- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Hebei University, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding, China
- 2The Third Department of Surgery, the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang Hebei, China
- 3Hebei Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Comprehensive Treatment of Gastric Cancer, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 4Big Data Analysis and Mining Application for Precise Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastric Cancer Hebei Provincial Engineering Research Center, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 5Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding, China
Gastric cancer is one of the most common cancers and is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in worldwide. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for a positive outcome. The integration of artificial intelligence in the pathology field is increasingly widespread, including histopathological images analysis. In recent years, the application of digital pathology technology emerged as a potential solution to enhance the understanding and management of gastric cancer. Through sophisticated image analysis algorithms, artificial intelligence technologies facilitate the accuracy and sensitivity of gastric cancer diagnosis and treatment and personalized therapeutic strategies. This review aims to evaluate the current landscape and future potential of artificial intelligence in transforming gastric cancer pathology, so as to provide ideas for future research.
1 Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC), a globally formidable health challenge, is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality (1). This malignancy exhibits a marked geographical variation, with high incidence rates in East Asia, Eastern Europe, and parts of South America, while lower rates are observed in North America and Africa (2, 3). The high mortality rate associated with GC is primarily due to late-stage diagnosis and the complexity of the disease, which present significant hurdles in both diagnosis and treatment (4, 5). The global impact of gastric cancer is profound, affecting millions of individuals and their families (6). GC frequently progresses silently, with many patients remaining asymptomatic until reaching advanced stages (7). Symptoms, such as weight loss, abdominal discomfort or nausea, are vague and nonspecific, and may delay medical assistance and diagnosis (8, 9). Early detection is crucial because it significantly improves patient survival (10). However, the absence of distinctive symptoms and the lack of robust screening procedures lead to delayed diagnosis (11). The management of GC generally comprises a multidisciplinary approach, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy. However, the efficacy of these treatments is contingent upon the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis (12, 13). The heterogeneity of GC, with its various histological and molecular subtypes (14), introduces additional complexity to its management, underscoring the necessity for precise diagnostic and therapeutic strategies (15).
Histopathologic examination has long been the cornerstone in cancer diagnosis (16, 17). Traditional pathology involving microscopic examination of tissue samples has limitations in terms of scalability, speed and objectivity (18, 19). Digital pathology involves converting glass slides into superresolution digital images that can be easily stored, shared and analyzed (20, 21). This transformation has potentially altered the operational paradigms of pathologists, facilitating more effective collaboration and laying the groundwork for the incorporation of sophisticated computational technologies (22).
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various fields, including pathology, by enabling advanced data analysis (23, 24). The potential capabilities of AI are particularly useful for identifying subtle or complex features and specific pathological conditions that might be challenging for a human pathologist to discern (25–28). In gastric cancer, AI could analyze digital histopathological images to aid in diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment decisions, offering critical insights, precise tumor classification, grading, and potentially predicting therapy responses (29).
2 Fundamentals of AI in digital pathology
Digital and computational pathology convert glass slides into digital images using high-resolution scanners, enabling viewing, management, and analysis on computers (30). This transition offers several advantages, such as easy sharing with experts globally, facilitating remote consultations, promoting standardized interpretations, and reducing inter-observer variability (31–33). Early pathology image analysis efforts, like those by Prewitt and Mendelson in 1966, were limited by scarce computational resources and simple algorithms (34). With the rise of AI and machine learning (ML), more powerful computing enabled sophisticated analyses, such as classifying types of cancer or predicting disease outcomes (35). Another breakthrough came in the 2010s with deep learning (DL), particularly CNNs, which automatically learn features from raw data, eliminating the need for manual selection (36). The potential of DL in computational pathology was driven by the availability of large annotated datasets (37).Initiatives like The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and public competitions provided essential data for training and validating models, accelerating progress in the field (38, 39).
The applications of AI in GC pathology are vast and transformative, promising for enhancing various aspects of pathology practice from diagnostics to research, including automated disease diagnosis, tumor detection and quantification, grading and staging cancer, predictive analytics for prognosis, treatment response, biomarker identification and data integration for holistic analysis (Figure 1).
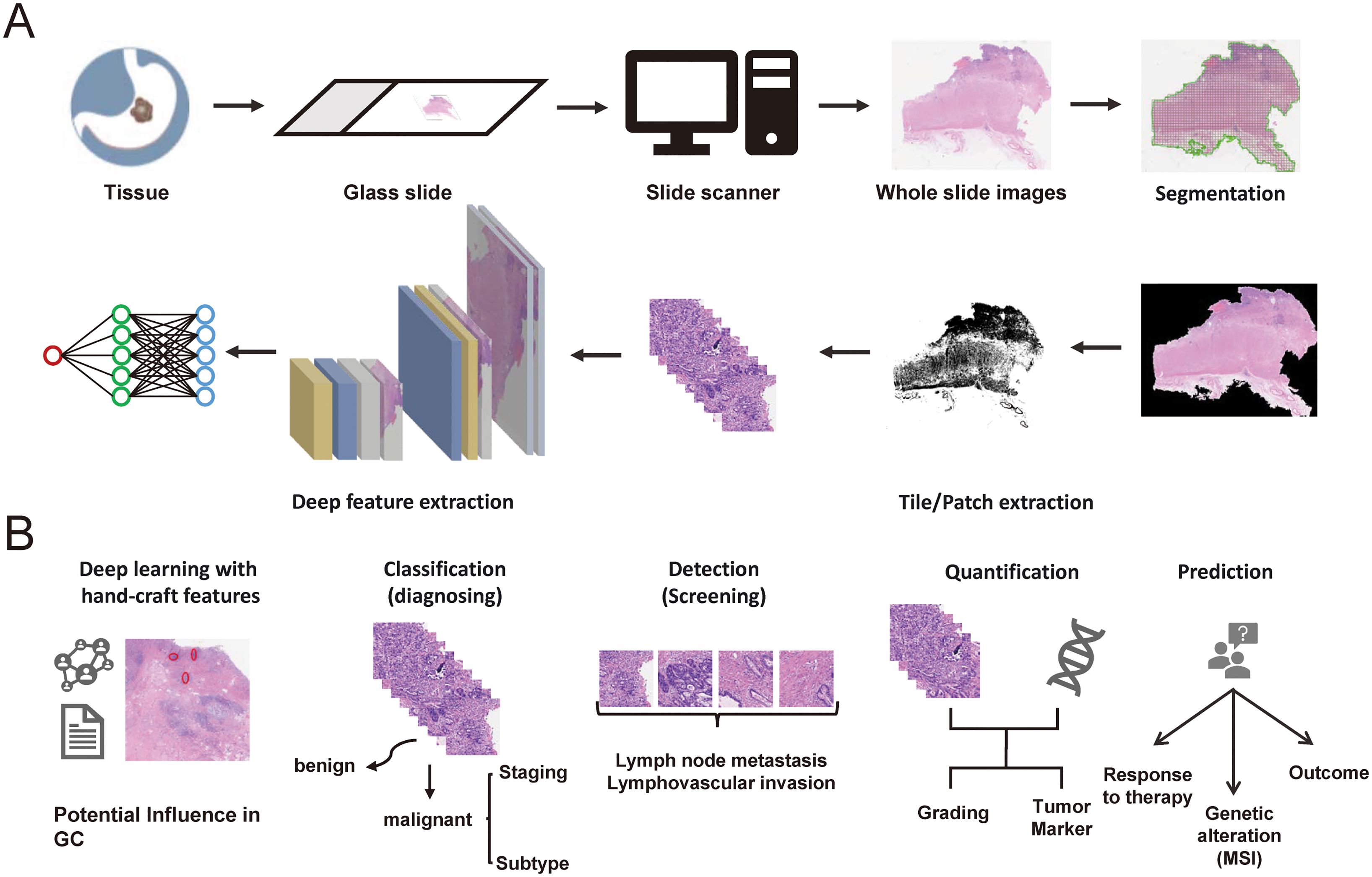
Figure 1. (A) The digital pathology workflows of AI for gastric cancer. (B) The potential clinical applications of AI in digital pathology for gastric cancer.
