
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 27 November 2024
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1472829
This article is a correction to:
Chamaejasmin B Decreases Malignant Characteristics of Mouse Melanoma B16F0 and B16F10 Cells
 Lingling Si1,2
Lingling Si1,2 Xinyan Yan3
Xinyan Yan3 Yan Wang4
Yan Wang4 Boxue Ren4
Boxue Ren4 Huanhuan Ren4
Huanhuan Ren4 Yangfang Ding4
Yangfang Ding4 Qiusheng Zheng1,4*
Qiusheng Zheng1,4* Defang Li1*
Defang Li1* Ying Liu1*
Ying Liu1*A Corrigendum on
Chamaejasmin B decreases malignant characteristics of mouse melanoma B16F0 and B16F10 cells
By Si L, Yan X, Wang Y, Ren B, Ren H, Ding Y, Zheng Q, Li D and Liu Y (2020) Front. Oncol. 10:415. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00415
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1 as published. The authors identified an image overlap issue in Figure 1E, specifically in the images colony formation of B16F0 cells treated with 9 μg/mL CHB. The corrected Figure and its caption appear below.
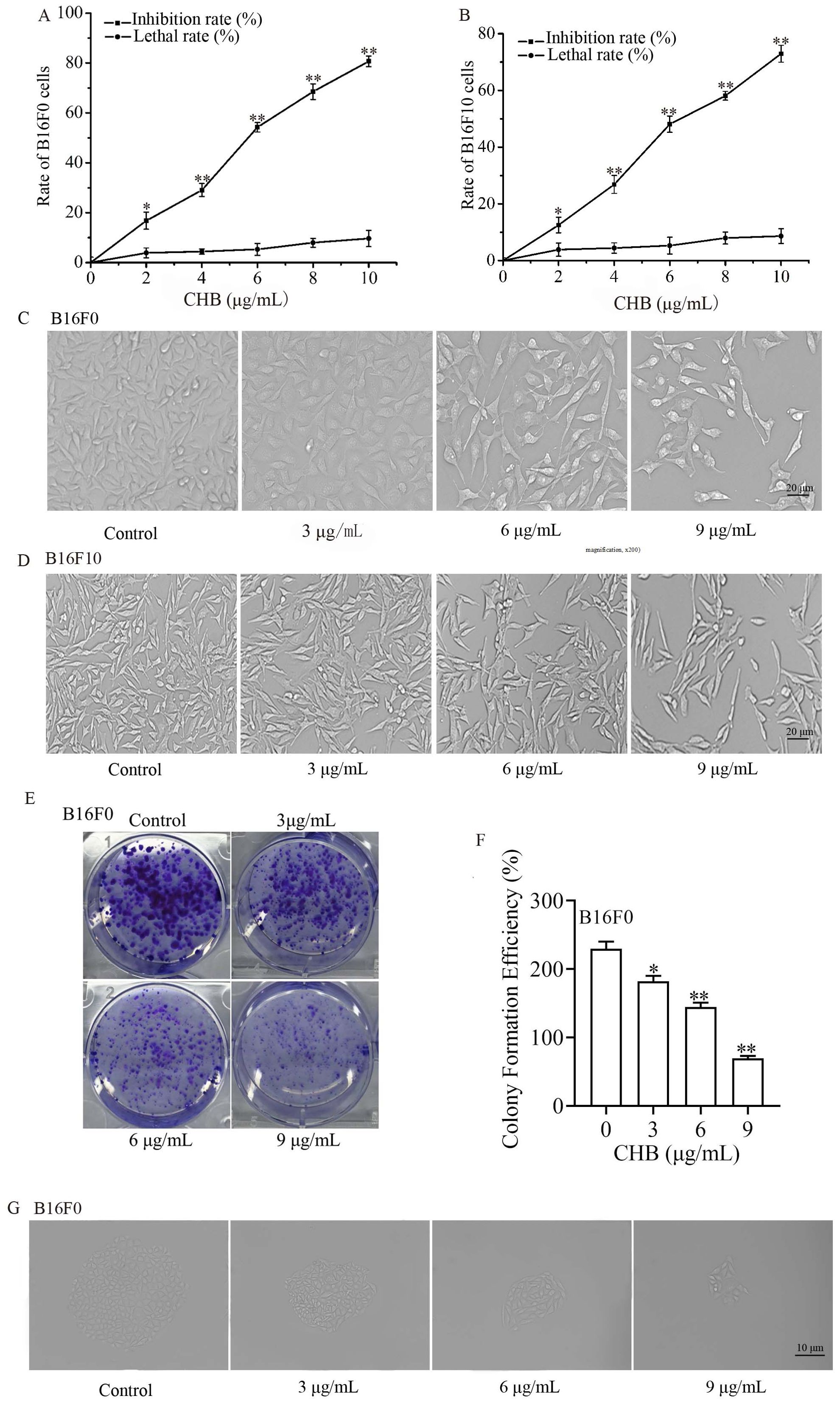
Figure 1. Effects of CHB on B16F0 and B16F10 cell proliferation. The inhibition rate and lethal ratio of B16F0 and B16F10 cells were determined by SRB assay and the trypan blue exclusion test, respectively (A, B). Morphological changes were observed by phase-contrast microscopy (C, D, magnification, x200). Colonies were photographed and counted under a microscope (E, F, magnification, x200). Effects of various CHB concentrations on colony formation of B16F0 cell (G, magnification, x200). Data were presented as mean ± SD for at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the control group cells.
“Figures 1E and 1F. Effects of various CHB concentrations on colony formation of B16F0 cell.”
