagy pathway. The autophagy pathway has a crucial role in IL-6-induced NED and chemoresistance in NEPC, and HOTAIR has demonstrated that HOTAIR may have a regulatory role in the autophagy pathway in developing NEPC and drug resistance (60).
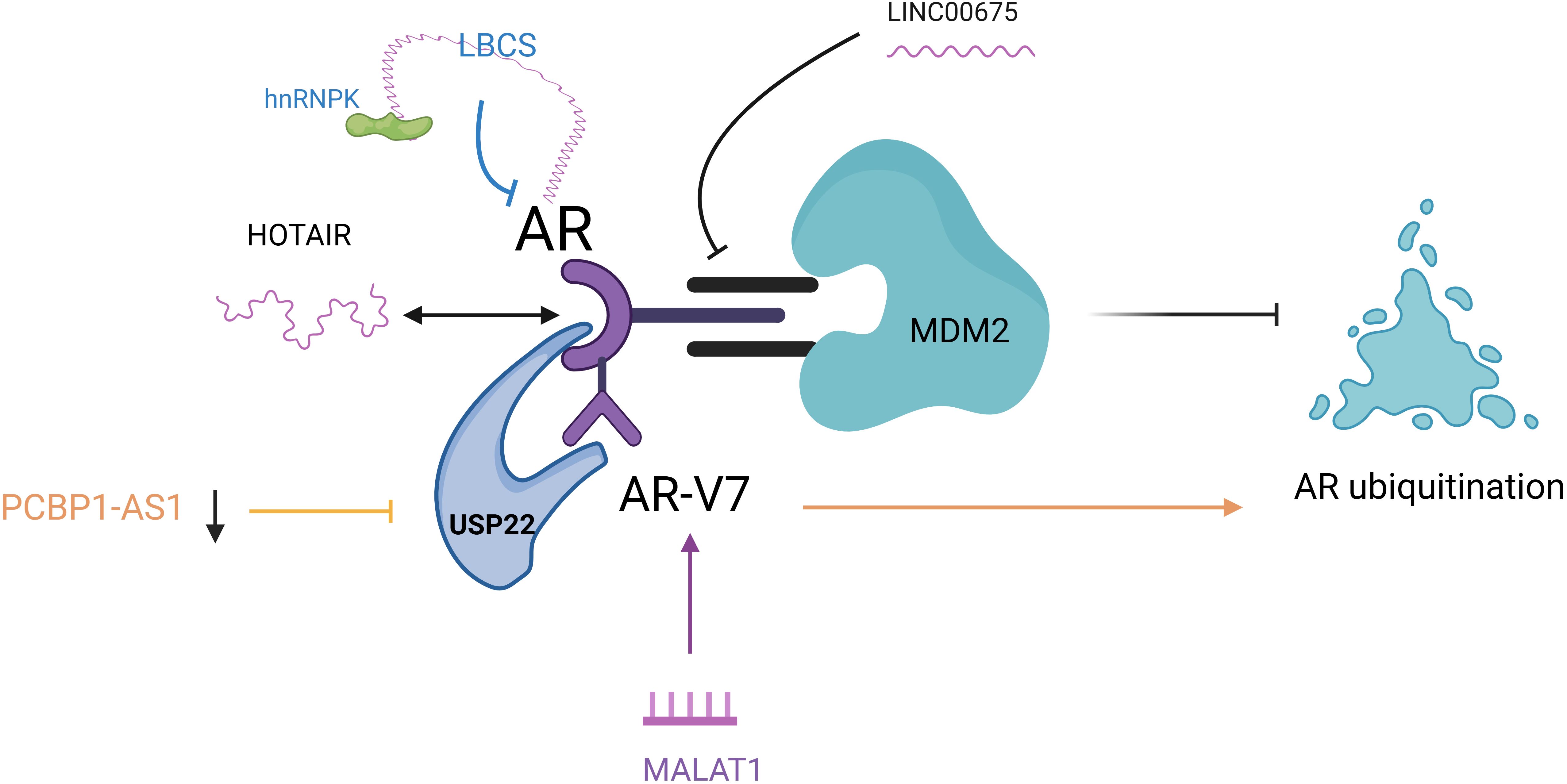
Figure 3. LncRNAs are involved in the AR pathway to regulate enzalutamide resistance. LINC00675: blocked the inter-AR and MDM2 region; HOTAIR: HOTAIR binds to AR to block its interaction with MDM2 and inhibit AR ubiquitination; PCBP1-AS1: PCBP1-AS1 expression was reduced to inhibit AR/AR-V7 and USP22 binding and promote AR ubiquitination; LBCS: acted as a scaffold for interaction with hnRNPK and AR mRNA interaction to inhibit AR expression; MALAT1: induced high expression of MALAT1/AR-V7 axis. AR, androgen receptor; MDM2, mousedouble minute 2; AR/AR-V7, Androgen receptor splicing variant 7; USP22, ubiquitin-specific processing peptidase 22; hnRNPK, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein; MALAT1, metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
Zhang (61) was the first to illustrate the vital role of lncRNA PCBP1-AS1 in CRPC resistance. They found that both PCBP1-AS1 and ubiquitin-specific processing peptidase 22 (USP22) could bind to the NTD of androgen receptor shear variant 7 (AR/AR-V7) region and interfere with PCBP1-AS1 in cells significantly attenuated the binding ability of AR/AR-V7 and USP22. At the same time, AR ubiquitination levels were significantly increased, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of C4-2EnzR cells to Enzalutamide. This Study demonstrated that targeting PCBP1-AS1 increases the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to Enzalutamide by reducing the binding of USP22 to AR-V7 or AR and decreasing the stability of the complex, providing new ideas for the clinical treatment of drug-resistant patients with CRPC. LncRNA-LBCS was significantly down-regulated in CRPC, and mechanistic studies revealed that LBCs can act as a scaffold to interact with RNA-binding protein hnRNPK and AR mRNA to form a complex as a way to inhibit AR expression (62). WANG (63) validated the role of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) in enzalutamide resistance using enzalutamide-resistant cell lines. It demonstrated that enzalutamide promotes the development of resistance by inducing high expression of the MALAT1/AR-V7 axis and that, in contrast, targeting the MALAT1/AR-V7 axis could restore the sensitivity of resistant cells to enzalutamide treatment.