3 Application of AI in the detection and pathological diagnosis of GC
GC is the prevailing malignancy in humans, emphasizing the paramount importance of early diagnosis to enhance cure rates and prognoses (40). Currently, pathological diagnosis continues to serve as the definitive method for diagnosing gastric cancer (41). Within the diagnostic procedure, the discrimination between benign and malignant lesions constitutes a pivotal and indispensable step. The application of AI in the detection and pathological diagnosis of GC are summarized in Table 1. Yoshida et al. proposed an image analysis software called “e-Pathologist,” which was the first application of an AI algorithm to categorize gastric biopsy Whole slide images (WSIs) as carcinoma, adenoma, or non-malignant. The sensitivity, detection specificity, negative predictive value, and positive predictive value of the e-Pathologist test were 90%, 50%, 99.8%, and 1.7% respectively (42). Abe et al. (43)designed an artificial intelligence‐based system grounded in a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) for diagnosing gastric biopsies (normal, carcinoma) through the use of H&E-stained WSIs. Their AI-system was tested on validation cohort including 3450 gastric biopsy samples of 1772 patients from 10 different institutes, with an accuracy of 91.3%. This shows the potential power of AI-based model in alleviating the pressure on pathologists in diagnosing gastric biopsies. In a similar study, Fan and colleagues (44) applied a DL model for automated gastric endoscopic biopsy classification. Five common CNN models (VGG-16, VGG-19, ResNet-50, Xception, and InceptionV3) were utilized for the Japanese “Group Classification” of Gastric Carcinoma. The ResNet-50 model demonstrated the best performance, with an accuracy of 93.16%. Likewise, Iizuka et al. (45) trained a CNN model based on the inception-v3 framework for stomach biopsy whole slide image (WSI) classification into three types: adenocarcinoma, adenoma, and non-neoplastic. Then a test cohort of 45 WSIs was used to confirm this model, and an accuracy of 95.6% and an AUC of 0.924 were obtained. These indicate the efficacy of AI model in classifying epithelial lesions in biopsy WSIs of gastric.
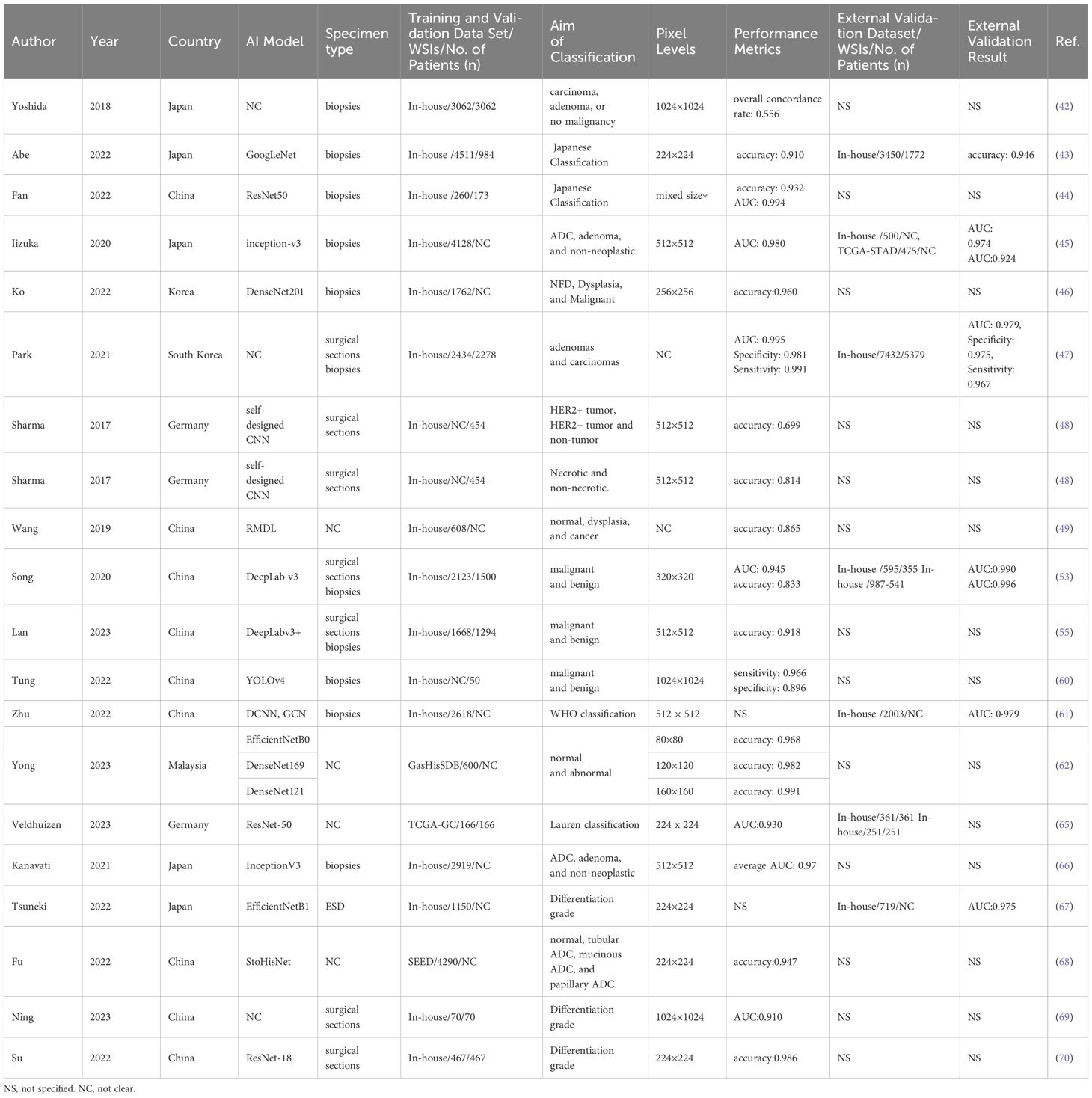
Table 1. Characteristics of the application of AI for the detection and pathological diagnosis in gastric cancer.
In a different study, Ko et al (46) proposed a rapid daily post-analytical AI-assisted quality control (QC) system for pathologists to evaluate stomach biopsy specimens. The QC system was composed of laboratory information and an AI WSI-classifier model based on the DenseNet algorithm. The AI WSI-classifier distinguished histopathological WSIs of biopsy specimens among three classes: negative for dysplasia, dysplasia, and malignant, and demonstrated high accuracy rates (95.8%) from their internal verification set, which included 150 gastric biopsy WSIs. Evidence like this demonstrates the clinical efficacy of AI algorithms in enhancing the diagnostic accuracy and consistency of GC. Park et al. (47) constructed a DL formula to classify gastric biopsy lesions into dysplasia, tubular adenoma, and carcinoma. The formula model obtained an accuracy of 97% with 100% sensitivity and 97% specificity in distinguishing gastric epithelial tumors. This showcases the aid of AI system could decrease the missed diagnosis of cancer, especially in biopsies with small areas of lesion. A dataset comprising 640 H&E-stained histopathological slides of GC tissues and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for the HER-2 gene was utilized by Sharma et al (48). They developed a CNN system capable of swiftly and accurately distinguishing between tumor and non-tumor regions in HE-stained WSIs. Compared to traditional methods and the AlexNet architecture, this model exhibited superior discrimination of necrotic tumor areas, achieving an overall accuracy of 0.8144. This highlights the potential of AI system in cancer classification and necrosis detection without immunohistochemical staining. Wang et al. (49) developed a two-stage deep learning model to automatically classify WSIs of gastric tissue lesions into normal, dysplasia, and cancer categories, and validated the accuracy at 86.5% using 200 WSIs in the testing set. The core strength of RMDL lies in its instance recalibration module, which autonomously identifies crucial instances for image-level forecasting. However, the application of AI model with a two-stage algorithm may significantly influence on pathologists in diagnosing cancer, which neglected the potential interaction between local tiles.
With the creation of exceptionally efficient algorithms, some pathology laboratories are adopting the routine utilization of digital slides in the format of WSIs as part of their daily diagnostic procedures (50–52). Song et al. (53) proposed a CNN of the DeepLab v3 network trained with 2123 pixel-level gastric cancer WSIs from 1500 GC patients, and the performance of the model exhibited nearly 100% sensitivity and 80.6% specificity for gastric carcinoma detection on 3,212 WSIs in the test cohort. It may assist pathologists in enhancing diagnostic precision and averting misdiagnoses in their everyday tasks. In another study, they assessed the support provided by the DL model in assisting pathologists with diagnosing gastric carcinoma, through the design of a comprehensive multireader multicase examination (54). The results showed that the assistance of DL model indeed enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of pathologists in distinguishing between malignant and benign lesions. However, with the assistantance of the DL model, the specificity of GC detection remains unaffected. In another analogous investigation, Lan et al. established a DL-driven pathological auxiliary diagnostic system based on 2,020 stomach H&E-stained WSIs (55). With the assistance of this system, pathologists experience a substantial decrease in the average false-negative rate and average false-positive rate and a reduction in the time of diagnosis. The incorporation of AI in disease diagnosis necessitates a careful and considered approach (56, 57). The consequences of false positive and false negative cases have far-reaching implications for patient welfare and should not be underestimated (58, 59).
