- 1Department of Nephrology, the Eighth Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Foshan, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan, China
- 3Department of Cardiovascular, the First Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China
- 4Department of Oncology, Shenzhen Bao’an Authentic TCM Therapy Hospital, Shenzhen, China
Aim: This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the potential of exosomal microRNAs(Exo-miRs) as diagnostic biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma(RCC).
Methods: Clinical studies reporting the use of Exo-miRs in the diagnosis of RCC were retrieved from PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang, VIP, and Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (SinoMed). After relevant data were screened and extracted, the quality of the included studies was assessed using the QUADAS-2 tool. The Meta-disc (version 1.4) software was used to analyze the heterogeneity of threshold/non-threshold effects in the included studies. The Stata MP (version 16.0) software was used to calculate sensitivity(Sen), specificity(Spe), positive likelihood ratio(+LR), negative likelihood ratio(-LR), area under the curve(AUC), diagnostic odds ratio(DOR), and publication bias.
Results: A total of 11 studies were included in this meta-analysis. Spearman correlation coefficient was 0.319 (P = 0.075; >0.05), indicating no threshold effects. The pooled Sen, Spe, +LR, -LR, DOR, and AUC were 0.73 (95% CI, 0.68–0.78), 0.81 (95% CI, 0.76–0.85), 3.80 (95% CI, 3.02–4.77), 0.33 (95% CI, 0.28–0.40), 11.48 (95% CI, 8.27–15.95), and 0.84 (95% CI, 0.80–0.87), respectively. No publication bias was detected among the included studies.
Conclusion: The expression of Exo-miRs plays an important role in the diagnosis of RCC. However, owing to the limited number of included studies and heterogeneity among them, further clinical research is necessary to verify the findings of this meta-analysis.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO, identifier CRD42023445956.
1 Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), commonly known as kidney cancer, originates from renal tubular epithelial cells. It is a common malignant tumor of the urinary system, accounting for 80%–90% of all malignant tumors originating from the kidney. The incidence of RCC is increasing worldwide, with cases accounting 2%–3% approximately of all adult malignancies (1), and varies across regions, with the highest incidence rates being observed in developed western countries such as North America and Western Europe. Over the past 20 years, the latest Global Cancer Watch data show an annual 2% increase in RCC incidence with more than 400 000 new diagnoses and almost 180 000 deaths per year worldwide by 2020 (2). The kidney can compensate for impaired function to some extent, thus makes early kidney dysfunction difficult to detect. Approximately one-third of patients with RCC have metastatic lesions at diagnosis, whereas another one-third of patients may develop metastasis during the course of the disease (3). RCC is often asymptomatic and cannot be palpated in the early stages. It is diagnosed incidentally during imaging in >50% of cases (4). Ultrasonography is a common method for diagnosing kidney diseases. However, owing to the influence of bowel gas and tumor depth, its accuracy in diagnosing RCC is relatively low. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) helps overcome the limitations but has the disadvantage of radiation exposure and other adverse events, such as allergic reactions and acute kidney injury (5). Blood-based biomarkers such as carcinoembryonic antigen and M2 pyruvate kinase have been evaluated for their potential in early detection of RCC. However, the low specificity and sensitivity limit their clinical utility. Early diagnosis and prognosis of advanced disease are key to improving the overall survival of patients with RCC. Therefore, non-invasive diagnostic methods with high sensitivity and specificity are urgently required to achieve early diagnosis and optimize disease management.
In recent years, owing to the advancement of biomedical technology, exosomes have received increased attention as potential biomarkers in RCC. Exosomes are membrane-bound vesicles formed through the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the cell membrane (6). They can carry various bioactive components, such as lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and cellular metabolites, and have been found in various body fluids, such as cerebrospinal fluid, blood, urine, saliva, and breast milk (7). They play an important role in mediating intercellular communication through endocrine or paracrine mechanisms and hence act on target cells. miRNAs are the most abundant RNA class in exosomes. They can regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by interacting with mRNAs (8). To date, more than 1400 human miRNAs have been identified, which are involved in the regulation of more than one-third of genes (9). Studies have shown that miRNAs are closely associated with the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of tumors (10). Owing to their resistance to endogenous ribonucleases, miRNAs are highly stable in various body fluids. Additionally, the ability of exosomes to maintain the stability of miRNAs allows them to exist more stably in the extracellular environment.
A large number of studies have shown that exosomal microRNAs(Exo-miRs) may have great potential in the diagnosis of RCC (11, 12). Exo-miRs not only have a close relationship with urogenital system tumors but also can reflect the miRNA expression profile of source cells. Therefore, they hold substantial promise in early detection, auxiliary staging, treatment response assessment, and prognosis prediction in urological tumors (13). However, studies on the abnormal expression and functional relevance of Exo-miRs in RCC are limited. Moreover, these studies are primarily conducted in different research institutions and hence lack consistent evidence-based results. Therefore, this meta-analysis aims to assess the diagnostic value of Exo-miRs in RCC, providing a more comprehensive reference for its early diagnosis.
2 Materials and methods
This meta-analysis followed the guidelines outlined in the PRISMA statement (14), and the detailed protocol has been registered in PROSPERO (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO) (Registration number: CRD42023445956).
2.1 Search strategy
Two researchers independently searched for relevant articles in four English electronic databases, namely, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, and four Chinese electronic databases, namely, WanFang, VIP, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (SinoMed). All relevant articles published before April 18, 2024, in English or Chinese were collected. The search terms included “exosomes”, “extracellular vesicles”, “kidney cancer”, “renal cell cancer”, and “renal cell carcinoma”. Subject term expansion was used during retrieval.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Articles in which the experimental group comprised individuals with RCC and the control group comprised individuals without RCC (including individuals with kidney diseases other than RCC and healthy individuals); (2) Articles in which postoperative histopathological examination served as the gold-standard method for diagnosis; (3) Articles that involved the use of extracellular vesicle-derived miRNAs as diagnostic markers for RCC and provided data on sample size and true-positive (TP), false-positive (FP), false-negative (FN), and true-negative (TN) rates; and (4) articles for which the full text was available in either Chinese or English.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Repetitively published articles; (2) comments, reviews, case studies, conference abstracts, and fundamental research; (3) articles without full-text availability or with missing data; (4) articles with a high risk of bias or a controversial design; and (5) articles with an unreasonable experimental design.
2.4 Data extraction
Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, two reviewers (L.Q. and T.J.) independently screened all articles to extract relevant data, including the name of the first author, publication year, country, sample size, histological results, detection methods, source of exosomes, Sen, Spe, and area under the curve(AUC) values. Outcome measures included the number of individuals with TP, FP, TN, and FN results. Disagreements were resolved through third-party adjudication (L.B. and L.H.).
2.5 Quality assessment
The methodological quality of the included articles was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) tool in the Review Manager (version 5.4) software (15). The QUADAS-2 tool consists of 14 items that are divided into two sections: risk of bias evaluation and clinical applicability. Each question is answered with “yes”, “no”, or “unclear”, and the risk of corresponding bias is determined as “low”, “high”, or “unclear”. If all signaling questions within a domain are answered with “yes”, the risk of bias is considered low. If any question is answered with “no”, the risk of bias is considered “high”.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The Meta-disc (version 1.4) software was used to assess threshold effects. If the Spearman correlation coefficient (P-value) between the logarithm of sensitivity and the logarithm of 1-specificity was >0.05, it indicated the absence of heterogeneity caused by a threshold effect. However, a P-value ≤ 0.05 suggested the presence of heterogeneity caused by a threshold effect (16). The MIDAS command in the Stata (version 16.0) software was used to fit a bivariate mixed-effect model and assess heterogeneity among the included articles. The level of heterogeneity was quantified using the I2 value, in which an I2 <50% indicated low heterogeneity and an I2≥50% indicated high heterogeneity. If I2<50%, the fixed effect model is adopted. If I2≥50%, a random effects model is used. In the case of high heterogeneity, subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis were performed to determine the sources of heterogeneity. The evaluation indicators for combining diagnostic tests included Sen, Spe, +LR,-LR, AUC, and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR). Additionally, a Deeks’ funnel plot was generated to detect heterogeneity and publication bias among the included articles (17), and a Fagan’s nomogram was established to evaluate the role and clinical value of Exo-miRs in RCC. All statistical analyses were reviewed by biostatistics experts at Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search and study characteristics
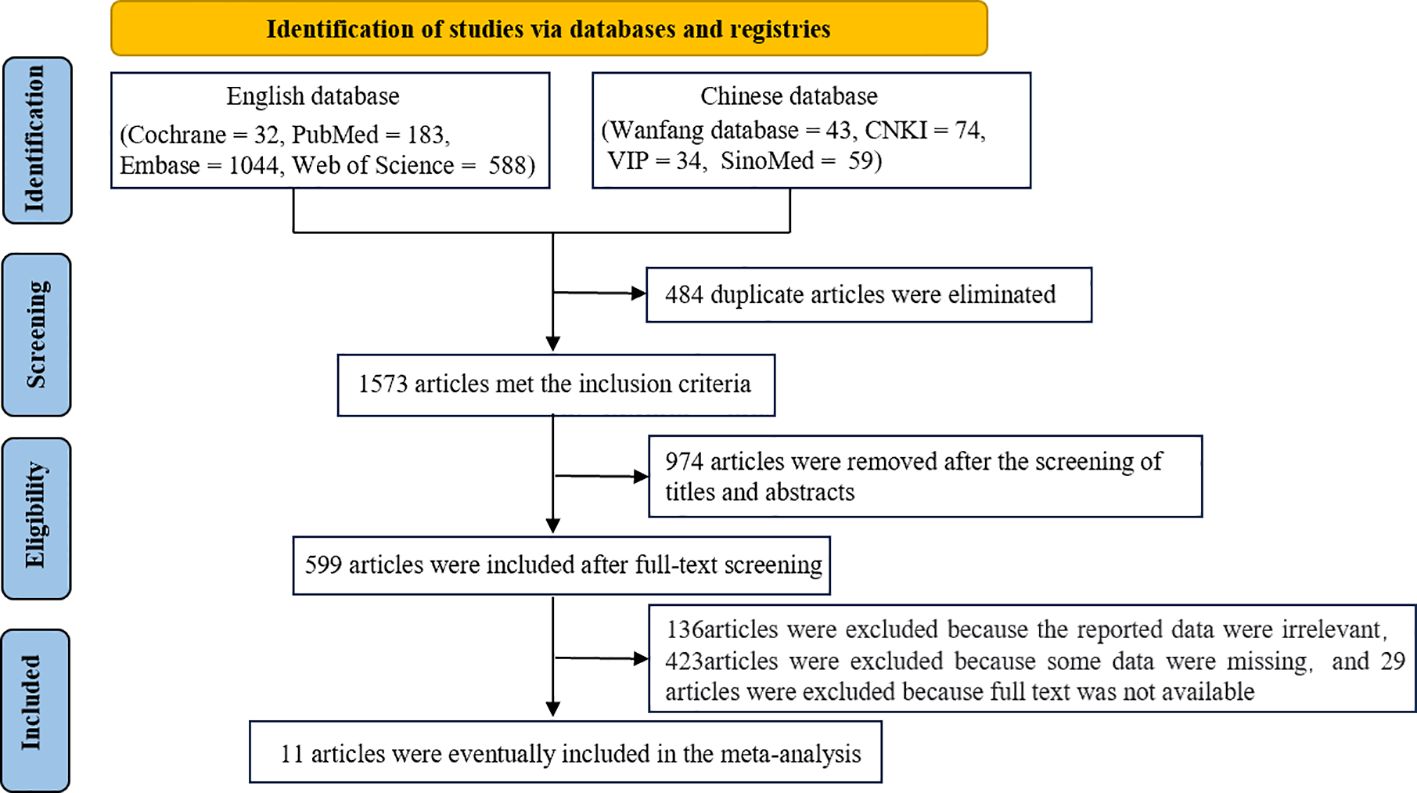
A total of 1573 articles were obtained after duplicate articles were eliminated. Of these articles, 1562 articles were excluded after screening. Specifically, 29 articles were excluded because the full text was not available owing to access rights and publisher restrictions. Eventually, 11 articles were included in this meta-analysis (18–28). The literature screening process is shown in Figure 1.
