
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 02 December 2024
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1468569
Adebrelimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and is also a novel immune checkpoint inhibitor, which has been used in the first-line treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC) with its unique mechanism of action and good clinical efficacy. Significant progress has been made in the treatment of adebrelimab in other malignancies such as non-small cell lung cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and the treatment of SCLC at different stages is also being explored. Therefore, adebrelimab emerges as a promising new treatment option for patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and other types of malignant tumors.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have become one of the remarkable breakthroughs in recent years, and their emergence has brought a new dawn for cancer treatment. It works mainly by blocking a class of proteins called immune checkpoints to restore the ability of the immune system to kill tumor cells (1). Inhibitors targeting programmed death-1 (PD-1), programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) have been successfully approved for the clinical treatment of various malignant tumors such as malignant lymphoma and non-small cell lung cancer (2–4). However, with the widespread use of ICIs, numerous patients experience varying degrees of immune related adverse events (irAEs), and even some patients interrupt treatment due to severe adverse reactions. Therefore, it is urgent to develop an immune checkpoint inhibitor with better efficacy and higher safety to break the dilemma for patients with malignant tumors. Adebrelimab is a PD-L1 monoclonal antibody using immunoglobulin (lg) G4 subtype immunoglobulin with superior antitumor activity and safety profile (5). In February 2023, it was approved in China for the first-line treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). According to the Chinese Medical Association guideline for clinical diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer (2023 edition) for ES-SCLC, the preferred upfront treatment is the adebrelimab combined with etoposide and carboplatin regimen, as it has demonstrated excellent efficacy compared with simple chemotherapy (6). In this review, we will expound the research progress of adebrelimab in malignant tumors.
With the deepening understanding of the tumor immune microenvironment, it has been found that PD-L1 is not only expressed on the surface of tumor cells, but also on the surface of T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages and other immune cells, and even the expression level on the surface of some immune cells is much higher than that of tumor cells (7). This poses a challenge for the application of antibody drugs with Fc segment effector function, as the retained Fc segment effector function may not only bind and accidentally damage immune cells, but also cause uncontrollable loss of efficacy and adverse effects. The so-called Fc segment effector function refers to the hydrolysis of Ig molecules into Fab segments and Fc segments, which mainly act as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) effects, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) effects, antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) and antibody-dependent cytokine release (ADCR) effects. Based on the pursuit of reliable efficacy and excellent safety, the researchers developed adebrelimab to screen an ICI with purer function, higher affinity and focus on blocking the PD-L1/PD-1 signaling pathway. Therefore, adebrelimab differs from previously marketed PD-L1 inhibitors in the following aspects. Firstly, the antibody subtype selection is different (Figure 1). Adebrelimab uses the IgG4 antibody subtype, which has no CDC effects and is associated with less ADCC and less ADCP effects than IgG1 (8). Secondly, the antibody Fc segment was modified. Further site-directed mutagenesis modification of 234A/235A in the Fc segment of adebrelimab reduced the ability to bind to FcγR on the surface of immune cells, eliminated the ADCC and ADCP effects, and also reduced the ADCR effects (9). Meanwhile, adebrelimab Fab segment was modified by S228P to avoid Fab segment replacement and improve the stable type of the drug. Finally, the molecular structure and pharmacological properties are different. Compared with previously marketed PD-L1 antibodies, adebrelimab has a unique binding epitope to PD-L1, with a more centered binding angle and a binding region closer to the binding area of the native ligand PD-1. Furthermore, adebrelimab exhibits a dissociation constant with PD-L1 that boasts a Kd value of merely 0.27*10-10 nmol/L, indicating a stronger affinity than both durvalumab and atezolizumab, which have Kd values of 6.67*10-10 nmol/L and 4.0*10-10 nmol/L, respectively. (The lower the Kd value, the greater the affinity between the antibody and the antigen.) (5). To sum up, during the development process, adebrelimab reduced the occurrence of accidental injury and side effects of immune cells through the selection of antibody types and structural modification, thus making adebrelimab more focused on blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway.