In the creation of simple AI-assisted diagnostic system, attaining a minimal false-negative rate holds the same significance as ensuring a high level of accuracy. Tung et al. (60) constructed a DL algorithm based on the YOLOv4 network structure to identify GC regions from endoscopic biopsy WSIs, and obtained a detection accuracy of 91%, with a sensitivity of 96.6% and a specificity of 89.6%. The advantageous features of this system are its ability to inspect all GC regions in an image and reduced false-negative rate. Zhu et al. created an endoscopic gastric biopsy assistant system bonding DCNN and graph convolutional networks for assisting pathologists in delineating crucial regions for diagnosis in gastric biopsy WSIs (61). This highlights the possibility and advantages of using AI system in the clinical routine work in routine practice scenarios. In 2023, Yong and colleagues propounded an assemblage DL model built uponbtransfer learning principles from multiple pre-trained architectures, including MobileNet, DenseNet, EfficientNet, InceptionV3, and Xception for gastric lesion categorization (62). The observations revealed that the ensemble model attained an advanced accuracy ranging from 97.72 to 99.20% which was verified on lower resolution WSIs from GasHisSDB. This demonstrates the potential of AI in classifying the pathological low-resolution images for cost reduction.
In intricate pathological assessments, gastric lesions should be subdivided into different histological subtypes rather than simply categorized as malignant or benign (63). As a highly heterogeneous disease, GC could be divided into two primary histological subcategories within the Lauren classification system (64). Veldhuizen et al. (65) sought to develop a classifier based on attention-based deep multiple-instance learning to distinguish between intestinal and diffuse type GC WSIs. The results demonstrated that the classifier achieved strong discriminatory performance (mean AUROC 0.93 ± 0.07). Furthermore, in comparison to the pathologist-based Lauren classification, the DL-based classifier exhibited improved stratification of the 5-year survival rates for GC patients. However, in two independent external validations, the DL-classifier performed unsatisfactorily. There are 54% of the samples that the DL-classifier identified as intestinal type while pathologist initially classified as diffuse type. These results showed that the progression of AI may enhance the diagnostic accuracy among pathologists and reduce observer disagreement in GC histological classification. In a similar study, GC histological patterns were categorized into diffuse-type adenocarcinoma (ADC) and others on H&E-stained slides using a CNN framework to train four individual models. The best model achieved the AUROC of 0.95–0.99 in five validation groups (66). Another gastric ADC classification DL model was developed by Tsuneki et al. and achieved an AUROC of 0.975 for classifying endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) WSIs into poorly differentiated ADCs and others (differentiated and non-tumor) (67). These show the promise of AI in accurately distinguishing poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma for improved clinical decision-making and outcomes. In a different study, Fu et al. created a novel architecture, StoHisNet, combining transformer and a CNN to classify GC WSIs into four subtypes (tubular, mucinous, and papillary adenocarcinoma, non-tumor), with a classification accuracy of 94.69% (68). Ning et al. utilized the U-Net algorithm and QuPath software to identify differentiated and undifferentiated lesions in WSIs of mixed-type GC (69). Finally, in the research of Su et al., a CNN-based DL-model was established to recognize the degree of tumor differentiation and status of microsatellite instability (MSI) in GC HE-stained WSIs, achieving F1 values of 0.86 and 0.89 for poor-differentiated ADC and well-differentiated ADC sorting, respectively and an accuracy of 83.87% for predicting MSI status (70).
4 Application of AI in molecular phenotype prediction of GC
Histological classification has been shown to be insufficient for identifying actionable molecular targets (71). In acknowledgment of limitations, extensive molecular profiling has given rise to a variety of classifications based on molecular characteristics to uncover the clinical features and biological characteristics to inform therapeutic decision-making and prognosis of GC patients (72–75). Harnessing AI holds the potential to ease the burden of molecular property testing to alleviate the pressure on pathologists (76–79). The application of AI in molecular phenotype prediction of GC are summarized in Table 2.
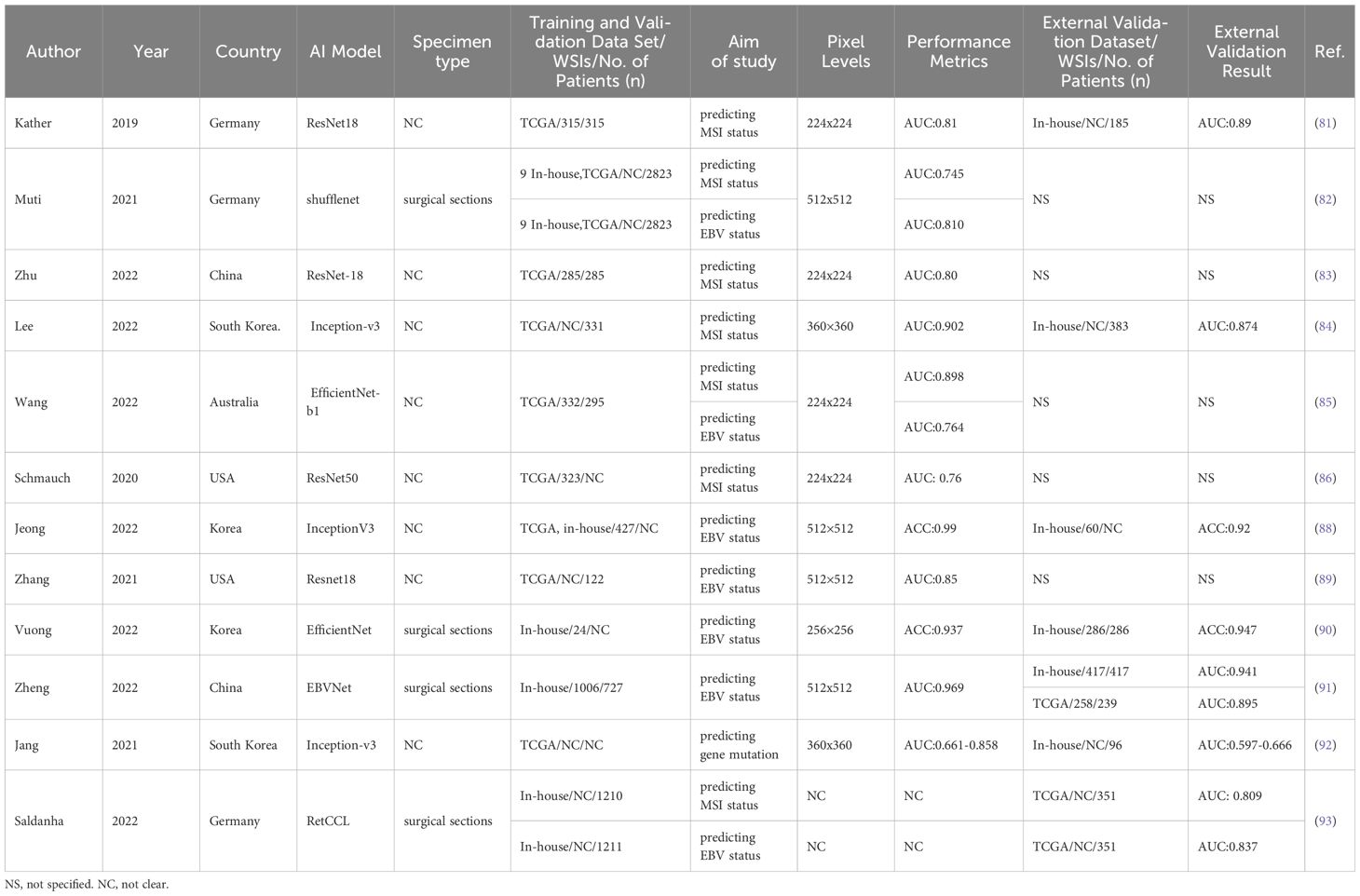
Table 2. Characteristics of the application of AI in molecular phenotype prediction of gastric cancer.
