
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol. , 15 November 2024
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1475000
 Ziheng Ni1†
Ziheng Ni1† Hao Zhang1†
Hao Zhang1† Fengyun Chen1
Fengyun Chen1 Mengjie Yang1
Mengjie Yang1 Liting Yang1
Liting Yang1 Yuan Zhou1
Yuan Zhou1 Xianmin Zhou1
Xianmin Zhou1 Jiayi Guo1
Jiayi Guo1 Xinyu Rao1
Xinyu Rao1 Jiaqi Cen1
Jiaqi Cen1 Qun Lv2
Qun Lv2 Jianjun Wang2
Jianjun Wang2 Lailing Du3*
Lailing Du3* Gongxing Chen1,4*
Gongxing Chen1,4* Shuiping Liu1,4*
Shuiping Liu1,4*In recent years, some components and active ingredients from the herbal formula “eight famous herbals in Zhejiang” (Zhe-Ba-Wei) have been reported to possess antitumor properties. However, there is still no systemic study on the role and mechanism of Zhe-Ba-Wei in cancer. To systematically investigate the anticancer efficacy of Zhe-Ba-Wei, we first identified 17 reported active ingredients with gene targets associated with various types of tumors. Second, we screened these active ingredients and their responding multiple shared targets by analyzing the convergence of diverse and tumor-specific target sites and identified four crucial active ingredients (ferulic acid, quercetin, rutin, luteolin), which were characterized by 27 overlapping gene targets. Third, these 27 gene targets were subsequently mapped onto the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway and Gene Ontology term, and among the 27 total potential targets, 12 were involved in plasma membrane function. Fourth, we investigated the binding affinities between the four crucial active ingredients and their potential targets such as EGFR and MET, both of which are well-known oncogenes in various cancers. Subsequently, an investigation of the computational ADMET properties showed that most of these four ingredients exhibited good ADMET properties. Finally, we found that three active ingredients (ferulic acid, luteolin, and quercetin) could inhibit the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells and decrease the protein expression of EGFR in a concentration-dependent manner. All these results shed light on the bioactive components, pharmacological effects, and drug development and utilization of Zhe-Ba-Wei, aiming to provide useful support for its further research and clinical application.
The traditional Chinese medicine “eight famous herbals in Zhejiang” (well-known as Zhe-Ba-Wei), consisting of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Fritillaria thunbergii Miq., Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat., Corydalis yanhusuo W., Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl., Ophiopogon japonicus (Thunb.) Ker-Gawl., and Curcuma wenyujin Y.H. Chen et C. Ling, is a famous herbal formula in Zhejiang (1, 2). Recently, increasing evidence shows that traditional Chinese medicine has been widely used in the treatment of various types of cancer, with reduced drug resistance and side effects (3–6).
Modern pharmacological studies have shown that some components or active ingredients of Zhe-Ba-Wei can exert therapeutic activities on various cancers such as malignant brain glioma (7), leukemia (8, 9), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (10–12), breast cancer (13), bladder cancer (14), prostate cancer (15, 16), colorectal cancer (17–19), cervical cancer (20), and gastric cancer (21–23). Taking A. macrocephala Koidz. as an example, it has a certain inhibitory effect on bladder cancer (24), colorectal cancer (25), breast cancer (26), and pancreatic cancer (27). Most recently, an increasing number of bioactive ingredients and their potential targets have been identified with the improvement of separation and identification technology (28–31). For instance, C. wenyujin Y.H. Chen et C. Ling, which is one component of Zhe-Ba-Wei exerting therapeutic activities on cancer, contains mainly volatile oils (elemene, furandiene, curcumenol, gemarone, diterpenoid C, curcumin), curcuminoid, and other relative active compounds (32–36).
Although several articles revealed the biofunction of the components or active ingredients of Zhe-Ba-Wei in various cancers, there is a limited systemic study on the therapeutic effects of Zhe-Ba-Wei as an entirety in cancer. This study primarily utilized network pharmacology inference to explore the potential therapeutic effects of Zhe-Ba-Wei on malignant tumor cells. Meanwhile, we analyzed and provided relevant information on the selected active ingredients and their potential targets, as well as conducted a prognostic analysis of these targets in various tumors. Furthermore, we conducted experiments to verify the anticancer effect of selected bioactive ingredients and their corresponding targets.
We retrieved pertinent information regarding the active ingredients of Zhe-Ba-Wei with anticancer properties from PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.gov), using Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Fritillaria thunbergii Miq., Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat., Corydalis yanhusuo W., Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl., Ophiopogon japonicus (Thunb.) Ker-Gawl., and Curcuma wenyujin Y.H. Chen et C. Ling as keywords.
SwissTargetPrediction (http://www.wisstargetprediction.ch) is a free database based on compound structures to predict the potential targets for active ingredients. OMIM (http://www.omim.org/) and GeneCards (http://www.genecards.org) are searchable and integrated human genes database that provide concise genomic information on all known and predicted human genes. Discovery Studio 2019 is a professional life science molecular simulation software applied to probe the binding affinity between active ingredients and potential disease targets through semiflexible docking. Discovery Studio 2019 receptors and ligands were obtained from the PDB database (https://www.rcsb.org/) and PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), respectively. The PDB codes of the receptor proteins are MET:5EOB and EGFR:1M17. These receptor proteins were treated in Discovery Studio 2019 as follows:1) delete water, 2) clean protein, 3) define receptor, 4) define binding sites, and 5) delete ligand.
Ligands were also processed in Discovery Studio 2019. We need to select “prepare ligands” and then “apply forcefield” operation on the prepared ligands. “CDOCKER Energy” was used for assessing the docking efficiency of these active ingredients, estimating their ability to form stable interactions.
The Discovery Studio 2019 software was used to predict the ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) properties of active ingredients including aqueous solubility, blood–brain barrier penetration, human intestinal absorption, hepatotoxicity, cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibition, and plasma protein binding. Similarly, the Discovery Studio 2019 was employed to predict the toxicity of active ingredients. The “TOPKAT” module was utilized to forecast toxicity parameters such as rodent carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, aerobic biodegradability, and rat oral LD50.
Human NSCLC cell lines (A549, PC9, and H1975) were from the ATCC and authenticated by short tandem repeat DNA profiling analysis. All cells were cultured with RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco BRL, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and incubated in a cell incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2. For the cell proliferation inhibition assays, 3,000 NSCLC cells in a 100-μL medium were inoculated into each well of a 96-well plate, together with an equal amount of PBS in the marginal wells to avoid edge effect. After treating with different concentrations of drugs for the indicated hours, 100 μL of the diluted CCK-8 solution was added into each well and incubated for 1–2 h according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, the OD value was evaluated by the Multiskan FC microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, USA), and GraphPad 7.0 was used to calculate and analyze the IC50 of the drug (37). All experiments were repeated at least three times.
The cells were collected and lysed with RIPA buffer (#P0013B, Beyotime, China). Twenty micrograms of total protein was used for SDS-PAGE after concentration measurement and then transferred to a PVDF membrane at 250 mA for an appropriate time. After blocking with 5% skim milk for 1 h, the membrane was incubated overnight with primary antibody (1:1,000). Subsequently, it was washed with PBST buffer and incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1,000) for 1 h. Finally, the ECL kit (#1705061, Bio-Rad, USA) was used and visualized with ChemiDoc Imaging System (Bio-Rad, USA) (38).