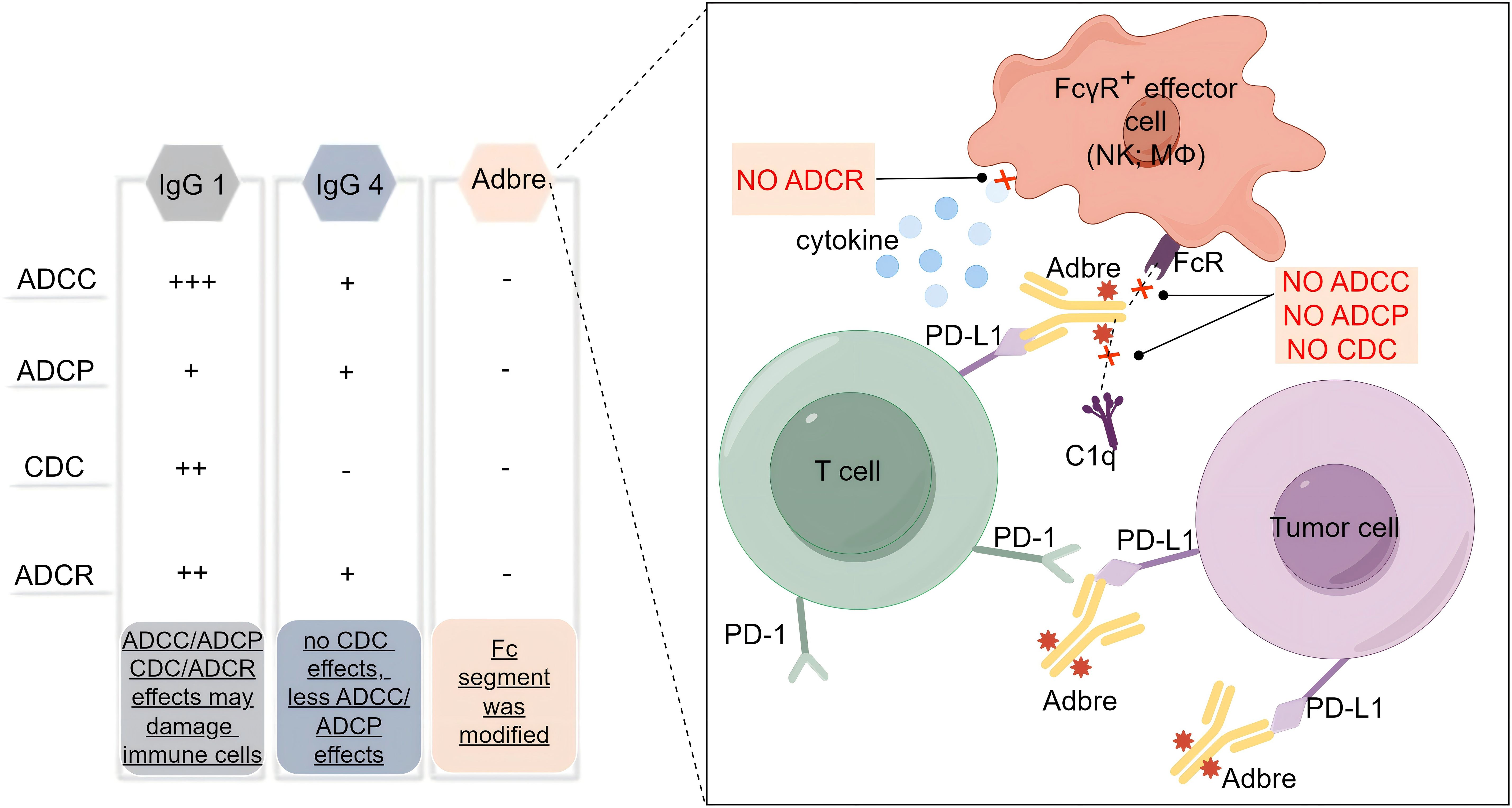
Figure 1. Subtype selection and structural modification of adebrelimab. Adbre, Adebrelimab; FcR, Fc receptor; FcγR, Fc gamma receptors; MΦ, macrophages; C1q, component 1q.
In a phase 1 trial of 41 patients with advanced solid tumors who had failed standard therapy or for whom no known effective therapy was available, adebrelimab demonstrated increased plasma exposure in a dose-proportional manner over the dose range of 3-20 mg/kg/q3w (10). After multiple administrations, the concentration reached steady state after 3-5 treatment cycles, with no obvious accumulation observed. No dose limiting toxicity was observed at any level and the maximum tolerated dose was not defined in this trial. Chen P, et al. aimed at exploring population pharmacokinetics of adebrelimab and suggested that distribution of simulated exposure metrics from the flat dose regimen (1200mg q3w) was similar to the marketed weight-based dosing regimen (20mg/kg q3w), supporting the alternative flat dose regimen in the clinic (11). In this study, there was no significant effect of baseline body weight, albumin levels, tumor size, neutrophil counts, and presence of anti-drug antibodies on CL of adebrelimab as per population-based analysis. The best structure of the adebrelimab popPK model was a two-compartmental, with time-varying linear CL described by the empirical time-dependent sigmoid-maximal model. The geometric mean of CL at baseline and at steady state (at 20th administration cycles) was 0.25L/day and 0.177L/day, respectively, and the volume of distribution at steady state was 4.91L. Geometric mean of the terminal half-life of adebrelimab at steady state was estimated at 19.9 days, which is similar to most of the mAbs.