In addition to their involvement in the AR signaling pathway, lncRNAs can regulate enzalutamide resistance accordingly through interactions with miRNAs and positive and negative feedback (Table 2). LncRNA TTTY15 from the Y chromosome regulates drug resistance in prostate cancer cells by upregulating cell division protein kinase 6 (cell division protein kinase 6) and fibronectin-1 (fibronectin-1) expression via sponge adsorption of miRNA-let-7 (64). A study by Chen (65) indicated that enzalutamide resistance-associated lncRNA NONHSAT-210528 can function as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) that promotes prostate cancer cell invasion and drug resistance through the miR-21-5p/YOD1 signaling pathway. They noted that NONHSAT-210528 promoted the expression of YOD1, an element involved in the regulation of enzalutamide resistance, by participating in the regulation of miR-21-5p expression in enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer cells and that when the miR-21-5p expression was inhibited, the invasive effect of LncRNA-NONHSAT-210528 on enzalutamide-resistant cells was significantly reduced. LncRNA PTTG3P can upregulate the expression of Pituitary tumor -transforming gene-1 (PTTG1) by competitive binding to miR-146a-3p, thereby promoting the development of enzalutamide resistance during prostate malignancy treatment (66). With the development of sequencing technologies, there is increasing evidence that novel lncRNAs are involved in human tumorigenesis and progression (67, 68). SHI (69) identified VIM-AS1 as a key LncRNA regulator; VIM-AS1 overexpression reduced the sensitivity to enzalutamide treatment, which plays a regulatory role in prostate cancer proliferation as well as enzalutamide sensitivity through the VIM-AS1/IGF2BP2/HMGCS1 axis. They showed that VIM-AS1 promotes the mRNA stability of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 1 (HMGCS1) by interacting with growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2), which enhances HMGCS1 expression.
Conversely, the knockdown of HMGCS1 expression ameliorated VIM-AS1 overexpression-induced prostate tumor cell progression and enzalutamide resistance. It was found that SNHG4, as one of the members of the SNHG family, belongs to the lncRNA subgroup, which is involved in the regulation of various biological expression processes in humans, such as transcription and translation of genes and modification of RNAs and proteins (70, 71). Dong (72) indicated that SNHG4 promotes prostate tumor cell growth and drug resistance through let-7a/RREB1 positive feedback and ceRNA network. The specific mechanism is that SNHG4 regulates the cell cycle control factors RRM2, EZH2, AURKA, and TK1 through a let-7 miRNA-mediated ceRNA regulatory network, which regulates gene expression, apoptosis, and tumor cell proliferation and enzalutamide resistance. In addition, RREB1 activates SNHG4 transcription and is regulated by the SNHG 4/let-7/RREB one feedback loop.
