- 1Cancer Center of Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Center of Basic Medical Research, Institute of Medical Innovation and Research, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
- 4Beijing Key Laboratory of Restoration of Damaged Ocular Nerve, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
- 5Oncology Tissue and Imaging Services, Johns Hopkins University Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore, MD, United States
Background and aims: Multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence (mIHC/IF), which uses the tyramide signal amplification (TSA) technique, enables sequential staining of multiple targets in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples without worrying about cross-reactivity. This approach has received considerable attention from researchers over the past decades. This article aims to provide a bibliometric analysis of the research progress and perspectives on the application of TSA-based mIHC/IF.
Methods: We collected all the TSA-based mIHC/IF documents published between 2007 and 2023 from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database. CiteSpace, VOSviewer and Bibliometrix R Package were used to perform the bibliometrics analysis, including details about annual publications, countries, institutions, authors, journals, and research topics and hotspots.
Results: A total of 873 relevant publications (811 articles and 62 reviews) with a time span of 17 years (2007-2023) were obtained. The number of annual publications started to increase rapidly since 2016. The United States (307, 35.17%) and the People’s Republic of China (297, 34.02%) are the top two listed countries for both the number of articles produced and the citations. The University of Texas System (53, 6.07%) was the most productive institution. Integrating these results of hotspot and frontier analysis, TSA-based mIHC/IF provides significant benefits, particularly in neurology, cancer and immunology.
Conclusion: This study conducted a comprehensive bibliometric analysis for the use of TSA-based mIHC/IF. As TSA-based mIHC/IF and its associated imaging systems and analytic software progress, it will become the most promising tool for describing the variety of the whole tissue for a better understanding of pathological or physiological behavior.
1 Introduction
Multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence (mIHC/IF) technologies are a suite of technologies for the simultaneous visualization of multiple biomarkers in a single tissue section (1) and can be divided into five classes: stain-removal technologies, fluorophore inactivation technologies, multiplex signal amplification, DNA barcoding technologies, and mass cytometry (2). Despite being created more than 20 years ago, tyramide signal amplification (TSA)-based mIHC/IF is still commonly utilized, identifying up to eight markers in a single formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) section using a cyclic staining protocol with tyramide-conjugated fluorophores (3–5). The extremely sensitive enzyme-catalyzed procedure detects modest levels of expression by increasing the signal above background tissue autofluorescence. Iterative cycles of antibody staining and antibody stripping by heat-induced epitope retrieval, generally conducted in the microwave, allow the use of primary antibodies from the same species with no species cross-reactivity (3, 6). Furthermore, TSA-based mIHC/IF is significantly photostable compared to conventional immunofluorescence, allowing slides to be stored and rescanned one year after staining without significant loss of signal (7). Nowadays, the procedure of TSA-based mIHC/IF, image acquisition, spectral unmixing, and data analysis have been optimized, making it suitable for both manual and automated assays (3, 6, 8, 9), and the reproducibility and validation of TSA-based mIHC/IF against traditional IHC have been verified (10–13). TSA-based mIHC/IF detects the co-expression of several molecules on single cells, assesses the distribution, abundance, and heterogeneity of expression of various cell types in tissues, and identifies spatial correlations between them. Several scholars have reviewed the application of mIHC/IF approach in research areas such as immune microenvironment and tumor immunotherapy (2, 14–16), suggesting that TSA-based mIHC/IF can increase researchers’ understanding of physiological processes and diseases at the molecular and cellular levels, making them crucial for disease categorization, etiology, diagnosis, and therapy. However, there is currently little information available on the applications, demographic distribution and general development trend of this innovative technology.
One of the most significant responsibilities in improving a field is to draw conclusions from prior research. Bibliometrics is a well-established bioinformatics quantitative tool that rigorously applies statistical and mathematical methods to large amounts of unstructured data, using the global document characteristics and literature landscape as the object of study, to decipher and map the cumulative scientific knowledge and evolution of a defined field (17). Several software integrating computer engineering, big data applications and statistics have been widely applied in this field, including CiteSpace, VOSviewer and Bibliometrix R Package (18). To date, no bibliometric analyses have been conducted in the TSA-based mIHC/IF field. In this particular study, we have collected literature that applied or reviewed TSA-based mIHC/IF from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database and performed a systematic bibliometric analysis of this method, and attempted to provide an overview and a different perspective to help understand the history of scientific activities and the evolution of hotspots, identify current research interests, guide potential future research directions and emerging trends, and promote further generalization of its application and development.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source and search strategy
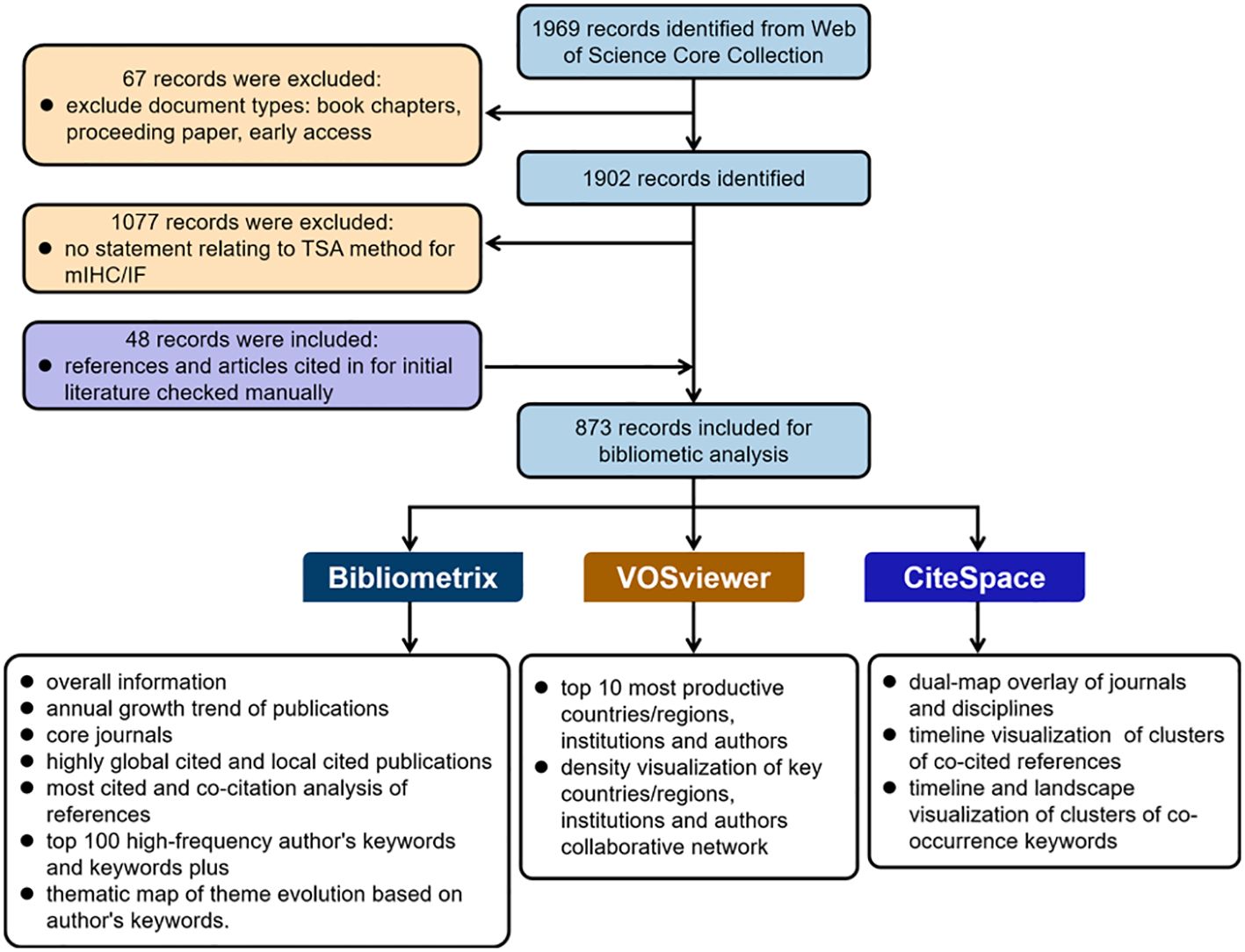
The literature content used in this study was extracted from the WoSCC databases including SSCI, SCI-Expanded, CPCI-S, A&HCl, ESCI, CPCI-SSH, CCR-Expanded and IC. The search strategy was: TS=(“multiplex* immunofluorescence” OR “multiplex* immunohistochemistry” OR “multiplex* immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence” OR “multiplex* immunohistochemistry/multiplex* immunofluorescence” OR “multiplex* fluorescent immunohistochemistry” OR “multiplex* IHC” OR “multiplex* IF” OR “multispectral fluorescent immunohistochemistry” OR “multiplex* immunohistochemical”) OR TS=(tyramide-based OR TSA-based OR “tyramide signal amplification”). Only “Article” and “Review Article” were included in the analysis, and the language of the literature was set to English. The publication period was from the start of the database until 21 December 2023. The “Full Record and Cited References” of the original data were also extracted in “Plain Text” format and downloaded on 21 December 2023. In addition, the full text of these records was examined by two authors to determine whether it includes any application or discussion of TSA-based mIHC/IF in the literature. Meanwhile, the references and articles cited in the original literature were manually checked to avoid missing articles. Any discrepancies were resolved by discussion. The flowchart of the data preparation and bibliometric analysis process is shown in Figure 1.
2.2 Bibliometric analysis
The data were imported into the Bibliometrix (4.1) R package (19), VOSviewer (version 1.6.16) (20) and CiteSpace (version 6.1.R3) (21, 22) for bibliometric analysis and graphical visualization.
The Bibliometrix (4.1) R package (19) performs a complete set of literature information analysis and the visualization of results. In this study, the Bibliometrix (4.1) R package was used to obtain the data of overall information, annual growth trend of publications, core journals, highly global cited and local cited publications, most cited and co-citation analysis of references, top 100 high-frequency author’s keywords and keywords plus, and thematic map of theme evolution based on author’s keywords. The thematic map (19) is a two-dimensional strategy diagram that divides the development of research themes into four quadrants according to their centrality (plotted on the x-axis) and density (plotted on the y-axis). The algorithm of the thematic map uses co-word and h-index indicators, then creates networks of keywords and calculates the relationship among them. Centrality measures the degree of interaction that a keyword network has with other keyword networks. Density measures the internal strength of a network, implying the closeness of these words to each other. Subsequently, the keywords were grouped according to subject areas and the subjects were distributed according to centrality and density.
VOSviewer (20) is a software tool for constructing and visualizing bibliometric co-occurrence networks based on citation, bibliographic coupling, co-citation, or co-authorship relations. It was used to obtain the data of the top 10 most productive countries/regions, institutions and authors, and to perform co-occurrence analysis of countries/regions, institutions and authors in density visualization.
CiteSpace (21, 22) is a Java application for visualizing and analyzing trends and patterns in scientific literature, with a focus on finding critical points in the development of a field or domain, especially intellectual inflection points and pivots. It provides structural and temporal analyses of a variety of networks derived from scientific publications to facilitate the understanding and interpretation of network patterns and historical patterns, including dual-map overlay of journals and disciplines, visualization networks and clusters of co-cited references and co-occurrence keywords.