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6 as published. The authors acknowledged that the first tumor image in the control group was mistakenly replaced with an incorrect tumor image in Figure 6B and Figure 6D. The corrected Figure 6 and its caption appear below.
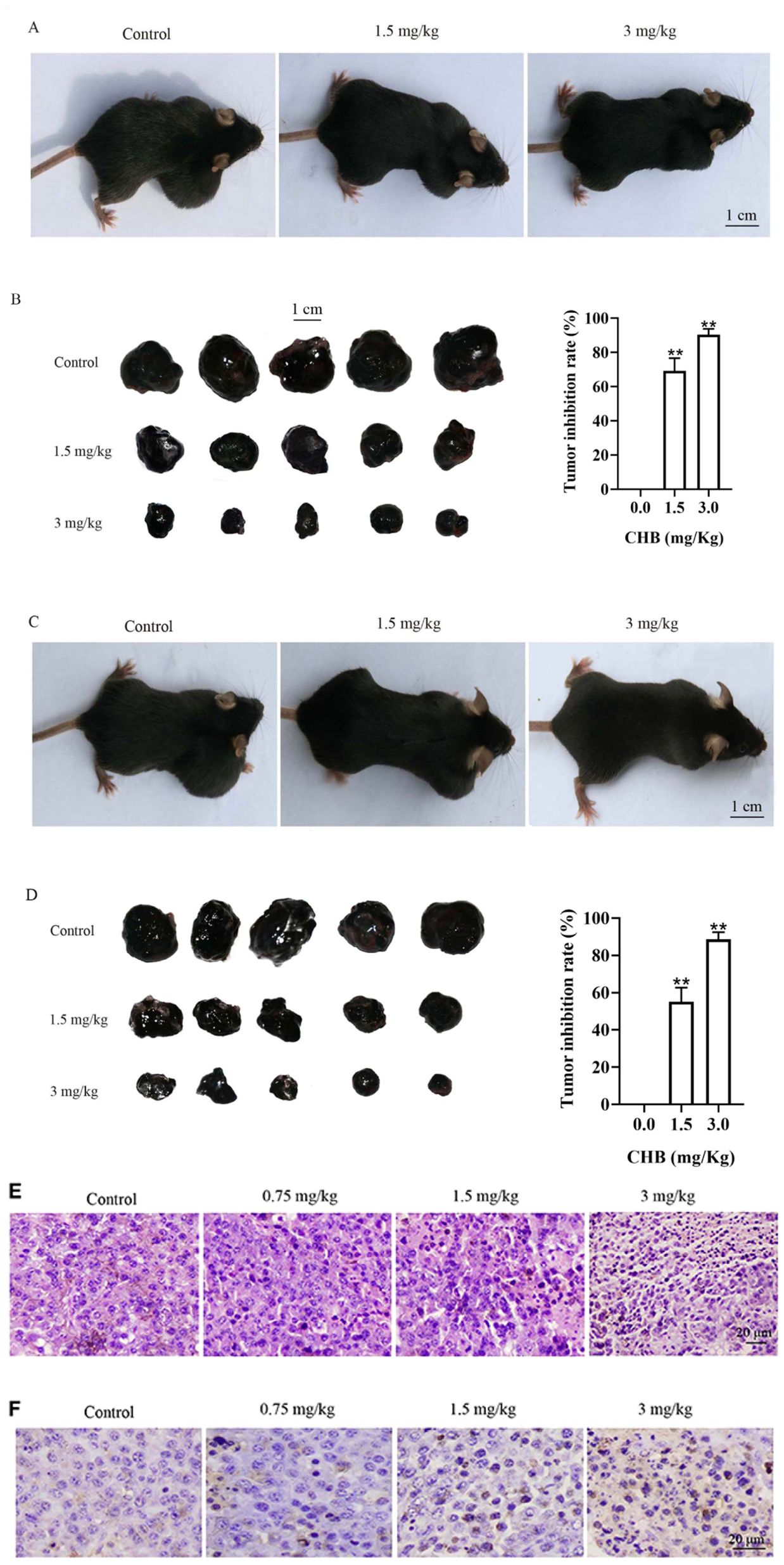
Figure 6. CHB inhibits growth in B16F0 tumor models in vivo. (A, C) Representative images of tumor suppression and tumor colony formation in tumor-bearing mice. (B, D) Typical picture of isolated tumors and inhibition effect of CHB on tumor suppression and tumor colony formation. (E, magnification, x200) Tumor tissues were stained with H&E. (F, magnification, x200) Tumor tissues were stained using TUNEL. Results were expressed as mean ± SD for three separate experiments. **P < 0.01 compared with control group cells.
“Figures 6B and 6D. Typical picture of isolated tumors and inhibition effect of CHB on tumor suppression and tumor colony formation.”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: chamaejasmin B, melanoma, cell cycle arrest, cell differentiation, metastasis, apoptosis, glycolysis
Citation: Si L, Yan X, Wang Y, Ren B, Ren H, Ding Y, Zheng Q, Li D and Liu Y (2024) Corrigendum: Chamaejasmin B decreases malignant characteristics of mouse melanoma B16F0 and B16F10 cells. Front. Oncol. 14:1472829. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1472829
Received: 30 July 2024; Accepted: 31 October 2024;
Published: 27 November 2024.
Edited by:
Jiang-Jiang Qin, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Wen Zhou, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Si, Yan, Wang, Ren, Ren, Ding, Zheng, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Defang Li, emhlbmdxaXVzaGVuZ0Biem1jLmVkdS5jbg==; Qiusheng Zheng, bGlkZWZhbmdAYnptYy5lZHUuY24=; Ying Liu, bGl1eWluZzE5ODJAYnptYy5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.