The ideal situation for tumor treatment is to kill tumor cells precisely and effectively without damaging normal cells. Early-stage limited prostate cancer can be cured by radical surgery or radiotherapy, while advanced prostate cancer is mainly treated with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT)-based combination therapy, but also gradually develops drug resistance and a neuroendocrine transformation. The current first-line treatment regimen for NEPC is a platinum-based chemotherapy regimen, but the results are poor. Targeted therapy based on small molecule inhibitors has made some breakthroughs in clinical trials for NEPC. NEPC highly expresses the oncogenic transcription factor MYCN and the cell cycle kinase AURK, and the small molecule inhibitor alisertib, which targets MYCN-AURKA, has achieved some efficacy in phase II clinical trials (73). Han (16) identified significant activation of the FOXA2-KIT signaling axis in t-NEPC, identifying the KIT signaling pathway as a therapeutic target for NEPC, but current clinical trials of KIT inhibitors in prostate cancer have not reached valid endpoints (phase III) (74). In addition, DLL3/CD3 dual-antibody Tarlatamab/AMG757 is effective in treating small-cell lung cancer (75, 76). Tarlatamab/AMG757 promotes immune response and immunotherapy by bidirectionally targeting DLL3-expressing neuroendocrine cancer cells and CD3-positive cytotoxic T cells (77). It has been shown that NEPC cells highly express DLL3, and DLL3 can sensitize the therapeutic effect of AMG757 in the t-NEPC model (78). This study provides preclinical basic research for the clinical application of AMG757 in NEPC, which is now in phase I clinical trials. lncRNAs are transcription products similar to most mRNAs, and they serve as targets for small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and small molecule inhibitors (79). This targeting of lncRNAs based on the use of siRNAs is very successful in vitro, but in vivo, the major challenge is targeting tumors with low efficiency and poor stability. However, in vivo, we found lncRNA-HOTAIR, which can act precisely on cancer cells using peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) bound to pH-(Low) Insertion Peptides (pHLIP) and inhibited the interaction of HOTAIR with EZH2. This also overcomes the challenges faced by in vivo siRNA technology (80).
Ongoing clinical trials of LncRNA-targeted therapies in prostate cancer are still minimal, which is a direction we need to explore further in the future (Table 3). We found that SSTR 5-AS1 is one of the solid predictive markers of t-NEPC. SSTR 5-AS1 has been extensively studied in neuroendocrine tumors of non-prostate origin with significant clinical potential (81–84). SSTR is used in the clinic for tumor imaging (85, 86), as a predictive marker for the prognosis of relevant tumors (87), and as a target involved in the course of therapy (82). A phase I clinical trial of SSTR 5 in patients with metastatic NEPC is now available (88). Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 (SNHG3) is expressed at high levels in prostate cancer tissues.SNHG3 mediates prostate cancer metastasis and progression by regulating TRIM25 through the sponge miR-487a-3p.SNHG3 expression and miR-487a-3p inhibitors can promote cell viability in prostate cancer (89). Targeting SNHG3 may help to prevent prostate cancer metastasis as well as the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer, for which research experiments are currently underway. In addition, relevant experiments have demonstrated that the expression of LncRNA-PRRT3-AS1 was significantly increased in prostate cancer cells, and the targeting relationship between lncRNA-PRRT3-AS1 and PPARN was demonstrated. PPARn expression was increased by targeting lncRNA-PRRT3-AS1, which inhibited the activation of the mTOR signaling pathway and thus inhibited the progression of prostate cancer cells. Therefore, targeting lncRNA-PRRT3-AS1 can also play an active role in the treatment of prostate cancer (90). In conclusion, lncRNAs have the potential to serve as non-invasive biomarkers and the ability to target therapies against tNEPC/NEPC, and they deserve to be tested in a clinical trial setting. In conclusion, lncRNAs have the potential to serve as non-invasive biomarkers and the ability to target therapies against tNEPC/NEPC, and they deserve to be tested in a clinical trial setting.
Finally, nanotherapeutic systems may be the future direction of development of anticancer drugs. Some researchers have utilized nanomaterials as a carrier, loaded with si-lncRNA, to construct a nanotherapeutic system (si-LNC@PB) targeting prostate cancer cells. The nanotherapeutic delivery system has the advantages of precise drug delivery, high stability, and improved controlled release effect, which can effectively enhance the efficacy of prostate cancer treatment (91–94). This is a specific direction that needs further research.
