- 1Department of Urology, Cixilntegrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Medical, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Urology, Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Objectives: This study evaluated the prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for survival outcomes in bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy.
Methods: Studies assessing NLR’s prognostic significance for bladder cancer after radical cystectomy were identified from PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases until April 2024. Survival outcomes analyzed included overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), relapse-free survival (RFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and progression-free survival (PFS).
Results: The meta-analysis comprised 15 cohort studies with 8,448 patients. Multivariate analysis showed significantly shorter OS, CSS, DFS, and RFS in the high NLR group compared to the low NLR group. However, no significant difference in PFS was observed between the groups.
Conclusions: NLR serves as an independent prognostic indicator for bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy, with elevated NLR associated with poorer survival. Further large-scale, prospective studies are warranted to validate the relationship between NLR and prognosis in bladder cancer.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42024549573.
1 Introduction
Bladder cancer, with urothelial carcinoma as the primary pathological type, ranks among the most prevalent malignancies affecting the urinary system. Up to 70-85% of patients with bladder cancer are initially diagnosed as non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), while 15-30% are diagnosed as or progress to muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) (1). The initial treatment strategy of patients with NMIBC is the transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), followed by intravesical therapy of bacillus Calmette–Guerin (BCG) or chemotherapy (according to grade and focality of the tumor). However, current studies have shown that different adjuvant intravesical BCG strains have no significant advantage in reducing the recurrence rate of bladder cancer (1), and 20% to 40% of these tumors may manifest as or progress to muscle-invasive cancer, a highly malignant form prone to early metastasis (2, 3).
In MIBC, neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy with bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy represents the mainstay of treatment, encompasses three main surgical approaches: traditional open radical cystectomy (ORC), laparoscopic radical cystectomy (LRC), and robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) (4, 5). Compared to ORC, LRC is effective in reducing intraoperative blood loss and injury, accelerating postoperative recovery, and significantly decreasing total postoperative complications (4, 5). Although RARC further diminishes intraoperative bleeding and surgical complication rates, it shows no significant advantage over LRC and substantially increases hospitalization costs (6). Currently, LRC is the most prevalent surgical modality for non-metastatic MIBC, offering certain benefits over ORC. However, the prognosis remains poor, with a 5-year postoperative survival rate of only about 50% (7, 8). In addition, for patients with MIBC, the standard neoadjuvant treatment before cystectomy is three or four cycles of cisplatin chemotherapy. Although guidelines recommend four cycles of cisplatin-gemcitabine treatment, three cycles of treatment are often used in clinical practice, and the survival difference between different neoadjuvant treatment regimens seems to be inconclusive (9). Thus, identifying independent predictors of survival risk in these patients, screening those who can benefit more from radical cystectomy, and closely monitoring high-risk patients for individualized treatment holds great clinical significance.
Numerous studies have established that the systemic inflammatory response significantly influences tumor occurrence and progression, serving as an independent factor impacting cancer patients’ prognosis (10, 11). In-depth studies on the direct or indirect interaction between tumor cells and inflammatory factors, such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, platelets, and C-reactive protein, have provided increasing evidence that the systemic inflammatory response affects patient prognosis by altering the tumor cell microenvironment (12–14). Several studies have shown that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can significantly reduce the risk of bladder cancer, stomach cancer, endometrial cancer, and other malignant tumors, while significantly improving patient prognosis (15–17). Neutrophils are essential for neovascularization through a series of enzymatic reactions, which also forms the basis for distant tumor metastasis via blood transport (18, 19). Based on extensive basic research, the human immune process involving lymphocytes has a certain inhibitory effect on tumor occurrence and development (20). Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), an effective indicator of systemic inflammatory response, can reflect body inflammation in clinical practice. Numerous studies have shown that a lower pre-surgery NLR level predicts better prognosis in various malignant tumors, such as gastric cancer, colon cancer, and small cell lung cancer, compared to patients with high NLR levels (21–26).
While numerous studies have reported the predictive value of NLR for prognosis in bladder cancer patients, conclusive evidence regarding its effectiveness in predicting long-term outcomes following radical cystectomy remains elusive due to variations in study duration, cancer types, treatment modalities, detection timing, and other factors (27–41). The present study aimed to investigate the clinical utility of NLR in predicting long-term prognosis after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer patients through a systematic review and meta-analysis, thereby providing the latest and most comprehensive evidence-based medical foundation for developing accurate postoperative prognosis prediction models in this patient population.
2 Methods
2.1 Literature search
In line with the PRISMA 2020 statement (42), this meta-analysis was conducted and prospectively registered in the PROSPERO database (CRD42024549573). A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases until April 2024 to identify studies evaluating the prognostic value of postoperative NLR in predicting survival outcomes for bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy. The literature search used the following terms: “bladder neoplasms”, “lymphocytes”, and “neutrophil”. The detailed search strategies were: ((((“Neutrophils”[Mesh]) OR (((Neutrophil) OR (Neutrophil Band Cells)) OR (Neutrophil Band Cell))) AND ((“Lymphocytes”[Mesh]) OR (((((Lymphocyte) OR (Lymphoid Cells)) OR (Cell, Lymphoid)) OR (Cells, Lymphoid)) OR (Lymphoid Cell)))) AND (ratio)) AND ((“Urinary Bladder Neoplasms”[Mesh]) OR ((((((Bladder Tumor) OR (Urinary Bladder Neoplasm)) OR (Bladder Neoplasm)) OR (Urinary Bladder Cancer)) OR (Bladder Cancer)) OR (Cancer of Bladder)))). Additionally, the reference lists of included studies were manually screened. Two authors independently retrieved and evaluated eligible articles, resolving any discrepancies through discussion.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Eligible studies fulfilled the following criteria: (1) randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, or case-control studies; (2) included bladder cancer patients who underwent radical cystectomy; (3) evaluated the prognostic significance of NLR for survival outcomes; (4) assessed at least one survival outcome measure [overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), relapse-free survival (RFS), progression-free survival (PFS), or cancer-specific survival (CSS)]; (5) provided adequate data for multivariate analysis of risk ratios (RR), odds ratios (OR), or hazard ratios (HR). Study protocols, unpublished research, non-original articles (letters, comments, abstracts, errata, replies), studies with insufficient data, and review articles were excluded from consideration.