Numerous active ingredients associated with antitumor properties have been discovered in Zhe-Ba-Wei as reported in the literature. Taking cancer-related ingredient as the criterion, five active ingredients from A. macrocephala Koidz., one from P. lactiflora Pall., five from C. morifolium Ramat., five from C. yanhusuo W., and one from C. wenyujin Y.H. Chen et C. Ling were selected (Table 1). It is worth noting that no literature has reported any active compounds with anticancer potential in F. thunbergii Miq., S. ningpoensis Hemsl., and O. japonicus (Thunb.) Ker-Gawl. Subsequently, the SMILES number of these 17 active ingredients were identified in PubChem, and the potential targets for various active ingredients were obtained through the online server SwissTargetPrediction (39) (Supplementary Table S1).
To investigate the overlapping targets of active ingredients, these 17 active ingredients were paired together to select the overlapping targets influenced by every two active ingredients. Subsequently, the overlapping targets of every two active ingredients were amalgamated, resulting in the formation of a merged group encompassing every three active ingredients’ overlapping targets. Similarly, the subset comprising the three active components with a greater number of overlapping targets underwent pairwise pairing to obtain a cohort of four active ingredients with the highest degree of shared targets. However, there were limited overlapping targets for every five active ingredients. Thus, based on the screening process, a group of four active ingredients, namely, ferulic acid, rutin, quercetin, and luteolin (referred to as group 1), characterized by a substantial number of overlapping targets, has been successfully identified (Table 2). Interestingly, all four active ingredients come from the same herbal C. morifolium Ramat. Meanwhile, an additional group, denoted as group 2 (such as palmatine, coptisine, tetrahydrocoptisine, and berberine), derived from the same herbal C. yanhusuo W., displayed a notable intersection of targets and possessed a considerable number of overlapping targets (Table 2).
Based on the literature reported, the antitumor properties of diverse active ingredients primarily target the following 12 types of cancers: lung cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, leukemia, pancreatic cancer, melanoma, and glioma. Henceforth, all the reported gene targets that correlated with each of these 12 types of cancer were identified from the OMIM (40) and GeneCards databases (41), respectively (Supplementary Table S2). Next, we analyzed the overlapping targets between the four active ingredients (group 1 or group 2) and cancer disease using Venn diagrams. As a result, the numbers of overlapping targets between group 1 and different cancers are shown in Figures 1A, B, but the numbers of overlapping targets between group 2 and cancer disease were limited for further analysis. Thus, we focus our study on the overlapping targets between group 1 and cancers.
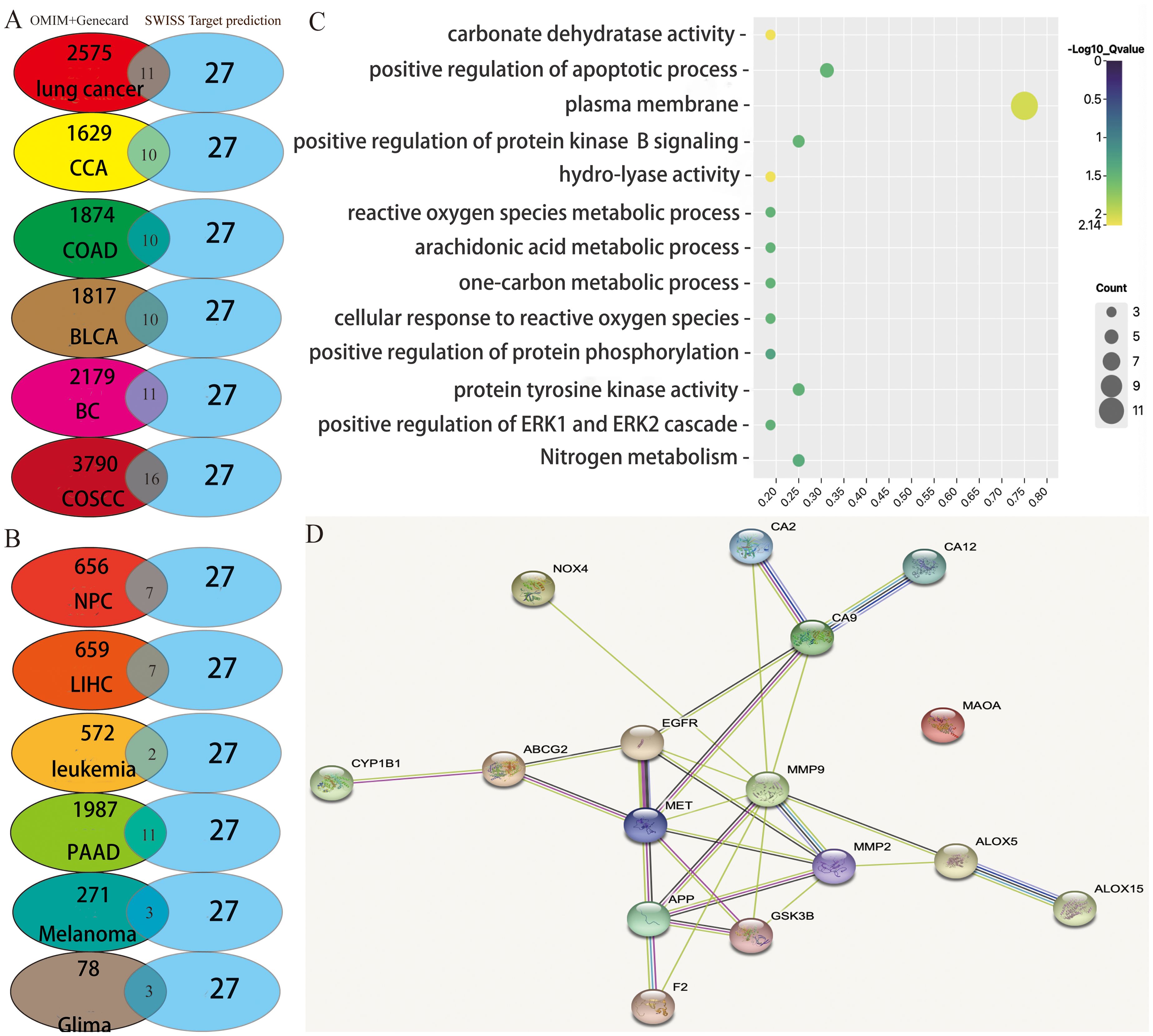
Figure 1. Potential target prediction and analysis of the KEGG pathway, GO_BP, and target–target interaction. (A, B) Overlapping target analysis by Venn diagrams; (C) KEGG pathway enrichment and GO_biological process analysis of the overlapping targets; (D) target–target interaction of the overlapping targets analyzed by STRING.
Through analysis of the Venn diagrams, it was observed that when the active ingredients of group 1 acted in concert, they shared nine common therapeutic targets among nine types of cancers: lung cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and pancreatic cancer. These targets included arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5), glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3B), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2), recombinant cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1), ATP-binding cassette superfamily G member 2 (ABCG2), carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and mesenchymal to epithelial transition factor (MET). These nine targets have been extensively studied and are known to play pivotal roles in tumor proliferation, drug resistance, and metastasis. Therefore, the potential of these active ingredients in treating tumors warrants further exploration in future studies. Nevertheless, melanoma and glioblastoma share only two overlapping targets (EGFR and MMP2). Furthermore, the active ingredients of group 1 exhibited seven additional targets—F2, ALOX15, NOX4, MAOA, APP, CA2, and CA12—that are distinct from the nine aforementioned cancer types.
Consequently, the complete array of target genes of these four active ingredients was charted into the KEGG pathways and subjected to analysis utilizing Gene Ontology (GO) terms through the DAVID tool (Figure 1C). This approach was undertaken to explore the signaling pathways and biological processes through which these four active ingredients exert their anticancer effects.