The molecular typing of NEPC is gradually demonstrated as the molecular pathologic typing of prostate cancer has been increasingly studied. Multiple transcription factors drive neuroendocrine carcinoma, and molecular typing of small cell carcinoma of the lung based on the transcription factors ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3, and YAP1 can provide a basis for precision targeted therapy for lung cancer patients (95). NEPC has more similarities with small cell carcinoma of the lung, but due to the small number of clinical NEPC tissue samples, multicenter cooperation is needed to conduct research related to molecular typing, which is also a challenge. We also need to conduct further research to establish molecular typing of NEPC, identify the drivers and underlying factors of the disease, and formulate corresponding therapeutic regimens, which can help to realize the precision targeted therapy of NEPC. With the development of high-throughput sequencing technologies (e.g., RNA-seq and microarrays), it has been found that noncoding RNAs, especially lncRNAs, play an essential role in the process of tumorigenesis and progression, instead of being considered as genomic “enomic or “rnomicr”. Combining morphological and multi-omics techniques with artificial intelligence to predict the evolutionary outcomes associated with prostate cancer and propose targeted intervention strategies to delay or reverse the transformation of adenocarcinoma to neuroendocrine carcinoma is a necessary intervention to prolong and enhance the quality of patient survival. Aberrant expression of lncRNAs, an indispensable component of the human transcriptome, is expected to be developed as a biomarker for interfering with NEPC formation and enzalutamide resistance. However, despite the large amount of experimental data suggesting that lncRNAs are promising for treating enzalutamide resistance, their clinical translation is still an urgent problem that needs to be solved. Furthermore, multiple resistance mechanisms can coexist due to the complexity of resistance, limiting the precision of a single therapy. Although challenging, the challenges facing enzalutamide resistance will eventually be overcome as research in preclinical work deepens.
ZZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Hu J, Sun F, Chen W, Zhang J, Zhang T, Qi M, et al. BTF3 sustains cancer stem-like phenotype of prostate cancer via stabilization of BMI1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:227. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1222-z
2. Harris WP, Mostaghel EA, Nelson PS, Montgomery B. Androgen deprivation therapy: progress in understanding mechanisms of resistance and optimizing androgen depletion. Nat Clin Pract Urol. (2009) 6:76–85. doi: 10.1038/ncpuro1296
3. Beer TM, Armstrong AJ, Rathkopf DE, Loriot Y, Sternberg CN, Higano CS, et al. Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer before chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:424–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1405095
4. Vlachostergios PJ, Puca L, Beltran H. Emerging variants of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. (2017) 19:32. doi: 10.1007/s11912-017-0593-6
5. Aggarwal R, Huang J, Alumkal JJ, Zhang L, Feng FY, Thomas GV, et al. Clinical and genomic characterization of treatment-emergent small-cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer: a multi-institutional prospective study. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:2492–503. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.77.6880
6. Hua JT, Chen S, He HH. Landscape of noncoding RNA in prostate cancer. Trends Genet. (2019) 35:840–51. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.08.004
7. Toden S, Zumwalt TJ, Goel A. Noncoding RNAs and potential therapeutic targeting in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2021) 1875:188491. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188491
8. Fine SW. Neuroendocrine tumors of the prostate. Mod Pathol. (2018) 31:S122–132. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.164
9. Hu J, Han B, Huang J. Morphologic spectrum of neuroendocrine tumors of the prostate: an updated review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2020) 144:320–5. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0434-RA
10. Alabi BR, Liu S, Stoyanova T. Current and emerging therapies for neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 238:108255. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108255
11. Kench JG, Amin MB, Berney DM, Compey EM, Cree IA, Gill AJ, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours fifth edition: evolving issues in the classification, diagnosis, and prognostication of prostate cancer. Histopathology. (2022) 81:447–58. doi: 10.1111/his.14711
12. Conteduca V, Oromendia C, Eng KW, Bareja R, Sigouros M, Molina A, et al. Clinical features of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. (2019) 121:7–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.08.011
13. Priemer DS, Montironi R, Wang L, Williamson SR, Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L. Neuroendocrine tumors of the prostate: emerging insights from molecular data and updates to the 2016 world health organization classification. Endocr Pathol. (2016) 27:123–35. doi: 10.1007/s12022-016-9421-z