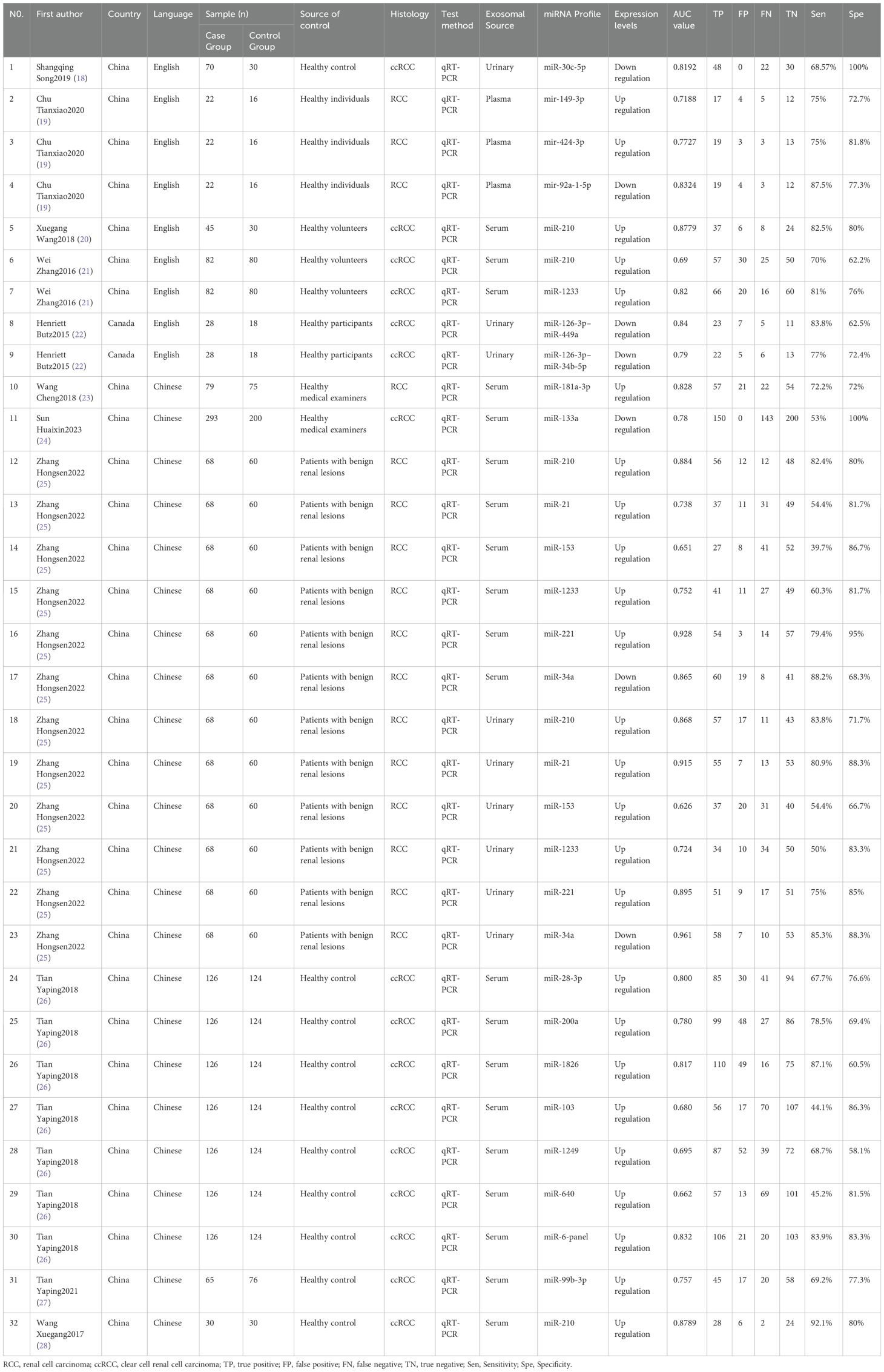
The characteristics of the included articles are shown in Table 1. Of the 11 included articles (18–28), 10 were journal articles (18–24, 26–28) and 1 was a master’s thesis (25). Six articles were published in Chinese (23–28) and five articles were published in English (18–22), with a total of 908 cases and 738 controls. Eight articles focused on clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (18, 20–22, 24, 26–28), whereas three articles focused on RCC (19, 23, 25). Three articles reported the use of urine-derived extracellular vesicles (18, 22, 25), one article reported the use of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (19), and seven articles reported the use of serum-derived extracellular vesicles (20, 21, 23–28). In all included articles, the experimental group comprised patients with cancer confirmed via pathological examination, whereas the control group comprised individuals with benign renal lesions (renal cysts and hematomas), adjacent normal tissue samples, or healthy adults.
3.2 Risk of bias in included studies
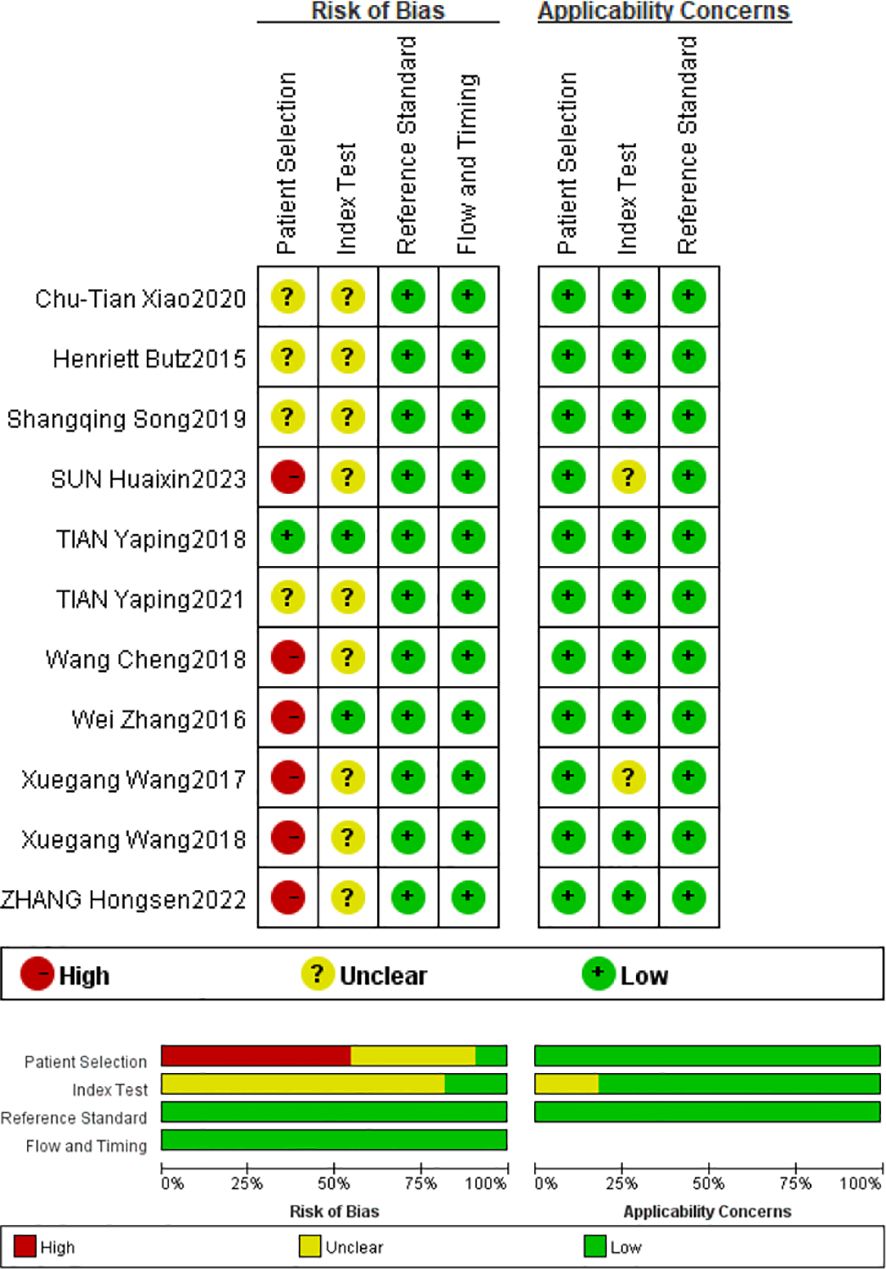
Based on QUADAS-2 scores, all included studies show a low risk of bias in the reference trial domain and the case process and progress domain, a high risk of bias in the patient selection domain, and an unclear risk of bias in the index domain. The risk of bias was primarily attributed to two aspects: the included articles were not randomized controlled trials and did not use prespecified thresholds. Overall, the methodological quality of the included articles was moderate to high, indicating that the articles were reliable. Based on QUADAS-2 scores, all included articles were identified to be of moderate to high quality (Figure 2).