A false discovery rate threshold of less than or equal to 0.05 was employed to sieve out the signaling pathways and biological processes of higher reliability. Interestingly, we solely acquired the nitrogen metabolism signaling pathway along with 12 additional GO terms (Figure 1C). Among them, the GO term exhibiting the strongest correlation with these targets was involved in the plasma membrane. Twelve among the 17 total potential targets (namely, ABCG2, MET, NOX4, APP, ALOX15, CA12, CA2, CA9, F2, EGFR, GSK3B, and MMP2) were associated with this particular biological function. It suggested that the active ingredients we screened potentially exert their anticancer effects by selectively targeting proteins situated on the cellular plasma membrane. In addition, the interconnections among target proteins were investigated using STRING (https://cn.string-db.org/), a highly convenient web platform that facilitates the retrieval of known and predicted protein interactions. The outcomes obtained from the aforementioned website unveil a notable level of interplay between the target proteins, excluding monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) (Figure 1D), which displays relatively lower interaction levels.
Considering that both EGFR (42) and MET (43) reside on the cellular membrane, we have opted to pursue further investigation into these two proteins as potential drug targets. Their localization on the cell membrane underscores their significance and motivates our continued research efforts in this direction. It is well-established that EGFR and its associated pathways significantly contribute to tumor progression. EGFR participates in the ERBB signaling pathway, whereas MET is expressed in its alternative pathway, and GSK3B is situated in its downstream pathway known as the PI3K–Akt signaling pathway (Figure 2) (44), which plays critical roles in NSCLC, breast cancer, glioma, etc. According to previous reports, EGFR on the plasma membrane is the receptor for epithelial growth factor (EGF), and mutation or overexpression of EGFR is associated with tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and apoptosis (45). MET is present in the bypass pathway of the ERBB signaling pathway and is a proto-oncogene that interacts with EGFR, thereby promoting drug resistance of the tumor (46). GSK3B is involved in the PI3K–Akt signaling pathway, which can promote the proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenesis of tumor cells (47, 48). In summary, the three proteins mentioned above are most likely the important targets of the four active ingredients we screened; therefore, we speculate that these four active ingredients may have expected therapeutic effects on NSCLC and breast cancer by inhibiting the EGFR and MET (49, 50) in the following text.
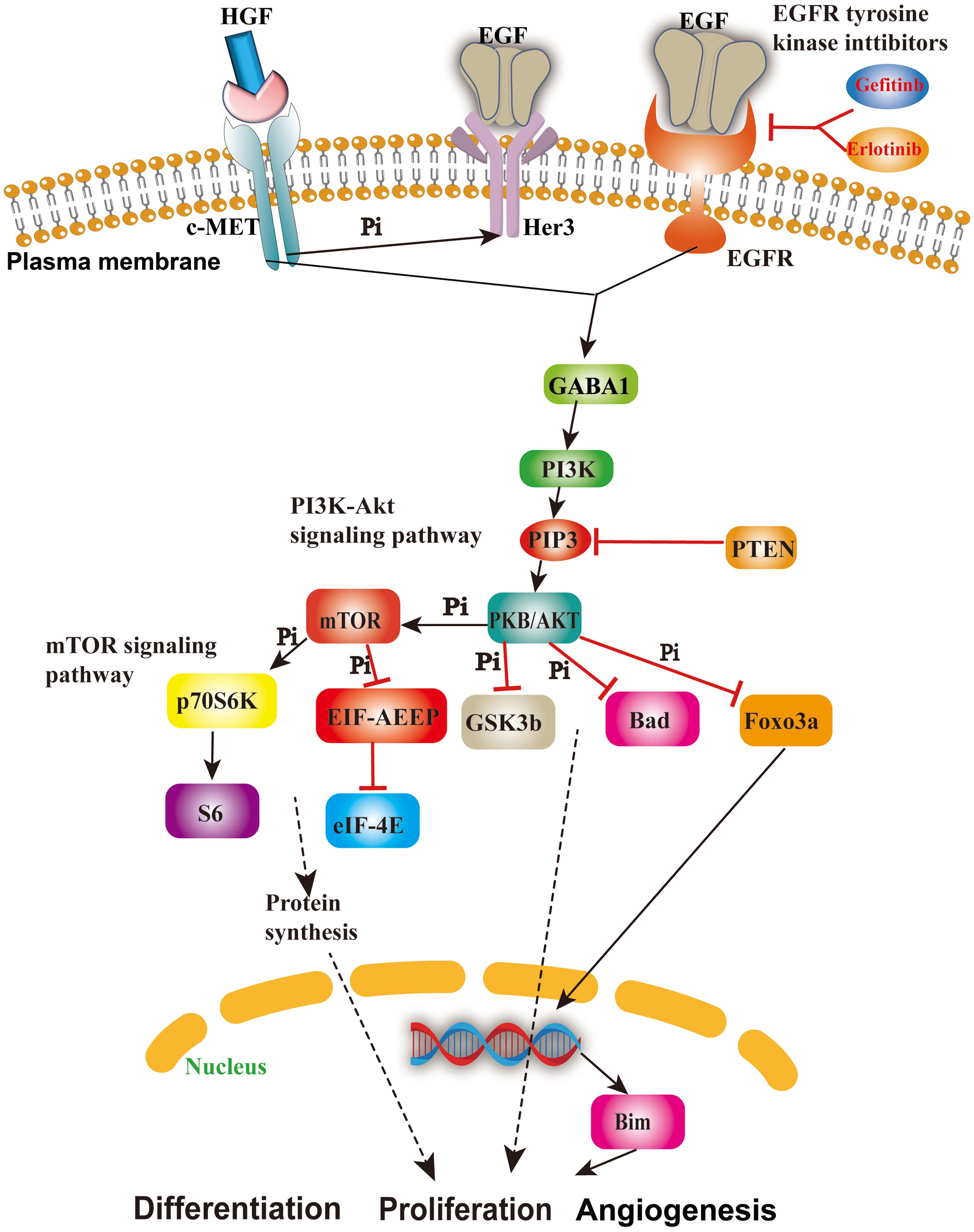
Figure 2. The role and mechanism of the EGFR/MET-mediated signaling pathway in cancer cells. This figure shows the important cascades associated with the EGFR/MET-mediated signaling pathway involved in cell angiogenesis, proliferation, and apoptosis.
To enhance our understanding of the potential interactions between small molecule active components and protein receptor targets, we employed molecular docking techniques utilizing Discovery Studio 2019. The results from this analysis revealed that ferulic acid (Figure 3A), quercetin (Figure 3B), and luteolin (Figure 3D) exhibited remarkable binding affinity toward the EGFR protein, as evidenced by their -CDOCKER energy values of 25.3315 kcal/mol, 36.8433 kcal/mol, and 36.801 kcal/mol, respectively. These findings highlighted the significant potential of EGFR as a target for these compounds. In addition, rutin (Figure 3C) exhibited relatively low binding affinity to EGFR protein with -CDOCKER energies of 3.6186 kcal/mol.