Immune-checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 showed good clinical activity in SCLC treatment. The results of the CAPSTONE-1 trial showed that adebrelimab as first-line treatment for ES-SCLC patients outperformed controls in overall survival and safety (5). In this phase 3 trial, 462 patients with ES-SCLC, were randomized to receive either adebrelimab combined with chemotherapy (n=230) or placebo combined with chemotherapy (n=232), and the results showed that adebrelimab combined with chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival compared to controls (median overall survival, mOS: 15.3 months vs 12.8 months) (5). The investigators used atezolizumab with first-line chemotherapy for ES-SCLC and found that at the median follow-up of 22.9 months, mOS and placebo with chemotherapy were 12.3 months and 10.3 months, respectively (12). And some other investigators treated durvalumab in first-line chemotherapy with a follow-up of more than 3 years. The results indicate that the mOS of durvalumab and placebo with chemotherapy was 12.9 months and 10.5 months, respectively (13). Furthermore, the ASTRUM-005 study administered a first-line treatment regimen consisting of serpliplimab in combination with chemotherapy to patients with ES-SCLC. The results showed that at a median follow-up of 12.3 months, the mOS of patients who received serpliplimab combined with chemotherapy and those who received placebo combined with chemotherapy were 15.4 months and 10.9 months, respectively (14). Wang BC et al. compared the survival data of adebrelimab (CAPSTONE-1 trial) with durvalumab (CASPIAN trial) and atezolizumab (IMpower133 trial) in the first-line setting of ES-SCLC patients, which result suggested that adebrelimab significantly prolonged survival outcomes against atezolizumab and durvalumab (15). Of course, further real-world evidence or head-to-head clinical trials are needed to confirm the differences between PD-L1 inhibitors in future studies. A network analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials (a total of 5544 ES-SCLC patients and 11 drug combination patterns) showed that PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors-based combinations including adebrelimab are associated with significant improvement in both progression-free survival (PFS) and OS for treatment-naive ES-SCLC patients (16). The results of an additional meta-analysis of seven randomized clinical trials involving 3822 patients showed that adebrelimab plus chemotherapy exhibited better PFS outcomes compared to chemotherapy in first-line immuno-chemotherapies for ES-SCLC (17). A network meta-analysis including six phase 3 and three phase 2 randomized controlled trials (4037 ES-SCLC patients and 10 first-line regimens) showed that adebrelimab in combination with etoposide-platinum had a similar safety profile to standard chemotherapy (18).
Data from the phase study of the front-line treatment of adebrelimab combined with chemotherapy with sequential thoracic radiotherapy for ES-SCLC in 2024 showed that as of December 22, 2023, a total of 67 eligible patients were enrolled, of which 45 patients underwent thoracic radiotherapy as planned. The confirmed objective response rate (ORR) was 71.6%, and 3 (4.5%) patients achieved a complete response (CR). The mOS at the primary study endpoint was 21.4 months, the 1-year and 2-year OS rates were 74.1% and 39.7%, respectively, and the median PFS was 10.1 months (19). In addition, the incidence of Grade 3 treatment-related adverse events was 58.2%. This study showed that adebrelimab combined with chemotherapy sequential thoracic radiotherapy for first-line treatment of ES-SCLC showed good efficacy and controlled toxicity.
Some scholars analyzed from the perspective of cost-effectiveness and found that adebrelimab may be a cost-effective first-line treatment strategy for ES-SCLC compared with chemotherapy alone (20, 21). However, the latest research by Long Y et al. suggests that adebrelimab in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of ES-SCLC was not economical compared with chemotherapy from the perspective of the Chinese healthcare system (22). Summarize the above studies, and the conclusions can be drawn that adebrelimab has good efficacy and safety in the field of ES-SCLC therapy but more studies are needed to prove its advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Concurrent chemoradiotherapy (cCRT) is generally considered the standard treatment for LS-SCLC, but the median survival of LS-SCLC is only 25-30 months, and there is still a huge unmet clinical needs (23). In March 2024, the European Lung Cancer Congress reported a randomized, multi-center phase 3 clinical study of adebrelimab and cCRT for LS-SCLC, and the results surprised many investigators. This clinical trial consists of two phases, where the first phase is a safety run-in study and the second phase is a randomized, controlled, double-blind phase 3 study. A total of 28 patients received adebrelimab combined with cCRT during the safety run-in period. At data cut-off (31 October 2023; final OS evaluation at a median follow-up of 29.4 months), the ORR was 92.9% (95% CI 76.5-99.1), disease control rate (DCR) was 100%, the median PFS was 17.9 months and the median OS has not yet reached (24). In the treatment mode of immunotherapy combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, no unexpected adverse reactions were found in the adverse reaction spectrum. Treatment related adverse events of 10% were all haematological toxicity with no treatment-related deaths. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase of the study is ongoing to further evaluate this trial.