3.3 Results of data analysis
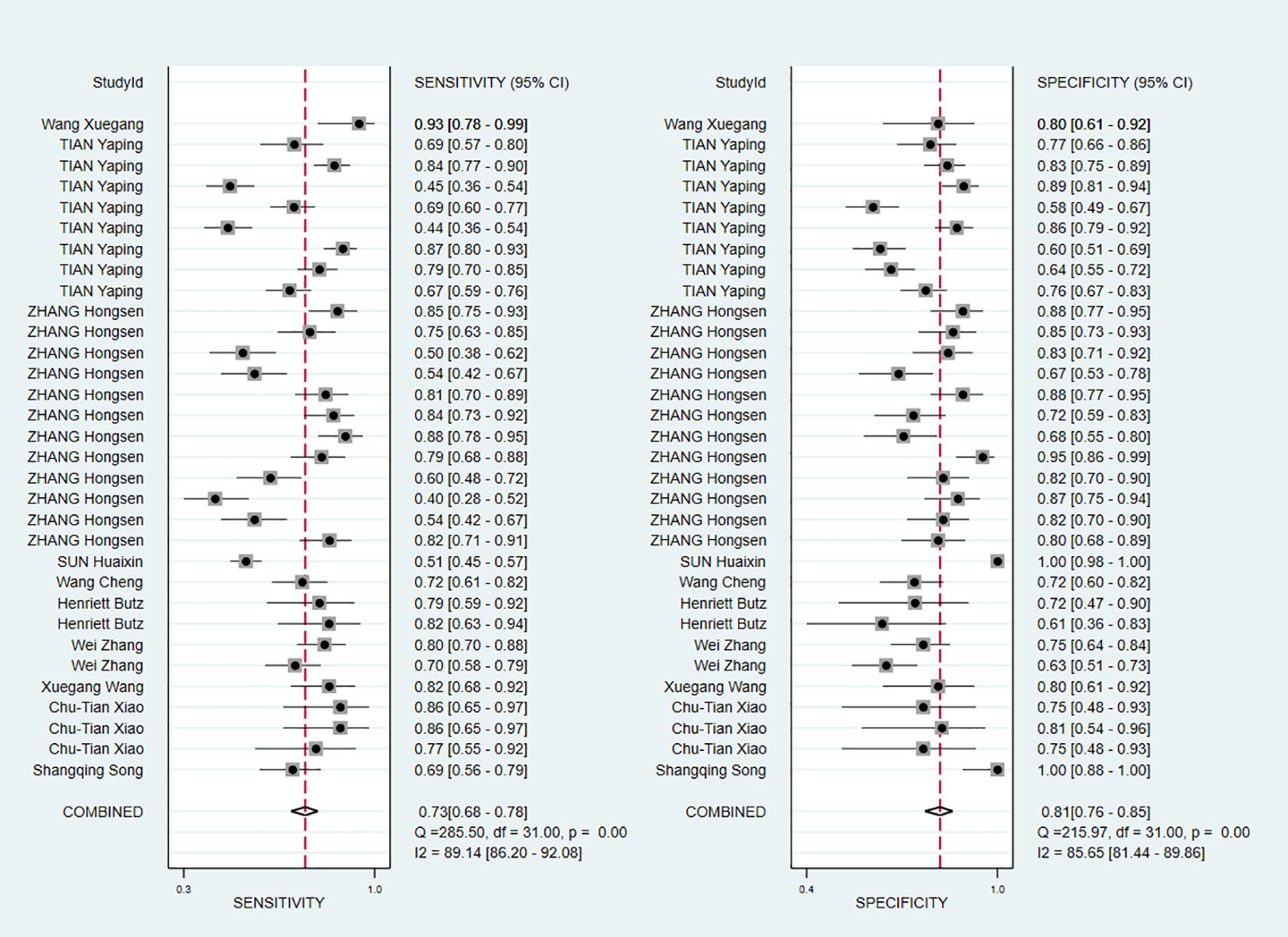
The Spearman correlation coefficient was 0.319 (P = 0.075), indicating the absence of threshold effects. The I2 values for pooled Sen and Spe were 89.14% and 85.65%, respectively, both P value were less than 0. 01, indicating the presence of heterogeneity. Therefore, the sources of heterogeneity were subsequently identified.
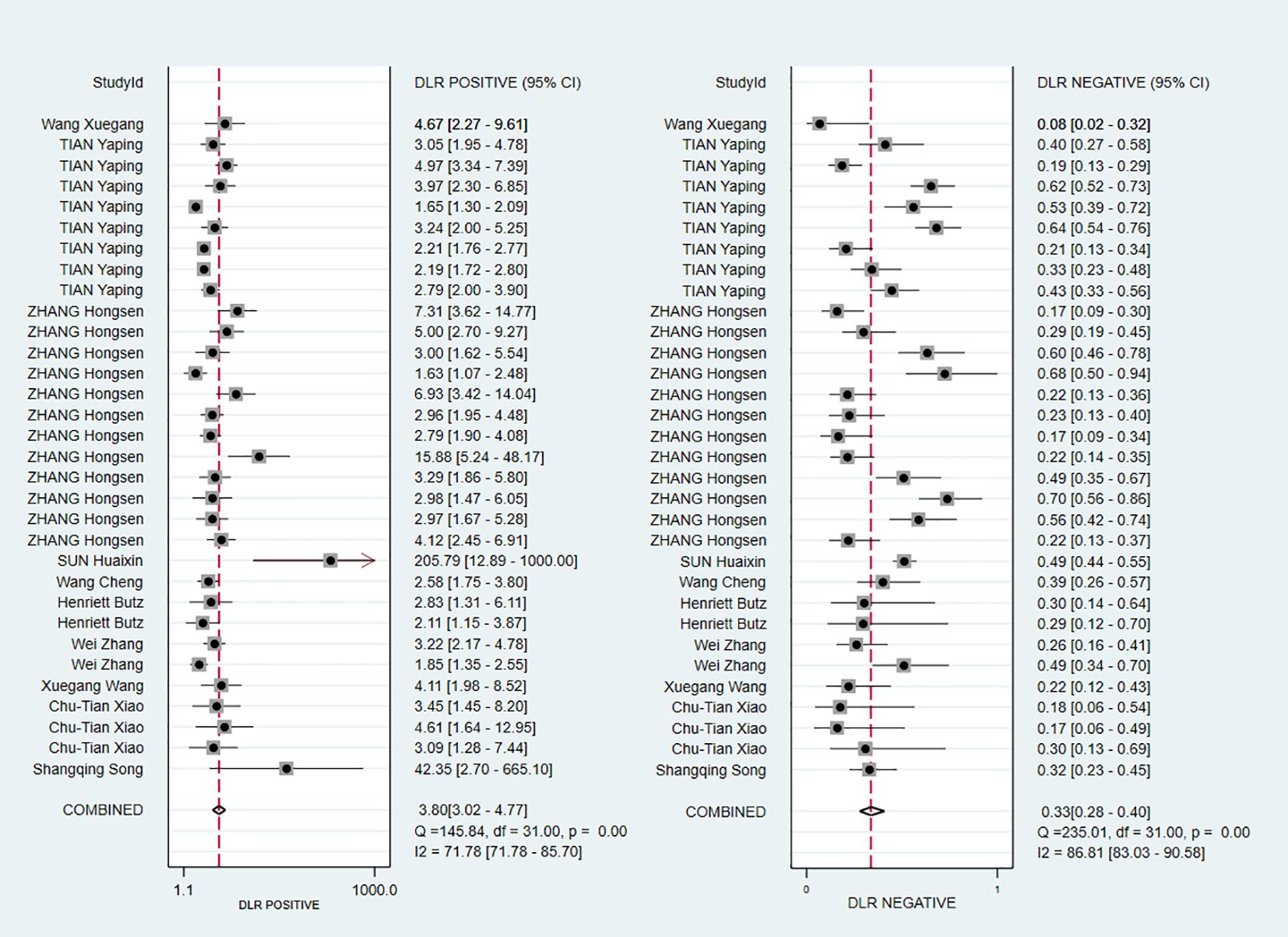
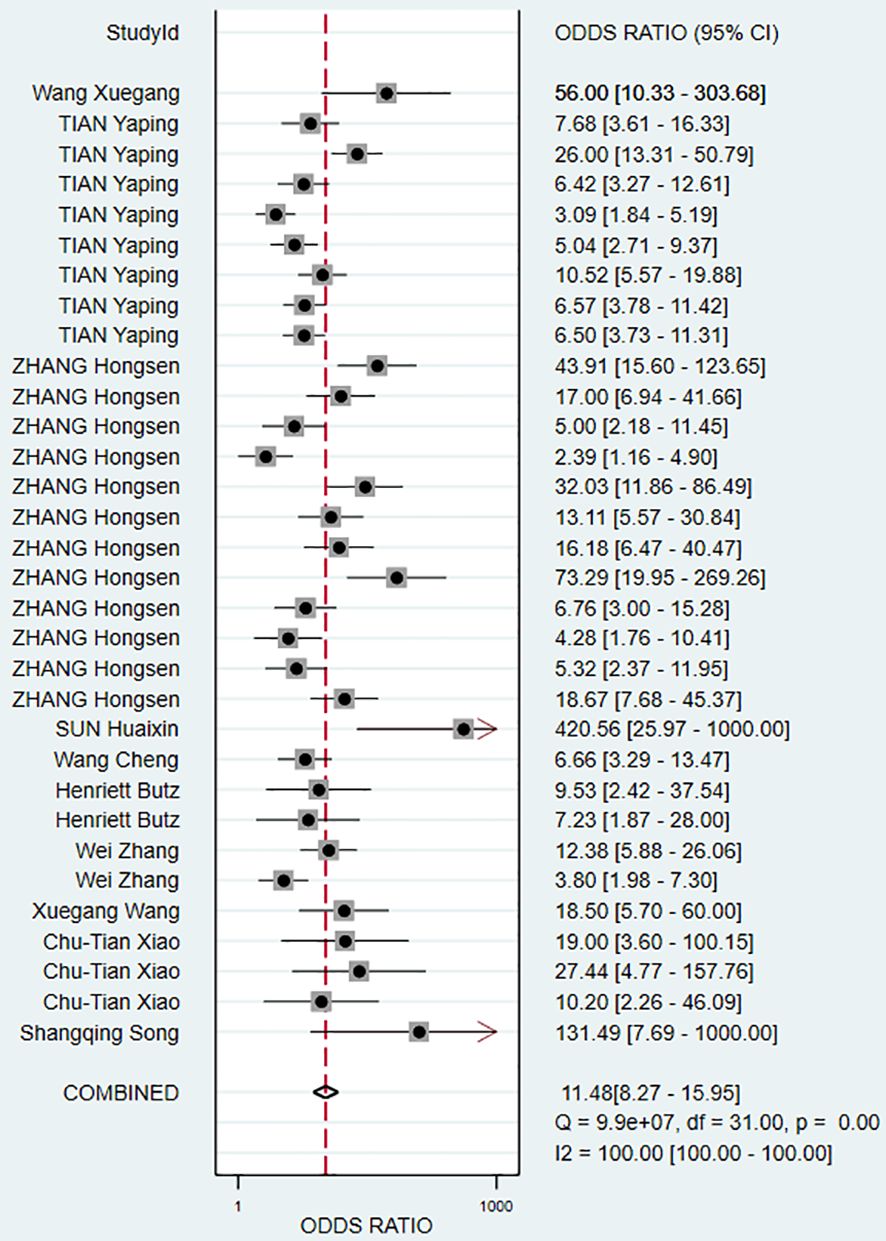
The pooled Sen and Spe were 0.73 (95% CI, 0.68–0.78) and 0.81 (95% CI, 0.76–0.85), respectively (Figure 3). Compared with Sen and Spe, +LR and -LR are considered to have higher clinical value. The pooled +LR, -LR, and DOR were 3.80 (95% CI, 3.02–4.77), 0.33 (95% CI, 0.28–0.40), and 11.48 (95% CI, 8.27–15.95) respectively (Figures 4, 5). The summary receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) of the included studies showed an AUC of 0.84 (95% CI, 0.80–0.87), indicating good diagnostic accuracy (Figure 6).
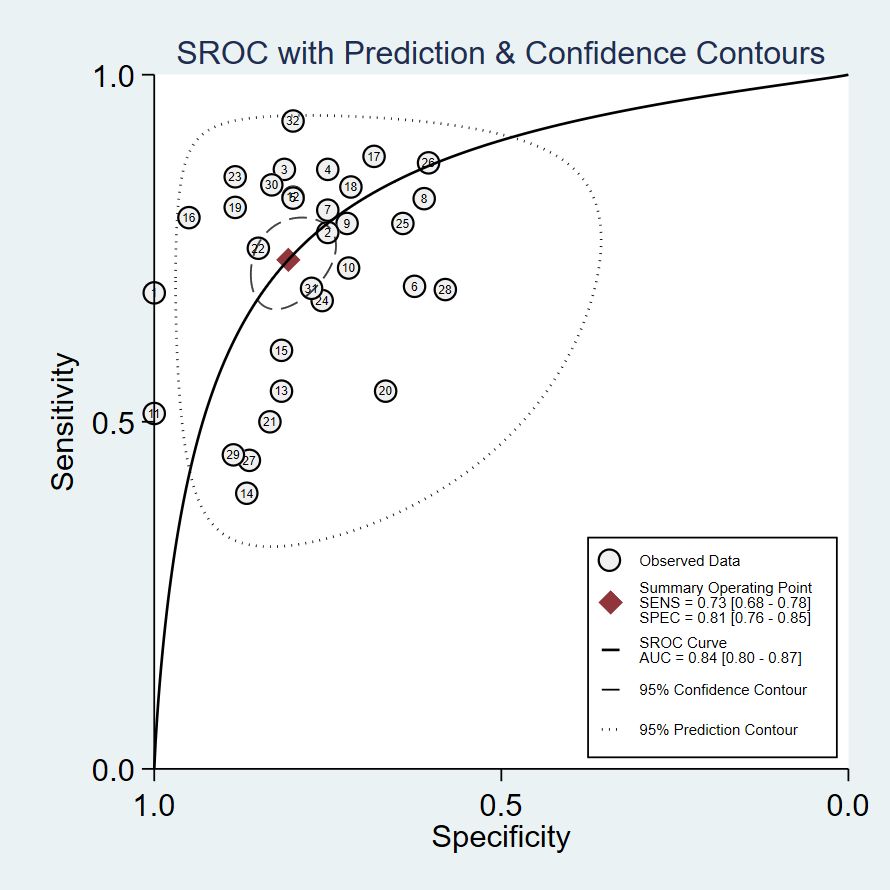