14. Sleiman W, Karray O, Abi Abdallah M, Bleichner-Perez S, Kourda J, Cosma-Opris M, et al. Large-cell neuroendocrine tumor of the prostate: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. (2021) 15:254. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02830-5
15. Lee JK, Phillips JW, Smith BA, Park JW, Stoyanova T, McCaffrey EF, et al. N-myc drives neuroendocrine prostate cancer initiated from human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Cell. (2016) 29:536–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.001
16. Han M, Li F, Zhang Y, Dai P, He J, Li Y, et al. FOXA2 drives lineage plasticity and KIT pathway activation in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. (2022) 40:1306–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.10.011
17. Wang Z, Wang T, Hong D, Dong B, Wang Y, Huang H, et al. Single-cell transcriptional regulation and genetic evolution of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. iScience. (2022) 25:104576. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104576
18. Crea F, Venalainen E, Ci X, Cheng H, Pikor L, Parolia A, et al. The role of epigenetics and long noncoding RNA MIAT in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Epigenomics. (2016) 8:721–31. doi: 10.2217/epi.16.6
19. Ramnarine VR, Alshalalfa M, Mo F, Nabavi N, Erho N, Takhar M, et al. The long noncoding RNA landscape of neuroendocrine prostate cancer and its clinical implications. Gigascience. (2018) 7. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy050
20. Wang ZA, Toivanen R, Bergren SK, Chambon P, Shen MM. Luminal cells are favored as the cell of origin for prostate cancer. Cell Rep. (2014) 8:1339–46. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.002
21. Cheng Q, Butler W, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Tang L, Perkinson K, et al. Pre-existing castration-resistant prostate cancer-like cells in primary prostate cancer promote resistance to hormonal therapy. Eur Urol. (2022) 81:446–55. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.12.039
22. Marklund M, Schultz N, Friedrich S, Berglund E, Tarish F, Tanoglidi A, et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of prostate tumors in situ suggests pre-existence of treatment-resistant clones. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:5475. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33069-3
23. Singh N, Ramnarine VR, Song JH, Pandey R, Padi SKR, Nouri M, et al. The long noncoding RNA H19 regulates tumor plasticity in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:7349. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26901-9
24. Wang HT, Yao YH, Li BG, Tang Y, Chang JW, Zhang J. Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer (NEPC) progressing from conventional prostatic adenocarcinoma: factors associated with time to development of NEPC and survival from NEPC diagnosis-a systematic review and pooled analysis. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:3383–90. doi: 10.1200/jco.2013.54.3553
25. Buttigliero C, Tucci M, Bertaglia V, Vignani F, Bironzo P, Di Maio M, et al. Understanding and overcoming the mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to abiraterone and enzalutamide in castration resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. (2015) 41:884–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.08.002
26. Qu X, Alsager S, Zhuo Y, Shan B. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) in cancer. Cancer Lett. (2019) 454:90–7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.04.016
27. Bridges MC, Daulagala AC, Kourtidis A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol. (2021) 220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202009045
28. Kondo Y, Shinjo K, Katsushima K. Long noncoding RNAs as an epigenetic regulator in human cancers. Cancer Sci. (2017) 108:1927–33. doi: 10.1111/cas.13342
29. Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:3965–81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-2634
30. Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Balbin OA, Dhanasekaran SM, Cao Q, Brenner JC, et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat Biotechnol. (2011) 29:742–9. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1914
31. Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U, Sahu A, Hosono Y, et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:199–208. doi: 10.1038/ng.3192
32. Jiang H, Deng W, Zhu K, Zeng Z, Hu B, Zhou Z, et al. LINC00467 Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression via M2 Macrophage Polarization and the miR-494-3p/STAT3 Axis. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:661431. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.661431
33. Zheng Y, Nie P, Xu S. Long noncoding RNA linc00467 plays an oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the miR-18a-5p/NEDD9 axis. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121:3135–44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29581
34. Chang Y, Yang L. LINC00467 promotes cell proliferation and stemness in lung adenocarcinoma by sponging miR-4779 and miR-7978. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121:3691–9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29510
35. Ding H, Luo Y, Hu K, Liu P, Xiong M. Linc00467 promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation via sponging miR-20b-5p to activate CCND1 expression. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 12:6733–43. doi: 10.2147/ott.S207748