3 Results
3.1 Global overview of publications
According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, this study comprised 873 publications (811 articles and 62 reviews) from the WOSCC database during a 17 years period (2007-2023), with an annual growth rate of 39.3%. The total number of citations in the retrieved publications totaled 13993, with an average of 20.61 citations per publication. In addition, 29 papers were cited more than 100 times. In total, the retrieved material was published in 296 journals globally by approximately 7245 authors representing 1401 institutions in 52 countries/regions.
3.2 Annual growth trend of publications
As shown in Figure 2, the overall trend of research on the use of TSA-based mIHC/IF has been expanding. The first article appeared in the Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry in 2007 (23). Toth ZE and Mezey E were the first to demonstrate the simultaneous visualization of multiple antigens with TSA using antibodies from the same species (23). Between 2007 and 2015, there were just a few publications. Since 2016, the number of annual publications has increased substantially. Between 2017 and 2023, 846 publications were released, accounting for 96.91% of all contained materials. The number of yearly publications grew progressively, from 119 in 2020 to 212 in 2021. As of December 21, 201 publications have been published in 2023.
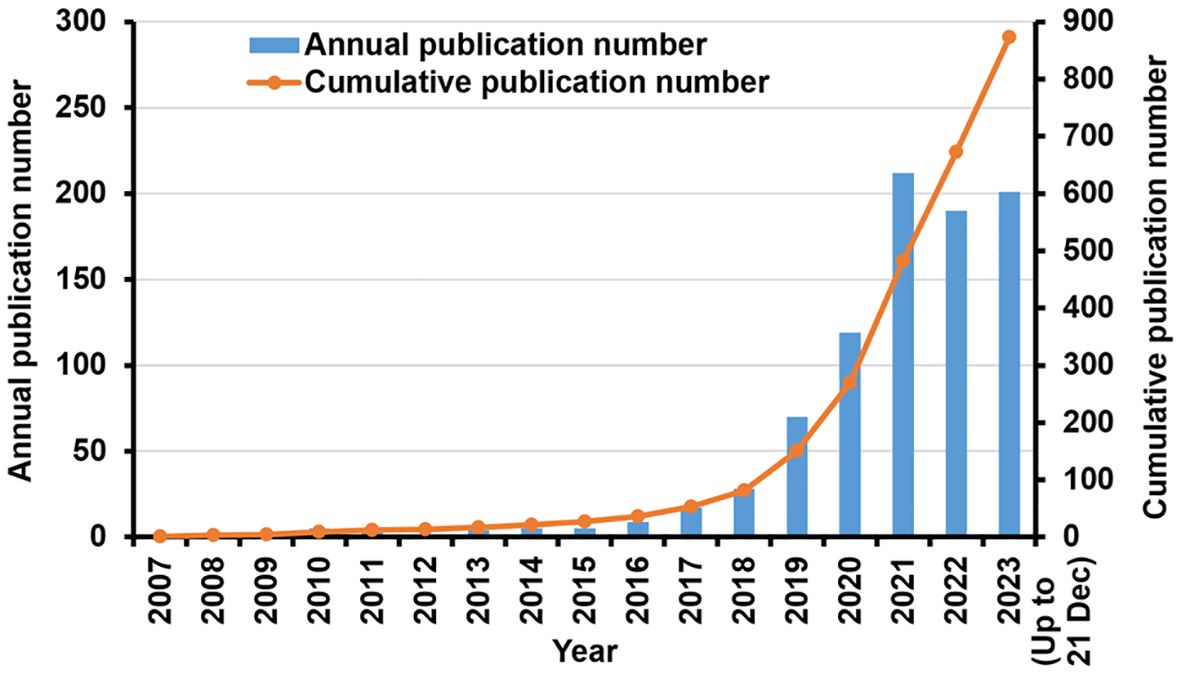
Figure 2. Research in TSA-based mIHC/IF method: Annual scientific production and cumulative number of publications.
3.3 Contributions of countries/regions, institutions and authors to global publications
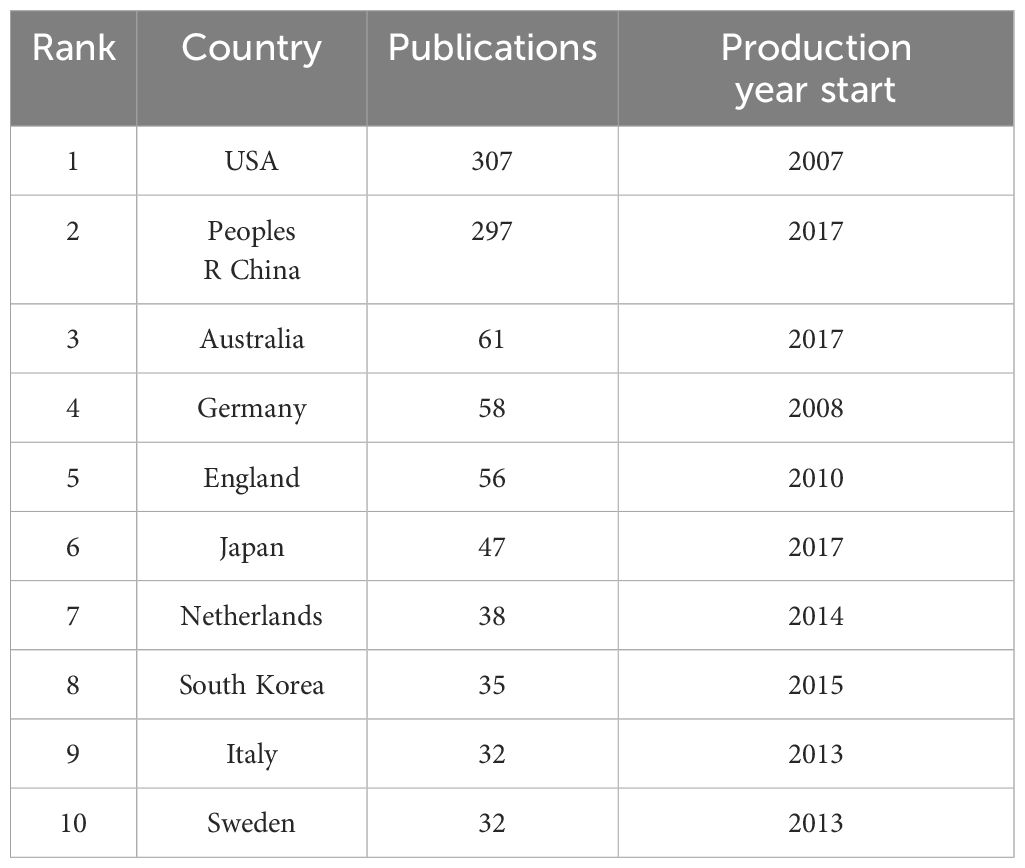
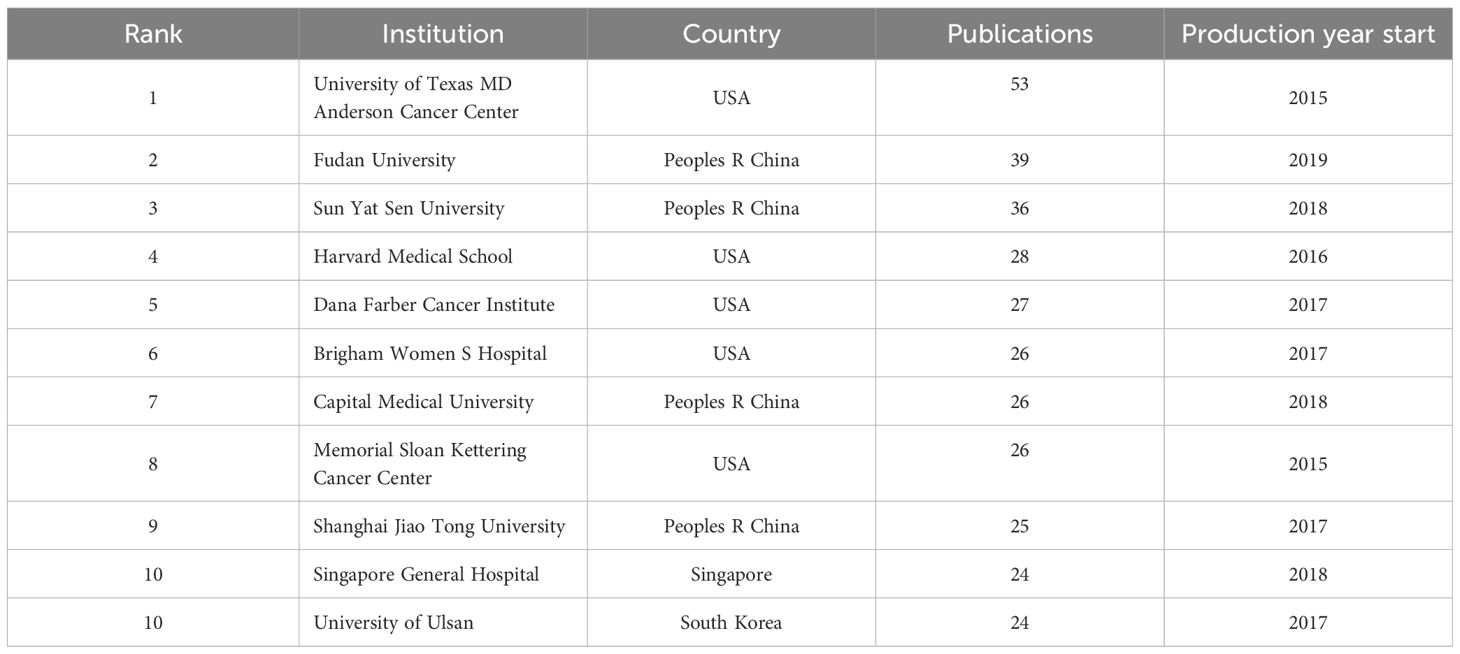
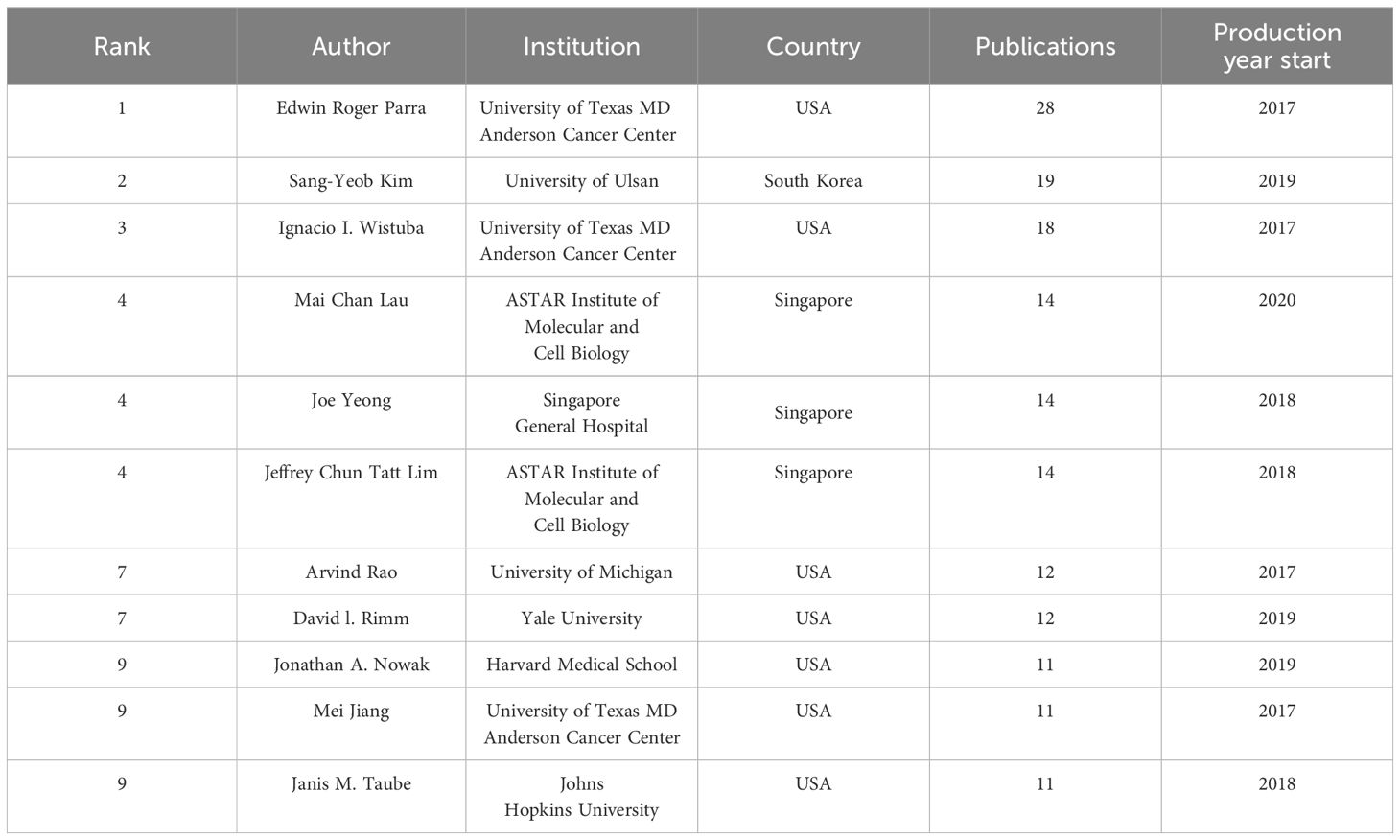
Four European countries, four Asian countries, one North American country, and one Oceania country make up the top ten most productive nations (Table 1). The two most productive countries, the United States (307 publications, 35.17%) and the People’s Republic of China (297 publications, 34.02%), contributed a total of 573 publications (65.64%). Table 2 shows the top 10 most productive institutions, with two colleges tied for tenth place. Similarly, the vast majority of the 11 institutions are from the United states (5 institutions) and the People’s Republic of China (4 institutions). Seven of the top nine writers with the most publications, seven are from the United States, three from Singapore and one from South Korea, with output years beginning in 2017 or later (Table 3). Parra Edwin Roger from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center published the most papers (28 publications). As shown in Figure 3, the clusters for key countries/regions, institutions, and authors are shown in density visualizations generated by VOSviewer.