2.3 Data abstraction
Two authors independently abstracted data from eligible studies, with any discrepancies resolved by a third author. The extracted information included first author name, year of publication, study duration, country, study design, study population, treatment modality, sample size, follow-up duration, timing of NLR assessment, age, gender, TNM stage, NLR cut-off value, and multivariate analysis (including Multivariate analysis variables) hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), relapse-free survival (RFS), and cancer-specific survival (CSS). In cases where study data were incomplete, the corresponding authors were contacted to obtain the missing information.
2.4 Quality evaluation
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (43), was used to assess the quality of included cohort studies, with scores of 7-9 considered high quality (44). Studies with NOS scores <7 were excluded from quantitative analysis. Two authors independently evaluated the quality of included studies, resolving discrepancies through discussion.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.4.1. Survival data were synthesized using hazard ratios (HRs) and presented with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity for each outcome was assessed using Cochran’s Q (chi-squared test) and I2 inconsistency index (45), with high heterogeneity defined as a P-value <0.1 or I2 >50%. The overall HR for each outcome was calculated using a random-effects model. Sensitivity analysis was conducted for results with ≥3 studies to evaluate each study’s impact on the overall HR. For outcomes with ≥10 studies, potential publication bias was assessed by generating funnel plots in Review Manager 5.4.1 and performing Egger’s regression tests (46) using Stata 15.1 (Stata Corp, College Station, Texas, USA). A P-value <0.05 indicated statistically significant publication bias.
3 Results
3.1 Literature retrieval, study characteristics, and baseline
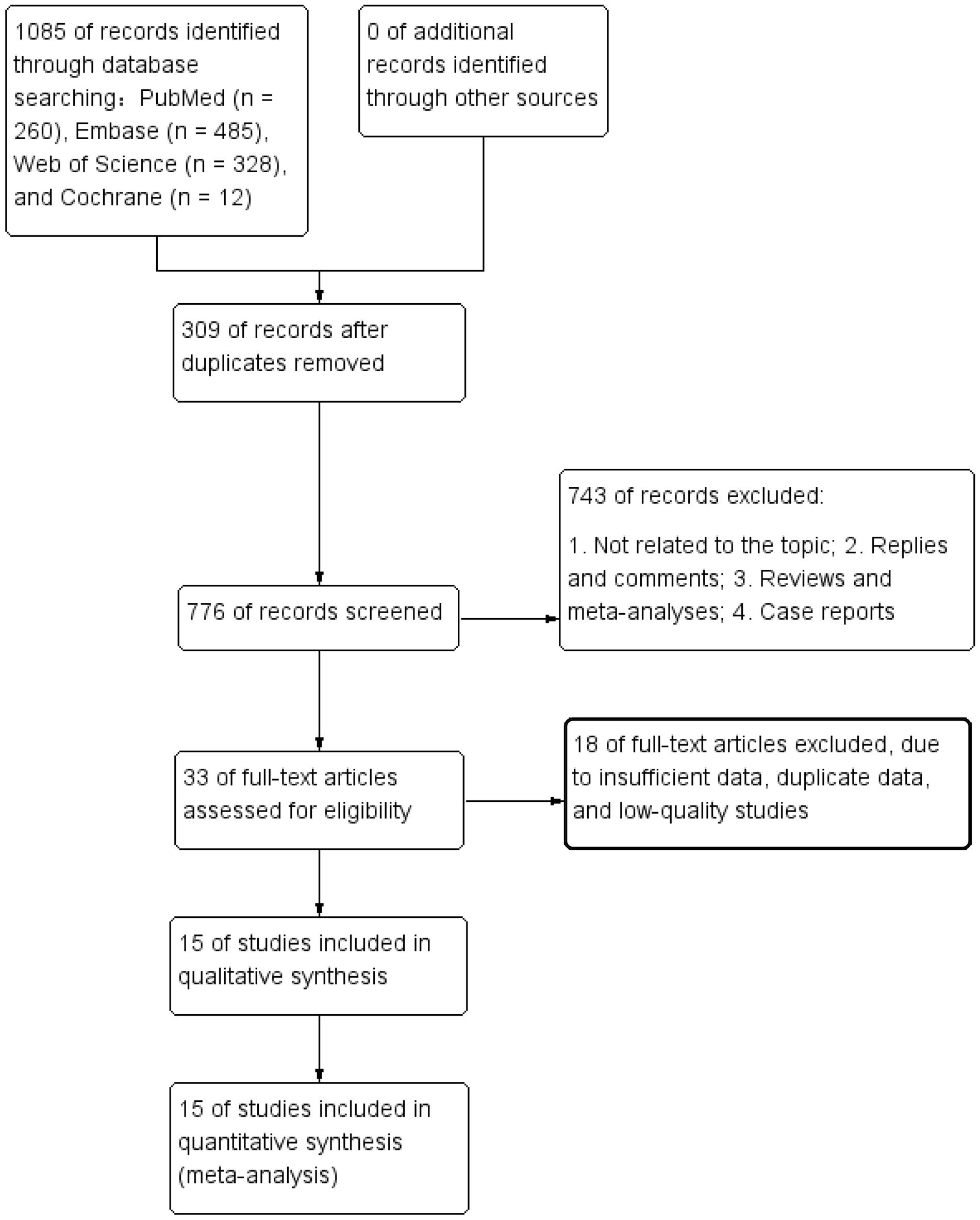
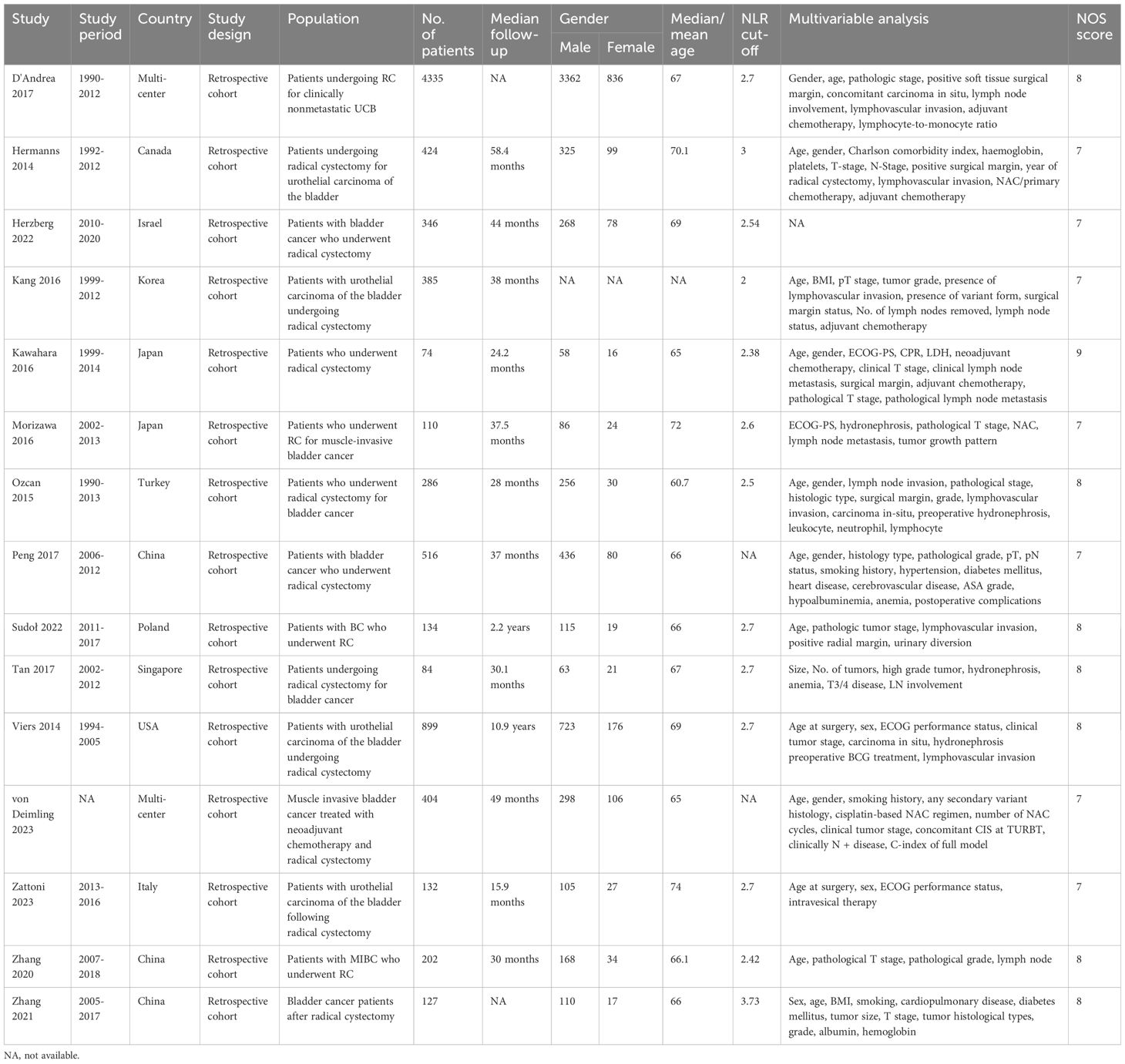
The literature retrieval and selection process is depicted in Figure 1. A systematic literature search identified 1,085 related studies in PubMed (n = 260), Embase (n = 485), Web of Science (n = 328), and Cochrane (n = 12). After duplicate removal, 776 titles and abstracts were assessed. The meta-analysis included 15 retrospective cohort studies with 8,448 patients (27–41). Characteristics and quality evaluation of eligible cohort studies are presented in Table 1.