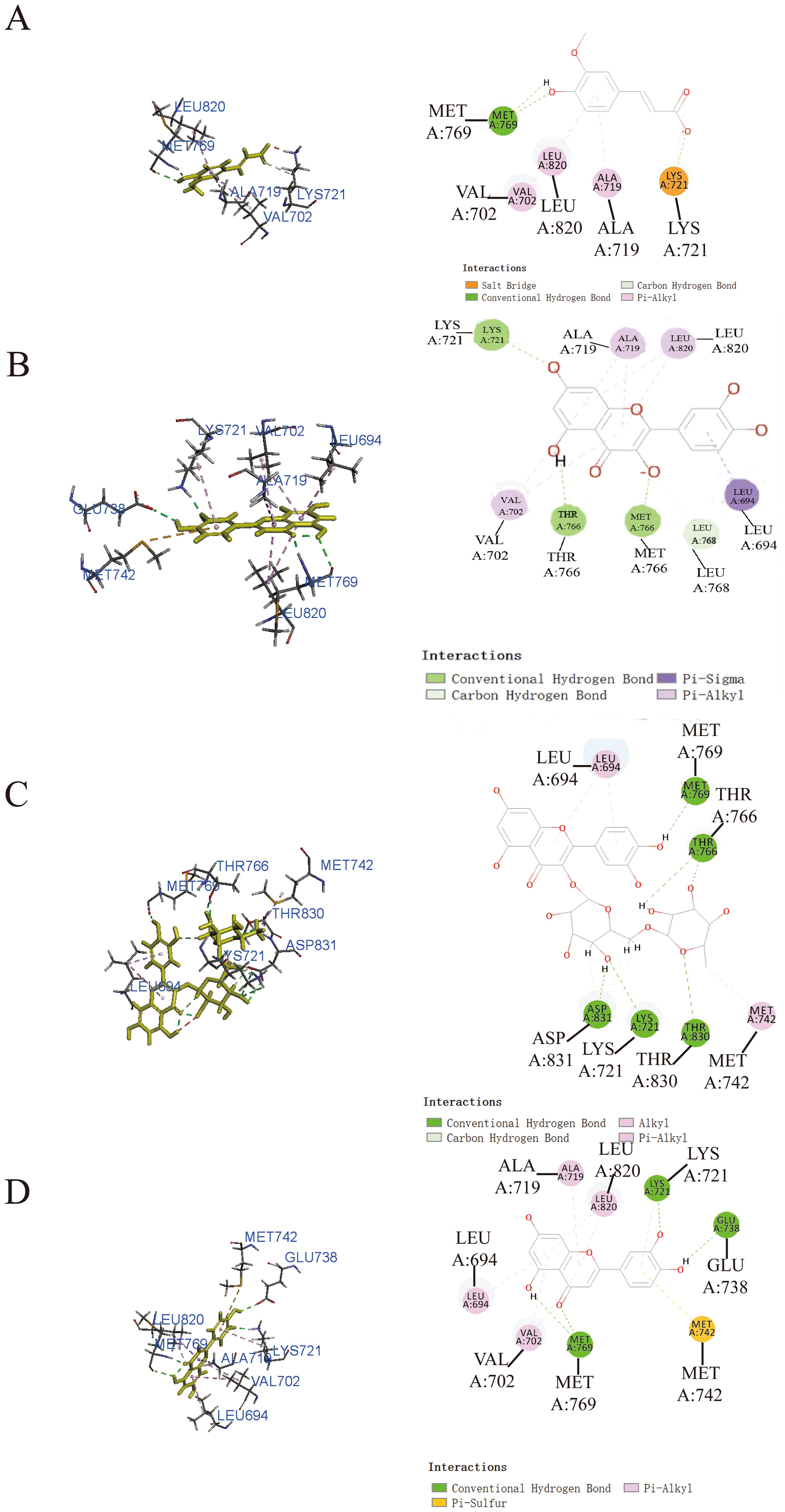
Figure 3. Prediction of the interaction between EGFR and indicated drug by molecular docking. Molecular docking diagrams of ferulic acid (A), quercetin (B), rutin (C), and luteolin (D) with the target protein EGFR.
Additionally, it was worth noting that ferulic acid (Figure 4A), quercetin (Figure 4B), and luteolin (Figure 4D) also exhibited notable binding affinity to MET, as supported by the theoretical analysis utilizing -CDOCKER energy values of 23.2231 kcal/mol, 33.6036 kcal/mol, and 35.1918 kcal/mol, respectively. In addition, rutin (Figure 4C) exhibited relatively low binding affinity to MET protein with -CDOCKER energies of 1.55349 kcal/mol.
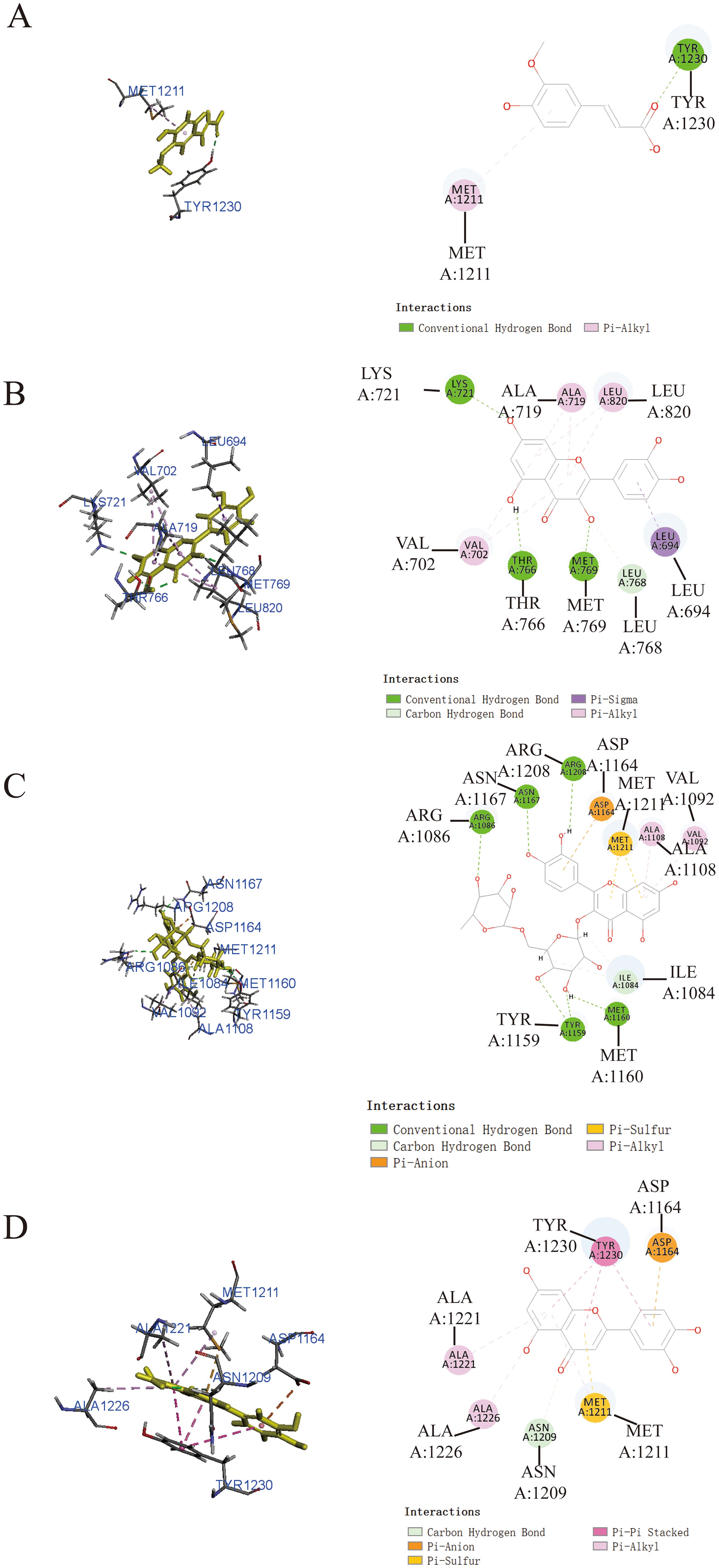
Figure 4. Prediction of the interaction between MET and indicated drug by molecular docking. Molecular docking diagrams of ferulic acid (A), quercetin (B), rutin (C), and luteolin (D) with the target protein MET.