36. Li GC, Xin L, Wang YS, Chen Y. Long Intervening Noncoding 00467 RNA Contributes to Tumorigenesis by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA against miR-107 in Cervical Cancer Cells. Am J Pathol. (2019) 189:2293–310. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.07.012
37. Li Z, Liu J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Shi H, Huang L, et al. Ferritin Light Chain (FTL) competes with long noncoding RNA Linc00467 for miR-133b binding site to regulate chemoresistance and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2020) 41:467–77. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz181
38. Liang R, Tang Y. LINC00467 knockdown repressed cell proliferation but stimulated cell apoptosis in glioblastoma via miR-339-3p/IP6K2 axis. Cancer Biomark. (2020) 28:169–80. doi: 10.3233/cbm-190939
39. Chen Y, Ding Y. LINC00467 enhances head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process via miR-299-5p/ubiquitin specific protease-48 axis. J Gene Med. (2020) 22:e3184. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3184
40. Yang Y, Li H, Hou S, Hu B, Liu J, Wang J. The noncoding RNA expression profile and the effect of lncRNA AK126698 on cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cell. PloS One. (2013) 8:e65309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065309
41. Jiang M, Huang O, Xie Z, Wu S, Zhang X, Shen A, et al. A novel long noncoding RNA-ARA: adriamycin resistance-associated. Biochem Pharmacol. (2014) 87:254–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.10.020
42. Yang QQ, Deng YF. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA in primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma by microarray. Histopathology. (2015) 66:1022–30. doi: 10.1111/his.12616
43. Mayr C, Bartel DP. Widespread shortening of 3’UTRs by alternative cleavage and polyadenylation activates oncogenes in cancer cells. Cell. (2009) 138:673–84. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.016
44. Park HJ, Ji P, Kim S, Xia Z, Rodriguez B, Li L, et al. 3’ UTR shortening represses tumor-suppressor genes in trans by disrupting ceRNA crosstalk. Nat Genet. (2018) 50:783–9. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0118-8
45. Jacob A, Raj R, Allison DB, Myint ZW. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer and therapeutic strategies. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215417
46. Schmidt KT, Huitema ADR, Chau CH, Figg WD. Resistance to second-generation androgen receptor antagonists in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. (2021) 18:209–26. doi: 10.1038/s41585-021-00438-4
47. Luo J, Wang K, Yeh S, Sun Y, Liang L, Xiao Y, et al. LncRNA-p21 alters the antiandrogen enzalutamide-induced prostate cancer neuroendocrine differentiation via modulating the EZH2/STAT3 signaling. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:2571. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09784-9
48. Huarte M, Guttman M, Feldser D, Garber M, Koziol MJ, Kenzelmann-Broz D, et al. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell. (2010) 142:409–19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.040
49. Lingadahalli S, Jadhao S, Sung YY, Chen M, Hu L, Chen X, et al. Novel lncRNA LINC00844 Regulates Prostate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through AR Signaling. Mol Cancer Res. (2018) 16:1865–78. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-18-0087
50. Shorning BY, Dass MS, Smalley MJ, Pearson HB. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and prostate cancer: at the crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT signaling. Int J Mol Sci. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124507
51. Zhou Y, Xu J, Luo H, Meng X, Chen M, Zhu D. Wnt signaling pathway in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. (2022) 525:84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.034
52. Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, Niu C, Li Y, Zhang X, et al. Wnt/g608.16/j signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:3. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00762-6
53. Shaw V, Srivastava S, Srivastava SK. Repurposing antipsychotics of the diphenylbutylpiperidine class for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. (2021) 68:75–83. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.10.007
54. Meng L, Li Z, Chen Y, Liu D, Liu Z. LINC00689 promotes prostate cancer progression via regulating miR-496/CTNNB1 to activate Wnt pathway. Cancer Cell Int. (2020) 20:215. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01280-1
55. Mather RL, Parolia A, Carson SE, Venalainen E, Roig-Carles D, Jaber M, et al. The evolutionarily conserved long noncoding RNA LINC00261 drives neuroendocrine prostate cancer proliferation and metastasis via distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic mechanisms. Mol Oncol. (2021) 15:1921–41. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12954
56. Ghildiyal R, Sawant M, Renganathan A, Mahajan K, Kim EH, Luo J, et al. Loss of long noncoding RNA NXTAR in prostate cancer augments androgen receptor expression and enzalutamide resistance. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:155–68. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-3845
57. Yao M, Shi X, Li Y, Xiao Y, Butler W, Huang Y, et al. LINC00675 activates androgen receptor axis signaling pathway to promote castration-resistant prostate cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:638. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02856-5