3.2 OS
OS results were synthesized from 14 cohort studies (27–38, 40, 41). Meta-analysis of multivariate data showed significantly shorter OS in the high NLR group compared to the low NLR group (HR: 1.18; 95% CI: 1.10, 1.27; P <0.00001). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 80%, P <0.00001) (Figure 2).
3.3 CSS
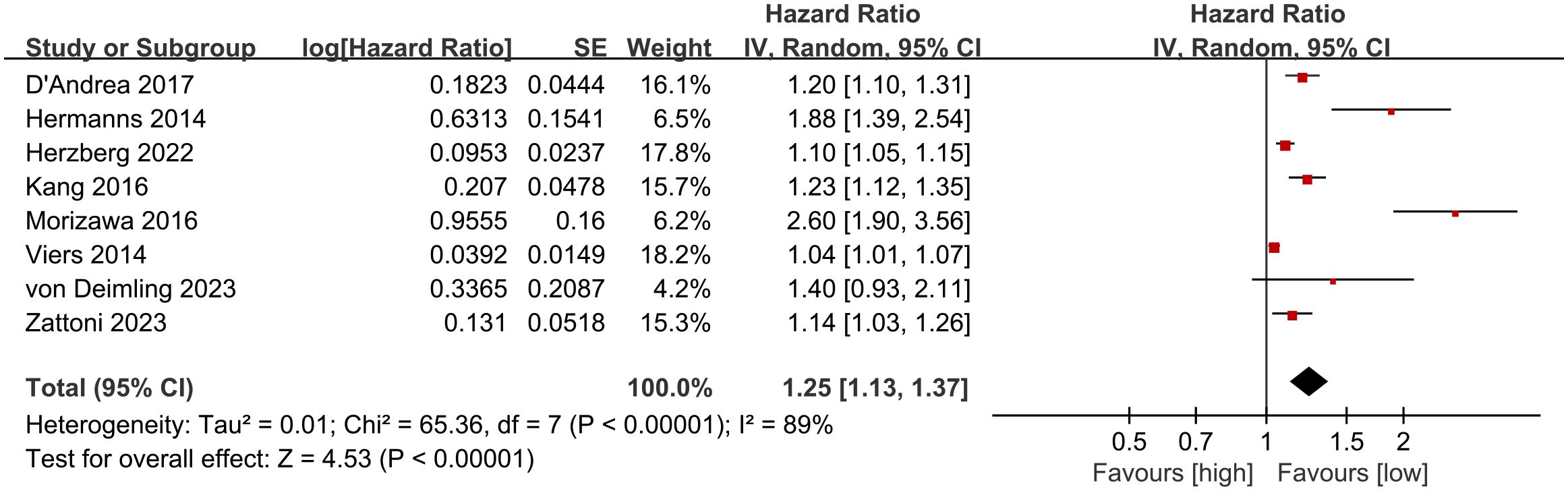
CSS results were synthesized from 8 cohort studies (27, 28, 30, 35, 36, 38, 40, 41). Meta-analysis of multivariate data showed significantly shorter CSS in the high NLR group compared to the low NLR group (HR: 1.25; 95% CI: 1.13, 1.37; P <0.00001). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 89%, P <0.00001) (Figure 3).
3.4 RFS
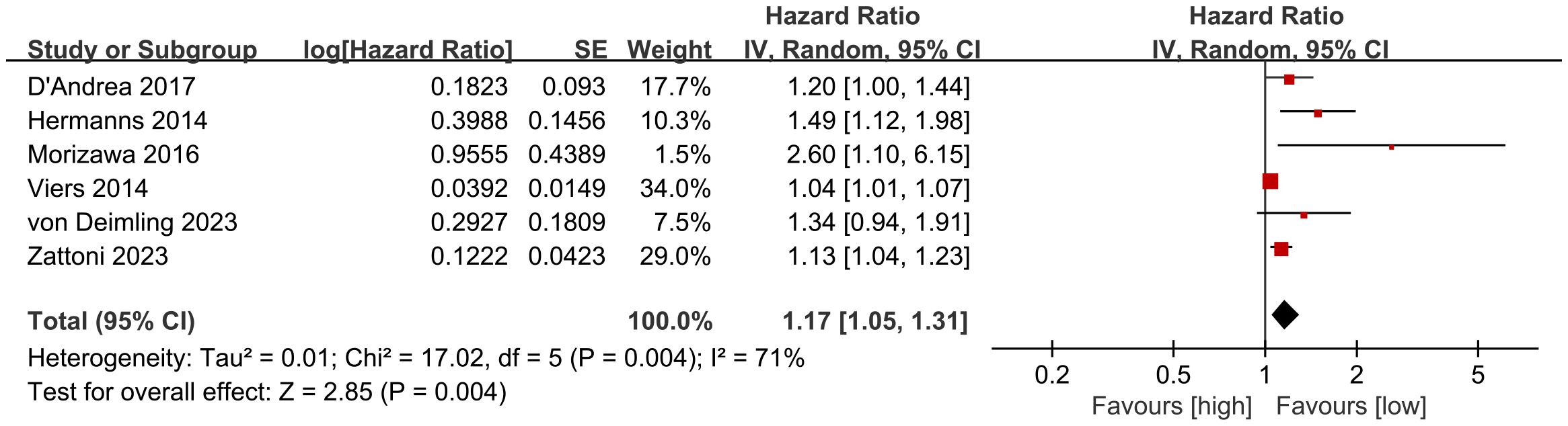
RFS results were synthesized from 6 cohort studies (27, 28, 35, 36, 40, 41). Meta-analysis of multivariate data showed significantly shorter RFS in the high NLR group compared to the low NLR group (HR: 1.17; 95% CI: 1.05, 1.31; P = 0.004). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 71%, P = 0.004) (Figure 4).