The in-silico prediction of ADMET properties stands as a pivotal stage in lead compound discovery and drug development, enabling substantial savings in time, manpower, material resources, and financial resources. The ADMET properties of the four active ingredients were individually predicted using the four most used anticancer drugs in clinics (namely, pemetrexed, osimertinib, gemcitabine, and taxol) as control, employing ADMET descriptors and the Lipinski filter tools provided by Discovery Studio 2019. The analysis provided essential physical parameters, such as aqueous solubility, blood–brain barrier penetration, human intestinal absorption, hepatotoxicity, cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibition, and plasma protein binding.
As shown in Figure 5, ferulic acid exhibited the most favorable ADMET characteristics among the four bioactive constituents. The parameters were evaluated according to Lipinski’s rule of five (ROF), which serves to assess the drug-like characteristics of the compounds. Furthermore, ferulic acid, luteolin, and quercetin exhibited reasonably favorable absorption parameters. However, the analysis results indicated that rutin’s absorption and blood–brain barrier permeability were not ideal.
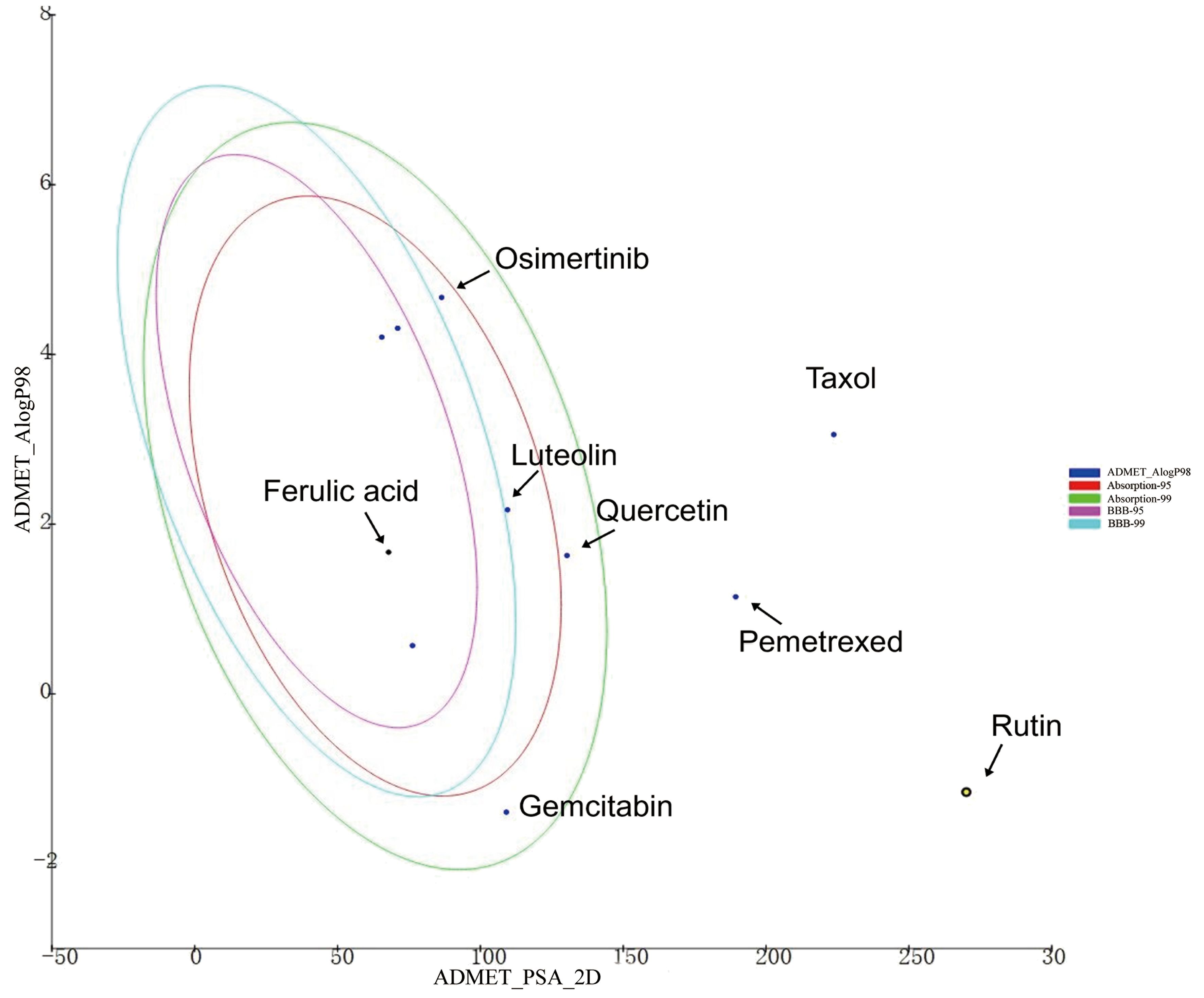
Figure 5. The ADMET plot of indicated drugs plotted by ADMET_PSA_2D vs. ADMET _AlogP98. The dark blue dots represent the AlogP98 of each drug. The red and green ellipses represent the 95% and 99% confidence intervals of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability model, respectively, and the rose red and light blue ellipses represent the 95% and 99% confidence intervals of the human intestinal absorption model, respectively.
Among the four active ingredients, rutin stood out with an AlogP value below 0, indicating its inferior blood–brain barrier capacity and favorable water solubility (Table 3). Except rutin, the other three active ingredients had good absorption in the body (Table 4). Meanwhile, we predicted the hepatotoxicity, cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibition, and plasma protein binding properties of these four active ingredients. Similar to many other anticancer drugs, most of them showed no inhibitory effects to cytochrome P450 2D6, except luteolin (Table 5). Moreover, quercetin, rutin, and luteolin exhibited low rates of plasma protein binding, indicating their favorable in-vivo activity and ability to undergo transmembrane transport, metabolism, and excretion (Table 6). Furthermore, quercetin, rutin, and luteolin demonstrated certain levels of hepatotoxicity, but comparatively lower than that of osimertinib and pemetrexed (Table 7). In addition, ferulic acid exhibited low hepatotoxicity similar to taxol (Table 7).