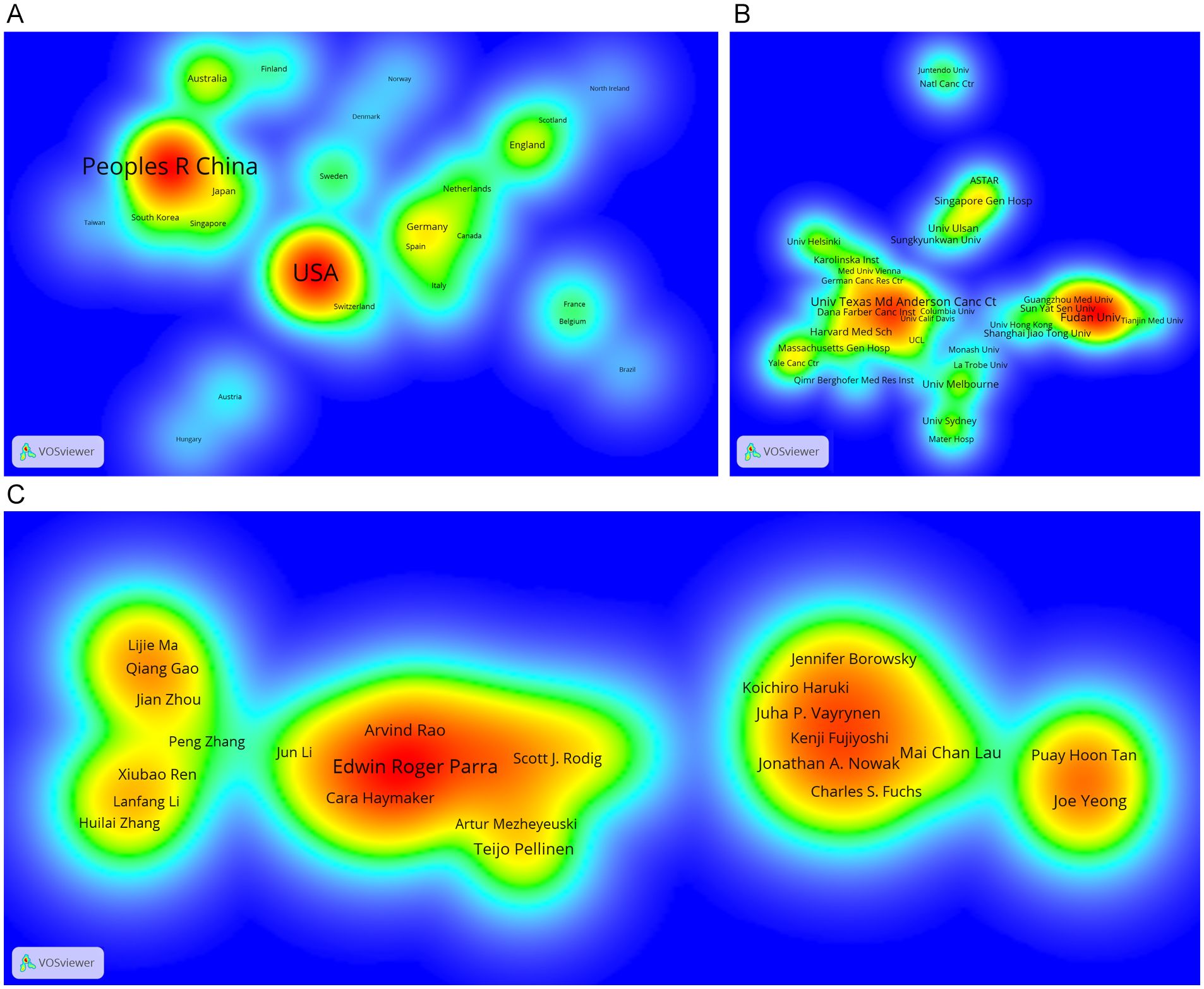
Figure 3. Density visualization of the most important countries/regions (A), institutions (B) and authors (C) in the co-occurrence network generated by VOSviewer. Only those countries/regions, institutions and authors with at least 5 records are shown in the network.
3.4 Core journals and disciplines
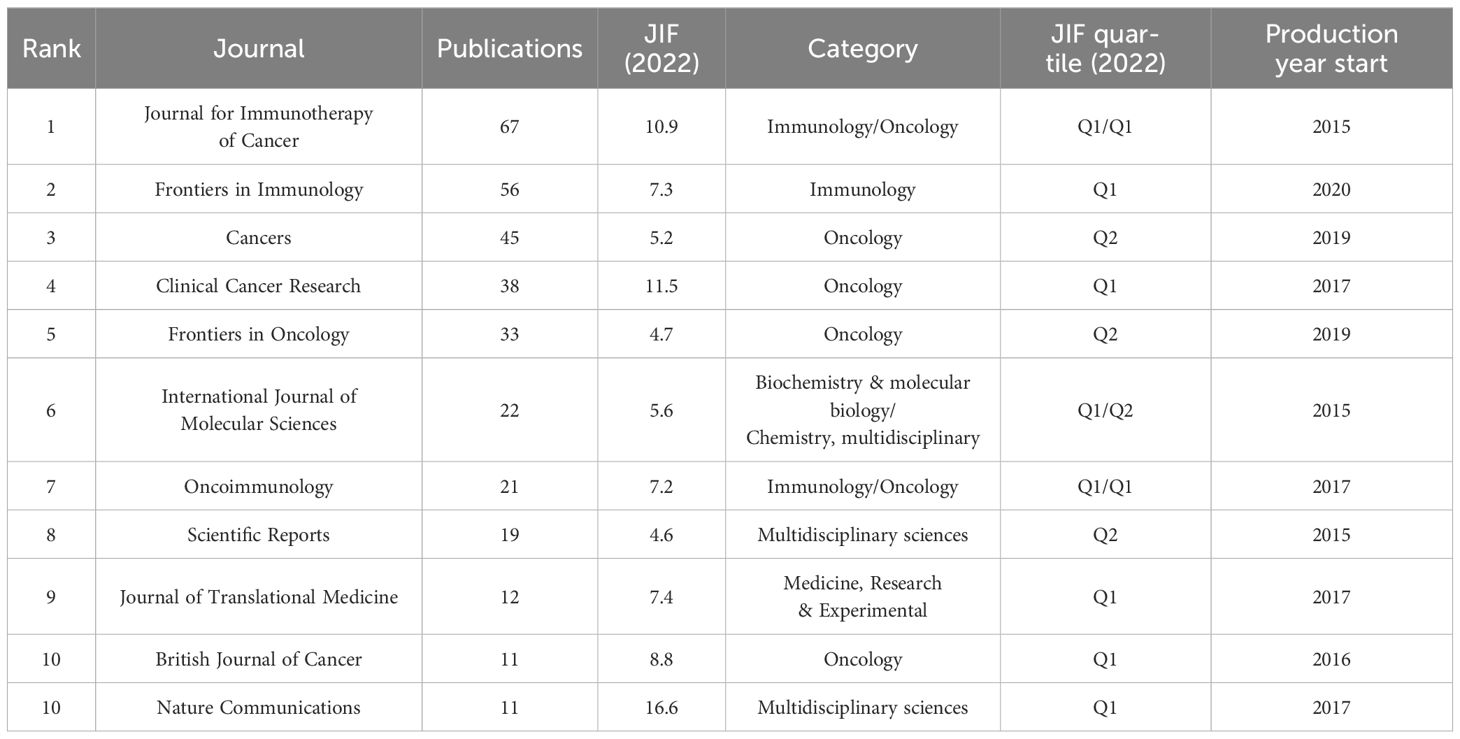
In all, 873 retrieved articles were published in 294 journals. Table 4 lists the top 10 journals that published the most literature, accounting for 38.37% of the total. Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer was the most active journal in this topic, followed by Frontiers in Immunology and Cancers. All 11 journals have a Journal Impact Factor 2022 (JIF2022) >3.00, with Nature Communications having the highest IF of 16.6. According to the JIF Quartile 2022 standards, the Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer, Cancers, Clinical Cancer Research, Oncoimmunology and British Journal of Cancer are classified as Q1 in the JCR category, which are professional and active journals in the field of oncology. In addition, a few articles were published in journals with a high JIF of more than 40, such as Science (JIF2022 = 56.9), Lancet Oncology (JIF2022 = 51.1), Cancer Cell (IF2022 = 50.3) and Nature Methods (JIF2022 = 8).