58. Zhang A, Zhao JC, Kim J, Fong KW, Yang YA, Chakravarti D, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances the androgen-receptor-mediated transcriptional program and drives castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. (2015) 13:209–21. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.069
59. Chang YT, Lin TP, Tang JT, Campbell M, Luo YL, Lu SY, et al. HOTAIR is a REST-regulated lncRNA that promotes neuroendocrine differentiation in castration resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. (2018) 433:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.06.029
60. Chang PC, Wang TY, Chang YT, Chu CY, Lee CL, Hsu HW, et al. Autophagy pathway is required for IL-6 induced neuroendocrine differentiation and chemoresistance of prostate cancer LNCaP cells. PloS One. (2014) 9:e88556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088556
61. Zhang B, Zhang M, Shen C, Liu G, Zhang F, Hou J, et al. LncRNA PCBP1-AS1-mediated AR/AR-V7 deubiquitination enhances prostate cancer enzalutamide resistance. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:856. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04144-2
62. Gu P, Chen X, Xie R, Xie W, Huang L, Dong W, et al. A novel AR translational regulator lncRNA LBCS inhibits castration resistance of prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:109. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1037-8
63. Wang R, Sun Y, Li L, Niu Y, Lin W, Lin C, et al. Preclinical study using malat1 small interfering RNA or androgen receptor splicing variant 7 degradation enhancer ASC-J9(®) to suppress enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer progression. Eur Urol. (2017) 72:835–44. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.04.005
64. Xiao G, Yao J, Kong D, Ye C, Chen R, Li L, et al. The long noncoding RNA TTTY15, which is located on the Y chromosome, promotes prostate cancer progression by sponging let-7. Eur Urol. (2019) 76:315–26. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.11.012
65. Ye C, Chen YG, Qin SF, Tang SY, Li S, Shi MF, et al. Enzalutamide-resistant related lncRNA NONHSAT210528 promotes the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer. Transl Androl Urol. (2022) 11:643–58. doi: 10.21037/tau-22-99
66. Huang S, Liao Q, Li W, Deng G, Jia M, Fang Q, et al. The lncRNA PTTG3P promotes the progression of CRPC via upregulating PTTG1. Bull Cancer. (2021) 108:359–68. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2020.11.022
67. Winkle M, El-Daly SM, Fabbri M, Calin GA. Noncoding RNA therapeutics - challenges and potential solutions. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2021) 20:629–51. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00219-z
68. Park EG, Pyo SJ, Cui Y, Yoon SH, Nam JW. Tumor immune microenvironment lncRNAs. Brief Bioinform. (2022) 23. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab504
69. Shi SJ, Han DH, Zhang JL, Li Y, Yang AG, Zhang R. VIM−AS1 promotes proliferation and drives enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer via IGF2BP2−mediated HMGCS1 mRNA stabilization. Int J Oncol. (2023) 62. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5482
70. Williams GT, Farzaneh F. Are snoRNAs and snoRNA host genes new players in cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:84–8. doi: 10.1038/nrc3195
71. Zimta AA, Tigu AB, Braicu C, Stefan C, Ionescu C, Berindan-Neagoe I. An emerging class of long noncoding RNA with oncogenic role arises from the snoRNA host genes. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:389. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00389
72. Dong Q, Qiu H, Piao C, Li Z, Cui X. LncRNA SNHG4 promotes prostate cancer cell survival and resistance to enzalutamide through a let-7a/RREB1 positive feedback loop and a ceRNA network. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:209. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02774-2
73. Beltran H, Oromendia C, Danila DC, Montgomery B, Hoimes C, Szmulewitz RZ, et al. A phase II trial of the aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib for patients with castration-resistant and neuroendocrine prostate cancer: efficacy and biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:43–51. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-18-1912
74. Michaelson MD, Oudard S, Ou YC, Sengeløv L, Saad F, Houede N, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial of sunitinib plus prednisone versus prednisone alone in progressive, metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:76–82. doi: 10.1200/jco.2012.48.5268
75. Paz-Ares L, Champiat S, Lai WV, Izumi H, Govindan R, Boyer M, et al. Tarlatamab, a first-in-class DLL3-targeted bispecific T-cell engager, in recurrent small-cell lung cancer: an open-label, phase I study. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:2893–903. doi: 10.1200/jco.22.02823
76. Yang W, Wang W, Li Z, Wu J, Huang X, Li J, et al. Delta-like ligand 3 in small cell lung cancer: Potential mechanism and treatment progress. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2023) 191:104136. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104136
77. Giffin MJ, Cooke K, Lobenhofer EK, Estrada J, Zhan J, Deegen P, et al. AMG 757, a half-life extended, DLL3-targeted bispecific T-cell engager, shows high potency and sensitivity in preclinical models of small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:1526–37. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-2845
