
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Oncol. , 12 December 2024
Sec. Surgical Oncology
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1471603
This article is part of the Research Topic Surgical Management and Outcomes for Gastric Cancer View all articles
Esophageal stricture is the most common and disabling complication of esophageal injury caused by ingestion of corrosive substances. In our case, the patient developed esophageal stenosis due to ingestion of strong alkaline substances and underwent colon replacement surgery after repeated failed dilation treatments. After surgery, anastomotic stenosis and tracheocolonic fistula occurred successively, and the entire diagnosis and treatment cycle of this disease lasted for more than 20 years. Based on experience and the actual situation of the patient, we conclude that esophageal stents should be the primary treatment option, while tracheal stents should be carefully selected, and secondary surgery is not recommended.
Esophageal injury caused by ingestion of corrosive substances is a relatively rare but potentially destructive event, which can lead to death in severe cases. Esophageal stricture caused by ingestion of corrosive substances is the most common and disabling long-term complication, typically occurring within 4 months after ingestion (1). Endoscopic dilation is the first-line treatment for early esophageal stenosis (2, 4), and esophageal reconstruction should be considered after five to seven unsuccessful attempts at dilation (5).
A 52-year-old man, 21 years ago, accidentally ingested industrial alkali (mainly sodium hydroxide) in an amount of approximately 40 mL. After active treatment such as gastric lavage in the local hospital’s gastroenterology department, multiple gastroscopy examinations showed persistent fibrotic stenosis in the esophagus. Over the next 2 years, multiple balloon dilations were performed under gastroscopy, but the effect was not satisfactory. Later, stage gastroscopy cannot pass through the esophagus smoothly; therefore, esophageal replacement surgery was recommended. The patient underwent total esophagectomy colon replacement surgery in 2005. Dysphagia occurred after oral eating for a period of time, and gastroscopy revealed two anastomotic strictures 23 cm and 31 cm away from the incisor. Within 3 years, the anastomotic cicatrix contracture and stenosis worsened progressively, and finally, the gastric tube placement under the guidance of gastroscopy failed. After many hospitals said that there was no special treatment, the patient gave up treatment. Under the guidance of a doctor, the patient underwent esophageal dilation on their own by a plastic tube after discharge. The inner diameter of the tube gradually increased and later reached 13 mm, allowing for normal oral feeding. This condition was maintained for 15 years, and the patient had a good quality of life. One year ago, the patient went to the hospital for a follow-up examination and underwent a bronchoscopy. Three locations were found to have tracheoesophageal fistulas, with the largest fistula opening being approximately 1 cm. Subsequently, a tracheal metal-covered stent was placed. After implantation, the patient repeatedly developed cough and sputum and pulmonary infection and came to our hospital for further treatment.
Chest CT findings are shown in Figure 1 and Supplementary Video 1. The tracheoscopic manifestations are shown in Figure 2. We created a schedule of major events during the course of the disease (Table 1). Combined with the medical history and current situation, the patient was discharged from the hospital considering that there was no chance of reoperation.
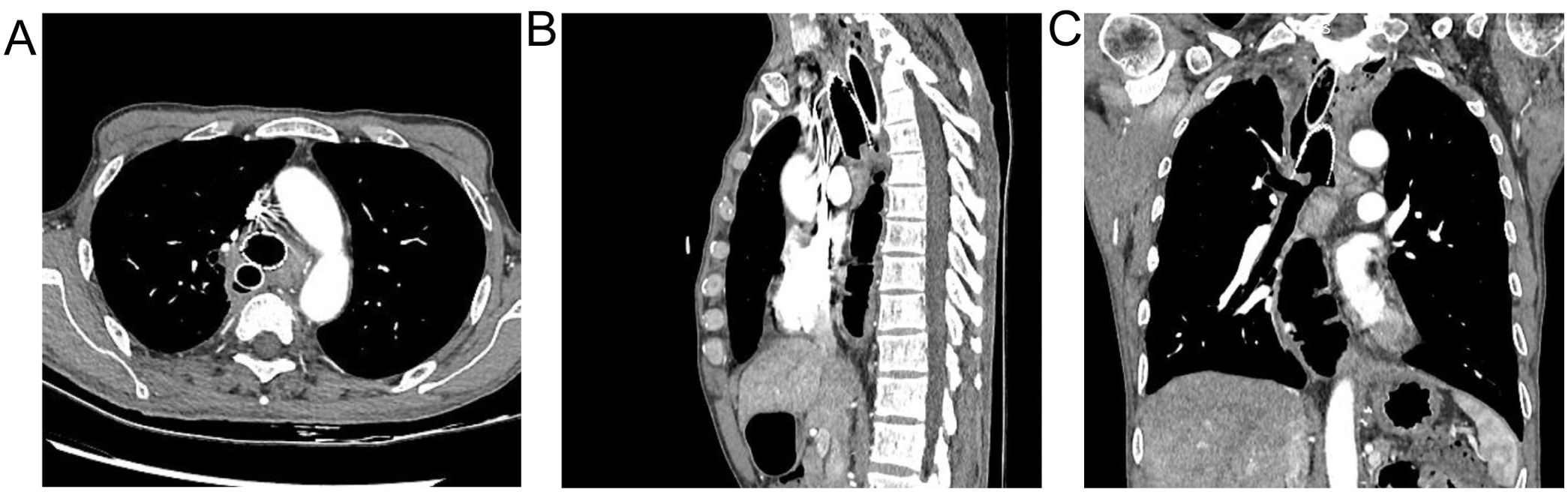
Figure 1. (A) the relationship between double stents and fistula was observed from the horizontal view. (B) observed from sagittal a double support with fistula. (C) the adjacent relationship between the double stent and the fistula was observed from the coronal view.