Each journal included in the WoSCC databases is classified into at least one of the subject categories related to a certain research field. TSA-based mIHC/IF was applied to 65 specialties, depending on the journal field. Among them, Oncology accounts for the largest number of publications (417 publications), followed by Immunology (200 publications), Pathology (56 publications), Multidisciplinary Sciences (56 publications) and Medicine Research Experimental (55 publications). In addition, a dual-map overlay of journals is created to illustrate the citation link between journals and disciplines by marking the journal’s topic area (Figure 4). The present map shows two major citation categories, suggesting that majority of articles were published in the domains of ‘Molecular, Biology, Immunology’ and ‘Medicine, Medical, Clinical’, and that they mainly cited journals in the fields of ‘Molecular, Biology, Genetics’.
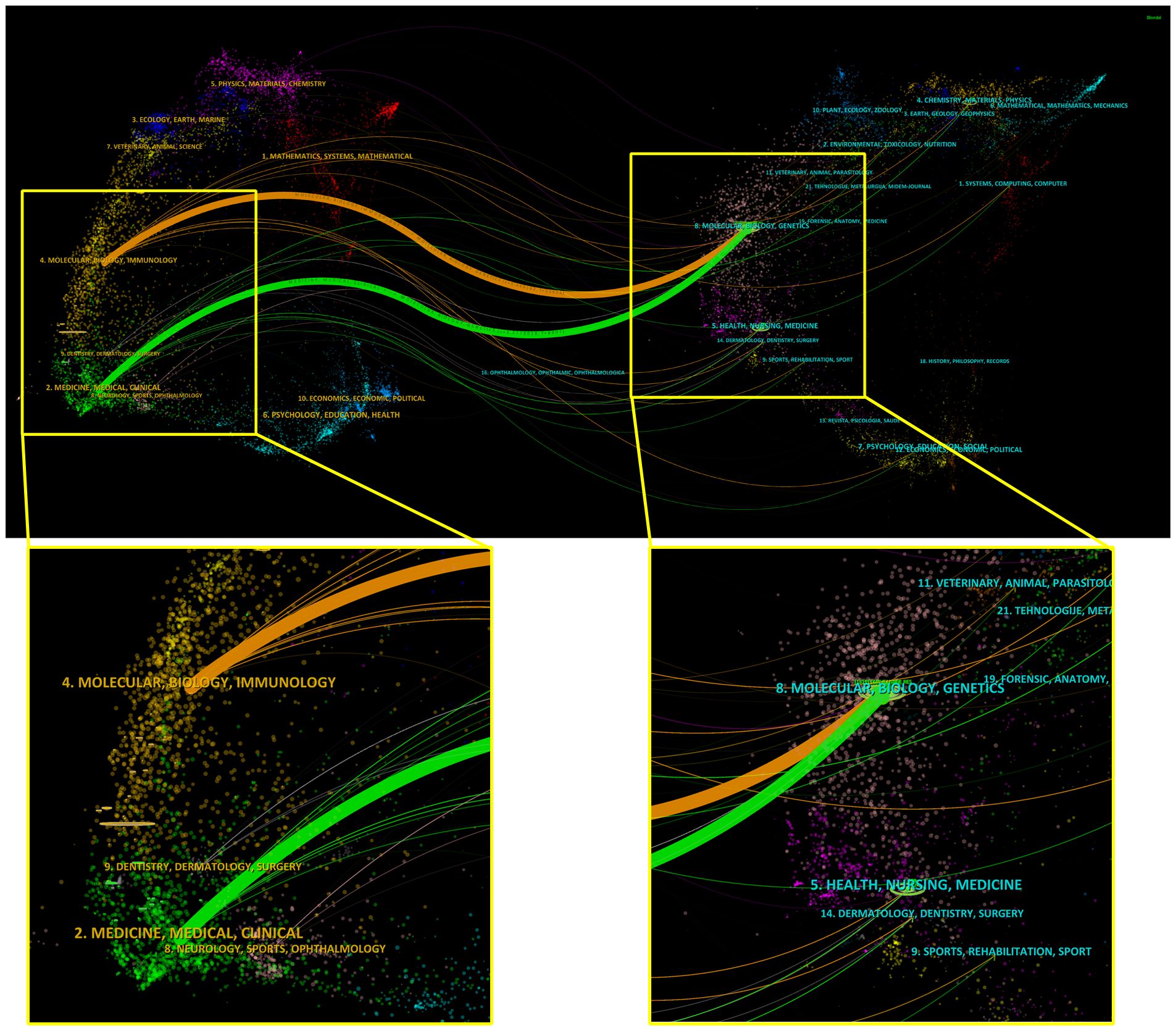
Figure 4. Dual map overlay and corresponding disciplines of citing and cited publications generated by CiteSpace. Labels indicate corresponding disciplines of citing and cited publications. The citing and cited trajectory using the z-score function.
3.5 Research topics and hotspots
3.5.1 Highly total global cited and local cited publications
The most referenced papers, whether worldwide or locally, have acted as watershed moments for key discoveries and research boosters.
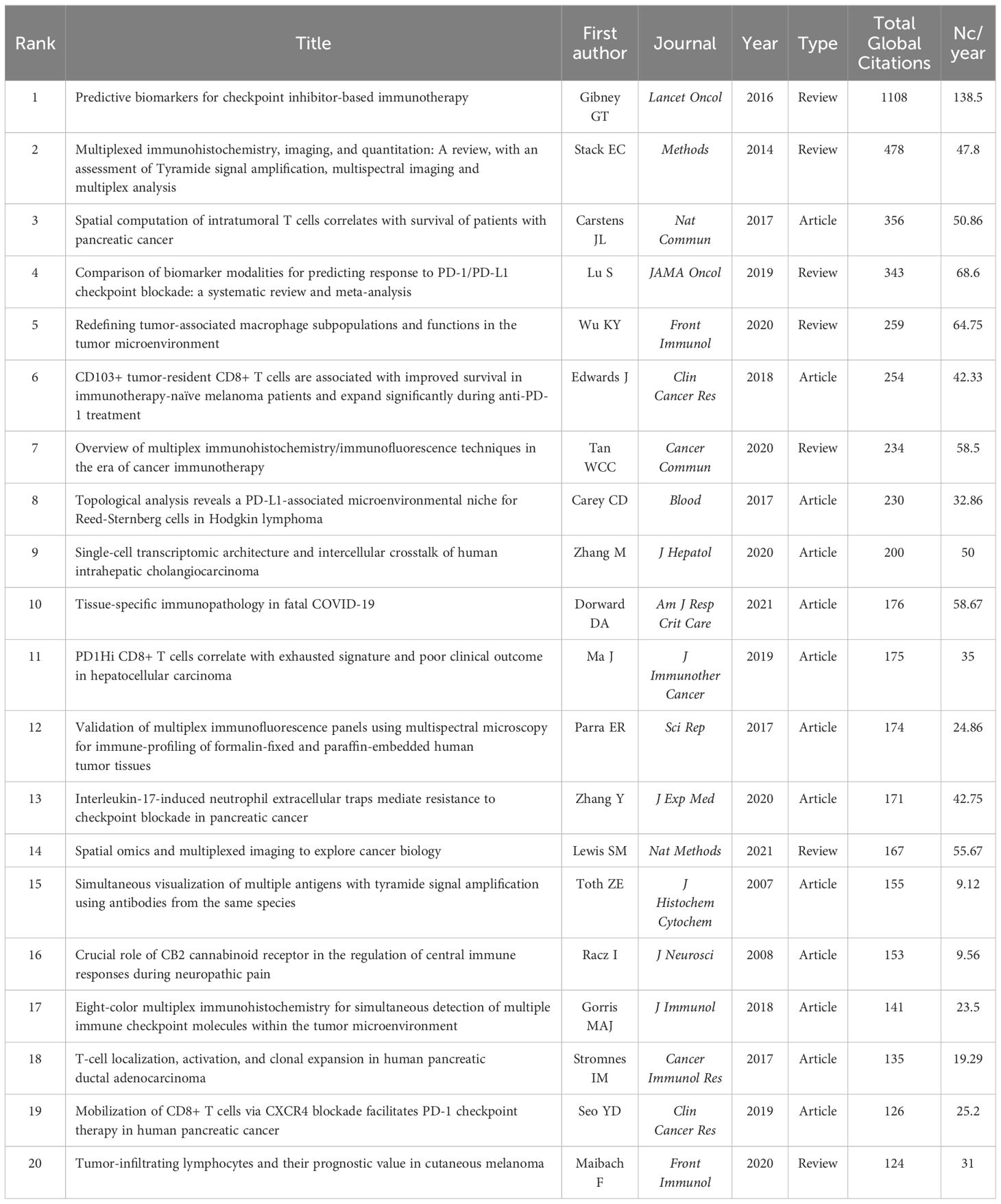
The total global citations (TC) and the average number of citations per year (Nc/year) may reflect the relevance and interest of other researchers in a certain study topic. The top 20 most cited publications (13 articles and 7 reviews) are ranked in Table 5 according to the total number of citations in the WoSCC databases. Eight publications had the Nc/year values greater than 50, seven of which were on oncology research topics and the remainder were COVID-19.
The Local Citation Score (LCS) is an essential indicator of a publication’s influence in this particular research field. Figure 5 depicts the details of the annual citation and the historical direct citation network of the top 20 publications in the LCS ranking. The majority of the high LCS publications have been published and referenced since 2017, indicating that TSA-based mIHC/IF has gained extensive attention and application among academics since then (Figure 5A). In the historical direct citation network, each node representing a cited paper is scaled according to the LCS, and the linkages reflect citations between publications (Figure 5B). The review published by Stack EC et al. (3) and the article published by Toth ZE et al. (23) in 2007 received the two highest LCS ratings as the most important early literature, representing two of the earliest publications reporting and reviewing this technique. Two automated staining protocols have also attracted a great deal of attention from the research community (8, 24). Oncology, the main application area of TSA-based mIHC/IF, accounts for the remaining 17 publications.

Figure 5. Annual citation (A) and historical direct citation network (B) of the top 20 publications in the Local Citation Score (LCS) ranking. (A) The size and color of the circles represent the annual LCS of the publication, with larger circles and redder colors indicating a higher LCS. (B) Historical direct citation network generated by the Bibliometrix R package. Each node in the historical direct citation network represents a key publication, and the directional arrow indicates the citation association between the two publications. The size of each node is proportional to the frequency of that publication among the other 19 publications.