Figure 6. Receiver operating characteristic curve. The lables in the figure correspond respectively to Table 1.
3.4 Sensitivity analysis
Data from included studies were subjected to goodness-of-fit and binary normality analyses. The research was found to be reliable, and outlier detection revealed one anomalous value from a study by Shangqing Song (18). The study exhibited high sensitivity, and other primary studies do not lead to incorrect assessment of the computational results (Figure 7). After the aforementioned study was excluded, the pooled Sen increased by 1% to 0.74 (95% CI, 0.68–0.78), the pooled Spe increased by 3% to 0.80 (95% CI, 0.75–0.84), and the pooled DOR decreased by 0.51 to 10.97 (95% CI, 7.95–15.14). These changes suggested that the abovementioned study contributed to significant heterogeneity when compared with the other 10 studies.
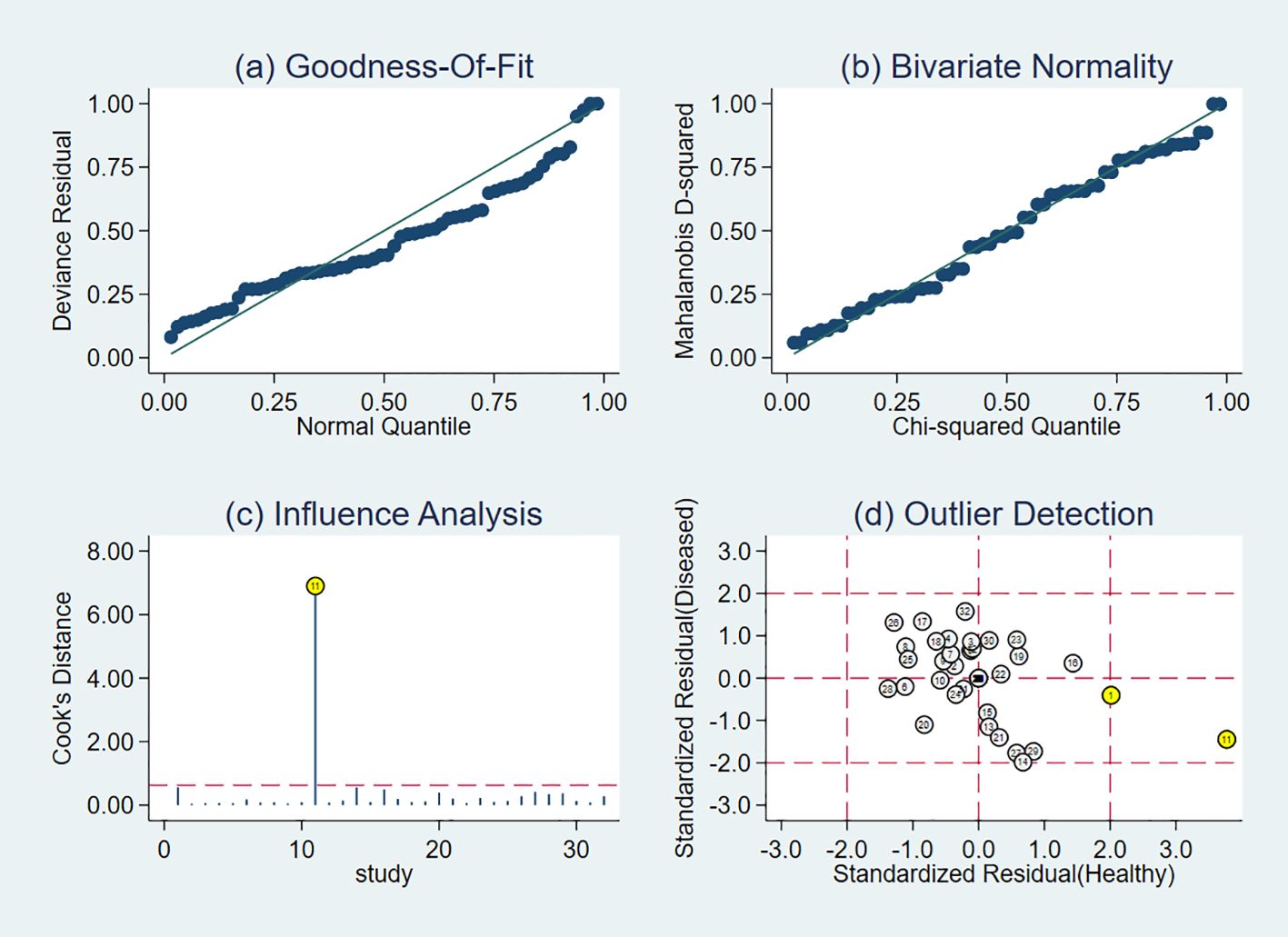
Figure 7. Results of sensitivity analysis. The lables in the figure correspond respectively to Table 1. (A) shows goodness of fit; (B) shows the bivariate normality test; (C) shows the impact analysis; (D) shows the outlier analysis.