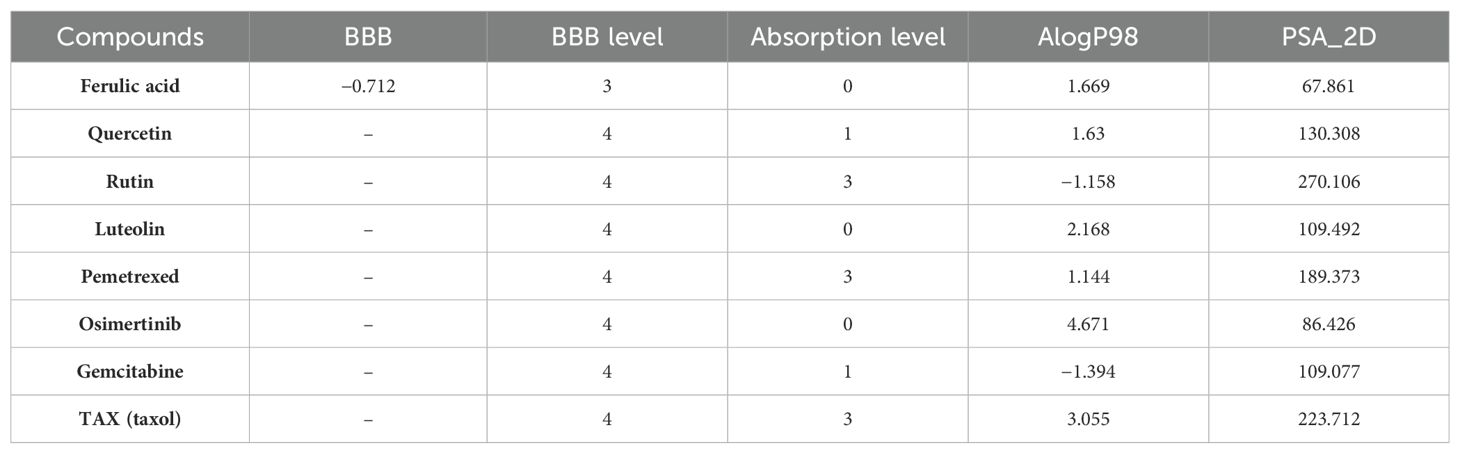
Table 3. Blood–brain barrier (BBB) penetration and human intestinal absorption prediction of group 1 and reference.
Next, the toxicity of the four ingredients was calculated through the “TOPKAT” module in Discovery Studio 2019. Predicted data on rodent carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and rat oral LD50 toxicity parameters were obtained. Quercetin exhibited the lowest levels of rodent carcinogenicity, but its rat oral LD50 was recorded as 175.2 mg/kg. On the other hand, ferulic acid exhibited the highest level of rodent carcinogenicity although its rat oral LD50 stood at 651.1 mg/kg, which is considered remarkable performance. In summary, ferulic acid had the most favorable parameters for drug development among these four ingredients because it exhibited minimal hepatotoxicity, the largest rat oral LD50 value, and diminished first-pass effect due to its potent inhibition on cytochrome P450 2D6.
Since rutin has poor absorption in the body, we chose ferulic acid, luteolin, and quercetin to verify their anticancer activity in NSCLC cells such as A549 (EGFR wild type), PC9 (EGFR mutant without T790M), and H1975 (EGFR mutant with T790M). After the concentration drug treatment was indicated, cell proliferation was detected using CCK-8. The results showed that all of them have good inhibitory effects on NSCLC cells. Notably, ferulic acid (Figure 6A), luteolin (Figure 6B), and quercetin (Figure 6C) showed lower IC50 in the EGFR wild-type cell line A549, compared with that of PC9 (EGFR mutant without T790M) and H1975 (EGFR mutant with T790M). However, there was no significant difference between PC9 (EGFR mutant without T790M) and H1975 (EGFR mutant with T790M), suggesting that these drugs may specifically target the EGFR protein. We further detected the expression of the EGFR protein with the indicated drug treatment by Western blot. The results indicated that all of these three active ingredients, namely, ferulic acid (Figure 7A), luteolin (Figure 7B), and quercetin (Figure 7C), had an inhibitory effect on the expression of the EGFR protein in a concentration-dependent manner.
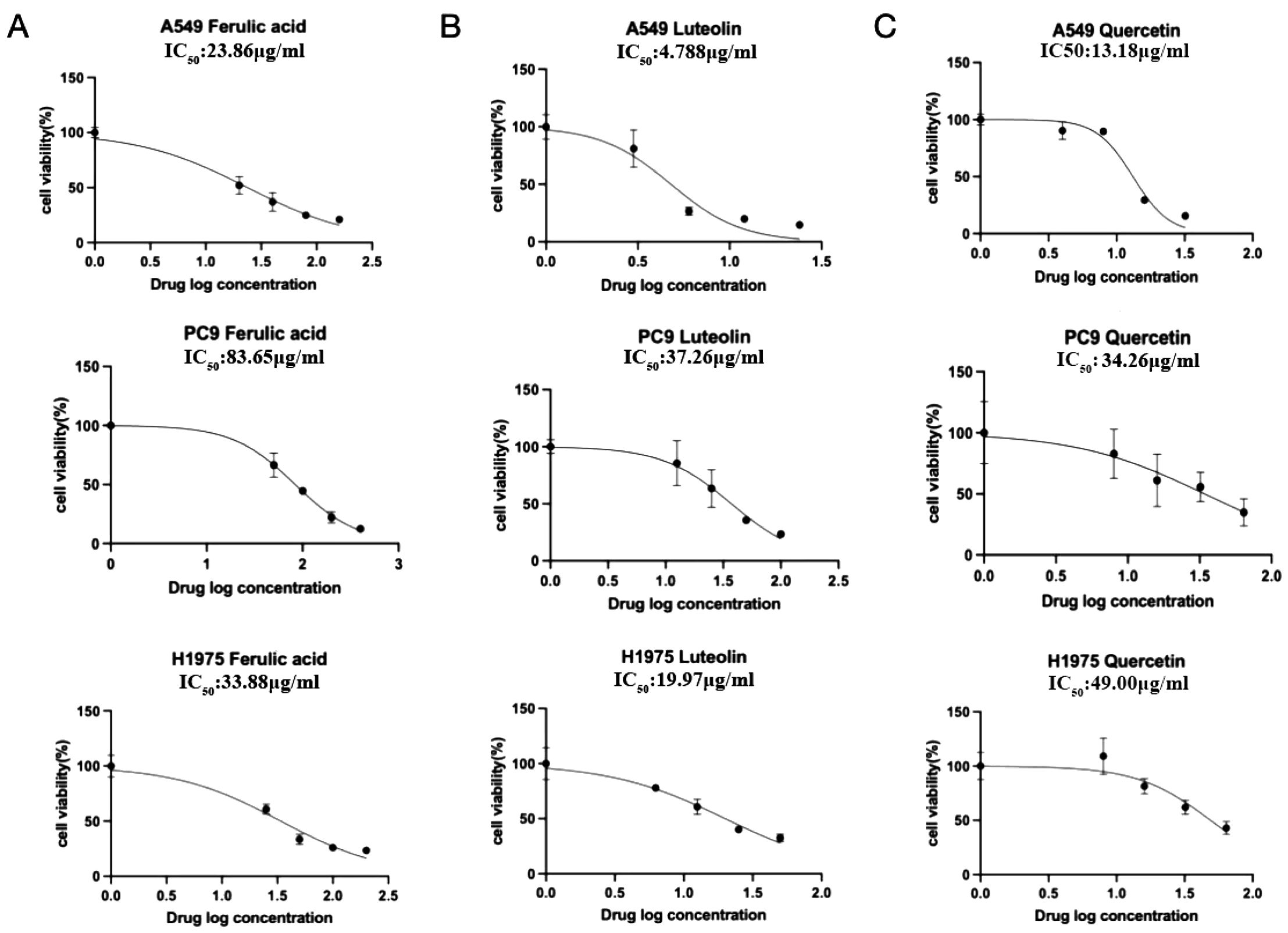
Figure 6. The IC50 of indicated drugs in NSCLC cells. The cell proliferation inhibition rate was detected by CCK-8. Ferulic acid (A), luteolin (B), and quercetin (C) could significantly inhibit cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner.

Figure 7. EGFR expression was detected by Western blot and the statistical analysis. Ferulic acid (A), luteolin (B), and quercetin (C) could reduce the expression of EGFR in a concentration-dependent manner. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant.