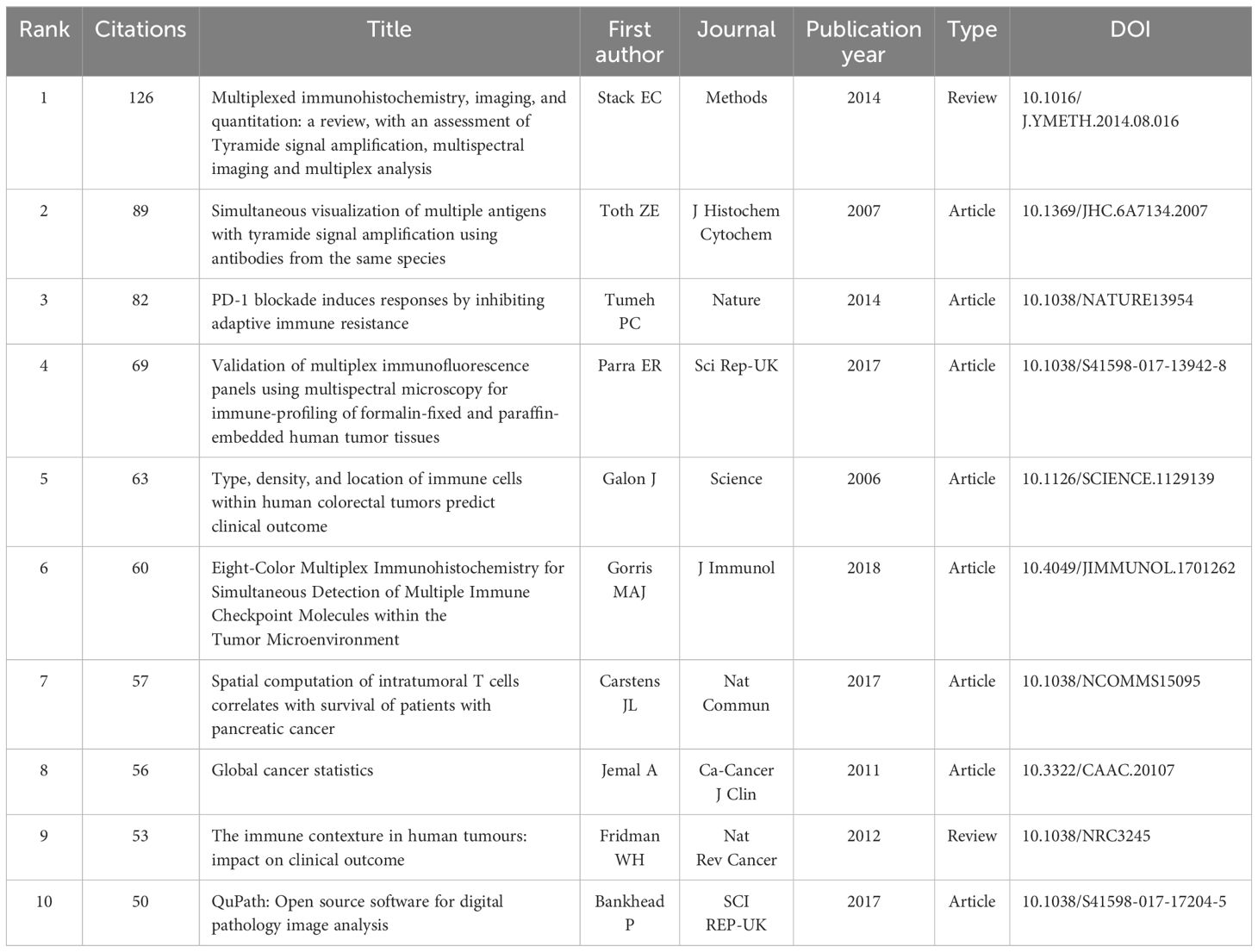
3.5.2 Most cited and co-citation analysis of references
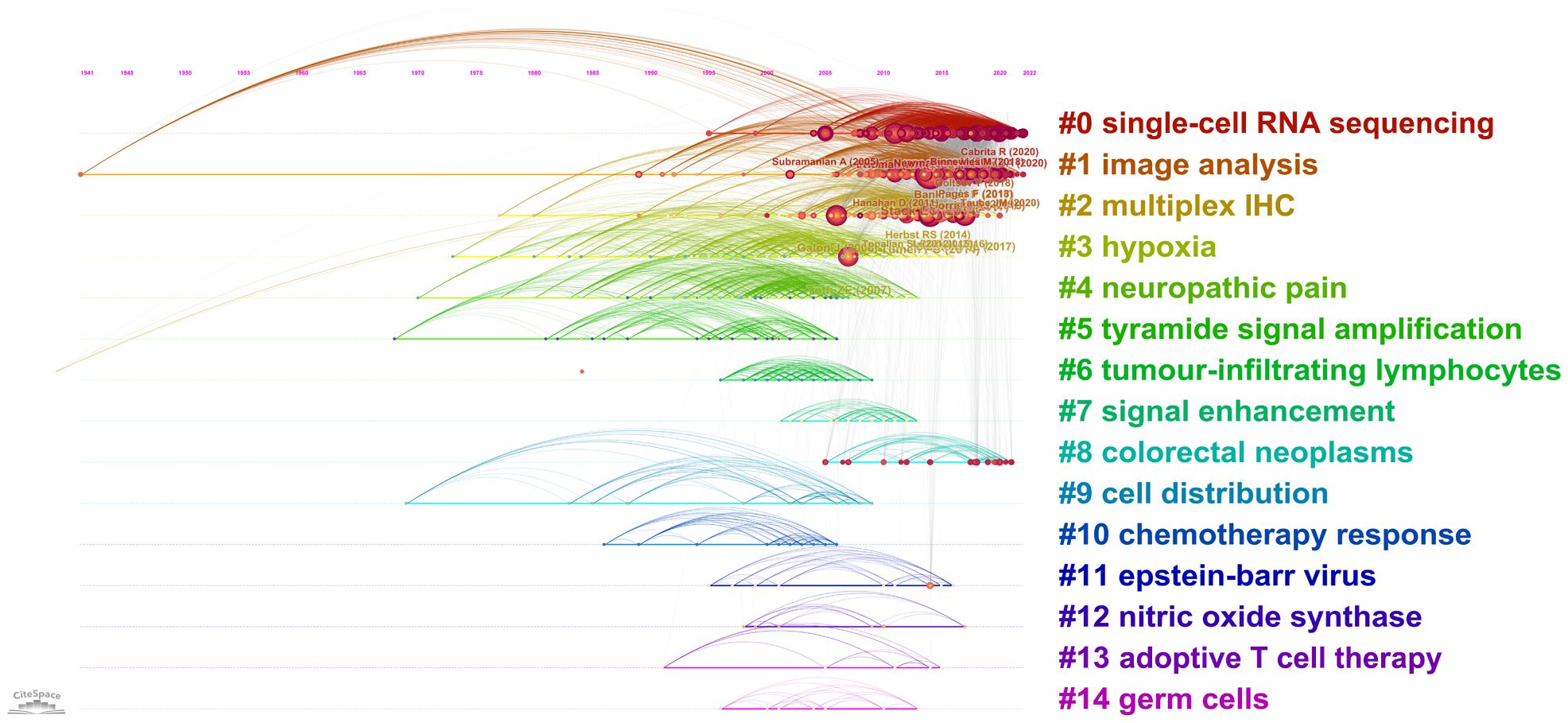
A total of 29173 references were involved in 873 publications. The top 10 most cited references are listed in Table 6. Six of them were published in very influential publications, including CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, Science, Nature, Nature Reviews Cancer, and Nature Communications. In the visualization network of co-cited references, the nodes representing the references are grouped into 15 particular clusters with the greatest K-values (Figure 6). The timeline view illustrates the evolutionary path of these conspicuous groupings. Each circle represents a major reference in a certain cluster, whereas the citation tree rings of varying widths on the timeline show citation rates. Large nodes are frequently noted in each time slice. The number of cluster labels is inversely proportional to the number of publications inside in each cluster. Five clusters, including ‘#0 single-cell RNA sequencing’, ‘#1 image analysis’, ‘#2 multiplex IHC’, ‘#3 hypoxia’ and ‘#4 neuropathic pain’, are larger than 100, suggesting that they have received special attention.
3.5.3 High-frequency, co-occurrence analysis and thematic map of keywords
Keywords are focused representations of a publication’s fundamental topic. A total of 1837 author keywords and 1906 additional keywords were collected from the 873 publications. After integrating synonyms, the word clouds in Figure 7A reflect the top 100 most often used author’s keywords and keywords plus, with font size positively correlated with frequency. In addition to multiplex IHC/IF, the following keywords appear with a frequency greater than 50: expression, cancer, survival, tumor microenvironment, immunotherapy, pd-l1, T cell, tumor, chemotherapy, nivolumab, microenvironment, immunohistochemistry, pembrolizumab, therapy.
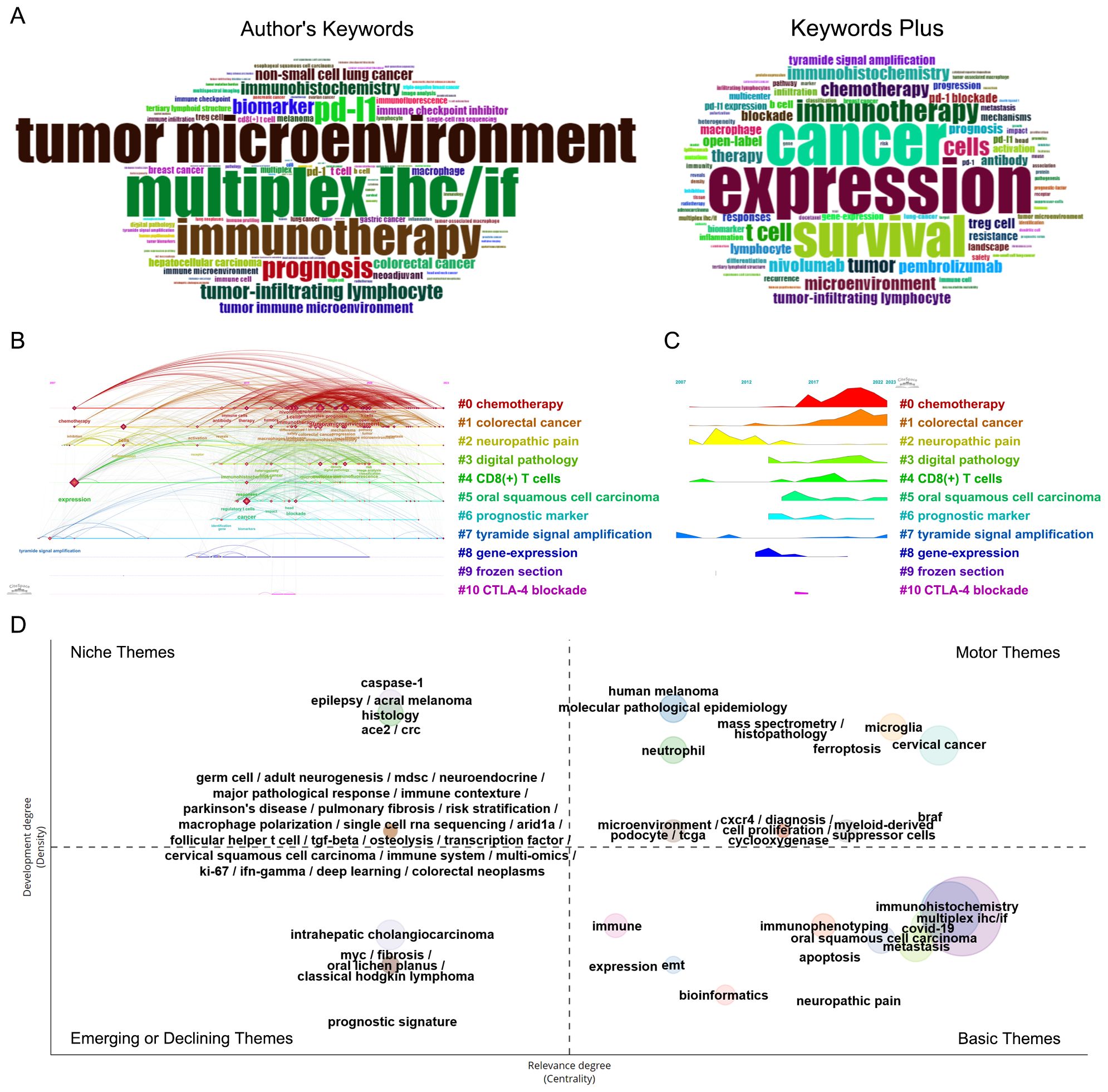
Figure 7. Co-occurring analysis of keywords of publications applying the TSA-based mIHC/IF method. (A) Word cloud of the top 100 high-frequency authors keywords and keywords plus generated by the Bibliometrix R package. (B) Timeline view of the significant clusters of keywords generated by CiteSpace. (C) Landscape of the significant clusters of keywords generated by CiteSpace. (D) Thematic map of keywords generated by the Bibliometrix R package.