With the advancement of AI technology, it has demonstrated promising results and the potential to predict MSI status in a cost-effective manner (80). In 2019, Kather et al. yielded the first entirely automated DL system based on the Resnet-18 framework to infer MSI status from GC histopathological images, with an AUC of 0.81 in the TCGA cohort and an AUC of 0.69 in the external validation cohort (81). Molecular phenotype prediction using AI and pathomics holds significant promise for enhancing the early management of GC. Subsequently several similar studies integrating advanced technical DL algorithms have provided further insights into the efficacy of ML for predicting MSI status in GC histological WSIs, and the model exhibited performances with AUCs ranging from 0.54 to 0.90 (82–86). This demonstrates the effectiveness of AI algorithms in accurately differentiating MSI status. AI has been applied widely to predict molecular categories directly from GC H&E-stained slices and exhibited equivalent performance compared with identification staining methods noticed on WHO rules (87). Such evidence highlights the potential of AI in areas like molecular identification and phenotype prediction, paving the way for advancements in personalized medicine.
EBV-associated GCs are recognized as molecularly and pathologically distinct from those EBV-negative. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of AI in predicting Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) status. Jeong et al., trained a DL classifier to detect the EBV status from H&E stained digital WSIs based on the InceptionV3 architecture, with the accuracy of 0.92 (88). In another research, a ResNet18-based CNN framework was adopted to identify EBV status through GC H&E-stained WSIs and obtained an AUC of 0.85 (89). In line with these findings, Vuong et al., first proposed a CNN model based on EfficientNet to evaluate the EBV status of H&E–stained WSIs from biopsy specimens of GC, and achieved admirable performance with an accuracy of 0.938 (90). This showcases the potential of AI in analyzing intricate patterns in medical imaging and discovering virus infection status. Moreover, Zheng et al. (91), proposed a human−machine collaboration approach that combined a DCNN model and pathologists for EBV prediction. With the collaboration of pathologists, the model attained the AUC ranging from 0.945 to 0.969 for predicting GC EBV status. This suggests the potential of human-AI fusion strategy in identifying EBV status and its role in revealing new insights into identify complex molecular subtypes.
AI systems offer a cost-effective and time-efficient alternative for detecting gene mutations from histologic image (92). A multistep CNN networks based on the Inception-v3 architecture were trained to assess the mutational status of 5 genes (CDH1, ERBB2, KRAS, PIK3CA, and TP53) in GC, with CDH1 and PIK3CA exhibiting the highest accuracies of 0.847 and 0.834, respectively, for frozen WSIs and KRAS and CDH1 having the best accuracies of 0.894 and 0.820, respectively, for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue WSIs (93). This indicates the potential of AI in identifying genetic alterations from H&E-stained slides, potentially offering an alternative from genomics research.
However, due to high tumor heterogeneity, DL-based models seem to have poorer performance in GC than in other carcinomas (94). To address these challenges, swarm learning (SL), a decentralized ML robust, was employed to acquire highly predictable AI-classifiers for MSI and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) status prediction in GC digital WSIs (95). These studies collectively demonstrate analyzing the morphology of a lesion and its microenvironment by AI could improve the accuracy of molecular phenotype predictions, potentially resulting in more personalized therapeutic approaches, particularly beneficial in resource-limited settings. Although the potential to implement molecular phenotype prediction from digitized H&E-stained tissue is promising, substantial validation is still necessary to determine the clinical utility of AI-pipelines.
5 Application of AI in determining GC prognosis
5.1 Prediction of lymph node metastasis
Lymph node metastases (LNM) stands as a key prognostic indicator for individuals diagnosed with GC (96, 97). Pathologically evaluating lymph nodes plays an essential role in ascertaining clinical staging and directing treatment interventions (98, 99). AI-based algorithm has the potential to alleviate pathologists’ workload while enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Currently, only a few studies have explored the application of artificial intelligence in evaluating LNM in lymph node WSIs. DL methods could extract information not only to predict LNM and patient outcomes from primary GC tissue (100) but also to explore prognostic features from WSI from LNs (101). Hu et al. proposed a cascade DL-based system for detecting and quantifying LNM in WSI of LNs, which achieved effectively performance for patients after neoadjuvant therapy (102). This underscores the effectiveness of the AI approach for automated lymph node metastatic quantification and identification. In the similar study, Huang et al. introduced an enhanced streaming CNN algorithm trained on gigapixel images of LN-level WSIs to detect LNM. The results showed that with the assistance of the AI model, the sensitivity of detecting micrometastases, and isolated tumor cells have been increased, with a less review time. However, in another study, different results were observed. The AI-diagnostic model has the potential to enhance the sensitivity of pathologists in identifying micrometastases, but the review time has extended (103). In comparison to manually review LNs microscopically, AI-based digital pathology systems provide easier input acquisition, greater diagnostic accuracy, and better scalability for clinical application.
Lymphovascular invasion (LVI) is a histomorphological feature indicating LNM in primary GC tissues (104, 105). In 2023, Lee et al. proposed an ensemble DL algorithm based on the ConViT and YOLOX architectures for detecting LVI foci from GC histopathology images, achieved an AUC of 0.9438 in the external validation cohort (106). In a similar study, hard negative mining algorithm was used to develop a DL model for lymphatic invasion screening with GC digital WSIs (107). In summary, the design of AI in identifying metastatic cells opens avenues for reviewing LNM and managing gastric cancer patients.
5.2 Prediction of survival and therapeutic responsiveness
The function of AI should not be confined to replicating pathologists’ assessments. Some studies indicated that the significance of AI has the capability to predict patient outcomes from histopathological slides. Huang et al. trained a CNN model, MIL-GC, for predicting the outcomes of patients with GC by analyzing WSIs (108). This stratification is crucial as it correlates with different survival rates, thereby providing prognostic insights that can inform clinical decision-making. Some studies have explored the connection between cancer pathological features and treatment responsiveness (109, 110). Chen et al. proposed a signature to predict GC patient outcomes and adjuvant chemotherapy responses based on pathomic features extracted from H&E-stained images via AI-based image analysis techniques (111). Zhou et al. applied three DL algorithms to create an ensemble model for predicting the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy from WSIs of GC patients (112). In another investigation, a DL-based network and corresponding digital pathology signature score were presented from WSIs for the assessment of GC patient outcomes and adjuvant treatment (113). These advanced AI models aid in the nuanced understanding of GC pathology, leading to better-informed prognosis and management plans.
5.3 Prediction of cancer recurrence
Despite the implementation of multimodal treatment strategies, the recurrence of GC remains a prevalent issue (114). Consequently, numerous ongoing studies are dedicated to identifying individuals at risk of recurrence following treatment. In 2023, the first pathomic signature was developed to predict peritoneal recurrence in GC patients with serosal invasion from digital H&E-stained images (115) by handcrafted feature-based approach. However, this approach could be both complex and time-consuming to use. Zhang et al. introduced a novel graph neural network, AGCNet, designed for predicting cancer recurrence by analyzing cancerous tissue WSIs. The network demonstrated notable effectiveness with an accuracy of 81.81% in bladder cancer, 69.66% in pancreatic cancer, and 81.96% in GC (116). AI as a collaborative tool offers a promising approach for cancer recurrence prediction and expands the application of digital pathology images.
6 Application of AI in GC immuno-oncology
Immuno-oncology is a field focused on the interaction between tumors and the immune system, delving into harnessing the immune system’s ability to combat cancer (117). Over the past three decades, remarkable progress has been made, underpinned by the emergence of innovative immunotherapies and their clinical triumphs, which have significantly revolutionized cancer treatment paradigms, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, and CAR-T cell therapy (118). Researchers have extensively explored the application of AI in forecasting the effectiveness of immunotherapy (119). In 2023, Wei et al., constructed a DL-based stratification system by analyzing GC WSIs to identify molecular phenotypic features associated with immunotherapy responses, including molecular subtypes, immune checkpoints, genetic mutations, and the intricacies of signaling pathways (120). AI-based pathomic methods emerge as predictors of immunotherapy response, offering valuable insights for making informed treatment decisions. The tumor mutational burden (TMB) is a pivotal predictive biomarker, associated with the effectiveness of immunotherapy in GC patients (121). Li et al., developed a DL multimodal fusion model that combined GC WSI features with omics information for TMB prediction, with a notable AUC of 0.971 (122). This study demonstrated that multimodal approaches could enhance the efficiency of prediction models compared to unimodal algorithms, representing a promising direction for future AI-pathology research.