3.5 Meta-regression and subgroup analyses
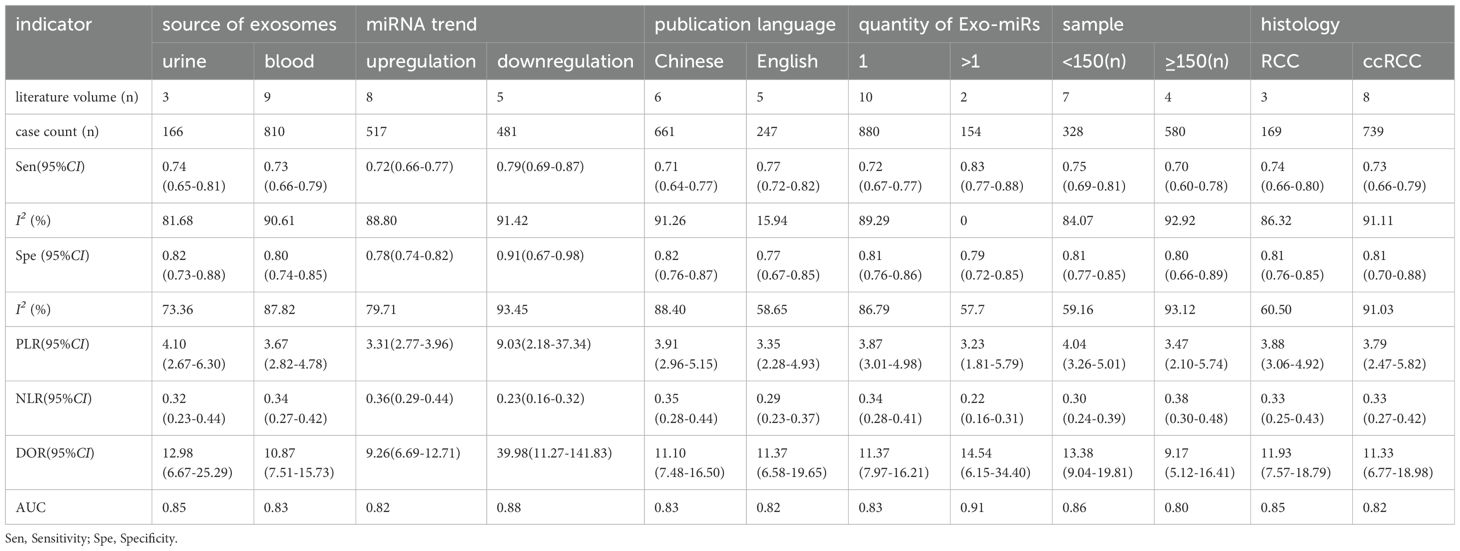
To determine the sources of heterogeneity caused by non-threshold effects, meta-regression analysis was performed using the publication language, source of exosomes, disease histotype, Exo-miRs quantity, miRNAs trend, and sample size as covariates. The results (Figure 8) showed that the publication language, source of exosomes, disease histotype, and sample size were potential sources of heterogeneity. On the contrary, the Exo-miRs quantity and miRNAs trend did not significantly contribute to heterogeneity.
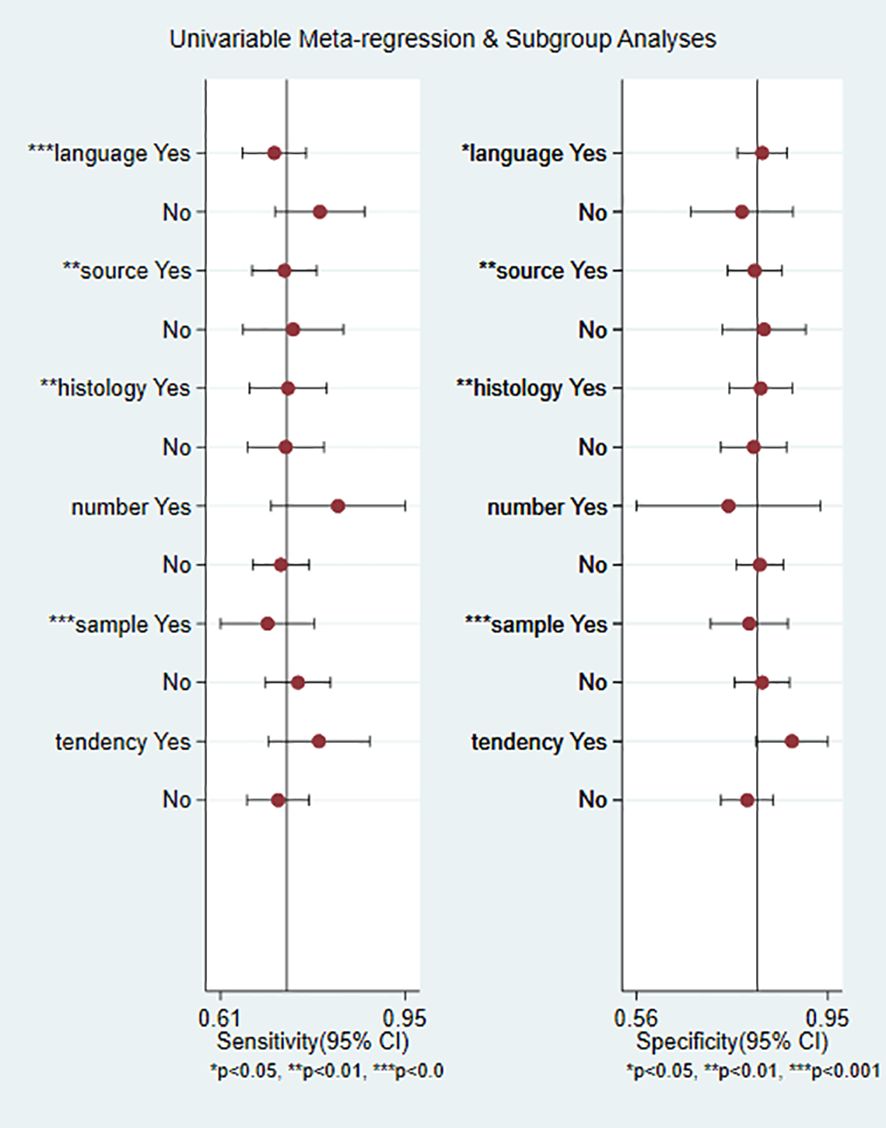
Figure 8. Results of meta-regression analysis. Language, publication language; source, source of exosomes, histology, histotype of RCC; number, the number of miRNA species carried by exosomes; sample, sample size of the included studies; tendency, miRNAs trend. * indicates a potential source of heterogeneity.
Subgroup analysis was performed to verify heterogeneity among the included articles. Based on the source of exosomes, 3 studies with 166 cases were included in the urinary exosome group, whereas 9 studies with 810 cases were included in the blood exosome group(Zhang Hongsen2022 (25) use both urinary and blood exosomes). The Sen (0.74 vs. 0.73) and Spe (0.82 vs. 0.80) of both groups were similar. Based on the miRNAs trend, 8 studies with 517 cases were in the upregulation group, whereas 5 studies with 481 cases were in the downregulation group (Chu Tianxiao2020 (19), Zhang Hongsen2022 (25) included both upregulation and downregulation group). Sen (0.79 vs. 0.72) and Spe (0.91 vs. 0.78) were higher in the downregulation group than in the upregulation group. Additionally, the DOR was significantly higher in the downregulation group (39.98 vs. 9.26). Based on the publication language, 6 studies with 661 cases were in the Chinese group, whereas 5 studies with 247 cases were in the English group. Studies published in English exhibited higher Sen (0.77 vs. 0.71) but lower Spe (0.77 vs. 0.82) than those published in Chinese. In addition, the heterogeneity of studies published in English was less than 50%(15.94%). Based on the Exo-miRs quantity, 10 studies included only 1 type of Exo-miRs, whereas 1 studies included multiple types of Exo-miRs (Henriett Butz2015 (22) and Tian Yaping2018 (26) included multiple types of Exo-miRs). The Sen of the two groups was 0.72 and 0.83 respectively, and the specificity was 0.81 and 0.79 respectively. The results showed a significant difference in Sen, with higher sensitivity being observed among studies including multiple types of Exo-miRs. Additionally, the heterogeneity of sensitivity among these studies was 0, and the AUC value was 0.91. However, owing to the limited number of included studies, the presence of heterogeneity could not be ruled out. Based on the sample size of included studies (with a cutoff of ≥150 cases), the results showed the following Sen and Spe: 0.75 vs. 0.70 and 0.81 vs. 0.80. Based on the histological subtype of renal cancer, 3 articles with 169 cases were included in the RCC group, whereas 8 articles with 739 cases were included in the ccRCC group. The sensitivity of the two groups was 0.74 and 0.73, respectively, whereas the specificity was 0.81 and 0.81 respectively (Table 2).
3.6 Publication bias
The Deeks’ funnel plot is commonly used to assess publication bias. In this meta-analysis, the funnel plot exhibited symmetry, with a p-value of 0.31 (>0.05), indicating no evidence of publication bias among the included studies. The results are shown in Figure 9.