Co-occurrence keywords can reveal meaningful knowledge components and insights based on the pattern and strength of links between keywords, indicating the hotspots and latest trends in the research field by uncovering knowledge mappings. After clustering the network map of keyword co-occurrence, 11 significant clusters with the highest K-value are generated with the hierarchical cluster labels of the most relevant terms (Figures 7B, C). The timeline view and landscape of the clusters demonstrate how TSA-based mIHC/IF have changed over time in various applications. More than 100 keywords are found in three clusters, “#0 chemotherapy”, “#1 colorectal cancer”, and “# neuropathic pain” The Cluster “#2 neuropathic pain” was common in former years. Chemotherapy and colorectal cancer remain typical applications for TSA-based mIHC/IF.
As shown in Figure 7D, the thematic map divides 65 clusters of author’s keywords into four quadrants according to their centrality and density rank: niche (top left, 30 clusters), motor (top right, 17 clusters), emerging or declining (left bottom, 6 clusters), and basic themes (right bottom, 12 clusters). The size of the bubble corresponds to the number of terms in the cluster. Each cluster is assigned with a descriptive label generated from high-frequency keywords that serve as primary themes and illustrate the breadth of application of TSA-based mIHC/IF. Partially overlapping clusters have the same centrality and relevance, with their labels separated by slashes. The basic themes in the bottom right quadrant are fundamental, significant, universal and cross-cutting to the research area. Among them, five clusters, including ‘immunohistochemistry’, ‘multiplex IHC/IF’, ‘covid-19’, ‘metastasis’ and ‘oral squamous cell carcinoma’ have the highest relevance according to the highest centrality. The motor themes, located in the top right quadrant, consist of 17 well-developed and essential clusters for organizing the study topic. The clusters labeled as ‘human melanoma’, ‘molecular pathological epidemiology’, ‘microglia’, ‘histopathology’ and ‘mass spectrometry’, have the highest density, while ‘cervical cancer’, ‘braf’, ‘microglia’, ‘ferroptosis’ and ‘myeloid-derived suppressor cells’ demonstrate the highest centrality. Niche themes in the upper left quadrant, characterized by low centrality and high density, are highly developed and isolated or specialized themes, such as ‘caspase-1’, ‘epilepsy’, ‘acral melanoma’, ‘ace2’ and ‘crc’. The six developing or decreasing themes in the bottom left quadrant, which include ‘intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma’, ‘myc’, ‘fibrosis’, ‘oral lichen planus’, ‘classical hodgkin lymphoma’, and ‘prognostic signature’, are marked by low centrality and density, suggesting poorly developed and marginal themes.
4 Discussion
Based on available data, this study summarizes research collaborations, current hotspots, new developments, and research trends in TSA-based mIHC/IF throughout the world. Overall, 672 English-language articles and reviews were obtained in this bibliometrics analysis. The first article applied TSA-based mIHC/IF was published in 2007 (23), but it wasn’t until 2016 that TSA-based mIHC/IF took off, and the number of insightful publications and the range of applied disciplines increased exponentially. This may be partly due to the marketing of commercial kits and the use of clinical FFPE samples (3, 25, 26). The USA and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center are the most productive and influential parties, contributing the highest number of publications and citations. It is worth mentioning that since 2017, China has begun to publish articles applied this method, and in the following years, the number of publications and citations has increased rapidly. In 2022, the total number of publications and citations reached 184 and 1722, respectively, placing second. Moreover, Fudan University (Rank 2), Capital Medical University (Rank 3), and Sun Yat-sen University (Rank 9) are in the top 10 institutions ranking list. It indicates that a growing number of Chinese institutions have created an experimental platform of TSA-based mIHC/IF to address diverse scientific challenges and generate high-quality papers.
The cutting-edge and trending concerns in TSA-based mIHC/IF are elucidated by co-citation and keyword analysis. The bulk of research was conducted in the fields of neuroscience, oncology, and immunology. As early as 2008, Ildiko Racz et al. applied fluorescein isothiocyanate TSA method to double staining for CB2 receptors and for microglia or for astrocytes, aiming to study the critical role of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor in the regulation of central immune responses during neuropathic pain (27). The TSA method was initially used in neuroscience research for the simultaneous labeling of multiple targets (28–36). TSA-based mIHC/IF has since gained popularity and interest among oncology researchers and is progressively becoming an essential tool for characterizing the TME of various cancers, in particular colorectal cancer (37, 38), oral squamous cell carcinoma (39, 40), melanoma (16, 41, 42) and cervical cancer (43–45), as indicated by the references and keyword analyses. Many different panels have been established for clinical research, in which the importance of tumor immune infiltrate densities, cell phenotypes, spatial localization, tertiary lymphoid structures, and the identification of targetable biomarkers for prognostic patterns, such as PD-L1, have been analyzed to study the effect of immunotherapy and potentially help to better match patients to appropriate treatment regimens (15, 46, 47). Since 2021, TSA-based mIHC/IF has been dramatically integrated with the omics technologies, such as single-cell sequencing (48–51) and mass spectrometry-based proteomics technologies (52, 53), in the preclinical research and clinical application to deepen the understanding of tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and responses to immunotherapy. Spatial proteomics, spatial transcriptomics, and spatial metabolomics have all gained popularity as a result of the ongoing advancements in spatial omics technologies. In addition to providing high-resolution and detailed analysis for single-cell omics approaches, spatial omics adds a spatial component that is essential for comprehending the intricate architecture and functional linkages found in biological systems (54). For spatial proteomics, the technology can be categorized based on the antibody labeling method (55). Firstly, one of the most popular techniques for moderate-to-low throughput in situ protein detection is the use of fluorescently labeled antibodies to detect multi-proteins This method allows for the visualization of multiple proteins within a single tissue section, such as TSA-based mIHC/IF, tissue-based cyclic immunofluorescence (t-CyCIF), iterative bleaching extends multiplexity (IBEX), iterative indirect immunofluorescence imaging (4i) (3, 56–58). Additionally, cyclic staining, antibody modification, and specialized detection equipment are needed when using DNA Barcode-labeled antibodies to detect multi-proteins like the CODEX (Co-Detection by indexing) platform (59). This approach offers higher multiplexing capabilities but comes with higher costs due to the need for advanced instrumentation and reagents. For high-throughput protein omics, such as Imaging Mass Cytometry (IMC) which used metal-labeled antibodies to overcomes the limitations of fluorescent detection channels (60). However, IMC also necessitates specific antibodies and tools, which raises capital and operating costs. While these methodologies are powerful tools for spatial proteomics, the type of sample, the goals of the study, practicality, and cost-effectiveness should all be considered when selecting a technology.
With the significant advantage of detecting multiple targets simultaneously, TSA-based mIHC/IF provides powerful tools and methods against the studies of immunopathology and neuroinflammation of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 (61–66). Using TSA-based mIHC/IF, the researchers have highlighted novel immunopathological mechanisms and pathological changes in the pancreas (64) and the central nervous system (61, 66). These findings will broaden the investigation of therapeutic targeting of aberrant cellular immune responses and facilitate clinical treatment in COVID-19.
Over the past few decades, TSA-based mIHC/IF has evolved fast. Researchers have completed a variety of processes, including slide preparation, antibody optimization, the design, validation, and standardization of a marker panel, and manual and automated staining protocol (8, 24, 41, 67–75). As pathology has advanced into the digital age, image acquisition has broadened from capturing small fields of view to scanning entire slides. This gets significantly more difficult when using multiplex fluorescent staining imaging. Spectral unmixing techniques address this challenge by extracting the specific spectral profiles of individual fluorophores and using unmixing algorithms to resolve overlapping fluorescence signals (76). Commercial platforms such as the PhenoImager HT system from Akoya Biosciences employ these advanced algorithms to achieve high-precision signal separation. Additionally, the use of custom-designed narrow-band filter sets can effectively mitigate the problem of spectral overlap (24). With carefully selecting and combining filters that allow only specific wavelengths to pass, it is possible to minimize cross-talk between different fluorescence channels, thereby enhancing the clarity and accuracy of the images. Currently, there are multiple commercial software, such as HALO (Indica Labs), inForm (Akoya Biosciences), and Visopharm TissueAlign (Visiopharm), as well as some open-source platforms like Qupath (77), histoCAT (78), CellProfiler (79), which can be widely used for the analysis of multiplex fluorescence staining images. Cell Segmentation, Tissue classification, Phenotype Characterization, and Positive Cell Rate/Expression Intensity Analysis are all common steps in the workflow for these investigations (80). Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are increasingly being integrated into the analysis pipeline to assist with nuclear segmentation, significantly improving the accuracy of cell quantification (81). Moreover, the analysis of cell-to-cell distances and intercellular interactions has gained prominence, offering a better understanding of cellular microenvironments (82). To further enhance the comprehensiveness of tissue microenvironment investigation, a growing number of analytical algorithms have been developed using the R programming language (83). In order to provide a more comprehensive understanding of biological processes, these algorithms enable more intricate and nuanced interpretations of spatial linkages and molecular interactions inside tissues.
The TSA-based mIHC technique offers notable advantages in application, including the capacity for analysis in FFPE (Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded) specimens, reduced reagent expenses relative to alternative multi-omics profiling methodologies. This technique supports implementation through either automated and manual detection processes. Due to its protocol bearing a strong resemblance to traditional immunohistochemical staining methods, the technology demands minimal specialized technical skill. However, considering epitope damage, signal loss and tissue integrity, each staining step still need intensive work to optimize. Specialized training, standard operating procedure and extensive cooperation will facilitate the dissemination and application of this technology (2, 3, 8, 84).