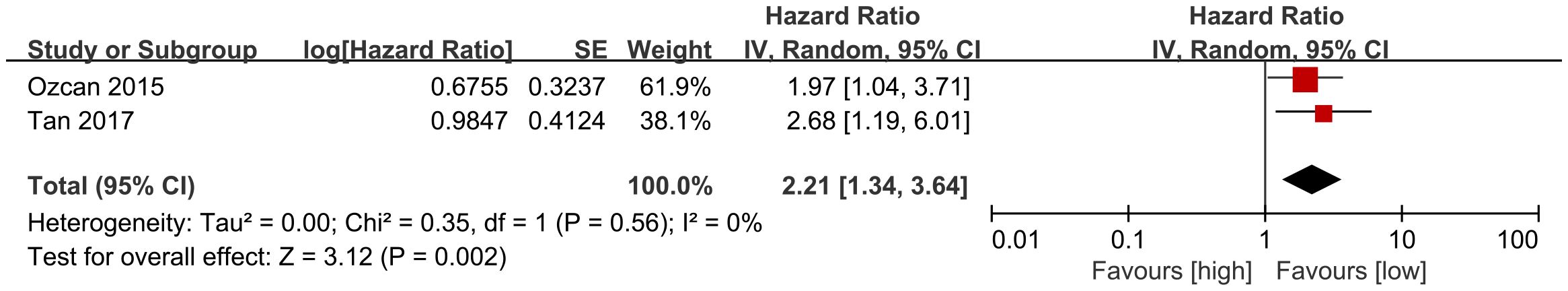
3.5 DFS
DFS results were synthesized from 2 cohort studies (33, 39). Meta-analysis of multivariate data showed significantly shorter DFS in the high NLR group compared to the low NLR group (HR: 2.21; 95% CI: 1.34, 3.64; P = 0.002). No significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 0%, P = 0.56) (Figure 5).
3.6 PFS
PFS results were synthesized from 2 cohort studies (31, 33). Meta-analysis of multivariate data showed similar PFS between the two groups (HR: 1.27; 95% CI: 0.83, 1.95; P = 0.27). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 64%, P = 0.10) (Supplementary Figure S1).
3.7 Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Potential publication bias for OS was evaluated using funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests. Significant publication bias for OS was detected visually (funnel plots) and statistically (Egger’s test P = 0.0001) (Supplementary Figure S2). Sensitivity analysis was conducted for OS, CSS, and RFS results to evaluate each cohort study’s impact on the overall HR by sequential exclusion. Sensitivity analysis revealed stable overall HRs after excluding each cohort study for OS (Supplementary Figure S3A), CSS (Supplementary Figure S3B), and RFS (Supplementary Figure S3C).
4 Discussion
For locally resectable MIBC without distant metastasis, radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection can improve survival and avoid local recurrence and distant metastasis (47). Currently, patient prognosis is mainly evaluated based on bladder tumor stage, grade, and local lymph node metastasis, with host systemic inflammatory response rarely considered (48–50). Studies have revealed that bladder tumor occurrence relates to long-term chronic inflammation, and long-term NSAID use can reduce bladder cancer incidence (17). In recent years, systemic inflammatory response and tumor occurrence/development have become a research hotspot, with evidence showing systemic inflammatory response’s involvement in cancer progression, promoting tumor occurrence/development at various stages, and enhancing tumor cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and anti-apoptosis (51, 52). Using systemic inflammatory response indicators to predict tumor recurrence and progression after surgery is clinically significant (64).
This meta-analysis evaluated the prognostic value of NLR for survival outcomes in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy. Results showed significantly shorter OS, CSS, RFS, and DFS in the high NLR group compared to the low NLR group, suggesting NLR’s predictive value for prognosis in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy, warranting attention in clinical treatment. Our findings support most previous research (53–57). Ofner et al. conducted a meta-analysis of the NLR-RFS relationship using studies before 2022 (53), including seven articles. Results showed a statistically significant association between elevated NLR and increased recurrence risk (53). This finding aligns with our conclusions, and we additionally found significant NLR associations with OS, CSS, and DFS, providing the most comprehensive evidence for using NLR to predict long-term prognosis after radical bladder cancer surgery.
Studies have shown tumor-associated neutrophils (TAN) significantly influence tumor biology. Based on activation pathways, TAN categorize into N1 (anti-tumor) and N2 (pro-tumor) types. In tumor tissues, N2 TAN secrete angiogenic factors, chemokines, cytokines, and reactive oxygen species, promoting tumor development (58). Bladder cancer cells secrete granulocyte colony-stimulating factors, leading to increased neutrophil production. These neutrophils facilitate the formation of new blood vessels by releasing elastase, breaking down histones, and degrading the extracellular matrix, thereby promoting tumor cell proliferation and metastatic spread (59). Thus, increased neutrophils in tumor patients closely associate with tumor progression. An effective anti-tumor immune response requires presence, activation, and co-stimulation of immune system lymphoid components, including CD8+T cells, B cells, and intrinsic lymphocytes (60). Recent immune studies have demonstrated lymphocytes, the immune core, participate in cellular and humoral immunity in vivo (61, 62). Decreased lymphocyte number in tumor tissue reduces local immune function, creating an immune-impaired environment favoring tumor growth. Additionally, tumor microenvironment components inhibit lymphocyte differentiation and maturation, leading to lymphocyte function loss and depletion (63).