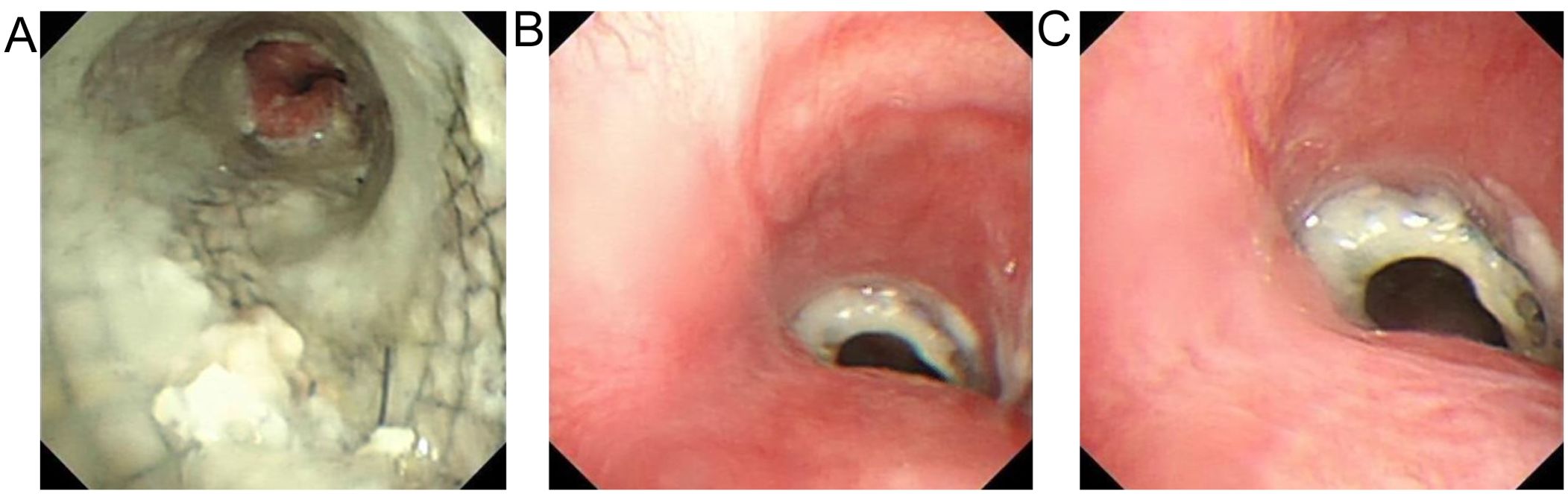
Figure 2. (A) the microscopic observation of tracheal stent. (B) the microscopic observation of tracheal stent top close shot (C) the microscopic observation of tracheal stent top vision.
In our case, the patient had a narrowing of the esophagus due to ingestion of a strongly alkaline substance. After several failed dilation treatments, colon replacement esophageal surgery was performed. Anastomotic stenosis and esophagotracheal fistula appeared after the operation. The diagnosis and treatment of the whole disease lasted for more than 20 years, and the process was complicated and tortuous. Cases are very rare. Unfortunately, due to the length of time, previous medical records are not currently available. The patient is currently in the state of tracheal stent implantation, and the coverage of the tracheal fistula is incomplete. The self-made plastic nutrition tube is placed into the stomach through the mouth, resulting in poor nutritional status and low quality of life due to repeated lung infections and cough. Based on this patient, we put forward our own treatment opinion.
We prefer comprehensive treatment with esophageal therapy as the main treatment. The main consideration is that from the perspective of nutrition, combined with the patient’s self-placement of self-made nutrition tubes in the past 15 years, we consider that the modified esophageal silicone stent can be placed, which can improve the patient’s nutritional status through oral feeding and is conducive to the healing of the fistula. Meanwhile, the modified esophageal silicone stent can be placed for a long time, the local irritation symptoms are mild, and the patient can operate it by himself without affecting work and life. In addition, the implantation of esophageal stents can seal the fistula opening, fundamentally preventing gastric contents from overflowing into the airway (8).