Using the WOSCC database and three bibliometric approaches, this study has compiled detailed information on the application of TSA-based mIHC/IF between 2007 and 2023, including publication volume and growth patterns, journals, countries/regions, institutions, authors, references, and keywords. However, several inevitable limitations of this study should be considered. To begin, searching and downloading literature from the WOSCC database may result in the omission of relevant studies from other databases. Secondly, the screening was confined to the English language. Therefore, non-English publications may receive insufficient attention. Nonetheless, this study still covers the majority of publications on TSA-based mIHC/IF and provides valuable insights into current research hotspots, evolutionary processes and trends in the field.
In conclusion, this is the first bibliometric analysis of the application of TSA-based mIHC/IF, exploring the features of the publications from 2007 to 2023 and revealing the current research priorities and future directions. With the promotion of transdisciplinary and technical progress, TSA-based mIHC/IF and its associated imaging systems and analysis software will continue to improve, broadening the scope of application and improving the depth and accuracy of analysis. This method has a growing impact and emerging applications in basic and translational research as well as in clinical medicine, based on its important ability to characterize the diversity of the entire tissue for a better understanding of pathological or physiological behavior, and with the ultimate goal of implementation in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of multiple diseases.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XY: Data curation, Writing – original draft. CH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. CZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. DY: Data curation, Writing – original draft. XD: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. DW: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AM: Writing – review & editing. HF: Writing – review & editing. YW: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (82203433), Peking University Third Hospital Clinical Key Project (BYSY2022070) and National Science and Technology Key R&D Program (2019YFC0118402).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Willemsen M, Krebbers G, Bekkenk MW, Teunissen MBM, Luiten RM. Improvement of opal multiplex immunofluorescence workflow for human tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. (2021) 69:339–46. doi: 10.1369/00221554211007793
2. Sheng WJ, Zhang CY, Mohiuddin TM, Al-Rawe M, Zeppernick F, Falcone FH, et al. Multiplex immunofluorescence: A powerful tool in cancer immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3086. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043086
3. Stack EC, Wang C, Roman KA, Hoyt CC. Multiplexed immunohistochemistry, imaging, and quantitation: A review, with an assessment of tyramide signal amplification, multispectral imaging and multiplex analysis. Methods. (2014) 70:46–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.08.016
4. Maiques O, Georgouli M, Sanz-Moreno V. Recent advances in tissue imaging for cancer research. F1000Res. (2019) 8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1980. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.19037.1
5. Bobrow MN, Moen PT Jr. Tyramide signal amplification (Tsa) systems for the enhancement of ish signals in cytogenetics. Curr Protoc Cytom. (2001) Chapter 8:Unit 8 9. doi: 10.1002/0471142956.cy0809s11.
6. Sun Z, Nyberg R, Wu Y, Bernard B, Redmond WL. Developing an enhanced 7-color multiplex ihc protocol to dissect immune infiltration in human cancers. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0247238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247238
7. Hoyt CC. Multiplex immunofluorescence and multispectral imaging: forming the basis of a clinical test platform for immuno-oncology. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:674747. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.674747
8. Lim JCT, Yeong JPS, Lim CJ, Ong CCH, Wong SC, Chew VSP, et al. An automated staining protocol for seven-colour immunofluorescence of human tissue sections for diagnostic and prognostic use. Pathology. (2018) 50:333–41. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2017.11.087
9. Wharton KA Jr., Wood D, Manesse M, Maclean KH, Leiss F, Zuraw A. Tissue multiplex analyte detection in anatomic pathology - pathways to clinical implementation. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:672531. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.672531
10. Yeong J, Lim JCT, Lee B, Li H, Ong CCH, Thike AA, et al. Prognostic value of cd8 + Pd-1+ Immune infiltrates and pdcd1 gene expression in triple negative breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:34. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0499-y
11. Taube JM, Roman K, Engle EL, Wang C, Ballesteros-Merino C, Jensen SM, et al. Multi-institutional tsa-amplified multiplexed immunofluorescence reproducibility evaluation (Mitre) study. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002197. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002197
12. Parra ER, Uraoka N, Jiang M, Cook P, Gibbons D, Forget MA, et al. Validation of multiplex immunofluorescence panels using multispectral microscopy for immune-profiling of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human tumor tissues. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:13380. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13942-8
13. Martinez-Morilla S, McGuire J, Gaule P, Moore L, Acs B, Cougot D, et al. Quantitative assessment of pd-L1 as an analyte in immunohistochemistry diagnostic assays using a standardized cell line tissue microarray. Lab Invest. (2020) 100:4–15. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0295-9
14. Rojas F, Hernandez S, Lazcano R, Laberiano-Fernandez C, Parra ER. Multiplex immunofluorescence and the digital image analysis workflow for evaluation of the tumor immune environment in translational research. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:889886. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889886
15. Hernandez S, Rojas F, Laberiano C, Lazcano R, Wistuba I, Parra ER. Multiplex immunofluorescence tyramide signal amplification for immune cell profiling of paraffin-embedded tumor tissues. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:667067. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.667067
16. Van Herck Y, Antoranz A, Andhari MD, Milli G, Bechter O, De Smet F, et al. Multiplexed immunohistochemistry and digital pathology as the foundation for next-generation pathology in melanoma: methodological comparison and future clinical applications. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:636681. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.636681
17. Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Business Res. (2021) 133:285–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
18. Chen C. Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. J Data Inf Sci. (2017) 2:1–40. doi: 10.1515/jdis-2017-0006
19. Aria M, Cuccurullo C. Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetrics. (2017) 11:959–75. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
20. Perianes-Rodriguez A, Waltman L, van Eck NJ. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. J Informetrics. (2016) 10:1178–95. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2016.10.006
21. Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, Tseng H. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: A scientometric analysis in citespace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2012) 12:593–608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
22. Synnestvedt MB, Chen C, Holmes JH. Citespace ii: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. (2005) 2005:724–8.
23. Toth ZE, Mezey E. Simultaneous visualization of multiple antigens with tyramide signal amplification using antibodies from the same species. J Histochem Cytochem. (2007) 55:545–54. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A7134.2007
24. Zhang W, Hubbard A, Jones T, Racolta A, Bhaumik S, Cummins N, et al. Fully automated 5-plex fluorescent immunohistochemistry with tyramide signal amplification and same species antibodies. Lab Invest. (2017) 97:873–85. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2017.37
25. Dixon AR, Bathany C, Tsuei M, White J, Barald KF, Takayama S. Recent developments in multiplexing techniques for immunohistochemistry. Expert Rev Mol Diagnostics. (2015) 15:1171–86. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1069182
26. Feng ZP, Puri S, Moudgil T, Wood W, Hoyt CC, Wang CC, et al. Multispectral imaging of formalin-fixed tissue predicts ability to generate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from melanoma. J Immunotherapy Cancer. (2015) 3:47. doi: 10.1186/s40425-015-0091-z
27. Racz I, Nadal X, Alferink J, Banos JE, Rehnelt J, Martin M, et al. Crucial role of cb2 cannabinoid receptor in the regulation of central immune responses during neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. (2008) 28:12125–35. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3400-08.2008
28. Dimitrov E, Usdin TB. Tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues modulates the mouse hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis via paraventricular glutamatergic neurons. J Comp Neurol. (2010) 518:4375–94. doi: 10.1002/cne.22462
29. Luongo L, Palazzo E, Tambaro S, Giordano C, Gatta L, Scafuro MA, et al. 1-(2 ',4 '-dichlorophenyl)-6-methyl-N-cyclohexylamine-1,4-dihydroindeno 1,2-C pyr azole-3-carboxamide, a novel cb2 agonist, alleviates neuropathic pain through functional microglial changes in mice. Neurobiol Dis. (2010) 37:177–85. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.09.021
30. Shields SD, Moore KD, Phelps PE, Basbaum AI. Olfactory ensheathing glia express aquaporin 1. J Comp Neurol. (2010) 518:4329–41. doi: 10.1002/cne.22459
31. Giordano C, Siniscalco D, Melisi D, Luongo L, Curcio A, Soukupova M, et al. The galactosylation of N-omega-nitro-L-arginine enhances its anti-nocifensive or anti-allodynic effects by targeting glia in healthy and neuropathic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. (2011) 656:52–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.01.045
32. Konczol K, Pinter O, Ferenczi S, Varga J, Kovacs K, Palkovits M, et al. Nesfatin-1 exerts long-term effect on food intake and body temperature. Int J Obes. (2012) 36:1514–21. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2012.2
33. Palazzo E, Marabese I, Luongo L, Boccella S, Bellini G, Giordano ME, et al. Effects of a metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 7 negative allosteric modulator in the periaqueductal grey on pain responses and rostral ventromedial medulla cell activity in rat. Mol Pain. (2013) 9:44. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-44
34. Dimitrov EL, Tsuda MC, Cameron HA, Usdin TB. Anxiety- and depression-like behavior and impaired neurogenesis evoked by peripheral neuropathy persist following resolution of prolonged tactile hypersensitivity. J Neurosci. (2014) 34:12304–12. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.0312-14.2014
35. Yeh CC, Sun HL, Huang CJ, Wong CS, Cherng CH, Huh BK, et al. Long-term anti-allodynic effect of immediate pulsed radiofrequency modulation through down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor 2 in a neuropathic pain model. Int J Mol Sci. (2015) 16:27156–70. doi: 10.3390/ijms161126013
36. Verstockt B, Volk V, Jaeckel C, Alsoud D, Sabino J, Nikolaus S, et al. Longitudinal monitoring of stat3 phosphorylation and histologic outcome of tofacitinib therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 56:282–91. doi: 10.1111/apt.16955
37. Ugai T, Vayrynen JP, Lau MC, Borowsky J, Akimoto N, Vayrynen SA, et al. Immune cell profiles in the tumor microenvironment of early-onset, intermediate-onset, and later-onset colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunotherapy. (2022) 71:933–42. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03056-6
38. Vayrynen JP, Haruki K, Lau MC, Vayrynen SA, Ugai T, Akimoto N, et al. Spatial organization and prognostic significance of nk and nkt-like cells via multimarker analysis of the colorectal cancer microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Res. (2022) 10:215–27. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-21-0772
39. Qiao B, Huang JW, Mei Z, Lam AKY, Zhao JF, Ying L. Analysis of immune microenvironment by multiplex immunohistochemistry staining in different oral diseases and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:555757. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.555757
40. Rong HX, Cai TT, Peng Y, Wang XJ, Lan TJ, Ou ZP, et al. Correlation between tcf7(+) T cells and prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:782058. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.782058
41. Yaseen Z, Gide TN, Conway JW, Potter AJ, Quek C, Hong A, et al. Validation of an accurate automated multiplex immunofluorescence method for immuno-profiling melanoma. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9:810858. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.810858