Zhe-Ba-Wei consists of traditional medicinal materials with a long history. In traditional Chinese medicine, Zhe-Ba-Wei plays critical roles in clearing heat and detoxification, reducing swelling and pain, tonifying “Qi” and the blood, regulating secretion, etc. In this study, to systemically study the role and potential application of Zhe-Ba-Wei in cancer, we firstly investigated its active ingredients together with overlapping targets in various types of cancers via network pharmacology and molecular docking. The results showed that 27 overlapping targets were shared by the four active ingredients (ferulic acid, quercetin, rutin, luteolin) that existed in nine types of tumors and were involved diverse biological functions (such as carbonate dehydratase activity, plasma membrane, and hydrolyase activity) and nitrogen metabolism signaling pathway. Meanwhile, based on the combination of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, molecular docking results, and prediction of ADMET properties, we selected the EGFR protein, which is related to the biological functions of the plasma membrane, as the target. Moreover, we observed the anticancer effects of ferulic acid, luteolin, and quercetin in A549 (EGFR wild type), PC9 (EGFR mutant without T790M), and H1975 (EGFR mutant with T790M) cells. The results showed that all these three drugs had good anticancer effects on A549, PC9, and H1975 cells, and showed lower IC50 in the EGFR wild-type cell line A549, compared with that of PC9 (EGFR mutant without T790M) and H1975. Moreover, all of these three drugs had a beneficial suppressive effect on the expression of the EGFR protein.
In summary, the potential anticancer targets of Zhe-Ba-Wei were predicted, and the potential target protein EGFR was experimentally verified. This research suggested that the combination of active components from Zhe-Ba-Wei has the potential to become new therapeutic agents. Besides EGFR, there are other targets identified through network pharmacology screening that may also serve as targets for Zhe-Ba-Wei that still need further research. Meanwhile, this study systematically analyzed the target genes and signaling pathways of ferulic acid, luteolin, quercetin, and rutin in terms of their antitumor effects, providing a basis for further study and potential clinical applications of these four drugs in cancer.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
ZN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation. HZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. MY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. JG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. XR: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. JC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. QL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LD: Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. GC: Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the China Scholarship Council (201908330151), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (LQ17H160009), Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (2023KY184, 2022PY084, 2021KY886, 2021RC117), and Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Fund Project (2022ZB230), Hangzhou health science and technology project (Z20230119).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1475000/full#supplementary-material
1. He BH, Dai LH, Jin L, Liu Y, Li XJ, Luo MM, et al. Bioactive components, pharmacological effects, and drug development of traditional herbal medicine Hu (Fu-Pen-Zi). Front Nutr. (2023) 9. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1052504
2. Huang XP, Chen ZH, Wang LL, Ran J, Wang JL, Jiang J, et al. Metabolite profiling and genomic properties of an endophytic strain with anti-tumor activity isolated from medicinal plant. Plant Cell Tiss Org. (2024) 156:64. doi: 10.1007/s11240-023-02671-8
3. Zou YQ, Wang SL, Zhang HH, Gu YX, Chen HJ, Huang ZH, et al. The triangular relationship between traditional Chinese medicines, intestinal flora, and colorectal cancer. Med Res Rev. (2024) 44:539–67. doi: 10.1002/med.21989
4. Zhu JH, Shen PP, Xu Y, Zhang XJ, Chen QQ, Gu K, et al. Ferroptosis: a new mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1290120
5. Wu P, Dong XM, Song GQ, Wei MM, Fang C, Zheng FB, et al. Bioactivity-guided discovery of quality control markers in rhizomes of based on spectrum-effect relationship against human lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine. (2021) 86:153559. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153559
6. Sui XB, Zhang MM, Han XM, Zhang RN, Chen LX, Liu Y, et al. Combination of traditional Chinese medicine and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. (2020) 99:32. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020683
7. Bai RR, Zhu JL, Bai ZQ, Mao Q, Zhang YQ, Hui Z, et al. Second generation β-elemene nitric oxide derivatives with reasonable linkers: potential hybrids against Malignant brain glioma. J Enzym Inhib Med Ch. (2022) 37:379–85. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.2016734
8. Zhu JL, Jiang XY, Luo XY, Zhao R, Li JJ, Cai H, et al. Combination of chemotherapy and gaseous signaling molecular therapy: Novel β-elemene nitric oxide donor derivatives against leukemia. Drug Dev Res. (2023) 84:718–35. doi: 10.1002/ddr.22051
9. Zhu JL, Jiang XY, Luo XY, Gao Y, Zhao R, Li JJ, et al. Discovery and bioassay of disubstituted β-elemene-NO donor con- jugates: synergistic enhancement in the treatment of leukemia. Chin J Nat Medicines. (2023) 21:916–26. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(23)60404-2
10. Qi X, Guo Z, Chen Q, Lan W, Chen Z, Chen W, et al. A data mining-based analysis of core herbs on different patterns (Zheng) of non-small cell lung cancer. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern Med. (2021) 2021:3621677. doi: 10.1155/2021/3621677
11. Liu SP, Li QJ, Li GH, Zhang Q, Zhuo LJ, Han XM, et al. The mechanism of mA methyltransferase METTL3-mediated autophagy in reversing gefitinib resistance in NSCLC cells by β-elemene. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:969. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03148-8
12. Song GQ, Wu P, Dong XM, Cheng LH, Lu HQ, Lin YY, et al. Elemene induces cell apoptosis via inhibiting glutathione synthesis in lung adenocarcinoma. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 311:116409. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116409
13. Kaya P, Lee SR, Lee YH, Kwon SW, Yang H, Lee HW, et al. Curcumae radix extract decreases mammary tumor-derived lung metastasis via suppression of C-C chemokine receptor type 7 expression. Nutrients. (2019) 11:410. doi: 10.3390/nu11020410
14. Zhai BT, Chen P, Wang WG, Liu SP, Feng J, Duan T, et al. An ATF peptide-functionalized β-elemene-nanostructured lipid carrier combined with cisplatin for bladder cancer treatment. Cancer Biol Med. (2020) 17:676–92. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0454
15. Wei MM, Zhao SJ, Dong XM, Wang YJ, Fang C, Wu P, et al. A combination index and glycoproteomics-based approach revealed synergistic anticancer effects of curcuminoids of turmeric against prostate cancer PC3 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 267:11346. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113467
16. Dong XM, Chen L, Wu P, Cheng LH, Wang Y, Yang YJ, et al. Targeted metabolomics reveals PFKFB3 as a key target for elemene-mediated inhibition of glycolysis in prostate cancer cells. Phytomedicine. (2024) 123:155185. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155185
17. He C, Liu X, Liu Y, Wang J, Chen D. A new alkaloid with cytotoxic activity from Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. Natural Product Res. (2022) 36:5297–303. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.1933970
18. Chen P, Li XJ, Zhang RN, Liu SP, Xiang Y, Zhang MM, et al. Combinative treatment of β-elemene and cetuximab is sensitive to KRAS mutant colorectal cancer cells by inducing ferroptosis and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Theranostics. (2020) 10:5107–19. doi: 10.7150/thno.44705
19. Zhang RN, Pan T, Xiang Y, Zhang MM, Feng J, Liu SP, et al. [amp]]beta;-elemene reverses the resistance of p53-deficient colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil by inducing pro-death autophagy and cyclin D3-dependent cycle arrest. Front Bioeng Biotech. (2020) 8. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00378