With tumor invasion and metastasis, the body’s immune function is inhibited, and lymphocyte proliferation in early stages is inhibited in later stages, resulting in reduced lymphocyte differentiation, maturation, and number (63–65). With malignant tumor progression, cancer cell infiltration manifests as a stronger inflammatory response, and neutrophils increase accordingly (63, 65). With later tumor stage and lymph node metastasis, NLR is higher and patient prognosis worse. Celik et al. (66) showed in bladder cancer patients with largest tumor diameter >3cm, NLR level differed by stage, and preoperative NLR level helped judge tumor stage. Zhang et al. (32) retrospectively analyzed 202 MIBC patients undergoing radical surgery, finding late pathological stage and positive lymph node status as risk factors for PFS and OS, while high NLR was a risk factor for OS.
This study revealed the significance of NLR, a commonly used hematological index, for prognosis in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy, with certain limitations. Firstly, no unified standard exists for selecting and calculating the optimal NLR cut-off value. ROC curve and median methods are commonly used. Different NLR cut-off calculation methods across included studies, with varying case numbers and cut-off values, led to heterogeneity in results. Secondly, while all subjects were bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy, included studies differed in patient characteristics, clinical stages, pathological types, tumor invasion, surgical methods, and adjuvant therapy. Additionally, included studies were retrospective with small sample sizes, mostly single-center data from Europe and Asia, inevitably leading to selective bias. Despite limitations, this meta-analysis is the most recent and comprehensive evidence-based study reporting NLR’s prognostic value for survival outcomes in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy. Results support focusing on NLR level changes in bladder cancer clinical treatment, especially post-surgery, and establishing a predictive model based on factors including NLR to improve post-surgery long-term survival.
5 Conclusion
Multivariate meta-analysis demonstrated NLR as an independent prognostic factor in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy, with high NLR associated with poor prognosis. Given retrospective study limitations, potential selection bias, and heterogeneity, large-scale, multicenter, prospective clinical studies are needed to further validate the NLR-bladder cancer prognosis relationship.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Formal analysis, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. TC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1463173/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Del Giudice F, Asero V, Bologna E, Scornajenghi CM, Carino D, Dolci V, et al. Efficacy of different bacillus of calmette-guérin (BCG) strains on recurrence rates among intermediate/high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancers (NMIBCs): single-arm study systematic review, cumulative and network meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:1937. doi: 10.3390/cancers15071937
2. Lopez-Beltran A, Cookson MS, Guercio BJ, Cheng L. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (2024) 384:e076743. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076743
3. Gnech M, van Uitert A, Kennedy U, Skott M, Zachou A, Burgu B, et al. European association of urology/European society for paediatric urology guidelines on paediatric urology: summary of the 2024 updates. Eur Urol. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.03.025
4. Compérat E, Amin MB, Cathomas R, Choudhury A, De Santis M, Kamat A, et al. Current best practice for bladder cancer: a narrative review of diagnostics and treatments. Lancet (London England). (2022) 400:1712–21. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01188-6
5. Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Compérat EM, Dominguez Escrig JL, et al. European association of urology guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Ta, T1, and carcinoma in situ). Eur urology. (2022) 81:75–94. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.08.010
6. Dyrskjøt L, Hansel DE, Efstathiou JA, Knowles MA, Galsky MD, Teoh J, et al. Bladder cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:58. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00468-9
7. van Hoogstraten LMC, Vrieling A, van der Heijden AG, Kogevinas M, Richters A, Kiemeney LA. Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: challenges for public health and clinical practice. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:287–304. doi: 10.1038/s41571-023-00744-3
8. Jubber I, Ong S, Bukavina L, Black PC, Compérat E, Kamat AM, et al. Epidemiology of bladder cancer in 2023: A systematic review of risk factors. Eur Urology. (2023) 84:176–90. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.03.029
9. Ferro M, de Cobelli O, Musi G, Lucarelli G, Terracciano D, Pacella D, et al. Three vs. Four cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for localized muscle invasive bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy: A retrospective multi-institutional analysis. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:651745. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.651745
10. Mempel TR, Lill JK, Altenburger LM. How chemokines organize the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. (2024) 24:28–50. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00635-w
11. McGettigan SE, Debes GF. Immunoregulation by antibody secreting cells in inflammation, infection, and cancer. Immunol Rev. (2021) 303:103–18. doi: 10.1111/imr.v303.1
12. Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G. Inflammasomes in carcinogenesis and anticancer immune responses. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:343–51. doi: 10.1038/ni.2224
13. Hanahan D, Coussens LM. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. (2012) 21:309–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.022
14. Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med. (2011) 17:1359–70. doi: 10.1038/nm.2537
15. Webb PM, Na R, Weiderpass E, Adami HO, Anderson KE, Bertrand KA, et al. Use of aspirin, other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and acetaminophen and risk of endometrial cancer: the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium. Ann Oncol. (2019) 30:310–6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy541
16. Hedberg ML, Peyser ND, Bauman JE, Gooding WE, Li H, Bhola NE, et al. Use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs predicts improved patient survival for PIK3CA-altered head and neck cancer. J Exp Med. (2019) 216:419–27. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181936
17. Castelao JE, Yuan JM, Gago-Dominguez M, Yu MC, Ross RK. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bladder cancer prevention. Br J Cancer. (2000) 82:1364–9. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.1106
18. Azab B, Bhatt VR, Phookan J, Murukutla S, Kohn N, Terjanian T, et al. Usefulness of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting short-and long-term mortality in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. (2012) 19:217–24. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-1814-0
19. Kusumanto YH, Dam WA, Hospers GAP, Meijer C, Mulder NH. Platelets and granulocytes, in particular the neutrophils, form important compartments for circulating vascular endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis. (2003) 6:283–7. doi: 10.1023/B:AGEN.0000029415.62384.ba