7 Application of large language models and generative AI in pathology
With the rise of large language models (LLMs) and the broader field of generative AI, computational pathology is poised to enter a new frontier. LLMs and generative AI can assist in extracting crucial information and automatic generating pathology reports (123). Choi et al., demonstrated that following LLMs to extract structured information from pathology reports can save significant time and costs compared to manual methods (124). In another study, ChatGPT was used to detect adenomas in 100 colorectal polyp photomicrographs, with sensitivity of 74% and specificity of 36% (125). This indicates the promise of LLMs in areas like diagnosis, though its limitations, emphasizing the need for expertise in pathology. “PathChat”, a Generative AI Copilot, was presented for assisting human pathology (126).It has the potential to significantly impact pathology education, research, and human-in-the-loop clinical decision-making. While the initial results are promising, there are abundant opportunities for further growth. The path forward in exploring LLMs and generative AI applications within the field of pathology is both challenging and intriguing.
8 Future directions and perspectives
The use of AI in gastric cancer (GC) pathology is showing a trend of dynamic growth worldwide (127, 128). In this review, we have outlined the primary research directions in the application of AI to GC pathology. The incorporation of AI has commenced demonstrating promising outcomes in augmenting diagnostic precision, forecasting patient prognoses, and uncovering innovative therapeutic targets in GC. The published data generally suggest that the application of AI in oncological histopathology could become feasible for routine clinical workflows in the foreseeable future (129, 130). However, several challenges need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of AI in this field (131).
Firstly, the demographic differences in GC prevalence must be considered. AI models developed and trained on datasets from specific populations may not perform well on others. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure diverse and representative training datasets that encompass various demographic and ethnic backgrounds. Histopathological heterogeneity presents another layer of complexity. GC can exhibit significant variability in their histological and molecular characteristics, which complicates the development of generalizable AI models. To tackle this, integrating multi-modal data analyses, combining histopathological information with other fields such as radiomics (132, 133), genomics (134) and proteomics, could provide a more holistic view for improving model accuracy and patient-specific predictions.
Additionally, one of the primary issues is the lack of transparency in AI models, often referred to as the “black box” problem, making it difficult to interpret their decisions directly (135, 136). Developing explainable AI (XAI) methods such as ablation study, visualization, that provide insights into how AI models arrive at their conclusions is essential. These methods can help bridge the gap between AI and clinical practice, ensuring that AI tools are both reliable and interpretable. Another challenge is data scarcity. The development of robust AI models requires large datasets, which are often unavailable, especially for rare cancer subtypes. Federated learning, a decentralized approach where models are trained across multiple centers without sharing patient data, could support collaborative efforts across institutions to share and pool data and overcome data scarcity while preserving privacy. For AI tools to be widely adopted, Ethical and legal Considerations must be seamlessly integrated into clinical workflows. This involves developing intuitive interfaces and ensuring that AI systems can work alongside existing diagnostic tools. Conducting clinical trials and pilot studies will be essential to validate the effectiveness of AI in real-world settings.
And to ensure protection of patient data, robust encryption, strict access control, data anonymization, and continuous monitoring must be implemented, in compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Anyone aiming to develop or implement AI solutions in clinical practice must comply with the strict regulatory controls and safeguards (137, 138). And AI-model performance validation should be a dynamic and continuous effort, focused on maintaining the quality and reliability of the results provided by AI tools. Therefore, regular audits are recommended to identify and correct any biases within AI systems (139). Furthermore, the advancement of AI in pathology in clinical practice also require ongoing collaboration between pathologists, data scientists, software engineers, and regulatory bodies. Such interdisciplinary efforts are crucial for overcoming technical challenges and ensuring that AI tools are developed with clinical applicability in mind. Finally, The potential of AI in the field of GC histopathology has not yet been fully realized, such as dissecting mutation prediction (140), and developing pan-cancer AI-foundation models for cancer detection and biomarker prediction (141), remain under explored.
9 Conclusion
In conclusion, this review summarizes the applications of AI in the diagnosis, histopathological classification, prognosis, and treatment response assessment of GC. AI holds significant potential to address the challenges of objectivity and inter-observer variability in histopathology, underscoring the importance of further research to facilitate its integration into routine clinical practice for GC patients.
Author contributions
SC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis. PD: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. HG: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LM: Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. López MJ, Carbajal J, Alfaro AL, Saravia LG, Zanabria D, Araujo JM, et al. Characteristics of gastric cancer around the world. Crit Rev oncology/hematology. (2023) 181:103841. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103841
3. Collatuzzo G, Santucci C, Malvezzi M, La Vecchia C, Boffetta P, Negri E. Trends in gastric cancer mortality 1990-2019 in 36 countries worldwide, with predictions to 2025, and incidence, overall and by subtype. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:9912–25. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5685
4. Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet (London England). (2020) 396:635–48. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
5. Feng B, Shi J, Huang L, Yang Z, Feng ST, Li J, et al. Robustly federated learning model for identifying high-risk patients with postoperative gastric cancer recurrence. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:742. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44946-4
6. Zhang Z, Wang J, Song N, Shi L, Du J. The global, regional, and national burden of stomach cancer among adolescents and young adults in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A population-based study. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1079248. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1079248
7. Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet (London England). (2020) 396:635–48. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
8. Lordick F, Carneiro F, Cascinu S, Fleitas T, Haustermans K, Piessen G, et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:1005–20. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.07.004
9. Wang Z, Liu Y, Niu X. Application of artificial intelligence for improving early detection and prediction of therapeutic outcomes for gastric cancer in the era of precision oncology. Semin Cancer Biol. (2023) 93:83–96. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.04.009
10. Fan XH, Zhang Y, Wang P, Song QQ, Wang M, Mejias-Luque R, et al. A noninvasive multianalytical approach establishment for risk assessment and gastric cancer screening. Int J Cancer. (2024) 154:1111–23. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34739
11. Wong MCS, Huang J, Chan PSF, Choi P, Lao XQ, Chan SM, et al. Global incidence and mortality of gastric cancer, 1980-2018. JAMA network Open. (2021) 4:e2118457. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18457
12. Zhang Z, Liu N, Sun M. Research progress of immunotherapy for gastric cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2023) 22:15330338221150555. doi: 10.1177/15330338221150555
13. Negura I, Pavel-Tanasa M, Danciu M. Regulatory T cells in gastric cancer: Key controllers from pathogenesis to therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. (2023) 120:102629. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102629
14. Ajani JA, Lee J, Sano T, Janjigian YY, Fan D, Song S. Gastric adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2017) 3:17036. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.36
15. Alsina M, Arrazubi V, Diez M, Tabernero J. Current developments in gastric cancer: from molecular profiling to treatment strategy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 20:155–70. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00703-w
16. Matias-Guiu X, Stanta G, Carneiro F, Ryska A, Hoefler G, Moch H, et al. The leading role of pathology in assessing the somatic molecular alterations of cancer: Position Paper of the European Society of Pathology. Virchows Archiv: an Int J Pathol. (2020) 476:491–7. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02757-0
17. Geaney A, O'Reilly P, Maxwell P, James JA, McArt D, Salto-Tellez M. Translation of tissue-based artificial intelligence into clinical practice: from discovery to adoption. Oncogene. (2023) 42:3545–55. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02857-6
18. Shen Z, Hu J, Wu H, Chen Z, Wu W, Lin J, et al. Global research trends and foci of artificial intelligence-based tumor pathology: a scientometric study. J Trans Med. (2022) 20:409. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03615-0
19. Jain RK, Mehta R, Dimitrov R, Larsson LG, Musto PM, Hodges KB, et al. Atypical ductal hyperplasia: interobserver and intraobserver variability. Modern Pathol. (2011) 24:917–23. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011.66