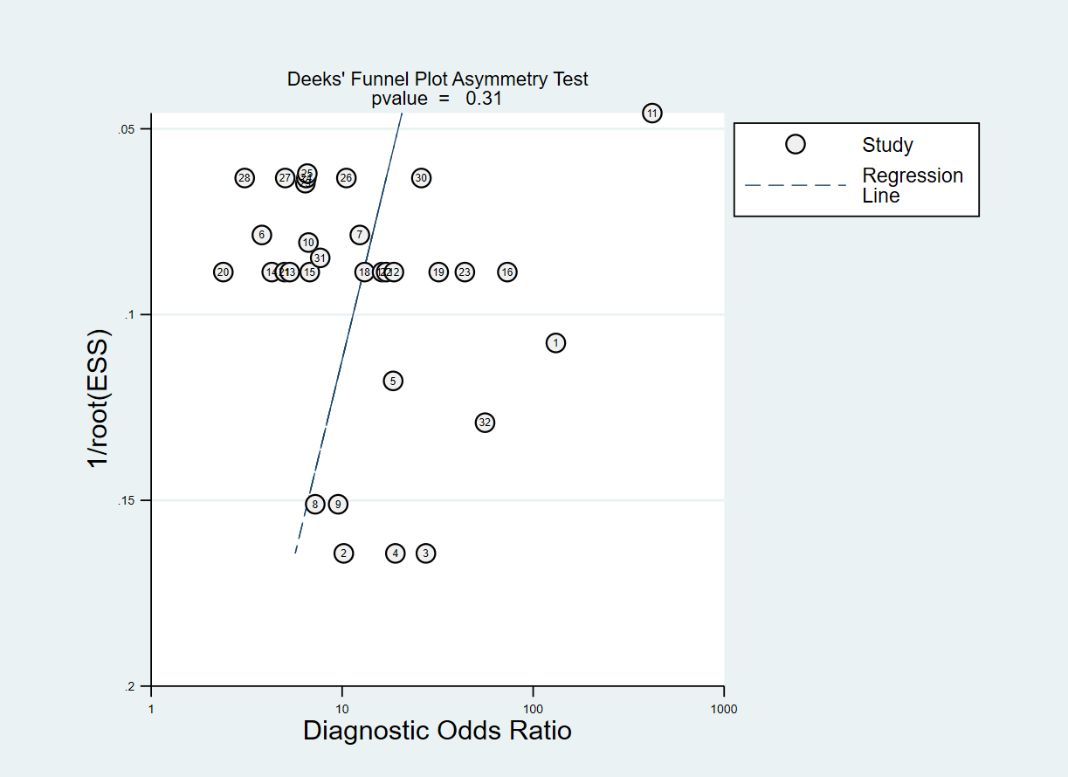
Figure 9. Deeks’ funnel plot for assessing publication bias. The lables in the figure correspond respectively to Table 1.
3.7 Evaluation of clinical utility
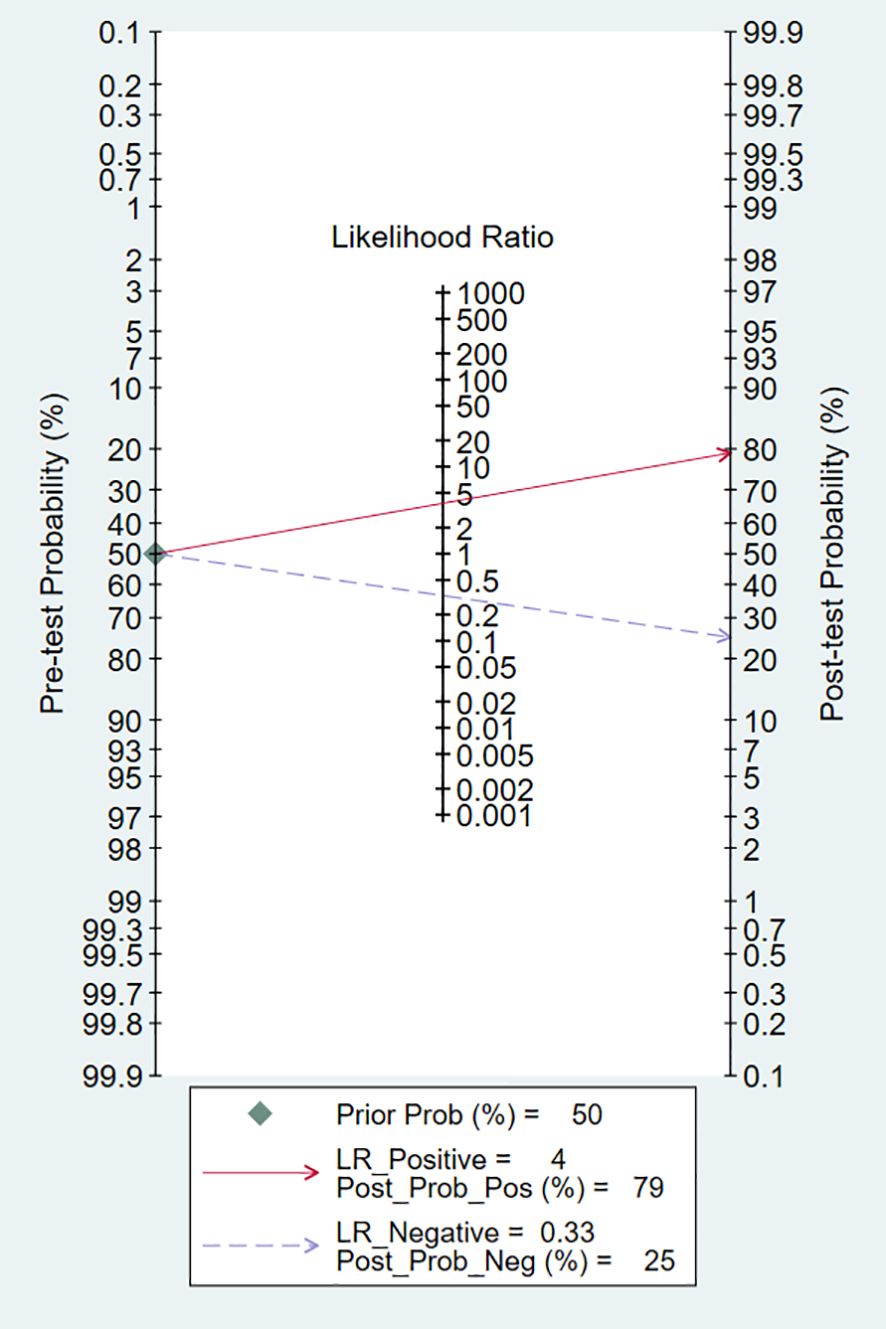
Technological developments primarily rely on clinical problems and the clinical utility of the technology. In this meta-analysis, the pretest probability of DLR and PLR was set at 50% to assess the clinical value of Exo-miRs in the diagnosis of RCC (Figure 10). A positive result increased the post-test probability of having cancer to 79%, whereas a negative result decreased the post-test probability to 25%. These results indicate that Exo-miRs can be used as non-invasive biomarkers to complement existing diagnostic methods.
4 Discussion
4.1 Synthesis of evidence
The incidence of RCC has increased in recent years, with cases being reported across different age groups. RCC is often referred to as a “silent tumor” without evident symptoms in the early stages. Most patients with RCC have advanced disease at diagnosis. Only approximately 6%–7% of patients exhibit the classic triad of symptoms (abdominal pain, abdominal mass, and gross hematuria). Owing to substantial differences in treatment approaches and prognosis among RCC subtypes, early detection is crucial. Although surgical methods for RCC have been continuously updated in recent years, which can effectively improve kidney function and enhance patients’ survival outcomes (29), the mortality rate would significantly decrease if tumors could be detected and identified before the spread of cancer cells. The accuracy of ultrasonography and CECT in early diagnosis is limited owing to issues such as low sensitivity and adverse reactions. Therefore, the early detection rate of RCC is low, and the time to diagnosis is prolonged. The use of biomarkers for molecular-level screening may help achieve early diagnosis and design individualized treatment strategies for RCC patients. In addition, specific biomarkers may assist in the characterization of RCC.
miRNAs are involved in various physiological and pathological processes. It can be stably expressed in body fluids, such as blood and urine, with an average half-life of 119 hours (30, 31). Owing to the stability, Exo-miRs are considered as valuable biomarkers and have shown great application potential in early diagnosis, disease monitoring, prognosis evaluation, and personalized medicine. In particular, they have demonstrated high diagnostic value in various diseases, including glioma (32), gastric cancer (33), lung cancer (34), breast cancer (35), and testicular cancer (36). In addition, they have been identified as novel biomarkers for various urinary tract diseases, such as bladder cancer and prostate cancer (37, 38). Free circulating miRNAs in the body are mostly released after cellular apoptosis or necrosis. Although they are highly stable in blood and urine, when exposed to these body fluids for a long time, they can be degraded by endogenous ribonucleases, at the same time they are lack sensitivity and specificity (39). Exosomes possess a lipid bilayer, which enables them to ensure the integrity and functionality of bioactive molecules during intercellular communication. Owing to these unique features, extracellular vesicles hold substantial promise in disease diagnosis. The lipid bilayer characteristics of exosomes enable them to ensure the integrity and function of active molecules when they transmit information. Compared with free miRNA detection, a large number of fresh samples are required, and exosomes can be stored at -20°C for 5 years without destruction of content components (40). These characteristics make them unique advantages in disease diagnosis.
At present, the detection of exosomes mainly includes electron microscopy, flow cytometry, nanoparticle tracking and other technologies (41). Among them, nanoparticle tracking technology has higher sensitivity and specificity, which can achieve rapid and accurate detection of exosomes (42). The quantitative assessment of Exo-miRs is crucial for disease diagnosis and longitudinal monitoring. The detection technologies for Exo-miRs and protein biomarkers are continually advancing. Through bioinformatics analyses, including proteomics and RNA sequencing, the protein and miRNA profiles of exosomes are thoroughly examined. Real-time quantitative PCR has emerged as a widely adopted method for assessing miRNA and mRNA expression levels (43–45). In addition, there are some emerging detection methods, such as using molecular beacon (46), and CRISPR/Cas13a sensing system to detect Exo-miRs without amplification and extraction (47), which makes the detection of salivary GCF exosomes more advanced and sensitive.