In recent years, the treatment of ICIs in NSCLC has achieved certain results, and various treatment modes are also being explored. A phase 1b study of 37 eligible patients in stage 2-3 NSCLC, 3 cycles of adebrelimab combined with nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin prior before surgery, and followed by 16 cycles of adebrelimab adjuvant treatment. The primary endpoint was major pathological response (MPR). The result displayed that pathologic remission was achieved in 19 patients out of 37 patients, 11 patients achieved a pathologic complete remission, 26 patients were in objective remission, the event-free survival rate at 12 months was 77.8% (25). In terms of safety, 100% of the patients enrolled in this study completed neoadjuvant therapy, which was well tolerated, found no new safety signals, mainly chemotherapy-related haematological toxicity, and no treatment-related deaths occurred. Therefore, the addition of adebrelimab with albumin combined with nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin as perioperative treatment results in a substantial proportion of MPR and high resectability with controlled toxicity. Other studies have found that the efficacy of neoadjuvant adebrelimab plus chemotherapy was basically comparable to that of nivolumab, and the resectability after neoadjuvant adebrelimab chemotherapy was similar to that of nivolumab (26, 27). Adebrelimab provides new options for the treatment of NSCLC, but further research is needed.
TNBC represents approximately 10-20% of all breast cancers, characterized by higher tumor mutation burden and more intensive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes infiltration in tumor microenvironment and is more sensitive to ICIs than any other subtypes (28–30). TNBC is chemotherapy sensitive, and this treatment remains the standard of care despite its limited benefit (31). Recent advances with novel agents have been made for specific subgroups with PD-L1+ tumors (32). MUKDEN 03 study investigated the efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) combined with adebrelimab and chemotherapy (nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin) as neoadjuvant treatment for TNBC. The results showed that adebrelimab combined with SBRT and chemotherapy for neoadjuvant treatment of TNBC had a pathological complete response (pCR) rate of 90%, ORR of 100% and with a better safety profile. This is the first study of immunotherapy combined with SBRT and chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant treatment of early TNBC, providing a novel and reliable treatment option for the neoadjuvant treatment of TNBC patients (33). In this study, 23.1% of patients experienced any level of irAEs, including 2 cases of hyperthyroidism and 1 case of hypothyroidism; One patient experienced treatment-related serious adverse reactions, but no radiation-related skin reactions or deaths occurred. This research is a great breakthrough in the field of TNBC radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy. It is of great significance and is expected to provide new treatment options for the early stages of this aggressive cancer, potentially conferring greater benefits upon patients.
ESCC is one of the common malignant tumors of the digestive tract. According to the global cancer data statistics, the incidence rate of ESCC ranks seventh, and the mortality rate ranks sixth (34). Neoadjuvant immunotherapy has achieved remarkable results in a variety of advanced solid tumors, but its efficacy and safety for locally advanced ESCC are still unclear (35, 36). NATION-1907 is the first study of neoadjuvant immune monotherapy for resectable ESCC, with participants being locally advanced resectable ESCC patients (37, 38). The primary endpoints were safety and feasibility, and secondary endpoints were pCR rate, OS, RFS, and R0 resection rate. A total of 25 patients completed two cycles of neoadjuvant therapy concurrent surgical resection. Research data shows the pCR rate of locally advanced resectable ESCC treated with adebrelimab neoadjuvant monotherapy is 8%, MPR rate is 24%, 2-year OS rate and RFS rate are 92% and 100%, respectively In this thrial 14 patients (56%, 14/25) had treatment-related adverse effects, most of which were grade CTCAE 1, with no new safety signals and no grade 3 or above adverse effects. A multicenter subphase study of 23 patients with inoperable resectable locally advanced or distant metastatic ESCC treated with adebrelimab combined with liposomal irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil every 14 days with primary endpoints of ORR, DCR, OS, and safety, 8.5 months, ORR and DCR of 52.2% and 73.9% after a median visit of 15.2 months, respectively, and mOS of 11.6 months (39).