We do not recommend tracheal stent placement, tracheal esophageal double stent placement, or surgical treatment. Consider the following points: 1) from the perspective of clinical symptoms, the patient’s recurrent cough and sputum were mainly caused by lung and bronchial inflammation caused by gastric contents regurgitating into the trachea, as well as airway irritation caused by stent. However, for tracheoesophageal fistula caused by benign lesions, the placement of an airway stent was only suitable for the treatment during the transitional period of surgery (7), and long-term retention was not appropriate. 2) Dual stent placement for the trachea and esophagus can seal bilateral fistulas, but there will be shear effects between the stents (3, 7), resulting in progressive enlargement of the fistula. In addition, the progressive enlargement of the fistula after the patient’s self-made nutrition tube is placed through the mouth, and the airway stent is placed, further verifying that the placement of double stents is not appropriate. 3) Once benign tracheoesophageal fistula is found, surgical treatment is often considered the key to successful treatment (6). Posterior mediastinal esophagectomy with gastric transposition has a good prognosis in children with esophageal stenosis caused by caustic substances (9, 10). Secondary gastro-esophagectomy was also considered, but the surrounding tissue adhesion and fistula area were large after colon and esophageal replacement surgery. Exposure to local anatomic relationships is very difficult, and secondary replacement surgery and flap implantation are not possible. At the same time, surgical treatment may damage the recurrent laryngeal nerve and peripheral blood vessels, resulting in later dyspnea and a high likelihood of recurrent avascular necrosis, so there is no indication of surgery.
Based on the above aspects, for patients with tracheocolonic fistula or tracheoesophageal fistula, we proposed a new concept focusing on esophageal treatment: the modified esophageal silicone stent was placed, and the stent could be removed because the implantation of the tracheal stent was only used as a short-term alternative treatment, while the treatment of pulmonary infection was also given. The tracheoscopy was periodically reviewed to observe the changes in the fistula, and growth factors were tried to stimulate the local mucosal tissue proliferation to narrow the fistula so that the long-term coexistence of the fistula and the patient could be achieved even if the fistula could not heal.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Methodology, Validation. LS: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. XZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. CX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JG: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1471603/full#supplementary-material
1. Chirica M, Bonavina L, Kelly MD, Sarfati E, Cattan P. Caustic ingestion. Lancet. (2017) 389:2041–52. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30313-0
2. Chirica M, Kelly MD, Siboni S, Aiolfi A, Riva CG, Asti E, et al. Esophageal emergencies: WSES guidelines. World J Emerg Surg. (2019) 14:26. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0245-2
3. Bruzzi M, Chirica M, Resche-Rigon M, Corte H, Voron T, Sarfati E, et al. Emergency computed tomography predicts caustic esophageal stricture formation. Ann Surg. (2019) 270:109–14. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002732
4. Contini S, Scarpignato C. Caustic injury of the upper gastrointestinal tract: a comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol. (2013) 19:3918–30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3918
5. Chirica M, Veyrie N, Munoz-Bongrand N, Zohar S, Halimi B, Celerier M, et al. Late morbidity after colon interposition for corrosive esophageal injury: risk factors, management, and outcome. A 20-years experience. Ann Surg. (2010) 252:271–80. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181e8fd40
6. Kim HK, Choi YS, Kim K, Kim J, Shim YM. Long-term results of surgical treatment in benign bronchoesophageal fistula. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2007) 134:411–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.04.030
7. Kim HS, Khemasuwan D, Diaz-Mendoza J, Mehta AC. Management of tracheo-oesophageal fistula in adults. Eur Respir Rev. (2020) 29:200094. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0094-2020
8. Freitag L, Tekolf E, Steveling H, Donovan TJ, Stamatis G. Management of Malignant esophagotracheal fistulas with airway stenting and double stenting. Chest. (1996) 110:1155–60. doi: 10.1378/chest.110.5.1155
9. Estevão-Costa JoséChecktae, Fragoso AC, Campos M, Trindade E, Amil-Dias J. Transhiatal esophagectomy with gastric transposition for esophageal replacement in post-corrosive stricture in children. Acta Med Port. (2011) 24 Suppl 2:107–12.
Keywords: tracheoesophageal fistula, esophageal stenosis, esophageal stent, tracheal stent, case report
Citation: Li X, Zou L, Shi L, Zheng X, Xu C and Guo J (2024) Twenty years of anastomotic stenosis combined with tracheocolonic fistula after colon replacement esophagectomy: a case report. Front. Oncol. 14:1471603. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1471603
Received: 28 July 2024; Accepted: 21 November 2024;
Published: 12 December 2024.
Edited by:
Jae-Seok Min, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
José Estevão-Costa, University of Porto, PortugalCopyright © 2024 Li, Zou, Shi, Zheng, Xu and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cuifang Xu, eHV4dTEyMDUwOEAxNjMuY29t; Jichao Guo, Z3VvamljaGFvMTAxMUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.