Currently, extensive research is being conducted on biomarkers. In addition to Exo-miRs, MUC1 and other factors have emerged as significant areas. MUC1, a high molecular weight glycoprotein, has been identified as a potential biomarker for RCC, which including cellular proliferation, metabolic reprogramming, and angiogenesis—processes that are essential for the progression of RCC (48). Furthermore, research has demonstrated that the expression of MUC1 on exosomes may influence immune cell proliferation within the tumor microenvironment (49). Both MUC1 and Exo-miRs are related to the occurrence and development of RCC, and are of great value in the diagnosis and treatment. Blood-based biomarkers such as carcinoembryonic antigen and M2 pyruvate kinase have been evaluated for their potential in early detection of RCC. However, the low specificity and sensitivity limit their clinical utility.
Currently, liquid biopsy primarily focuses on molecular markers in blood to identify circulating tumor cells (CTCs), circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), and exosomes. CTCs can be utilized for efficacy assessment and postoperative monitoring. However, a significant limitation is the insufficient quantity of CTCs in blood, which hampers effective early routine detection. ctDNA offers comprehensive insights into tumor progression but faces limitations due to its susceptibility to degradation in the bloodstream (50). Traditional RCC detection biomarkers include PAX8, CAIX, AE1/AE3, etc. (51). They usually need to be obtained through tissue biopsy, which is somewhat invasive. As a liquid biopsy procedure, Exo-miRs offer a minimally invasive alternative. In addition, Exo-miRs can provide more dynamic information than traditional biomarkers on reflect biological changes in tumors.
This meta-analysis included 23 Exo-miRs. These Exo-miRs play an important role in the pathological progression of RCC. For example, overexpression of miR-30c-5p can inhibit tumor growth in nude mice and suppress the growth of ACHN cells (17), indicating its tumor-suppressor role in ccRCC. miR-21 is a commonly overexpressed oncogene in various cancers. Plasma-derived exosomal miR-21 can exert anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects by targeting the PDCD4/NF-κB and PTEN/AKT pathways in renal tubular epithelial cells (52). On the contrary, miR-210 can activate HIF-1 by targeting the SDHD gene. Upregulation of HIF-1 can promote changes in the expression of VEGF and miR-210, thereby influencing angiogenesis in kidney tumors (53). These findings suggest that Exo-miRs play dual roles in RCC, as they can both promote and inhibit the growth of tumor cells. Therefore, research on Exo-miRs is important to develop strategies for early diagnosis and prompt treatment of RCC. It can also expand the applications of Exo-miRs in the fields of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine for other kidney diseases. With the continuous progress of research into the intrinsic mechanisms of Exo-miRs, the findings may revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of genitourinary tumors. In particular, Exo-miRs may not only serve as non-invasive biomarkers for early diagnosis of RCC but also be targeted to modulate their expression to yield the desired therapeutic effects.
This meta-analysis included 11 studies with 1,646 samples, including 908 cases and 738 controls. The results indicated that Exo-miRs served as biomarkers for the diagnosis of RCC with high sensitivity and specificity. The probability of detecting abnormal Exo-miRs in patients with RCC was 3.8 times higher than that in healthy individuals, with the false-positive rate for 33%. Subgroup and regression analyses showed that studies published in English had higher sensitivity than those published in Chinese. Studies involving the use of exosomes carrying multiple miRNAs had higher sensitivity than those involving the use of exosomes with a single miRNA. In addition, studies including downregulated miRNAs had higher sensitivity than those upregulated miRNAs. Heterogeneity among the included studies was mainly attributed to the publication language, source of exosomes, disease histotype, and sample size of included studies. The number of included studies was limited, especially for subgroup analysis. Moreover, the predominance of single-center studies might have increased heterogeneity.
Although research on Exo-miRs diagnosis of RCC is still in its infancy and has not yet been widely applied in clinical practice, with continuous research and technological advancements, Exo-miRs are expected to become an important pathway. Building on further exploration of the mechanisms of exosome action and optimizing treatment plans to improve therapeutic effects, exosomes are expected to become an important pathway for the diagnosis of RCC, bringing more precise and effective treatment options to patients. Of course, optimizing the path of exosomes in medical applications requires addressing several core challenges. First, large-scale production must be realized to counteract the current low efficiency exosome production, which is fundamental to the widespread application of exosome-based therapeutic strategies. Second, it is essential to ensure the collection of high-quality and consistent exosomes. The physicochemical properties and purity of exosomes are directly influenced by the separation techniques employed, and so far there is no recognized “gold standard” for the isolation of exosomes. Which make the exploration and optimization of these methods to obtain stable quality a crucial step in advancing their clinical utility. Third, standardizing storage conditions is equally important. Maintaining the activity and stability of exosomes during storage is vital for the success of subsequent therapeutic applications. Lastly, further development of the therapeutic potential of exosomes is the ultimate goal. To address the limited efficacy of exosomes themselves, strategies such as overexpression or enrichment of therapeutic biomolecules can effectively enhance their therapeutic effects, paving new avenues for the broad application of exosomes in the medical field.
The application of Exo-miRs as diagnostic tools in clinical practice is still faces the impact of costs. As an emerging diagnostic tool, the development process of Exo-miRs requires a substantial financial investment, including various stages such as basic research, clinical trials, and technological optimization. The steps of Exo-miRs extraction, isolation, purification, and quantitative analysis require specific techniques and equipment, which may lead to higher production costs. In addition, the stability of Exo-miRs and storage conditions (such as the need for storage at -80°C) may also increase the costs of storage and transportation. Despite the aforementioned costs, Exo-miRs as diagnostic tools have higher sensitivity and specificity. Compared with existing diagnostic methods, they are non-invasive and convenient, capable of early diagnosis and providing more accurate diagnostic results. This can reduce repeated testing and unnecessary treatments. Overall, although the integration of exosomes as diagnostic tools may bring higher costs in the initial stage, in the long run, they can improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary medical expenses, thereby reducing overall medical costs in the long term.
4.2 Limitations
(1) The research on using Exo-miRs for the diagnosis of RCC is relatively limited, often lacking relevant data. Consequently, the small number of included articles in this meta-analysis might have resulted in partial heterogeneity. Additionally, given the limited sample size, this may restrict the generalizability of the findings. Differences in the sampling and testing methods as well as limited geographical diversity, may lead to significant heterogeneity. (2) The QUADAS-2 tool was used to assess the methodological quality of all articles. The results showed that the included articles were of moderate-to-high quality, supporting the findings. However, during assessment, certain limitations in the design and execution were found. These limitations may impede the unbiased interpretation of the findings. First, it is noteworthy that a majority of the studies included healthy individuals as the control group. This approach, although common, may not accurately reflect the complexity of a cancerous state and may lead to an overestimation the diagnostic potential. To address this limitation, future studies should use tumor or benign tumor models and investigate the diagnostic efficacy of Exo-miRs in early-stage disease. (3) Owing to the limited number of included articles, the correlation between Exo-miRs and pathological stages or specific histological subtypes could not be analyzed. Therefore, the quality of the included article needs to be improved. In the future research, we will focus on collecting larger scale, multi-center and multi-regional sample data to enhance the wide applicability and statistical significance of the research conclusions. (4) The use of ROC curves determine the diagnostic accuracy of Exo-miRs was prevalent among included studies. This method often lacks a pre-specified threshold and validation in independent cohorts, which can decrease the robustness of the evidence presented. Therefore, future studies should incorporate validation techniques to evaluate the generalizability of statistical findings across different datasets. Additionally, to enhance internal and external validity, as well as the reproducibility of the results, future studies should strictly adhere to the updated guidelines established by the Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy. Altogether, larger and prospective studies that focus on technical nuances and adhere to standardized protocols in reporting are warranted. Such studies are crucial for generating robust and reliable data that may guide clinical decision-making.
4.3 Practical significance and inspiration
Exo-miRs serve as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of RCC. Detection of Exo-miRs offers a non-invasive approach to obtaining biological information from patients, thus facilitating early diagnosis and individualized treatment and eventually improving the prognosis and quality of life of patients with RCC. Further research on Exo-miRs may elucidate the pathogenesis and disease course of RCC. Changes in the expression patterns of Exo-miRs may help understand their regulatory mechanisms and provide a theoretical basis for further investigation. Despite certain limitations, this meta-analysis highlights that the quality of data and the standardization of methods should be considered when conducting relevant studies. Improving the design and methodology of studies and controlling and reducing heterogeneity may help evaluate the potential of Exo-miRs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets, providing a more reliable basis for their use in clinical practice.
5 Conclusion
Based on quantitative analysis of data extracted from included articles, this meta-analysis suggests that Exo-miRs possess great potential in the diagnosis of RCC. The combination of multiple Exo-miRs or the combination of Exo-miRs with traditional biomarkers may represent an effective method for improving the diagnosis of RCC. This method is not only highly sensitive and specific but also non-invasive and radiation-free. Furthermore, Exo-miRs can be used as potential indicators of clinicopathological characteristics of RCC. However, given the limitations of this study, further validation through large-scale, multicenter, prospective, high-quality evidence-based clinical research is still needed to explore the mechanisms of action of Exo-miRs in RCC, standardize the sources of exosomes, and establish testing technology standards.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
QL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JT: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. CC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81973806), the Research Projects in Health and Medicine in Bao’an District, Shenzhen (2022JD064), and the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No.SZZYSM202311015).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
RCC, Renal cell carcinoma; Exo-miRs, exosomal microRNAs; Sen, Sensitivity; Spe, Specificity; SROC, Summary receiver operating characteristic curve; +LR, Positive likelihood ratio; -LR, Negative likelihood ratio; AUC, Area under the curve; DOR, Diagnostic odds ratio; CECT, Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; SinoMed, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database; CNKI, China National Knowledge Infrastructure; TP, True positive; FP, False positive; FN, False negative; TN, True negative; ccRCC, Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; CTCs, Circulating tumor cells; ctDNA, Circulating tumor DNA.