78. Chou J, Egusa EA, Wang S, Badura ML, Lee F, Bidkar AP, et al. Immunotherapeutic targeting and PET imaging of DLL3 in small-cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:301–15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-22-1433
79. Li CH, Chen Y. Targeting long noncoding RNAs in cancers: progress and prospects. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2013) 45:1895–910. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.030
80. Öze AR, Wang Y, Zong X, Fang F, Pilrose J, Nephew KP. Therapeutic targeting using tumor specific peptides inhibits long noncoding RNA HOTAIR activity in ovarian and breast cancer. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00966-3
81. Tsuta K, Wistuba II, Moran CA. Differential expression of somatostatin receptors 1-5 in neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Pathol Res Pract. (2012) 208:470–4. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2012.05.014
82. Lapa C, Hänscheid H, Wild V, Pelzer T, Schirbel A, Werner RA, et al. Somatostatin receptor expression in small cell lung cancer as a prognostic marker and a target for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:20033–40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7706
83. Herrera-Mart AD, Gahete MD, Pedraza-Arevalo S, draza-Arevalo R, Ortega-Salas R, Serrano-Blanch R, et al. Clinical and functional implication of the components of somatostatin system in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocrine. (2018) 59:426–37. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1482-3
84. Veenstra MJ, van Koetsveld PM, Dogan F, Farrell WE, Feelders RA, Lamberts SWJ, et al. Epidrug-induced upregulation of functional somatostatin type 2 receptors in human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cells. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:14791–802. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9462
85. Hope TA, Bergsland EK, Bozkurt MF, Graham M, Heaney AP, Herrmann K, et al. Appropriate use criteria for somatostatin receptor PET imaging in neuroendocrine tumors. J Nucl Med. (2018) 59:66–74. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.202275
86. Chen SH, Chang YC, Hwang TL, Chen JS, Chou WC, Hsieh CH, et al. 68Ga-DOTATOC and 18F-FDG PET/CT for identifying the primary lesions of suspected and metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: A prospective study in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. (2018) 117:480–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2017.07.007
87. Roininen N, Takala S, Haapasaari KM, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Mattson J, Heikkilä P, et al. Neuroendocrine breast carcinomas share prognostic factors with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a putative prognostic role of menin, p27, and SSTR-2A. Oncology. (2019) 96:147–55. doi: 10.1159/000493348
88. Thakur MK, Heilbrun L, Dobson K, Boerner J, Stark K, Li J, et al. Phase I trial of the combination of docetaxel, prednisone, and pasireotide in metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2018) 16:e695–703. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.01.019
89. Yu L, Ren Y. Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 mediates prostate cancer migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-487a-3p to regulate TRIM25. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. (2022) 37:451–65. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.3988
90. Fan L, Li H, Wang W. Long non-coding RNA PRRT3-AS1 silencing inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis and autophagy. Exp Physiol. (2020) 105:793–808. doi: 10.1113/ep088011
91. Pavitra E, Dariya B, Srivani G, Kang SM, Alam A, Sudhir PR, et al. Engineered nanoparticles for imaging and drug delivery in colorectal cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2021) 69:293–306. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.06.017
92. Huang P, Wang X, Liang X, Yang J, Zhang C, Kong D, et al. Nano-, micro-, and macroscale drug delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. (2019) 85:1–26. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.12.028
93. Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2021) 20:101–24. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
94. Nikezić AVV, Bondzić AM, Vasić VM. Drug delivery systems based on nanoparticles and related nanostructures. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2020) 151:105412. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105412
Keywords: long noncoding RNA, enzalutamide, enzalutamide resistance, neuroendocrine prostate cancer, AR, prostate cancer
Citation: Zhu Z, Xuan W, Wang C and Li C (2024) Long noncoding RNA mediates enzalutamide resistance and transformation in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Front. Oncol. 14:1481777. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1481777
Received: 16 August 2024; Accepted: 08 November 2024;
Published: 25 November 2024.
Edited by:
Chunbo He, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Ritika Tiwari, University of Miami, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Zhu, Xuan, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chancan Li, bGloYW5jYW5Ac2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.