HCC has an overall poor prognosis and is the third most common cause of tumor-related death worldwide (40). Some scholars have conducted a retrospective study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of adebrelimab and apatinib combined with HAIC-FOLFOX in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A total of 20 patients with unresectable HCC who received treatment with adebrelimab combined with apatinib and HAIC-FOLFOX were included in the study for analysis. The results showed that according to the RECIST v1.1 criteria, 7 patients achieved partial remission after treatment, with a confirmed ORR of 35% (7/20) and a disease control rate (DCR) of 85% (17/20). According to the mRECIST criteria, 2 patients achieved complete remission after treatment, and 12 patients achieved partial remission after treatment. The confirmed ORR was 70% (14/20) and DCR was 85% (17/20) (41). Another prospective phase 1b/2 clinical trial (CARES-310) aims to explore whether adebrelimab plus camrelizumab and apatinib will further increase the clinical benefit of advanced HCC therapy. At a subsequent data cut-of (4 February 2024), in the first dose group, 6 HCC patients with disease progression or intolerance after first-line treatment (systemic therapy ± surgical resection) were treated. Immune-related adverse effects were similar to other checkpoint inhibitors, and no deaths due to drug-related adverse events occurred (42). The above study demonstrated the good efficacy and controllable safety of adebrelimab combination in advanced HCC, requiring further research and exploration in the future to provide new therapeutic strategies for patients.
Due to the difficulty of early diagnosis of CCA, many patients have lost the opportunity of surgery at the time of diagnosis, resulting in a poor prognosis, and the 5-year OS is only 7%~20% (43). There was an ongoing open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of using adebrelimab in combination with CTLA-4 inhibitor IBI310 for the treatment of advanced iCCA patients. In this trial, 39 patients who had failed first or subsequent-line therapy were enrolled in the regimen of adebrelimab (IV 20mg/kg q3w) and IBI310 (IV 3mg/kg q3w) administered for 4 cycles, followed by SHR-1316 monotherapy until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or a maximum of 2 years after enrollment. At date cut-off, the median follow-up was 6.1 months (95%CI, 0.2-18.7), 28 patients were alive, 18 patients remained on treatment. Of 25 evaluable patients, 2 patients achieved complete response and 3 had partial response. The confirmed ORR and DCR were 20.0% and 60.0%, respectively. Notably, the ORR for patients previously treated with anti-PD-1 antibody was 16.7% (2/13). Median PFS and OS was not reached yet. Grade 3 or higher AEs occurred in 16 patients (41.0%), most commonly jaundice (15.4%), rash (10.3%), etc. The treatment of adebrelimab combined with IBI310 was tolerable and showed promising antitumor activity in iCCA refractory to standard therapy (44). Further studies are required to identify predictive/prognostic biomarkers to improve selection of patients most likely to benefit from this treatment strategy.
Several ongoing clinical trials investigating the adjuvant treatment of adebrelimab for malignant tumors are summarised in Table 1. For example there is a multicenter, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 study (NCT06234007) investigating the efficacy and safety of short-course radiotherapy sequential fruquintinib, combined with adebrelimab in the total neoadjuvant therapy of locally advanced rectal cancer. Primary endpoint was CR rate (including clinical CR & pathologic CR) (45). Another an open-label, single-arm, prospective phase 2 trial will enroll 30 patients with III-IVB locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) eligible for resection eligible for surgery to evaluate Neoadjuvant adebrelimab plus dalpiciclib in HPV-negative locally advanced HNSCC (46). One more open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study aims to evaluate the anti-tumor activity and safety of adebrelimab in combination with fuzuloparib in approximately 37 patients with homologous recombination-deficient-positive, recurrent platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer or primary peritoneal cancer (hereinafter referred to as ovarian cancer) (47). Furthermore, a phase 4, prospective single-center, two-arm, double-blind clinical trial designed to include 110 patients with locally advanced gastric adenocarcinoma to accept adebrelimab/placebo combined with SOX regimen. The main efficacy indicators of this trial are pCR and the secondary efficacy indicators are R0 resection rate, safety indicators (Table 1). Outcomes from these ongoing trials may further change the treatment paradigm of patients with Patients with malignant tumors.