20. Ohtani H. Focus on TILs: prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunity. (2007) 7:4.
21. Wang Z, Li X, Chen J, Hua Y, Zhong X, Tang C, et al. The significance of inflammatory markers in prognosticating the effectiveness and safety of immunotherapy in conjunction with chemotherapy during the primary intervention of advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2024) 192:107817. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.107817
22. Sundaram B, Tweedell RE, Prasanth Kumar S, Kanneganti TD. The NLR family of innate immune and cell death sensors. Immunity. (2024) 57:674–99. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.03.012
23. Staniewska E, Grudzien K, Stankiewicz M, Raczek-Zwierzycka K, Rembak-Szynkiewicz J, Nowicka Z, et al. The prognostic value of the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and red cell distribution width (RDW) in patients with cervical cancer treated using radiotherapy. Cancers. (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081542
24. Pang H, Dai L, Chen L, Chen X, Chen Z, Zhang S, et al. Prognostic value of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index in patients with gastric cancer after radical gastrectomy: a propensity-score matching cohort study and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:583. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12349-9
25. Morais M, Fonseca T, MaChado-Neves R, Honavar M, Coelho AR, Lopes J, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-neutrophil (PN) index in locally advanced rectal cancer patients: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Med Surg (2012). (2024) 86:2474–80.
26. Minici R, Venturini M, Guzzardi G, Fontana F, Coppola A, Piacentino F, et al. A multicenter international retrospective investigation assessing the prognostic role of inflammation-based scores (Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, lymphocyte-to-monocyte, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios) in patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) undergoing chemoembolizations of the liver. Cancers. (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091618
27. Zattoni F, Novara G, Iafrate M, Carletti F, Reitano G, Randazzo G, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor for patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder following radical cystectomy. Cent Eur J Urology. (2023) 76:90–103.
28. von Deimling M, Schuettfort VM, D'Andrea D, Pradere B, Grossmann NC, Kawada T, et al. Predictive and prognostic role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in muscle invasive bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy. Clin Genitourinary Cancer. (2023) 21:430–41. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2023.01.008
29. Sudoł D, Widz D, Mitura P, Płaza P, Godzisz M, Kuliniec I, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of overall survival and cancer advancement in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Cent Eur J Urology. (2022) 75:41–6.
30. Herzberg H, Lifshitz K, Golan S, Baniel J, Malshy K, Hoffman A, et al. Association between early change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio after radical cystectomy and treatment outcomes. BJU Int. (2022) 130:470–7. doi: 10.1111/bju.v130.4
31. Zhang W, Yang F, Kadier A, Chen Y, Yu Y, Zhang J, et al. Development of nomograms related to inflammatory biomarkers to estimate the prognosis of bladder cancer after radical cystectomy. Ann Trans Med. (2021) 9:1440. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4097
32. Zhang J, Zhou X, Ding H, Wang L, Liu S, Liu Y, et al. The prognostic value of routine preoperative blood parameters in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BMC Urology. (2020) 20:31. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00602-9
33. Tan YG, Eu E, Lau Kam On W, Huang HH. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts worse survival outcomes and advanced tumor staging in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Asian J Urology. (2017) 4:239–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2017.01.004
34. Peng D, Gong YQ, Hao H, He ZS, Li XS, Zhang CJ, et al. Preoperative Prognostic Nutritional Index is a Significant Predictor of Survival with Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy: a retrospective study. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:391. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3372-8
35. D'Andrea D, Moschini M, Gust KM, Abufaraj M, Özsoy M, Mathieu R, et al. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as biomarkers for predicting lymph node metastasis and survival in patients treated with radical cystectomy. J Surg Oncol. (2017) 115:455–61. doi: 10.1002/jso.v115.4
36. Morizawa Y, Miyake M, Shimada K, Hori S, Tatsumi Y, Nakai Y, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a detection marker of tumor recurrence in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after radical cystectomy. Urologic Oncol. (2016) 34:257.e11–7. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.02.012
37. Kawahara T, Furuya K, Nakamura M, Sakamaki K, Osaka K, Ito H, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic marker in bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy. BMC Cancer. (2016) 16:185. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2219-z
38. Kang M, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH. The prognostic significance of the early postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder undergoing radical cystectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:335–42. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4708-8
39. Ozcan C, Telli O, Ozturk E, Suer E, Gokce MI, Gulpinar O, et al. The prognostic significance of preoperative leukocytosis and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients who underwent radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Can Urological Assoc J = J l'Association Des urologues du Canada. (2015) 9:E789–94. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.3061
40. Viers BR, Boorjian SA, Frank I, Tarrell RF, Thapa P, Karnes RJ, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with advanced pathologic tumor stage and increased cancer-specific mortality among patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder undergoing radical cystectomy. Eur Urology. (2014) 66:1157–64. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.042
41. Hermanns T, Bhindi B, Wei Y, Yu J, Noon AP, Richard PO, et al. Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as predictor of adverse outcomes in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Cancer. (2014) 111:444–51. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.305
42. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (2021) 372:n71.
43. Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses(2011). Available online at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
44. Kim SR, Kim K, Lee SA, Kwon SO, Lee JK, Keum N, et al. Effect of red, processed, and white meat consumption on the risk of gastric cancer: an overall and dose⁻Response meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2019) 11. doi: 10.3390/nu11040826
45. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.v21:11
46. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
47. Alfred Witjes J, Max Bruins H, Carrión A, Cathomas R, Compérat E, Efstathiou JA, et al. European association of urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2023 guidelines. Eur Urology. (2024) 85:17–31. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.08.016
48. Xie T, Peng S, Liu S, Zheng M, Diao W, Ding M, et al. Multi-cohort validation of Ascore: an anoikis-based prognostic signature for predicting disease progression and immunotherapy response in bladder cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:30. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01945-9
49. van der Kwast TH, Bubendorf L, Cheng L. International society of urological pathology consensus conference on current issues in bladder cancer: main conclusions and recommendations. Eur Urology. (2024) 85:411–3. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.02.009
50. Kim SK, Byun YJ, Park SH, Piao XM, Zheng CM, Moon S, et al. A 23-gene prognostic index predicts progression and bacillus calmette-guérin response in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urology. (2024) 85:400–2. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.01.001
51. Ma X, Aoki T, Tsuruyama T, Narumiya S. Definition of prostaglandin E2–EP2 signals in the colon tumor microenvironment that amplify inflammation and tumor growth. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:2822–32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0125
52. Clatot F, Gouérant S, Mareschal S, Cornic M, Berghian A, Choussy O, et al. The gene expression profile of inflammatory, hypoxic and metabolic genes predicts the metastatic spread of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. (2014) 50:200–7. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.12.009
53. Ofner H, Laukhtina E, Hassler MR, Shariat SF. Blood-based biomarkers as prognostic factors of recurrent disease after radical cystectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065846
54. Mjaess G, Chebel R, Karam A, Moussa I, Pretot D, Abi Tayeh G, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in urological tumors: an umbrella review of evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Acta Oncol (Stockholm Sweden). (2021) 60:704–13. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2021.1886323
55. Suh J, Jung JH, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH. Clinical significance of pre-treated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in the management of urothelial carcinoma: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1365. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01365
56. Hu G, Xu F, Zhong K, Wang S, Xu Q, Huang L, et al. The prognostic role of preoperative circulating neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in primary bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy: a meta-analysis. World J Urology. (2019) 37:1817–25. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2593-z
57. Vartolomei MD, Porav-Hodade D, Ferro M, Mathieu R, Abufaraj M, Foerster B, et al. Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Urologic Oncol. (2018) 36:389–99. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.05.014
58. Song S, Chen H, Dou X, Wang K, Yan J, Yu C. The prognostic value of before treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. (2022), 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07070-3
59. Tang X, Cao Y, Liu J, Wang S, Yang Y, Du P. Diagnostic and predictive values of inflammatory factors in pathology and survival of patients undergoing total cystectomy. Mediators Inflammation. (2020) 2020. doi: 10.1155/2020/9234067
60. Paijens ST, Vledder A, de Bruyn M, Nijman HW. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in the immunotherapy era. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:842–59. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00565-9
61. Block MS, Dietz AB, Gustafson MP, Kalli KR, Erskine CL, Youssef B, et al. Th17-inducing autologous dendritic cell vaccination promotes antigen-specific cellular and humoral immunity in ovarian cancer patients. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:5173. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18962-z
62. Poultsidi A, Dimopoulos Y, He TF, Chavakis T, Saloustros E, Lee PP, et al. Lymph node cellular dynamics in cancer and HIV: what can we learn for the follicular CD4 (Tfh) cells? Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2233. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02233
63. Zhao Y, Shao Q, Peng G. Exhaustion and senescence: two crucial dysfunctional states of T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:27–35. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0344-8
64. Wang Y, Zhuang J, Wang S, Wu Y, Chen L. The prognostic value of preoperative neoindices consisting of lymphocytes, neutrophils and albumin (LANR) in operable breast cancer: a retrospective study. PeerJ. (2024) 12:e17382. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17382
65. Jing W, Wang G, Cui Z, Li X, Zeng S, Jiang X, et al. Tumor-neutrophil cross talk orchestrates the tumor microenvironment to determine the bladder cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2024) 121:e2312855121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2312855121
Keywords: neutrophil, lymphocyte, NLR, bladder cancer, radical cystectomy, meta-analysis
Citation: Chen Z, Zhang Y and Chen T (2024) Prognostic value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 14:1463173. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1463173
Received: 11 July 2024; Accepted: 02 October 2024;
Published: 24 October 2024.
Edited by:
Biagio Barone, ASL Napoli 1 Centro, ItalyReviewed by:
Jiten Jaipuria, Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust, United KingdomBenito Fabio Mirto, University of Naples Federico II, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Zhang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Telei Chen, dGVycnljaGFuMTE5MTEwQDE2My5jb20=
 Zhan Chen1
Zhan Chen1 Telei Chen
Telei Chen