20. Baxi V, Edwards R, Montalto M, Saha S. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice. Modern Pathol. (2022) 35:23–32. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00919-2
21. Pell R, Oien K, Robinson M, Pitman H, Rajpoot N, Rittscher J, et al. The use of digital pathology and image analysis in clinical trials. J pathology Clin Res. (2019) 5:81–90. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.127
22. Niazi MKK, Parwani AV, Gurcan MN. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence. Lancet Oncol. (2019) 20:e253–61. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30154-8
23. Hilgers L, Ghaffari Laleh N, West NP, Westwood A, Hewitt KJ, Quirke P, et al. Automated curation of large-scale cancer histopathology image datasets using deep learning. Histopathology. (2024) 84(7):1139–53. doi: 10.1111/his.15159
24. Morishita EC, Nakamura S. Recent applications of artificial intelligence in RNA-targeted small molecule drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discovery. (2024) 19(4):415–31. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2024.2313455
25. Fisher TB, Saini G, Rekha TS, Krishnamurthy J, Bhattarai S, Callagy G, et al. Digital image analysis and machine learning-assisted prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer research: BCR. (2024) 26:12. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01752-y
27. Hubbard-Perez M, Luchian A, Milford C, Ressel L. Use of deep learning for the classification of hyperplastic lymph node and common subtypes of canine lymphomas: a preliminary study. Front veterinary Sci. (2024) 10:1309877. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1309877
28. Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. (2012) 25. doi: 10.1145/3065386
29. Codipilly DC, Faghani S, Hagan C, Lewis J, Erickson BJ, Iyer PG. The evolving role of artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal histopathology: an update. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 22(6):1170–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.044
30. Barisoni L, Lafata KJ, Hewitt SM, Madabhushi A, Balis UGJ. Digital pathology and computational image analysis in nephropathology. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2020) 16:669–85. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0321-6
31. Mroz P, Parwani AV, Kulesza P. Central pathology review for phase III clinical trials: the enabling effect of virtual microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2013) 137:492–5. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0093-RA
32. Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. (2019) 25:44–56. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0300-7
33. Clarke E, Doherty D, Randell R, Grek J, Thomas R, Ruddle RA, et al. Faster than light (microscopy): superiority of digital pathology over microscopy for assessment of immunohistochemistry. J Clin Pathol. (2023) 76:333–8. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2021-207961
34. Prewitt JM, Mendelsohn ML. The analysis of cell images. Ann New York Acad Sci. (1966) 128:1035–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11715.x
35. Kann BH, Hosny A, Aerts HJWL. Artificial intelligence for clinical oncology. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39:916–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.002
36. Srinidhi CL, Ciga O, Martel AL. Deep neural network models for computational histopathology: A survey. Med image Anal. (2021) 67:101813. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101813
37. Verghese G, Lennerz JK, Ruta D, Ng W, Thavaraj S, Siziopikou KP, et al. Computational pathology in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction - present day and prospects. J Pathol. (2023) 260:551–63. doi: 10.1002/path.6163
38. Gutman DA, Cobb J, Somanna D, Park Y, Wang F, Kurc T, et al. Cancer Digital Slide Archive: an informatics resource to support integrated in silico analysis of TCGA pathology data. J Am Med Inf Association: JAMIA. (2013) 20:1091–8. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001469
39. Ehteshami Bejnordi B, Veta M, Johannes van Diest P, van Ginneken B, Karssemeijer N, Litjens G, et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA. (2017) 318:2199–210. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.14585
40. Mok JW, Oh YH, Magge D, Padmanabhan S. Racial disparities of gastric cancer in the USA: an overview of epidemiology, global screening guidelines, and targeted screening in a heterogeneous population. Gastric Cancer. (2024) 27(3):426–38. doi: 10.1007/s10120-024-01475-9
41. Yasui W, Oue N, Kuniyasu H, Ito R, Tahara E, Yokozaki H. Molecular diagnosis of gastric cancer: present and future. Gastric Cancer. (2001) 4:113–21. doi: 10.1007/pl00011733
42. Yoshida H, Shimazu T, Kiyuna T, Marugame A, Yamashita Y, Cosatto E, et al. Automated histological classification of whole-slide images of gastric biopsy specimens. Gastric Cancer. (2018) 21:249–57. doi: 10.1007/s10120-017-0731-8
43. Abe H, Kurose Y, Takahama S, Kume A, Nishida S, Fukasawa M, et al. Development and multi-institutional validation of an artificial intelligence-based diagnostic system for gastric biopsy. Cancer Sci. (2022) 113:3608–17. doi: 10.1111/cas.15514
44. Fan X, Yu L, Qi X, Lin X, Zhao J, Wang D, et al. Primary investigation of deep learning models for Japanese "Group classification" of whole-slide images of gastric endoscopic biopsy. Comput Math Methods Med. (2022) 2022:6899448. doi: 10.1155/2022/6899448
45. Iizuka O, Kanavati F, Kato K, Rambeau M, Arihiro K, Tsuneki M. Deep learning models for histopathological classification of gastric and colonic epithelial tumours. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:1504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58467-9
46. Ko YS, Choi YM, Kim M, Park Y, Ashraf M, Quiñones Robles WR, et al. Improving quality control in the routine practice for histopathological interpretation of gastrointestinal endoscopic biopsies using artificial intelligence. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0278542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278542
47. Park J, Jang BG, Kim YW, Park H, Kim BH, Kim MJ, et al. A prospective validation and observer performance study of a deep learning algorithm for pathologic diagnosis of gastric tumors in endoscopic biopsies. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:719–28. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3159
48. Sharma H, Zerbe N, Klempert I, Hellwich O, Hufnagl P. Deep convolutional neural networks for automatic classification of gastric carcinoma using whole slide images in digital histopathology. Computerized Med Imaging Graphics Off J Computerized Med Imaging Soc. (2017) 61:2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2017.06.001
49. Wang S, Zhu Y, Yu L, Chen H, Lin H, Wan X, et al. RMDL: Recalibrated multi-instance deep learning for whole slide gastric image classification. Med image Anal. (2019) 58:101549. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101549
50. Jang HJ, Go JH, Kim Y, Lee SH. Deep learning for the pathologic diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancers. (2023) 15:5389. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225389
51. Retamero JA, Aneiros-Fernandez J, Del Moral RG. Complete digital pathology for routine histopathology diagnosis in a multicenter hospital network. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2020) 144:221–8. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2018-0541-OA
52. Saillard C, Dubois R, Tchita O, Loiseau N, Garcia T, Adriansen A, et al. Validation of MSIntuit as an AI-based pre-screening tool for MSI detection from colorectal cancer histology slides. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:6695. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42453-6
53. Song Z, Zou S, Zhou W, Huang Y, Shao L, Yuan J, et al. Clinically applicable histopathological diagnosis system for gastric cancer detection using deep learning. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:4294. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18147-8
54. Ba W, Wang S, Shang M, Zhang Z, Wu H, Yu C, et al. Assessment of deep learning assistance for the pathological diagnosis of gastric cancer. Modern Pathol. (2022) 35:1262–8. doi: 10.1038/s41379-022-01073-z
55. Lan J, Chen M, Wang J, Du M, Wu Z, Zhang H, et al. Using less annotation workload to establish a pathological auxiliary diagnosis system for gastric cancer. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101004
56. Patel H, Zanos T, Hewitt DB. Deep learning applications in pancreatic cancer. Cancers. (2024) 16:436. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020436
57. Price WN, Gerke S, Cohen IG. Potential liability for physicians using artificial intelligence. JAMA. (2019) 322:1765–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.15064
58. Nazir S, Dickson DM, Akram MU. Survey of explainable artificial intelligence techniques for biomedical imaging with deep neural networks. Comput Biol Med. (2023) 156:106668. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106668
59. Singh RK, Pandey R, Babu RN. COVIDScreen: explainable deep learning framework for differential diagnosis of COVID-19 using chest X-rays. Neural computing Appl. (2021) 33:8871–92. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05636-6
60. Tung CL, Chang HC, Yang BZ, Hou KJ, Tsai HH, Tsai CY, et al. Identifying pathological slices of gastric cancer via deep learning. J Formosan Med Assoc = Taiwan yi zhi. (2022) 121:2457–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2022.05.004
61. Zhu Y, Yuan W, Xie CM, Xu W, Wang JP, Feng L, et al. Two-step artificial intelligence system for endoscopic gastric biopsy improves the diagnostic accuracy of pathologists. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1008537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1008537
62. Yong MP, Hum YC, Lai KW, Lee YL, Goh CH, Yap WS, et al. Histopathological gastric cancer detection on gasHisSDB dataset using deep ensemble learning. Diagnostics (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 13:1793. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13101793
63. Costache S, Sajin M, Wedden S, D'Arrigo C. A consolidated working classification of gastric cancer for histopathologists (Review). Biomed Rep. (2023) 19:58. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1640
64. Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at A histo-clinical classification. Acta pathologica microbiologica Scandinavica. (1965) 64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31
65. Veldhuizen GP, Röcken C, Behrens HM, Cifci D, Muti HS, Yoshikawa T, et al. Deep learning-based subtyping of gastric cancer histology predicts clinical outcome: a multi-institutional retrospective study. Gastric Cancer. (2023) 26:708–20. doi: 10.1007/s10120-023-01398-x
66. Kanavati F, Tsuneki M. A deep learning model for gastric diffuse-type adenocarcinoma classification in whole slide images. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:20486. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99940-3
67. Tsuneki M, Kanavati F. Weakly supervised learning for poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma classification in gastricEndoscopic submucosal dissection whole slide images. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 21:15330338221142674. doi: 10.1177/15330338221142674
68. Fu B, Zhang M, He J, Cao Y, Guo Y, Wang R. StoHisNet: A hybrid multi-classification model with CNN and Transformer for gastric pathology images. Comput Methods programs biomedicine. (2022) 221:106924. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106924
69. Ning X, Liu R, Wang N, Xiao X, Wu S, Wang Y, et al. Development of a deep learning-based model to diagnose mixed-type gastric cancer accurately. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2023) 162:106452. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2023.106452
70. Su F, Li J, Zhao X, Wang B, Hu Y, Sun Y, et al. Interpretable tumor differentiation grade and microsatellite instability recognition in gastric cancer using deep learning. Lab investigation; J Tech Methods Pathol. (2022) 102:641–9. doi: 10.1038/s41374-022-00742-6
71. Kim IH. Emerging targets for systemic treatment of gastric cancer: HER2 and beyond. J gastric Cancer. (2024) 24:29–56. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2024.24.e6
72. Li J, He L, Zhang X, Li X, Wang L, Zhu Z, et al. GCclassifier: An R package for the prediction of molecular subtypes of gastric cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2024) 23:752–8. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.01.010
73. Oh SC, Sohn BH, Cheong JH, Kim SB, Lee JE, Park KC, et al. Clinical and genomic landscape of gastric cancer with a mesenchymal phenotype. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:1777. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04179-8
74. Nemtsova MV, Kuznetsova EB, Bure IV. Chromosomal instability in gastric cancer: role in tumor development, progression, and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:16961. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316961
75. Ricker CA, Meli K, Van Allen EM. Historical perspective and future directions: computational science in immuno-oncology. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2024) 12:e008306. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008306
76. El Nahhas OSM, Loeffler CML, Carrero ZI, van Treeck M, Kolbinger FR, Hewitt KJ, et al. Regression-based Deep-Learning predicts molecular biomarkers from pathology slides. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:1253. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45589-1
77. Bychkov A, Fukuoka J. Evaluation of the global supply of pathologists. Modern Pathol: Official J US Canadian Acad Pathol. (2022) 102(1):1361. doi: 10.1038/s41379-022-01050-6
78. Heinz CN, Echle A, Foersch S, Bychkov A, Kather JN. The future of artificial intelligence in digital pathology - results of a survey across stakeholder groups. Histopathology. (2022) 80:1121–7. doi: 10.1111/his.14659
79. Shmatko A, Ghaffari Laleh N, Gerstung M, Kather JN. Artificial intelligence in histopathology: enhancing cancer research and clinical oncology. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:1026–38. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00436-4
80. Alam MR, Abdul-Ghafar J, Yim K, Thakur N, Lee SH, Jang HJ, et al. Recent applications of artificial intelligence from histopathologic image-based prediction of microsatellite instability in solid cancers: A systematic review. Cancers. (2022) 14:2590. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112590
81. Kather JN, Pearson AT, Halama N, Jäger D, Krause J, Loosen SH, et al. Deep learning can predict microsatellite instability directly from histology in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Med. (2019) 25:1054–6. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0462-y
82. Muti HS, Heij LR, Keller G, Kohlruss M, Langer R, Dislich B, et al. Development and validation of deep learning classifiers to detect Epstein-Barr virus and microsatellite instability status in gastric cancer: a retrospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet Digital Health. (2021) 3:e654–64. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00133-3
83. Zhu J, Wu W, Zhang Y, Lin S, Jiang Y, Liu R, et al. Computational analysis of pathological image enables interpretable prediction for microsatellite instability. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:825353. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.825353
84. Lee SH, Lee Y, Jang HJ. Deep learning captures selective features for discrimination of microsatellite instability from pathologic tissue slides of gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. (2023) 152:298–307. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34251
85. Wang Y, Hu C, Kwok T, Bain CA, Xue X, Gasser RB, et al. DEMoS: a deep learning-based ensemble approach for predicting the molecular subtypes of gastric adenocarcinomas from histopathological images. Bioinf (Oxford England). (2022) 38:4206–13. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac456
86. Schmauch B, Romagnoni A, Pronier E, Saillard C, Maillé P, Calderaro J, et al. A deep learning model to predict RNA-Seq expression of tumours from whole slide images. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:3877. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17678-4
87. Flinner N, Gretser S, Quaas A, Bankov K, Stoll A, Heckmann LE, et al. Deep learning based on hematoxylin-eosin staining outperforms immunohistochemistry in predicting molecular subtypes of gastric adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. (2022) 257:218–26. doi: 10.1002/path.5879
88. Jeong Y, Cho CE, Kim JE, Lee J, Kim N, Jung WY, et al. Deep learning model to predict Epstein-Barr virus associated gastric cancer in histology. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:18466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22731-x
89. Zhang B, Yao K, Xu M, Wu J, Cheng C. Deep learning predicts EBV status in gastric cancer based on spatial patterns of lymphocyte infiltration. Cancers. (2021) 13:6002. doi: 10.3390/cancers13236002
90. Vuong TTL, Song B, Kwak JT, Kim K. Prediction of epstein-barr virus status in gastric cancer biopsy specimens using a deep learning algorithm. JAMA network Open. (2022) 5:e2236408. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36408
91. Zheng X, Wang R, Zhang X, Sun Y, Zhang H, Zhao Z, et al. A deep learning model and human-machine fusion for prediction of EBV-associated gastric cancer from histopathology. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:2790. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30459-5
92. Alam MR, Seo KJ, Abdul-Ghafar J, Yim K, Lee SH, Jang HJ, et al. Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers. Briefings Bioinf. (2023) 24:bbad151. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad151
93. Jang HJ, Lee A, Kang J, Song IH, Lee SH. Prediction of genetic alterations from gastric cancer histopathology images using a fully automated deep learning approach. World J Gastroenterol. (2021) 27:7687–704. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i44.7687
94. Cifci D, Foersch S, Kather JN. Artificial intelligence to identify genetic alterations in conventional histopathology. J Pathol. (2022) 257:430–44. doi: 10.1002/path.5898
95. Saldanha OL, Muti HS, Grabsch HI, Langer R, Dislich B, Kohlruss M, et al. Direct prediction of genetic aberrations from pathology images in gastric cancer with swarm learning. Gastric Cancer. (2023) 26:264–74. doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01347-0
96. Lu C, Xie L, Qiu S, Jiang T, Wang L, Chen Z, et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Helicobacter Pylori-Infected Gastric Cancer Cells Induce Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Remodeling via Transfer of miR-1246. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse Germany). (2023) 20(13):e2308688. doi: 10.1002/smll.202308688
97. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition). Gastric Cancer. (2021) 24:1–21. doi: 10.1007/s10120-020-01042-y
98. Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, et al. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2017) 67:93–9. doi: 10.3322/caac.21388
99. Zeng Y, Cai F, Wang P, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhang L, et al. Development and validation of prognostic model based on extragastric lymph nodes metastasis and lymph node ratio in node-positive gastric cancer: a retrospective cohort study based on a multicenter database. Int J Surg (London England). (2023) 109:794–804. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000308
100. Muti HS, Röcken C, Behrens HM, Löffler CML, Reitsam NG, Grosser B, et al. Deep learning trained on lymph node status predicts outcome from gastric cancer histopathology: a retrospective multicentric study. Eur J Cancer (Oxford Engl 1990). (2023) 194:113335. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113335
101. Wang X, Chen Y, Gao Y, Zhang H, Guan Z, Dong Z, et al. Predicting gastric cancer outcome from resected lymph node histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1637. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21674-7
102. Hu Y, Su F, Dong K, Wang X, Zhao X, Jiang Y, et al. Deep learning system for lymph node quantification and metastatic cancer identification from whole-slide pathology images. Gastric Cancer. (2021) 24:868–77. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01158-9