Besides clinical efficacy, the safety profile is another important issue to consider in clinical settings. In the CAPSTONE-1 study, the most common irAEs were alanine aminotransferase increased (41%), alanine aminotransferase increased (35%) and hypothyroidism (12%) among which the incidence of ≥3 irAE did not exceed 1.8% (5). As can be seen from the Table 2, adebrelimab exhibited better safety profile when compared with durvalumab and atezolizumab in ES-SCLC. Due to the different patients enrolled in different studies, it is not scientific and rigorous to list the absolute values in the safety comparison. However, in the same study, the improvement rate of the test group compared with the control group can bring some enlightenment. Taking the three PD-L1 inhibitors in the field of ES-SCLC as an example, the overall improvement rate of immune combination chemotherapy compared with control groups were no more than 20%, among which the improvement rate of adebrelimab was lower, only 10.6%. In contrast, durvalumab and atezolizumab were 17.0% and 16.9%, respectively. These data presented here are merely for reference and not head-to-head study data. We eagerly anticipate more robust studies that will rigorously compare the safety profiles of PD-L1 inhibitors in the context of ES-SCLC.
In the era of precision cancer therapy and personalized treatment, identifying effective biomarkers is crucial. RATIONALE 206 revealed that distinct gene expression profiles were evident among various subgroups of patients, indicating that potential biomarkers might vary across different subtypes of advanced lung cancer (48). Yu et al. found that patients with higher CD274 or YAP 1 expression showed longer PFS. Furthermore, patients with higher numbers of ZNF683+CD8+ T cells at baseline received more survival benefit from adebrelimab plus chemotherapy and sequential radiotherapy compared to patients with higher numbers of regulatory T cells at baseline (49). SCLC exhibits significant heterogeneity, with a multitude of factors influencing the regulation of its tumor immune microenvironment. Consequently, relying on a single marker to accurately predict treatment efficacy is challenging. The exploration of biomarkers for SCLC is still progressing, and the transcriptome and genomic biomarkers discovered in the above studies provide a direction for predicting the efficacy of SCLC immunotherapy. Future research needs to further validate the clinical value of these biomarkers and explore more effective therapeutic targets.
Adebrelimab, a fully humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody, offers distinctive pharmacodynamic properties devoid of CDC and ADCC effects. It has shown remarkable clinical efficacy, a favorable safety profile, and broad therapeutic potential in the treatment of malignant tumors. This paper reviews the currently available data on the use of adebrelimab in patients with ES-CLSC. We eagerly anticipate the results from ongoing trials investigating adebrelimab in combination with other agents for various other types of cancer.
Simultaneously, we will encounter numerous problems and challenges, including the primary issue of how to precisely tailor adebrelimab to the individual characteristics of patients. Secondly, how to optimize the selection of treatment options for adebrelimab monotherapy or combination chemotherapy or anti angiogenic drugs is a hot topic for future research and exploration. The efficacy and economic evaluation of adebrelimab maintenance therapy following first or second-line treatment will also be a significant area of future inquiry. In addition, further exploration is needed to screen the advantageous population and reliable biomarkers for the treatment of adebrelimab, which will be a challenge in future research. Finally, it is imperative to further tackle the issue of acquired resistance to adebrelimab. It is expected that as an increasing number of high-quality clinical studies progress and evolve, further research findings will come to light. There are grounds to believe that the applications of adebrelimab in the treatment of malignant tumors are expected to expand, thereby enabling a greater number of patients with cancer to benefit from this therapy.