42. Attrill GH, Lee H, Tasker AT, Adegoke NA, Ferguson AL, da Silva IP, et al. Detailed spatial immunophenotyping of primary melanomas reveals immune cell subpopulations associated with patient outcome. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:979993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.979993
43. Liu H, Xu RY, Gao C, Zhu T, Liu LT, Yang YF, et al. Metabolic molecule pla2g2d is a potential prognostic biomarker correlating with immune cell infiltration and the expression of immune checkpoint genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:755668. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.755668
44. Heeren AM, van Luijk IF, Lakeman J, Pocorni N, Kole J, de Menezes RX, et al. Neoadjuvant cisplatin and paclitaxel modulate tumor-infiltrating T cells in patients with cervical cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunotherapy. (2019) 68:1759–67. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02412-x
45. Yang XH, Shen XY, Li ZJ, Li WC, Liu Y. Reduction in immune cell number and loss of 5hmc are associated with lesion grade in cervical carcinogenesis. 3 Biotech. (2021) 11:486. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-03028-8
46. Ijsselsteijn ME, Brouwer TP, Abdulrahman Z, Reidy E, Ramalheiro A, Heeren AM, et al. Cancer immunophenotyping by seven-colour multispectral imaging without tyramide signal amplification. J Pathol Clin Res. (2019) 5:3–11. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.113
47. Yam C, Yen EY, Chang JT, Bassett RL, Alatrash G, Garber H, et al. Immune phenotype and response to neoadjuvant therapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:5365–75. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0144
48. Zhang JW, Wang ZY, Zhang X, Dai ZY, Zhi-Peng W, Yu J, et al. Large-scale single-cell and bulk sequencing analyses reveal the prognostic value and immune aspects of cd147 in pan-cancer. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:810471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810471
49. Laumont CM, Wouters MCA, Smazynski J, Gierc NS, Chavez EA, Chong LC, et al. Single-cell profiles and prognostic impact of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes coexpressing cd39, cd103, and pd-1 in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:4089–100. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-4394
50. Gao GC, Xue QF, He J, Wu M, Jiang YN, Li QQ, et al. Single-cell rna sequencing in double-hit lymphoma: impdh2 induces the progression of lymphoma by activating the pi3k/akt/mtor signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 125:13. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111125
51. Zhang Q, Liu Y, Wang XY, Zhang C, Hou MX, Liu YE. Integration of single-cell rna sequencing and bulk rna transcriptome sequencing reveals a heterogeneous immune landscape and pivotal cell subpopulations associated with colorectal cancer prognosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1184167. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1184167
52. Stevenson J, Barrow-McGee R, Yu L, Paul A, Mansfield D, Owen J, et al. Proteomics of replicant perfusate detects changes in the metastatic lymph node microenvironment. NPJ Breast Cancer. (2021) 7:24. doi: 10.1038/s41523-021-00227-7
53. Ye SB, Cheng YK, Li PS, Zhang L, Zhang LH, Huang Y, et al. High-throughput proteomics profiling-derived signature associated with chemotherapy response and survival for stage ii/iii colorectal cancer. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2023) 7:12. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00400-0
54. Vandereyken K, Sifrim A, Thienpont B, Voet T. Methods and applications for single-cell and spatial multi-omics. Nat Rev Genet. (2023) 24:494–515. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00580-2
55. Hickey JW, Neumann EK, Radtke AJ, Camarillo JM, Beuschel RT, Albanese A, et al. Spatial mapping of protein composition and tissue organization: A primer for multiplexed antibody-based imaging. Nat Methods. (2022) 19:284–95. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01316-y
56. Lin JR, Izar B, Wang S, Yapp C, Mei S, Shah PM, et al. Highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging of human tissues and tumors using T-cycif and conventional optical microscopes. Elife. (2018) 7:e31657. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31657
57. Radtke AJ, Kandov E, Lowekamp B, Speranza E, Chu CJ, Gola A, et al. Ibex: A versatile multiplex optical imaging approach for deep phenotyping and spatial analysis of cells in complex tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2020) 117:33455–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2018488117
58. Gut G, Herrmann MD, Pelkmans L. Multiplexed protein maps link subcellular organization to cellular states. Science. (2018) 361:eaar7042. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7042
59. Goltsev Y, Samusik N, Kennedy-Darling J, Bhate S, Hale M, Vazquez G, et al. Deep profiling of mouse splenic architecture with codex multiplexed imaging. Cell. (2018) 174:968–81.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.010
60. Giesen C, Wang HA, Schapiro D, Zivanovic N, Jacobs A, Hattendorf B, et al. Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nat Methods. (2014) 11:417–22. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2869
61. Bocci M, Oudenaarden C, Saenz-Sarda X, Simren J, Eden A, Sjolund J, et al. Infection of brain pericytes underlying neuropathology of Covid-19 patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:11622. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111622
62. Dorward DA, Russell CD, Um IH, Elshani M, Armstrong SD, Penrice-Randal R, et al. Tissue-specific immunopathology in fatal Covid-19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2021) 203:192–201. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202008-3265OC
63. Goh D, Lim JCT, Fernaindez SB, Joseph CR, Edwards SG, Neo ZW, et al. Case report: persistence of residual antigen and rna of the Sars-Cov-2 virus in tissues of two patients with long Covid. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:939989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.939989
64. Ji NF, Zhang MS, Ren L, Wang YY, Hu BC, Xiang J, et al. Sars-Cov-2 in the pancreas and the impaired islet function in Covid-19 patients Sars-Cov-2 infection impairs islet function. Emerging Microbes Infections. (2022) 11:1115–25. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2059400
65. Speranza E, Purushotham JN, Port JR, Schwarz B, Flagg M, Williamson BN, et al. Age-related differences in immune dynamics during Sars-Cov-2 infection in rhesus macaques. Life Sci Alliance. (2022) 5. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101314
66. Madden N, Mei YZJ, Jakubiak K, Li JC, Hargus G, Goldman JE, et al. The link between Sars-Cov-2 related microglial reactivity and astrocyte pathology in the inferior olivary nucleus. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1198219. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1198219
67. Wee YTF, Alkaff SMF, Lim JCT, Loh JJH, Hilmy MH, Ong C, et al. An integrated automated multispectral imaging technique that simultaneously detects and quantitates viral rna and immune cell protein markers in fixed sections from epstein-barr virus-related tumours. Ann Diagn Pathol. (2018) 37:12–9. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2018.09.002
68. Cappi G, Dupouy DG, Comino MA, Ciftlik AT. Ultra-fast and automated immunohistofluorescent multistaining using a microfluidic tissue processor. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:4489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41119-y
69. Li L, Sun RF, Miao Y, Tran T, Adams L, Roscoe N, et al. Pd-1/pd-L1 expression and interaction by automated quantitative immunofluorescent analysis show adverse prognostic impact in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma having T-cell infiltration: A study from the international dlbcl consortium program. Modern Pathol. (2019) 32:741–54. doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0193-5
70. Nearchou IP, Lillard K, Gavriel CG, Ueno H, Harrison DJ, Caie PD. Automated analysis of lymphocytic infiltration, tumor budding, and their spatial relationship improves prognostic accuracy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. (2019) 7:609–20. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-18-0377
71. Surace M, DaCosta K, Huntley A, Zhao WG, Bagnall C, Brown C, et al. Automated multiplex immunofluorescence panel for immuno-oncology studies on formalin-fixed carcinoma tissue specimens. Jove-Journal Visualized Experiments. (2019) 143:e58390. doi: 10.3791/58390
72. Bhaumik S, Boyer J, Banerjee C, Clark S, Sebastiao N, Vela E, et al. Fluorescent multiplexing of 3d spheroids: analysis of biomarkers using automated immunohistochemistry staining platform and multispectral imaging. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121:4974–90. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29827
73. Parra ER, Zhai J, Tamegnon A, Zhou N, Pandurengan RK, Barreto C, et al. Identification of distinct immune landscapes using an automated nine-color multiplex immunofluorescence staining panel and image analysis in paraffin tumor tissues. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:4530. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83858-x
74. Sachdeva A, Hart CA, Carey CD, Vincent AE, Greaves LC, Heer R, et al. Automated quantitative high-throughput multiplex immunofluorescence pipeline to evaluate oxphos defects in formalin-fixed human prostate tissue. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:6660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10588-z
75. Ehrenberg AJ, Morales DO, Piergies AMH, Li SH, Tejedor JS, Mladinov M, et al. A manual multiplex immunofluorescence method for investigating neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurosci Methods. (2020) 339:108708. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108708
76. Garini Y, Young IT, McNamara G. Spectral imaging: principles and applications. Cytometry A. (2006) 69:735–47. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20311
77. Bankhead P, Loughrey MB, Fernandez JA, Dombrowski Y, McArt DG, Dunne PD, et al. Qupath: open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17204-5
78. Schapiro D, Jackson HW, Raghuraman S, Fischer JR, Zanotelli VRT, Schulz D, et al. Histocat: analysis of cell phenotypes and interactions in multiplex image cytometry data. Nat Methods. (2017) 14:873–6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4391
79. McQuin C, Goodman A, Chernyshev V, Kamentsky L, Cimini BA, Karhohs KW, et al. Cellprofiler 3.0: next-generation image processing for biology. PLoS Biol. (2018) 16:e2005970. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005970
80. Tan WCC, Nerurkar SN, Cai HY, Ng HHM, Wu D, Wee YTF, et al. Overview of multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence techniques in the era of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2020) 40:135–53. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12023
81. Zhang J, Wu J, Zhou XS, Shi F, Shen D. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence for breast cancer: image augmentation, segmentation, diagnosis, and prognosis approaches. Semin Cancer Biol. (2023) 96:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.09.001
82. Nagl S, Haas M, Lahmer G, Büttner-Herold M, Grabenbauer GG, Fietkau R, et al. Cell-to-cell distances between tumor-infiltrating inflammatory cells have the potential to distinguish functionally active from suppressed inflammatory cells. Oncoimmunology. (2016) 5:e1127494. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1127494
83. Feng Y, Yang T, Zhu J, Li M, Doyle M, Ozcoban V, et al. Spatial analysis with spiat and spasim to characterize and simulate tissue microenvironments. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2697. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37822-0
Keywords: multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence, tyramide signal amplification, bibliometric analysis, CiteSpace, VOSviewer
Citation: Yu X, Huang C, Song Y, Zhang C, You D, Dong X, Wu D, Meeker AK, Feng H and Wang Y (2025) Research progress and perspectives on the application of tyramide signal amplification-based multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence: a bibliometrics analysis. Front. Oncol. 14:1473414. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1473414
Received: 31 July 2024; Accepted: 31 December 2024;
Published: 24 January 2025.
Edited by:
Tamer Saad Kaoud, The University of Texas at Austin, United StatesReviewed by:
Alessandro D’Amuri, Azienda Sanitaria Locale di Brindisi, ItalyKeren Jia, Peking University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Huang, Song, Zhang, You, Dong, Wu, Meeker, Feng and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuqing Wang, d2FuZ3l1cWluZ0Biam11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors share first authorship
 Xiaotong Yu
Xiaotong Yu Chen Huang
Chen Huang Yan Song1,2
Yan Song1,2 Chun Zhang
Chun Zhang Alan Keith Meeker
Alan Keith Meeker Yuqing Wang
Yuqing Wang