20. Sun XY, Zheng YP, Lin DH, Zhang H, Zhao F, Yuan CS. Potential anti-cancer activities of Furanodiene, a Sesquiterpene from Curcuma wenyujin. Am J Chin Med. (2009) 37:589–96. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X09007077
21. Jin HF, Dai JF, Meng LN, Lu B. Curcuma wenyujin Y. H. Chen et C. Ling n-Butyl Alcohol Extract Inhibits AGS Cell Helicobacter pylori(CagA+VacA+) Promoted Invasiveness by Down-Regulating Caudal Type Homeobox Transcription Factor and Claudin-2 Expression. Chin J Integr Med. (2020) 26:122–9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2958-y
22. Liu SP, Chen L, Zhang YT, Zhou Y, He Y, Chen Z, et al. M6AREG: mA-centered regulation of disease development and drug response. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:D1333–D44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac801
23. Liu Y, Chen LX, Zhang RN, Chen B, Xiang Y, Zhang MM, et al. Efficacy and safety of elemene combined with chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer A Meta-analysis. Medicine. (2020) 99:11. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019481
24. Yu R, Yu BX, Chen JF, Lv XY, Yan ZJ, Cheng Y, et al. Anti-tumor effects of Atractylenolide I on bladder cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 35:40. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0312-4
25. Li Y, Wang Y, Liu Z, Guo X, Miao Z, Ma S. Atractylenolide I induces apoptosis and suppresses glycolysis by blocking the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00273
26. Wang T, Long F, Zhang X, Yang Y, Jiang X, Wang L. Chemopreventive effects of atractylenolide II on mammary tumorigenesis via activating Nrf2-ARE pathway. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:77500–14. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20546
27. Li Y, Gong L, Qi R, Sun Q, Xia X, He H, et al. Paeoniflorin suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth by upregulating HTRA3 expression. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2017) 11:2481–91. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S134518
28. Duan JL, Wang CC, Yuan YH, Hui Z, Zhang H, Mao ND, et al. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of novel pyridazinone-based PARP7/HDACs dual inhibitors for elucidating the relationship between antitumor immunity and HDACs inhibition. J Med Chem. (2024) 67:4950–76. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00090
29. Xu YX, Chen YM, Zhang MJ, Ren YY, Wu P, Chen L, et al. Screening of anti-cancer compounds from Vaccariae Semen by lung cancer A549 cell fishing and UHPLC-LTQ Orbitrap MS. J Chromatogr B. (2023) 1228:123851. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2023.123851
30. Li JJ, Zhao R, Miao PR, Xu FF, Chen JH, Jiang XY, et al. Discovery of anti-inflammatory natural flavonoids: Diverse scaffolds and promising leads for drug discovery. Eur J Med Chem. (2023) 260:115791. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115791
31. Kong N, Chen XY, Feng J, Duan T, Liu SP, Sun XN, et al. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in bladder cancer cells by downregulating FTH1. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:4045–54. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.03.036
32. Liu YY, Wu SY, Lan K, Wang Q, Ye TY, Jin HN, et al. An investigation of the JAZ family and the cwMYC2-like protein to reveal their regulation roles in the meJA-induced biosynthesis of β-elemene in curcuma wenyujin. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:15004. doi: 10.3390/ijms241915004
33. Gao Y, Mao NAD, Che H, Xu L, Bai RR, Wang LW, et al. Novel hydroxyl carboximates derived from β-elemene: design, synthesis and anti-tumour activities evaluation. J Enzym Inhib Med Ch. (2022) 37:2403–16. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2117314
34. Qi X, Jiang SW, Hui Z, Gao Y, Ye Y, Lirussi F, et al. Design, synthesis and antitumor efficacy evaluation of a series of novel 8-elemene-based macrocycles. Bioorgan Med Chem. (2022) 74:117049. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2022.117049
35. Bai ZQ, Yao CS, Zhu JL, Xie YY, Ye XY, Bai RR, et al. Anti-tumor drug discovery based on natural product β-elemene: anti-tumor mechanisms and structural modification. Molecules. (2021) 26:1499. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061499
36. Gao Y, Duan JL, Dang XW, Yuan YH, Wang Y, He XR, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors derived from β-elemene scaffold. J Enzym Inhib Med Ch. (2023) 38:2195991. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2195991
37. Liu SP, Fei WQ, Shi QL, Li Q, Kuang YY, Wang C, et al. CHAC2, downregulated in gastric and colorectal cancers, acted as a tumor suppressor inducing apoptosis and autophagy through unfolded protein response. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e3009. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.405
38. Liu SP, Zhuo L, Chen L, He Y, Chen XD, Zhang H, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF148 functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer by ubiquitination-mediated degradation of CHAC2. Carcinogenesis. (2024) 45:247–61. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgae002
39. Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. (2019) 47:W357–W64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz382
40. Amberger JS, Bocchini CA, Schiettecatte F, Scott AF, Hamosh A. OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. (2014) 43:D789–98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1205
41. Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, Rosen N, Iny Stein T, Shmoish M, et al. GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database. (2010) 2010:baq020. doi: 10.1093/database/baq020
42. Beauvais DM, Nelson SE, Adams KM, Stueven NA, Jung O, Rapraeger AC. Plasma membrane proteoglycans syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 engage with EGFR and RON kinase to sustain carcinoma cell cycle progression. 298:102029. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102029
43. Werbin JL, Avendaño MS, Becker V, Jungmann R, Yin P, Danuser G, et al. Multiplexed Exchange-PAINT imaging reveals ligand-dependent EGFR and Met interactions in the plasma membrane. (2017) 7:12150. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12257-y
44. Stewart RL, O'Connor KL. Clinical significance of the integrin α6β4 in human Malignancies. Lab Invest. (2015) 95:976–86. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.82
45. Jones S, Rappoport JZ. Interdependent epidermal growth factor receptor signalling and trafficking. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2014) 51:23–8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.014
46. Ghosh G, Lian X, Kron SJ, Palecek SP. Properties of resistant cells generated from lung cancer cell lines treated with EGFR inhibitors. BMC Cancer. (2012) 12:95. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-95
47. Barreto RA, Walker FR, Dunkley PR, Day TA, Smith DW. Fluoxetine prevents development of an early stress-related molecular signature in the rat infralimbic medial prefrontal cortex. Implications for depression? BMC Neurosci. (2012) 13:125. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-125
48. Qiu HJ, Lu XH, Yang SS, Weng CY, Zhang EK, Chen FC. MiR-769 promoted cell proliferation in human melanoma by suppressing GSK3B expression. BioMed Pharmacother. (2016) 82:117–23. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.04.052
49. Govindan R, Ding L, Griffith M, Subramanian J, Dees ND, Kanchi KL, et al. Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in smokers and never-smokers. Cell. (2012) 150:1121–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.024
Keywords: Zhe-Ba-Wei, cancer, active ingredients, drug target, network pharmacology
Citation: Ni Z, Zhang H, Chen F, Yang M, Yang L, Zhou Y, Zhou X, Guo J, Rao X, Cen J, Lv Q, Wang J, Du L, Chen G and Liu S (2024) The role and mechanism of “eight famous herbals in Zhejiang” in cancer via network pharmacology and experimental validation. Front. Oncol. 14:1475000. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1475000
Received: 02 August 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 15 November 2024.
Edited by:
Yau Tuen Chan, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Chao Han, China Pharmaceutical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Ni, Zhang, Chen, Yang, Yang, Zhou, Zhou, Guo, Rao, Cen, Lv, Wang, Du, Chen and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lailing Du, ZHVsYWlsaW5nQHpqc3J1LmVkdS5jbg==; Gongxing Chen, aG5jaGVuMzY5QHNvaHUuY29t; Shuiping Liu, bHNwQGh6bnUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.