103. Matsushima J, Sato T, Yoshimura Y, Mizutani H, Koto S, Matsusaka K, et al. Clinical utility of artificial intelligence assistance in histopathologic review of lymph node metastasis for gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:1033–42. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02356-4
104. Takada K, Yoshida M, Aizawa D, Sato J, Ono H, Sugino T. Lymphovascular invasion in early gastric cancer: impact of ancillary D2-40 and elastin staining on interobserver agreement. Histopathology. (2020) 76:888–97. doi: 10.1111/his.14075
105. He Y, Yang M, Hou R, Ai S, Nie T, Chen J, et al. Preoperative prediction of perineural invasion and lymphovascular invasion with CT radiomics in gastric cancer. Eur J Radiol Open. (2024) 12:100550. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2024.100550
106. Lee J, Cha S, Kim J, Kim JJ, Kim N, Jae Gal SG, et al. Ensemble deep learning model to predict lymphovascular invasion in gastric cancer. Cancers. (2024) 16:430. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020430
107. Lee J, Ahn S, Kim HS, An J, Sim J. A robust model training strategy using hard negative mining in a weakly labeled dataset for lymphatic invasion in gastric cancer. J pathology Clin Res. (2024) 10:e355. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.355
108. Huang B, Tian S, Zhan N, Ma J, Huang Z, Zhang C, et al. Accurate diagnosis and prognosis prediction of gastric cancer using deep learning on digital pathological images: A retrospective multicentre study. EBioMedicine. (2021) 73:103631. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103631
109. Li F, Yang Y, Wei Y, He P, Chen J, Zheng Z, et al. Deep learning-based predictive biomarker of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy from histological images in breast cancer. J Trans Med. (2021) 19:348. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03020-z
110. Zeng H, Qiu S, Zhuang S, Wei X, Wu J, Zhang R, et al. Deep learning-based predictive model for pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer from biopsy pathological images: a multicenter study. Front Physiol. (2024) 15:1279982. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1279982
111. Chen D, Fu M, Chi L, Lin L, Cheng J, Xue W, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of a pathomics signature in gastric cancer. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:6903. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34703-w
112. Zhou Z, Ren Y, Zhang Z, Guan T, Wang Z, Chen W, et al. Digital histopathological images of biopsy predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. (2023) 26:734–42. doi: 10.1007/s10120-023-01407-z
113. Tian M, Yao Z, Zhou Y, Gan Q, Wang L, Lu H, et al. DeepRisk network: an AI-based tool for digital pathology signature and treatment responsiveness of gastric cancer using whole-slide images. J Trans Med. (2024) 22:182. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04838-5
114. Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:57. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01451-3
115. Chen D, Lai J, Cheng J, Fu M, Lin L, Chen F, et al. Predicting peritoneal recurrence in gastric cancer with serosal invasion using a pathomics nomogram. iScience. (2023) 26:106246. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106246
116. Zhang F, Geng J, Zhang DG, Gui J, Su R. Prediction of cancer recurrence based on compact graphs of whole slide images. Comput Biol Med. (2023) 167:107663. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107663
117. Ricker CA, Meli K, Van Allen EM. Historical perspective and future directions: computational science in immuno-oncology. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2024) 12:e008306. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008306
118. Waldman AD, Fritz JM, Lenardo MJ. A guide to cancer immunotherapy: from T cell basic science to clinical practice. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:651–68. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0306-5
119. Xie J, Luo X, Deng X, Tang Y, Tian W, Cheng H, et al. Advances in artificial intelligence to predict cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Front Immunol. (2023) 13:1076883. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1076883
120. Wei Z, Zhao X, Chen J, Sun Q, Wang Z, Wang Y, et al. Deep learning-based stratification of gastric cancer patients from hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole slide images by predicting molecular features for immunotherapy response. Am J Pathol. (2023) 193:1517–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.06.004
121. Li X, Xiong F, Hu Z, Tao Q, Yang Y, Qiao X, et al. A novel biomarker associated with EBV infection improves response prediction of immunotherapy in gastric cancer. J Trans Med. (2024) 22:90. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04859-8
122. Li J, Liu H, Liu W, Zong P, Huang K, Li Z, et al. Predicting gastric cancer tumor mutational burden from histopathological images using multimodal deep learning. Briefings Funct Genomics. (2023) 23(3):228–38. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elad032
123. Shah A, Wahood S, Guermazi D, Brem CE, Saliba E. Skin and syntax: large language models in dermatopathology. Dermatopathology (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 11:101–11. doi: 10.3390/dermatopathology11010009
124. Choi HS, Song JY, Shin KH, Chang JH, Jang BS. Developing prompts from large language model for extracting clinical information from pathology and ultrasound reports in breast cancer. Radiat Oncol J. (2023) 41:209–16. doi: 10.3857/roj.2023.00633
125. Laohawetwanit T, Namboonlue C, Apornvirat S. Accuracy of GPT-4 in histopathological image detection and classification of colorectal adenomas. J Clin Pathol. (2024) jcp-2023-209304. Advance online publication. doi: 10.1136/jcp-2023-209304
126. Lu MY, Chen B, Williamson DFK, Chen RJ, Zhao M, Chow AK, et al. A multimodal generative AI copilot for human pathology. Nature. (2024) 634(8033):466–73. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07618-3
127. Sultan AS, Elgharib MA, Tavares T, Jessri M, Basile JR. The use of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in oncologic histopathology. J Oral Pathol medicine: Off Publ Int Assoc Oral Pathologists Am Acad Oral Pathol. (2020) 49:849–56. doi: 10.1111/jop.13042
128. Steiner DF, Chen PC, Mermel CH. Closing the translation gap: AI applications in digital pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2021) 1875:188452. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188452
129. Echle A, Ghaffari Laleh N, Quirke P, Grabsch HI, Muti HS, Saldanha OL, et al. Artificial intelligence for detection of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer-a multicentric analysis of a pre-screening tool for clinical application. ESMO Open. (2022) 7:100400. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100400
130. Echle A, Grabsch HI, Quirke P, van den Brandt PA, West NP, Hutchins GGA, et al. Clinical-grade detection of microsatellite instability in colorectal tumors by deep learning. Gastroenterology. (2020) 159:1406–1416.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.021
131. van Diest PJ, Flach RN, van Dooijeweert C, Makineli S, Breimer GE, Stathonikos N, et al. Pros and cons of artificial intelligence implementation in diagnostic pathology. Histopathology. (2024) 84(6):924–34. doi: 10.1111/his.15153
132. Zhang YF, Zhou C, Guo S, Wang C, Yang J, Yang ZJ, et al. Deep learning algorithm-based multimodal MRI radiomics and pathomics data improve prediction of bone metastases in primary prostate cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:78. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05574-5
133. Deng R, Cui C, Remedios LW, Bao S, Womick RM, Chiron S, et al. Cross-scale multi-instance learning for pathological image diagnosis. Med image Anal. (2024) 94:103124. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2024.103124
134. Prelaj A, Miskovic V, Zanitti M, Trovo F, Genova C, Viscardi G, et al. Artificial intelligence for predictive biomarker discovery in immuno-oncology: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:29–65. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.125
135. Marcus E, Teuwen J. Artificial intelligence and explanation: How, why, and when to explain black boxes. Eur J Radiol. (2024) 173:111393. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111393
136. Hroub NA, Alsannaa AN, Alowaifeer M, Alfarraj M, Okafor E. Explainable deep learning diagnostic system for prediction of lung disease from medical images. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 170:108012. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108012
137. Duffourc MN, Gerke S. Health care AI and patient privacy-dinerstein v google. JAMA. (2024) 331:909–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.1110
138. Pantanowitz L, Hanna M, Pantanowitz J, Lennerz J, Henricks WH, Shen P, et al. Regulatory aspects of AI-ML. Modern Pathol. (2024) 37(12):100609. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2024.100609
139. Lang J, Repp H. Artificial intelligence in medical education and the meaning of interaction with natural intelligence - an interdisciplinary approach. GMS J Med Educ. (2020) 37:Doc59. doi: 10.3205/zma001352
140. Dernbach G, Kazdal D, Ruff L, Alber M, Romanovsky E, Schallenberg S, et al. Dissecting AI-based mutation prediction in lung adenocarcinoma: A comprehensive real-world study. Eur J Cancer (Oxford Engl 1990). (2024) 211:114292. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2024.114292
Keywords: gastric cancer, machine learning, digital pathology, artificial intelligence, computational pathology
Citation: Chen S, Ding P, Guo H, Meng L, Zhao Q and Li C (2024) Applications of artificial intelligence in digital pathology for gastric cancer. Front. Oncol. 14:1437252. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1437252
Received: 23 May 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 28 October 2024.
Edited by:
Arkadiusz Gertych, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Zhenzhong Deng, University of Southern California, United StatesGopika SenthilKumar, Medical College of Wisconsin, United States
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Ding, Guo, Meng, Zhao and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cong Li, Y29uZ2xpNjYxNDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Sheng Chen
Sheng Chen Ping’an Ding2,3,4
Ping’an Ding2,3,4