References
1. Hu X, Tan C, Zhu G. Clinical characteristics of molecularly defined renal cell carcinomas. Curr Issues Mol Biol. (2023) 45:4763–77. doi: 10.3390/cimb45060303
2. Campi R, Rebez G, Klatte T, Roussel E, Ouizad I, Ingels A, et al. Effect of smoking, hypertension and lifestyle factors on kidney cancer - perspectives for prevention and screening programmes. Nat Rev Urol. (2023) 20:669–81. doi: 10.1038/s41585-023-00781-8
3. Cosso F, Roviello G, Nesi G, Shabani S, Spatafora P, Villari D, et al. Adjuvant therapy for renal cell carcinoma: hype or hope? Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4243. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044243
4. Dovalova D, Rybar L, El Falougy H, Kubikova E, Mifkovic A. Renal cell carcinoma - summarizing overview, biomarkers, metastases and new perspectives. Bratisl Lek Listy. (2022) 123:697–704. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2022_111
5. Cinque A, Capasso A, Vago R, Lee MW, Floris M, Trevisani F. The role of circulating biomarkers in the oncological management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: where do we stand now? Biomedicines. (2021) 10:90. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010090
6. Lee YJ, Shin KJ, Chae YC. Regulation of cargo selection in exosome biogenesis and its biomedical applications in cancer. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:877–89. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01209-y
7. Isaac R, Reis FCG, Ying W, Olefsky JM. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:1744–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.08.006
8. Garcia-Martin R, Wang G, Brandão BB, Zanotto TM, Shah S, Kumar Patel S, et al. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature. (2022) 601:446–51. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04234-3
9. Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. (2019) 47:D155–62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1141
10. Paskeh MDA, Entezari M, Mirzaei S, Zabolian A, Saleki H, Naghdi MJ, et al. Emerging role of exosomes in cancer progression and tumor microenvironment remodeling. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:83. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01305-4
11. Yu X, Du Z, Zhu P, Liao B. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic potential of exosomal microRNAs in renal cancer. Pharmacol Rep. (2024) 76:273–86. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00568-7
12. Sequeira JP, Constâncio V, Lobo J, Henrique R, Jerónimo C. Unveiling the world of circulating and exosomal microRNAs in renal cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:5252. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215252
13. Boussios S, Ovsepian SV. Exosomes in renal cell cancer: diagnostic and therapeutic nanovehicles. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2024) 23:15330338241275403. doi: 10.1177/15330338241275403
14. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PloS Med. (2009) 6:e1000100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
15. Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. (2011) 155:529–36. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
16. Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K, Coomarasamy A. Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2006) 6:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-6-31
17. Boston RC, Sumner AE. STATA: a statistical analysis system for examining biomedical data. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2003) 537:353–69. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9019-8_23
18. Song S, Long M, Yu G, Cheng Y, Yang Q, Liu J, et al. Urinary exosome miR-30c-5p as a biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma that inhibits progression by targeting HSPA5. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:6755–65. doi: 10.1111/jcmm
19. Xiao CT, Lai WJ, Zhu WA, Wang H. MicroRNA derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for diagnosing renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. (2020) 13:10765–74. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S271606
20. Wang X, Wang T, Chen C, Wu Z, Bai P, Li S, et al. Serum exosomal miR-210 as a potential biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:1492–502. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27347
21. Zhang W, Ni M, Su Y, Wang H, Zhu S, Zhao A, et al. MicroRNAs in serum exosomes as potential biomarkers in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus. (2018) 4:412–9. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.09.007
22. Butz H, Nofech-Mozes R, Ding Q, Khella HWZ, Szabó PM, Jewett M, et al. Exosomal microRNAs are diagnostic biomarkers and can mediate cell-cell communication in renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus. (2016) 2:210–8. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2015.11.006
23. Wang C, Tian Y, Ding M, Zhang C, Wang J, Zhang C. The clinical value of serum exosomal miR-181a-3p levels in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Chin J Clin Lab Manage. (2018) 6:84–8. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5820.2018.02.005
24. Sun H, Shao X, Xu D, Chen B, Qi L, Liu M, et al. Expression and clinical significance of exosome miR-133a in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Chin Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:105–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2023.02.002
25. Zhang H, Guo G, Huang Q, Yang C. The diagnostic value of serum and urine exosomal miRNAs expression level in renal cell carcinoma tissues. J Modern Oncol. (2022) 30:2786–92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2022.15.021
26. Tian Y. The clinical study of serum exosomal miRNAs as novel molecular markers for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. (dissertation/master’s thesis). Jiangsu University, Jiangsu Chongqing. (2018)
27. Tian Y, Zhang M, Ge J, Zhang C, Wang J, Wang C. Clinical value of serum extracellular vesicles miR-99b-3p levels in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Chin J Clin Lab Sci. (2021) 39:178–81. doi: 10.13602/j.cnki.jcls.2021.03.04
28. Wang X, Yang J, Chen C, Zhao S, Xu B, Chen B, et al. Serum exosomal miR-210 as a noninvasive molecular diagnosis biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Chin J Urol. (2017) 38:707–11. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2017.09.017
29. Pandolfo SD, Wu Z, Campi R, Bertolo R, Amparore D, Mari A, et al. Outcomes and techniques of robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) for renal hilar masses: A comprehensive systematic review. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16:693. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040693
30. Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H, Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ Res. (2010) 107:677–84. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.215566
31. Gantier MP, McCoy CE, Rusinova I, Saulep D, Wang D, Xu D, et al. Analysis of microRNA turnover in mammalian cells following Dicer1 ablation. Nucleic Acids Res. (2011) 39:5692–703. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr148
32. Zhou Q, Liu J, Quan J, Liu W, Tan H, Li W. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. (2018) 109:2651–9. doi: 10.1111/cas.13714
33. Li Z, Liu ZM, Xu BH. A meta-analysis of the effect of microRNA-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2018) 22:8281–7. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16525
34. Shao C, Yang F, Qin Z, Jing X, Shu Y, Shen H. The value of miR-155 as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:1103. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6297-6
35. Lv P, Zhang Z, Hou L, Zhang Y, Lu L, Wang C, et al. Meta-analysis of the clinicopathological significance of miRNA-145 in breast cancer. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20193974. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193974
36. Ditonno F, Franco A, Manfredi C, Fasanella D, Abate M, La Rocca R, et al. The role of miRNA in testicular cancer: current insights and future perspectives. Medicina (Kaunas). (2023) 59:2033. doi: 10.3390/medicina59112033
37. Lin H, Shi X, Li H, Hui J, Liu R, Chen Z, et al. Urinary Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers of bladder Cancer and experimental verification of mechanism of miR-93-5p in bladder Cancer. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:1293. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08926-x
38. Rode MP, Silva AH, Cisilotto J, Rosolen D, Creczynski-Pasa TB. miR-425-5p as an exosomal biomarker for metastatic prostate cancer. Cell Signal. (2021) 87:110113. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110113
39. Gu Y, Yuan J. Diagnostic significance of miRNAs as potential biomarkers for human renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. (2022) 22:437–44. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2022.2051483
40. Nik Mohamed Kamal NNSB, Shahidan WNS. Non-exosomal and exosomal circulatory microRNAs: which are more valid as biomarkers? Front Pharmacol. (2020) 10:1500. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01500
41. Bari SMI, Hossain FB, Nestorova GG. Advances in biosensors technology for detection and characterization of extracellular vesicles. Sens (Basel). (2021) 21:7645. doi: 10.3390/s21227645
42. Liu H, Tian Y, Xue C, Niu Q, Chen C, Yan X. Analysis of extracellular vesicle DNA at the single-vesicle level by nano-flow cytometry. J Extracell Vesicles. (2022) 11:e12206. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12206
43. Zhu J, Liu B, Wang Z, Wang D, Ni H, Zhang L, et al. Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC migration and proliferation. Theranostics. (2019) 9:6901–19. doi: 10.7150/thno.37357
44. Jiang M, Jike Y, Liu K, Gan F, Zhang K, Xie M, et al. Exosome-mediated miR-144-3p promotes ferroptosis to inhibit osteosarcoma proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating ZEB1. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:113. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01804-z
45. Ko SY, Lee W, Weigert M, Jonasch E, Lengyel E, Naora H. The glycoprotein CD147 defines miRNA-enriched extracellular vesicles that derive from cancer cells. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12:e12318. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12318
46. Rhee WJ, Jeong S. Extracellular vesicle miRNA detection using molecular beacons. Methods Mol Biol. (2017) 1660:287–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7253-1_23
47. Hong JS, Son T, Castro CM, Im H. CRISPR/cas13a-based microRNA detection in tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2301766. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301766
48. Milella M, Rutigliano M, Lasorsa F, Ferro M, Bianchi R, Fallara G, et al. The role of MUC1 in renal cell carcinoma. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:315. doi: 10.3390/biom14030315
49. Chen W, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Zhu P, Ko JK, Yung KK. MUC1: structure, function, and clinic application in epithelial cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:6567. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126567
50. Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, Chakrabortty SK, Enderle D, Noerholm M, et al. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:466–77. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc
51. Wang AX, Tian T, Liu LB, Yang F, He HY, Zhou LQ. TFEB rearranged renal cell carcinoma: pathological and molecular characterization of 10 cases, with novel clinical implications: A single center 10-year experience. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:245. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020245
52. Pan T, Jia P, Chen N, Fang Y, Liang Y, Guo M, et al. Delayed Remote Ischemic Preconditioning ConfersRenoprotection against Septic Acute Kidney Injury via Exosomal miR-21. Theranostics. (2019) 9:405–23. doi: 10.7150/thno.29832
Keywords: exosomal microRNAs, renal cell carcinoma, miRNA, meta-analysis, diagnosis
Citation: Li Q, Tian J, Chen C, Liu H and Li B (2024) Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of exosomal microRNAs in renal cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 14:1441429. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1441429
Received: 04 June 2024; Accepted: 03 October 2024;
Published: 28 October 2024.
Edited by:
Shenglong Li, China Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Juan Antonio Fafian Labora, University of A Coruña, SpainSavio Domenico Pandolfo, Federico II University Hospital, Italy
Achille Aveta, University of Naples Federico II, Italy
Zhiyuan Qin, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Misba Khan, University of Turku, Finland
Copyright © 2024 Li, Tian, Chen, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong Liu, ZnNzenl5MTIzQDE2My5jb20=; Binyi Li, ODM1NDkyOTY3QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Qingru Li
Qingru Li Jing Tian3
Jing Tian3