PC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PPC: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KC: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figure 1 is created using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Rossi S, Masini S, Finocchiaro G, Lorenzi E, Toschi L, Santoro A. Retreatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors in the new scenario of immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16:1683. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091683
2. Harrington KJ, Burtness B, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, et al. Pembrolizumab with or without chemotherapy in recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: updated results of the phase III KEYNOTE-048 study. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:790–802. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02508
3. Li J, Deng Y, Zhang W, Zhou AP, Guo W, Yang J, et al. Subcutaneous envafolimab monotherapy in patients with advanced defective mismatch repair/microsatellite instability high solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:95. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01095-1
4. Peters S, Scherpereel A, Cornelissen R, Oulkhouir Y, Greillier L, Kaplan MA, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy in patients with unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma: 3-year outcomes from CheckMate 743. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:488–99. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.01.074
5. Wang J, Zhou C, Yao W, Wang Q, Min X, Chen G, et al. Adebrelimab or placebo plus carboplatin and etoposide as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CAPSTONE-1): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:739–47. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00224-8
6. Oncology Society of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Medical Association Publishing House. Chinese Medical Association guideline for clinical diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer (2023 edition). Chin J Oncol. (2023) 45:539–74. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20230510-00200
7. Venetis K, Sajjadi E, Peccatori FA, Guerini-Rocco E, Fusco N. Immune plasticity in pregnancy-associated breast cancer tumorigenesis. Eur J Cancer Prev. (2023) 32:364–9. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000803
8. Gogesch P, Dudek S, van Zandbergen G, Waibler Z, Anzaghe M. The role of fc receptors on the effectiveness of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:8947. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168947
9. Liu R, Oldham RJ, Teal E, Beers SA, Cragg MS. Fc-engineering for modulated effector functions-improving antibodies for cancer treatment. Antibodies (Basel). (2020) 9:64. doi: 10.3390/antib9040064
10. Hu X, Fan Y, Jing W, Shen Y, Ma X. 744P Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and preliminary anti-tumor activity of adebrelimab: A phase I trial. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:S884. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.07.870
11. Chen P, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ma K, Shi W, Djebli N, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of adebrelimab - Support of alternative flat dose regimen in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. (2024) 13:1238–51. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13155
12. Liu SV, Reck M, Mansfield AS, Mok T, Scherpereel A, Reinmuth N, et al. Updated overall survival and PD-L1 subgroup analysis of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide (IMpower133). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:619–30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01055
13. Paz-Ares L, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, Statsenko G, et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: 3-year overall survival update from CASPIAN. ESMO Open. (2022) 7:100408. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100408
14. Cheng Y, Han L, Wu L, Chen J, Sun H, Wen G, et al. Effect of first-line serplulimab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: the ASTRUM-005 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2022) 328:1223–32. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.16464
15. Wang BC, Fu C, Lin GH. The efficacy of adebrelimab compared with durvalumab and atezolizumab in untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a survival analysis of reconstructed patient-level data. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1185577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1185577
16. Yang C, Xuan T, Gong Q, Dai X, Wang C, Zhang R, et al. Efficacy and safety of novel immune checkpoint inhibitor-based combinations versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Thorac Cancer. (2024) 15:1246–62. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15310
17. Zhu Y, Liu K, Zhu H, Cao H, Zhou Y. Comparative efficacy and safety of novel immuno-chemotherapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:17588359231206147. doi: 10.1177/17588359231206147
18. Du J, Wang X, Fan L, Shan X, Li M, Liu L. Effectiveness and safety of first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients with extensive-stage small cell lung carcinoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e14794. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14794
19. Chen D, Gao A, Zou B, Huang W, Shao Q, Meng X, et al. Overall survival of adebrelimab plus chemotherapy and sequential thoracic radiotherapy as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:8014. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.8014
20. You M, Chen R, Wu Q, Zhu W, He Y, Huang Y. Cost-effectiveness analysis of adebrelimab combined with chemotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1019826. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1019826
21. Wang T, Li Y, Zheng X. Cost-effectiveness of the combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. (2023) 23:691. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09727-7
22. Long Y, Wang H, Xie X, Li J, Xu Y, Zhou Y. Updated cost-effectiveness analysis of adebrelimab plus chemotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in China. BMJ Open. (2024) 14:e077090. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077090
23. Malakouti-Nejad B, Moore S, Wheatley-Price P, Tiberi D. Management of very early small cell lung cancer: A canadian survey study. Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:6006–18. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30070449
24. Cheng Y, Wang H, Min X, Hu D, Wang Q, Li B, et al. 198P-Adebrelimab with concurrent chemoradiation (cCRT) for limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC): Safety run-in results of a phase III trial. Ann Oncol. (2024) 9:1–11. doi: 10.1016/esmoop/esmoop102577
25. Yan W, Zhong WZ, Liu YH, Chen Q, Xing W, Zhang Q, et al. Adebrelimab (SHR-1316) in combination with chemotherapy as perioperative treatment in patients with resectable stage II to III NSCLCs: an open-label, multicenter, phase 1b trial. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:194–203. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.09.222
26. Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, Provencio M, Mitsudomi T, Awad MM, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:1973–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202170
27. Provencio M, Serna-Blasco R, Nadal E, Insa A, García-Campelo MR, Casal Rubio J, et al. Overall Survival and Biomarker Analysis of Neoadjuvant Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy in Operable Stage IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NADIM phase II trial). J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2924–33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02660
28. Zhu S, Wu Y, Song B, Yi M, Yan Y, Mei Q, et al. Recent advances in targeted strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:100. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01497-3
29. So JY, Ohm J, Lipkowitz S, Yang L. Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): Non-genetic tumor heterogeneity and immune microenvironment: Emerging treatment options. Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 237:108253. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108253
30. Lee J. Current treatment landscape for early triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1524. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041524
31. Wall SW, Echeverria GV. Avoiding extinction: cancer-associated fibroblasts help triple-negative breast cancer outrun chemotherapy. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:3667–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2770
32. Agostinetto E, Losurdo A, Nader-Marta G, Santoro A, Punie K, Barroso R, et al. Progress and pitfalls in the use of immunotherapy for patients with triple negative breast cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2022) 31:567–91. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2049232
33. Chen G, Gu X, Xue J, Zhang X, Yu X, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of neoadjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy plus adebrelimab and chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: A pilot study. Elife. (2023) 12:e91737. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91737
34. Yan X, Duan H, Ni Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Qi H, et al. Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy as neoadjuvant therapy for surgically resectable esophageal cancer: A prospective, single-arm, phase II study (TD-NICE). Int J Surg. (2022) 103:106680. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106680
35. Yu YK, Meng FY, Wei XF, Chen XK, Li HM, Liu Q, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy versus neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2024) 168:417–28.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2023.12.030
36. Hong Z, Xu J, Chen Z, Xu H, Huang Z, Weng K, et al. Additional neoadjuvant immunotherapy does not increase the risk of anastomotic leakage after esophagectomy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. (2023) 109:2168–78. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000487
37. Yin J, Yuan J, Li Y, Fang Y, Wang R, Jiao H, et al. Neoadjuvant adebrelimab in locally advanced resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a phase 1b trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:2068–78. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02469-3
38. Yin J, Yuan J, Li Y, Fang Y, Wang R, Jiao H, et al. Publisher Correction: Neoadjuvant adebrelimab in locally advanced resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a phase 1b trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:2376. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02511-4
39. Mu L, Song Y, Zhao K, Liu Y, Fan Q, Wang X, et al. SHR-1316, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, plus chemotherapy as the first-line treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A multicentre, phase 2 study. Thorac Cancer. (2021) 12:1373–81. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13913
40. Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey YA, Pose E, Kamath PS. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:516–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017
41. Chen B, Lin R, Huang YH, Dai HT, Tang KY, Zhang GY. The safety and efficacy of adebelimumab combined apatinib and hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy in the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:e16175. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.e16175
42. Long Y, Yang Q, Huang ZQ, He XD, Huang J, Liao JG, et al. Preliminary data of a phase Ib/II trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of adebrelimab, camrelizumab plus apatinib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:e16221. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.e16221
43. Bronte F, Sferrazza S, Carbone FG. Editorial: cholangiocarcinoma a new multimodality approach. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:935340. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.935340
44. Fan J, Zhou J, Shi G, Huang X, Guo X, Lu J, et al. 105P A phase II study of SHR-1316 plus IBI310 in patients with advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after failure of first-line therapy. Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:S221. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.1398
45. Lin ZY, Zhang P, Tao KX, Zhang T. Short-course radiotherapy (SCRT) followed by fruquintinib plus adebrelimab and CAPOX in the total neoadjuvant therapy of locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC): A multicenter, single-arm, open-label, phase II study. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:TPS3643. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.TPS3643
46. Liu L, Li Y, Chen F, Li CJ, Xie HX, Zhang ZY, et al. Neoadjuvant adebrelimab plus dalpiciclib in HPV-negative locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A phase II clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:TPS6129. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.TPS6129
47. Chen J, Zou JP, Yu HJ, Liu L, Zang LL, Sun Y. Open-label, phase 2 study of adebrelimab combined with fuzuloparib in the treatment of patients with HRD-positive, recurrent platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:TPS5634. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.TPS5634
48. Wang Z, Zhao J, Ma Z, Cui J, Shu Y, Liu Z, et al. A phase 2 study of tislelizumab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced lung cancer in chinese patientsr. Lung Cancer. (2020) 147:259–68. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.06.007
Keywords: adebrelimab, programmed death-ligand 1, immune checkpoint inhibitor, extensive stage small cell lung cancer, malignant tumors
Citation: Cheng P, He J, Cheng P, Chen K and Zhao G (2024) Progress of research on PD-L1 inhibitor adebrelimab usage in malignant tumors. Front. Oncol. 14:1468569. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1468569
Received: 22 July 2024; Accepted: 14 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited by:
Jose A. Garcia-Sanz, Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), SpainReviewed by:
Ran Wang, Anhui Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Cheng, He, Cheng, Chen and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kaixia Chen, a2FpeGlhY2hlbl8yMEBzaW5hLmNvbQ==; Guangyu Zhao, ODQzMjExODMzQHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.